

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (9): 20220334.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220334
收稿日期:2022-05-13
出版日期:2022-09-10
发布日期:2022-06-21
通讯作者:
寇宗魁
E-mail:zongkuikou@whut.edu.cn
基金资助:
JIANG Bowen, CHEN Jingxuan, CHENG Yonghua, SANG Wei, KOU Zongkui( )
)
Received:2022-05-13
Online:2022-09-10
Published:2022-06-21
Contact:
KOU Zongkui
E-mail:zongkuikou@whut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
电化学传感器具有响应速度快、 专一性强及准确性高等特点, 已成为生物传感快速检测的重要发展方向之一, 但目前难以达到对单个生物分子的检测水平, 这主要受限于作为核心部件的探针材料. 单原子材料由于其简单明确的原子局域结构, 且具有媲美于生物酶的统一活性位点, 是一种极具潜力的探针材料, 因此受到了广泛关注. 本文综合评述了具有均一局域配位环境的单原子材料的合成, 以及其在电化学生物传感中的应用, 并对单原子材料在未来电化学生物传感中面临的挑战和机遇进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
江博文, 陈敬轩, 成永华, 桑微, 寇宗魁. 单原子材料在电化学生物传感中的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220334.
JIANG Bowen, CHEN Jingxuan, CHENG Yonghua, SANG Wei, KOU Zongkui. Recent Progress of Single-atom Materials in Electrochemical Biosensing. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220334.
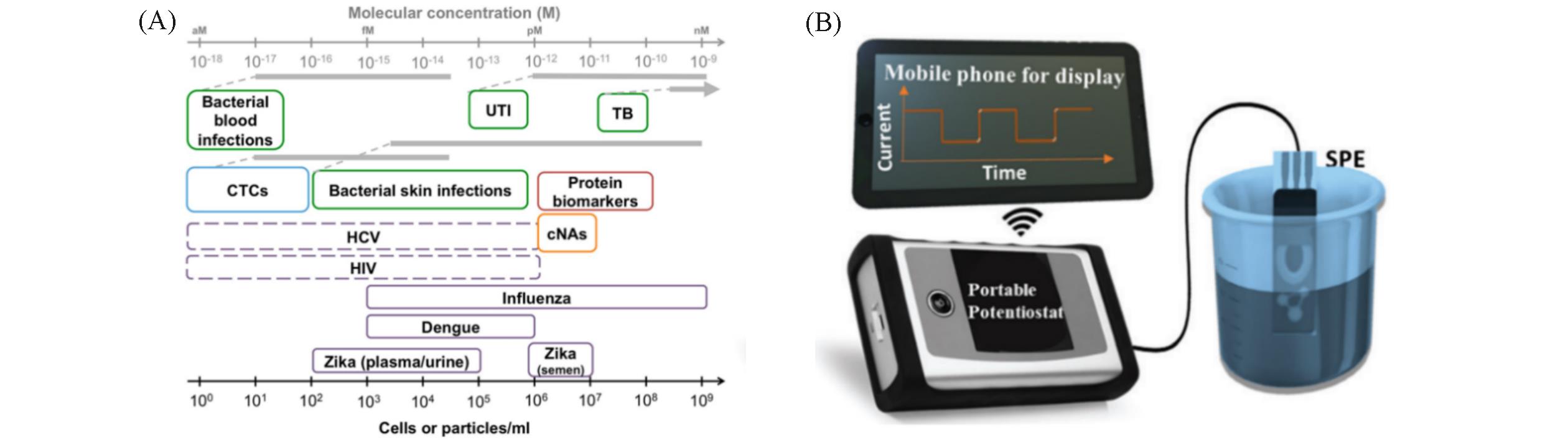
Fig.1 Applications of bacterial detection(green), viral targets(purple), and cancer biomarkers(blue: circulating tumor cells, red: protein biomarkers, orange: circulating nucleic acids) (A) [ 7], a portable sensing platform using an all?in?one screen?printed electrode(SPE) and a hand?held commercial potentiostat(PalmSens)(B) [ 12](A) A dotted line for indications where quantitative monitoring is required. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2022, Royal Society of Chemistry.
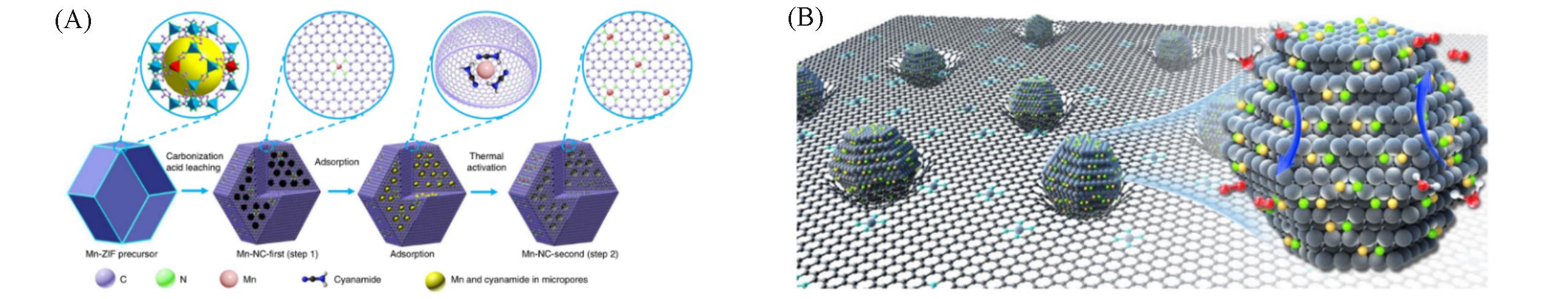
Fig.2 Schematic of atomically dispersed Mn?N4 site catalyst synthesis(A) [ 29], schematic illustration of WC x ?FeNi catalyst consisting of Fe and Ni atoms stabilized on WC x nanocrystallites(majority component) surrounded by carbon sheets(B) [ 31](A) Copyright 2018, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
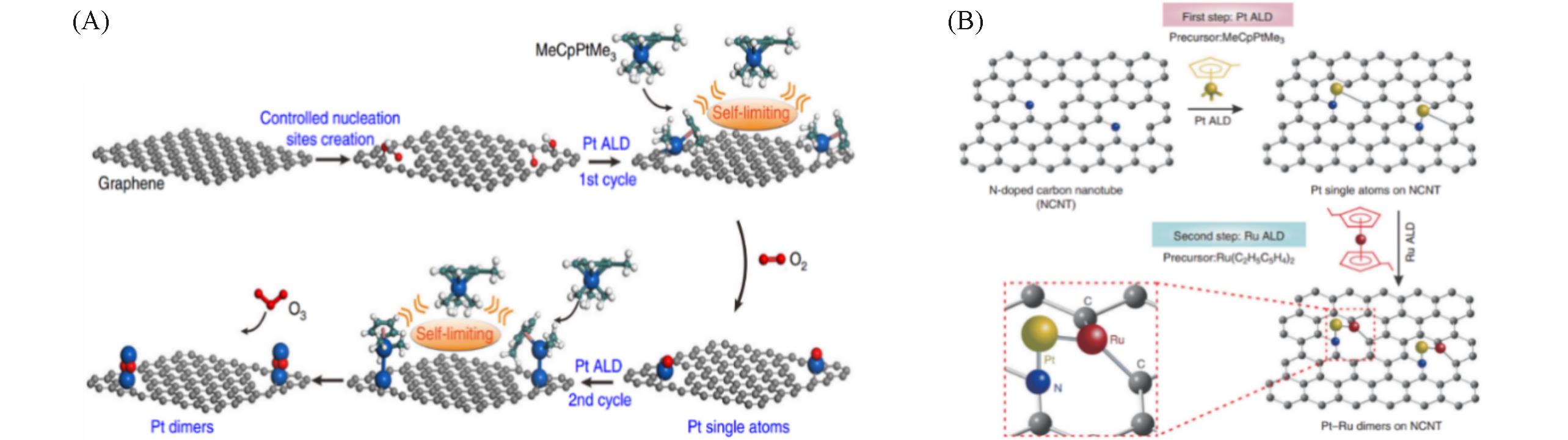
Fig.3 Schematic illustration of bottom?up synthesis of dimeric Pt2/graphene catalysts(A) [ 34], schematic illustration of ALD synthesis of Pt?Ru dimers on nitrogen?doped carbon nanotubes(B) [ 35](A) The balls in cyan, white, red, and blue represent C, H, O, and Pt while the balls in gray represent C atoms in the graphene support. Copyright 2017, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2019, Springer Nature.
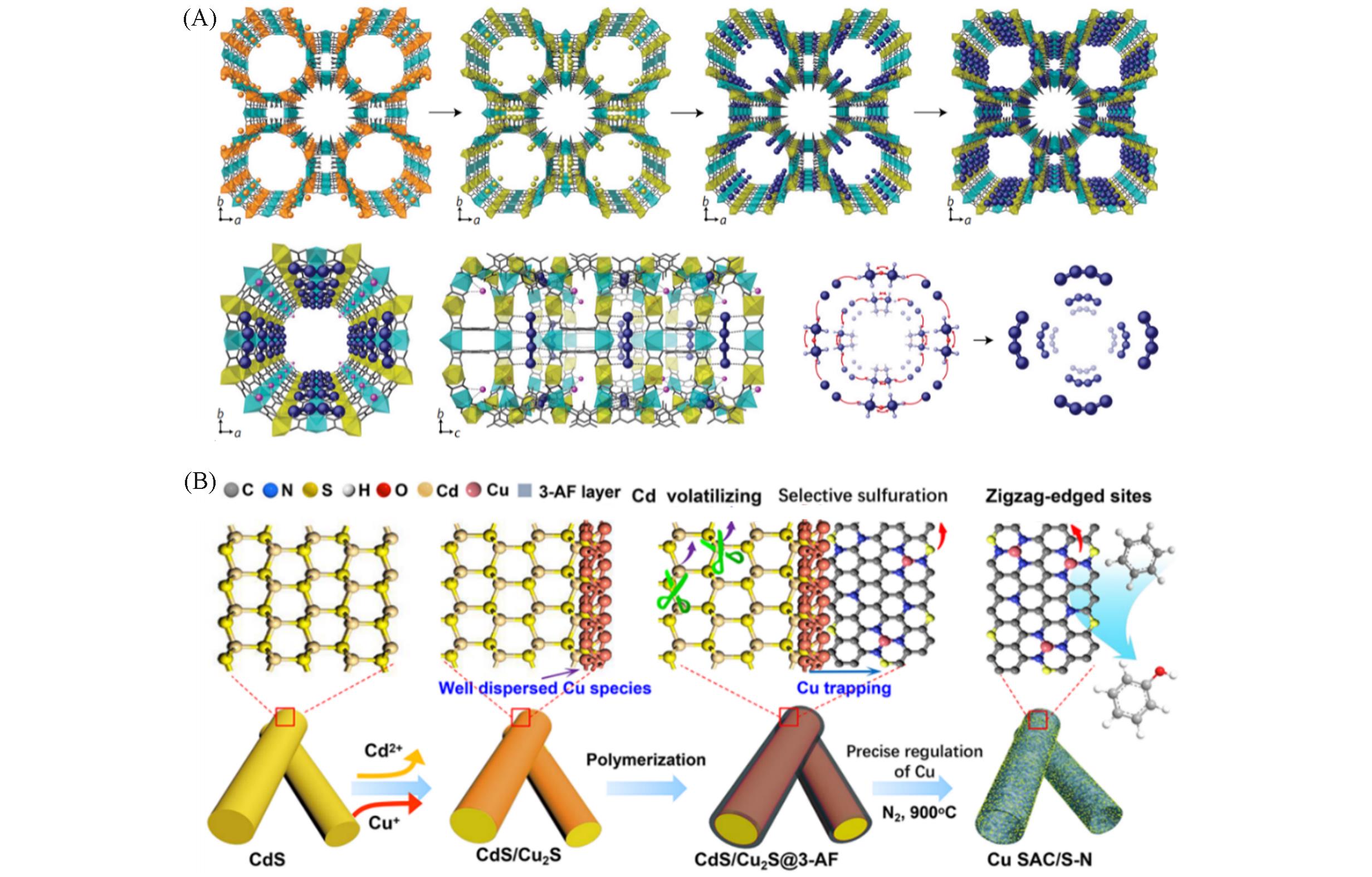
Fig.4 Schematic illustration of the formation of Pd4?MOF catalyst(A) [ 38], scheme illustrating the proposed formation mechanisms of Cu SAM(B) [ 40](A) Copyright 2017, Springer Nature; (B) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| Detection method | Target | Sample | Limit of detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical biosensing | Dopamine(DA) | Ru SAM | 20 nmol/L | [ |
| Fe SAM | 0.007 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Mn SAM | 0.05 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Glucose | Co SAM | 1.2×10 5 nmol/L | [ | |
| H2O2 | 100 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Electrochemiluminescence biosensing | Ascorbic acid(AA) | Ni SAM | 95 nmol/L | [ |
| Trolox | Fe SAM | 800 nmol/L | [ | |
| Thrombin(TB) | Ru SAM | 0.03 nmol/L | [ | |
| Zn SAM | 1.0×10 -7 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Colorimetric biosensing | Acetylcholin esteras(AChE) | Fe SAM | 0.2 mU/mL | [ |
| Photoelectrochemical biosensors | Organophosphorus pesticides(Ops) | Pd SAM | 500 nmol/L | [ |
| Prostate specific antigen(PSA) | Pt SAM | 6.6×10 -6 nmol/L | [ |
Table 1 Summary of single-atom materials biosensing
| Detection method | Target | Sample | Limit of detection | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrochemical biosensing | Dopamine(DA) | Ru SAM | 20 nmol/L | [ |
| Fe SAM | 0.007 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Mn SAM | 0.05 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Glucose | Co SAM | 1.2×10 5 nmol/L | [ | |
| H2O2 | 100 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Electrochemiluminescence biosensing | Ascorbic acid(AA) | Ni SAM | 95 nmol/L | [ |
| Trolox | Fe SAM | 800 nmol/L | [ | |
| Thrombin(TB) | Ru SAM | 0.03 nmol/L | [ | |
| Zn SAM | 1.0×10 -7 nmol/L | [ | ||
| Colorimetric biosensing | Acetylcholin esteras(AChE) | Fe SAM | 0.2 mU/mL | [ |
| Photoelectrochemical biosensors | Organophosphorus pesticides(Ops) | Pd SAM | 500 nmol/L | [ |
| Prostate specific antigen(PSA) | Pt SAM | 6.6×10 -6 nmol/L | [ |
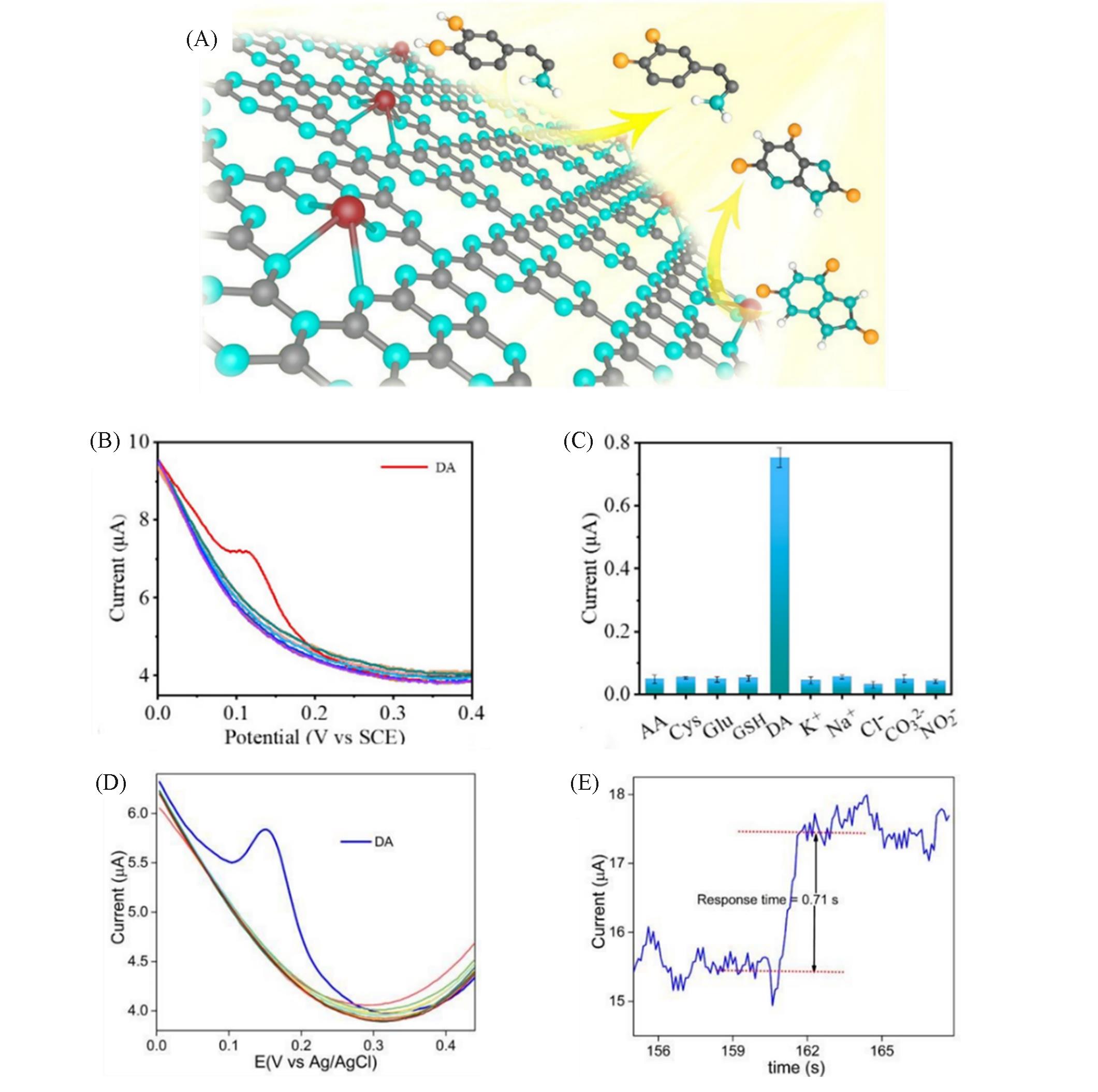
Fig.5 Schematic diagram of structural single?atom Ru catalyst(A), selectivity of Ru?Ala?C3N4/GCE toward DA(B,C) [ 43], differential pulse voltammetry(DPV) selectivity test of the GCE/Fe?N5 SAM sensor toward DA(10.0 μmol/L) having 1000 nmol/L of other biological, cations and anions in the solutions(pH=7.4)(D) and response time of the GCE/Fe?N5 SAM sensor towards DA(E) [ 44](A—C) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society. (D—E) Copyright 2021, Elsevier.
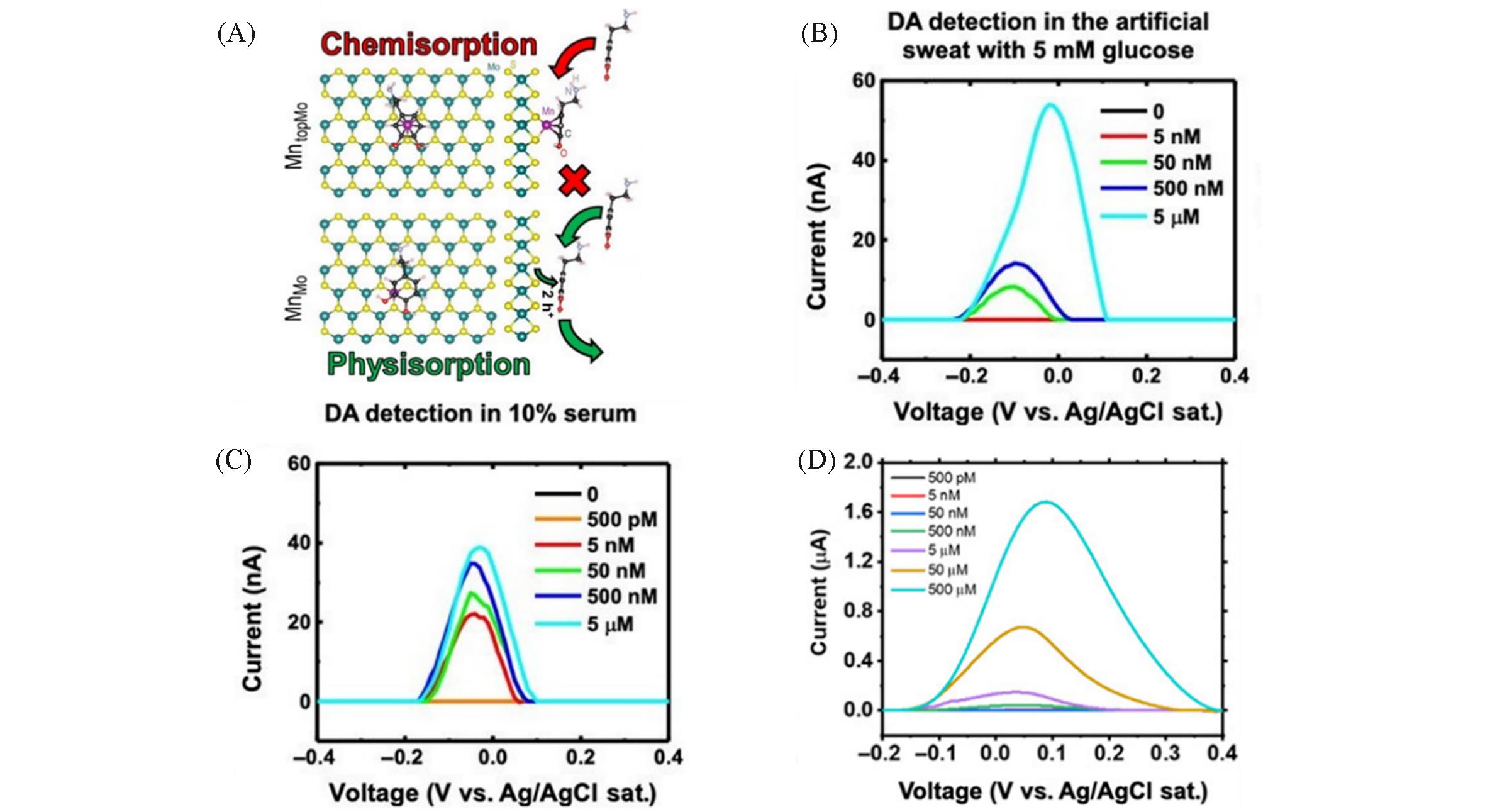
Fig.6 Top and side views of DA interacting with MntopMo(neutral defect) forming a chemical bond and DA adsorbed(physisorbed) on MnMo(A), the detection of 500 nmol/L DA in artificial sweat containing 5000 nmol/L glucose(B), 10% serum in PBS using Pt CE and Ag/AgCl RE(C) and PBS(D) [ 45](B, C) The Mn-MoS2/PGS sensor is able to detect 50 nmol/L DA in artificial sweat with 5000 nmol/L glucose and 5 nmol/L DA in 10% serum. (A—D) Copyright 2020, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
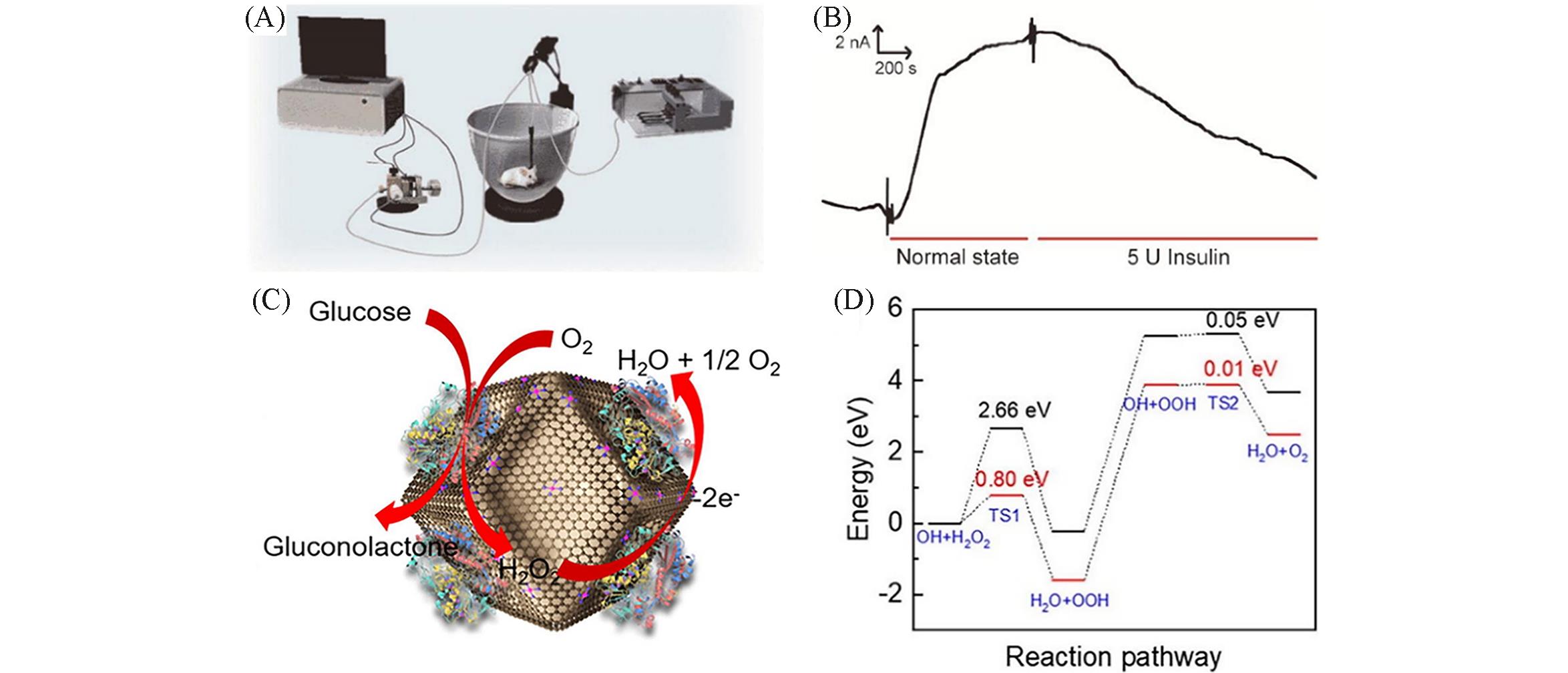
Fig.7 Schematic of online electrochemical system(OECS) with the GO x /Co?SAM?based biosensor for continuous monitoring of glucose in the brain of rats(A), typical amperometric responses of the OECS toward the microdialysate sampled from rat striatum under normal state and after intraperitoneal injection of 5 U insulin(B) [ 46], the oxidation of glucose at the concave?shaped Co SAM & GO x modified gate electrode(C), free energy diagrams for H2O2 oxidation reaction on concave?shaped Co SAM(red line) and pyrolyzed ZIF?8(black line)(D) [ 47](B) The biosensor was polarized at 0.20 V. Flow rate: 3 μL/min(coloronline). (A, B) Copyright 2019, Springer Nature; (C, D) Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
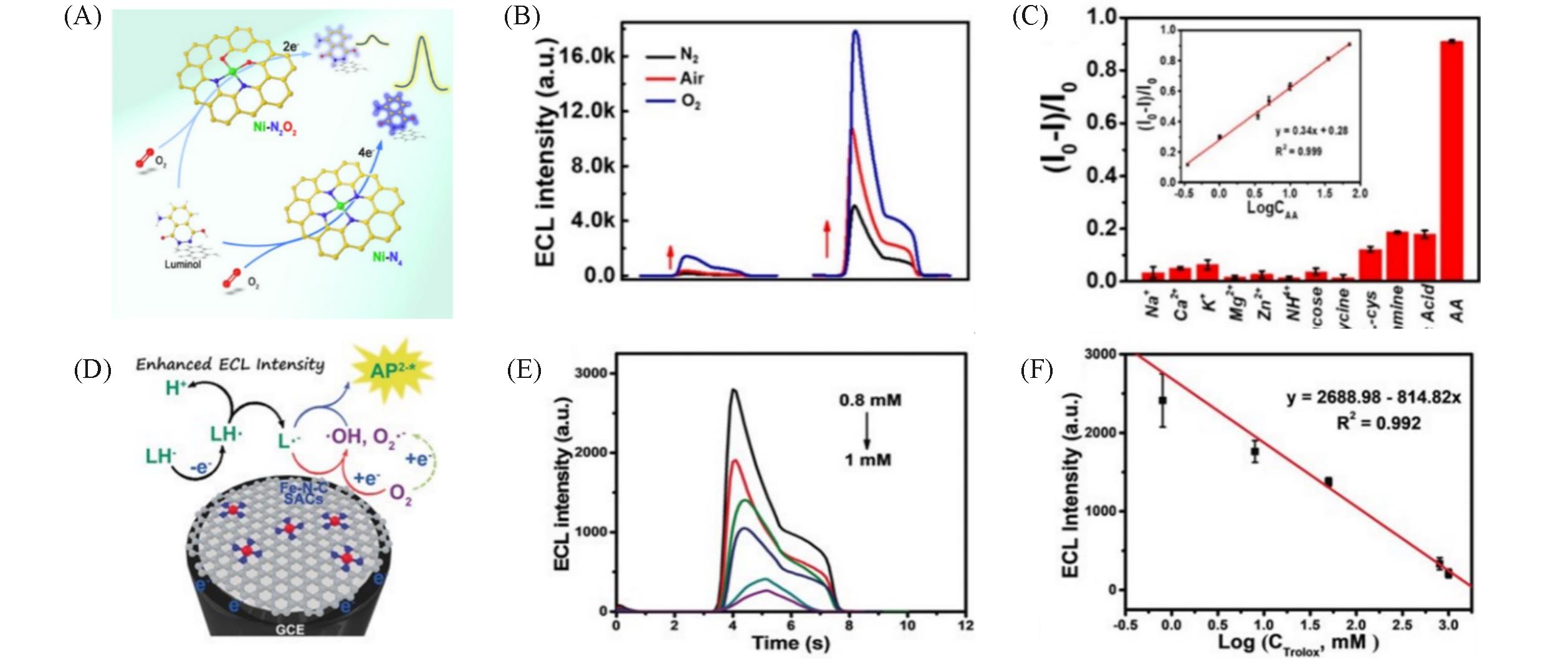
Fig.8 Two carbon?supported nickel SAM with the active centers of Ni?N4(Ni?N4/C) and Ni?N2O2(Ni?N2O2/C)(A), ECL intensity of the modified GCE with C, C?N, Ni?N4/C, and Ni?N2O2/C(B), selectivity of the developed Ni SAM luminol ECL sensor(inset: linear relationship between AA concentration and ECL intensity)(C) [ 48], the mechanism of luminol?O2 ECL systems with Fe?N?C SAM as coreactant accelerator(D), the varied ECL signal with Trolox concentration in the range of 800—10 6 nmol/L(E), the linear relationship between the Trolox concentration and ECL peak intensity(F) [ 49](A—C) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (D—F) Copyright 2020, Wiley ?VCH.
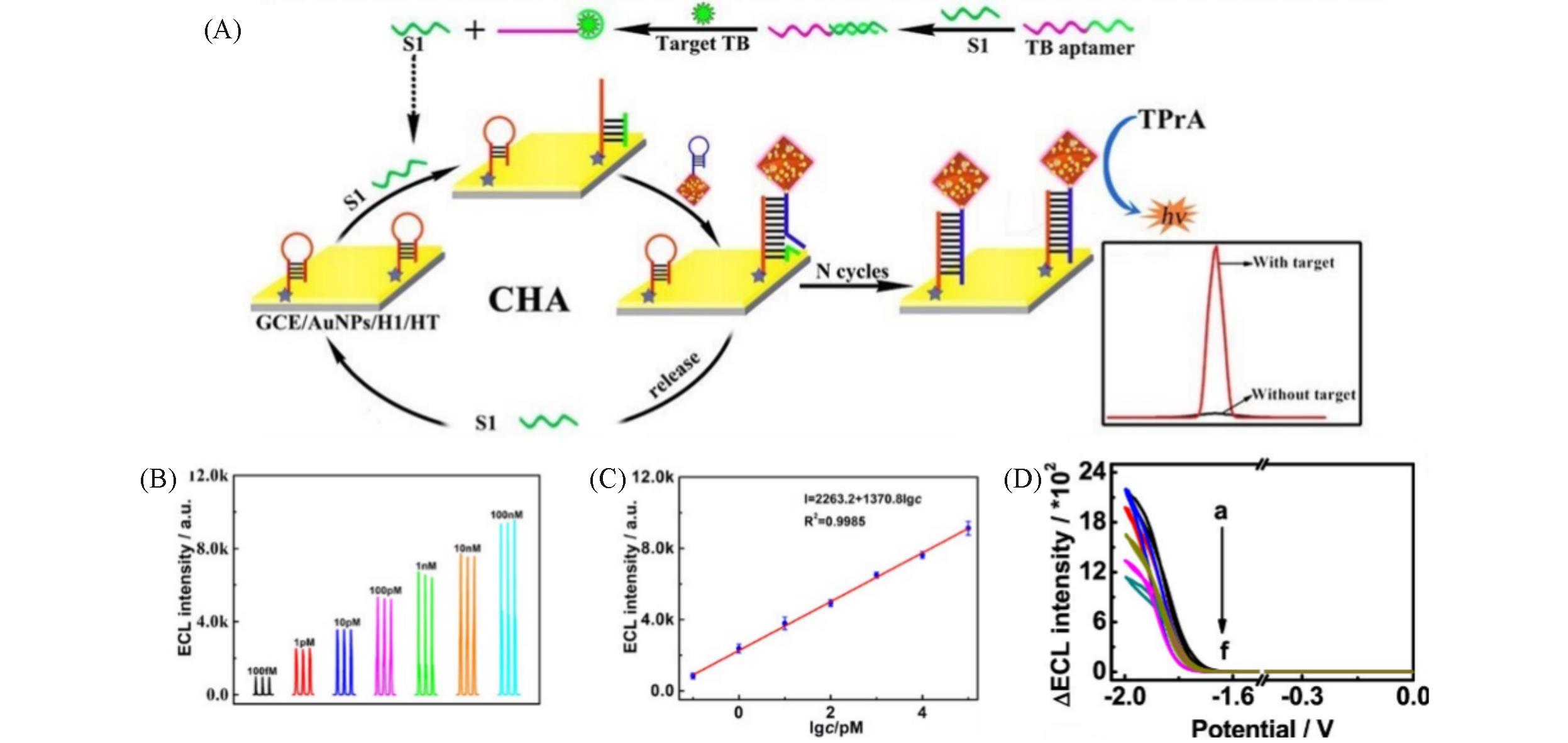
Fig.9 Diagram for construction of the HH?Ru?UiO?66?NH2 ECL aptasensor(A), ECL responses of different TB concentrations(B), calibrating plot for TB detection(C) [ 50], the ECL signals toward different TB concentrations of 10 -7—0.001 nmol/L(D) [ 51](A—C) Copyright 2021, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
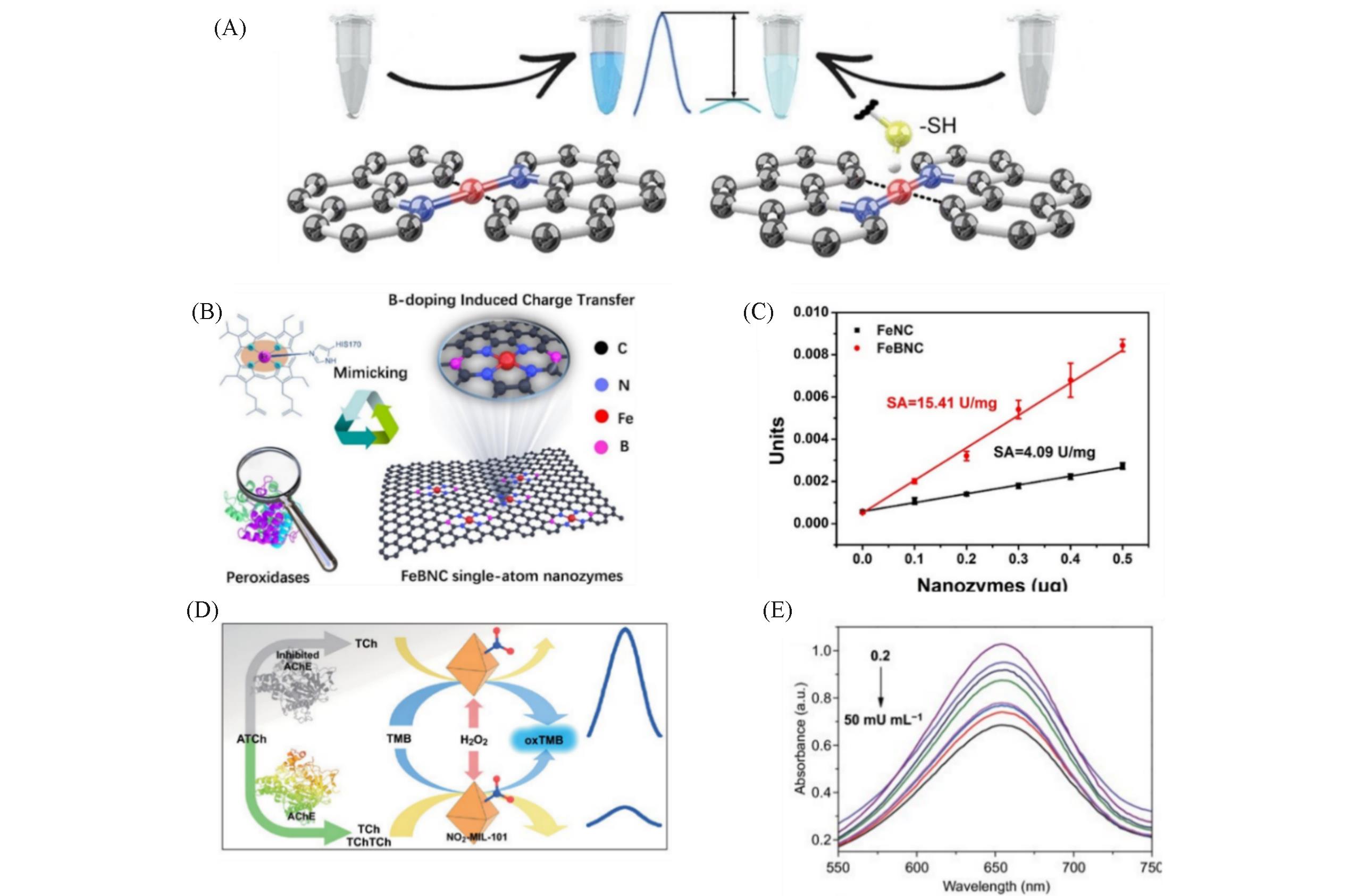
Fig.10 Schematic illustration of the inhibition of the oxidase?like activity of Fe?N?C SAzymes by mercapto molecules(A) [ 75], FeBNC SAzymes with similar single metal atom?based sites(B), the specific activities(U/mg) of FeBNC SAzymes and Fe NC SAzymes(C) [ 78], schematic illustration of detecting AChE activity using a NO2?MIL?101?based biosensor(D), absorption spectra of NO2?MIL?101?based biosensor in the presence of different AChE concentrations(E) [ 52](A) Copyright 2019, Wiley ?VCH; (B, C) Copyright 2020, Elsevier; (D, E) Copyright 2020, Springer Nature.
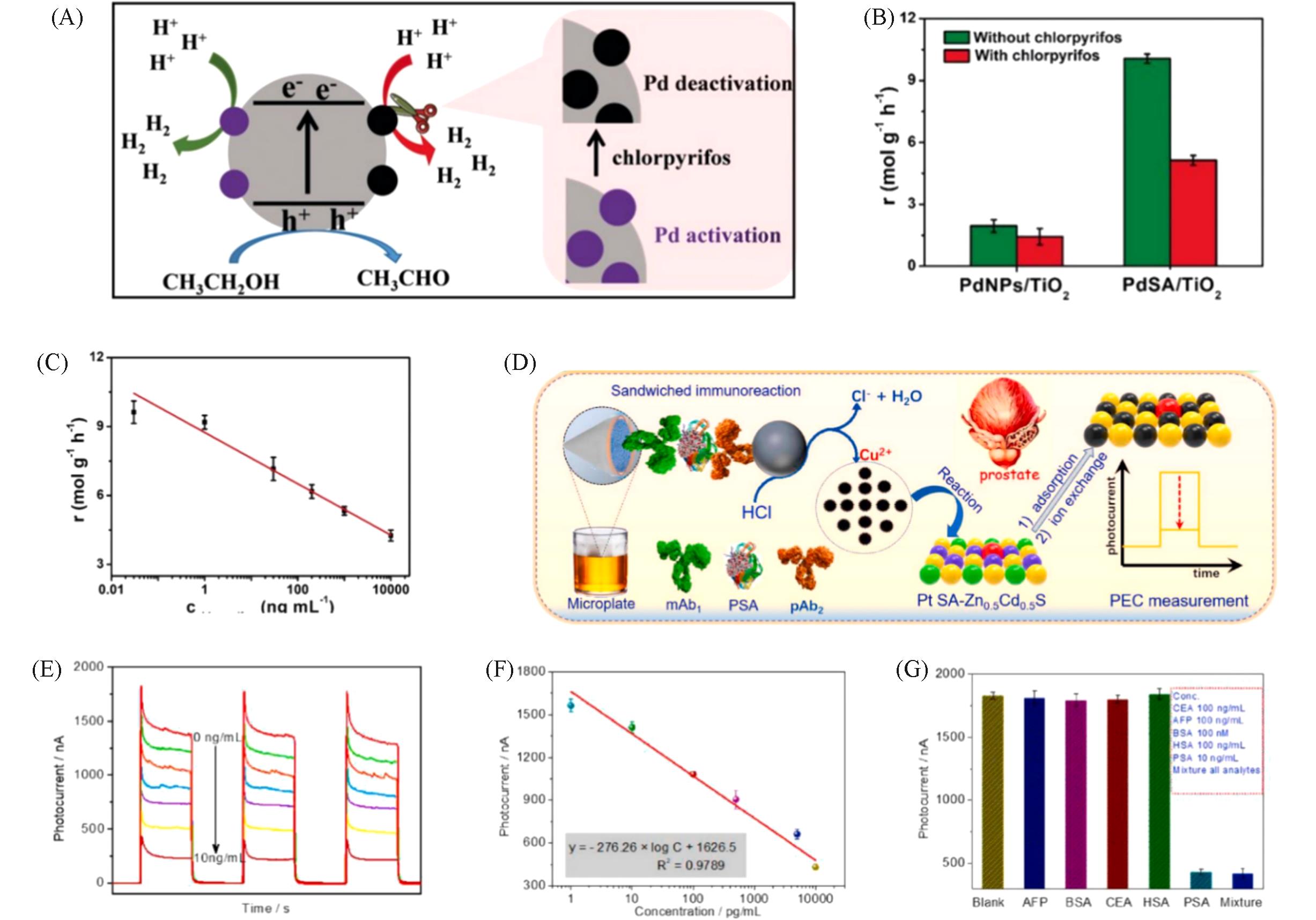
Fig.11 Principle of the PdSA/TiO2?based sensing platformutilizing photocatalytic H2 production(A), the inhibition behavior of chlorpyrifos on the photocatalytic HER performance of both PdSA/TiO2 and PdNPs/TiO2(B), the typically photocatalytic response of PdSA/TiO2 toward different concentrations(0.03 ng/mL, 1 ng/mL, 30 ng/mL, 200 ng/mL, 1 mg/mL) of chlorpyrifos, 10 mg/mL(C) [ 53], ion?exchange reaction between single?atom platinum?anchored Zn0.5Cd0.5S and the released copper ion(Cu 2+) from CuO nano label(D), photocurrents of Pt SA?Zn0.5Cd0.5S?based photoelectrochemical immunoassay toward different PSA standards(0, 1, 10, 100, 500, 5000, and 10000 pg/mL)(E), calibration curve of Pt SA?Zn0.5Cd0.5S?based photoelectrochemical(PEC) immunoassay(F), specificity of Pt SA?Zn0.5Cd0.5S?based photoelectrochemical immunoassay(G) [ 54](D) mAb1: Mouse monoclonal anti?human PSA antibody; pAb2: rabbit polyclonal anti?human PSA antibody;
| 1 | Paganelli A. I., Mondéjar A. G., Silva A. C. D., Silva⁃Calpa G., Teixeira M. F., Carvalho F., Raposo A., Endler M., J. Biomed. Inf., 2022, 127, 104009 |
| 2 | Miriam M., Blish C. A., Sallusto F., Iwasaki A., Science, 2022, 375(6585), 1122—1127 |
| 3 | Chan M., Nat. Med., 2021, 27(3), 363 |
| 4 | Wagner C. E., Saad⁃Roy C. M., Grenfell B. T., Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2022, 22(3), 139—141 |
| 5 | Verhoeven P. O., Grattard F., Carricajo A., Lucht F., Cazorla C., Garraud O., Pozzetto B., Berthelot P., J. Clin. Microbiol., 2012, 50(6), 2063—2065 |
| 6 | Wu Z., Guo W. J., Bai Y. Y., Zhang L., Hu J., Pang D. W., Zhang Z. L., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(3), 1683—1690 |
| 7 | Kelley S. O., ACS Sens., 2017, 2(2), 193—197 |
| 8 | Huff H. V., Clin. Infect. Dis., 2021, 73(9), e3053—e3054 |
| 9 | Inal S., Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2022, 6(3), 223—224 |
| 10 | Haas P., Then P., Wild A., Grange W., Zorman S., Hegner M., Calame M., Aebi U., Flammer J., Hecht B., Anal. Chem., 2010, 82(14), 6299—6302 |
| 11 | Xu J., Chau Y., Lee Y. K., Micromachines, 2019, 10(12), 855 |
| 12 | Riaz M. A., Chen Y., Nanoscale Horiz., 2022, 7, 463—479 |
| 13 | Yakoh A., Pimpitak U., Rengpipat S., Hirankarn N., Chailapakul O., Chaiyo S., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2021, 176, 112912 |
| 14 | Dincer C., Bruch R., Kling A., Dittrich P. S., Trends Biotechnol., 2017, 35(8), 728—742 |
| 15 | Jiang J., Xia J., Zang Y., Diao G., Sensors, 2021, 21(22), 7742 |
| 16 | Bueno P. R., Davis J. J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(21), 7505—7515 |
| 17 | Lei S., Xu L., Liu Z., Zou L., Li G., Ye B., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2019, 1081, 59—64 |
| 18 | Jiao L., Yan H., Wu Y., Gu W., Zhu C., Du D., Lin Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2020, 59(7), 2565—2576 |
| 19 | Qiao B., Wang A., Yang X., Allard L. F., Jiang Z., Cui Y., Liu J., Li J., Zhang T., Nat. Chem., 2011, 3(8), 634—641 |
| 20 | Zang W., Kou Z., Pennycook S. J., Wang J., Adv. Energy Mater., 2020, 10(9), 1903181 |
| 21 | Li P., Jin Z., Qian Y., Fang Z., Xiao D., Yu G., Mater. Today, 2020, 35, 78—86 |
| 22 | Lu B., Liu Q., Chen S., ACS Catal., 2020, 10(14), 7584—7618 |
| 23 | Echarri A. R., Cox J. D., Abajo J. G. D., Optica, 2019, 6(5), 630—641 |
| 24 | Li L., Chang X., Lin X., Zhao Z. J., Gong J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2020, 49(22), 8156—8178 |
| 25 | Gawande M. B., Ariga K., Yamauchi A. Y., Small, 2017, 17, 2101584 |
| 26 | Jiao L., Xu W., Wu Y., Yan H., Gu W., Du D., Lin Y., Zhu C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2021, 50(2), 750—765 |
| 27 | Yang S., Tak Y. J., Kim J., Soon A., Lee H., ACS Catal., 2017, 7(2), 1301—1307 |
| 28 | Yin P., Yao T., Wu Y., Zheng L., Lin Y., Liu W., Ju H., Zhu J., Hong X., Deng Z., Zhou G., Wei S., Li Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2016, 55(36), 10800—10805 |
| 29 | Li J., Chen M., Cullen D. A., Hwang S., Wang M., Li B., Liu K., Karakalos S., Lucero M., Zhang H., Lei C., Xu H., Sterbinsky G. E., Feng Z., Su D., More K. L., Wang G., Wang Z., Wu G., Nat. Catal., 2018, 1(12), 935—945 |
| 30 | Yang H., Shang L., Zhang Q., Shi R., Waterhouse G. I. N., Gu L., Zhang T., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 4585 |
| 31 | Li S., Chen B., Wang Y., Ye M. Y., Aken P. A. V., Cheng C., Thomas A., Nat. Mater., 2021, 20(9), 1240—1247 |
| 32 | Ahonen M., Pessa M., Suntola T., Thin Solid Films, 1980, 65(3), 301—307 |
| 33 | Fonseca J., Lu J., ACS Catal., 2021, 11(12), 7018—7059 |
| 34 | Yan H., Lin Y., Wu H., Zhang W., Sun Z., Cheng H., Liu W., Wang C., Li J., Huang X., Yao T., Yang J., Wei S., Lu J., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 1070 |
| 35 | Zhang L., Si R., Liu H., Chen N., Wang Q., Adair K., Wang Z., Chen J., Song Z., Li J., Banis M. N., Li R., Sham T. K., Gu M., Liu L. M., Botton G. A., Sun X., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 4936 |
| 36 | Xu D., Wang S., Wu B., Zhang B., Qin Y., Huo C., Huang L., Wen X., Yang Y., Li Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11(33), 29858—29867 |
| 37 | Chen C. H., Wu D., Li Z., Zhang R., Kuai C. G., Zhao X. R., Dong C. K., Qiao S. Z., Liu H., Du X. W., Adv. Energy Mater., 2019, 9(20), 1803913 |
| 38 | Fortea⁃Pérez F. R., Mon M., Ferrando⁃Soria J., Boronat M., Leyva⁃Pérez A., Corma A., Herrera J. M., Osadchii D., Gascon J., Armentano D., Pardo E., Nat. Mater., 2017, 16(7), 760—766 |
| 39 | Mon M., Rivero⁃Crespo M. A., Ferrando⁃Soria J., Vidal⁃Moya A., Boronat M., Leyva⁃Pérez A., Corma A., Hernández⁃Garrido J. C., López⁃Haro M., Calvino J. J., Ragazzon G., Credi A., Armentano D., Pardo E., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(21), 6186—6191 |
| 40 | Zhou H., Zhao Y., Gan J., Xu J., Wang Y., Lv H., Fang S., Wang Z., Deng Z., Wang X., Liu P., Guo W., Mao B., Wang H., Yao T., Hong X., Wei S., Duan X., Luo J., Wu Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2020, 142(29), 12643—12650 |
| 41 | Xiao K., Lin R. T., Wei J. X., Li N., Li H., Ma T., Liu Z. Q., Nano Res., 2022, 15(6), 4980—4985 |
| 42 | Xia B., Zhang Y., Ran J., Jaroniec M., Qiao S. Z., ACS Cent. Sci., 2021, 7(1), 39—54 |
| 43 | Xie X., Wang D. P., Guo C., Liu Y., Rao Q., Lou F., Li Q., Dong Y., Li Q., Yang H. B., Hu F. X., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(11), 4916—4923 |
| 44 | Bushira F. A., Kitte S. A., Li H., Zheng L., Wang P., Jin Y., J. Electroanal. Chem., 2022, 904, 115956 |
| 45 | Lei Y., Butler D., Lucking M. C., Zhang F., Xia T., Fujisawa K., Granzier⁃Nakajima T., Cruz⁃Silva R., Endo M., Terrones H., Terrones M., Ebrahimi A., Sci. Adv., 2020, 6(32), eabc4250 |
| 46 | Hou H., Mao J., Han Y., Wu F., Zhang M., Wang D., Mao L., Li Y., Sci. China: Chem., 2019, 62(12), 1720—1724 |
| 47 | Xiong C., Tian L., Xiao C., Xue Z., Zhou F., Zhou H., Zhao Y., Chen M., Wang Q., Qu Y., Hu Y., Wang W., Zhang Y., Zhou X., Wang Z., Yin P., Mao Y., Yu Z. Q., Cao Y., Duan X., Zheng L., Wu Y., Sci. Bull., 2020, 65(24), 2100—2106 |
| 48 | Gu W., Wang X., Wen J., Cao S., Jiao L., Wu Y., Wei X., Zheng L., Hu L., Zhang L., Zhu C., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(24), 8663—8670 |
| 49 | Gu W., Wang H., Jiao L., Chen Y., Hu L., Gong J., Du D., Zhu C., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 132, 3562—3566 |
| 50 | Huang W., Hu G. B., Liang W. B., Wang J. M., Lu M. L., Yuan R., Xiao D. R., Anal. Chem., 2021, 93(15), 6239—6245 |
| 51 | Fang Y., Wang H. M., Gu Y. X., Yu L., Wang A. J., Yuan P. X., Feng J. J., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(4), 3206—3212 |
| 52 | Xu W., Kang Y., Jiao L., Wu Y., Yan H., Li J., Gu W., Song W., Zhu C., Nano⁃Micro Lett., 2020, 12(1), 184 |
| 53 | Ge X., Zhou P., Zhang Q., Xia Z., Chen S., Gao P., Zhang Z., Gu L., Guo S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(1), 232—236 |
| 54 | Li B., Guo L., Chen M., Guo Y., Ge L., Kwok H. F., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2022, 202, 114006 |
| 55 | Jiang S., Zhang C., Zou T., Nanomaterials, 2020, 10(12), 2518 |
| 56 | Wu J., Wu Y., Lu L., Zhang D., Wang X., Talanta, 2021, 4, 100075 |
| 57 | Wang Y., Liu Y., Liu W., Wu J., Li Q., Feng Q., Chen Z., Xiong X., Wang D., Lei Y., Energy Environ. Sci., 2020, 13(12), 4609—4624 |
| 58 | Cui T., Wang Y. P., Ye T., Wu J., Chen Z., Li J., Lei Y., Wang D., Li Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2022, 61(12), e202115219 |
| 59 | Bakirhan N. K., Topal B. D., Ozcelikay G., Karadurmus L., Ozkan S. A., Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem., 2022, 52(3), 519—534 |
| 60 | Zhu C., Yang G., Li H., Du D., Lin Y., Anal. Chem., 2015, 87(1), 230—249 |
| 61 | Tiwari J. N., Vij V., Kemp K. C., Kim K. S., ACS Nano, 2016, 10(1), 46—80 |
| 62 | Zhou W. Y., Li S. S., Xiao X. Y., Chen S. H., Liu J. H., Huang X. J., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54(67), 9329—9332 |
| 63 | Zhuo Y., Wang H. J., Lei Y. M., Zhang P., Liu J. L., Chai Y. Q., Yuan R., Analyst, 2018, 143(14), 3230—3248 |
| 64 | Jin H., Ye D., Shen L., Fu R., Tang Y., Jung J. C., Zhao H., Zhang J., Anal. Chem., 2022, 94(3), 1499—1509 |
| 65 | Wang Y., Tang Y. J., Zhou K., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(36), 14115—14119 |
| 66 | Yebra⁃Biurrun M. C., Talanta, 2000, 52, 367—383 |
| 67 | Hu G. B., Xiong C. Y., Liang W. B., Zeng X. S., Xu H. L., Yang Y., Yao L. Y., Yuan R., Xiao D. R., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(18), 15913—15919 |
| 68 | Chen R., Zhang J., Chelora J., Xiong Y., Kershaw S. V., Li K. F., Lo P. K., Cheah K. W., Rogach A. L., Zapien J. A., Lee C. S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(7), 5699—5708 |
| 69 | Yin H. Q., Yang J. C., Yin X. B., Anal. Chem., 2017, 89(24), 13434—13440 |
| 70 | Wu Y., Wu J., Jiao L., Xu W., Wang H., Wei X., Gu W., Ren G., Zhang N., Zhang Q., Huang L., Gu L., Zhu C., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(4), 3373—3379 |
| 71 | Wang Y., Qi K., Yu S., Jia G., Cheng Z., Zheng L., Wu Q., Bao Q., Wang Q., Zhao J., Cui X., Zheng W., Nano⁃Micro Lett., 2019, 11(1), 102 |
| 72 | Chen M., Zhou H., Liu X., Yuan T., Wang W., Zhao C., Zhao Y., Zhou F., Wang X., Xue Z., Yao T., Xiong C., Wu Y., Small, 2020, 16(31), e2002343 |
| 73 | Zhang X., Li G., Chen G., Wu D., Zhou X., Wu Y., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2020, 418, 213376 |
| 74 | Huang L., Chen J., Gan L., Wang J., Dong S., Sci. Adv., 2019, 5(5), eaav549 |
| 75 | Wu Y., Jiao L., Luo X., Xu W., Wei X., Wang H., Yan H., Gu W., Xu B. Z., Du D., Lin Y., Zhu C., Small, 2019, 15(43), e1903108 |
| 76 | Huo M., Wang L., Wang Y., Chen Y., Shi J., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(2), 2643—2653 |
| 77 | Zhao C., Xiong C., Liu X., Qiao M., Li Z., Yuan T., Wang J., Qu Y., Wang X., Zhou F., Xu Q., Wang S., Chen M., Wang W., Li Y., Yao T., Wu Y., Li Y., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55(16), 2285—2288 |
| 78 | Jiao L., Xu W., Zhang Y., Wu Y., Gu W., Ge X., Chen B., Zhu C., Guo S., Nano Today, 2020, 35, 100971 |
| 79 | Zhao W. W., Xu J. J., Chen H. Y., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(1), 615—627 |
| 80 | Qiu Z., Tang D., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2020, 8(13), 2541—2561 |
| 81 | Kaiser S. K., Chen Z., Akl D. F., Mitchell S., Pérez⁃Ramirez J., Chem. Rev., 2020, 120(21), 11703—11809 |
| 82 | Shu J., Tang D., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(1), 363—377 |
| 83 | Zhao C. Q., Ding S. N., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2019, 391, 1—14 |
| [1] | 沙蒙, 许维庆, 吴志超, 顾文玲, 朱成周. 单原子材料类酶催化及生物医学应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220077. |
| [2] | 王春燕,蒋晓青,周泊. 基于Cu-TPA的电化学生物传感器对黄曲霉毒素B1的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(11): 2301. |
| [3] | 刘仁植, 李晓严. MoS2中空纳米球的制备及在超灵敏microRNA电化学生物传感器中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(3): 383. |
| [4] | 王青, 刘卫, 羊小海, 王柯敏, 刘沛, 何磊良. 纳米金颗粒增强信号的电化学生物传感器用于谷胱甘肽和半胱氨酸的检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(8): 1845. |
| [5] | 封科军, 姚艳玲, 沈国励, 俞汝勤. 基于单壁碳纳米管-DNA酶复合结构的电化学生物传感器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(08): 1676. |
| [6] | 郑静,冯婉娟,程圭芳,黄翠华,林莉,何品刚,方禹之 . 利用互补核酸杂交富集金胶实现信号扩增的电化学凝血酶蛋白生物传感器研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(12): 2274. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||