

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 20220235.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220235
周紫璇1,2, 杨海艳1,2, 孙予罕1,3,4( ), 高鹏1,2(
), 高鹏1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2022-04-11
出版日期:2022-07-10
发布日期:2022-04-30
通讯作者:
孙予罕,高鹏
E-mail:sunyh@sari.ac.cn;gaopeng@sari.ac.cn
基金资助:
ZHOU Zixuan1,2, YANG Haiyan1,2, SUN Yuhan1,3,4( ), GAO Peng1,2(
), GAO Peng1,2( )
)
Received:2022-04-11
Online:2022-07-10
Published:2022-04-30
Contact:
SUN Yuhan,GAO Peng
E-mail:sunyh@sari.ac.cn;gaopeng@sari.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
化石燃料的利用为人类社会带来了前所未有的繁荣和发展. 然而, 化石燃料燃烧引起的过量的二氧化碳(CO2)排放导致全球气候变化和海洋酸化; 而且作为一种有限的资源, 化石燃料的消耗将迫使人们寻找其它碳源以维持可持续的发展. 利用可再生能源获取电能分解水制得的绿色氢气(H2)与捕集后的CO2反应制成甲醇, 不仅能有效利用工业废气中多余的CO2, 还能获取清洁、 可再生的甲醇化学品, 该过程的技术核心是开发高效稳定的CO2加氢制甲醇催化剂. 本文综合评述了现有研究关注较多的多相催化CO2加氢制甲醇催化剂的反应机理和构效关系, 总结了目前多相催化CO2加氢制甲醇催化剂(Cu基催化剂、 贵金属与双金属催化剂、 氧化物催化剂以及其它新型催化剂)的设计与合成方面的研究进展, 最后对该领域所面临的机遇和挑战进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235.
ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235.
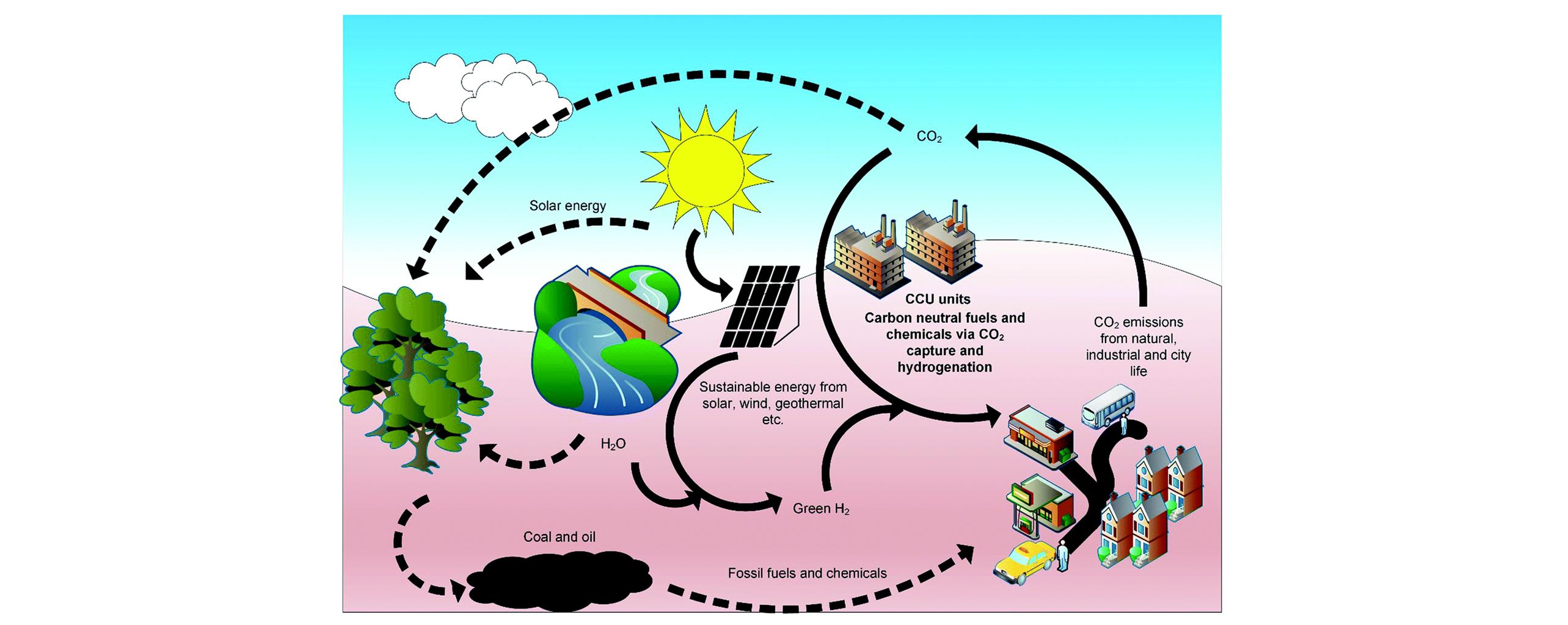
Fig.1 General concept of a future sustainable carbon neutral cycle(black arrows) based on hydrogenation industries vs. current carbon cycle(black dotted?arrows) via fossil resources based industries[3]Copyright 2021, Royal Society of Chemistry.
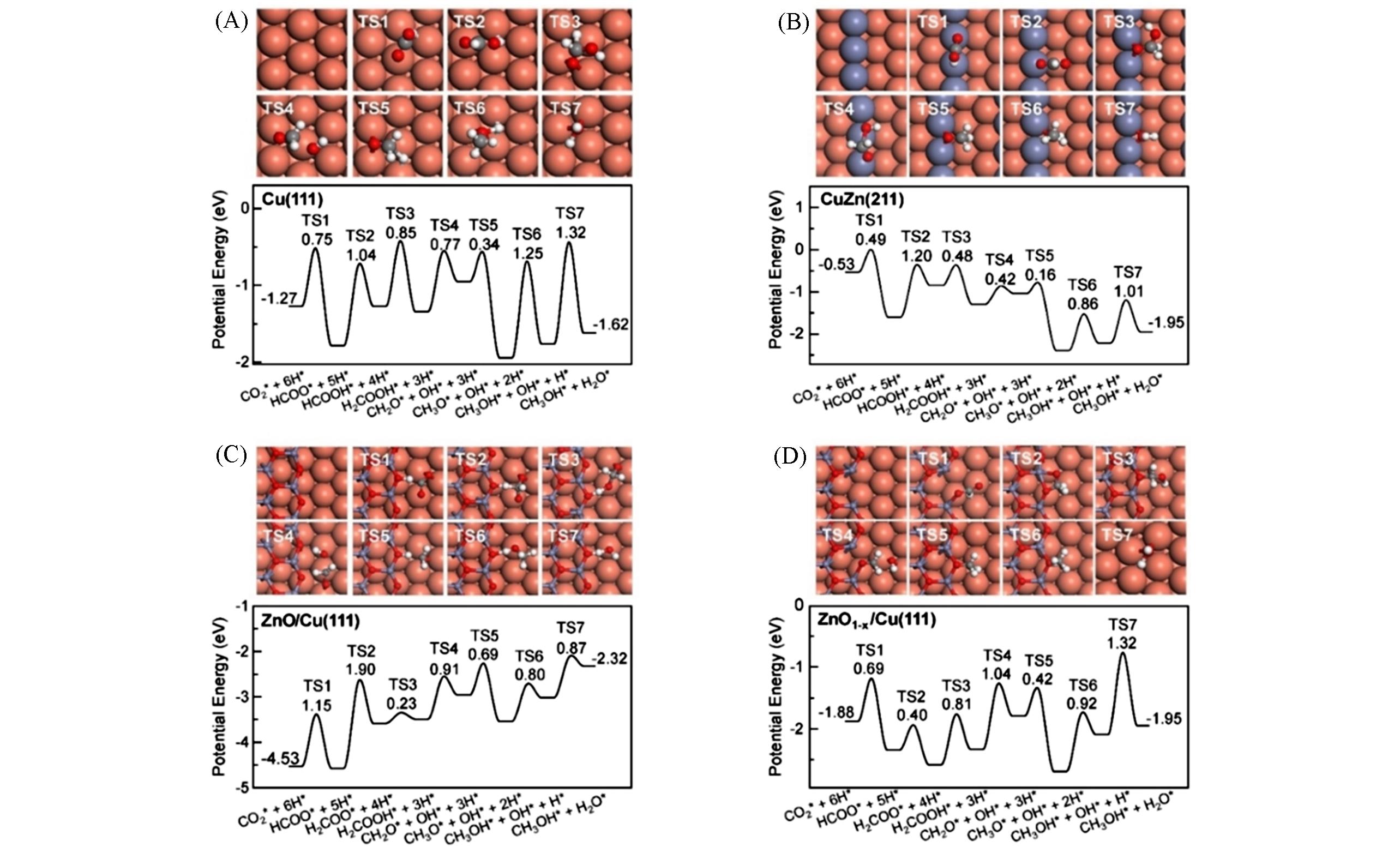
Fig.3 Reaction energy profiles of CO2 hydrogenation on Cu(111)(A), CuZn(211)(B), ZnO/Cu(111)(C) and ZnO1-x /Cu(111)(D) in the favorable formate pathway, indicating the top views of transition states(TS) configurations and corresponding barriers[13]The brown, red, gray, black and white balls represent Cu, O, Zn, C and H atoms, respectively. The energy reference zero corresponds to the energy of H2 and CO2 in gas phase. Copyright 2020, John Wiley and Sons.
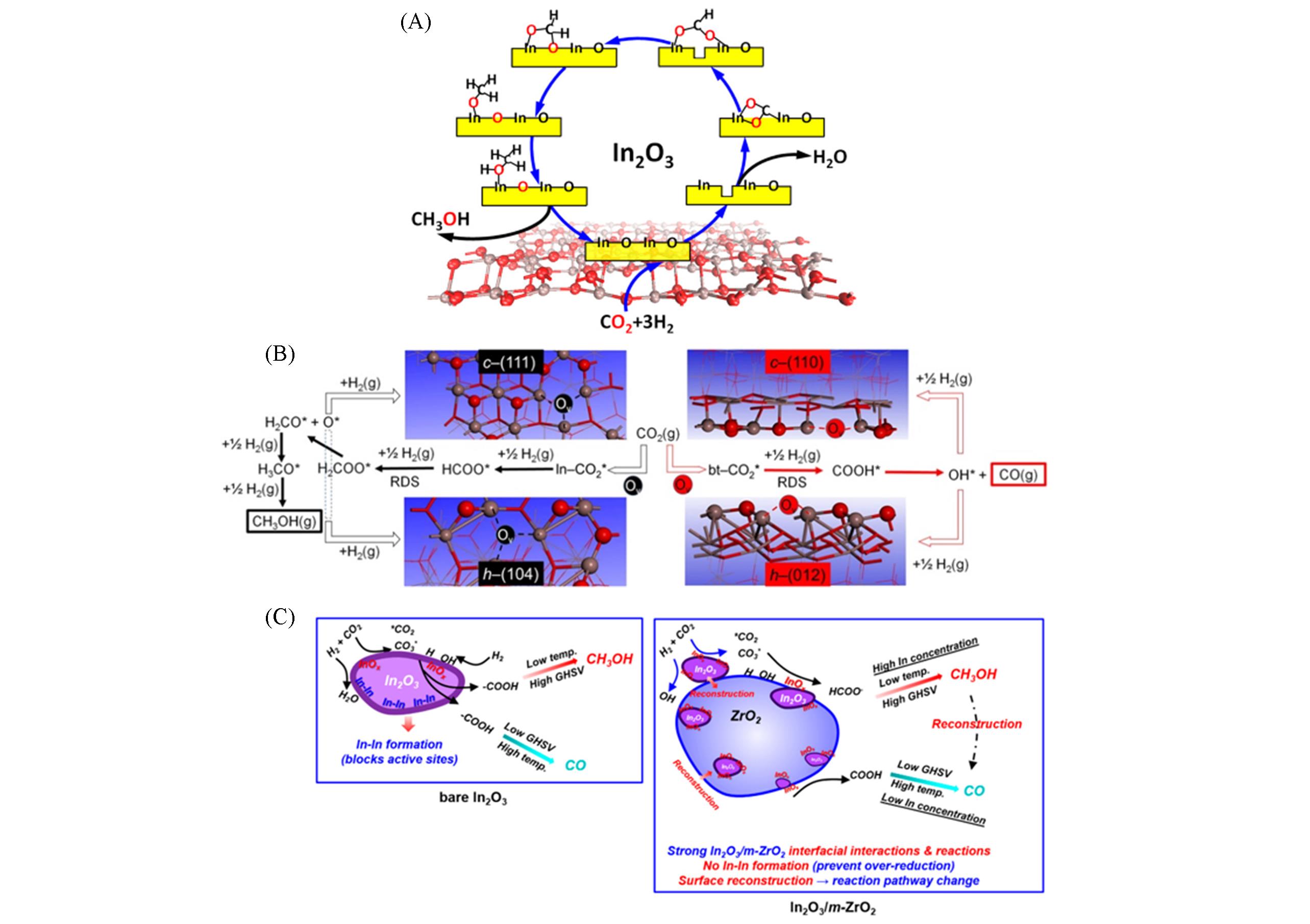
Fig.4 Active oxygen vacancy site for CO2 hydrogenation to methanol on the defective In2O3(110) surface[15](A); schematic illustration of the most favorable CO2 hydrogenation pathways on different c?In2O3 and h?In2O3 surfaces[16](B) and cartoons summarizing the chemical and structural characteristics of different In2O3?based catalysts under in situ conditions[19](C)(A) Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2020, Science; (C) Copyright 2022, American Chemical Society.
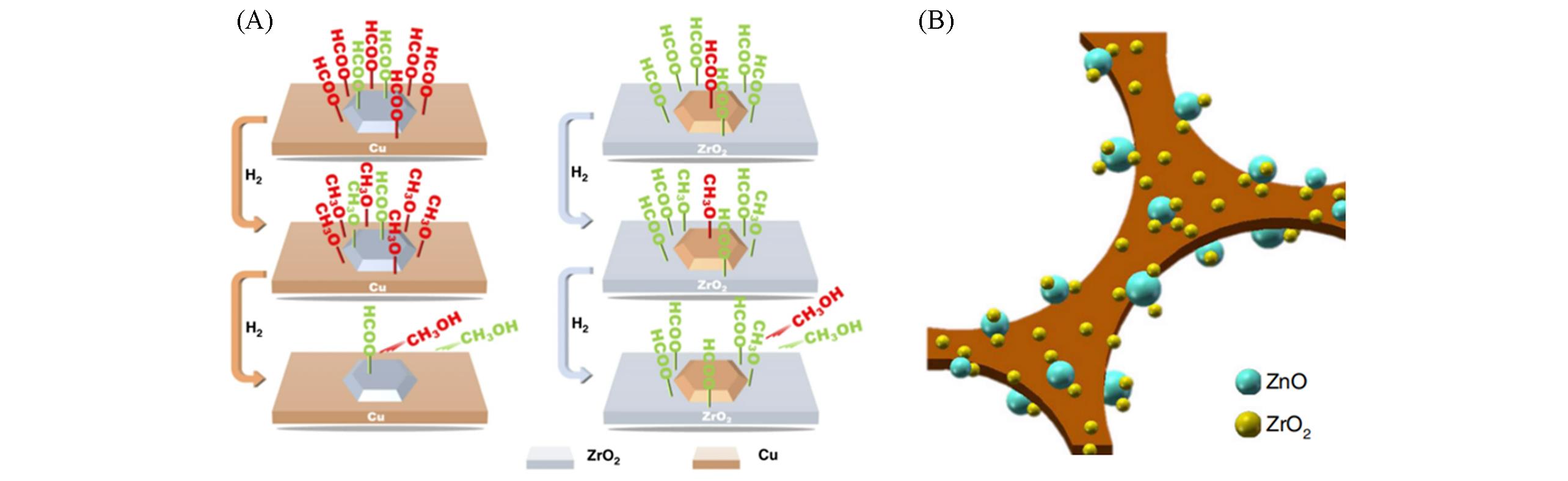
Fig.5 Scheme illustrating the reaction behaviors of the HCOO?Cu and HCOO?Zr intermediates on inverse ZrO2/Cu and Cu/ZrO2 catalysts[23](A) and structural diagrammatic sketch of the macroporous catalyst[27](B)(A) Copyright 2020, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.
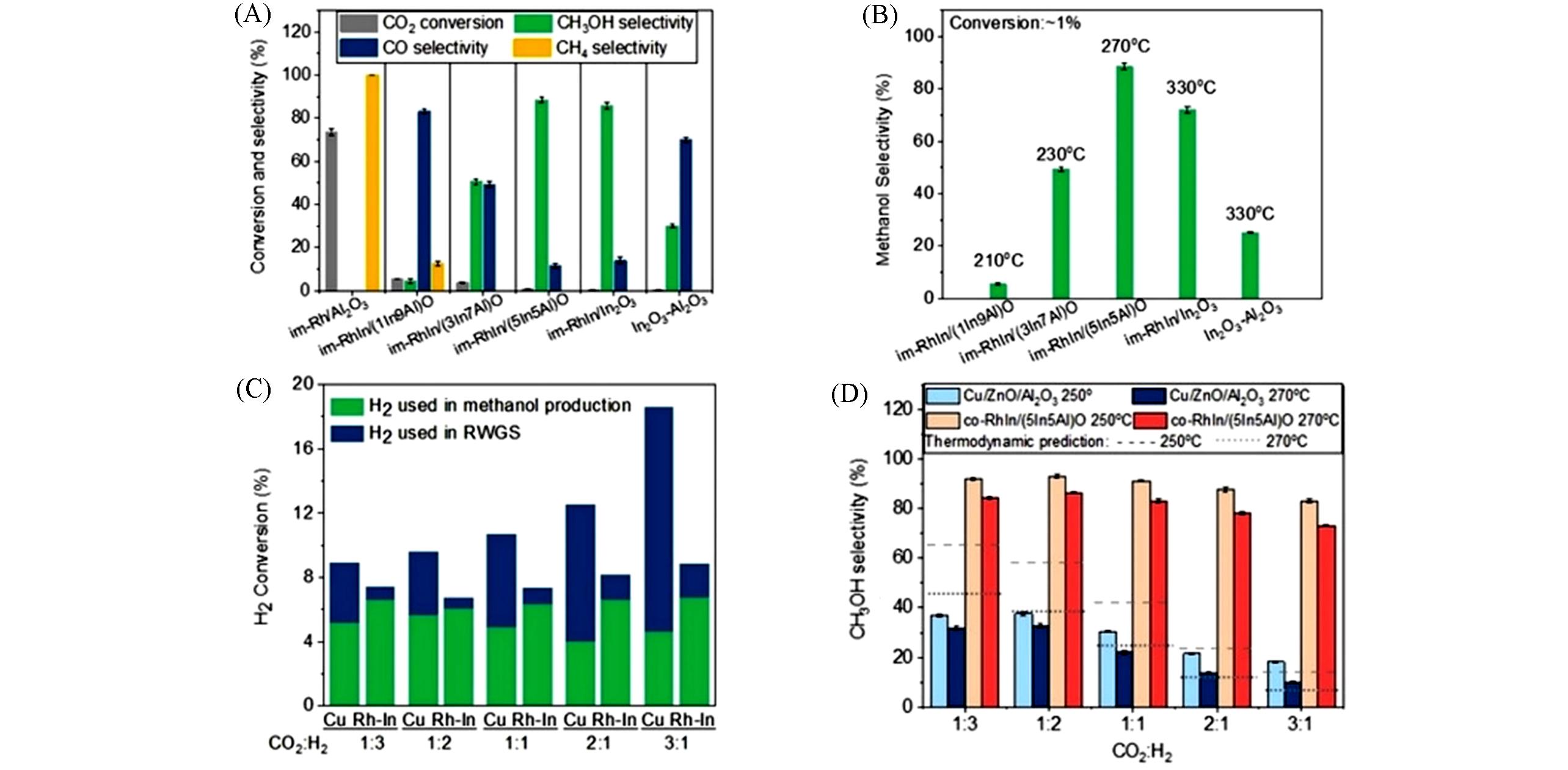
Fig.6 Catalytic performance of CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[42](A) CO2 conversions and the selectivities of CO, CH3OH, and CH4 of Rh catalysts with different In/Al ratios prepared via the wet-impregnation method; (B) methanol selectivities of Rh catalysts prepared by wet-impregnation methods when evaluated under the same CO2 conversion of 1%; (C) H2 conversion toward methanol production and RWGS reaction of co-RhIn/(5In5Al)O compared with Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst under different CO2/H2 ratios; (D) methanol selectivities at 250 ℃ and 270 ℃ of co-RhIn/(5In5Al)O sample compared with the commercial Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 catalyst under different CO2/H2 ratios. Typical testing conditions are the pressure of 4.5 MPa, reactant mixture of CO2/H2=1∶3, reaction temperature of 270 ℃, WHSV of 18000 mL/(gcat.·h) unless otherwise indicated. Copyright 2020, John Wiley and Sons Wiely.
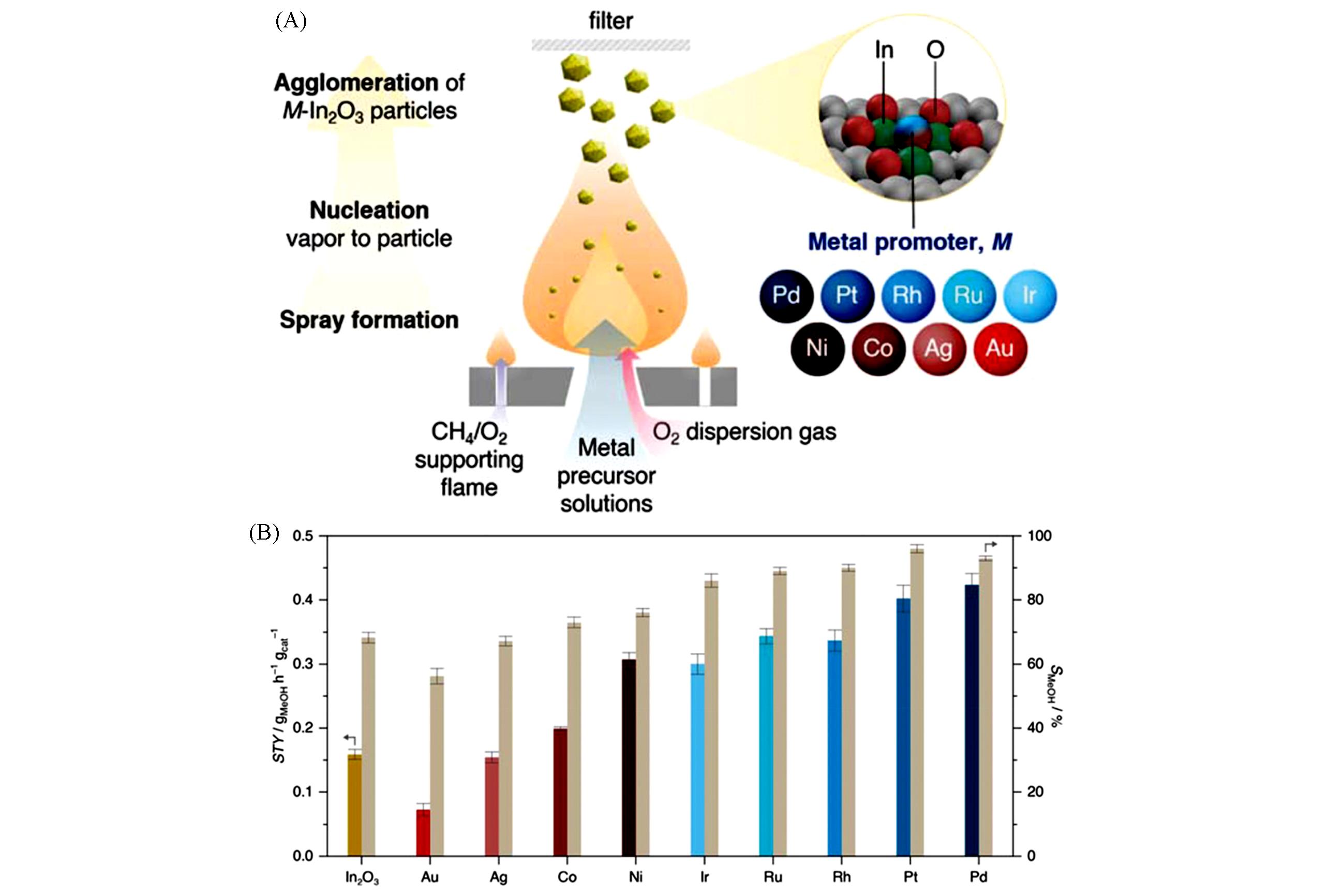
Fig.7 Scheme of the FSP method for the preparation of M?In2O3 catalysts(A) and methanol space?time yield(STY, colored bars) and selectivity(SMeOH, beige bars) during CO2 hydrogenation over undoped In2O3 and M?In2O3 catalysts(0.5% of metal) prepared by FSP(B)[58]The methanol STY is assessed at WHSV=24000 cm3/(kgcat.?h), while SMeOH at constant CO2 conversion(≈3%) and variable WHSV. Averaged values measured over 24 h on stream are presented with their corresponding error bars. Reaction conditions: 553 K, 5 MPa, H2/CO2=4. Copyright 2022, John Wiley and Sons.
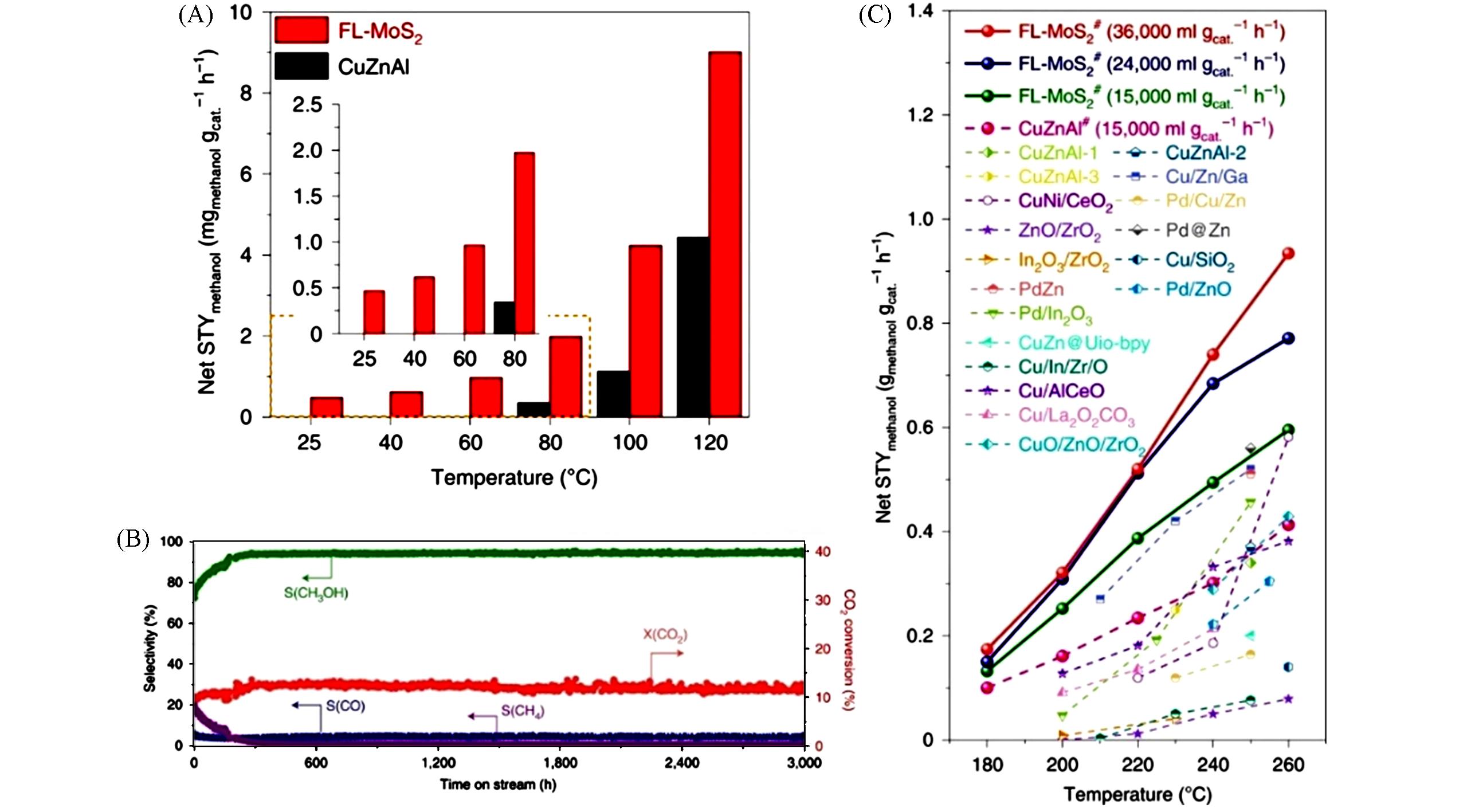
Fig.8 Catalytic properties of different catalysts in CO2 hydrogenation to methanol[32](A) Comparison of net space-time-yield of methanol(STYmethanol, calculated based on the amount of catalyst) on the Cu/ZnO/Al2O3(CuZnAl) and FL-MoS2 catalysts from 25?℃ to 120?℃ at a GHSV of 1500 ?mL/(gcat.?h). The inset shows an enlargement of the dashed box area. (B) Stability test of the FL-MoS2 catalyst in the CO2 hydrogenation reaction at 3000?mL/(gcat.?h), measuring the selectivity(S) and conversion(X) over 3000?h. (C) Comparison of the net STYmethanol over the FL-MoS2 and other state-of-the-art catalysts under similar reaction conditions.Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
| 1 | Zhang X., Zhang G., Song C., Guo X., Front. Energy Res., 2021, 8, 621119 |
| 2 | Shih C. F., Zhang T., Li J., Bai C., Joule, 2018, 2(10), 1925—1949 |
| 3 | Bai S., Smet G. D., Liao Y., Sun R., Zhou C., Beller M., Maes B. U. W., Sels B. F., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(7), 4259—4298 |
| 4 | Wang J., Zhang G., Zhu J., Zhang X., Ding F., Zhang A., Guo X., Son C., ACS Catal., 2021, 11(3), 1406—1423 |
| 5 | Wang Y. Y., Liu H. Z., Han B. X., Chem. J. Chinese University, 2020, 41(11), 2393—2403 |
| 王艳燕, 刘会贞, 韩布兴. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11), 2393—2403 | |
| 6 | Jiang X., Nie X., Guo X., Song C., Chen J. G., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(15), 7984—8034 |
| 7 | Zhong J., Yang X., Wu Z., Liang B., Huang Y., Zhang T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(5), 1385—1413 |
| 8 | Francesco A., Katia B., Giuseppe I., Giuseppe B., Lorenzo S., Francesco F., J. Catal., 2007, 249(2), 185—194 |
| 9 | Arena F., Italiano G., Barbera K., Bonura G., Spadaro L., Frusteri F., Catal. Today, 2009, 143(1/2), 80—85 |
| 10 | Ian A. F., Alexis T. B., J. Catal., 1997, 172(1), 222—237 |
| 11 | Arena F., Italiano G., Barbera K., Bordiga S., Bonura G., Spadaro L., Frusteri F., Appl. Catal., A, 2008, 350(1), 16—23 |
| 12 | Qi S., Liu X., Zhu R., Xue D., Liu X., Sun L., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 430, 132784 |
| 13 | Liu X., Luo J., Wang H., Huang L., Wang S., Li S., Sun Z., Sun F., Jiang Z., Wei S., Li W. X., Lu J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, e202202330 |
| 14 | Thrane J., Kuld S., Nielsen N. D., Jensen A. D., Sehested J., Christensen J. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(41), 18189—18193 |
| 15 | Ye J. Y., Liu C. J., Mei D. H., Ge Q. F., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(6), 1296—1306 |
| 16 | Dang S. S., Qin B., Yang Y., Li S. G., Gao P., Sun Y. H., Sci. Adv., 2020, 6, eaaz2060 |
| 17 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Cesarini A., Krumeich F., Hauert R., Stewart J. A., Curulla Ferré D., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., ACS Catalysis, 2019, 10(2), 1133—1145 |
| 18 | Yang C., Pei C., Luo R., Liu S., Wang Y., Wang Z., Zhao Z. J., Gong J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(46), 19523—19531 |
| 19 | Zhang X., Kirilin A. V., Rozeveld S., Kang J. H., Pollefeyt G., Yancey D. F., Chojecki A., Vanchura B., Blum M., ACS Catal., 2022, 12(7), 3868—3880 |
| 20 | Xiao S., Zhang Y. F., Gao P., Zhong L. S., Li X. P., Zhang Z. Z., Wang H., Wei W., Sun Y. H., Catal. Today, 2017, 281, 327—333 |
| 21 | Zhou Z. X., Gao P., Chin. J. Catal., 2022, 43, 2045—2056 |
| 22 | Raudaskoski R., Turpeinen E., Lenkkeri R., Pongrácz E., Keiski R. L., Catal. Today, 2009, 144(3/4), 318—323 |
| 23 | Wu C., Lin L., Liu J., Zhang J., Zhang F., Zhou T., Rui N., Yao S., Deng Y., Yang F., Xu W., Luo J., Zhao Y., Yan B., Wen X. D., Rodriguez J. A., Ma D., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 5767 |
| 24 | Mauro M., Francesca F., Alberto P., Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 258, 117941 |
| 25 | Yu J., Liu S., Mu X., Yang G., Luo X., Lester E., Wu T., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 419, 129656 |
| 26 | Zhu Y., Zheng J., Ye J., Cui Y., Koh K., Kovarik L., Camaioni D. M., Fulton J. L., Truhlar D. G., Neurock M., Cramer C. J., Gutierrez O. Y., Lercher J. A., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 5849 |
| 27 | Wang Y., Kattel S., Gao W., Li K., Liu P., Chen J. G., Wang H., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 1166 |
| 28 | Zhong C., Guo X., Mao D., Wang S., Wu G., Lu G., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(65), 52958—52965 |
| 29 | Chen K., Duan X. P., Fang H. H., Liang X. L., Yuan Y. Z., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2018, 4(8), 1062—1069 |
| 30 | Chen K., Fang H. H., Wu S., Liu X., Zheng J. W., Zhou S., Duan X. P., Zhuang Y. C., Tsang S. C. E., Yuan Y. Z., Appl. Catal., B, 2019, 251, 119—129 |
| 31 | Yu J., Yang M., Zhang J., Ge Q., Zimina A., Pruessmann T., Zheng L., Grunwaldt J. D., Sun J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(24), 14694—14706 |
| 32 | Hu J., Yu L., Deng J., Wang Y., Cheng K., Ma C., Zhang Q., Wen W., Yu S., Pan Y., Yang J., Ma H., Qi F., Wang Y., Zheng Y., Chen M., Huang R., Zhang S., Zhao Z., Mao J., Meng X., Ji Q., Hou G., Han X., Bao X., Wang Y., Deng D., Nat. Catal., 2021, 4(3), 242—250 |
| 33 | Matsumur Y., Shen W. J., Ichihashi Y., Okumura M., J. Catal., 2001, 197(2), 267—272 |
| 34 | Hasliza B., Michael B., Graham H., Nikolaos D., Peter W., Emma G., Wilm J., Catherine B., David M., Georgi L., J. Catal., 2016, 343, 133—146 |
| 35 | Maxim Z., Vitaly L. S., Mark A. N., Frank K., Maarten N., Jeroen A. V. B., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(31), 17053—17059 |
| 36 | Song J., Liu S., Yang C., Wang G., Tian H., Zhao Z. J., Mu R., Gong J., Appl. Catal., B, 2020, 263, 118367 |
| 37 | Dybbert V., Fehr S. M., Klein F., Schaadt A., Hoffmann A., Frei E., Erdem E., Ludwig T., Hillebrecht H., Krossing I., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58(37), 12935—12939 |
| 38 | Li H., Wang L., Dai Y., Pu Z., Lao Z., Chen Y., Wang M., Zheng X., Zhu J., Zhang W., Si R., Ma C., Zeng J., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2018, 13(5), 411—417 |
| 39 | Toyao T., Kayamori S., Maeno Z., Siddiki S. M. a. H., Shimizu K. I., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(9), 8187—8196 |
| 40 | Letícia F. R., Rafael A. D. S., Luiz H. V., Vivianne K. O. R., Lucas G. V., José M. A., Juarez L. F. D. S., Elisabete M. A., Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 302, 120842 |
| 41 | Snider J. L., Streibel V., Hubert M. A., Choksi T. S., Valle E., Upham D. C., Schumann J., Duyar M. S., Gallo A., Abild⁃Pedersen F., Jaramillo T. F., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(4), 3399—3412 |
| 42 | Li M. M. J., Zou H., Zheng J., Wu T. S., Chan T. S., Soo Y., Wu X. P., Gong X. Q., Chen T., Roy K., Held G., Tsang S. C. E., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(37), 16039—16046 |
| 43 | Zhang M. H., Dou M. B., Yu Y. Z., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 433, 780—789 |
| 44 | Dou M. B., Zhang M. H., Chen Y. F., Yu Y. Z., New J. Chem., 2018, 42(5), 3293—3300 |
| 45 | Shen C., Sun K., Zhang Z., Rui N., Jia X., Mei D., Liu C. J., ACS Catal., 2021, 11(7), 4036—4046 |
| 46 | Martin O., Martin A. J., Mondelli C., Mitchell S., Segawa T. F., Hauert R., Drouilly C., Curulla⁃Ferre D., Perez⁃Ramirez J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(21), 6261—6265 |
| 47 | Han Z., Tang C., Wang J., Li L., Li C., J. Catal., 2020, 394, 236—244 |
| 48 | Sun K., Rui N., Zhang Z., Sun Z., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Green Chem., 2020, 22, 5059—5066 |
| 49 | Rui N., Wang Z., Sun K., Ye J., Ge Q., Liu C. J., Appl. Catal., B, 2017, 218, 488—497 |
| 50 | Matthias S. F., Cecilia M., Rodrigo G. M., Klara S. K., Begoña P., Núria L., Olga V. S., Joseph A. S., Daniel Curulla F., Javier P. R., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 3377 |
| 51 | Cai Z., Huang M., Dai J., Zhan G., Sun F. L., Zhuang G. L., Wang Y., Tian P., Chen B., Ullah S., Huang J., Li Q., ACS Catal., 2021, 12(1), 709—723 |
| 52 | Rui N., Sun K., Shen C., Liu C. J., J. CO2 Util., 2020, 42, 101313 |
| 53 | Rui N., Zhang F., Sun K., Liu Z., Xu W., Stavitski E., Senanayake S. D., Rodriguez J. A., Liu C. J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(19), 11307—11317 |
| 54 | Shi Z., Tan Q., Tian C., Pan Y., Sun X., Zhang J., Wu D., J. Catal., 2019, 379, 78—89 |
| 55 | Anastasiya B., Irina Y., Abdullah J. A. A., Lieven G., Mohamed Nejib H., Xiaohe M., Adrian Ramírez G., Alexey P., Alla D., Amandine C., Antonio A. T., Jean-Louis H., Sergey M. K., Samy O. C., Luigi C., Jorge G., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(8), 6910—6918 |
| 56 | Jia X., Sun K., Wang J., Shen C., Liu C. J., J. Energy Chem., 2020, 50, 409—415 |
| 57 | Frei M. S., Mondelli C., Garcia⁃Muelas R., Morales⁃Vidal J., Philipp M., Safonova O. V., Lopez N., Stewart J. A., Ferre D. C., PerezRamirez J., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 1960 |
| 58 | Araújo T. P., Morales⁃Vidal J., Zou T. S., García⁃Muelas R., Willi P. O., Engel K. M., Safonova O. V., Akl D. F., Krumeich F., Grass R. N., Mondelli C., López N., Pérez⁃Ramírez J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(14), 2103707 |
| 59 | Cai Z., Dai J., Li W., Tan K. B., Huang Z., Zhan G., Huang J., Li Q., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(22), 13275—13289 |
| 60 | Jiang F., Wang S., Liu B., Liu J., Wang L., Xiao Y., Xu Y., Liu X., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(19), 11493—11509 |
| 61 | Wang J., Li G., Li Z., Tang C., Feng Z., An H., Liu H., Liu T., Li C., Sci. Adv., 2017, 3, e1701290 |
| 62 | Wang J., Tang C., Li G., Han Z., Li Z., Liu H., Cheng F., Li C., ACS Catal., 2019, 9(11), 10253—10259 |
| 63 | Sha F., Tang C., Tang S., Wang Q., Han Z., Wang J., Li C., J. Catal., 2021, 404, 383—392 |
| 64 | Kyungho L., Uzma A., Thaylan Pinheiro A., Cecilia M., Qian H., Shinya F., Javier P. R., Sergey M. K., Ning Y., Appl. Catal., B, 2021, 304, 120994, |
| 65 | Wang L. X., Guan E., Wang Y. Q., Wang L., Gong Z. M., Cui Y., Meng X. J., Gates B. C., Xiao F. S., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 1033 |
| 66 | Meng C., Zhao G., Shi X. R., Chen P., Liu Y., Lu Y., Sci. Adv., 2021, 7, eabi6012 |
| [1] | 张昕昕, 许狄, 王艳秋, 洪昕林, 刘国亮, 杨恒权. CO2加氢制低碳醇CuFe基催化剂中的Mn助剂效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [2] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [3] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [4] | 李加富, 张凯, 王宁, 孙启明. 分子筛限域单原子金属催化剂的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220032. |
| [5] | 孙翠红, 吕立强, 刘迎, 王妍, 杨静, 张绍文. 硝酸异丙酯与Cl原子、 OH和NO3自由基反应的机理及动力学[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [6] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [7] | 孟繁伟, 高琦, 叶青, 李晨曦. Cu-SAPO-18催化剂氨选择性催化还原NOx钾中毒机理的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [8] | 杨一莹, 朱荣秀, 张冬菊, 刘成卜. 金催化炔基苯并二𫫇英环化合成8-羟基异香豆素的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [9] | 李心怡, 刘永军. 人工设计逆醛缩酶RA95.5-8F催化β-羟基酮C—C裂解的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2306. |
| [10] | 李宜蔚, 申屠江涛, 王静波, 李象远. 燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法: C1燃料燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1871. |
| [11] | 田胜侨, 韦美菊. Rh(Ⅱ)催化吲哚衍生物[3+3]环化机理及产物性质分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1899. |
| [12] | 任颖, 李昌华, 王涛, 薛珊珊, 张婷婷, 贾建峰, 武海顺. 钯催化氧化N—H键羰基化反应合成1,3,4⁃噁二唑⁃2(3H)⁃酮杂环化合物机理的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1793. |
| [13] | 刘瀚林, 尹琳琳, 陈西凤, 李国栋. 氧化铟基纳米催化剂用于二氧化碳选择性加氢的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1430. |
| [14] | 齐国栋, 叶晓栋, 徐君, 邓风. 分子筛上糖类催化转化的核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(1): 148. |
| [15] | 张维中,温月丽,宋镕鹏,王斌,张倩,黄伟. 催化剂表面Cu0含量对二氧化碳加氢合成C2+醇性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6): 1297. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||