

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 20230155.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230155
廖首维1, 刘炎昌1, 石泽南1, 赵道辉2, 魏嫣莹1,3( ), 李理波1,3(
), 李理波1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2023-03-30
出版日期:2023-10-10
发布日期:2023-05-31
通讯作者:
魏嫣莹,李理波
E-mail:ceyywei@scut.edu.cn;celbli@scut.edu.cn
作者简介:第一联系人:共同第一作者.
基金资助:
LIAO Shouwei1, LIU Yanchang1, SHI Zenan1, ZHAO Daohui2, WEI Yanying1,3( ), LI Libo1,3(
), LI Libo1,3( )
)
Received:2023-03-30
Online:2023-10-10
Published:2023-05-31
Contact:
WEI Yanying, LI Libo
E-mail:ceyywei@scut.edu.cn;celbli@scut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
受限在二维纳米孔道的盐溶液的研究对离子输运与筛分、 超级电容等领域具有重要意义, 而分子动力学(MD)模拟已成为其中重要的手段. 但通常MD模拟力场却很难准确描述石墨烯等二维材料与离子之间的离子-π相互作用; 溶剂效应对离子在材料表面吸附的调控作用也缺乏深入研究. 针对Li+, Na+, K+, Mg2+, Ca2+, Cl-离子与石墨烯材料, 本文基于平均力势(PMF)发展了模拟它们之间相互作用的力场参数. 使用该力场模拟的(溶液中)石墨烯表面离子吸附自由能与量子化学计算结果一致, 验证了其准确性. 进一步发现离子水合半径、 离子接近石墨烯时水合数的拐点、 PMFwat(溶剂对离子吸附在石墨烯表面PMF的贡献)极小值位置及石墨烯表面水层位置之间有明显关联. 在此基础上阐明了离子脱水及石墨烯表面水层状分布对PMFwat的调控作用. 模拟了1 mol/L盐溶液/石墨烯界面体系. 以上体系使用通常力场参数模拟时, 离子在石墨烯表面吸附都很微弱, 这表明离子-π相互作用对准确模拟盐溶液-石墨烯体系不可或缺.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
廖首维, 刘炎昌, 石泽南, 赵道辉, 魏嫣莹, 李理波. 水/石墨烯界面离子吸附的分子动力学模拟: 力场参数优化与吸附机制. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230155.
LIAO Shouwei, LIU Yanchang, SHI Zenan, ZHAO Daohui, WEI Yanying, LI Libo. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Ion Adsorption at Water/Graphene Interface: Force Field Parameter Optimization and Adsorption Mechanism. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2023, 44(10): 20230155.
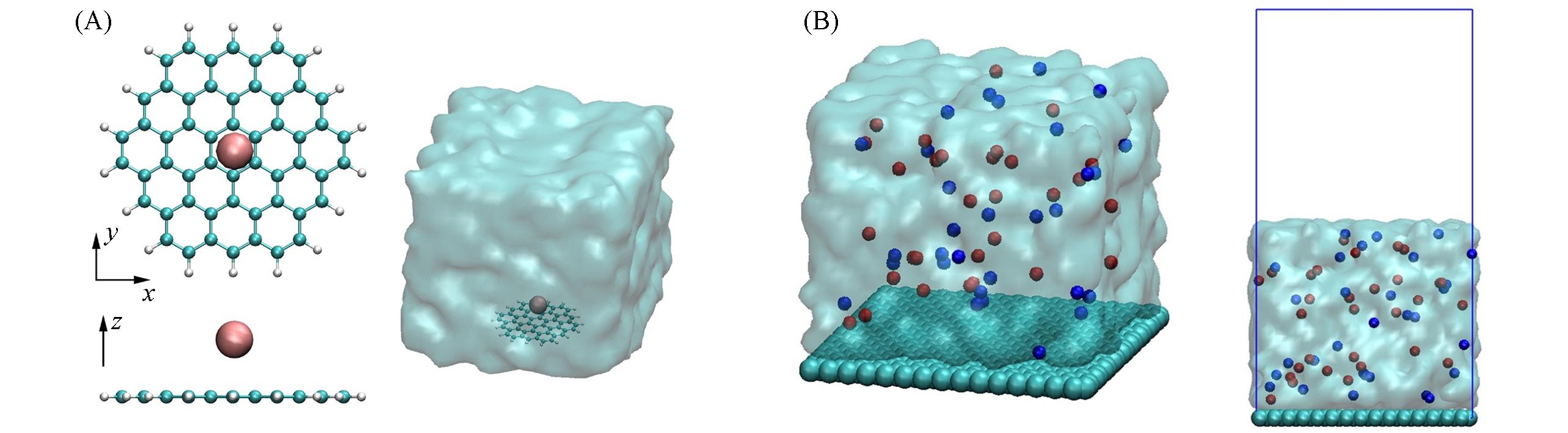
Fig.1 Simulation system of single ion + graphene in aqueous solution(A) and 1 mol/L salt solution/graphene interface(B)(A) The ion is placed above the center of the graphene flake(cyan and white balls represent carbon atoms and terminated hydrogen atoms, respectively) and the simulation box is filled with water; for clarity, only the oblique view shows water(cyan translucent area); (B) the cyan, red and blue balls stand for carbon atoms, cations and anions, respectively. The cyan translucent areas are water molecules. The blue lines refer to the boundaries of the simulation box[periodic boundary conditions(PBCs) are applied in x, y and z directions].
| Force field | Ion | σi⁃C/nm | Optimized parameter | Initial parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||||
| Merz | Li+ | -10.4 | 0.2805 | 1.503 | -10.4 | 0.110 | -4.0 |
| Na+ | -13.8 | 0.2924 | 1.951 | -13.8 | 0.244 | -1.2 | |
| K+ | -12.6 | 0.3161 | 1.827 | -12.4 | 0.591 | -2.9 | |
| Ca2+ | -16.5 | 0.3043 | 4.102 | -16.8 | 0.413 | -2.9 | |
| Mg2+ | -15.7 | 0.2868 | 5.405 | -15.9 | 0.175 | -2.5 | |
| Cl- | -6.9 | 0.3552 | 1.483 | -6.8 | 1.044 | -0.4 | |
| Netz | Li+ | -10.4 | 0.3042 | 0.839 | -10.8 | 0.017 | -4.8 |
| Na+ | -13.8 | 0.3512 | 0.935 | -13.6 | 0.017 | -1.6 | |
| K+ | -12.6 | 0.3872 | 0.836 | -12.5 | 0.017 | -0.9 | |
| Ca2+ | -16.5 | 0.2812 | 5.242 | -16.1 | 0.679 | -2.1 | |
| Mg2+ | -15.7 | 0.2422 | 14.458 | -15.9 | 0.538 | -1.4 | |
| Cl- | -6.9 | 0.3807 | 1.040 | -6.8 | 0.448 | — | |
Table 1 LJ i-C parameters and adsorption energy of ion-graphene simulated with Merz and Netz force fields
| Force field | Ion | σi⁃C/nm | Optimized parameter | Initial parameter | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||||
| Merz | Li+ | -10.4 | 0.2805 | 1.503 | -10.4 | 0.110 | -4.0 |
| Na+ | -13.8 | 0.2924 | 1.951 | -13.8 | 0.244 | -1.2 | |
| K+ | -12.6 | 0.3161 | 1.827 | -12.4 | 0.591 | -2.9 | |
| Ca2+ | -16.5 | 0.3043 | 4.102 | -16.8 | 0.413 | -2.9 | |
| Mg2+ | -15.7 | 0.2868 | 5.405 | -15.9 | 0.175 | -2.5 | |
| Cl- | -6.9 | 0.3552 | 1.483 | -6.8 | 1.044 | -0.4 | |
| Netz | Li+ | -10.4 | 0.3042 | 0.839 | -10.8 | 0.017 | -4.8 |
| Na+ | -13.8 | 0.3512 | 0.935 | -13.6 | 0.017 | -1.6 | |
| K+ | -12.6 | 0.3872 | 0.836 | -12.5 | 0.017 | -0.9 | |
| Ca2+ | -16.5 | 0.2812 | 5.242 | -16.1 | 0.679 | -2.1 | |
| Mg2+ | -15.7 | 0.2422 | 14.458 | -15.9 | 0.538 | -1.4 | |
| Cl- | -6.9 | 0.3807 | 1.040 | -6.8 | 0.448 | — | |
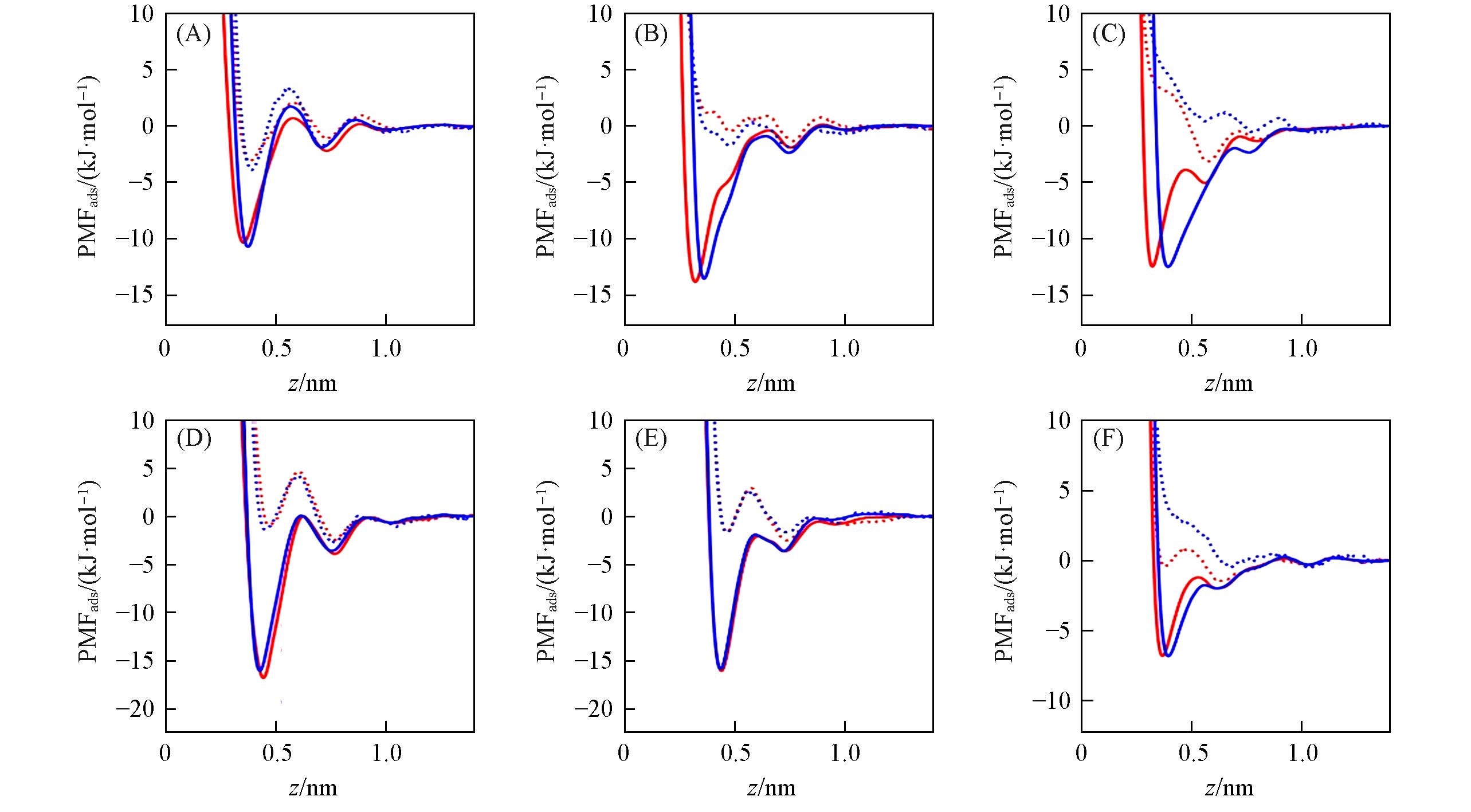
Fig.2 PMFads for Li+(A), Na+(B), K+(C), Ca2+(D), Mg2+(E) and Cl-(F) ions adsorbed at the water/graphene interfaceThe graphene flake’s position is z=0. Red and blue lines stand for results of Merz and Netz force field, respectively. Dot and solid lines stand for results of initial parameters(εi-CLB) and optimized parameters(εi-Cion-π), respectively.
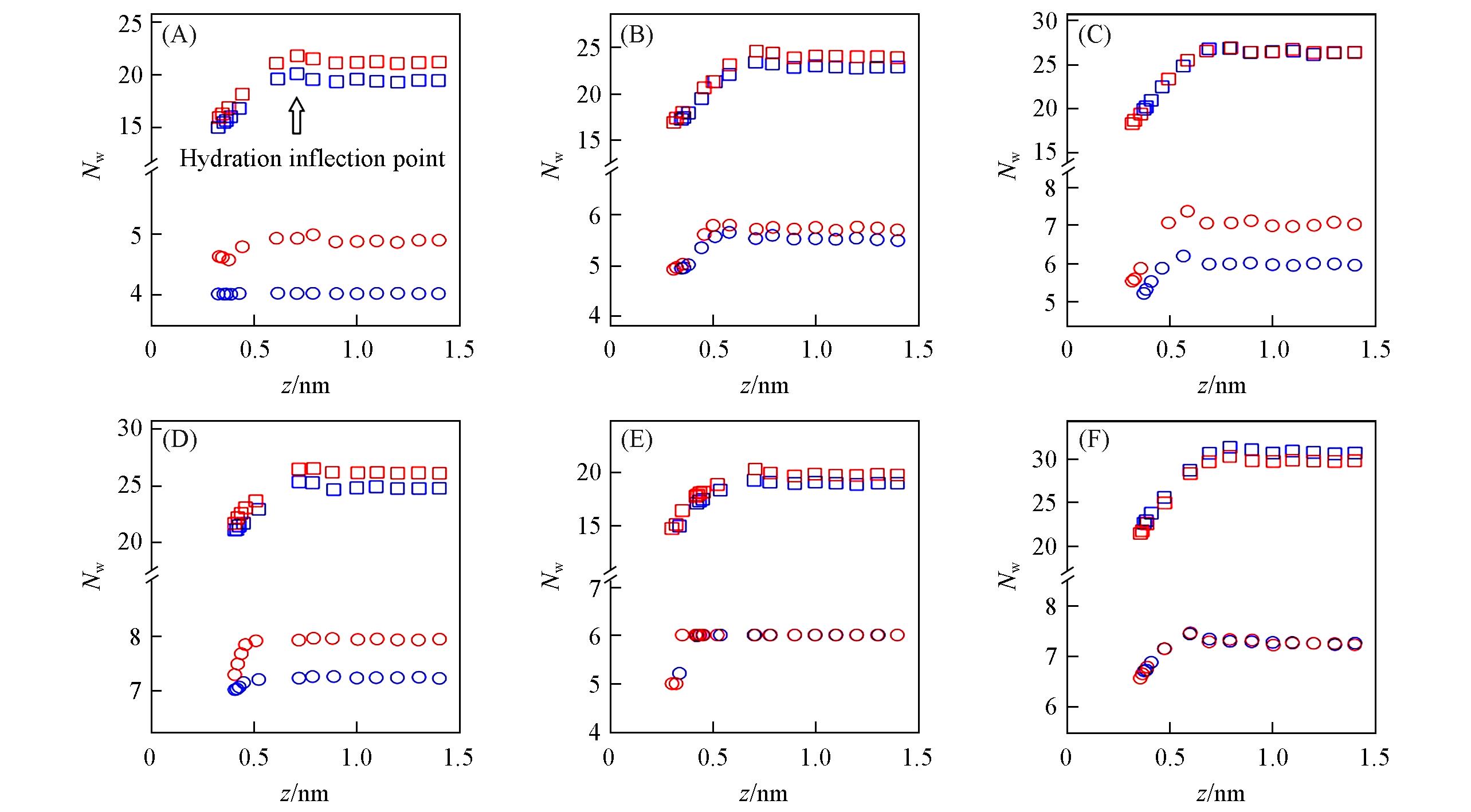
Fig.3 Relationship between ion⁃graphene distance and coordination numbers for the first(circle) and second(squares) hydration shells(denoted as Nw1 and Nw2, respectively) for Li+(A), Na+(B), K+(C), Mg2+(D), Ca2+(E) and Cl-(F)Red and blue points stand for results of Merz and Netz force fields, respectively. The arrow in Fig.3(A) represents where the dehydration of Li+ ion’s second hydration shell starts(i.e., the 2nd hydration inflection point). For simplicity, all ions’ hydration inflection points are listed in Table S2. Nw1doesn’t change when Netz force field’s Li+ approaches the graphene flake[blue circles in Fig.3(A)], see Table S2(see the Supporting Information of this paper) for explanation.
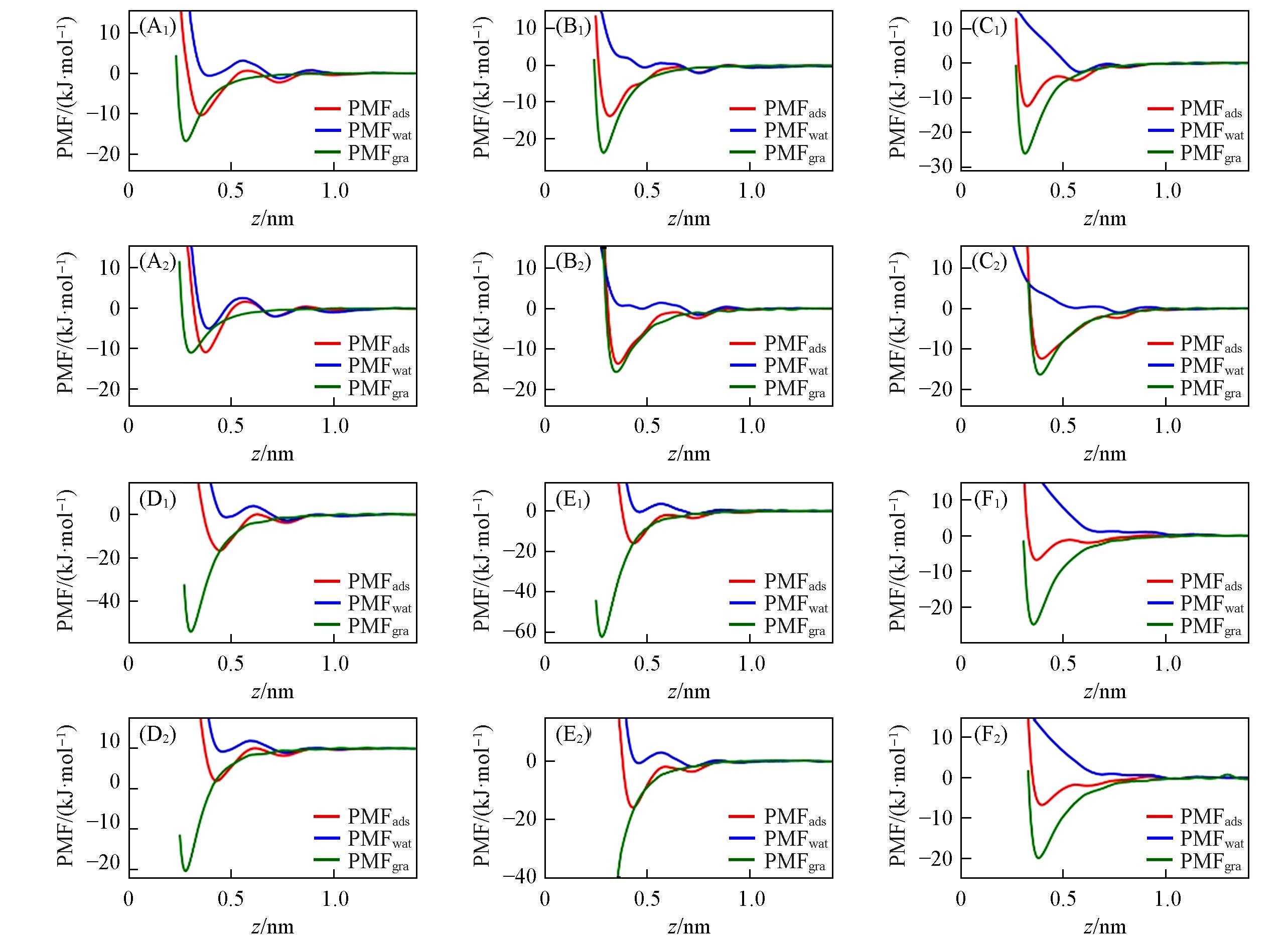
Fig.4 PMFads, PMFgra(contribution of ion⁃graphene interactions to PMFads) and PMFwat(contribution of ion⁃water interactions to PMFads) for Li+(A), Na+(B), K+(C), Ca2+(D), Mg2+(E) and Cl-(F) ions adsorbed at the water/graphene interface(A1)—(F1) Merz force field; (A2)—(F2) Netz force field. The graphene flake’s position is z=0. Simulations were performed using εi-Cion-π parameters[see Fig. S8(see the Supporting Information of this paper) for εi-Cion-π parameters’ results].
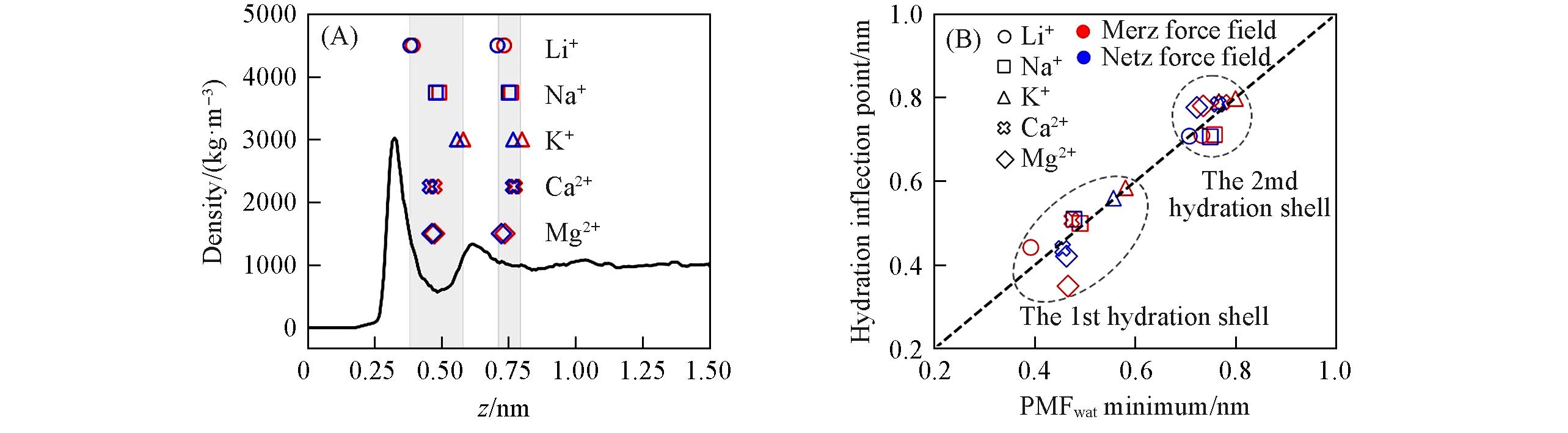
Fig.5 Water density distribution above graphene flake(black curve) and the positions of cation PMFwat’s minimum(A), PMFwat’s 1st and 2nd minimum positions agree with correspondinghydration inflection points’ position(B)(A) The scattering points stand for PMFwat’s 1st and 2nd minimum positions of cations(red and blue points represent results of Merz and Netz force fields, respectively), and the shadows stand for their ranges; (B) red and blue dots represent the results of Merz and Netz force fields, respectively. Black dashed line is the guide line; data points of 1st and 2nd hydration shells are circled, respectively. Li+ of Netz force field does not show inflection point for its 1st hydration layer(see Table S2 for explanation).
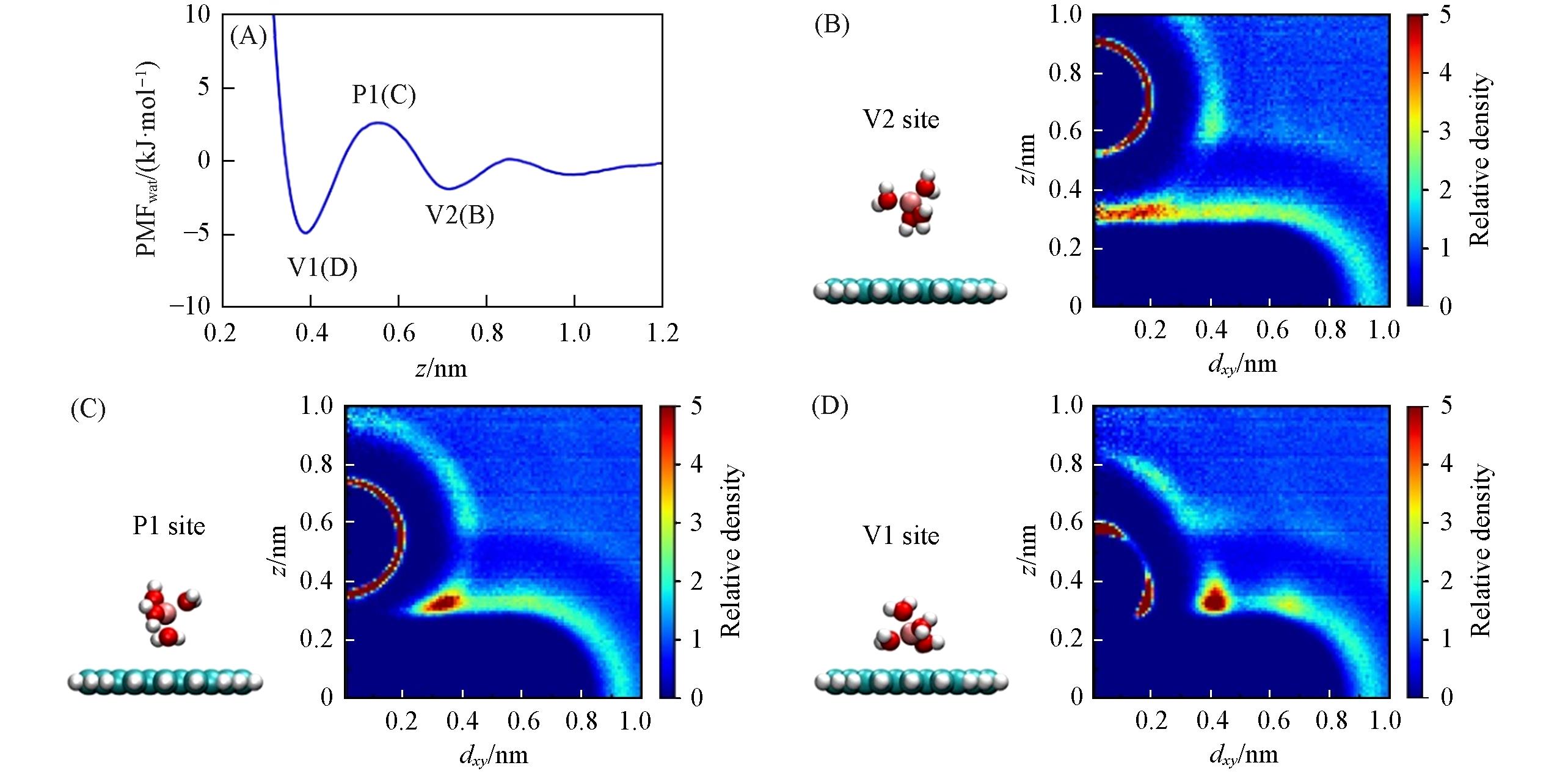
Fig.6 PMFwat of Netz force field’s Li+(P1, V1, V2 represent the 1st maximum, the 1st and 2nd minima, respectively)(A), corresponding snapshots of the ion’s 1st hydration shell and the relative density distribution of water(B—D)(B—D) Left: other water molecules are omitted for clarity; right: bulk water’s relative density is 1; dxy is the horizontal distance between water’s oxygen atom and the center of the graphene flake. The hydration shell was distorted when Li+ approaches graphene(B→C→D).
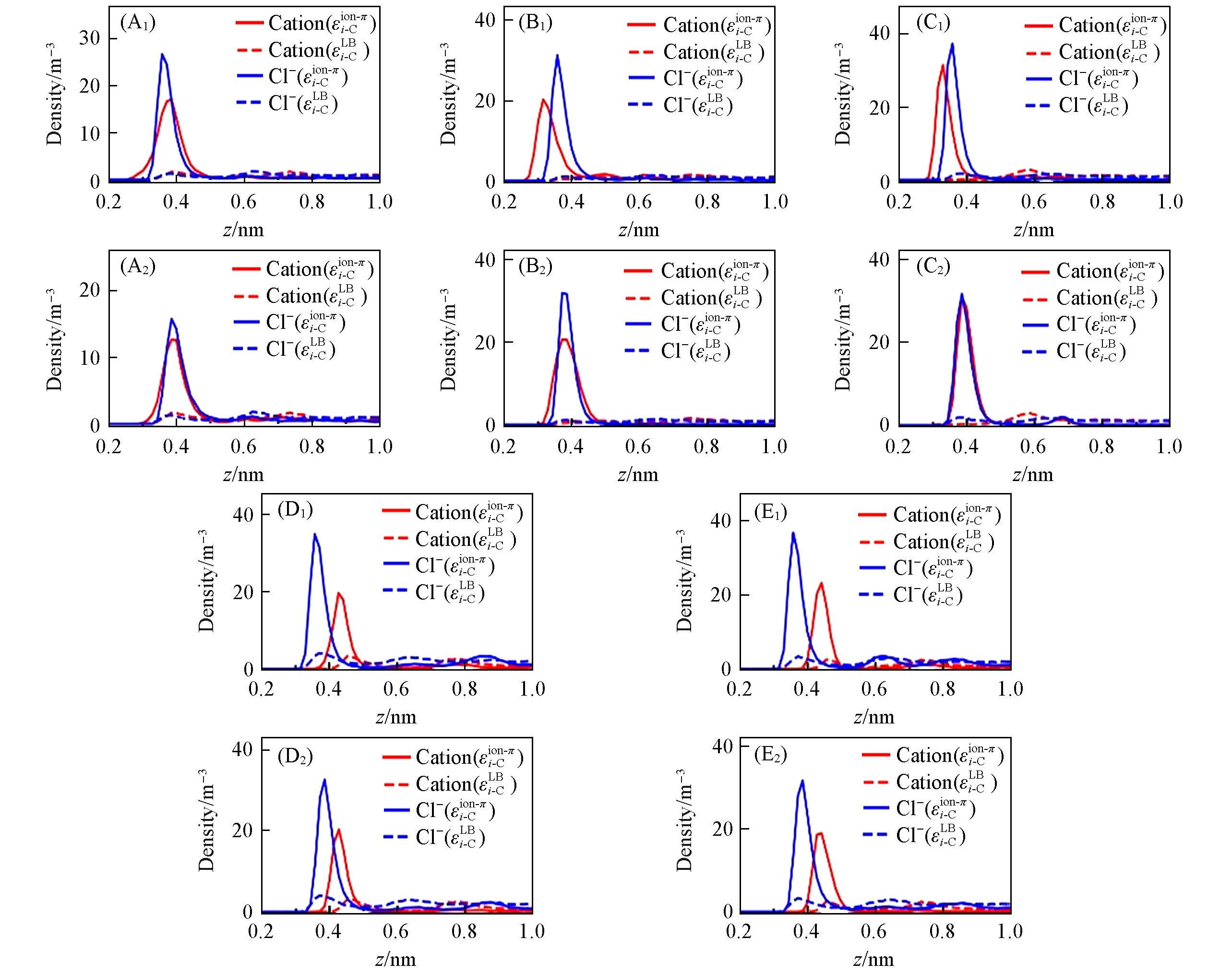
Fig.7 Ion’s density profile along 1 mol/L electrolyte solution/graphene interface(A1)—(F1) Merz force field; (A2)—(F2) Netz force field. The graphene flake’s position is z=0, the electrolyte solutions are LiCl(A), NaCl(B), KCl(C), CaCl2(D) and MgCl2(E). The red and blue lines represent cations and anions, respectively; solid and dashed lines represent simulation results of optimized(εi-Cion-π) and initial parameters(εi-CLB), respectively.
| 1 | Shen J., Liu G., Han Y., Jin W., Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6(4), 294—312 |
| 2 | Mohammadi A. V., Rosen J., Gogotsi Y., Science, 2021, 372(6547), 1165 |
| 3 | Zhan H., Xiong Z., Cheng C., Liang Q., Liu J. Z., Li D., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(18), 1904562 |
| 4 | Liu X., Zhang L., Cui X., Zhang Q., Hu W., Du J., Zeng H., Xu Q., Adv. Sci., 2021, 8(23), 2102493 |
| 5 | Radha B., Esfandiar A., Wang F. C., Rooney A. P., Gopinadhan K., Keerthi A., Mishchenko A., Janardanan A., Blake P., Fumagalli L., Lozada⁃Hidalgo M., Garaj S., Haigh S. J., Grigorieva I. V., Wu H. A., Geim A. K., Nature, 2016, 538(7624), 222—225 |
| 6 | Kang Y., Xia Y., Wang H., Zhang X., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(29), 1902014 |
| 7 | Robin P., Emmerich T., Ismail A., Nigues A., You Y., Nam G. H., Keerthi A., Siria A., Geim A. K., Radha B., Bocquet L., Science, 2023, 379(6628), 161—167 |
| 8 | Keerthi A., Goutham S., You Y., Iamprasertkun P., Dryfe R. A. W., Geim A. K., Radha B., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 3092 |
| 9 | Chen L., Shi G., Shen J., Peng B., Zhang B., Wang Y., Bian F., Wang J., Li D., Qian Z., Xu G., Liu G., Zeng J., Zhang L., Yang Y., Zhou G., Wu M., Jin W., Li J., Fang H., Nature, 2017, 550(7676), 380—383 |
| 10 | Abraham J., Vasu K. S., Williams C. D., Gopinadhan K., Su Y., Cherian C. T., Dix J., Prestat E., Haigh S. J., Grigorieva I. V., Carbone P., Geim A. K., Nair R. R., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2017, 12(6), 546—550 |
| 11 | Gopinadhan K., Hu S., Esfandiar A., Lozada⁃Hidalgo M., Wang F. C., Yang Q., Tyurnina A. V., Keerthi A., Radha B., Geim A. K., Science, 2019, 363(6423), 145—147 |
| 12 | Fu H., Wang Z., Li P., Qian W., Zhang Z., Zhao X., Feng H., Yang Z., Kou Z., He D., Nano Res., 2023, 16, 1826—1834 |
| 13 | Wang L., Yuan Z., Zhang Y., Guo W., Sun X., Duan X., Sci. China Mater., 2022, 65(3), 803—810 |
| 14 | Xiao K., Jiang L., Antonietti M., Joule, 2019, 3(10), 2364—2380 |
| 15 | Ding L., Xiao D., Lu Z., Deng J., Wei Y., Caro J., Wang H., Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2020, 59(22), 8720—8726 |
| 16 | Tanimoto I. M. F., Cressiot B., Greive S. J., Le Pioufle B., Bacri L., Pelta J., Nano Res., 2022, 15, 9906—9920 |
| 17 | Zhao Y., Xin W., Qian Y., Zhang Z., Wu Y., Lin X., Kong X. Y., Jiang L., Wen L., Sci. China Mater., 2022, 65, 2729—2736 |
| 18 | Xiao J., Zhan H., Wang X., Xu Z. Q., Xiong Z., Zhang K., Simon G. P., Liu J. Z., Li D., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2020, 15(8), 683 |
| 19 | Xia Y., Mathis T. S., Zhao M. Q., Anasori B., Dang A., Zhou Z., Cho H., Gogotsi Y., Yang S., Nature, 2018, 557(7705), 409 |
| 20 | Mo T., Bi S., Zhang Y., Presser V., Wang X., Gogotsi Y., Feng G., ACS Nano, 2020, 14(2), 2395—2403 |
| 21 | Robin P., Kavokine N., Bocquet L., Science, 2021, 373(6555), 687 |
| 22 | Mouterde T., Keerthi A., Poggioli A. R., Dar S. A., Siria A., Geim A. K., Bocquet L., Radha B., Nature, 2019, 567(7746), 87—90 |
| 23 | Bocquet L., Nat. Mater., 2020, 19(3), 254—256 |
| 24 | al⁃Badri M. A., Smith P., Sinclair R. C., al⁃Jamal K. T., Lorenz C. D., Carbon, 2021, 174, 266—275 |
| 25 | Cheng C., Jiang G., Garvey C. J., Wang Y., Simon G. P., Liu J. Z., Li D., Sci. Adv., 2016, 2(2), e1501272 |
| 26 | Abal J. P. K., Dillenburg R. F., Kohler M. H., Barbosa M. C., ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2021, 4(10), 10467—10476 |
| 27 | Zhao W., Sun Y., Zhu W., Jiang J., Zhao X., Lin D., Xu W., Duan X., Francisco J. S., Zeng X. C., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12(1), 5602 |
| 28 | Zhao N., Deng J., Zhu Y., Chen Y., Qin Y., Ruan Y., Zhang Y., Gao Q., Lu X., Carbon, 2020, 164, 305—316 |
| 29 | Tan J., Guo Y., Guo W., Nano Res., 2023, 16, 1792—1797 |
| 30 | Li L., Fennell C. J., Dill K. A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118(24), 6431—6437 |
| 31 | Xin W. W., Wen L. P., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2), 445—455 |
| 辛伟闻, 闻利平. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2), 445—455 | |
| 32 | McCaffrey D. L., Nguyen S. C., Cox S. J., Weller H., Alivisatos A. P., Geissler P. L., Saykally R. J., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2017, 114(51), 13369—13373 |
| 33 | Shi G., Ding Y., Fang H., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33(14), 1328—1337 |
| 34 | Chen L., Guo Y., Xu Z., Yang X., ChemPhysChem, 2018, 19(21), 2954—2960 |
| 35 | Misra R. P., Blankschtein D., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2021, 125(4), 2666—2679 |
| 36 | Zhan C., Ceron M. R., Hawks S. A., Otani M., Woods B. C., Tuan Anh P., Stadermann M., Campbell P. G., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 4858 |
| 37 | Zhao G., Zhu H., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(22), 1905756 |
| 38 | Williams C. D., Dix J., Troisi A., Carbone P., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(3), 703—708 |
| 39 | Aydin F., Moradzadeh A., Bilodeau C. L., Lau E. Y., Schwegler E., Aluru N. R., Pham T. A., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2021, 17(3), 1596—1605 |
| 40 | Liao S., Ke Q., Wei Y., Li L., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2022, 603, 154477 |
| 41 | Heiranian M., Wu Y., Aluru N. R., J. Chem. Phys., 2017, 147(10), 104706 |
| 42 | Kraemer A., Pickard F. C., Huang J., Venable R. M., Simmonett A. C., Reith D., Kirschner K. N., Pastor R. W., Brooks B. R., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2019, 15(6), 3854—3867 |
| 43 | Ashbaugh H. S., Liu L., Surampudi L. N., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(5), 054510 |
| 44 | Torras J., Aleman C., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117(36), 10513—10522 |
| 45 | Kahlen J., Salimi L., Sulpizi M., Peter C., Donadio D., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2014, 118(14), 3960—3972 |
| 46 | Liao S., Ke Q., Wei Y., Li L., Nano Res., 2023, 16, 6298—6307 |
| 47 | Hu B., Zhu H. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2), 20210614 |
| 胡波, 朱昊辰. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2), 20210614 | |
| 48 | Li L., Duan Y., Liao S., Ke Q., Qiao Z., Wei Y., Chem. Eng. J., 2020, 386, 123945 |
| 49 | Razmjou A., Hosseini E., Cha⁃Umpong W., Korayem A. H., Asadnia M., Moazzam P., Orooji Y., Karimi⁃Maleh H., Chen V., Desalination, 2020, 496, 114729 |
| 50 | Zhao T., Qing L., Long T., Xu X., Zhao S., Lu X., Aiche J., 2021, 67(7), e17266 |
| 51 | Zhou K., Xu Z., Nano Lett., 2020, 20(11), 8392—8398 |
| 52 | Li P. F., Song L. F., Merz K. M., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2015, 11(4), 1645—1657 |
| 53 | Li P. F., Roberts B. P., Chakravorty D. K., Merz K. M., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2013, 9(6), 2733—2748 |
| 54 | Mamatkulov S., Fyta M., Netz R. R., J. Chem. Phys., 2013, 138(2), 024505 |
| 55 | Horinek D., Mamatkulov S. I., Netz R. R., J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 130(12), 124507 |
| 56 | Vorobyov I., Li L., Allen T. W., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112(32), 9588—9602 |
| 57 | Torrie G. M., Valleau J. P., J. Comput. Phys., 1977, 23(2), 187—199 |
| 58 | Kumar S., Bouzida D., Swendsen R. H., Kollman P. A., Rosenberg J. M., J. Comput. Chem., 1992, 13(8), 1011—1021 |
| 59 | Hub J. S., de Groot B. L., Grubmueller H., Groenhof G., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2014, 10(1), 381—390 |
| 60 | Yu Y., Fan J., Esfandiar A., Zhu Y., Wu H., Wang F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123(2), 1462—1469 |
| 61 | Wang S., Yang L., He G., Shi B., Li Y., Wu H., Zhang R., Nunes S., Jiang Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(4), 1071—1089 |
| 62 | Werder T., Walther J. H., Jaffe R. L., Halicioglu T., Koumoutsakos P., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2003, 107(6), 1345—1352 |
| 63 | Berendsen H. J. C., Grigera J. R., Straatsma T. P., J. Phys. Chem., 1987, 91(24), 6269—6271 |
| 64 | Bayly C. I., Cieplak P., Cornell W. D., Kollman P. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 97(40), 10269—10280 |
| 65 | Lu T., Chen F., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33(5), 580—592 |
| 66 | Abraham M. J., Murtola T., Schulz R., Pall S., Smith J. C., Hess B., Lindahl E., SoftwareX, 2015, 1/2, 19—25 |
| 67 | Humphrey W., Dalke A., Schulten K., J. Mol. Graph. Model., 1996, 14(1), 33—38 |
| 68 | Darden T., York D., Pedersen L., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98(12), 10089—10092 |
| 69 | Miyamoto S., Kollman P. A., J. Comput. Chem., 1992, 13(8), 952—962 |
| 70 | Hoover W. G., Phys. Rev. A, 1985, 31(3), 1695—1697 |
| 71 | Nose S., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 81(1), 511—519 |
| 72 | Ke Q., Gong X., Liao S., Duan C., Li L., J. Mol. Liq., 2022, 365, 120116 |
| 73 | Nose S., Klein M. L., Mol. Phys., 1983, 50(5), 1055—1076 |
| 74 | Parrinello M., Rahman A., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1980, 45(4), 1196—1199 |
| 75 | Yu Y., Fan J., Xia J., Zhu Y., Wu H., Wang F., Nanoscale, 2019, 11(17), 8449—8457 |
| 76 | Li L., Vorobyov I., Allen T. W., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2008, 112(32), 9574—9587 |
| 77 | Li L., Vorobyov I., Allen T. W., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117(40), 11906—11920 |
| 78 | Shi G., Liu J., Wang C., Song B., Tu Y., Hu J., Fang H., Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 3436 |
| [1] | 富忠恒, 陈翔, 姚楠, 余乐耕, 沈馨, 张睿, 张强. 固态电解质锂离子输运机制研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220703. |
| [2] | 唐梦珂, 江亮, 徐文轩, 张子林, 唐道远, 黄东辉, 杨皓然, 高杰峰, 吉祥, 王延庆, 徐欢. 微波辅助仿生矿化增强石墨烯与聚乳酸的界面相互作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(4): 20220601. |
| [3] | 李吉辰, 蔡珊珊, 彭巨擘, 李宏飞, 段晓征. 电场下离子型聚合物复合囊泡结构变化的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220553. |
| [4] | 胡诗颖, 沈佳艳, 韩峻山, 郝婷婷, 李星. CoO纳米颗粒/石墨烯纳米纤维复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220462. |
| [5] | 沈琦, 陈海瑶, 高登辉, 赵熹, 那日松, 刘佳, 黄旭日. 天然产物法卡林二醇与人类GABAA受体相互作用的机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220500. |
| [6] | 胡宏苏, 申传喆, 王宇航, 王青青, 何士龙, 李鹏. 石墨烯复合多孔碳毡气体扩散阴极的H2O2催生性能与机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230245. |
| [7] | 周子豪, 王思皓, 黄玳川, 刘波, 甯红波. 正丙苯高温氧化机理的分子动力学模拟研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230276. |
| [8] | 王瑞娜, 孙瑞粉, 钟添华, 池毓务. 大尺寸石墨烯量子点组装体的制备及电化学发光性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [9] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [10] | 闫嘉森, 韩现英, 党兆涵, 李建刚, 何向明. 石蜡/膨胀石墨/石墨烯复合相变储热材料的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [11] | 曹磊, 陈美君, 袁刚, 常钢, 张修华, 王升富, 何汉平. 冠醚功能化的栅控石墨烯场效应晶体管的制备及对汞离子的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [12] | 郑雪莲, 杨翠翠, 田维全. 全椅式边含薁缺陷石墨烯纳米片的二阶非线性光学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [13] | 杨隽阁, 高成乾, 李博鑫, 尹德忠. 改性氧化石墨烯稳定Pickering乳液法制备高导热相变整体材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [14] | 张志博, 尚涵, 徐文轩, 韩广东, 崔金声, 杨皓然, 李瑞鑫, 张生辉, 徐欢. 氧化石墨烯插层聚β-羟基丁酸酯复合材料的结晶形态与宏观性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [15] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||