

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 20220196.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220196
收稿日期:2022-03-30
出版日期:2022-08-10
发布日期:2022-05-09
通讯作者:
夏文生
E-mail:wsxia@xmu.edu.cn
基金资助:
HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng( ), ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin
), ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin
Received:2022-03-30
Online:2022-08-10
Published:2022-05-09
Contact:
XIA Wensheng
E-mail:wsxia@xmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
二氧化碳(CO2)和化石能源气体燃料甲烷(CH4)均是化学稳定、 温室效应较大的分子, 因而对其活化、 转化和利用的研究具有显著的理论和实际意义. 本文采用密度泛函理论方法, 计算研究了羟基氧化铟团簇与CO2, CH4和(CO2+CH4)的作用. 结果表明, 氧化铟团簇通过其活性位点—In—O(桥氧)—对CO2和CH4分子进行[2+2]加成活化, 而羟基的引入调变了氧化铟团簇活性位点上的局部电荷, 显著降低了其与CO2和CH4分子作用的活化自由能垒, 使得CO2和CH4分子的活化变得容易进行. 活性位点—In—O(桥氧)—中的In, O上的局部电荷差值(qIn-qO)越大, 其对CO2和CH4分子作用的活化自由能垒越低. 羟基氧化铟与CO2和CH4分子作用时, 电子由羟基氧化铟流向CO2和CH4分子(亲核活化); 而羟基引入前的氧化铟与CO2和CH4分子作用时, 电子则由CO2和CH4分子流向氧化铟(亲电活化).
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196.
HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196.
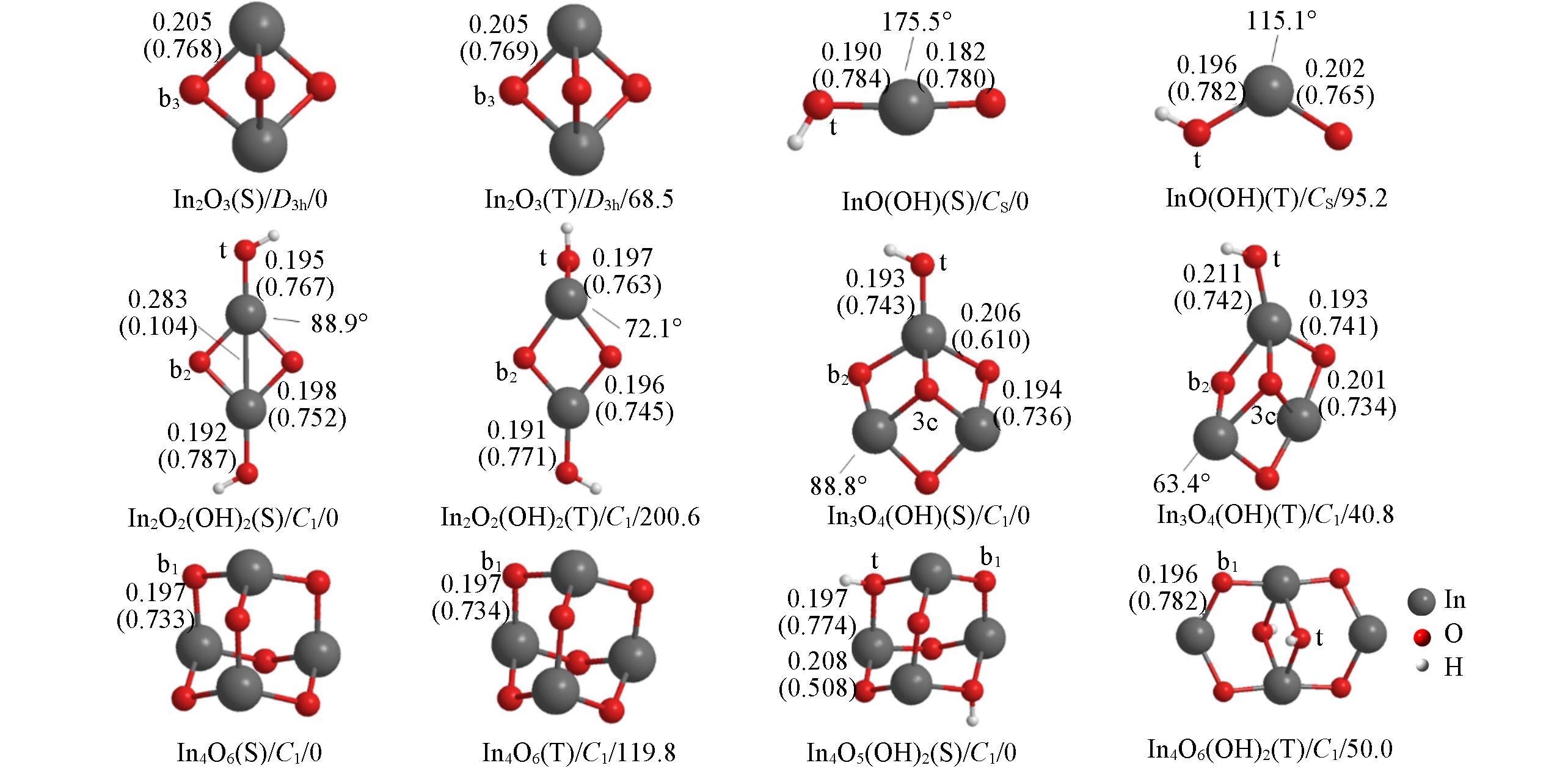
Fig.1 Structures(singlet S, triplet T)/point group/Gibbs free energy(kJ/mol, 298 K) of (hydroxyl)indium oxide clusters optimized at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVPO(t), O(b1), O(b2), O(b3) and O(3c) stand for terminal, homonuclear single?bridged, homonuclear double?bridged, homonuclear triple?bridged and three?coordinated oxygen, respectively. Bond lengths(order) are in nm.
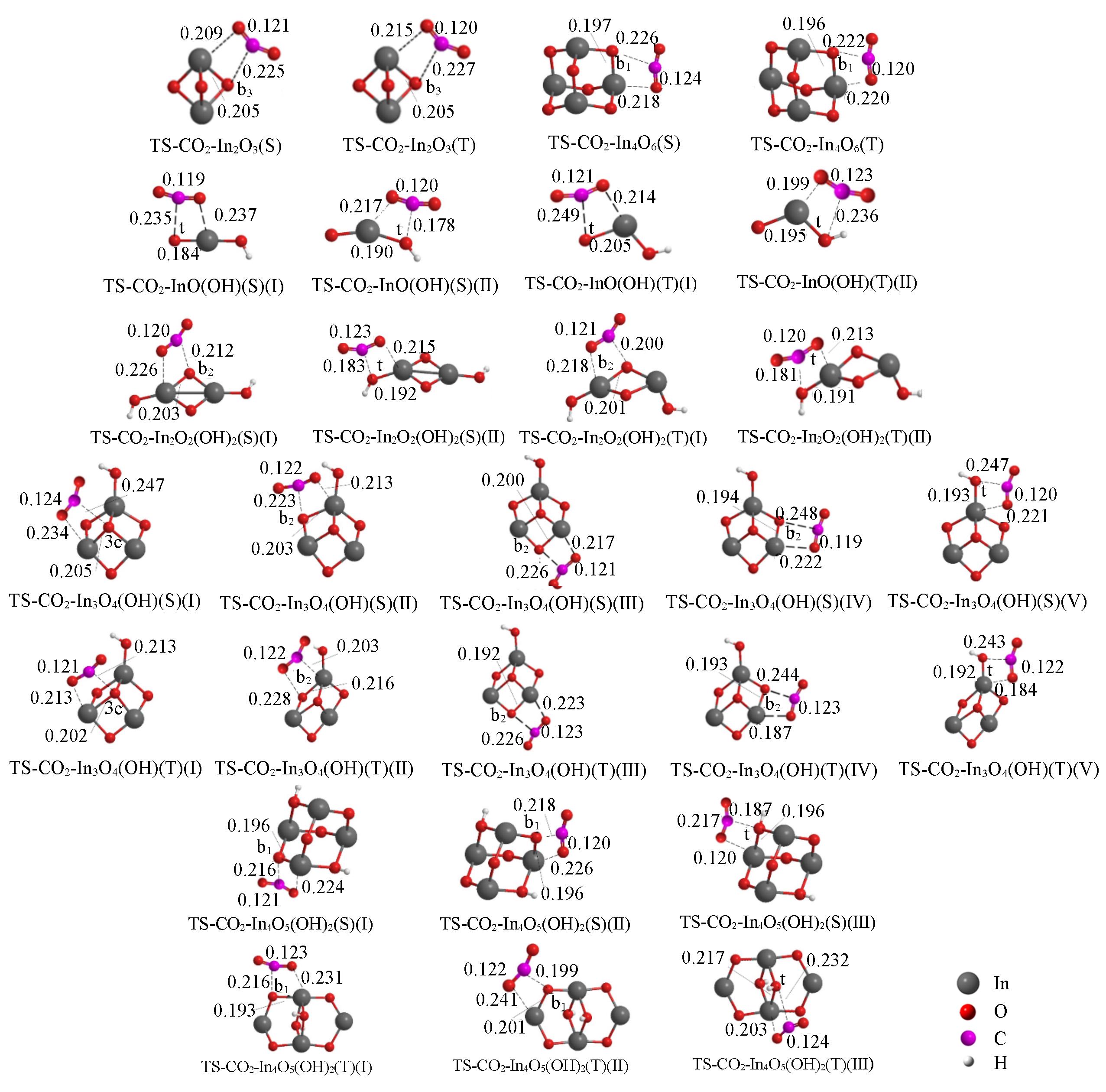
Fig.2 Optimized structures of the transition states for the interaction of singlet/triplet(S/T) clusters with CO2 at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVPBond lengths are in nm.
| Cluster | Interaction with CO2 | Interaction with CH4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active site* | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGr/(kJ·mol-1) | Active site* | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGr/(kJ·mol-1) | |
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | 87.11 | -262.63 | In—O(b3) | 150.08 | 96.48 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | 97.07 | -115.77 | In—O(b3) | 163.39 | -274.05 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | 110.92 | -64.64 | In—O(b1) | 148.74 | -129.54 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | 134.43 | -105.98 | In—O(b1) | 167.78 | -97.40 |
| InO(OH)(S) | In—O(t)I | 8.87 | -98.62 | In—O(t) | 104.01 | -197.57 |
| In—O(t)II | 56.82 | 42.97 | ||||
| InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t)I | 39.58 | -54.18 | In—O(t) | 108.87 | 15.77 |
| In—O(t)II | 44.23 | 1.13 | ||||
| In2O2(OH)2(S) | In—O(b2) I | 16.99 | -31.63 | In—O(b2) | 113.09 | -3.72 |
| In—O(t) II | 36.90 | -17.20 | ||||
| In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2) I | 41.51 | 6.36 | In—O(b2) | 122.80 | -74.52 |
| In—O(t) II | 52.84 | 44.52 | ||||
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(3c) I | 19.12 | -56.65 | In—O(b2)I | 51.25 | -241.21 |
| In—O(b2)II | 61.34 | 24.64 | In—O(3c)II | 68.74 | -94.31 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 5.86 | -66.32 | In—O(b2)III | 52.93 | -54.31 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 9.67 | -57.32 | ||||
| In—O(t)V | 71.67 | -3.68 | ||||
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(3c)I | 60.29 | 5.02 | In—O(b2)I | 87.19 | -146.02 |
| In—O(b2)II | 50.21 | -34.60 | In—O(3c)II | 118.91 | -95.94 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 12.05 | -32.01 | In—O(b2)III | 134.98 | -43.97 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 10.88 | -62.76 | ||||
| In—O(t)V | 75.77 | 17.28 | ||||
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 18.24 | -55.02 | In—O(b1)I | 79.58 | -59.83 |
| In—O(b1)II | 13.89 | -63.68 | In—O(b1)II | 38.74 | -194.68 | |
| In—O(t)III | 33.01 | 76.23 | In—O(b1)III | 38.79 | -91.55 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 16.36 | -63.68 | In—O(b1)I | 92.55 | -74.81 |
| In—O(b1)II | 34.98 | -52.55 | In—O(b1)II | 123.72 | -84.14 | |
| In—O(t)III | 98.41 | 23.81 | ||||
Table 1 Predicted activation free energy barrier(ΔGa) and reaction free energy(ΔGr) for the interaction of singlet/triplet(S/T) clusters with CO2 and CH4 at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVP and 298 K
| Cluster | Interaction with CO2 | Interaction with CH4 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Active site* | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGr/(kJ·mol-1) | Active site* | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGr/(kJ·mol-1) | |
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | 87.11 | -262.63 | In—O(b3) | 150.08 | 96.48 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | 97.07 | -115.77 | In—O(b3) | 163.39 | -274.05 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | 110.92 | -64.64 | In—O(b1) | 148.74 | -129.54 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | 134.43 | -105.98 | In—O(b1) | 167.78 | -97.40 |
| InO(OH)(S) | In—O(t)I | 8.87 | -98.62 | In—O(t) | 104.01 | -197.57 |
| In—O(t)II | 56.82 | 42.97 | ||||
| InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t)I | 39.58 | -54.18 | In—O(t) | 108.87 | 15.77 |
| In—O(t)II | 44.23 | 1.13 | ||||
| In2O2(OH)2(S) | In—O(b2) I | 16.99 | -31.63 | In—O(b2) | 113.09 | -3.72 |
| In—O(t) II | 36.90 | -17.20 | ||||
| In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2) I | 41.51 | 6.36 | In—O(b2) | 122.80 | -74.52 |
| In—O(t) II | 52.84 | 44.52 | ||||
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(3c) I | 19.12 | -56.65 | In—O(b2)I | 51.25 | -241.21 |
| In—O(b2)II | 61.34 | 24.64 | In—O(3c)II | 68.74 | -94.31 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 5.86 | -66.32 | In—O(b2)III | 52.93 | -54.31 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 9.67 | -57.32 | ||||
| In—O(t)V | 71.67 | -3.68 | ||||
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(3c)I | 60.29 | 5.02 | In—O(b2)I | 87.19 | -146.02 |
| In—O(b2)II | 50.21 | -34.60 | In—O(3c)II | 118.91 | -95.94 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 12.05 | -32.01 | In—O(b2)III | 134.98 | -43.97 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 10.88 | -62.76 | ||||
| In—O(t)V | 75.77 | 17.28 | ||||
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 18.24 | -55.02 | In—O(b1)I | 79.58 | -59.83 |
| In—O(b1)II | 13.89 | -63.68 | In—O(b1)II | 38.74 | -194.68 | |
| In—O(t)III | 33.01 | 76.23 | In—O(b1)III | 38.79 | -91.55 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 16.36 | -63.68 | In—O(b1)I | 92.55 | -74.81 |
| In—O(b1)II | 34.98 | -52.55 | In—O(b1)II | 123.72 | -84.14 | |
| In—O(t)III | 98.41 | 23.81 | ||||
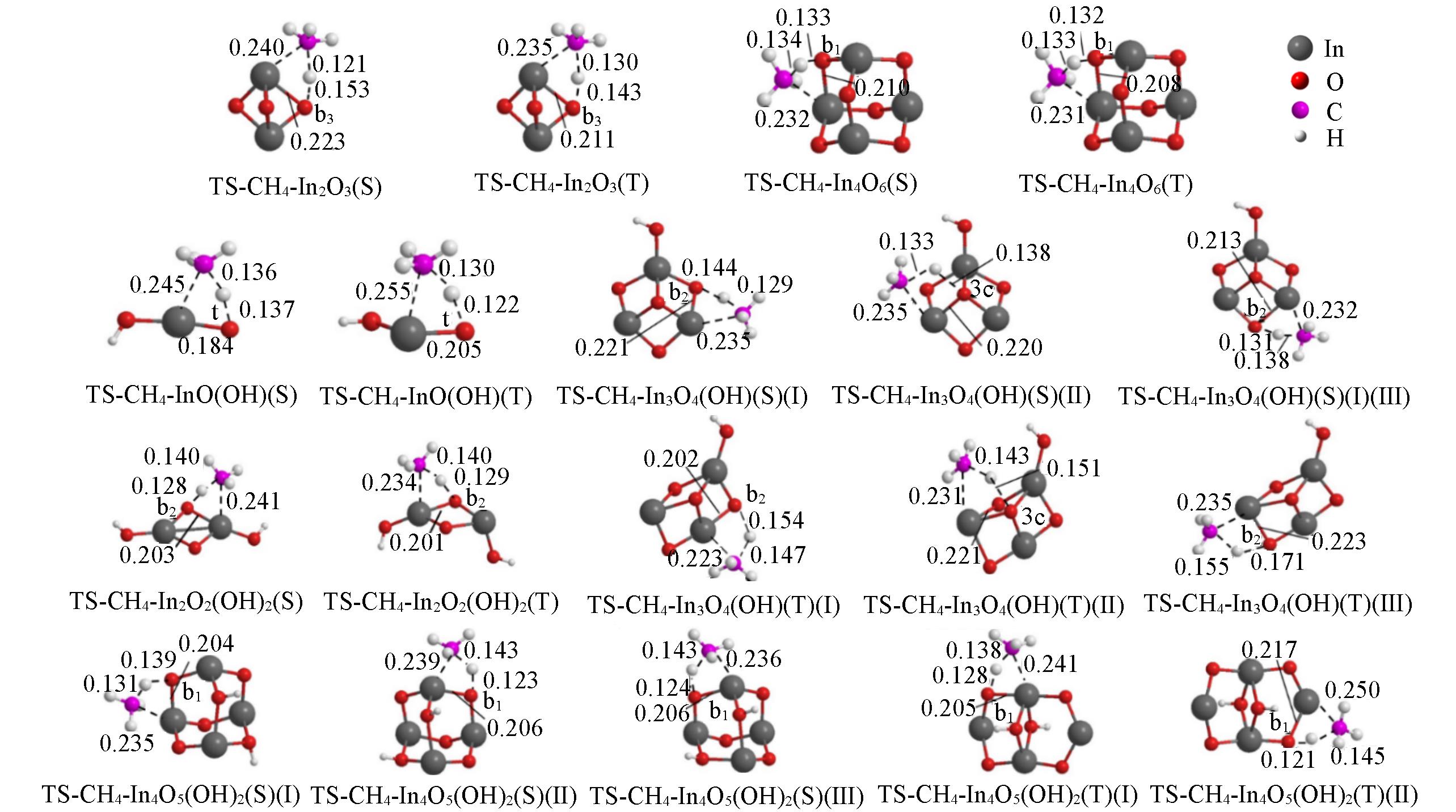
Fig.3 Optimized structures of the transition states for the interaction of singlet/triplet(S/T) clusters with CH4 at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVPBond lengths are in nm.
| Cluster | Active site* | q/e | Interaction with CO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster in TS | CO2 in TS | In in free cluster, qIn | O in free cluster, qO | qIn-qO | vTS/cm-1 | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | -0.184 | 0.184 | 1.878 | -1.131 | 3.009 | 187i | 87.11 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | -0.143 | 0.143 | 1.869 | -1.009 | 2.878 | 196i | 97.07 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | -0.103 | 0.103 | 1.956 | -1.416 | 3.372 | 195i | 110.92 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | -0.105 | 0.105 | 1.972 | -1.214 | 3.186 | 130i | 134.43 |
| InO(OH)(S) | In—O(t)I | 0.193 | -0.193 | 1.889 | -1.204 | 3.903 | 170i | 8.87 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.181 | -0.181 | 1.870 | -1.054 | 2.924 | 281i | 56.82 | |
| InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t)I | 0.172 | -0.172 | 1.883 | -0.663 | 2.546 | 417i | 39.58 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.125 | -0.125 | 1.380 | -1.087 | 2.466 | 275i | 44.23 | |
| In2O2(OH)2(S) | In—O(b2)I | 0.124 | -0.124 | 2.077 | -1.366 | 3.443 | 199i | 16.99 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.154 | -0.154 | 2.075 | -1.158 | 3.233 | 235i | 36.90 | |
| In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2)I | 0.062 | -0.062 | 2.098 | -1.084 | 3.182 | 237i | 41.51 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.165 | -0.165 | 2.093 | -1.060 | 3.153 | 251i | 52.84 | |
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(3c)I | 0.133 | -0.133 | 2.019 | -1.319 | 3.338 | 145i | 19.12 |
| In—O(b2)II | 0.124 | -0.124 | 2.021 | -1.221 | 3.241 | 157i | 61.34 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.137 | -0.137 | 2.014 | -1.361 | 3.375 | 129i | 5.86 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 0.134 | -0.134 | 2.016 | -1.334 | 3.350 | 135i | 9.67 | |
| In—O(t)V | 0.432 | -0.432 | 2.111 | -1.077 | 3.188 | 158i | 71.67 | |
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(3c)I | 0.226 | -0.226 | 1.480 | -1.341 | 2.820 | 209i | 60.29 |
| In—O(b2)II | 0.245 | -0.245 | 2.030 | -1.046 | 3.076 | 265i | 50.21 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.213 | -0.213 | 2.029 | -1.273 | 3.202 | 147i | 12.05 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 0.101 | -0.101 | 2.026 | -1.279 | 3.205 | 146i | 10.88 | |
| In—O(t)V | 0.254 | -0.254 | 1.486 | -1.377 | 2.863 | 237i | 75.77 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 0.436 | -0.436 | 2.082 | -1.301 | 3.382 | 181i | 18.24 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.171 | -0.171 | 2.014 | -1.407 | 3.421 | 184i | 13.89 | |
| In—O(t)III | 0.376 | -0.376 | 2.001 | -1.407 | 3.207 | 186i | 33.01 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 0.144 | -0.144 | 2.014 | -1.327 | 3.340 | 152i | 16.36 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.347 | -0.347 | 2.014 | -1.201 | 3.215 | 197i | 34.98 | |
| In—O(t)III | 0.333 | -0.333 | 2.131 | -1.001 | 3.131 | 189i | 98.41 | |
Table 2 Natural bond orbital(NBO) charge population(q) and transition state(TS) frequency(vTS) for the interaction of CO2 with singlet/triplet(S/T) indium oxyhydroxide clusters and the activation free energy barrier(ΔGa, 298 K) at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVP
| Cluster | Active site* | q/e | Interaction with CO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster in TS | CO2 in TS | In in free cluster, qIn | O in free cluster, qO | qIn-qO | vTS/cm-1 | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | -0.184 | 0.184 | 1.878 | -1.131 | 3.009 | 187i | 87.11 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | -0.143 | 0.143 | 1.869 | -1.009 | 2.878 | 196i | 97.07 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | -0.103 | 0.103 | 1.956 | -1.416 | 3.372 | 195i | 110.92 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | -0.105 | 0.105 | 1.972 | -1.214 | 3.186 | 130i | 134.43 |
| InO(OH)(S) | In—O(t)I | 0.193 | -0.193 | 1.889 | -1.204 | 3.903 | 170i | 8.87 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.181 | -0.181 | 1.870 | -1.054 | 2.924 | 281i | 56.82 | |
| InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t)I | 0.172 | -0.172 | 1.883 | -0.663 | 2.546 | 417i | 39.58 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.125 | -0.125 | 1.380 | -1.087 | 2.466 | 275i | 44.23 | |
| In2O2(OH)2(S) | In—O(b2)I | 0.124 | -0.124 | 2.077 | -1.366 | 3.443 | 199i | 16.99 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.154 | -0.154 | 2.075 | -1.158 | 3.233 | 235i | 36.90 | |
| In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2)I | 0.062 | -0.062 | 2.098 | -1.084 | 3.182 | 237i | 41.51 |
| In—O(t)II | 0.165 | -0.165 | 2.093 | -1.060 | 3.153 | 251i | 52.84 | |
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(3c)I | 0.133 | -0.133 | 2.019 | -1.319 | 3.338 | 145i | 19.12 |
| In—O(b2)II | 0.124 | -0.124 | 2.021 | -1.221 | 3.241 | 157i | 61.34 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.137 | -0.137 | 2.014 | -1.361 | 3.375 | 129i | 5.86 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 0.134 | -0.134 | 2.016 | -1.334 | 3.350 | 135i | 9.67 | |
| In—O(t)V | 0.432 | -0.432 | 2.111 | -1.077 | 3.188 | 158i | 71.67 | |
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(3c)I | 0.226 | -0.226 | 1.480 | -1.341 | 2.820 | 209i | 60.29 |
| In—O(b2)II | 0.245 | -0.245 | 2.030 | -1.046 | 3.076 | 265i | 50.21 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.213 | -0.213 | 2.029 | -1.273 | 3.202 | 147i | 12.05 | |
| In—O(b2)IV | 0.101 | -0.101 | 2.026 | -1.279 | 3.205 | 146i | 10.88 | |
| In—O(t)V | 0.254 | -0.254 | 1.486 | -1.377 | 2.863 | 237i | 75.77 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 0.436 | -0.436 | 2.082 | -1.301 | 3.382 | 181i | 18.24 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.171 | -0.171 | 2.014 | -1.407 | 3.421 | 184i | 13.89 | |
| In—O(t)III | 0.376 | -0.376 | 2.001 | -1.407 | 3.207 | 186i | 33.01 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 0.144 | -0.144 | 2.014 | -1.327 | 3.340 | 152i | 16.36 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.347 | -0.347 | 2.014 | -1.201 | 3.215 | 197i | 34.98 | |
| In—O(t)III | 0.333 | -0.333 | 2.131 | -1.001 | 3.131 | 189i | 98.41 | |
| Cluster | Active site* | q/e | Interaction with CH4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster in TS | CH4 in TS | In in free cluster, qIn | O in free cluster, qO | qIn-qO | vTS/cm-1 | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | -0.068 | 0.068 | 1.863 | -1.246 | 3.109 | 1566i | 150.08 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | -0.023 | 0.023 | 1.846 | -1.069 | 2.915 | 1479i | 163.39 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | -0.013 | 0.013 | 1.932 | -1.344 | 3.276 | 1411i | 148.74 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | -0.034 | 0.034 | 1.967 | -1.031 | 2.998 | 1345i | 167.78 |
InO(OH)(S) InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t) | 0.213 | -0.213 | 1.921 | -1.151 | 3.072 | 1676i | 104.01 |
| In—O(t) | 0.237 | -0.237 | 1.956 | -0.904 | 2.860 | 1218i | 108.87 | |
In2O2(OH)2(S) In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2) | 0.079 | -0.079 | 2.051 | -1.312 | 3.363 | 1511i | 113.09 |
| In—O(b2) | 0.059 | -0.059 | 2.056 | -1.079 | 3.135 | 1627i | 122.80 | |
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(b2)I | 0.012 | -0.012 | 2.002 | -1.348 | 3.349 | 1293i | 51.25 |
| In—O(3c)II | 0.002 | -0.002 | 1.874 | -1.322 | 3.196 | 1406i | 68.74 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.014 | -0.014 | 1.978 | -1.305 | 3.283 | 1347i | 52.93 | |
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(b2)I | 0.020 | -0.020 | 2.003 | -1.329 | 3.332 | 1469i | 87.19 |
| In—O(3c)II | 0.032 | -0.032 | 1.374 | -1.130 | 2.504 | 1476i | 118.91 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.023 | -0.023 | 1.374 | -1.050 | 2.424 | 1509i | 134.98 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 0.011 | -0.011 | 2.013 | -1.040 | 3.052 | 1376i | 79.58 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.067 | -0.067 | 2.081 | -1.252 | 3.333 | 1460i | 38.74 | |
| In—O(b1)III | 0.077 | -0.077 | 2.086 | -1.245 | 3.331 | 1462i | 38.79 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 0.039 | -0.039 | 2.062 | -1.139 | 3.201 | 1545i | 92.55 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.082 | -0.082 | 1.415 | -1.297 | 2.711 | 1496i | 123.72 | |
Table 3 Natural bond orbital(NBO) charge population(q) and transition state(TS) frequency(vTS) for the interaction of CH4 with singlet/triplet(S/T) indium oxyhydroxide clusters and the activation free energy barrier (ΔGa, 298 K) at the level of UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVP
| Cluster | Active site* | q/e | Interaction with CH4 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cluster in TS | CH4 in TS | In in free cluster, qIn | O in free cluster, qO | qIn-qO | vTS/cm-1 | ΔGa/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
| In2O3(S) | In—O(b3) | -0.068 | 0.068 | 1.863 | -1.246 | 3.109 | 1566i | 150.08 |
| In2O3(T) | In—O(b3) | -0.023 | 0.023 | 1.846 | -1.069 | 2.915 | 1479i | 163.39 |
| In4O6(S) | In—O(b1) | -0.013 | 0.013 | 1.932 | -1.344 | 3.276 | 1411i | 148.74 |
| In4O6(T) | In—O(b1) | -0.034 | 0.034 | 1.967 | -1.031 | 2.998 | 1345i | 167.78 |
InO(OH)(S) InO(OH)(T) | In—O(t) | 0.213 | -0.213 | 1.921 | -1.151 | 3.072 | 1676i | 104.01 |
| In—O(t) | 0.237 | -0.237 | 1.956 | -0.904 | 2.860 | 1218i | 108.87 | |
In2O2(OH)2(S) In2O2(OH)2(T) | In—O(b2) | 0.079 | -0.079 | 2.051 | -1.312 | 3.363 | 1511i | 113.09 |
| In—O(b2) | 0.059 | -0.059 | 2.056 | -1.079 | 3.135 | 1627i | 122.80 | |
| In3O4(OH)(S) | In—O(b2)I | 0.012 | -0.012 | 2.002 | -1.348 | 3.349 | 1293i | 51.25 |
| In—O(3c)II | 0.002 | -0.002 | 1.874 | -1.322 | 3.196 | 1406i | 68.74 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.014 | -0.014 | 1.978 | -1.305 | 3.283 | 1347i | 52.93 | |
| In3O4(OH)(T) | In—O(b2)I | 0.020 | -0.020 | 2.003 | -1.329 | 3.332 | 1469i | 87.19 |
| In—O(3c)II | 0.032 | -0.032 | 1.374 | -1.130 | 2.504 | 1476i | 118.91 | |
| In—O(b2)III | 0.023 | -0.023 | 1.374 | -1.050 | 2.424 | 1509i | 134.98 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(S) | In—O(b1)I | 0.011 | -0.011 | 2.013 | -1.040 | 3.052 | 1376i | 79.58 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.067 | -0.067 | 2.081 | -1.252 | 3.333 | 1460i | 38.74 | |
| In—O(b1)III | 0.077 | -0.077 | 2.086 | -1.245 | 3.331 | 1462i | 38.79 | |
| In4O5(OH)2(T) | In—O(b1)I | 0.039 | -0.039 | 2.062 | -1.139 | 3.201 | 1545i | 92.55 |
| In—O(b1)II | 0.082 | -0.082 | 1.415 | -1.297 | 2.711 | 1496i | 123.72 | |
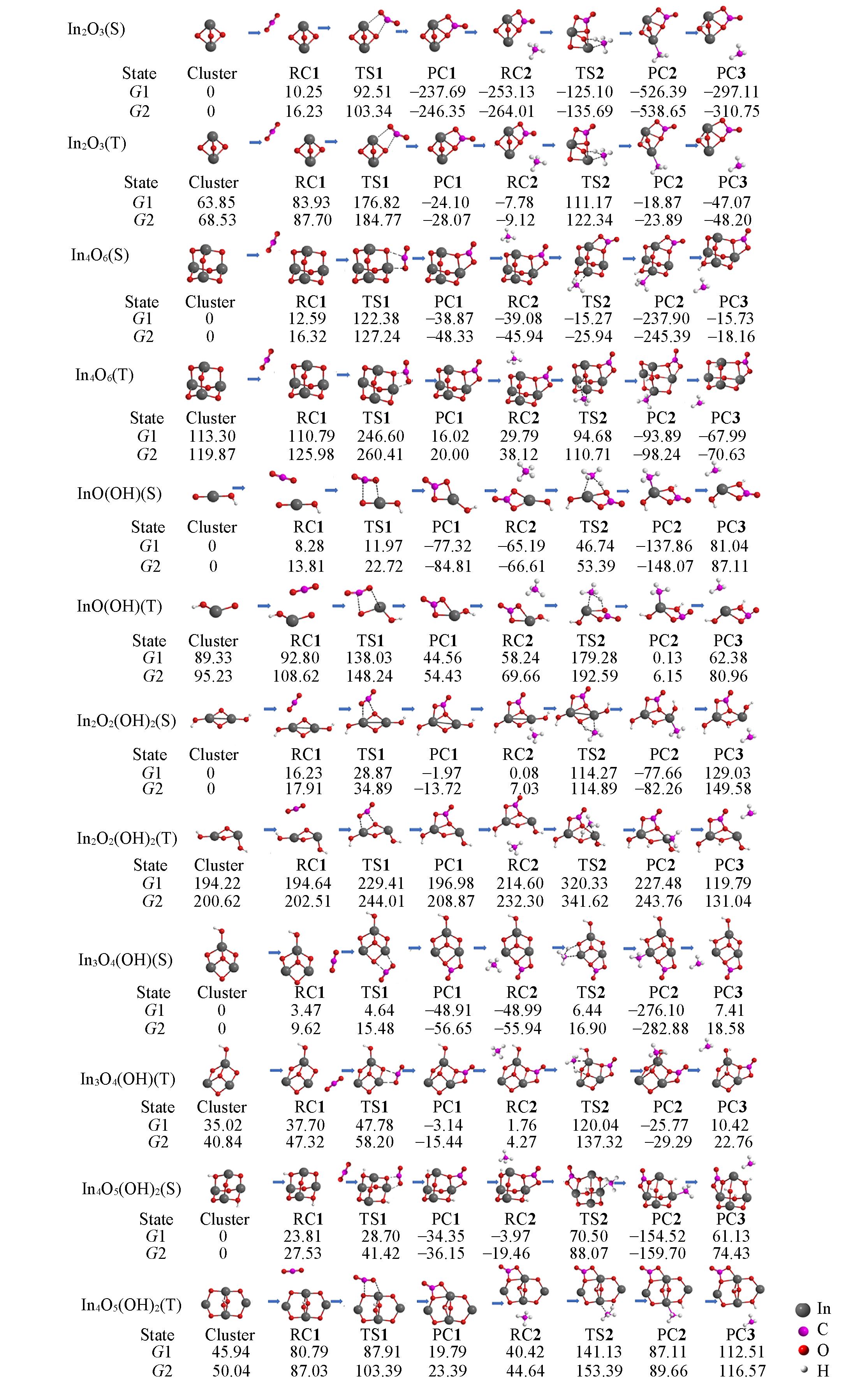
Fig.4 Predicted relative Gibbs free energy G1 and G2(kJ/mol, 298 K) for the interaction of singlet/triplet(S/T) clusters with (CO2+CH4) at the level of UCCSD(T)//UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVP and UB3LYP/SDD+Def2TZVP, respectively
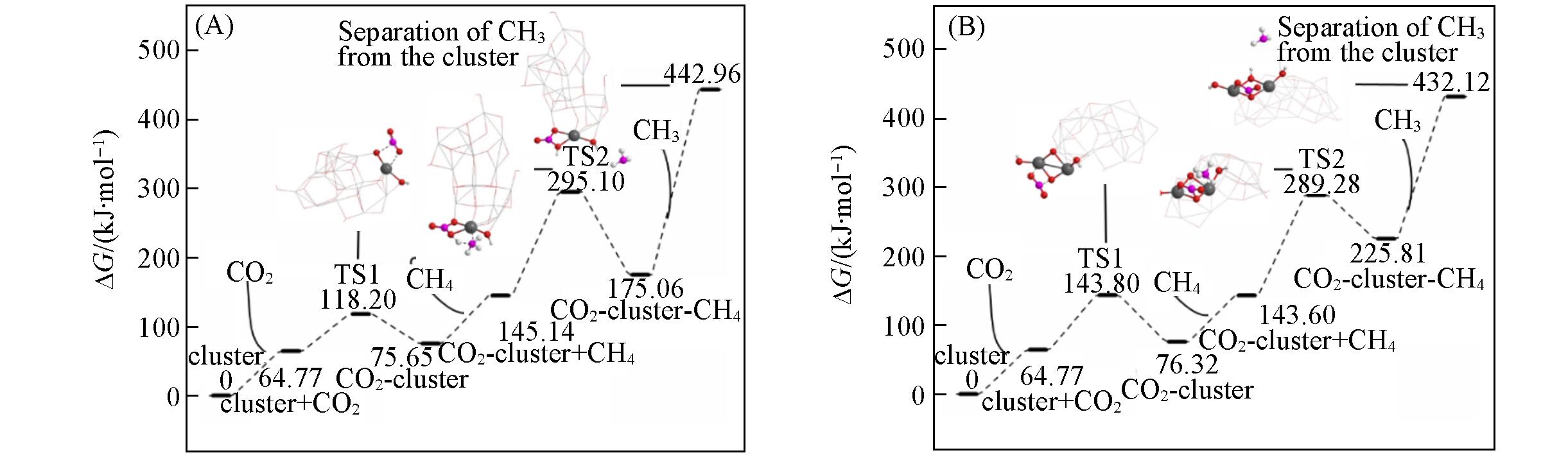
Fig.6 Predicted Gibbs free energy(ΔG, 298 K) for the interaction of extended clusters derived to InO(OH)(A) and In2O2(OH)2(B) with (CO2+CH4) at the level of UB3LYP/(SDD+Def2SVP) :UB3LYP/(Def2SVP+6?31G*)
| 1 | Xu W., Chen Y., Song M., Liu X., Zhao Y., Zhang M., Zhang C., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2020, 124(15), 8110—8118 |
| 2 | Koytsoumpa E. I., Bergins C., Kakaras E., J. Supercrit. Fluid, 2018, 132, 3—16 |
| 3 | Chakravartula Srivatsa S., Bhattacharya S., J. CO2 Util., 2018, 26, 397—407 |
| 4 | Cong L., Zhao Y., Li S., Sun Y., Chin. J. Catal., 2017, 38(5), 899—907 |
| 5 | Wang Z. Q., Wang D., Gong X. Q., ACS Catal., 2019, 10(1), 586—594 |
| 6 | Yang C., Mu R., Wang G., Song J., Tian H., Zhao Z. J., Gong J., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10(11), 3161—3167 |
| 7 | Bowker M., ChemCatChem, 2019, 11(17), 4238—4246 |
| 8 | Higham M. D., Quesne M. G., Catlow C. R. A., Dalton Trans., 2020, 49(25), 8478—8497 |
| 9 | Zheng H., Narkhede N., Han L., Zhang H., Li Z., Res. Chem. Intermed., 2019, 46(3), 1749—1769 |
| 10 | Li S., Guo L., Ishihara T., Catal. Today, 2020, 339, 352—361 |
| 11 | Sha F., Han Z., Tang S., Wang J., Li C., ChemSusChem, 2020, 13(23), 6160—6181 |
| 12 | Kattel S., Ramírez P. J., Chen J. G., Rodriguez J. A., Liu P., Science, 2017, 355(6331), 1296—1299 |
| 13 | Dang S., Qin B., Yang Y., Wang H., Cai J., Han Y., Li S., Gao P., Sun Y., Sci. Adv., 2020, 6(25), eaaz2060 |
| 14 | Rui N., Zhang F., Sun K., Liu Z., Xu W., Stavitski E., Senanayake S. D., Rodriguez J. A., Liu C. J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(19), 11307—11317 |
| 15 | Posada⁃Borbon A., Gronbeck H., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21(39), 21698—21708 |
| 16 | Wang W., Chen Y., Zhang M., Surf. Interfaces, 2021, 25, 101244 |
| 17 | Ye J., Liu C., Ge Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(14), 7817—7825 |
| 18 | Ye J., Liu C., Mei D., Ge Q., ACS Catal., 2013, 3(6), 1296—1306 |
| 19 | Lei Y., Chu C., Li S., Sun Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118(15), 7932—7945 |
| 20 | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision D.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| 21 | Lee C., Yang W., Parr R. G., Phys. Rev. B, 1988, 37(2), 785—789 |
| 22 | Becke A. D., Phys. Rev. A, 1988, 38(6), 3098—3100 |
| 23 | Dolg M., Stoll H., Preuss H., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(3), 1730—1734 |
| 24 | Purvis G. D., Bartlett R. J., J. Chem. Phys., 1982, 76(4), 1910—1918 |
| 25 | Watts J. D., Gauss J., Bartlett R. J., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98(11), 8718—8733 |
| 26 | Raghavachari K., Trucks G. W., Pople J. A., Head⁃Gordon M., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2013, 589, 37—40 |
| 27 | Bauschlicher C. W. Jr., Astrophys. J. Lett., 1998, 509, 125—127 |
| 28 | Glendening E. D., Badenhoop J. K., Reed A. D., Carpenter J. E., Weinhold F., NBO 3.1, Theoretical Chemistry Institute, University of Wisconsin, Madison, 1996 |
| 29 | Weigend F., Ahlrichs R., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2005, 7(18), 3297—3305 |
| 30 | Rassolov V. A., Ratner M. A., Pople J. A., Redfern P. C., Curtiss L., J. Computl. Chem., 2001, 22(9), 976—984 |
| 31 | Wagner M., Meyer B., Setvin M., Schmid M., Diebold U., Nat. Catal., 2021, 592, 722—725 |
| 32 | Qin B., Zhou Z., Li S., Gao P., J. CO2 Util., 2021, 49, 101543 |
| 33 | Liu S., Winter L. R., Chen J. G., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(4), 2855—2871 |
| 34 | Chen Y., Zhai Z., Liu J., Zhang J., Geng Z., Lyu H., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21(43), 23906—23915 |
| 35 | Ohtsuka Y., Nishikawa Y., Ogihara H., Yamanaka I., Ratanasak M., Nakayama A., Hasegawa J. Y., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2019, 123(41), 8907—8912 |
| 36 | Ma D., Cao Z., Chem. Asian J., 2022, e202101383 |
| 37 | Hoch L. B., He L., Qiao Q., Liao K., Reyes L. M., Zhu Y., Ozin G. A., Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(12), 4160—4168 |
| [1] | 吴玉, 李轩, 杨恒攀, 何传新. 钴单原子的双重限域制备策略及高效CO2电还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [2] | 王新天, 李攀, 曹越, 洪文浩, 耿忠璇, 安志洋, 王昊宇, 王桦, 孙斌, 朱文磊, 周旸. 单原子材料在二氧化碳催化中的技术经济分析与产业化应用前景[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220347. |
| [3] | 秦永吉, 罗俊. 单原子催化剂在CO2转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [4] | 崔伟, 赵德银, 白文轩, 张晓东, 余江. CO2在非质子溶剂与铁基离子液体复合体系中的吸收[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220120. |
| [5] | 郭志强, 杨博如, 席婵娟. 硼氢化试剂在二氧化碳还原官能化反应中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220199. |
| [6] | 张昕昕, 许狄, 王艳秋, 洪昕林, 刘国亮, 杨恒权. CO2加氢制低碳醇CuFe基催化剂中的Mn助剂效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220187. |
| [7] | 周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [8] | 彭奎霖, 李桂林, 江重阳, 曾少娟, 张香平. 电解液调控CO2电催化还原性能微观机制的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220238. |
| [9] | 张振, 邓煜, 张琴芳, 余达刚. 可见光促进二氧化碳参与的羧基化反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220255. |
| [10] | 王丽君, 李欣, 洪崧, 詹新雨, 王迪, 郝磊端, 孙振宇. 调节氧化镉-炭黑界面高效电催化CO2还原生成CO[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [11] | 邱丽琪, 姚向阳, 何良年. 可见光驱动丰产金属卟啉类配合物催化的二氧化碳选择性还原反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220064. |
| [12] | 王征文, 高凤翔, 曹瀚, 刘顺杰, 王献红, 王佛松. 基于二氧化碳共聚物的紫外光固化高分子材料的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220236. |
| [13] | 黄孝舜, 马海英, 柳淑娟, 王斌, 王红利, 钱波, 崔新江, 石峰. 二氧化碳间接转化制化学品的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220222. |
| [14] | 宋德文, 汪明旺, 王亚旎, 焦振梅, 宁汇, 吴明铂. 二氧化碳电还原制草酸研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220248. |
| [15] | 赵润瑶, 纪桂鹏, 刘志敏. 吡咯氮配位单原子铜催化剂的电催化二氧化碳还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||