

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 1687.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150133
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Lijun1,2, ZHANG Lihua1,*( ), MAO Hongju2,*(
), MAO Hongju2,*( ), WANG Ping2, JIANG Youxu1, LI Panpan1, JIN Qinghui2, ZHAO Jianlong2
), WANG Ping2, JIANG Youxu1, LI Panpan1, JIN Qinghui2, ZHAO Jianlong2
Received:2015-02-06
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-07-17
Contact:
ZHANG Lihua,MAO Hongju
E-mail:zlhxp@126.com;hjmao@mail.sim.ac.cn
CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Lijun, ZHANG Lihua, MAO Hongju, WANG Ping, JIANG Youxu, LI Panpan, JIN Qinghui, ZHAO Jianlong. Detection of Myocardial Injury Markers Based on Double Gold Nanoparticles Probes and Protein Chip†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1687.
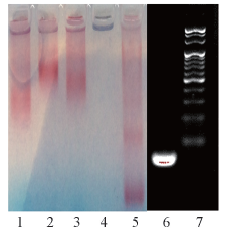
Fig.3 Electrophoresis results of AuNPs before and after modificationLane 1: HFABP detection probe; lane 2: cTnⅠ detection probe; lane 3: MYO detection probe; lane 4: AuNPs; lane 5: signal probe; lane 6: DNA probe(25 nt); lane 7: DNA ladder(20 bp).
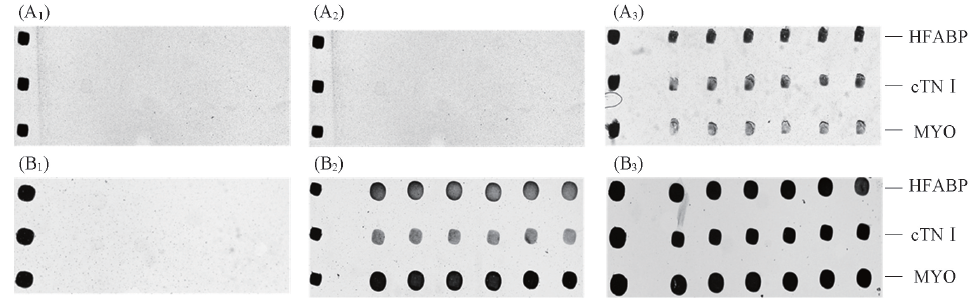
Fig.5 Detection results of protein chips before and after amplification(A1—A3) Detection results of signal AuNPs probe; (B1—B3) detection results of double AuNPs probes hybridization.(A1), (B1) blank control; (A2), (B2) 1 ng/mL; (A3), (B3) 32 ng/mL.
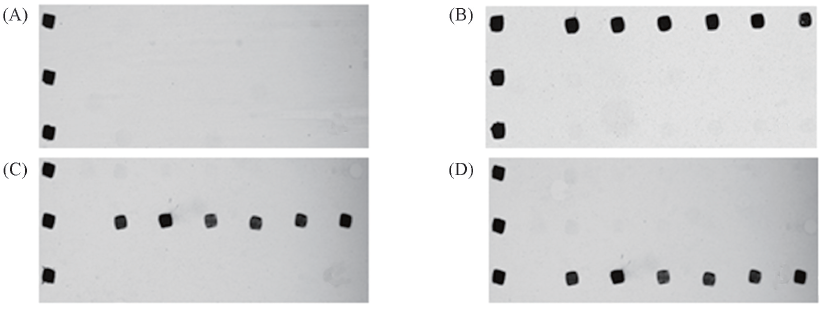
Fig.6 Specificity of myocardial injury markers detected by the developed protein chip(A) Blank control; (B) specific test of HFABP; (C) specific test of cTnⅠ; (D) specific test of MYO.
| Method | AMI(n=42) | UA(n=30) | Normal control(n=30) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cTnⅠ | MYO | cTnⅠ | MYO | cTnⅠ | MYO | |||||||
| + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | |
| Protein chip | 31 | 11 | 37 | 5 | 6 | 24 | 15 | 15 | 1 | 29 | 7 | 23 |
| ECLIA kit | 30 | 12 | 35 | 7 | 6 | 24 | 16 | 14 | 1 | 29 | 6 | 24 |
| χ2 | 0.060 | 0.389 | 0 | 0.067 | 0 | 0.098 | ||||||
| P | 0.807 | 0.533 | 1.000 | 0.796 | 1.000 | 0.754 | ||||||
Table 1 Comparision between ECLIA and protein chip for the detection of cTnⅠ and MYO in serum
| Method | AMI(n=42) | UA(n=30) | Normal control(n=30) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cTnⅠ | MYO | cTnⅠ | MYO | cTnⅠ | MYO | |||||||
| + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | + | - | |
| Protein chip | 31 | 11 | 37 | 5 | 6 | 24 | 15 | 15 | 1 | 29 | 7 | 23 |
| ECLIA kit | 30 | 12 | 35 | 7 | 6 | 24 | 16 | 14 | 1 | 29 | 6 | 24 |
| χ2 | 0.060 | 0.389 | 0 | 0.067 | 0 | 0.098 | ||||||
| P | 0.807 | 0.533 | 1.000 | 0.796 | 1.000 | 0.754 | ||||||
| Method | AMI(n=42) | UA(n=30) | Normal control(n=30) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFABP | HFABP | HFABP | ||||
| + | - | + | - | + | - | |
| Protein chip | 39 | 3 | 9 | 21 | 3 | 27 |
| ELISA kit | 36 | 6 | 11 | 19 | 4 | 28 |
| χ2 | 0.498 | 0.300 | 0.097 | |||
| P | 0.480 | 0.584 | 0.756 | |||
Table 2 Comparision between protein chip and ELISA for the detection of HFABP in serum
| Method | AMI(n=42) | UA(n=30) | Normal control(n=30) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HFABP | HFABP | HFABP | ||||
| + | - | + | - | + | - | |
| Protein chip | 39 | 3 | 9 | 21 | 3 | 27 |
| ELISA kit | 36 | 6 | 11 | 19 | 4 | 28 |
| χ2 | 0.498 | 0.300 | 0.097 | |||
| P | 0.480 | 0.584 | 0.756 | |||
| [1] | Murray C. J., Lopez A. D., The Lancet, 1997, 349(9064), 1498—1504 |
| [2] | Boersma E., Mercado N., Poldermans D., Gardien M., Vos J., Simoons M. L., The Lancet, 2003, 361(9360), 847—858 |
| [3] | Mion M. M., Novello E., Altinier S., Rocco S., Zaninotto M., Plebani M., Clin. Biochem., 2007, 40(16), 1245—1251 |
| [4] | Adams J., Trent R., Rawles J., Brit. Med. J., 1993, 307(6901), 409—413 |
| [5] | Hung C. L., Hou C. J. Y., Yeh H. I., Chang W. H., Int. J. Gerontol., 2010, 4(1), 1—8 |
| [6] | Vittorini S., Clerico A., Clin. Chem. Lab. Med., 2008, 46(6), 748—763 |
| [7] | Gobi K. V., Tanaka H., Shoyama Y., Miura N., Sensor Actuat. B: Chem., 2005, 111, 562—571 |
| [8] | Nakamura H., Karube I., Anal. Bioanal. Chem., 2003, 377(3), 446—468 |
| [9] | Mohammed M. I., Desmulliez M. P. Y., Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014, 61, 478—484 |
| [10] | Gul O., Calay E., Sezerman U., Basaga H., Gurbuz Y., Sensor Actuat. B: Chem., 2007, 125, 581—588 |
| [11] | Matveeva E. G., Gryczynski Z., Lakowicz J. R., J. Immunol. Methods, 2005, 302(1), 26—35 |
| [12] | Han K. N., Le T. H., Pham X. H., Huynh-Nguyen B. C., Kim J. H., Ko E., Kwon H. T., Seong G. H., Sensor Actuat. B: Chem., 2015, 207, 470—476 |
| [13] | Zhu Z., Ravelet C., Perrier S., Guieu V., Fiore E., Peyrin E., Anal. Chem., 2012, 84(16), 7203—7211 |
| [14] | Fan Y., Fang Y., Chen H. T., Gao D., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9), 1933—1940 |
| (樊晔, 方云, 陈韩婷, 高迪. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(9), 1933—1940) | |
| [15] | Ruta J., Perrier S., Ravelet C., Fize J., Peyrin E., Anal. Chem., 2009, 81, 7468—7473 |
| [16] | Cui L., Zou Y., Lin N. H., Zhu Z., Jenkins G., Yang C. Y., Anal. Chem., 2012, 84, 5535—5541 |
| [17] | Joshi V. G., Chindera K., Singh A. K., Sahoo A. P., Dighe V. D., Thakuria D., Kumar S., Anal. Chim. Acta, 2013, 795, 1—7 |
| [18] | Suprun E. V., Shilovskaya A. L., Lisitsa A. V., Bulko T. V., Shumyantseva V. V., Archakov A. I., Electroanalysis, 2011, 23, 1051—1057 |
| [19] | Mihailescu C. M., Stan D., Iosub R., Moldovan C., Savin M., Talanta, 2015, 132, 37—43 |
| [20] | Periyakaruppan A., Gandhiraman R. P., Meyyappan M., Koehne J. E., Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 3858—3863 |
| [21] | Wang Y., Ni Y., Talanta, 2014, 119, 320—330 |
| [22] | Okamoto F., Sohmiya K., Ohkaru Y., Kawamura K., Asayama K., Kimura H., Tanaka T., Clin. Chem. Lab. Med., 2000, 38(3), 231—238 |
| [1] | CHEN Weiqin, LYU Jiamin, YU Shen, LIU Zhan, LI Xiaoyun, CHEN Lihua, SU Baolian. Preparation of Organic Hybrid Mesoporous Beta Zeolite for Alkylation of Mesitylene with Benzyl Alcohol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220086. |
| [2] | SUN Quanhu, LU Tiantian, HE Jianjiang, HUANG Changshui. Advances in the Study of Heteratomic Graphdiyne Electrode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 366. |
| [3] | DING Ying-Tao, WANG Li-Heng, LI Fu-Xiao, GAO Feng, GAO Fei, WANG Qing-Xiang. Low-background Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Using an Electrically Neutral Osmium Complex as Hybridization Indicator [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(4): 823. |
| [4] | FAN Yu-Xia, TAN Hui, LIU Ling-Wei, WU Zhao-Yang, SHEN Guo-Li, YU Ru-Qin. Novel Nucleic Acid Signal Amplification Liquid Crystal Biosensor for Detection of p53 Gene Mutation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(4): 806. |
| [5] | XING Ya-Si, ZOU Neng-Li, MAO Hong-Ju, XU Xia, GE Yu-Qing, JIN Qing-Hui, ZHAO Jian-Long. Detection of Hepatitis B Virus DNA Hybridization Based on Dual Gold Nano-probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(07): 1420. |
| [6] | LIANG Xue-Ying, LIU Qiong, CHEN Ping, HUO Ke-Ke, HU Tian-Yong, NI Jia-Zuan. Screen and Verification of Interactive Protein of Selenoprotein K in Human Liver [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(02): 313. |
| [7] | LI Hui, ZHONG Wen-Ying*, XU Dan-Ke*. Preparation of Biotinylated Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application of Visual Detection Method for Protein Chip [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2010, 31(11): 2184. |
| [8] | XU Li-Fang, LI An-Yong*, LUO Hong-Juan, JI Hong-Bo. Theoretical Studies on Bifurcated Blue-shifted Dihydrogen Bonds of NH3BH3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(9): 1865. |
| [9] | ZHANG Yu, YU Hao, DONG Xiu-Ling, QIN Jian-Hua*, LIN Bin-Cheng*. Immobilization of DNA Hydrogel Plugs in Glass Microfluidic Channels and Its Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(6): 1128. |
| [10] | ZHU Xiang-Bin, AI Shi-Yun*, YIN Huan-Shun, SHI Wei-Jie, LIU Zhen-Zhen. Label-free Electrochemical Detection of Gene Mutation with the Electrode Modified by Polyamidoamine Dendrimers and Cobalt Hexacyanoferrate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2009, 30(12): 2387. |
| [11] | LIU Hong-Na1, LI Song1,2*, WANG Zhi-Fei2, HE Nong-Yue2, HE Quan-Guo1*. High-throughput SNP Genotyping Method with PCR on Magnetic Nanoparticles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2007, 28(6): 1035. |
| [12] | GU Yu1,3, DU Zhi-You2, LANG Qiu-Lei2, CHEN Ji-Shuang2, HE Nong-Yue3. Detection of Potato Spindle Tuber Viroid Using RNA Hybridized Chips [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2006, 27(11): 2106. |
| [13] | CAI Hong, WANG Yan-Qin, HE Pin-Gang, FANG Yu-Zhi . Studies on an Electrochemical DNA Biosensor Based on Gold Nanoparticle-labeled DNA Probe [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2003, 24(8): 1390. |
| [14] | CHENG Qiong, PENG Tu-Zhi. A Biosensor for Nucleic Acid Hybridization Using 2,3,5-Triphenyl-tetrazoliam Chloride as Electrochemical Intercalator [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(9): 1680. |
| [15] | DONG Li-Qin, ZHOU Jian-Zhang, WU Ling-Ling, DONG Ping, LIN Zhong-Hua . Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering(SERS) Studies on Adsorption Orientation on Self-assembled DNA [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2002, 23(12): 2303. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||