

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (8): 20220136.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220136
翁美琪1, 商桂铭1, 王家泰1, 李盛华1, 樊志1, 林松2, 郭敏杰1( )
)
收稿日期:2022-03-03
出版日期:2022-08-10
发布日期:2022-04-15
通讯作者:
郭敏杰
E-mail:guomj@tust.edu.cn
基金资助:
WENG Meiqi1, SHANG Guiming1, WANG Jiatai1, LI Shenghua1, FAN Zhi1, LIN Song2, GUO Minjie1( )
)
Received:2022-03-03
Online:2022-08-10
Published:2022-04-15
Contact:
GUO Minjie
E-mail:guomj@tust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用DFT/B3LYP-D3(BJ)/6-31G(d,p)计算模拟方法分析探讨了双(对硝基苯基)磷酸酯(BNPP)替代对氧磷(PO)用作有机磷神经毒剂分子印迹聚合物(MIPs)模板分子模拟物的可行性. 通过对比BNPP和PO两种模板分子分别与各种功能单体形成的复合物的构型稳定性和结合能大小, 确认了以4-甲基丙烯酰胺基安替比林(MAAP)为第一功能单体、 甲基丙烯酸(MAA)为第二功能单体组成的双功能单体体系是最佳功能单体体系. 以BNPP为模板分子、 MAAP-MAA为单体体系、 乙二醇二甲基丙烯酸酯(EGDMA)为交联剂、 纳米二氧化硅为载体, 采用表面印迹技术制备了SiO2@BNPP分子印迹聚合物, 并对聚合物的表面形貌和吸附性能进行了分析. 实验结果表明, 当n(BNPP)/n(MAAP)/n(MAA)/n(EGDMA)为1∶1∶4∶20时, MIPs的吸附容量最大可达19.03 mg/g, 对4-硝基苯酚(4-NP)的分离因子为17.50; MIPs能够快速吸附模板分子, 5 min即可达到吸附平衡量的92%, 动态吸附平衡时间仅为15 min, 重复使用5次后仍能保持良好的吸附能力; 吸附过程符合准二级动力学模型和Langmuir等温吸附模型, Scatchard方程分析表明MIPs中存在两类吸附作用位点. 实验结果与计算模拟结果的一致性表明, 计算模拟对有机磷神经毒剂MIPs的设计和研究具有一定的指导意义.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
翁美琪, 商桂铭, 王家泰, 李盛华, 樊志, 林松, 郭敏杰. 有机磷神经毒剂分子印迹聚合物的模拟模板分子. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220136.
WENG Meiqi, SHANG Guiming, WANG Jiatai, LI Shenghua, FAN Zhi, LIN Song, GUO Minjie. Template Simulation of Organophosphorus Nerve Agent Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220136.
| MIPs | n(BNPP)/n(MAAP)/n(MAA) | n(BNPP)/n(EGDMA) | n(BNPP)/n(AIBN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP1 | 1∶1∶2 | 1∶12 | 1∶0.37 |
| MIP2 | 1∶1∶3 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
| MIP3 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶20 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP4 | 1∶1∶5 | 1∶24 | 1∶0.73 |
| MIP5 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶15 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP6 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶25 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP7 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶30 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP8 | 1∶4∶0 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
| MIP9 | 1∶0∶4 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
Table 1 Synthetic conditions of different MIPs
| MIPs | n(BNPP)/n(MAAP)/n(MAA) | n(BNPP)/n(EGDMA) | n(BNPP)/n(AIBN) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP1 | 1∶1∶2 | 1∶12 | 1∶0.37 |
| MIP2 | 1∶1∶3 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
| MIP3 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶20 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP4 | 1∶1∶5 | 1∶24 | 1∶0.73 |
| MIP5 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶15 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP6 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶25 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP7 | 1∶1∶4 | 1∶30 | 1∶0.61 |
| MIP8 | 1∶4∶0 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
| MIP9 | 1∶0∶4 | 1∶16 | 1∶0.49 |
| Complex | ΔEa / (kJ?mol-1) | ΔGb / (kJ?mol-1) | Bond length/nm | H?bond number | Complex | ΔEa / (kJ?mol-1) | ΔGb / (kJ?mol-1) | Bond length/nm | H?bond number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNPP?MAAP | -79.941 | -25.911 | 0.191/0.147 | 2 | PO?MAAP | -20.208 | 22.881 | 0.193 | 1 |
| BNPP?AM | -76.591 | -29.022 | 0.186/0.133 | 2 | PO?AM | -10.780 | 20.277 | 0.196 | 1 |
| BNPP?4?VP | -85.940 | -40.976 | 0.157 | 1 | PO?4?VP | -3.544 | 31.511 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?MAA | -72.543 | -26.357 | 0.163/0.150 | 2 | PO?MAA | -33.160 | 3.909 | 0.169 | 1 |
| BNPP?IA | -71.175 | -18.397 | 0.163/0.151 | 2 | PO?IA | -31.425 | 9.254 | 0.170 | 1 |
| BNPP?4?VINA | -72.188 | -21.671 | 0.163/0.150 | 2 | PO?4?VINA | -30.298 | 9.221 | 0.168 | 1 |
| BNPP?MMA | -37.487 | 13.983 | 0.160 | 1 | PO?MMA | -3.589 | 26.772 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?APTES | -5.899 | 44.983 | — | 0 | PO?APTES | -7.525 | 21.456 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?SM | -2.200 | 41.110 | — | 0 | PO?SM | -2.912 | 28.361 | — | 0 |
Table 2 Relevant parameters of binding energy(ΔE) between templates and functional monomers in the most stable complex*
| Complex | ΔEa / (kJ?mol-1) | ΔGb / (kJ?mol-1) | Bond length/nm | H?bond number | Complex | ΔEa / (kJ?mol-1) | ΔGb / (kJ?mol-1) | Bond length/nm | H?bond number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BNPP?MAAP | -79.941 | -25.911 | 0.191/0.147 | 2 | PO?MAAP | -20.208 | 22.881 | 0.193 | 1 |
| BNPP?AM | -76.591 | -29.022 | 0.186/0.133 | 2 | PO?AM | -10.780 | 20.277 | 0.196 | 1 |
| BNPP?4?VP | -85.940 | -40.976 | 0.157 | 1 | PO?4?VP | -3.544 | 31.511 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?MAA | -72.543 | -26.357 | 0.163/0.150 | 2 | PO?MAA | -33.160 | 3.909 | 0.169 | 1 |
| BNPP?IA | -71.175 | -18.397 | 0.163/0.151 | 2 | PO?IA | -31.425 | 9.254 | 0.170 | 1 |
| BNPP?4?VINA | -72.188 | -21.671 | 0.163/0.150 | 2 | PO?4?VINA | -30.298 | 9.221 | 0.168 | 1 |
| BNPP?MMA | -37.487 | 13.983 | 0.160 | 1 | PO?MMA | -3.589 | 26.772 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?APTES | -5.899 | 44.983 | — | 0 | PO?APTES | -7.525 | 21.456 | — | 0 |
| BNPP?SM | -2.200 | 41.110 | — | 0 | PO?SM | -2.912 | 28.361 | — | 0 |
| Complex | H?bond number | Bond length/nm | ΔE/ (kJ?mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ?mol-1) | Complex | H?bond number | Bond length /nm | ΔE/ (kJ?mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ?mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BNPP?MAAP?AM?a | 3 | 0.189 0.147 0.194 | -92.948 | 7.428 | PO?MAAP?AM?a | 2 | 0.188 0.197 | -35.035 | 48.451 |
BNPP?MAAP?AM?b | 3 | 0.178 0.146 0.178 | -101.696 | -0.4 | PO?MAAP?AM?b | 2 | 0.194 0.194 | -36.093 | 51.124 |
| PO?MAAP?AM?c | 2 | 0.193 0.191 | -28.862 | 62.757 | |||||
| PO?MAAP?AM?d | 2 | 0.195 0.198 | -33.155 | 56.850 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?a | 2 | 0.164 0.145 | -98.498 | -6.280 | PO?MAAP?AM?e | 2 | 0.198 0.189 | -35.520 | 48.931 |
| PO?MAAP?MAA?a | 2 | 0.165 0.189 | -55.422 | 31.178 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?b | 2 | 0.169 0.145 | -86.754 | 9.840 | PO?MAAP?MAA?b | 2 | 0.167 0.202 | -41.352 | 48.404 |
| PO?MAAP?MAA?c | 2 | 0.190 0.160 | -56.750 | 31.582 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?c | 3 | 0.187 0.146 0.170 | -111.492 | -9.407 | PO?MAAP?MAA?d | 2 | 0.197 0.163 | -54.177 | 29.495 |
| BNPP?MAAP?4?VP?a | 2 | 0.195 0.148 | -87.403 | 6.474 | PO?MAAP?4?VP?a | 1 | 0.194 | -23.362 | 57.449 |
| BNPP?MAAP?4?VP?b | 2 | 0.191 0.158 | -107.824 | 13.075 | PO?MAAP?4?VP?b | 1 | 0.192 | -29.792 | 50.234 |
Table 3 Relevant parameters of hydrogen bond and binding energy(ΔE) between templates and bifunctional monomer*
| Complex | H?bond number | Bond length/nm | ΔE/ (kJ?mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ?mol-1) | Complex | H?bond number | Bond length /nm | ΔE/ (kJ?mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ?mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
BNPP?MAAP?AM?a | 3 | 0.189 0.147 0.194 | -92.948 | 7.428 | PO?MAAP?AM?a | 2 | 0.188 0.197 | -35.035 | 48.451 |
BNPP?MAAP?AM?b | 3 | 0.178 0.146 0.178 | -101.696 | -0.4 | PO?MAAP?AM?b | 2 | 0.194 0.194 | -36.093 | 51.124 |
| PO?MAAP?AM?c | 2 | 0.193 0.191 | -28.862 | 62.757 | |||||
| PO?MAAP?AM?d | 2 | 0.195 0.198 | -33.155 | 56.850 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?a | 2 | 0.164 0.145 | -98.498 | -6.280 | PO?MAAP?AM?e | 2 | 0.198 0.189 | -35.520 | 48.931 |
| PO?MAAP?MAA?a | 2 | 0.165 0.189 | -55.422 | 31.178 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?b | 2 | 0.169 0.145 | -86.754 | 9.840 | PO?MAAP?MAA?b | 2 | 0.167 0.202 | -41.352 | 48.404 |
| PO?MAAP?MAA?c | 2 | 0.190 0.160 | -56.750 | 31.582 | |||||
BNPP?MAAP?MAA?c | 3 | 0.187 0.146 0.170 | -111.492 | -9.407 | PO?MAAP?MAA?d | 2 | 0.197 0.163 | -54.177 | 29.495 |
| BNPP?MAAP?4?VP?a | 2 | 0.195 0.148 | -87.403 | 6.474 | PO?MAAP?4?VP?a | 1 | 0.194 | -23.362 | 57.449 |
| BNPP?MAAP?4?VP?b | 2 | 0.191 0.158 | -107.824 | 13.075 | PO?MAAP?4?VP?b | 1 | 0.192 | -29.792 | 50.234 |
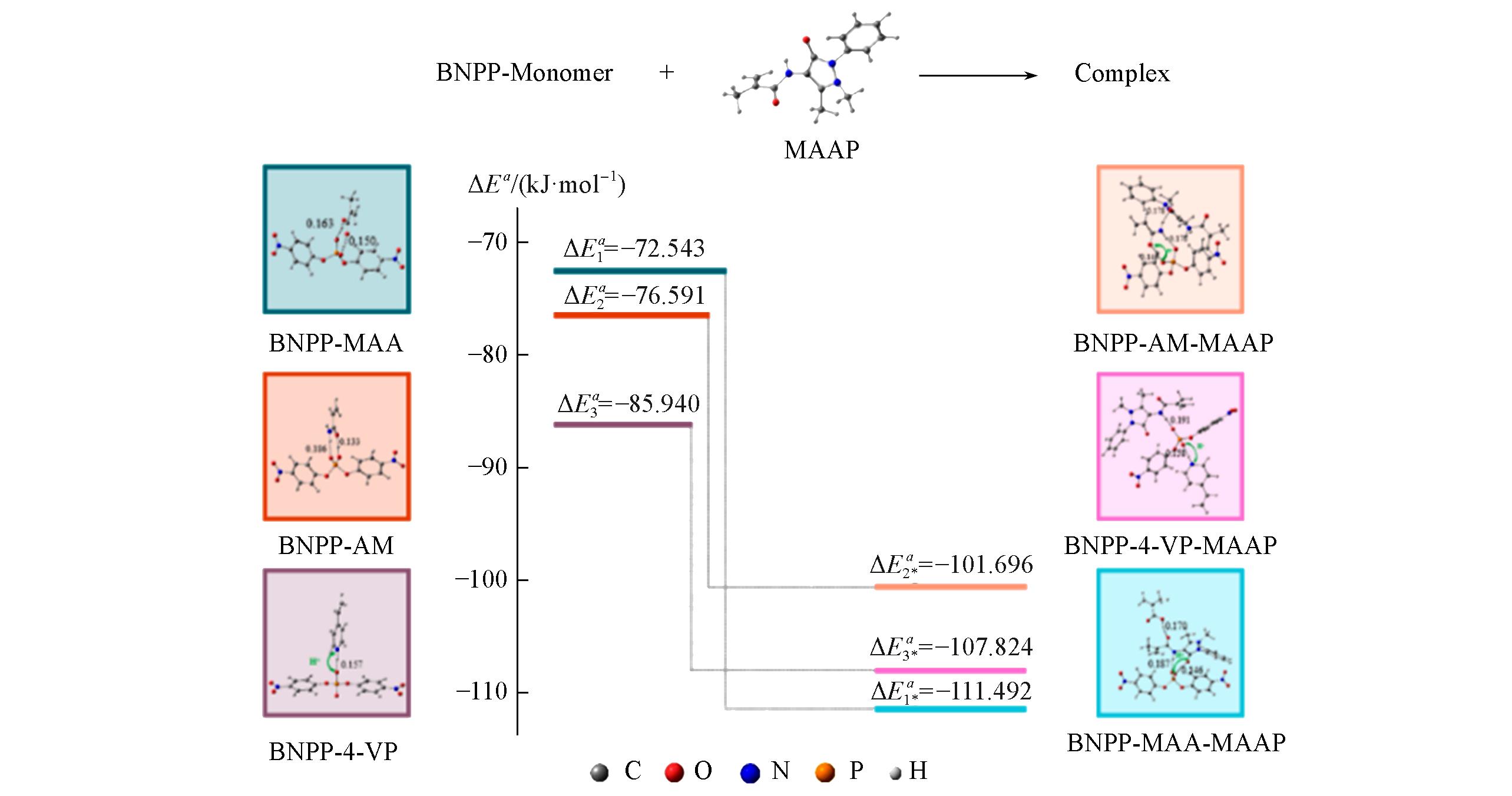
Fig.3 ΔE values for interaction complexes*ΔE1a,ΔE2a and ΔE3a are the binding energies of BNPP?MAA, BNPP?AM and BNPP?4?VP, respectively. ΔEa1 *,ΔEa2 * and ΔEa3 * are the lowest binding energies of BNPP?MAA?MAAP, BNPP?AM?MAAP and BNPP?4?VP?MAAP, respectively.
| Sample | Surface area/(m2?g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3?g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP3 | 25.995 | 0.073 | 3.826 |
| NIP3 | 6.419 | 0.028 | 3.428 |
Table 4 Specific surface area, pore size and volume of the samples
| Sample | Surface area/(m2?g-1) | Pore volume/(cm3?g-1) | Pore diameter/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP3 | 25.995 | 0.073 | 3.826 |
| NIP3 | 6.419 | 0.028 | 3.428 |
| Coating | High?affinity site | Low?affinity site | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd/(mg?mL-1) | Qmax/(mg?g-1) | Kd/(mg?mL-1) | Qmax/(mg?g-1) | |
| MIP3 | 0.036 | 12.798 | 0.218 | 26.074 |
| NIP3 | — | — | 0.146 | 13.201 |
Table 5 Affinity constant(Ka) and maximum number of binding sites(Qmax) for MIP3 and NIP3
| Coating | High?affinity site | Low?affinity site | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kd/(mg?mL-1) | Qmax/(mg?g-1) | Kd/(mg?mL-1) | Qmax/(mg?g-1) | |
| MIP3 | 0.036 | 12.798 | 0.218 | 26.074 |
| NIP3 | — | — | 0.146 | 13.201 |
| 1 | Kwantwi⁃Barima P., Ouyang H., Hogan C. J., Clowers B. H., Anal. Chem., 2017, 89(22), 12416—12424 |
| 2 | Kloske M., Witkiewicz Z., Chemosphere, 2019, 221, 672—682 |
| 3 | Zhou X. Y., Zeng C., Li Y., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016, 55(15), 4729—4733 |
| 4 | Secara C. A., Patrinchi B., Tudosie M. S., Taina F. N., Caragea G., Popescu D., Voicu V. A., Toxicol. Lett., 2016, 238(2), S262 |
| 5 | Yang Y. C., Baker J. A., Ward J. R., Chem. Rev., 1992, 92(8), 1729—1743 |
| 6 | Pan J., Liu S., Jia H., Yang J., Qin M., Zhou T., Chen Z., Jia X., Guo T., J. Catal., 2019, 380, 83—90 |
| 7 | Chen L., Wang X., Lu W., Wu X., Li J., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(8), 2137—2211 |
| 8 | Aroniadou⁃Anderjaska V., Apland J. P., Figueiredo T. H., de Araujo Furtado M., Braga M. F., Neuropharmacology, 2020, 181, 108298 |
| 9 | Uzun L., Turner A. P. F., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2016, 76, 131—144 |
| 10 | Kiran T. R., Atar N., Yola M. L., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2019, 166(12), H495—H501 |
| 11 | Meier F., Schott B., Riedel D., Mizaikoff B., Analy. Chim. Acta, 2012, 744, 68—74 |
| 12 | Canfarotta F., Poma A., Guerreiro A., Piletsky S., Nat. Protoc., 2016, 11(3), 443—455 |
| 13 | Li G. Y., Zhang K., Fizir M., Niu M. C., Sun C., Xi S. L., Hui X. H., Shi J. R., He H., New J. Chem., 2017, 41(15), 7092—7101 |
| 14 | Liang D., Wang Y., Li S., Li Y., Zhang M., Li Y., Tian W., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2016, 17(11), 1750 |
| 15 | Xu W. Z., Qiu C. X., Huang W. H., Liu H., Yang W. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7), 1155—1162 |
| 徐婉珍, 邱春孝, 黄卫红, 刘鸿, 杨文明. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(7), 1155—1162 | |
| 16 | Hassan A. H. A., Moura S. L., Ali F. H. M., Moselhy W. A., Taboada M. D. P., Pividori M. I., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 118, 181—187 |
| 17 | Barros L. A., Custodio R., Rath S., J. Brazil. Chem. Soc., 2016, 27(12), 2300—2311 |
| 18 | Angelini D. J., Moyer R. A., Cole S., Willis K. L., Oyler J., Dorsey R. M., Salem H., Int. J. Toxicol., 2015, 34(5), 433—441 |
| 19 | Lorke D. E., Nurulain S. M., Hasan M. Y., Kuca K., Petroianu G. A., J. Appl. Toxicol., 2014, 34(10), 1096—1103 |
| 20 | Xie Y., Chen J., Xu B., Yan L., Tang J. J., Xie J. W., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5), 758—763 |
| 谢琰, 陈佳, 徐斌, 闫珑, 唐吉军, 谢剑炜. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(5), 758—763 | |
| 21 | Lenina O. A., Zueva I. V., Zobov V. V., Semenov V. E., Masson P., Petrov K. A., Sci. Rep., 2020, 10(1), 16611 |
| 22 | Say R., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2006, 579(1), 74—80 |
| 23 | Ozkutuk E. B., Diltemiz S. E., Ozalp E., Uzun L., Ersoz A., Appl. Phys. A: Mater., 2015, 119(1), 351—357 |
| 24 | Wang R. Y., Pan J. P., Qin M., Guo T. Y., Eur. Polym. J., 2019, 110, 1—8 |
| 25 | Barone V., Cossi M., Tomasi J., J. Chem. Phys., 1997, 107(8), 3210—3221 |
| 26 | Pereira T. F. D., da Silva A. T. M., Borges K. B., Nascimento C. S., J. Mol. Struct., 2019, 1177, 101—106 |
| 27 | Bates F., Busato M., Piletska E., Whitcombe M. J., Karim K., Guerreiro A., del Valle M., Sep. Sci. Technol., 2017, 52(8), 1441—1453 |
| 28 | Li P., Wang W. H., Bi S. W., Song R., Bu Y. X., Sci. China Ser. B, 2008, (11), 976—980 |
| 李平, 王卫华, 毕思玮, 宋蕊, 步宇翔. 中国科学(B辑: 化学), 2008, (11), 976—980 | |
| 29 | Yi P. G., Zhang Z. Y., Tao H. W., Li Y. Y., Li Q., Peng W. Y., Li Y. R., J. At. Mol. Phy., 2020, 37(1), 25—32 |
| 易平贵, 张志于, 陶洪文, 李洋洋, 李庆, 彭文宇, 李玉茹. 原子与分子物理学报, 2020, 37(1), 25—32 | |
| 30 | De Rycke E., Trynda A., Jaworowicz M., Dubruel P., De Saeger S., Beloglazova N., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2021, 172, 112773 |
| 31 | Bai J., Zhang Y., Zhang W., Ma X., Zhu Y., Zhao X., Fu Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2020, 511, 145506 |
| 32 | Li Q., Zhao W., Guo H., Yang J., Zhang L., Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(23), 25546—25556 |
| 33 | Xie L. W., Guo J. F., Zhang Y. P., Hu Y. C., You Q. P., Shi S. Y., Food Chem., 2015, 178, 18—251 |
| [1] | 侯翠岭,朱国龙,戴晓彬,徐子阳,陈鹏宇,张轩钰,高丽娟,燕立唐. 熵驱大分子胶体粒子的柱状受限结晶[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(1): 44. |
| [2] | 王岩, 刘俊渤, 唐珊珊, 靳瑞发, 常海波. 计算机辅助三聚氰胺分子印迹聚合物的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(5): 945. |
| [3] | 于岚岚, 毛烨炫, 白希希, 冉瑜, 李爱荣, 朱艳艳, 于斐, 屈凌波. 具有双活性序列的新型抗菌肽的设计及性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(5): 1166. |
| [4] | 刘俊渤, 唐珊珊, 孙佳妮, 靳瑞发. 环丙沙星与三氟甲基丙烯酸分子印迹自组装体系的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(11): 2566. |
| [5] | 于岚岚, 冉瑜, 白希希, 李爱荣, 朱艳艳, 覃韵, 屈凌波. 新型抗菌肽的设计、活性研究及与磷脂相互作用的计算模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(12): 2681. |
| [6] | 陈超, 丁红, 李光华, 毕明辉, 伊卓, 李乙, 李守贵, 孟河, 刘丽, 庞文琴. 具有开放骨架结构氟化磷酸钛的水热合成及分子动力学辅助确定骨架中模板剂的位置[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2005, 26(7): 1189. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||