

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (11): 3493.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210458
收稿日期:2021-07-01
出版日期:2021-11-10
发布日期:2021-08-18
通讯作者:
石沐玲,刘高强
E-mail:mulingshi@hnu.edu.cn;gaoliuedu@csuft.edu.cn
基金资助:
HUANG Ling, ZHUANG Zijian, LI Xiang, SHI Muling( ), LIU Gaoqiang(
), LIU Gaoqiang( )
)
Received:2021-07-01
Online:2021-11-10
Published:2021-08-18
Contact:
SHI Muling,LIU Gaoqiang
E-mail:mulingshi@hnu.edu.cn;gaoliuedu@csuft.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
自研究者证实外泌体承担了细胞外RNA等物质的运输功能以来, 关于外泌体来源与功能的研究一直备受关注. 近年来外泌体被发现具有作为疾病生物标志物的潜力, 使得拥有特定表面蛋白以及特定装载物的外泌体成为分析化学领域有价值的检测对象. 从化学本质角度来说, 外泌体的获取与分析需要依赖特异性的分子识别过程. 核酸适体作为分子识别单元, 因其特异性强、 亲和力高、 生物活性稳定、 易于合成和保存、 而且其序列和结构上具有可编程性, 易于设计和修饰, 已成功地用在外泌体相关的生物传感体系中. 本文从外泌体的化学组成及其具有生理、 病理意义的组分出发, 从外泌体通用生物标志物识别、癌细胞来源外泌体的检测及外泌体蛋白谱的分析这3个方面综述了以核酸适体作为分子识别单元在外泌体分析领域的代表性工作, 总结了现有的靶向外泌体的核酸适体序列信息以及应用场景, 阐述了利用化学合成与修饰以及DNA自组装等化学调控手段增强核酸适体分子识别性能的最新进展, 并从适用于外泌体分子识别的核酸适体的筛选以及化学修饰的角度, 对未来的研究方向进行了展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
黄玲, 庄梓健, 李翔, 石沐玲, 刘高强. 基于核酸适体的外泌体分子识别研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3493.
HUANG Ling, ZHUANG Zijian, LI Xiang, SHI Muling, LIU Gaoqiang. Advances in Molecular Recognition of Exosomes Based on Aptamers. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3493.
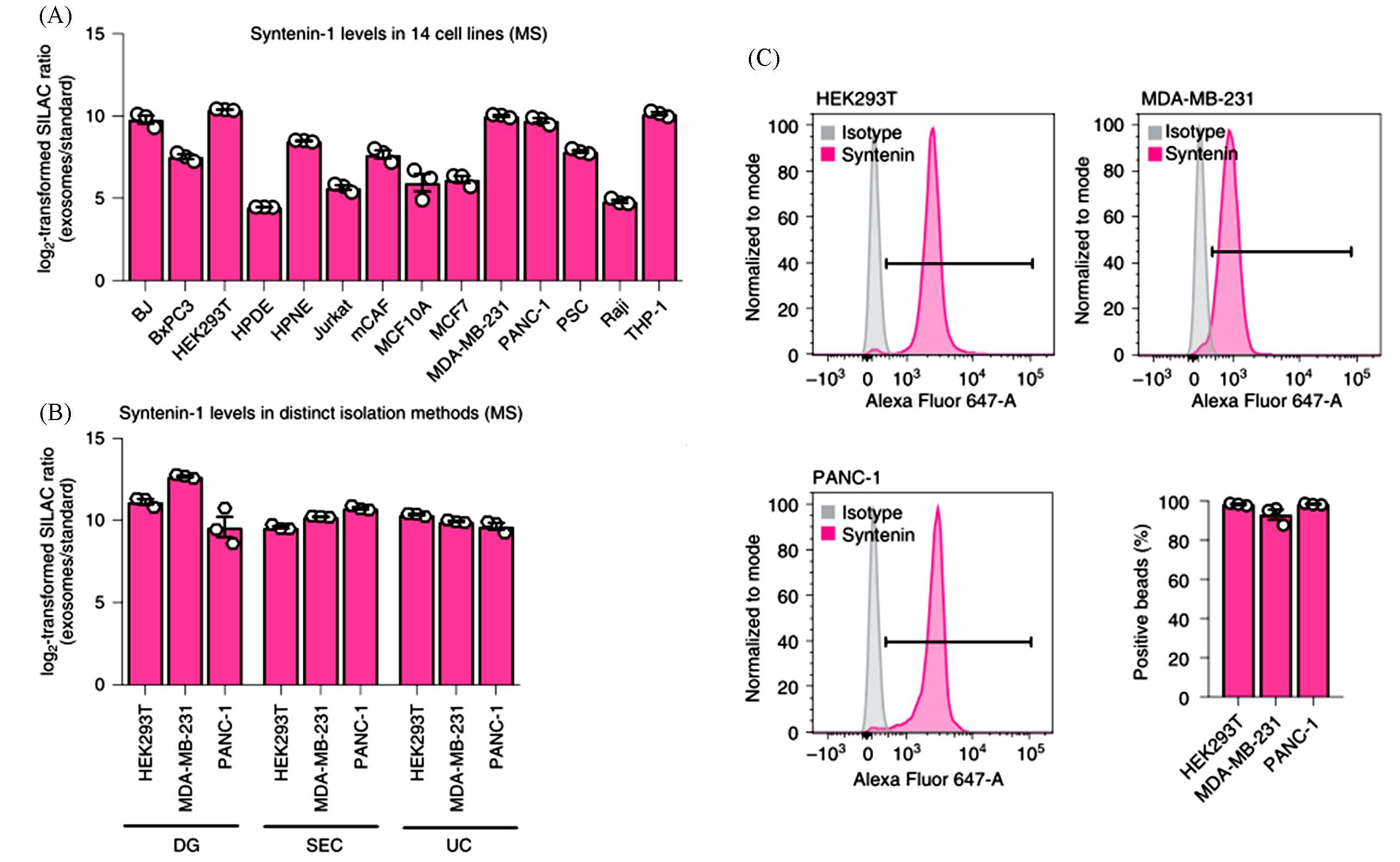
Fig.2 Representative results of the identification of Syntenin?1 as a consistently abundant protein in exosomes from different species and biofluids[9](A) Syntenin?1 abundance in exosomes from the 14 cell lines determined by MS. (B) Syntenin?1 levels in distinct isolation methods. Data are mean±s.e.m., Individual data points from three biological replicates. (C) Representative histograms show the profile of the syntenin?1 levels in comparison to isotype?control?stained beads. All data are mean±s.e.m. of the percentage of positive beads. Individual data points from three biological replicates.Copyright 2021, Springer Nature.
| Aptamer | Target | Source | Sequence (5'?3') | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AptCD63 | CD63 | Human urine | CACCCCACCTCGCTCCCGTGACACTAATGCTA | [ | |
| A549 | Lung cancer | [ | |||
| CEM | Leukemia tumor | [ | |||
| LNCaP | Prostate cancer | [ | |||
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| Ramos | Human acute Lymphoblastic leukemia | [ | |||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| [ | |||||
| CACCCCACCT | [ | ||||
| TCTAATAACTTACCTCT | [ | ||||
| CD63?1 | CD63 | MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | TAACACGACAGACGTTCGGAGGTCGAACCCTGACAGCGTGGGC | [ |
| AptCD109 | CD109 | 5?8F | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCATCTGAGAATAGTGGTTTGCTGT?ATGGTGGGCGTTG AAAGAGGGGTGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT | [ |
| SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | [ | |||
| AptCEA | CEA | T84 | Colorectal cancer | TCGCGCGAGTCGTCTGGGGAACCATCGAGTTACACCGAC?CTTCTATGTGCGGCCCCCCGCATCGTCCTCCC | [ |
| BT474 | Breast cancer | ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT | [ | ||
| MDA?MB?231 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | |||||
| MCF?7 | [ | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | ||||
| AptEpCAM | EpCAM | LNCaP | Prostate cancer | CACTACAGAGGTTGCGTCTGTCCCACGTTGTCATGGGGG?GTTGGCCTG | [ |
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| SW480 | Colorectal cancer | [ | |||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | TCACTACAGAGGTTGCGTCTGTCCCACGTTGTCATGGGG?GGTTGGCCTG | [ | ||
| BT474 | [ | ||||
| AptHER2 | HER2 | MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GGGCCGTCGAACACGAGCATGGTGCGTGGACCTAGGATGACCTGAGTACTGTCC | [ |
| MCF?7 | [ | ||||
| BT474 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | |||||
| MCF?7/MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GCAGCGGTGTGGGGGCAGCGGTGTGGGGGCAGCGGTGTGGGG | [ | ||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| Ramos | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | ||||
| AptMUC1 | MUC1 | SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | TACTGCATGCACACCACTTCAACTA | [ |
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | TTGATCCTTTGGATACC/GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [44,54―57] | ||
| BT474 | GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | [ | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| Aptamer | Target | Source | Sequence (5'?3') | Reference | |
| AptMUC1 | MUC1 | HeLa | Cervical cancer | GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [ |
| Ramos | Human acute lymphoblastic leukemia | ||||
| AS1411 | Nucleolin | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | AGTCTAGGATTCGGCGTGGGTTAATTTTTTTTTGGTGGTGGTGGTTGTGGTGGTGGTGG | [ |
| HL?60 cell | Leukemia | GGTGGTGGTGGTTGTGGTGGTGGTGG | [ | ||
| AptPSMA | PSMA | LNCaP | Prostate cancer | GCGTTTTCGCTTTTGCGTTTTGGGTCATCTGCTTACGATAGCAATGCT | [ |
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | ||||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| LNCaP | Prostate cancer | GGGAGGACGAUGCGGAUCAGCCAUGUUUACGUCACUCCU/CATCCATGGGAATTCGTCGACCCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT?TCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTGCCTAGGCTCGAGCTCG | [ | ||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | CATCCATGGGAATTCGTCGACCCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT?TCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTGCCTAGGCTCGAGCTCG | [ | ||
| Sgc8c | PTK7 | CEM | Humanacute lymphoblastic leukemia | ATCTAACTGCTGCGCCGCCGGGAAAATACTGTACGGTTAGA | [15,61―63] |
| Serum of lymphoma patient serum | [ | ||||
| AptCA125 | CA125 | Serum of ovarian cancer | TATCAATTACTTACCCTAGTGGTGTGATGTCGTATGGATG | ||
| AptPSA | PSA | Serum of prostate cancer | AATTAAAGCTCGCCATCAAATAGC | ||
| AptAFP | AFP | HepG2 | Liver cancer | AACAAGCTTGGCGGCGGGAAGGTGTTTAAATTCCCGGGT?CTGCGTGGTCTGTGGTGCTG | [ |
| GGCAGGAAGACAAACAAGCTTGGCGGCGGGAAGGTGTTT?AAATTCCCGGGTCTGCGTGGTCTGTGGTGCTGT | [ | ||||
| AptPDGF | PDGF | MCF?7 | Breast cancer | CAGGCTACGGCACGTAGAGCATCACCATGATCCTG | [ |
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | ||||
| AptEGFR | EGFR | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | TACCAGTGCGATGCTCAGTGCCGTTTCTTCTCTTTCGCTTT?TTTTGCTTTTGAGCATGCTGACGCATTCGGTTGA | [ |
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GCCTTAGUAACGTGCTTTGATGTCGATTCGACAGGAGGC | [ | ||
| AptPD?L1 | PD?L1 | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | AGTCTAGGATTCGGCGTGGGTTAATTTTTTTTTACGCTCGG?ATGCCACTACAGACGGGCC | [ |
| ACATCAACTCATTGATAGACAATGCGTCCACTGCCCGTCTCATGGACGTGCTGGTGAC | |||||
| AptLZH8 | ― | Liver cancer | ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCATATTAGTACGGCTTAACCCPCA?TGGTGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT(P: Artificial nucleotide) | [ | |
RNA aptamer | Exosomes | Primary epithelialbreast cancer & normal breast hyperplasia | UGUGGCAGUUAAGAAUAGAUCUUCGCUGCGAUU | [ | |
Table 1 Reported aptamers with exosome recognition function
| Aptamer | Target | Source | Sequence (5'?3') | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AptCD63 | CD63 | Human urine | CACCCCACCTCGCTCCCGTGACACTAATGCTA | [ | |
| A549 | Lung cancer | [ | |||
| CEM | Leukemia tumor | [ | |||
| LNCaP | Prostate cancer | [ | |||
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| Ramos | Human acute Lymphoblastic leukemia | [ | |||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| [ | |||||
| CACCCCACCT | [ | ||||
| TCTAATAACTTACCTCT | [ | ||||
| CD63?1 | CD63 | MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | TAACACGACAGACGTTCGGAGGTCGAACCCTGACAGCGTGGGC | [ |
| AptCD109 | CD109 | 5?8F | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCATCTGAGAATAGTGGTTTGCTGT?ATGGTGGGCGTTG AAAGAGGGGTGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT | [ |
| SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | [ | |||
| AptCEA | CEA | T84 | Colorectal cancer | TCGCGCGAGTCGTCTGGGGAACCATCGAGTTACACCGAC?CTTCTATGTGCGGCCCCCCGCATCGTCCTCCC | [ |
| BT474 | Breast cancer | ATACCAGCTTATTCAATT | [ | ||
| MDA?MB?231 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | |||||
| MCF?7 | [ | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | ||||
| AptEpCAM | EpCAM | LNCaP | Prostate cancer | CACTACAGAGGTTGCGTCTGTCCCACGTTGTCATGGGGG?GTTGGCCTG | [ |
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | [ | |||
| SW480 | Colorectal cancer | [ | |||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | TCACTACAGAGGTTGCGTCTGTCCCACGTTGTCATGGGG?GGTTGGCCTG | [ | ||
| BT474 | [ | ||||
| AptHER2 | HER2 | MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GGGCCGTCGAACACGAGCATGGTGCGTGGACCTAGGATGACCTGAGTACTGTCC | [ |
| MCF?7 | [ | ||||
| BT474 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | |||||
| MCF?7/MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GCAGCGGTGTGGGGGCAGCGGTGTGGGGGCAGCGGTGTGGGG | [ | ||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| Ramos | Acute lymphoblastic leukemia | ||||
| AptMUC1 | MUC1 | SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | TACTGCATGCACACCACTTCAACTA | [ |
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | TTGATCCTTTGGATACC/GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [44,54―57] | ||
| BT474 | GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [ | |||
| MDA?MB?231 | |||||
| SK?BR?3 | [ | ||||
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| Aptamer | Target | Source | Sequence (5'?3') | Reference | |
| AptMUC1 | MUC1 | HeLa | Cervical cancer | GCAGTTGATCCTTTGGATACCCTGG | [ |
| Ramos | Human acute lymphoblastic leukemia | ||||
| AS1411 | Nucleolin | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | AGTCTAGGATTCGGCGTGGGTTAATTTTTTTTTGGTGGTGGTGGTTGTGGTGGTGGTGG | [ |
| HL?60 cell | Leukemia | GGTGGTGGTGGTTGTGGTGGTGGTGG | [ | ||
| AptPSMA | PSMA | LNCaP | Prostate cancer | GCGTTTTCGCTTTTGCGTTTTGGGTCATCTGCTTACGATAGCAATGCT | [ |
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | [ | |||
| MCF?7 | Breast cancer | ||||
| HeLa | Cervical cancer | ||||
| LNCaP | Prostate cancer | GGGAGGACGAUGCGGAUCAGCCAUGUUUACGUCACUCCU/CATCCATGGGAATTCGTCGACCCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT?TCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTGCCTAGGCTCGAGCTCG | [ | ||
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | CATCCATGGGAATTCGTCGACCCTGCAGGCATGCAAGCTT?TCCCTATAGTGAGTCGTATTACTGCCTAGGCTCGAGCTCG | [ | ||
| Sgc8c | PTK7 | CEM | Humanacute lymphoblastic leukemia | ATCTAACTGCTGCGCCGCCGGGAAAATACTGTACGGTTAGA | [15,61―63] |
| Serum of lymphoma patient serum | [ | ||||
| AptCA125 | CA125 | Serum of ovarian cancer | TATCAATTACTTACCCTAGTGGTGTGATGTCGTATGGATG | ||
| AptPSA | PSA | Serum of prostate cancer | AATTAAAGCTCGCCATCAAATAGC | ||
| AptAFP | AFP | HepG2 | Liver cancer | AACAAGCTTGGCGGCGGGAAGGTGTTTAAATTCCCGGGT?CTGCGTGGTCTGTGGTGCTG | [ |
| GGCAGGAAGACAAACAAGCTTGGCGGCGGGAAGGTGTTT?AAATTCCCGGGTCTGCGTGGTCTGTGGTGCTGT | [ | ||||
| AptPDGF | PDGF | MCF?7 | Breast cancer | CAGGCTACGGCACGTAGAGCATCACCATGATCCTG | [ |
| HepG2 | Liver cancer | ||||
| SGC7901 | Gastric cancer | ||||
| AptEGFR | EGFR | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | TACCAGTGCGATGCTCAGTGCCGTTTCTTCTCTTTCGCTTT?TTTTGCTTTTGAGCATGCTGACGCATTCGGTTGA | [ |
| MDA?MB?231 | Breast cancer | GCCTTAGUAACGTGCTTTGATGTCGATTCGACAGGAGGC | [ | ||
| AptPD?L1 | PD?L1 | SUNE2 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | AGTCTAGGATTCGGCGTGGGTTAATTTTTTTTTACGCTCGG?ATGCCACTACAGACGGGCC | [ |
| ACATCAACTCATTGATAGACAATGCGTCCACTGCCCGTCTCATGGACGTGCTGGTGAC | |||||
| AptLZH8 | ― | Liver cancer | ATCCAGAGTGACGCAGCATATTAGTACGGCTTAACCCPCA?TGGTGGACACGGTGGCTTAGT(P: Artificial nucleotide) | [ | |
RNA aptamer | Exosomes | Primary epithelialbreast cancer & normal breast hyperplasia | UGUGGCAGUUAAGAAUAGAUCUUCGCUGCGAUU | [ | |
| 1 | EL Andaloussi S., Mager I., Breakefield X. O., Wood M. J., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2013, 12(5), 347―357 |
| 2 | Thery C., Zitvogel L., Amigorena S., Nat. Rev. Immunol., 2002, 2(8), 569―579 |
| 3 | Jeppesen D. K., Fenix A. M., Franklin J. L., Higginbotham J. N., Zhang Q., Zimmerman L. J., Liebler D. C., Ping J., Liu Q., Evans R., Fissell W. H., Patton J. G., Rome L. H., Burnette D. T., Coffey R. J., Cell, 2019, 177(2), 428―445 |
| 4 | Li H. L., Xing S., Xu J. H., He Y., Lai Y. Z., Wang Y., Zhang G., Guo S. H., Deng M., Zeng M. S., Liu W. L., Talanta, 2021, 221, 121670 |
| 5 | Karttunen J., Stewart S. E., Kalmar L., Grant A. J., Frankl F. E. K., Williams T. L., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2021, 22(9), 4881 |
| 6 | Xu Y., Leng K. M., Yao Y., Kang P. C., Liao G. Q., Han Y., Shi G. J., Ji D. L., Huang P., Zheng W. Y., Li Z. L., Li J. L., Huang L. N., Yu L., Zhou Y. X., Jiang X. M., Wang H., Li C. L., Su Z. L., Tai S., Zhong X. Y., Wang Z. D., Cui Y. F., Hepatology, 2021, 73(4), 1419―1435 |
| 7 | Mathivanan S., Simpson R. J., Proteomics, 2009, 9(21), 4997―5000 |
| 8 | Zhu N. H., Li G. H., Zhou J., Zhang Y. J., Kang K., Ying B. W., Yi Q. Y., Wu Y., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2021, 9(10), 2483―2493 |
| 9 | Kugeratski F. G., Hodge K., Lilla S., McAndrews K. M., Zhou X. N., Hwang R. F., Zanivan S., Kalluri R., Nat. Cell Biol., 2021, 23(6), 631―641 |
| 10 | Zhang N., Sun N., Deng C., Talanta, 2021, 221, 121571 |
| 11 | Hoshino A., Costa⁃Silva B., Shen T. L., Rodrigues G., Hashimoto A., Mark M. T., Molina H., Kohsaka S., Di Giannatale A., Ceder S., Singh S., Williams C., Soplop N., Uryu K., Pharmer L., King T., Bojmar L., Davies A. E., Ararso Y., Zhang T., Zhang H., Hernandez J., Weiss J. M., Dumont⁃Cole V. D., Kramer K., Wexler L. H., Narendran A., Schwartz G. K., Healey J. H., Sandstrom P., Labori K. J., Kure E. H., Grandgenett P. M., Hollingsworth M. A., de Sousa M., Kaur S., Jain M., Mallya K., Batra S. K., Jarnagin W. R., Brady M. S., Fodstad O., Muller V., Pantel K., Minn A. J., Bissell M. J., Garcia B. A., Kang Y., Rajasekhar V. K., Ghajar C. M., Matei I., Peinado H., Bromberg J., Lyden D., Nature, 2015, 527(7578), 329―335 |
| 12 | Zhang Z. B., Yu X. H., Zhou Z., Li B., Peng J. W., Wu X., Luo X. J., Yang L. F., Cancer Med., 2019, 8(13), 6082―6094 |
| 13 | van Niel G., D’Angelo G., Raposo G., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2018, 19(4), 213―228 |
| 14 | Melo S. A., Luecke L. B., Kahlert C., Fernandez A. F., Gammon S. T., Kaye J., LeBleu V. S., Mittendorf E. A., Weitz J., Rahbari N., Reissfelder C., Pilarsky C., Fraga M. F., Piwnica⁃Worms D., Kalluri R., Nature, 2015, 523(7559), 177―182 |
| 15 | Hou M., He D. G., Bu H. C., Wang H. Z., Huang J., Gu J. Q., Wu R., Li H. W., He X. X., Wang K. M., Analyst, 2020, 145(19), 6232―6236 |
| 16 | Zhao X. X., Luo C. J., Mei Q., Zhang H. M., Zhang W. Q., Su D. W., Fu W. L., Luo Y., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 5411―5418 |
| 17 | Tovar⁃Camargo O. A., Toden S., Goel A., Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn., 2016, 16(5), 553―567 |
| 18 | Jin D., Yang F., Zhang Y. L., Liu L., Zhou Y. J., Wang F. B., Zhang G. J., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(24), 14402―14411 |
| 19 | Wang L., Pan Y. H., Liu Y. F., Sun Z. W., Huang Y., Li J. L., Yang J., Xiang Y., Li G. X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(1), 322―329 |
| 20 | Record M., Carayon K., Poirot M., Silvente⁃Poirot S., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2014, 1841(1), 108―120 |
| 21 | Nishida⁃Aoki N., Izumi Y., Takeda H., Takahashi M., Ochiya T., Bamba T., Metabolites, 2020, 10(2), 67 |
| 22 | Valadi H., Ekstrom K., Bossios A., Sjostrand M., Lee J. J., Lotvall J. O., Nat. Cell Biol., 2007, 9(6), 654―659 |
| 23 | Hunter M. P., Ismail N., Zhang X., Aguda B. D., Lee E. J., Yu L., Xiao T., Schafer J., Lee M. L., Schmittgen T. D., Nana⁃Sinkam S. P., Jarjoura D., Marsh C. B., PLoS One, 2008, 3(11), e3694 |
| 24 | Pasini L., Notarangelo M., Vagheggini A., Burgio M. A., Crino L., Chiadini E., Prochowski A. I., Delmonte A., Ulivi P., D’Agostino V. G., Mol. Oncol., 2021, 15(9), 2423―2438 |
| 25 | Walravens A. S., Smolgovsky S., Li L., Kelly L., Antes T., Peck K., Quon T., Ibrahim A., Marban E., Berman B., Marban L., R⁃Borlado L., de Couto G., Sci. Rep., 2021, 11(1), 8666 |
| 26 | Zhou D. P., Gu J., Wang Y. P., Wu H. G., Cheng W., Wang Q. P., Zheng G. P., Wang X. D., Cell Biosci., 2021, 11(1), 68 |
| 27 | Jia Y. Y., Wang W. J., Liang L., Yuan Q., Acta Chim. Sin., 2020, 78(11), 1177―1184 |
| 28 | Ellington A. D., Szostak J. W., Nature, 1990, 346, 818―822 |
| 29 | Robertson D. L., Joyce G. F., Nature, 1990, 344, 467―468 |
| 30 | Tuerk C., Gold L., Science, 1990, 249, 505―510 |
| 31 | Tan W. H., Donovan M. J., Jiang J. H., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113(4), 2842―2862 |
| 32 | Zhang L., Yang Y., Tan J., Yuan Q., Mater. Chem. Front., 2020, 4(5), 1315―1327 |
| 33 | Zhang Z., Tang C., Zhao L., Xu L., Zhou W., Dong Z., Yang Y., Xie Q., Fang X., Nanoscale, 2019, 11(20), 10106―10113 |
| 34 | Yu Y., Zhang W. S., Guo Y., Peng H., Zhu M., Miao D., Su G., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 167, 112482 |
| 35 | Jiang J., Yu Y., Zhang H., Cai C., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2020, 1130, 1―9 |
| 36 | Gao M. L., Yin B. C., Ye B. C., Analyst, 2019, 144(20), 5996―6003 |
| 37 | Gao M. L., He F., Yin B. C., Ye B. C., Analyst, 2019, 144(6), 1995―2002 |
| 38 | Chen X., Lan J., Liu Y., Li L., Yan L., Xia Y., Wu F., Li C., Li S., Chen J., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2018, 102, 582―588 |
| 39 | Xu H. Y., Liao C., Zuo P., Liu Z. W., Ye B. C., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(22), 13451―13458 |
| 40 | Cao Y., Li L., Han B., Wang Y., Dai Y., Zhao J., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 141, 111397 |
| 41 | Song Z., Mao J., Barrero R. A., Wang P., Zhang F., Wang T., Molecules, 2020, 25(23), 5585 |
| 42 | Jia W. T., Ren C. P., Wang L., Zhu B., Jia W., Gao M. H., Zeng F., Zeng L., Xia X. M., Zhang X. B., Fu T., Li S. S., Du C., Jiang X. J., Chen Y. X., Tan W. H., Zhao Z. L., Liu W. D., Oncotarget, 2016, 7(34), 55328―55342 |
| 43 | Wang Z. L., Zong S. F., Wang Y. J., Li N., Li L., Lu J., Wang Z. Y., Chen B. A., Cui Y. P., Nanoscale, 2018, 10(19), 9053― 9062 |
| 44 | An Y., Li R., Zhang F., He P., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 5404―5410 |
| 45 | Zhang H. X., Wang Z. H., Zhang Q. X., Wang F., Liu Y., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 124, 184―190 |
| 46 | Kashefi⁃Kheyrabadi L., Kim J., Chakravarty S., Park S., Gwak H., Kim S. I., Mohammadniaei M., Lee M. H., Hyun K. A., Jung H. I., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 169(112622) |
| 47 | Wang Y. H., Luo D. W., Fang Y., Wu W. H., Wang Y. J., Xia Y. K., Wu F., Li C. Y., Lan J. M., Chen J. H., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2019, 298, 126900 |
| 48 | Liu C., Zhao J., Tian F., Cai L., Zhang W., Feng Q., Chang J., Wan F., Yang Y., Dai B., Cong Y., Ding B., Sun J., Tan W., Nat. Biomed. Eng., 2019, 3(3), 183―193 |
| 49 | Wang H., Chen H., Huang Z. P., Li T. D., Deng A. M., Kong J. L., Talanta, 2018, 184, 219―226 |
| 50 | Li B., Liu C. C., Pan W. L., Shen J. L., Guo J. Y., Luo T. T., Feng J. J., Situ B., An T. X., Zhang Y., Zheng L., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 168, 112520 |
| 51 | Wang L. L., Wang Y. R., Li J., Zeng L. P., Liao Y. J., Mao H. F., Chen W. Q., Zhang J., Yang H. H., Chen J. H., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(24), 16023―16023 |
| 52 | Liu C., Zhao J., Tian F., Chang J., Zhang W., Sun J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(9), 3817―3821 |
| 53 | Huang R., He L., Li S., Liu H., Jin L., Chen Z., Zhao Y., Li Z., Deng Y., He N., Nanoscale, 2020, 12(4), 2445―2451 |
| 54 | Zhang J. L., Shi J. J., Liu W., Zhang K. X., Zhao H. J., Zhang H. L., Zhang Z. Z., Sens. Actuators B: Chem., 2018, 276, 552―559 |
| 55 | Zhou Y., Xu H. Y., Wang H., Ye B. C., Analyst, 2020, 145(1), 107―114 |
| 56 | Zhang K., Yue Y., Wu S., Liu W., Shi J., Zhang Z., ACS Sens., 2019, 4(5), 1245―1251 |
| 57 | Wang L., Pan Y., Liu Y., Sun Z., Huang Y., Li J., Yang J., Xiang Y., Li G., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12(1), 322―329 |
| 58 | Xing S., Lu Z., Huang Q., Li H., Wang Y., Lai Y., He Y., Deng M., Liu W., Theranostics, 2020, 10(22), 10262―10273 |
| 59 | Jin D., Yang F., Zhang Y., Liu L., Zhou Y., Wang F., Zhang G. J., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90(24), 14402―14411 |
| 60 | Zhou Y. G., Mohamadi R. M., Poudineh M., Kermanshah L., Ahmed S., Safaei T. S., Stojcic J., Nam R. K., Sargent E. H., Kelley S. O., Small, 2016, 12(6), 727―732 |
| 61 | Chen J., Meng H. M., An Y., Geng X., Zhao K., Qu L., Li Z., Talanta, 2020, 209, 120510 |
| 62 | Im H., Shao H. L., Park Y. I., Peterson V. M., Castro C. M., Weissleder R., Lee H., Nat. Biotechnol., 2014, 32(5), 490―495 |
| 63 | Jiang Y., Shi M. L., Liu Y., Wan S., Cui C., Zhang L. Q., Tan W. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(39), 11916―11920 |
| 64 | Ning C. F., Wang L. Y., Tian Y. F., Yin B. C., Ye B. C., Analyst, 2020, 145(7), 2795―2804 |
| 65 | Esposito C. L., Quintavalle C., Ingenito F., Rotoli D., Roscigno G., Nuzzo S., Thomas R., Catuogno S., de Franciscis V., Condorelli G., Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids, 2021, 23, 982―994 |
| 66 | Zhou Q., Rahimian A., Son K., Shin D. S., Patel T., Revzin A., Methods, 2016, 97, 88―93 |
| 67 | Yu Q., Zhao Q., Wang S., Zhao S., Zhang S., Yin Y. G., Dong Y. Y., Anal. Biochem., 2020, 594, 113591 |
| 68 | Zhao X., Luo C., Mei Q., Zhang H., Zhang W., Su D., Fu W., Luo Y., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 5411―5418 |
| 69 | Miao P., Tang Y., Chem. Commun.(Camb.), 2020, 56(37), 4982―4985 |
| 70 | Li B., Pan W., Liu C., Guo J., Shen J., Feng J., Luo T., Situ B., Zhang Y., An T., Xu C., Zheng W., Zheng L., ACS Sens., 2020, 5(7), 2052―2060 |
| 71 | Li H., Xing S., Xu J., He Y., Lai Y., Wang Y., Zhang G., Guo S., Deng M., Zeng M., Liu W., Talanta, 2021, 221, 121670 |
| 72 | Wang Q., Zou L., Yang X., Liu X., Nie W., Zheng Y., Cheng Q., Wang K., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2019, 135, 129―136 |
| 73 | Wang S., Zhang L., Wan S., Cansiz S., Cui C., Liu Y., Cai R., Hong C., Teng I. T., Shi M., Wu Y., Dong Y., Tan W., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(4), 3943―3949 |
| 74 | Dirks R. M., Pierce N. A., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2004, 101(43), 15275―15278 |
| 75 | Wan S., Zhang L. Q., Wang S., Liu Y., Wu C. C., Cui C., Sun H., Shi M. L., Jiang Y., Li L., Qiu L. P., Tan W. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139(15), 5289―5292 |
| 76 | Shen W., Guo K., Adkins G. B., Jiang Q., Liu Y., Sedano S., Duan Y., Yan W., Wang S. E., Bergersen K., Worth D., Wilson E. H., Zhong W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57(48), 15675―15680 |
| 77 | Huang R., He L., Xia Y., Xu H., Liu C., Xie H., Wang S., Peng L., Liu Y., Liu Y., He N., Li Z., Small, 2019, 15(19), e1900735 |
| 78 | Xu L. Z., Chopdat R., Li D. Y., Al―Jamal K. T., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2020, 169, 112576 |
| 79 | Zhang Y. Z., Wang D. N., Yue S., Lu Y. B., Yang C. G., Fang J., Xu Z. R., ACS Sens., 2019, 4(12), 3210―3218 |
| 80 | Wu M., Chen Z., Xie Q., Xiao B., Zhou G., Chen G., Bian Z., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2021, 171, 112733 |
| 81 | Zhang H., Wang Z., Wang F., Zhang Y., Wang H., Liu Y., Anal. Chem., 2020, 92(7), 5546―5553 |
| 82 | Chang X., Zhang C., Lv C., Sun Y., Zhang M., Zhao Y., Yang L., Han D., Tan W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141(32), 12738―12743 |
| 83 | Zhang H., Qiao B., Guo Q., Jiang J., Cai C., Shen J., Analyst, 2020, 145(10), 3557―3563 |
| 84 | Pan B. T., Teng K., Wu C., Adam M., Johnstone R. M., JCB, 1985, 101(3), 942―948 |
| 85 | Zou J. M., Shi M. L., Liu X. J., Jin C., Xing X. J., Qiu L. P., Tan W. H., Anal. Chem., 2019, 91(3), 2425―2430 |
| 86 | Yi K. Z., Rong Y., Huang L. X., Tang X., Zhang Q., Wang W., Wu J. Y., Wang F. B., ACS Sens., 2021, 6(4), 1418―1429 |
| 87 | Esposito C. L., Quintavalle C., Ingenito F., Rotoli D., Roscigno G., Nuzzo S., Thomas R., Catuogno S., de Franciscis V., Condorelli G., Mol. Ther. Nucleic. Acids, 2021, 23, 982―994 |
| 88 | Shangguan D., Li Y., Tang Z., Cao Z. C., Chen H. W., Mallikaratchy P., Sefah K., Yang C. J., Tan W., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2006, 103(32), 11838―11843 |
| 89 | Zhang L. Q., Wang S., Yang Z. Y., Hoshika S., Xie S. T., Li J., Chen X. G., Wan S., Li L., Benner S. A., Tan W. H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2020, 59(2), 663―668 |
| 90 | Zhou J. H., Rossi J., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2017, 16(6), 181―202 |
| 91 | Xie X. D., Nie H. F., Zhou Y., Lian S., Mei H., Lu Y. S., Dong H. Y., Li F. Q., Li T., Li B. F., Wang J., Lin M., Wang C. H., Shao J. W., Gao Y., Chen J. M., Xie F. W., Jia L., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 5476 |
| [1] | 王隆杰, 范鸿川, 秦渝, 曹秋娥, 郑立炎. 金属有机框架材料在分离分析领域的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1167. |
| [2] | 张晓荣, 陈岚岚, 胡善文. 基于分子识别的细菌检测研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3468. |
| [3] | 吉采灵, 程兴, 谈洁, 袁荃. 功能化核酸适体的筛选及分子识别应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3457. |
| [4] | 解忱, 陈娜, 杨雁冰, 袁荃. 核酸适体功能化的二维材料场效应晶体管传感器研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3406. |
| [5] | 赵卓, 王雪强. 核酸适体偶联药物的生物偶联构建技术与应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3367. |
| [6] | 刘学娇, 杨帆, 刘爽, 张春娟, 刘巧玲. 核酸适体靶向的膜蛋白识别与功能调控研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3277. |
| [7] | 刘园, 邓瑾琦, 赵帅, 田飞, 李轶, 孙佳姝, 刘超. 基于分子识别的免疫层析技术用于新冠肺炎感染的快速诊断[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3390. |
| [8] | 林宁钦, 姚克, 陈祥军. 晶状体蛋白识别互作与白内障的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3379. |
| [9] | 刘珂, 靳宇, 梁建功, 吴园. 化学修饰提高核酸适体结合亲和力的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3477. |
| [10] | 彭与煜,王煜,于鑫垚,曾巨澜,肖忠良,曹忠. 基于单(6-巯基-6-去氧)-β-环糊精修饰金电极对L-半胱氨酸的快速灵敏检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 268. |
| [11] | 董倩, 李兆倩, 彭天欢, 陈卓, 谭蔚泓. 核酸适体在癌症诊疗中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12): 2648. |
| [12] | 张怡萌, 张慧欣, 刘洋. 外泌体生物分析及其临床应用研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2306. |
| [13] | 马玉聪, 樊保民, 郝华, 吕金玉, 冯云皓, 杨彪. 十八胺基分子组装体在碳钢表面的作用机理与模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 96. |
| [14] | 沈晓琴, 李智, 王刚林, 王莉, 孙权洪, 罗序成, 马楠. 基于氧化石墨烯和DNA量子点组装体的DNA二元逻辑检测及循环可逆设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(12): 2176. |
| [15] | 宋春霞, 羊小海, 王柯敏, 王青, 刘剑波, 黄晋, 李文山, 黄海花, 刘卫. 聚合物在荧光检测领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(2): 201. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||