

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (9): 20220325.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220325
收稿日期:2022-05-11
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-07-15
通讯作者:
滕镇远,苏陈良
E-mail:zy.teng@foxmail.com;chmsuc@szu.edu.cn
基金资助:
TENG Zhenyuan1( ), ZHANG Qitao2, SU Chenliang2(
), ZHANG Qitao2, SU Chenliang2( )
)
Received:2022-05-11
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-07-15
Contact:
TENG Zhenyuan,SU Chenliang
E-mail:zy.teng@foxmail.com;chmsuc@szu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
近10年来, 研究者制备了大量的单原子催化剂(SACs), 其在光、 电、 热等催化体系中展现出优异的催化性能及较高的实用性和经济性. 光催化过程的独特性使其在催化本质上明显不同于热催化和电催化过程, 即处于激发态的电子和空穴参与反应, 而非基态的价电子. 本文首先探讨了有机聚合半导体与传统无机金属化合物半导体的区别, 指出聚合物半导体介电常数通常较小且光生电子与空穴的中心距离过短(计算上通常 <1 nm), 导致其界面处几乎不存在明显的能带弯曲. 将金属离子引入聚合物半导体的骨架中可以有效引入给体-受体对, 在提高载流子分离效率的同时延长其寿命. 在高效聚合物基单原子光催化剂的设计过程中, 引入单原子金属位点后的激发态电荷分布及捕获态电子对反应的驱动力是决定催化剂整体性能的关键因素. 时间-空间双因子布局分析法和瞬态吸收光谱可为研究者提供相关信息. 随着人工智能的进一步发展, 建立回归精度接近或达到密度泛函理论水准的能量函数, 从而反推激发态下体系的能量变化, 有望为光催化反应的激发特性与反应活性建立可靠的联系. 此外, 配体和溶剂化效应在今后的研究中也应被仔细考虑.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
滕镇远, 张启涛, 苏陈良. 聚合物单原子光催化剂的载流子分离和表面反应机制. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220325.
TENG Zhenyuan, ZHANG Qitao, SU Chenliang. Charge Separation and Surface Reaction Mechanisms for Polymeric Single-atom Photocatalysts. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220325.
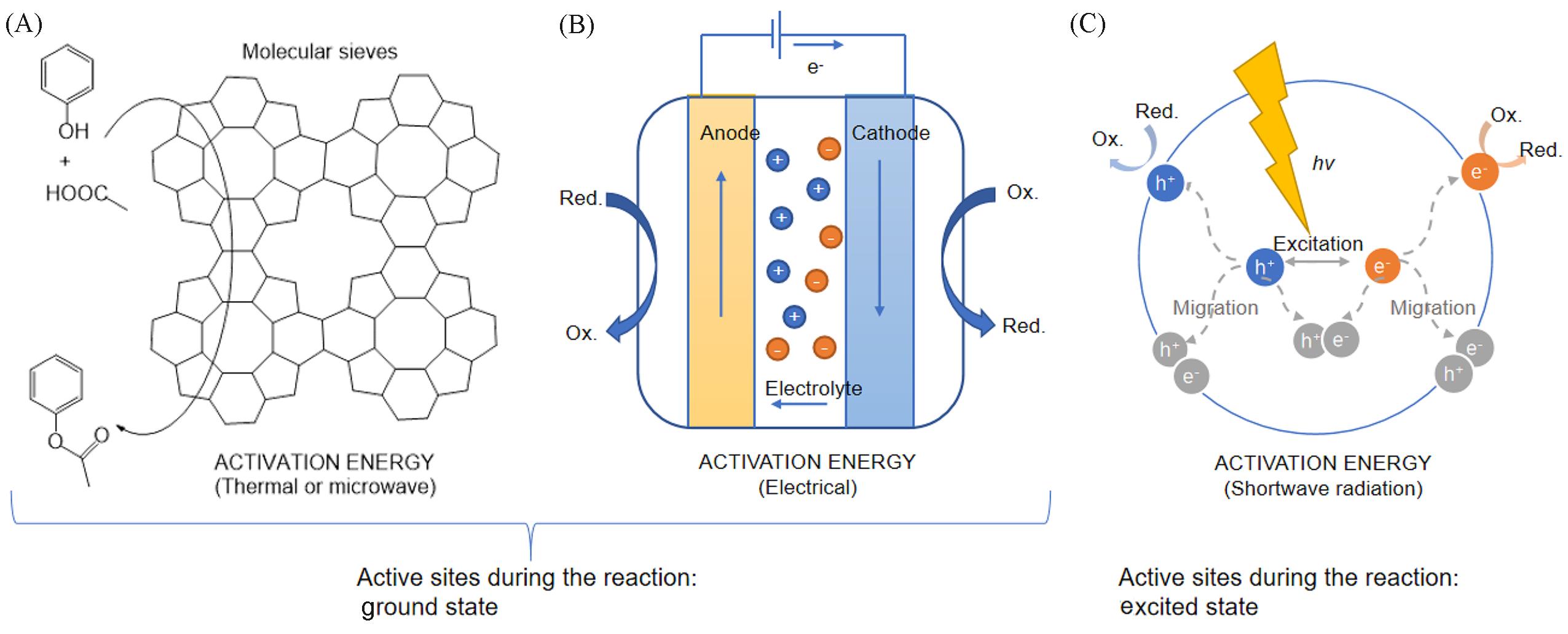
Fig.1 Differences and similarities among thermocatalysis, electrocatalysis and photocatalysis(A) The activation energy barrier of a thermocatalyst is usually overcome by internal energy. (B) Activation energy barriers for electrocatalysis are usually overcome by electrical energy. In thermocatalysis and electrocatalysis, the valence electrons of the catalyst are all at their ground states. (C) The energy used to drive photocatalysis is derived from shortwave radiation, and the activation energy barrier is generally considered to be overcome by light energy. The valence electrons are at excited states during the catalytic reaction.
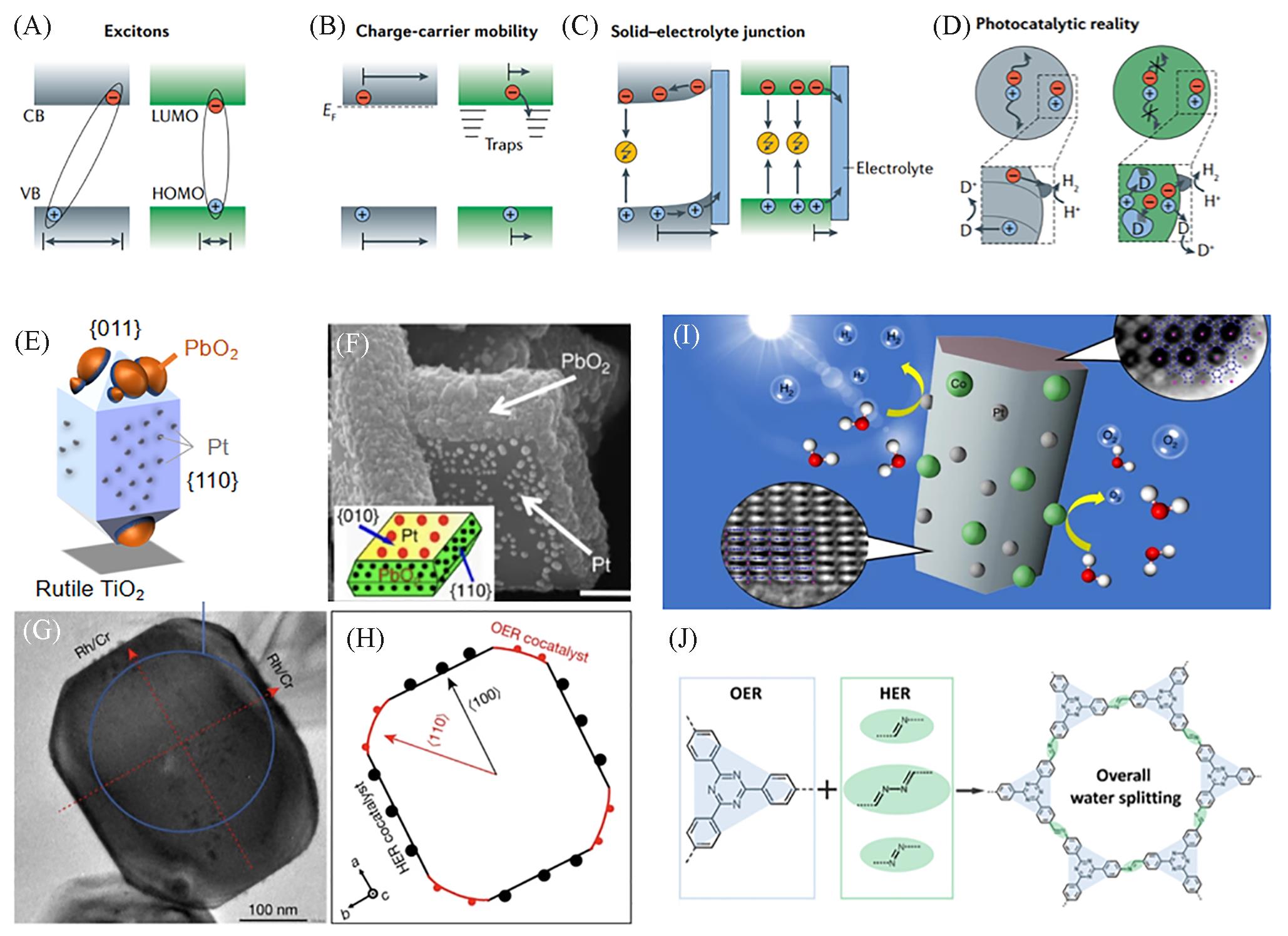
Fig.2 Differences and similarities between polymer?based photocatalysts and traditional inorganic photocatalysts(A) Photogenerated excitons or free charge carriers show higher mobilities in inorganic semiconductors than in polymer-based materials[37]. (B) The modes of carrier transfer in inorganic semiconductors are usually band-like transport[37]. Polymer-based semiconductors typically exhibit a charge transfer model like “hopping” by trapping- detrapping because carrier mobility is limited to shorter ranges in organic frameworks. (C) Inorganic semiconductors have larger dielectric constants, so the carriers in the bulk phase can be transported to the surface through the band bending[37].The binding energy of excitons in polymer-based semiconductors is high, so there is almost no band bending and the most effective excitation occurs at the surface. (D) For inorganic semiconductors, the sites where the oxidation and reduction reactions take place are far apart due to the long-range carrier transfer through energy band bending. On the contrary, the reaction sites of polymer-based semiconductors with few energy bands are fairly close together[37].Inorganic metal oxides with redox reactions occurring on different crystal planes: (E) Rutile TiO2; (F) BiVO4[67]; (G, H) SrTiO3:Al[64]. Highly crystallized carbon nitrides(I)[70] and covalent organic frameworks(J)[71] for photocatalytic water splitting.(A—D) Copyright 2021, Springer Nature Limited; (F) Copyright 2013, Springer Nature Limited; (G, H) Copyright 2020, Springer Nature Limited; (I) Copyright 2020, Springer Nature Limited; (J) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
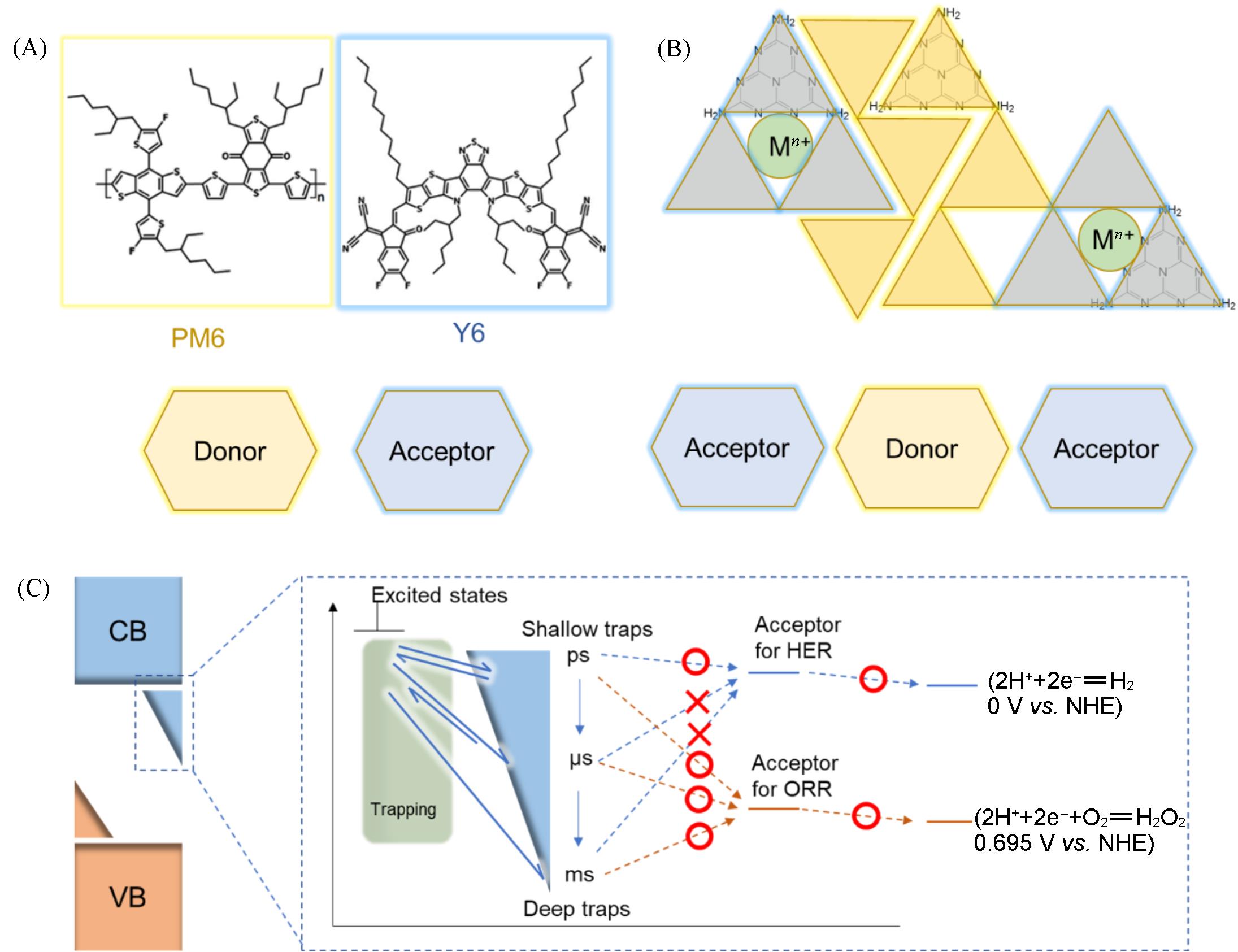
Fig.3 Effects of single?atom sites on carrier kinetics in polymer?based photocatalysts(A) Construction of traditional organic semiconductor containing donor(PM6)-acceptor(Y6) pairs; (B) formed donor-acceptor pairs after introducing metal sites into polymer-based semiconductors; (C) the effects of carriers with different energies and lifetimes on different reactions (Hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen reduction reactions are used as examples).
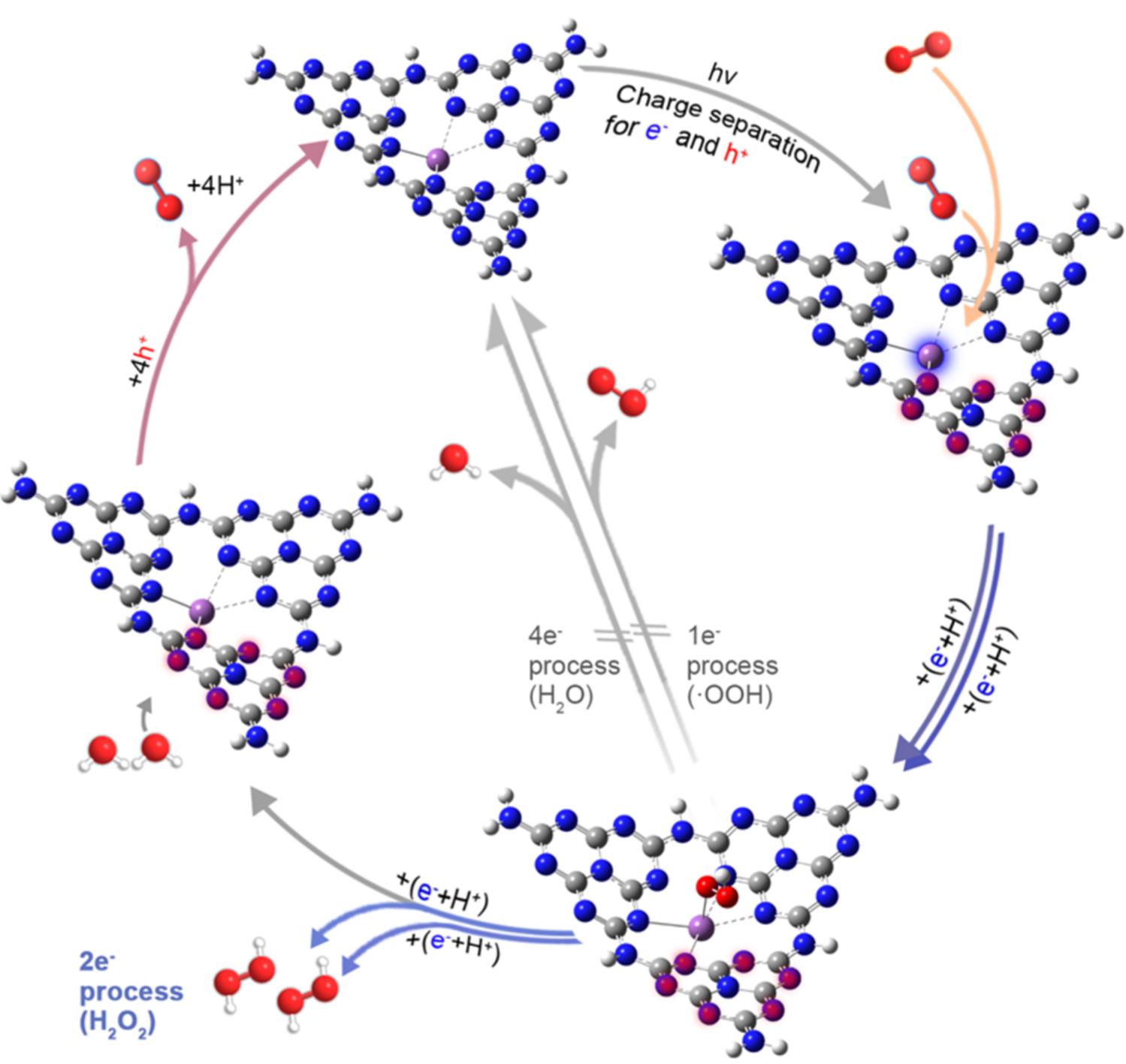
Fig.5 Mechanism of photocatalytic H2O2 production[23]The white, gray, bule, red and magenta spheres refer to hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and Sb atoms. After shining visible light, the photogenerated electrons are localized at the Sb sites(with blue glow), while the photogenerated holes are localized at the N atoms at the melem units(with red glow). Subsequently, the dissolved O2 molecules are adsorbed(orange arrows) onto the Sb sites and then get reduced(blue arrows) via a 2e- transfer pathway through forming an electron μ-peroxide as the intermediate. Simultaneously, water molecules are oxidized(pink arrows) to generate O2 by the highly concentrated holes on the melem units. Copyright 2021, Springer Nature Limited.
| 1 | Wang A., Li J., Zhang T., Nat. Rev. Chem., 2018, 2, 65—81 |
| 2 | Qiao B., Wang A., Yang X., Lawrence F. A., Jiang Z., Cui Y., Liu J., Li J., Zhang T., Nat. Chem., 2011, 3, 634—641 |
| 3 | Lang R., Du X., Huang Y., Jiang X., Zhang Q., Guo Y., Liu K., Qiao B., Wang A., Zhang T., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 11986—12043 |
| 4 | Gao C., Low J., Long R., Kong T., Zhu, J., Xiong Y., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 12175—12216 |
| 5 | Hai X., Xi S., Mitchell S., Harrath K., Xu H., Akl D. F., Kong D., Li J., Li Z., Sun T., Yang H., Cui Y., Su C., Zhao X., Li J., Perez⁃Ramirez J., Lu J., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2022, 17, 174—181 |
| 6 | Yang H., Shang L., Zhang Q., Shi R., Geoffrey I. N. W., Gu L., Zhang T., Nat. Commum., 2019, 10, 4585 |
| 7 | Yan H., Su C., He J., Chen W., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 8793—8814 |
| 8 | Yan H., Zhao X., Guo N., Lyu Z., Du Y., Xi S., Guo R., Cheng C., Chen Z., Liu W., Yao C., Li J., Pennycook S., J., Chen W., Su C., Zhang C., Lu J., Nat. Commun., 2018, 9, 1—9 |
| 9 | Li X., Bi W., Zhang L., Tao S., Chu W., Zhang Q., Luo Y., Wu C., Xie Y., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 2427—2431 |
| 10 | Li X., Fang Y., Wang J., Fang H., Xi S., Zhao X., Xu D., Xu H., Yu W., Hai X., Chen C., Yao C., Tao H. B., Howe A. G. R., Pennycook S. J., Liu B., Lu J., Su C., Nat. Commun., 2021, 12, 2351 |
| 11 | Ji S., Chen Y.,Wang X., Zhang Z., Wang D., Li Y., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120, 11900—11955 |
| 12 | Hai X., Zhao X., Guo N., Yao C., Chen C., Liu W., Du Y., Yan H., Li J., Chen Z., Li X., Li Z., Xu H., Lyu P., Zhang J., Lin M., Su C., Stephen J. P., Zhang C., Xi S., Lu J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 5862—5870 |
| 13 | Xue Z. H., Luan D., Zhang H., Lou X. W., Joule, 2022, 6, 92—133 |
| 14 | Zhang Y., Cao Q., Wu X., Xiao Y., Meng A., Zhang Q., Yu Y., Zhang W. D., Chem. Eng. J., 2022, 427, 132042 |
| 15 | Chen C., Ou W., Yam K.-M., Xi S., Zhao X., Chen S., Li J., Lyu P., Ma L., Du Y., Yu W., Fang H., Yao C., Hai X., Xu H., Koh M. J., Pennycook S. J., Lu J., Lin M., Su C., Zhang C., Lu J., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2008471 |
| 16 | Hai X., Zhao X., Guo N., Yao C., Chen C., Liu W., Du Y., Yan H., Li J., Chen Z., Li X., Li Z., Xu H., Lyu P., Zhang J., Lin M., Su C., Pennycook S. J., Zhang C., Xi S., Lu J., ACS Catal., 2020, 10, 5862—5870 |
| 17 | Sun H., Ma Y., Zhang Q., Su C., Trans. Tianjin Univ., 2021, 27, 313—330 |
| 18 | Zhang S., Ao X., Huang J., Wei B., Zhai Y., Zhai D., Deng W., Su C., Wang D., Li Y., Nano Lett., 2021, 21, 9691—9698 |
| 19 | Sun T., Zang W., Yan H., Li J., Zhang Z., Bu Y., Chen W., Wang J., Lu J., Su C., ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 4498—4509 |
| 20 | Wang F., Li J., Zhao J., Yang Y., Su C., Zhong Y. L., Yang Q. H., Lu J., ACS Mater. Lett., 2020, 2, 1450—1463 |
| 21 | Ciriminna R., Pagliaro M., Luque R., Green Energy Environ., 2021, 6, 161—166 |
| 22 | Sun T., Zhang G., Xu D., Lian X., Li H., Chen W., Su C., Mater. Today Energy, 2019, 12, 215—238 |
| 23 | Teng Z., Zhang Q., Yang H., Kato K., Yang W., Lu Y. R., Liu S., Wang C., Yamakata A., Su C., Liu B., Ohno T., Nat. Catal., 2021, 4, 374—384 |
| 24 | Xiong T., Cen W., Zhang Y., Dong F., ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 2462—2472 |
| 25 | Qiu C., Xu Y., Fan X., Xu D., Tandiana R., Ling X., Jiang Y., Liu C., Yu L., Chen W., Su C., Adv. Sci., 2019, 6, 1801403 |
| 26 | Jiang W., Zhao Y., Zong X., Nie H., Niu L., An L., Qu D., Wang X., Kang Z., Sun Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60, 6124—6129 |
| 27 | Hendrik S., Julia K., Gökcen S., Maxwell W. T., Sebastian B., Igor M., Viola D., Filip P., Renée S., Jürgen S., Robert E. D., Christian O., Bettina V. L., Chem. Mater., 2019, 18, 7478—7486 |
| 28 | Li Y., Li B., Zhang D., Cheng L., Xiang Q., ACS Nano, 2020, 14, 10552—10561 |
| 29 | Dong P., Wang Y., Zhang A., Cheng T., Xi X., Zhang J., ACS Catal., 2021, 11, 13266—13279 |
| 30 | Gao G., Jiao Y., Waclawik E. R., Du A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 6292—6297 |
| 31 | Li Y., Wang Y., Dong C. L., Huang Y. C., Chen J., Zhang Z., Meng F., Zhang Q., Huangfu Y., Zhao D., Gu L., Shen S., Chem. Sci., 2021, 12, 3633—3643 |
| 32 | Chu C., Zhu Q., Pan Z., Gupta S., Huang D., Du Y., Weon S., Wu Y., Muhich C., Stavitski E., Domen K., Kim J. H., PNAS, 2020, 117, 6376—6382 |
| 33 | Nosaka Y., Nosaka A., Introduction to Photocatalysis: From Basic Science to Applications, the Royal Society of Chemistry, London, 2016 |
| 34 | Tao X., Zhao Y., Wang S., Li C., Li R., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2022, 51, 3561—3608 |
| 35 | Schneider J., Matsuoka M., Takeuchi M., Zhang J., Horiuchi Y., Anpo M., Bahnemann D. W., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 9919—9986 |
| 36 | Fang Y., Hou Y., Fu X., Wang X., Chem. Rev., 2022, 122, 4204—4256 |
| 37 | Banerjee T., Podjaski F., Kroeger J., Biswal B. P., Lotsch B. V., Nat. Rev. Mater., 2021, 6, 168—190 |
| 38 | Zhang Z., Yates J. T. Jr., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 5520—5551 |
| 39 | María Q., Tomas E., Anders H., Gerrit B., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2006, 111, 1035 |
| 40 | Williams F., Nozik A. J., Nature, 1984, 312, 21—27 |
| 41 | Juan B., Peter C., Luca B., Sixto G., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2013, 5,205—207 |
| 42 | Wang Q., Domen K., Chem. Rev., 2019, 2, 919—985 |
| 43 | Liu T., Pan Z., Junie Jhon M. V., Kato K., Wu B., Yamakata A., Katayama K., Chen B., Chu C., Domen K., Nat. Commun., 2022, 13, 1034 |
| 44 | Nosaka Y., Nosaka A. Y., Chem. Rev., 2017, 117, 11302—11336 |
| 45 | Zhang Z., Xu Y., Zhang Q., Fang S., Sun H., Ou W., Su C., Sci. Bull., 2022, 67, 71—78 |
| 46 | Li Q., Ren C., Qiu C., He T., Zhang Q., Ling X., Xu Y., Su C., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2021, 32, 3463—3468 |
| 47 | Xu Y., Fan M., Yang W., Xiao Y., Zeng L., Wu X., Xu Q., Su C., He Q., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33, 2101455 |
| 48 | Meng A., Teng Z., Zhang Q., Su C., Asian J. Chem., 2020, 15, 3405—3415 |
| 49 | Zhang Z., Qiu C., Xu Y., Han Q., Tang J., Loh K. P., Su C., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11, 4722 |
| 50 | Wang X., Maeda K., Thomas A., Takanabe K., Xin G., Carlsson J. M., Domen K., Antonietti M., Nat. Mater., 2009, 8, 76—80 |
| 51 | Park H., Kim H. I., Moon G. H., Choi W., Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 9, 411—433 |
| 52 | Le Bahers T., Rerat M., Sautet P., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014, 118, 5997—6008 |
| 53 | Takanabe K., ACS Catal., 2017, 7, 8006—8022 |
| 54 | Guiglion P., Butchosa C., Zwijnenburg M. A., Macromol. Chem. Phys., 2016, 217, 344—353 |
| 55 | Clarke T. M., Durrant J. R., Chem. Rev., 2010, 110, 6736—6767 |
| 56 | Teng Z., Cai W., Sim W., Zhang Q., Wang C., Su C., Ohno T., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2021, 282, 119589 |
| 57 | Lu T., Chen F., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33, 580—592 |
| 58 | Puschnig P., Ambrosch⁃Draxl C., C. R. Physique, 2009, 10, 504—513 |
| 59 | Rahman M. Z., Mullins C. B., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 248—257 |
| 60 | Merschjann C., Tschierlei S., Tyborski T., Kailasam K., Orthmann S., Hollmann D., Schedel⁃Niedrig T., Thomas A., Lochbrunner S., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27, 7993—7999 |
| 61 | Pelzer K. M., Darling S. B., Mol. Syst. Des. Eng., 2016, 1, 10—24 |
| 62 | Bredas J. L., Mater. Horiz., 2014, 1, 17—19 |
| 63 | Lin L., Ou H., Zhang Y., Wang X., ACS Catal., 2016, 6, 3921—3931 |
| 64 | Takata T., Jiang J., Sakata Y., Nakabayashi M., Shibata N., Nandal V., Seki K., Hisatomi T., Domen K., Nature, 2020, 581, 411—414 |
| 65 | Zhao D., Wang Y., Dong C. L., Huang Y. C., Chen J., Xue F., Shen S., Guo L., Nat. Energy, 2021, 6, 388—397 |
| 66 | Ohno T., Sarukawa K., Matsumura M., New J. Chem., 2002, 26, 1167—1170 |
| 67 | Li R., Zhang F., Wang D., Yang J., Li M., Zhu J., Zhou X., Han H., Li C., Nat. Commun., 2013, 4, 1432 |
| 68 | Petousis I., Mrdjenovich D., Ballouz E., Liu M., Winston D., Chen W., Graf T., Schladt T. D., Persson K. A., Prinz F. B., Sci. Data, 2017, 4, 160134 |
| 69 | Patra P. C., Mohapatra Y. N., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2021, 118 |
| 70 | Lin L., Lin Z., Zhang J., Cai X., Lin W., Yu Z., Wang X., Nat. Catal., 2020, 3, 649—655 |
| 71 | Wan Y., Wang L., Xu H., Wu X., Yang J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 142, 4508—4516 |
| 72 | Guiglion P., Monti A., Zwijnenburg M. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 1498—1506 |
| 73 | Noda Y., Merschjann C., Tarabek J., Amsalem P., Koch N., Bojdys M. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 9394—9398 |
| 74 | Tamai Y., Ohkita H., Benten H., Ito S., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6, 3417—3428 |
| 75 | Teng Z., Yang N., Lv H., Wang S., Hu M., Wang C., Wang D., Wang G., Chem., 2019, 5, 664—680 |
| 76 | Botiz I., Schaller R. D., Verduzco R., Darling S. B., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115, 9260—9266 |
| 77 | Kosco J., Gonzalez⁃Carrero S., Howells C. T., Fei T., Dong Y., Sougrat R., Harrison G. T., Firdaus Y., Sheelamanthula R., Purushothaman B., Moruzzi F., Xu W., Zhao L., Basu A., de Wolf S., Anthopoulos T. D., Durrant J. R., McCulloch I., Nat. Energy, 2022, 7, 340—351 |
| 78 | Lau V. W. H., Klose D., Kasap H., Podjaski F., Pignie M. C., Reisner E., Jeschke G., Lotsch B. V., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56, 510—514 |
| 79 | Yang W., Godin R., Kasap H., Moss B., Dong Y., Hillman S. A. J., Steier L., Reisner E., Durrant J. R., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 11219—11229 |
| 80 | Zhang P., Tong Y., Liu Y., Vequizo J. J. M., Sun H., Yang C., Yamakata A., Fan F., Lin W., Wang X., Choi W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59, 16209—16217 |
| 81 | Dong Z., Zhang L., Gong J., Zhao Q., Chem. Eng. J., 2021, 403, 2021 |
| 82 | Casida M. E., Huix⁃Rotllant M., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2012, 63, 287—323 |
| 83 | Laurent A. D., Jacquemin D., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2013, 113, 2019—2039 |
| 84 | Ghuman K. K., Hoch L. B., Szymanski P., Loh J. Y. Y., Kherani N. P., E⁃Sayed M. A., Ozin G. A., Singh C. V., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 1206—1214 |
| 85 | Norskov J. K., Rossmeisl J., Logadottir A., Lindqvist L., Kitchin J. R., Bligaard T., Jonsson H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2004, 108, 17886—17892 |
| 86 | Feng C., Wu Z. P., Huang K. W., Ye J., Zhang H., Adv. Mater., 2022, 2200180 |
| 87 | Esterhuizen J. A., Goldsmith B. R., Linic S., Nat. Catal., 2022, 5, 175—184 |
| 88 | Lin C., Kim T., Schultz J. D., Young R. M., Wasielewski M. R., Nat. Chem., 2022, 14, 786—793 |
| 89 | Wahab M. A., Joseph J., Atanda L., Sultana U. K., Beltramini J. N., Ostrikov K., Will G., O'Mullane A. P., Abdala A., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2020, 3, 1439—1447 |
| [1] | 王茹玥, 魏呵呵, 黄凯, 伍晖. 单原子材料的冷冻合成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220428. |
| [2] | 秦永吉, 罗俊. 单原子催化剂在CO2转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220300. |
| [3] | 林治, 彭志明, 贺韦清, 沈少华. 单原子与团簇光催化: 竞争与协同[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220312. |
| [4] | 杨静怡, 李庆贺, 乔波涛. 铱单原子和纳米粒子在N2O分解反应中的协同催化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220388. |
| [5] | 林高鑫, 王家成. 单原子掺杂二硫化钼析氢催化的进展和展望[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220321. |
| [6] | 任诗杰, 谯思聪, 刘崇静, 张文华, 宋礼. 铂单原子催化剂同步辐射X射线吸收谱的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220466. |
| [7] | 楚宇逸, 兰畅, 罗二桂, 刘长鹏, 葛君杰, 邢巍. 单原子铈对弱芬顿效应活性位点氧还原稳定性的提升[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220294. |
| [8] | 翁美琪, 商桂铭, 王家泰, 李盛华, 樊志, 林松, 郭敏杰. 有机磷神经毒剂分子印迹聚合物的模拟模板分子[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220136. |
| [9] | 邱丽琪, 姚向阳, 何良年. 可见光驱动丰产金属卟啉类配合物催化的二氧化碳选择性还原反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220064. |
| [10] | 赵润瑶, 纪桂鹏, 刘志敏. 吡咯氮配位单原子铜催化剂的电催化二氧化碳还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [11] | 夏雾, 任颖异, 刘京, 王锋. 壳聚糖包裹CdSe量子点组装体的水相可见光催化CO2还原[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220192. |
| [12] | 丁杨, 王万辉, 包明. 多孔骨架固定分子催化剂催化CO2加氢制备甲酸研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220309. |
| [13] | 赵盈喆, 张建玲. 金属-有机框架基材料在二氧化碳光催化转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220223. |
| [14] | 龚妍熹, 王建兵, 柴歩瑜, 韩元春, 马云飞, 贾超敏. 钾掺杂g-C3N4薄膜光阳极的制备及光电催化氧化降解水中双氯芬酸钠性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220005. |
| [15] | 宋颖颖, 黄琳, 李庆森, 陈立妙. CuO/BiVO4光催化剂的制备及光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||