

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (1): 102.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170377
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Chanchan1,2, ZHANG Fanghui1,*( ), DING Lei1,*(
), DING Lei1,*( ), NI Zhenjie3, JIANG Lang3, DONG Huanli3, ZHANG Xiaotao2, LI Rongjin2, HU Wenping2
), NI Zhenjie3, JIANG Lang3, DONG Huanli3, ZHANG Xiaotao2, LI Rongjin2, HU Wenping2
Received:2017-06-12
Online:2018-01-10
Published:2017-12-04
Contact:
ZHANG Fanghui,DING Lei
E-mail:zhangfanghui@sust.edu.cn;dinglei@sust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Chanchan, ZHANG Fanghui, DING Lei, NI Zhenjie, JIANG Lang, DONG Huanli, ZHANG Xiaotao, LI Rongjin, HU Wenping. Organic Phototransistor Based on Surface Plasmon Resonance Effect†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 102.
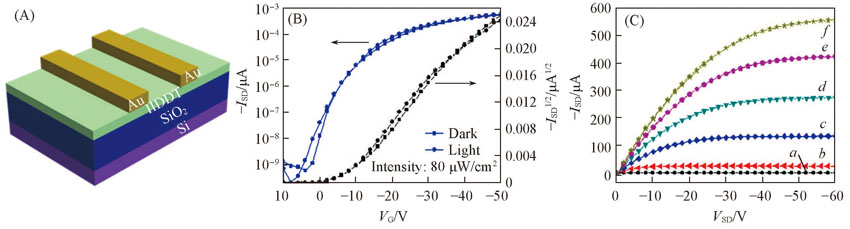
Fig.6 Schematic structure of OFET device(A), transfer(B) and output(C) characteristics of OFET with IIDDT as the semiconductorVG/V: a. -10; b. -20; c. -30; d. -40; e. -50; f. -60.
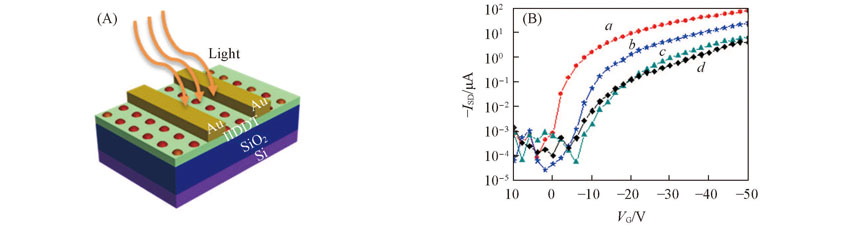
Fig.7 Schematic diagram of PhotOFET with Au NPs(A) and transfer curves of PhotOFET under white light irradiation(80 μW/cm2) with different semiconductor layers(B)a. C6 SAM-Au NPs; b. C8 SAM-Au NPs; c. C11 SAM-Au NPs; d. Au NPs.
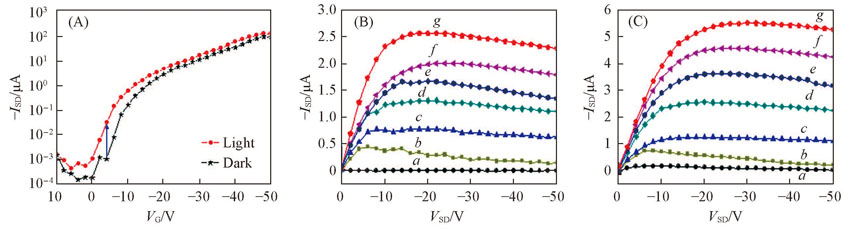
Fig.8 Transfer(A) and output characteristics of PhotOFET with C6 SAM-Au NPs in the dark(B) and under white light irradiation with 80 μW/cm2(C)VG/V: a. -20; b. -30; c. -40; d. -50; e. -60; f. -70; g. -80.
| Semiconductor | Structure (Dielectric) | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) | Responsivity/ (A·W-1) | Intensity/ (mW·cm-2) | Id,ph/Id,dark | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3OT | BG/TC(PVA) | 10-3—10-4 | 1 | 1 | 102—103 | [9] |
| P3HT | BG/TC(PVA) | 2.6×10-3 | NA* | 1 | NA* | [10] |
| F8T2 | BG/BC(SiO2) | 1.2×10-4 | 18.5 | 1 | ca. 102 | [15] |
| TA-PPE | BG/TC(SiO2) | NA | 0.036 | 1 | 3.3×103 | [17] |
| IIDDT | BG/TC(SiO2) | 0.12 | 11.6 | 0.08 | 700 | This work |
Table 1 PhotOFETs property based on polymer semiconductors
| Semiconductor | Structure (Dielectric) | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) | Responsivity/ (A·W-1) | Intensity/ (mW·cm-2) | Id,ph/Id,dark | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3OT | BG/TC(PVA) | 10-3—10-4 | 1 | 1 | 102—103 | [9] |
| P3HT | BG/TC(PVA) | 2.6×10-3 | NA* | 1 | NA* | [10] |
| F8T2 | BG/BC(SiO2) | 1.2×10-4 | 18.5 | 1 | ca. 102 | [15] |
| TA-PPE | BG/TC(SiO2) | NA | 0.036 | 1 | 3.3×103 | [17] |
| IIDDT | BG/TC(SiO2) | 0.12 | 11.6 | 0.08 | 700 | This work |
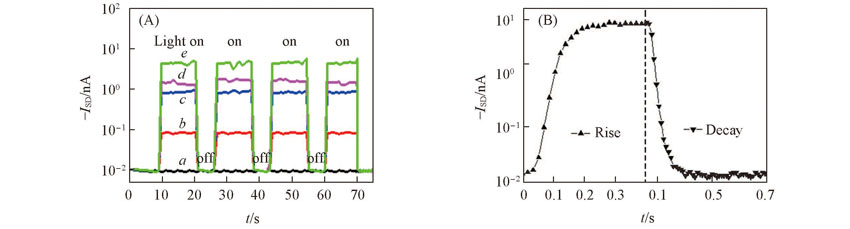
Fig.9 Photoswitch properties(A) and photocurrent change(B) of the PhotOFETa. IIDDT; b. bare-Au NPs; c. C11 SAM-Au NPs; d. C8 SAM-Au NPs; e. C6 SAM-Au NPs.
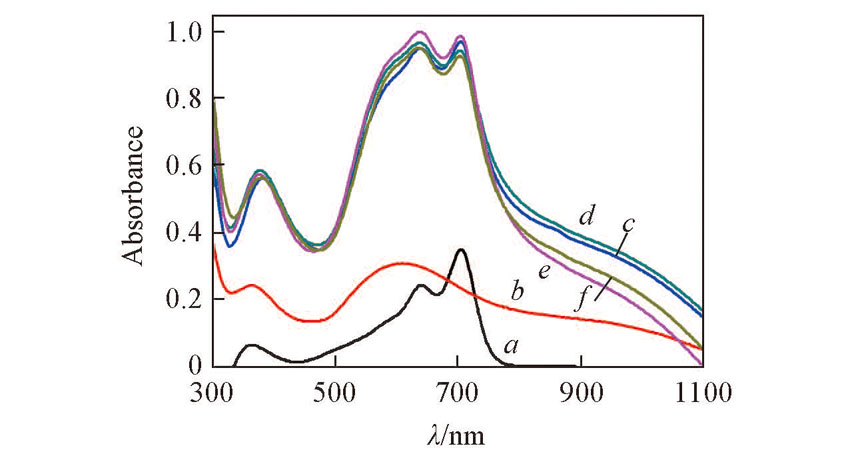
Fig.10 UV-Vis absorption spectra at different semiconductor layersa. IIDDT; b. Au NPs; c. Au NPs-IIDDT; d. C6 SAM-Au NPs; e. C8 SAM-Au NPs; f. C11 SAM-Au NPs.
| [1] | Narayan K. S., Kumar N., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 79(12), 1891—1893 |
| [2] | Arias A. C., Mackenzie J. D., Mcculloch I., Rivnay J., Salleo A., Chem. Rev., 2010, 110(1), 3—24 |
| [3] | Lei T., Wang J. Y., Pei J., Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47(4), 1117—1126 |
| [4] | Reichmanis E., Katz H., Kloc C., Maliakal A., Bell Labs Tech. J., 2005, 10(3), 8—105 |
| [5] | Facchetti A., Yoon M. H., Marks T., Adv. Mater., 2010, 17(14), 1705—1725 |
| [6] | Yang F., Shtein M., Forrest S. R., Nature, 2004, 428(6986), 911—918 |
| [7] | Wang C., Dong H., Hu W., Liu Y., Zhu D., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112(4), 2208—2267 |
| [8] | Li R., Hu W., Liu Y., Zhu D., Acc. Chem. Res., 2010, 43(4), 529—54 |
| [9] | Marjanovic N., Photoresponsive Organic Field Effect Transistor, VDM Verlag Dr. Müller Aktiengesellschaft & Co. KG, Austria, 2008, 383—475 |
| [10] | Ma X. Y., Yang J. M., Cai W. S., Zhu G. D., Liu J. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2016, 32(4), 702—708 |
| [11] | Narayan K. S., Kumar N., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2001, 79(12), 1891—1893 |
| [12] | Dutta S., Narayan K. S., Synth. Met., 2004, 146(3), 321—324 |
| [13] | Tanusri P., Arif M., Saiful I. K., Nanotechnology, 2010, 21(32), 325201—325205 |
| [14] | Wasapinyokul K., Milne W. I., Chu D. P., J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 105(2), 024509—024517 |
| [15] | Hamilton M. C., Kanicki J., IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quant., 2004, 10(4), 840—848 |
| [16] | Hamilton M. C., Martin S., Kanicki J., IEEE T. Electron. Dev., 2004, 51(6), 877—885 |
| [17] | Wang X., Wasapinyokul K., Tan W. D., Rawcliffe R., Campbell A. J., Bradley D. D. C., J. Appl. Phys., 2010, 107(2), 599—602 |
| [18] | Xu Y., Berger P. R., Wilson J. N., Bunz U. H. F., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2004, 85(18), 4219—4221 |
| [19] | Dong H., Li H., Wang E., Nakashima H., Torimitsu K., Hu W., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 112(49), 19690—19693 |
| [20] | Zakaria R., Lin W. K., Lim C. C., Appl. Phys. Exp., 2012, 5(8), 082002—082005 |
| [21] | Liu Y., Cheng R., Liao L., Zhou H. L., Bai J. W., Liu G., Liu L. X., Huang Y., Duan X. F., Nat. Commun., 2011, 2(1), 579—583 |
| [22] | Green M. A., Pillai S., Nat. Photon, 2012, 6(3), 130—132 |
| [23] | Ferry V. E., Munday J. N., Atwater H. A., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22(43), 4794—4808 |
| [24] | Atwater H. A., Polman A., Nat. Mater., 2010, 9(3), 205—213 |
| [25] | Wu X. L., Liu L. L., Xie Z. Q., Ma Y. G., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3), 409—425 |
| (吴小龑, 刘琳琳, 解增旗, 马於光.高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3), 409—425) | |
| [26] | Lei T., Cao Y., Fan Y. L., Liu C. J., Yuan S. C., Pei J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133(16), 6099—6101 |
| [27] | Feng H. Y., Gao L., Ye X. H., Wang L., Xue Z. C., Kong J. M., Li L. Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2017, 33(2), 155—159 |
| [28] | Green M. A., Pillai S., Nat. Photon., 2012, 6(3), 130—132 |
| [1] | BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252. |
| [2] | WANG Tingting, LI Yuan, YANG Lili, BAO Changhao, CHENG Han. In vivo Dynamic Detection of Aloe Polysaccharides Using Carbon Fiber Microelectrodes Modified with Gold Nanoparticles † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 87. |
| [3] | ZHU Qinfu,HU Kezhen,LI Xiaojie,CHEN Mingqing. Preparation of Dendrimer-gold Nanoparticle Composites for pH Responsive Drug Delivery† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 1065. |
| [4] | Siqi SUN,Ying WANG,Chuanyin SUN,Runwei WANG,Zhendong ZHANG,Zongtao ZHANG,Shilun QIU. Preparation and Catalytic Performance of Bowl-shaped Amphiphilic ZSM-5 Zeolites Supported Gold Nanoparticles † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2436. |
| [5] | HE Caimei,ZHENG Jingyi,LI Xiaoxia. MoS2-Gold Nanoparticles and Thionine-gold Nanoparticle Based Signal-enhanced Electrochemical Aptasensor for the Detection of 17β-Estradiol † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(10): 2090. |
| [6] | FENG Wei,WANG Bowei,ZHENG Yan,JIANG Yang. Preparation and Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS) of Single Au Nanodot† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1875. |
| [7] | LI Aiju, WANG Yuxi, LU Shaoyong, LIU Kun. Ligand Exchange of Gold Nanoparticles with Thiol-terminated Polystyrene† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(3): 552. |
| [8] | WANG Li, LI Zhi, SHEN Xiaoqin, MA Nan. Programming Single Quantum Dot Valencies via DNA Caging† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(1): 32. |
| [9] | HUANG Haiping, YUE Yafeng, XU Liang, LÜ Lianlian, HU Yongmei. Glucose Biosensor Based on Dy2(MoO4)3-AuNPs Composite Nanomaterial† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(4): 554. |
| [10] | MENG Qingnan, WANG Kai, TANG Yufei, ZHAO Kang, XIANG Siyuan, ZHANG Kai, ZHAO Lang. Preparation of Gold Nanoparticles Loaded Hollow Silica Spheres and Their Catalytic Performance† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 503. |
| [11] | LI Dan, WU Qian, LIU Li, SUN Xiaori, GUO Meng, FENG Yimin. Preparation and Stability of Gemini Surfactant Modified Gold Nanofluids† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1829. |
| [12] | ZHAO Tiantian, CHEN Yuqing, ZHANG Min, WANG Yuerong, ZHANG Hongyang, HU Ping. Fabrication of Paper-based Microfluidic Chips and the Application on the Determination of Uric Acid in Serum Based on Gold Nanoparticle-assisted Catalysis† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(5): 829. |
| [13] | HUANG Lijun, ZHANG Lihua, MAO Hongju, WANG Ping, JIANG Youxu, LI Panpan, JIN Qinghui, ZHAO Jianlong. Detection of Myocardial Injury Markers Based on Double Gold Nanoparticles Probes and Protein Chip† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1687. |
| [14] | FANG Yan, MA Linlin, SHAN Duoliang, LU Xiaoquan. Preparation of Graphene/Gold Nanoparticle Composite Film Modified Electrode and Its Application for Determination of Bisphenol A† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1491. |
| [15] | WANG Bicui, WANG Wei, ZHANG Jingwei, YUAN Zhi. Influences on Adhesion and Proliferation of Endothelial Cells with AuNPs† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(8): 1619. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||