

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 20220749.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220749
收稿日期:2022-12-06
出版日期:2023-05-10
发布日期:2023-01-09
通讯作者:
于海鹏,窦烁
E-mail:yuhaipeng20000@nefu.edu.cn;doushuo@nefu.edu.cn
基金资助:
XU Jianing, BAI Wenjing, LOU Yuhan, YU Haipeng( ), DOU Shuo(
), DOU Shuo( )
)
Received:2022-12-06
Online:2023-05-10
Published:2023-01-09
Contact:
YU Haipeng, DOU Shuo
E-mail:yuhaipeng20000@nefu.edu.cn;doushuo@nefu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
木质素是一种天然可再生芳香族聚合物, 通过催化反应过程可实现其解聚制备芳香族化学品, 其高附加值转化对实现生物燃料、 精细化学品和大宗化学品的绿色生产具有重要意义. 其中, 电催化氧化解聚为木质素的高值化利用提供了一种高效节能途径. 凭借电催化过程中电位或电流易于调节的特性, 可实现产物的选择性和反应物转化率的有效调控. 但实现木质素的可控降解, 首先需对其解聚机理充分了解掌握. 其中, 由催化剂、 电解质和催化反应池等组成的电催化系统均需合理设计. 本文以木质素解聚过程中C—C键和C—O键的断裂机理为基础, 综合评述了近年来木质素及其模型化合物在电催化氧化制备芳香族单体过程中不同的断键机制, 总结了自由基中间体在C—O和C—C键的高选择性断裂中发挥的决定作用. 最后, 展望了电催化木质素解聚的发展前景以及面临的挑战.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
徐佳宁, 白文静, 楼雨寒, 于海鹏, 窦烁. 电催化氧化木质素解聚: 温和高效的生物质增值策略. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220749.
XU Jianing, BAI Wenjing, LOU Yuhan, YU Haipeng, DOU Shuo. Electrocatalytic Oxidative Cleavage of Lignin: Facile and Efficient Biomass Valorization Strategy. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(5): 20220749.
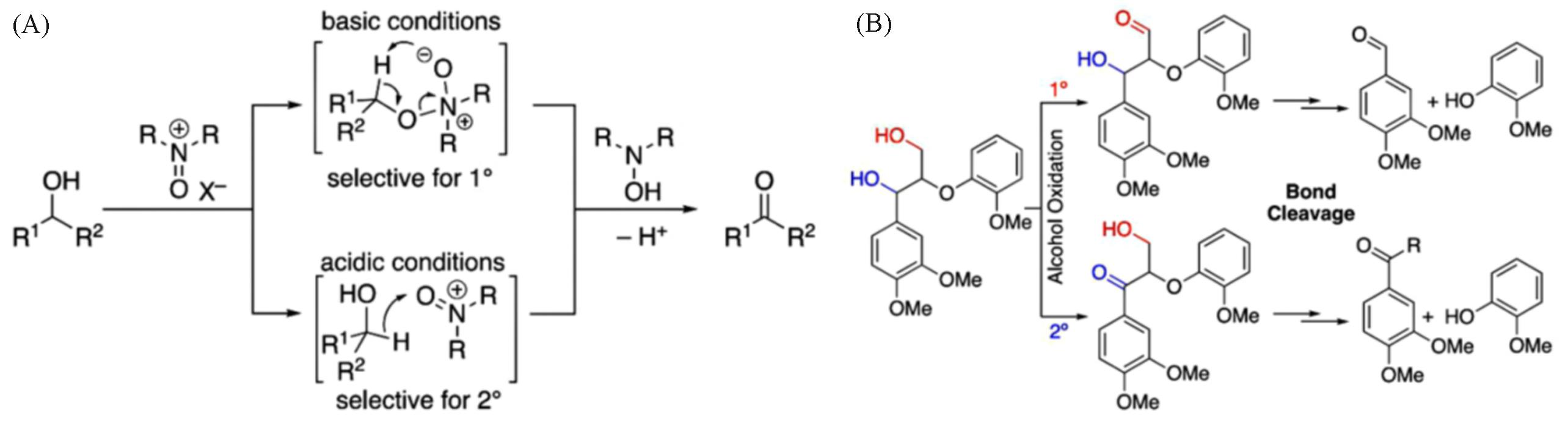
Fig.2 Mechanism of alcohol oxidation by oxoammonium under basic and acidic conditions(A) and chemoselective alcohol oxidation strategies for cleavage of β⁃O⁃4 lignin model(B)[48]
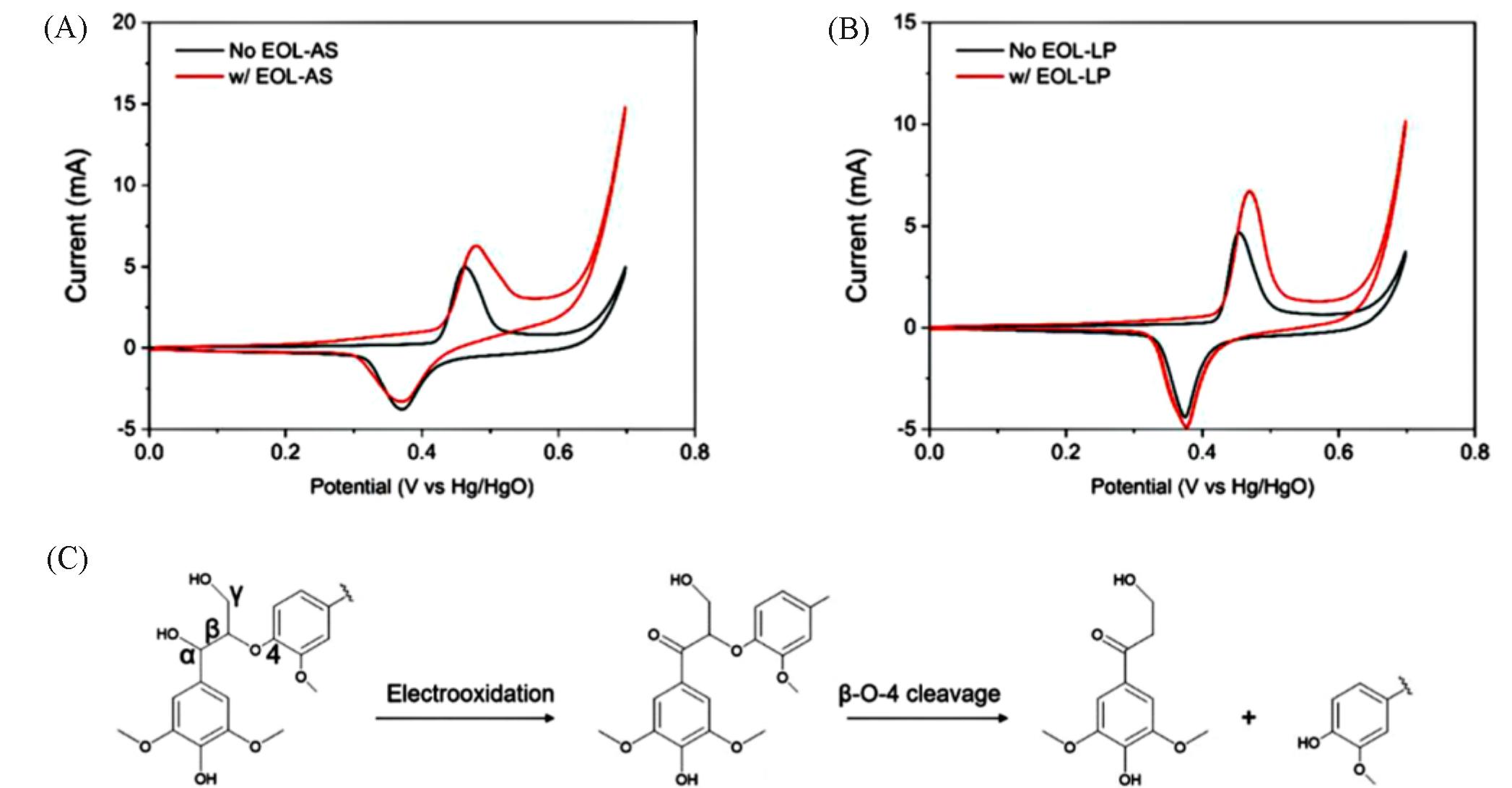
Fig.4 Cyclic voltammograms of nickel foam in 1.0 mol/L KOH before and after the addition of 20 mg of EOL⁃AS(A) and EOL⁃LP(B) lignin and schematic representation of the oxidation and cleavage of the lignin β⁃O⁃4 unit(C)[59]
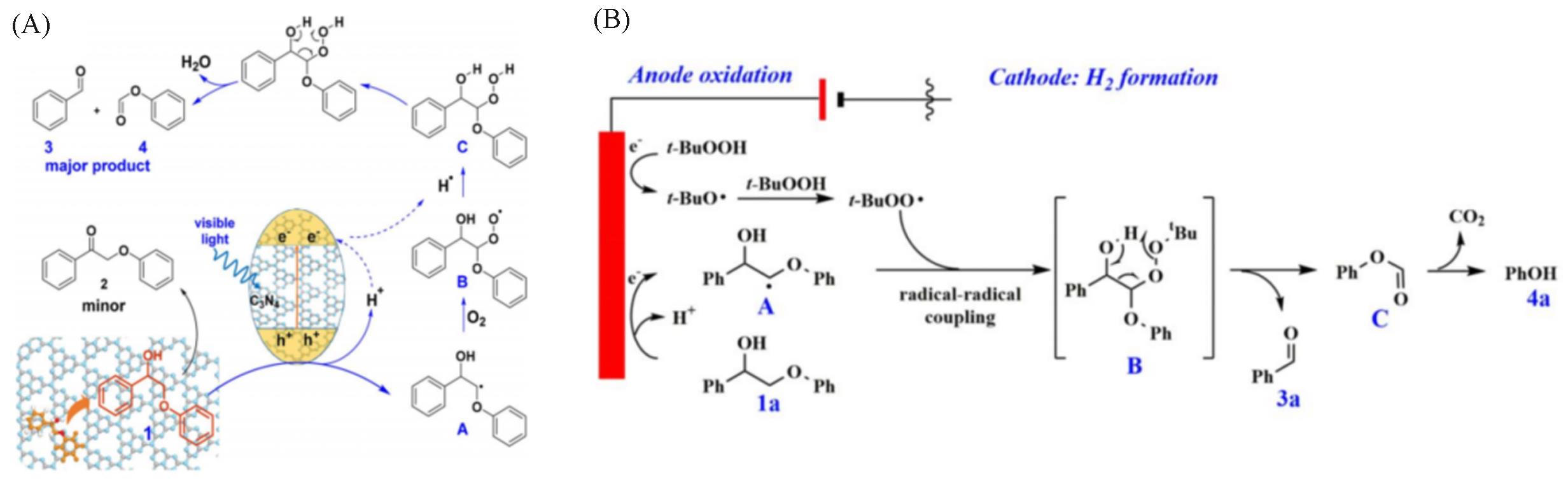
Fig.5 Mechanism of mesoporous graphitic carbon nitrides on catalyzing the transformation of lignin model molecule(A)[82] and mechanism for the electrocatalytic C α —C β bond cleavage of the lignin model compound(B)[83](A) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society
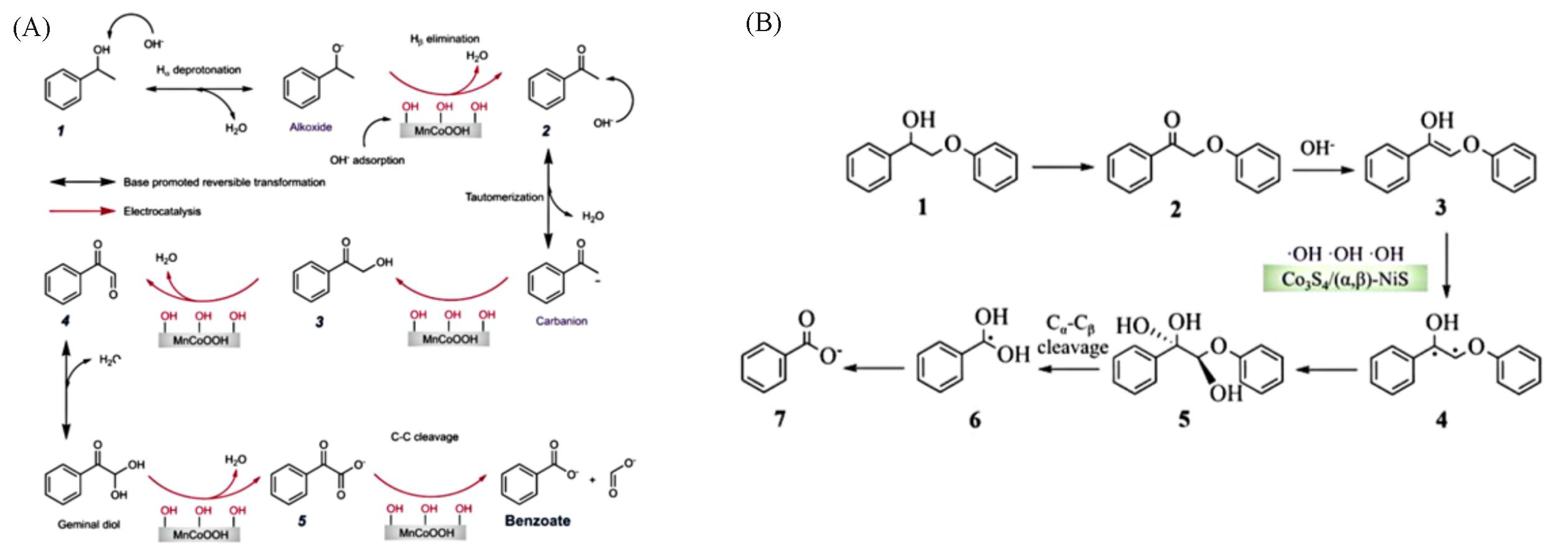
Fig.6 A plausible tandem nucleophilic oxidation reaction(NOR) mechanism for electrochemical oxidation (A)[87] and proposed oxidation pathways of PPE(B)[88]1. PPE; 2. 2⁃Phenoxy⁃1⁃phe⁃nylethanone; 3. (Z)⁃2⁃phenoxy⁃1⁃phenylethen⁃1⁃ol; 4. the intermediates of free radical
| 1 | Yang C., Maldonado S., Stephenson C. R. J., ACS Catal., 2021, 11(16), 10104—10114 |
| 2 | Zhang L. J., Rao T. U., Wang J. Y., Ren D. Z., Sirisommboonchai S., Choi C., Machida H., Huo Z. B., Norinaga K., Fuel Process. Technol., 2022, 226, 107097 |
| 3 | Li C. Z., Zhao X. C., Wang A. Q., Huber G. W., Zhang T., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115(21), 11559—11624 |
| 4 | Park J. H., Jin M. H., Lee D. W., Lee Y. J., Song G. S., Park S. J., Namkung H., Song K. H., Choi Y. C., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2019, 53(23), 14041—14053 |
| 5 | Lei L. J., Wang Y. H., Zhang Z. X., An J. H., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(15), 8788—8814 |
| 6 | Jing Y. X., Guo Y., Xia Q. N., Liu X. H., Wang Y. Q., Chem., 2019, 5(10), 2520—2546 |
| 7 | Rinaldi R., Jastrzebski R., Clough M. T., Ralph J., Kennema M., Bruijnincx P. C. A., Weckhuysen B. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(29), 8164—8215 |
| 8 | Luo N. C., Wang M., Li H. J., Zhang J., Liu H. F., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(11), 7716—7721 |
| 9 | Hendry A., Åhlén M., Fernandes T., Cheung O., Sanna A., Bioresource Technol., 2020, 317, 124008 |
| 10 | Shen X. J., Zhang C. F., Han B. X., Wang, F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51(5), 1608—1628 |
| 11 | Sudarsanam P., Zhong R. Y., van den Bosch S., Coman S. M., Parvulescu V. I., Sels B. F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47(22), 8349—8402 |
| 12 | da Cruz M. G. A., Gueret R., Chen J. H., Piątek J., Beele B., Sipponen M. H., Frauscher M., Budnyk S., Rodrigues B. V. M., Slabon A., ChemSusChem, 2022, 15(15), e20220718 |
| 13 | Chatterjee S., Saito T., ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(23), 3941—3958 |
| 14 | Zhou S. J., Wang H. M., Xiong S. J., Sun J. M., Wang Y. Y., Yu S. X., Sun Z. H., Wen J. L., Yuan T. Q., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(36), 12017—12042 |
| 15 | Ashokkumar V., Venkatkarthick R., Jayashree S., Chuetor S., Dharmaraj S., Kumar G., Chen W. H., Ngamcharussrivichai C., Bioresource Technol., 2022, 344, 126195 |
| 16 | Zhang C. F., Wang F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2020, 53(2), 470—484 |
| 17 | Zhang Z. R., Song J. L., Han B. X., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117(10), 6834—6880 |
| 18 | Lee K., Jing Y. X., Wang Y. Q., Yan N., Nature Rev. Chem., 2022, 6(9), 635—652 |
| 19 | Garedew M., Lin F., Song B., DeWinter T. M., Jackson J. E., Saffron C. M., Lam C. H., Anastas P. T., ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(17), 4214—4237 |
| 20 | Kumar A., Biswas B., Saini K., Kumar A., Kumar J., Krishna B. B., Bhaskar T., Renew. Energ., 2021, 172, 121—129 |
| 21 | Yang C. X., Chen H. N., Peng T., Liang B. Y., Zhang Y., Zhao W., Chinese J. Catal., 2021, 42(11), 1831—1842 |
| 22 | Weng J. K., Chapple C., New Phytol., 2010, 187(2), 273—285 |
| 23 | Xia Q. Q., Chen C. J., Yao Y. G., He S. M., Wang X. Z., Li, J. G., Gao J. L., Gan W. T., Jiang B., Cui M. J., Hu L. B., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(8), 2001588 |
| 24 | Bajwa D. S., Pourhashem G., Ullah A. H., Bajwa S. G., Ind. Crop. Prod., 2019, 139, 111526 |
| 25 | Gao M., Jiang Z. C., Ding W., Shi B., Green Chem., 2022, 24(1), 375—383 |
| 26 | Kubo S., Kadla J. F., J. Polym. Environ., 2005, 13(2), 97—105 |
| 27 | Galkin M. V., Samec J. S. M., ChemSusChem, 2016, 9(13), 1544—1558 |
| 28 | Peng T., Zhuang T. T., Yan Y., Qian J., Dick G. R., de Bueren J. B., Hung S. F., Zhang Y., Wang Z. Y., Wicks J., de Arquer F. P. G., Abed J., Wang N., Rasouli A. S., Lee G., Wang M., He D. P., Wang Z., Liang Z. X., Song L., Wang X., Chen B., Ozden A., Lum Y. W., Leow W. R., Luo M. C., Meira D. M., Ip A. H., Luterbacher J. S., Zhao W., Sargent E. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(41), 17226—17235 |
| 29 | Tian H. F., Guo G. P., Fu X. W., Yao Y. Y., Yuan L., Xiang A. M., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 120, 475—490 |
| 30 | Fan Y. Y., Liu C., Kong X. C., Han Y., Lei M., Xiao R., Green Energy Environ., 2022, 7(6), 1318—1326 |
| 31 | Wu X. J., Luo N. C., Xie S. J., Zhang H. K., Zhang Q. H., Wang F., Wang Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(17), 6198—6223 |
| 32 | Zaheer M., Kempe R., ACS Catal., 2015, 5(3), 1675—1684 |
| 33 | Ha J. M., Hwang K. R., Kim Y. M., Jae J., Kim K. H., Lee H. W., Kim J. Y., Park Y. K., Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev., 2019, 111, 422—441 |
| 34 | Beckham G. T., Johnson C. W., Karp E. M., Salvachúa D., Vardon D. R., Curr. Opin. Biotech., 2016, 42, 40—53 |
| 35 | Perez J. M., Sener C., Misra S., Umana G. E., Coplien J., Haak D., Li Y. D., Maravelias C. T., Karlen S. D., Ralph J., Donohue T. J., Noguera D. R., Green Chem., 2022, 24(7), 2795—2811 |
| 36 | Zirbes M., Waldvogel S. R., Curr. Opin. Green Sust., 2018, 14, 19—25 |
| 37 | Garedew M., Lam C. H., Petitjean L., Huang S. Q., Song B., Lin F., Jackson J. E., Saffron C. M., Anastas P. T., Green Chem., 2021, 23(8), 2868—2899 |
| 38 | Deuss P. J., Barta K., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2016, 306, 510—532 |
| 39 | Ma R. S., Guo M., Zhang X., Catal. Today, 2018, 302, 50—60 |
| 40 | Luo J. Z., Melissa P., Zhao W. G., Wang Z., Zhu Y. H., ChemistrySelect, 2016, 1(15), 4596—4601 |
| 41 | Guadix⁃Montero S., Sankar M., Top. Catal., 2018, 61(3/4), 183—198 |
| 42 | Kärkäs M. D., Matsuura B. S., Monos T. M., Magallanes G., Stephenson C. R. J., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2016, 14(6), 1853—1914 |
| 43 | Fang Z., Flynn M. G., Jackson J. E., Hegg E. L., Green Chem., 2021, 23(1), 412—421 |
| 44 | Limosin D., Pierre G., Cauquis G., Holzforschung, 1986, 40(1), 31—36 |
| 45 | Vanholme R., Demedts B., Morreel K., Ralph J., Boerjan W., Plant Physiol., 2010, 153(3), 895—905 |
| 46 | Liu Y. Q., Wang X. C., Wu Q. M., Pei W. H., Teo M. J., Chen Z. S., Huang C. X., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2022, 222, 994—1006 |
| 47 | Kishioka S, Yamada A., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2005, 578(1), 71—77 |
| 48 | Rafiee M., Alherech M., Karlen S. D., Stahl S. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(38), 15266—15276 |
| 49 | Bosque I., Magallanes G., Rigoulet M., Kärkäs M. D., Stephenson C. R. J., ACS Central. Science, 2017, 3(6), 621—628 |
| 50 | Gao W. J., Lam C. M., Sun B. G., Little R. D., Zeng C. C., Tetrahedron, 2017, 73(17), 2447—2454 |
| 51 | Pan K., Tian M., Jiang Z. H., Kjartanson B., Chen A. C., Electrochim. Acta, 2012, 60, 147—153 |
| 52 | Wang Y. S., Yang F., Liu Z. H., Yuan L., Li G., Catal. Commun., 2015, 67, 49—53 |
| 53 | Beliaeva K., Grimaldos⁃Osorio N., Ruiz⁃Lopez E., Burel L., Vernoux P., Caravaca A., Int. J. Hydrogen Energ., 2021, 46(72), 35752—35764 |
| 54 | Naderi Nasrabadi M., Bateni F., Chen Z. W., Harrington P. B., Staser J. A., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166(10), E317—E322. |
| 55 | Zhao H., Li C. F., Liu L. Y., Palma B., Hu Z. Y., Renneckar S., Larter S., Li Y., Kibria M. G., Hu J. G., Su B. L., J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2021, 585, 694—704 |
| 56 | Schmitt D., Regenbrecht C., Hartmer M., Stecker F., Waldvogel S. R., Beilstein J. Org. Chem., 2015, 11, 473—480 |
| 57 | Smith C. Z., Utley J. H. P., Hammond J. K., J. Appl. Electrochem., 2011, 41(4), 363—375 |
| 58 | Zirbes M., Schmitt D., Beiser N., Pitton D., Hoffmann T., Waldvogel S. R., ChemElectroChem, 2019, 6(1), 155—161 |
| 59 | Yan K. L., Zhang Y., Tu M. B., Sun Y. J., Energ. Fuel., 2020, 34(10), 12703—12709 |
| 60 | Ma X., Ma J., Li M., Gu Y., Wang T., Polym. Degrad. Stabil., 2022, 204, 110091 |
| 61 | Ghahremani R., Staser J. A., Holzforschung, 2018, 72(11), 951—960 |
| 62 | Honorato A. M. B., Khalid M., Curvelo A. A. D., Varela H., Shahgaldi S., Polymers⁃Basel, 2022, 14(18), 3781 |
| 63 | Deng Z., Fan H. X., Lan C. X., Zhang S. M., Li G., J. Ind. Eng. Chem., 2022, 108, 130—138 |
| 64 | Fraile J. M., García J. I., Hormigón Z., Mayoral J. A., Saavedra C. J., Salvatella L., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2018, 6(2), 1837—1847 |
| 65 | Zeng J. J., Mills M. J. L., Simmons B. A., Kent M. S., Sale K. L., Green Chem., 2017, 19(9), 2145—2154 |
| 66 | Sturgeon M. R., Kim S., Lawrence K., Paton R. S., Chmely S. C., Nimlos M., Foust T. D., Beckham G. T., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2014, 2(3), 472—485 |
| 67 | Jiang X. Y., Qiang L., Dong X. C., Bin H., Dong,C. Q., J. Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2016, 44(3), 335—341 |
| 68 | Zhou Y., Remón J., Jiang Z., Matharu A. S., Hu C., Green Energy Environ., 2023, doi: org/10.1016/j.gee.2022.03.001 |
| 69 | Kim S., Chmely S. C., Nimlos M. R., Bomble Y. J., Foust T. D., Paton R. S., Beckham G. T., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2(22), 2846—2852 |
| 70 | Beste A., Buchanan A. C., J. Org. Chem., 2011, 76(7), 2195—2203 |
| 71 | Dong L., Lin L. F., Han X., Si X. Q., Liu X. H., Guo Y., Lu F., Rudić S., Parker S. F., Yang S. H., Wang Y. Q., Chem, 2019, 5(6), 1521—1536 |
| 72 | Huang J. B., Wu S. B., Cheng H., Ming L., Liang J. J., Hong T., J. Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2015, 43(4), 429—436 |
| 73 | Pandey M. P., Kim C. S., Chem. Eng. Technol., 2011, 34(1), 29—41 |
| 74 | Du X., Tricker A. W., Yang W. S., Katahira R., Liu W., Kwok T. T., Gogoi P., Deng Y. L., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(23), 7719—7727 |
| 75 | Du X., Zhang H. C., Sullivan K. P., Gogoi P., Deng Y. L., Chemsuschem, 2020, 13(17), 4318—4343 |
| 76 | Wu K., Cao M., Zeng Q., Li X., Green Energy Environ., 2022, 8(2), 383—405 |
| 77 | Zhang C. F., Wang F., Chinese J. Catal., 2017, 38(7), 1102—1107 |
| 张超锋, 王峰. 催化学报, 2017, 38(7), 1102—1107 | |
| 78 | Han G. Q., Yan T., Zhang W., Zhang Y. C., Lee D. Y., Cao Z., Sun Y. J., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(12), 11341—11349 |
| 79 | Cui T. T., Ma L. N., Wang S. B., Ye C. L., Liang X., Zhang Z. D., Meng G., Zheng L. R., Hu H. S., Zhang J. W., Duan H. H., Wang D. S., Li Y. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2021, 143(25), 9429—9439 |
| 80 | Sedai B., Diaz⁃Urrutia C., Baker R. T., Wu R. L., Silks L. P., Hanson S. K., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(12), 3111—3122 |
| 81 | Wang X. T., Chu S., Shao J. J., Liu C., Luo Z. C., Xiao R., Zhang H. Y., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2022, 10(35), 11555—11566 |
| 82 | Liu H. F., Li H. J., Lu J. M., Zeng S., Wang M., Luo N. C., Xu S. T., Wang F., ACS Catal., 2018, 8(6), 4761—4771 |
| 83 | Ma L. N., Zhou H., Kong X. G., Li Z. H., Duan H. H., ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng., 2021, 9(4), 1932—1940 |
| 84 | Amadio E., Di Lorenzo R., Zonta C., Licini G., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2015, 301, 147—162 |
| 85 | Rahimi A., Azarpira A., Kim H., Ralph J., Stahl S. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(17), 6415—6418 |
| 86 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Ma L. N., Duan H. H., Chem. Commun., 2022, 58(7), 897—907 |
| 87 | Zhou H., Li Z. H., Xu S. M., Lu L. L., Xu M., Ji K. Y., Ge R. X., Yan Y. F., Ma L. N., Kong X. G., Zheng L. R., Duan H. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 133(16), 9058—9064 |
| 88 | Wang N., Xue R.,Yang N., Sun H., Zhang B. Y., Ma Z. M., Ma Y. Q., Zang L. H., J. Alloy. Compd., 2022, 929, 167324 |
| 89 | Gao H., Wang J., Liu M., Wang S., Li W., An Q., Li K., Wei L., Han C., Zhai S., Bioresource Technol., 2022, 127333 |
| 90 | Kang Y., Lu X. M., Zhang G. J., Yao X. Q., Xin J. Y., Yang S. Q., Yang Y. Q., Xu J. L., Feng M., Zhang S. J., ChemSusChem, 2019, 12(17), 4005—4013 |
| [1] | 池丽萍, 牛壮壮, 廖洁, 唐凯斌, 高敏锐. 过渡金属氧化物插层化学及其电催化应用的新进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220740. |
| [2] | 李轩, 亓帅, 周伟良, 李小杰, 景玲胭, 冯超, 蒋兴星, 杨恒攀, 胡琪, 何传新. 纤维基氧化还原电催化剂的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 316. |
| [3] | 张潇然, 郑建云, 吕艳红, 王双印. 绿色路径C-N偶联合成尿素的最新研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220717. |
| [4] | 杜磊, 刘兆清. 非贵金属催化剂在羟甲基糠醛电氧化增值中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220710. |
| [5] | 夏文文, 于洪晶, 王时野, 姚丽, 李象远. 用于燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法—芳香烃燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220616. |
| [6] | 高凤雨, 陈都, 罗宁, 姚小龙, 段二红, 易红宏, 赵顺征, 唐晓龙. MnO x -CeO2催化剂的氯苯氧化性能及反应机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220690. |
| [7] | 刘至辰, 张宏伟, 张博稳, 陈鹏, 袁珮. 吸附法制备金属/碳催化剂用于5-羟基甲基糠醛高效电催化氧化的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220631. |
| [8] | 杨庆凤, 吕良, 赖小勇. 中空MOFs材料制备及电催化应用的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220666. |
| [9] | 匡华艺, 陈晨. 贵金属纳米框架设计合成及电催化性能的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220586. |
| [10] | 林高鑫, 王家成. 单原子掺杂二硫化钼析氢催化的进展和展望[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [11] | 汪思聪, 庞贝贝, 刘潇康, 丁韬, 姚涛. XAFS技术在单原子电催化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220487. |
| [12] | 秦永吉, 罗俊. 单原子催化剂在CO2转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [13] | 姚青, 俞志勇, 黄小青. 单原子催化剂的合成及其能源电催化应用的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220323. |
| [14] | 范建玲, 唐灏, 秦凤娟, 许文静, 谷鸿飞, 裴加景, 陈文星. 氮掺杂超薄碳纳米片复合铂钌单原子合金催化剂的电化学析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [15] | 韩付超, 李福进, 陈良, 贺磊义, 姜玉南, 徐守冬, 张鼎, 其鲁. CoSe2/C复合电催化材料修饰隔膜对高载量锂硫电池性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220163. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||