

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 20230276.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230276
收稿日期:2023-06-10
出版日期:2023-11-10
发布日期:2023-09-04
通讯作者:
甯红波
E-mail:hbning@swjtu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHOU Zihao, WANG Sihao, HUANG Daichuan, LIU Bo, NING Hongbo( )
)
Received:2023-06-10
Online:2023-11-10
Published:2023-09-04
Contact:
NING Hongbo
E-mail:hbning@swjtu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
正丙苯是Jet A、 Jet A-1及国产RP-3航空煤油中芳香烃的典型替代组分. 本文采用基于反应力场的分子动力学模拟研究了正丙苯高温氧化过程的主要反应网络、 主要产物的形成机理以及在不同温度、 密度和当量比条件下正丙苯氧化主要产物的分布规律, 并结合反应动力学理论计算了正丙苯高温氧化的速率常数. 结果表明, 正丙苯高温氧化主要发生在烷基侧链, 包括6种C—C和C—H键断裂单分子分解反应以及3种侧链氢原子与氧气或其它小自由基的氢提取反应, 其中与苄基相连的C—C键具有最小断键能, 是最重要的单分子分解反应, 而不同位点的自由基氢提取反应的贡献相似; 体系的模拟温度和密度/压力与正丙苯的氧化速率呈正相关, 但当量比对氧化速率的影响则严重依赖于体系温度. 计算所得正丙苯高温氧化表观活化能和指前因子与文献报道的实验值相比在可接受的范围内.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
周子豪, 王思皓, 黄玳川, 刘波, 甯红波. 正丙苯高温氧化机理的分子动力学模拟研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230276.
ZHOU Zihao, WANG Sihao, HUANG Daichuan, LIU Bo, NING Hongbo. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on High Temperature Oxidation Mechanism of n-Propylbenzene. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(11): 20230276.
| Equivalence ratio(ϕ) | n(n⁃Propylbenzene)/n(Oxygen) | T/K | Density/(g·cm-3) | Ensemble |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 50/600 | 2900 | 0.35 | NVT |
| 0.5 | 10/240 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
| 1.0 | 10/120 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
| 2.0 | 10/60 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
Table 1 Temperature, density, and equivalence ratio of n-propylbenzene oxidation system
| Equivalence ratio(ϕ) | n(n⁃Propylbenzene)/n(Oxygen) | T/K | Density/(g·cm-3) | Ensemble |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0 | 50/600 | 2900 | 0.35 | NVT |
| 0.5 | 10/240 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
| 1.0 | 10/120 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
| 2.0 | 10/60 | 2300—3500 | 0.05—0.35 | NVT |
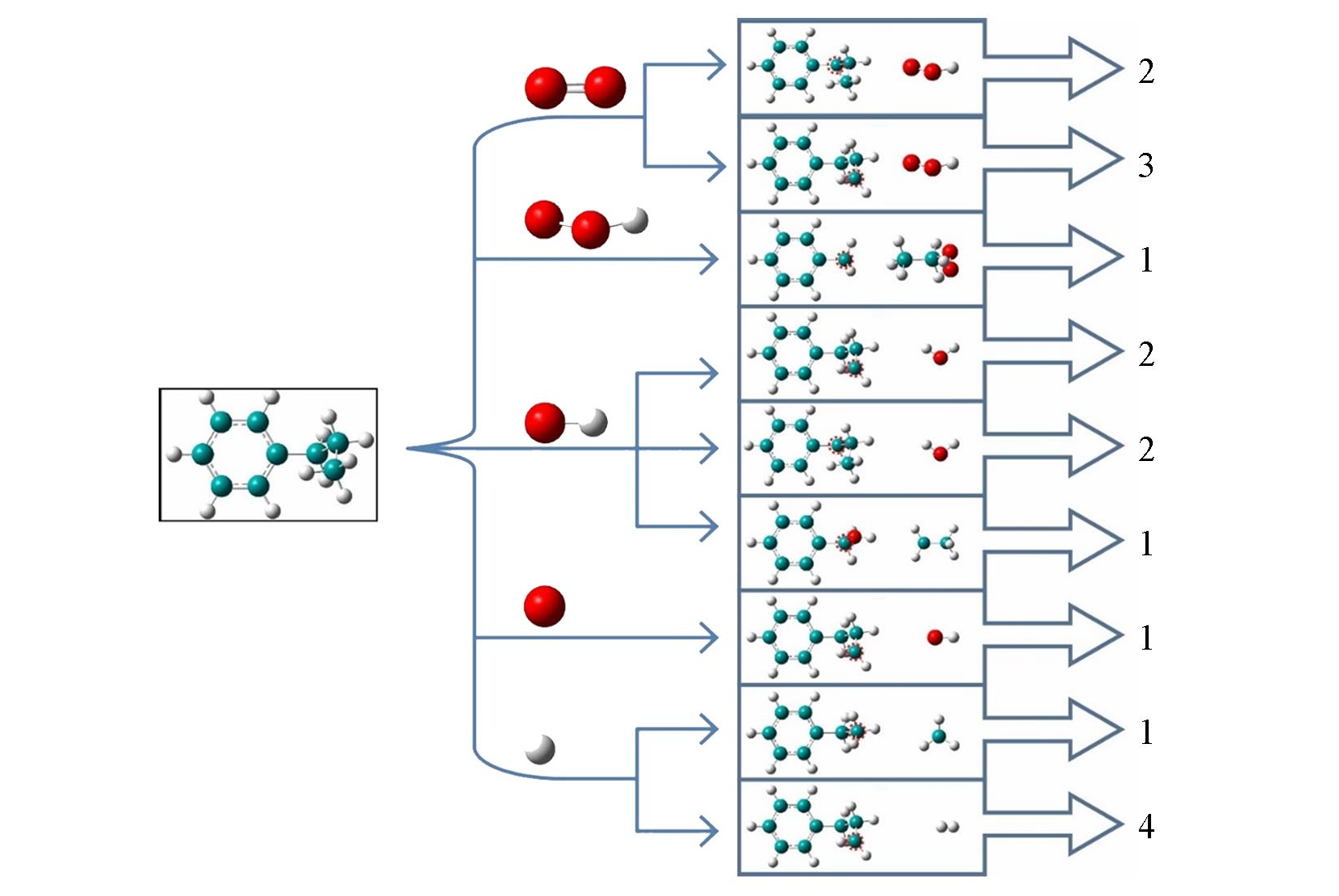
Fig.2 Nine reaction pathways of n⁃propylbenzene reacting with different small radicals and oxygenGreen, red and white spheres represent carbon, oxygen and hydrogen atoms, respectively.
| Reaction | Ebond/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP | ReaxFF | Ref. | |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH2CH2·+H· | 424.19 | 444.38 | 420.09[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH·CH3+H· | 407.55 | 435.89 | 408.80[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH·CH2CH3+H· | 359.52 | 381.68 | 366.17[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH2·+CH3· | 358.02 | 372.39 | 371.60[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2·+CH3CH2· | 290.30 | 298.74 | 322.28[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5·+CH3CH2CH2· | 400.32 | 424.86 | 421.34[ |
Table 2 Calculated bond dissociation energies of n-propylbenzene using B3LYP and ReaxFF methods and the corresponding literature results
| Reaction | Ebond/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP | ReaxFF | Ref. | |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH2CH2·+H· | 424.19 | 444.38 | 420.09[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH·CH3+H· | 407.55 | 435.89 | 408.80[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH·CH2CH3+H· | 359.52 | 381.68 | 366.17[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2CH2·+CH3· | 358.02 | 372.39 | 371.60[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5CH2·+CH3CH2· | 290.30 | 298.74 | 322.28[ |
| C6H5CH2CH2CH3→C6H5·+CH3CH2CH2· | 400.32 | 424.86 | 421.34[ |
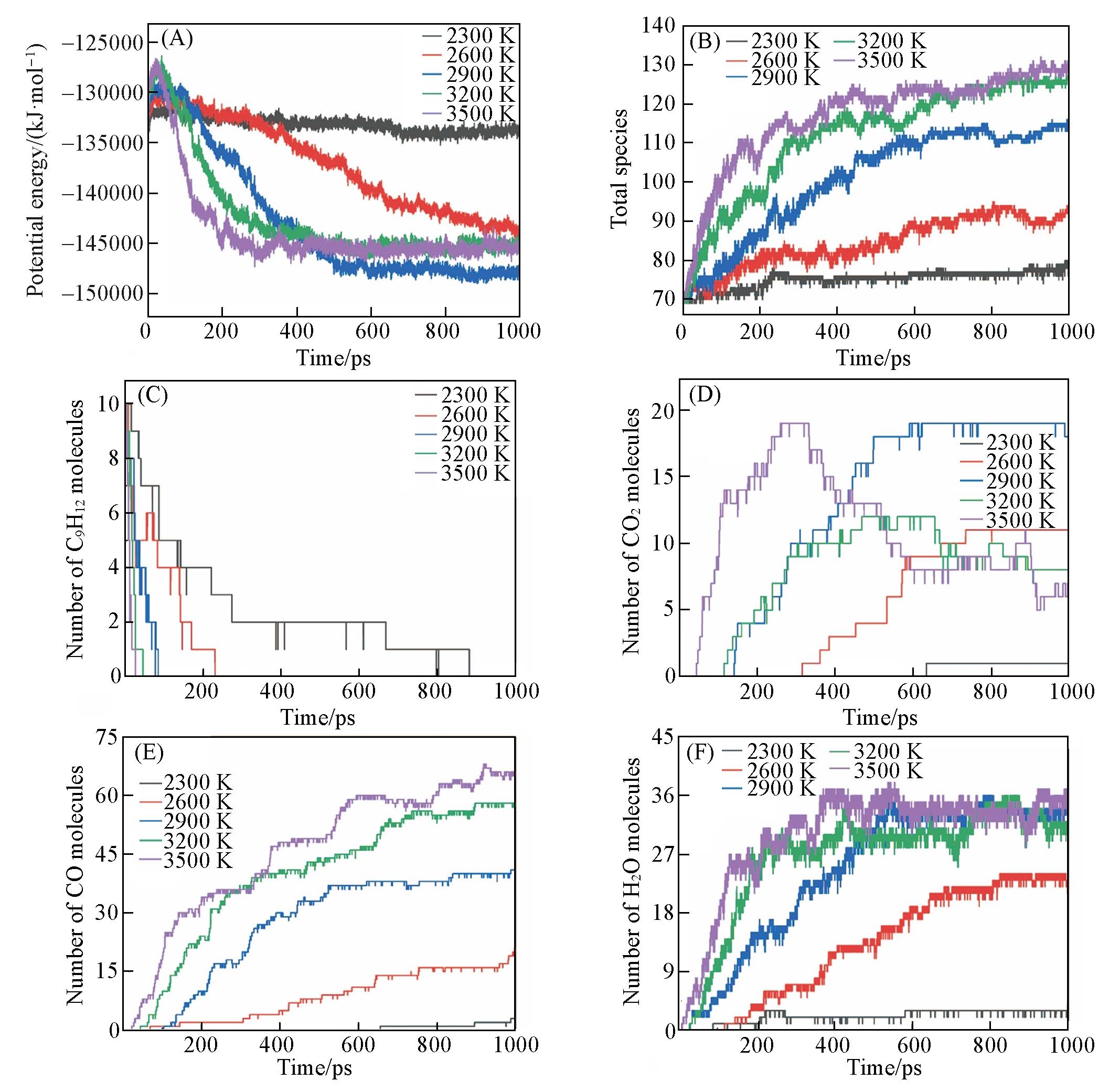
Fig.4 Time evolution of the potential energies(A), total number of species(B), n⁃propylbenzene(C) and main products of CO2(D), CO(E), H2O(F) at different temperatures(ρ=0.35 g/cm3, ϕ=2.0)
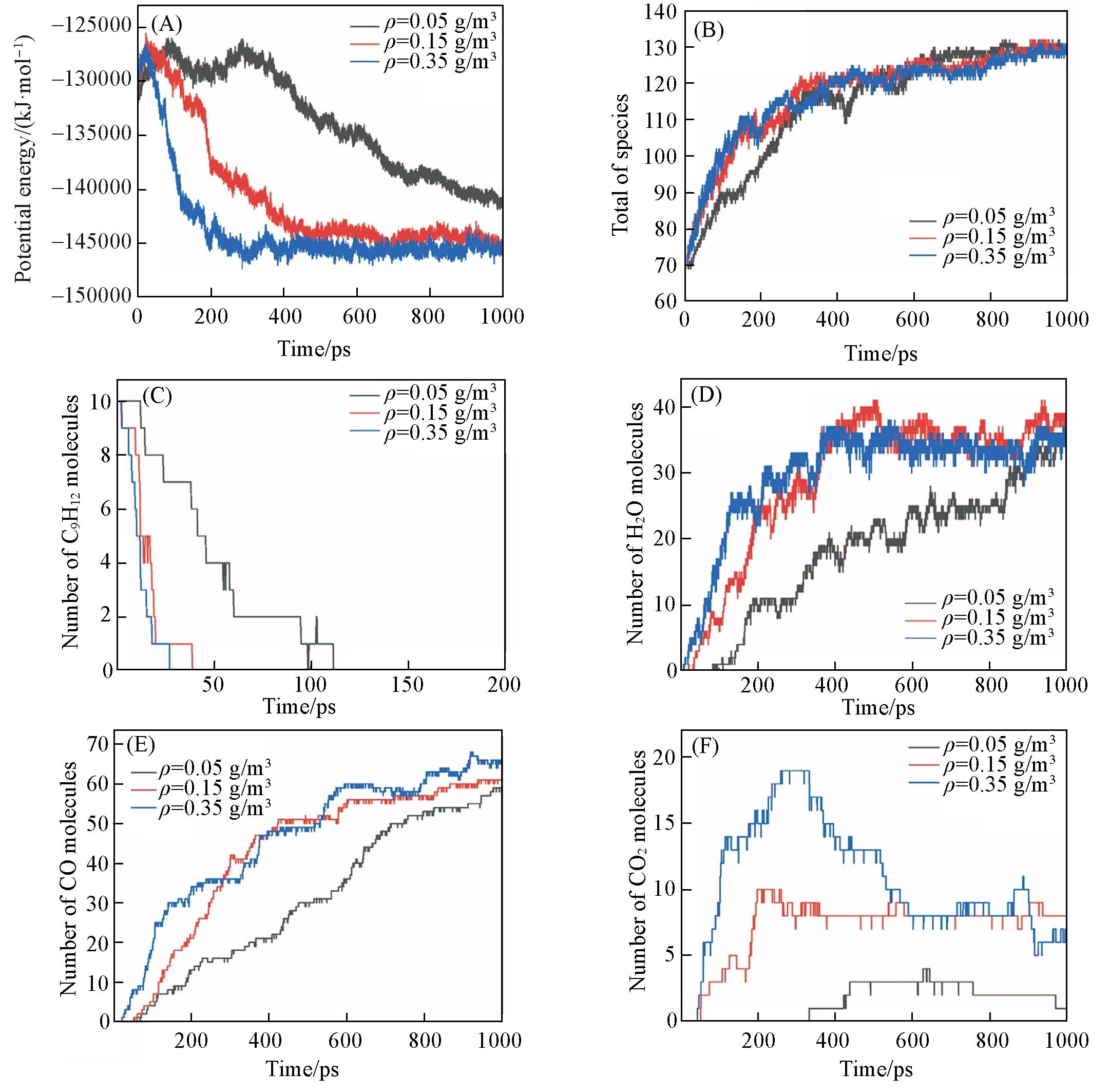
Fig.5 Time evolution of the potential energies(A), total number of species(B), n⁃propylbenzene(C), and main products of H2O(D), CO(E), CO2(F) at different densities(T=3500 K, ϕ=2.0)
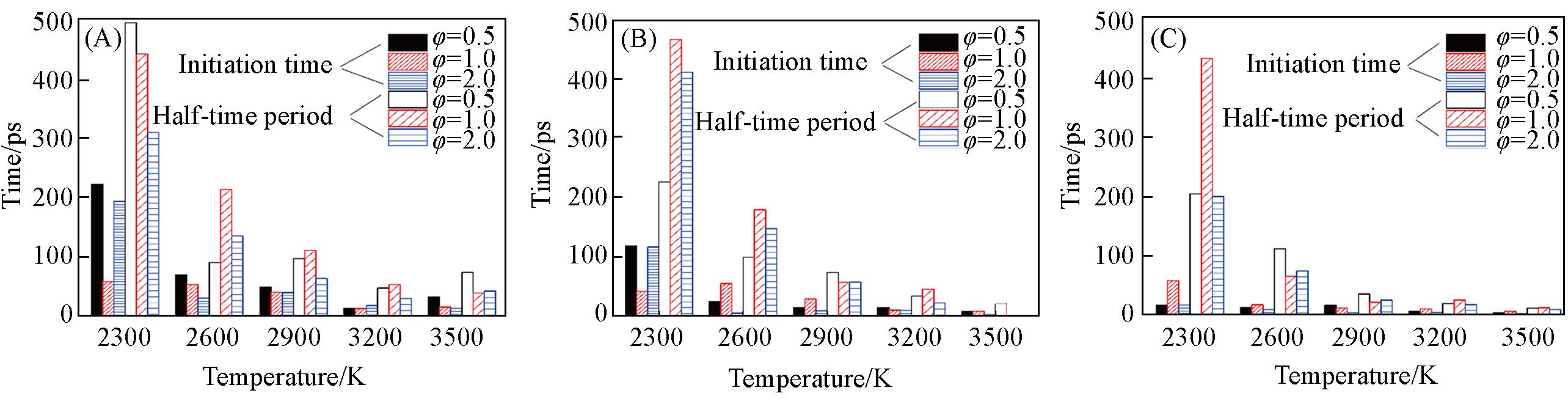
Fig.6 Temperature evolution of the initiation time as well as half⁃time period of n⁃propylbenzene oxidation at different densities of 0.05(A), 0.15(B), 0.35 g/cm3(C) and equivalence ratios
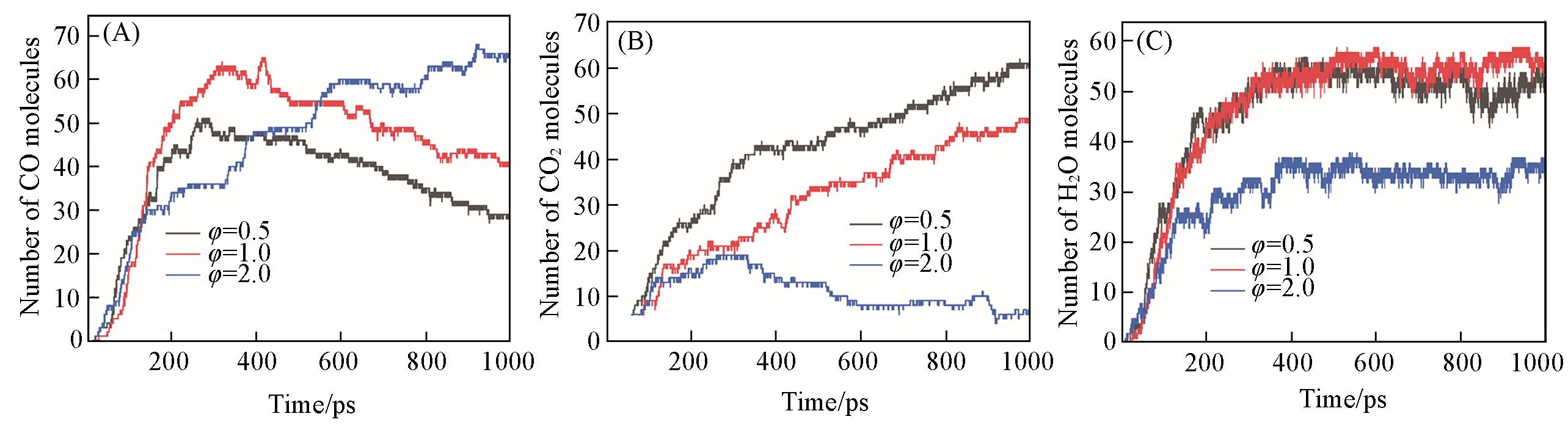
Fig.7 Time evolution of the main products of CO(A), CO2(B), H2O(C) of n⁃propylbenzene oxidation at different equivalence ratios(T=3500 K, ρ=0.35 g/cm3)
| Method | Density/(g·cm-3) | Equivalence ratio | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) | A/(cm3·mol-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReaxFF | 0.05 | 0.5 | 129.66 | 0.66×109 |
| 1.0 | 135.98 | 0.91×109 | ||
| 2.0 | 129.08 | 0.90×109 | ||
| 0.15 | 0.5 | 135.52 | 1.72×109 | |
| 1.0 | 172.43 | 5.24×109 | ||
| 2.0 | 205.28 | 2.65×1010 | ||
| 0.35 | 0.5 | 183.17 | 1.67×1010 | |
| 1.0 | 180.49 | 1.48×1010 | ||
| 2.0 | 142.04 | 0.38×109 | ||
| Expt.[ | — | — | 138.02 | 6.04×1010 |
Table 3 Fitted Arrhenius parameters including Ea and A
| Method | Density/(g·cm-3) | Equivalence ratio | Ea/(kJ·mol-1) | A/(cm3·mol-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReaxFF | 0.05 | 0.5 | 129.66 | 0.66×109 |
| 1.0 | 135.98 | 0.91×109 | ||
| 2.0 | 129.08 | 0.90×109 | ||
| 0.15 | 0.5 | 135.52 | 1.72×109 | |
| 1.0 | 172.43 | 5.24×109 | ||
| 2.0 | 205.28 | 2.65×1010 | ||
| 0.35 | 0.5 | 183.17 | 1.67×1010 | |
| 1.0 | 180.49 | 1.48×1010 | ||
| 2.0 | 142.04 | 0.38×109 | ||
| Expt.[ | — | — | 138.02 | 6.04×1010 |
| 1 | Liu Y. X., Wang B. Y., Weng J. J., Yu D., Richter S., Kick T., Tian Z. Y., Combust. Flame, 2018, 191, 53—65 |
| 2 | Dagaut P., El Bakali A., Ristori A., Fuel, 2006, 85(7/8), 944—956 |
| 3 | Xu J. Q., Guo J. J., Liu A. K., Wang J. L., Tan N. X., Li X. Y., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2015, 31(4), 643—652 |
| 徐佳琪, 郭俊江, 刘爱科, 王健礼, 谈宁馨, 李象远. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(4), 643—652 | |
| 4 | Dooley S., Won S. H., Heyne J., Farouk T. I., Ju Y., Dryer F. L., Brezinsky K., Combust. Flame, 2012, 159(4), 1444—1466 |
| 5 | Johnston R. J., Farrell J. T., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2005, 30(1), 217—224 |
| 6 | Hui X., Das A. K., Kumar K., Sung C. J., Dooley S., Dryer F. L., Fuel, 2012, 97, 695—702 |
| 7 | Hui X., Sung C. J., Fuel, 2013, 109, 191—200 |
| 8 | Ji C., Dames E., Wang H., Egolfopoulos F. N., Combust. Flame, 2012, 159(3), 1070—1081 |
| 9 | Mehl M., Herbinet O., Dirrenberger P., Bounaceur R., Glaude P. A., Battin⁃Leclerc F., Pitz W. J., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2015, 35(1), 341—348 |
| 10 | Roubaud A., Minetti R., Sochet L. R.., Combust. Flame, 2000, 121(3), 535—541 |
| 11 | Darcy D., Mehl M., Simmie J. M., Würmel J., Metcalfe W. K., Westbrook C. K., Curran H. J., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2013, 34(1), 411—418 |
| 12 | Darcy D., Nakamura H., Tobin C. J., Mehl M., Metcalfe W. K., Pitz W. J., Curran H. J., Combust. Flame, 2014, 161(1), 65—74 |
| 13 | Darcy D., Nakamura H., Tobin C. J., Mehl M., Metcalfe W. K., Pitz W. J., Curran H. J., Combust. Flame, 2014, 161(6), 1460—1473 |
| 14 | Gudiyella S., Brezinsky K., Combust. Flame, 2012, 159(3), 940—958 |
| 15 | Gudiyella S., Brezinsky K., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2013, 34(1), 1767—1774 |
| 16 | Anderson H., McEnally C. S., Pfefferle L. D., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2000, 28(2), 2577—2583 |
| 17 | Wang Z., Li Y., Zhang F., Zhang L., Yuan W., Wang Y., Qi F., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2013, 34(1), 1785—1793 |
| 18 | Li Y., Cai J., Zhang L., Yang J., Wang Z., Qi F., Proc. Combust. Inst., 2011, 33(1), 617—624 |
| 19 | Darcy D., Tobin C. J., Yasunaga K., Simmie J. M., Würmel J., Metcalfe W. K., Tidjani N., Ahmed S. S., Westbrook C. K., Curran H. J., Combust. Flame, 2012, 159(7), 2219—2232 |
| 20 | Robinson R. K., Lindstedt R. P., Combust. Flame, 2013, 160(12), 2642—2653 |
| 21 | Altarawneh M., Dlugogorski B. Z., Combust. Flame, 2015, 162(4), 1406—1416 |
| 22 | Zhou C. W., Simmie J. M., Somers K. P., Goldsmith C. F., Curran H. J., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2017, 121(9), 1890—1899 |
| 23 | Shang Y., Ning H., Shi J., Luo S. N., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2021, 37(3), 711—717 |
| 24 | van Duin A. C. T., Dasgupta S., Lorant F., Goddard W. A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2001, 105(41), 9396—9409 |
| 25 | Li X., Zheng M., Ren C., Guo L., Energy Fuels, 2021, 35(15), 11707—11739 |
| 26 | Chenoweth K., van Duin A. C. T., Goddard W. A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2008, 112(5), 1040—1053 |
| 27 | Chenoweth K., van Duin A. C. T., Dasgupta S., Goddard W. A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113(9), 1740—1746 |
| 28 | Wang Q. D., Wang J. B., Li J. Q., Tan N. X., Li X. Y., Combust. Flame, 2011, 158(2), 217—226 |
| 29 | Cheng X. M., Wang Q. D., Li J. Q., Wang J. B., Li X. Y., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2012, 116(40), 9811—9818 |
| 30 | Liu X. L., Li, X. X., Han S., Qiao X. J., Zhong B. J., Guo L., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2016, 32(6), 1424—1433 |
| 刘晓龙, 李晓霞, 韩嵩, 乔显杰, 钟北京, 郭力. 物理化学学报, 2016, 32(6), 1424—1433 | |
| 31 | Liu J. X., Min J., Xu H. J., Ren H. S., Tan N. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4),20210834 |
| 刘嘉欣, 闵杰, 许华杰, 任海生, 谭宁馨. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4),20210834 | |
| 32 | Berendsen H. J., Postma J., Gunsteren W., DiNola A. D., Haak J. R., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 81(8), 3684—3690 |
| 33 | Lindgren E. B., Monteiro J. G. S., dos Santos A. R., Fleming F. P., Barbosa A. G. H., Fuel, 2021, 303, 121205 |
| 34 | So M. R., Rensen., Voter A. F., J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 112(21), 9599—9606 |
| 35 | Ashraf C., van Duin A. C. T., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2017, 121(5), 1051—1068 |
| 36 | Martínez L., Andrade R., Birgin E. G., Martínez J. M., J. Comput. Chem., 2010, 30(13), 2157—2164 |
| 37 | Plimpton S., J. Comput. Phys., 1995, 117(1), 1—19 |
| 38 | Döntgen M., Przybylski⁃Freund M. D., Kröger L. C., Kopp W. A., Ismail A. E., Leonhard K., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, 11(6), 2517—2524 |
| 39 | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Li X., Caricato M., Marenich A. V., Bloino J., Janesko B. G., Gomperts R., Mennucci B., Hratchian H. P., Ortiz J. V., Izmaylov A. F., Sonnenberg J. L., Williams⁃Young D., Ding F., Lipparini F., Egidi F., Goings J., Peng B., Petrone A., Henderson T., Ranasinghe D., Zakrzewski V. G., Gao J., Rega N., Zheng G., Liang W., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Throssell K., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M. J., Heyd J. J., Brothers E. N., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T. A., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A. P., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Millam J. M., Klene M., Adamo C., Cammi R., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Fox D. J., Gaussian 16., Revision B. 01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2016 |
| 40 | Luo Y. R., Comprehensive Handbook of Chemical Bond Energies, CRC Press, London, 2007 |
| 41 | Kirkpatrick A. T., Internal Combustion Engines: Applied Thermosciences, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, 2020 |
| 42 | Liang J., Li F., Cao S., Li X., Jia M. X., Wang Q. D., Fuel, 2022, 325, 124940 |
| 43 | Yuan W., Li Y., Dagaut P., Wang Y., Wang Z., Qi F., Combust. Flame, 2017, 186, 178—192 |
| [1] | 富忠恒, 陈翔, 姚楠, 余乐耕, 沈馨, 张睿, 张强. 固态电解质锂离子输运机制研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220703. |
| [2] | 徐佳宁, 白文静, 楼雨寒, 于海鹏, 窦烁. 电催化氧化木质素解聚: 温和高效的生物质增值策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220749. |
| [3] | 高凤雨, 陈都, 罗宁, 姚小龙, 段二红, 易红宏, 赵顺征, 唐晓龙. MnO x -CeO2催化剂的氯苯氧化性能及反应机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220690. |
| [4] | 夏文文, 于洪晶, 王时野, 姚丽, 李象远. 用于燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法—芳香烃燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220616. |
| [5] | 李吉辰, 蔡珊珊, 彭巨擘, 李宏飞, 段晓征. 电场下离子型聚合物复合囊泡结构变化的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220553. |
| [6] | 沈琦, 陈海瑶, 高登辉, 赵熹, 那日松, 刘佳, 黄旭日. 天然产物法卡林二醇与人类GABAA受体相互作用的机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220500. |
| [7] | 廖首维, 刘炎昌, 石泽南, 赵道辉, 魏嫣莹, 李理波. 水/石墨烯界面离子吸附的分子动力学模拟: 力场参数优化与吸附机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230155. |
| [8] | 周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [9] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [10] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [11] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [12] | 刘嘉欣, 闵杰, 许华杰, 任海生, 谈宁馨. 基于反应力场分子模拟的乙烯燃烧自由基与氮气相互作用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [13] | 孙翠红, 吕立强, 刘迎, 王妍, 杨静, 张绍文. 硝酸异丙酯与Cl原子、 OH和NO3自由基反应的机理及动力学[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [14] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [15] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||