

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1210.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170078
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Deli1, YANG Pengyong1, WU Shengnan1, HE Sihui2, WANG Fangfang2,*( )
)
Received:2017-02-08
Online:2017-07-10
Published:2017-05-22
Contact:
WANG Fangfang
E-mail:wangff@zjnu.cn
Supported by:TrendMD:
CHEN Deli, YANG Pengyong, WU Shengnan, HE Sihui, WANG Fangfang. Ab initio Molecular Dynamics Simulations on the Structures and Stabilities of Pd Clusters Encapsulated UiO-66 Materials†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1210.
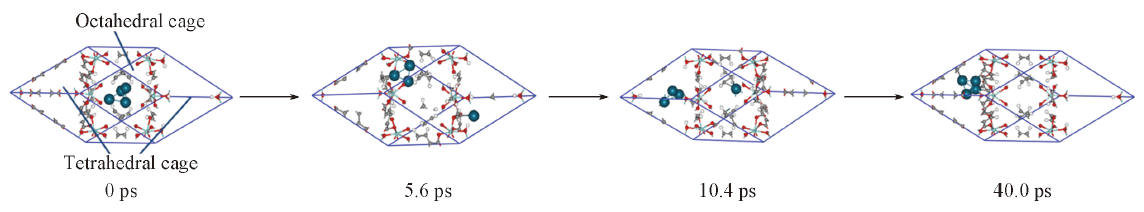
Fig.2 Diffusion path for Pd4 cluster from octahedral to tetrahedral cage in UiO-66The four snapshots represent different simulation time of 0, 5.6, 10.4, and 40.0 ps, respectively. The red, white, gray, cyan, and green balls represent the oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, zirconium, and palladium atoms, respectively.
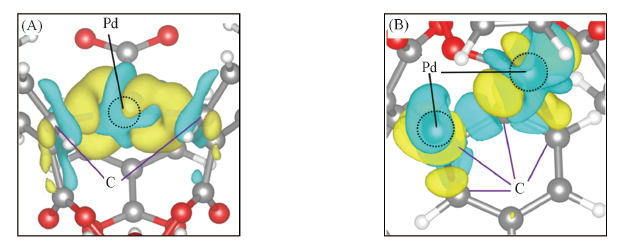
Fig.3 Computed charge density difference of Pd1@UiO-66(A) and Pd2@UiO-66(B) The yellow and blue colors represent the electron accumulation and depletion, respectively.
| Cluster | n | EPd(n)/eV | Charge/|e| | Ed/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd1 | 1 | -1.99 | 0.21 | 0.25 |
| Pd4 | 4 | -2.22 | 0.27 | 0.38 |
| Pd8 | 8 | -2.59 | 0.69 | 1.41 |
| Pd12 | 12 | -2.82 | 0.92 | 2.82 |
| Pd16 | 16 | -2.91 | 1.21 | 3.02 |
| Pd20 | 20 | -2.91 | 1.55 | 2.98 |
| Pd24 | 24 | -2.92 | 1.78 | 3.75 |
| Pd28 | 28 | -2.93 | 2.00 | 4.67 |
| Pd32 | 32 | -2.90 | 1.89 | 6.86 |
Table 1 Average binding energy, charge transfer, and deformation energy of Pdn@UiO-66
| Cluster | n | EPd(n)/eV | Charge/|e| | Ed/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd1 | 1 | -1.99 | 0.21 | 0.25 |
| Pd4 | 4 | -2.22 | 0.27 | 0.38 |
| Pd8 | 8 | -2.59 | 0.69 | 1.41 |
| Pd12 | 12 | -2.82 | 0.92 | 2.82 |
| Pd16 | 16 | -2.91 | 1.21 | 3.02 |
| Pd20 | 20 | -2.91 | 1.55 | 2.98 |
| Pd24 | 24 | -2.92 | 1.78 | 3.75 |
| Pd28 | 28 | -2.93 | 2.00 | 4.67 |
| Pd32 | 32 | -2.90 | 1.89 | 6.86 |
| [1] | Zhou H. C., Kitagawa S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5415—5418 |
| [2] | Zhu Q. L., Xu Q., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 5468—5512 |
| [3] | Wu J., Zhao B. W., Huang C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(6), 1069—1074 |
| (吴娟, 赵博文, 黄超.高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6), 1069—1074) | |
| [4] | Du T., Long Y., Tang Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(2),225—230 |
| (杜涛, 龙渊, 汤琦,.高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(2), 225—230) | |
| [5] | Lu H. S., Bai L., Xiong W. W., Li P., Ding J., Zhang G., Wu T., Zhao Y., Lee J. M., Yang Y., Geng B., Zhang Q., Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 8529—8537 |
| [6] | Gao J., Ye K., Yang L., Xiong W. W., Ye L., Wang Y., Zhang Q., Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53, 691—693 |
| [7] | Zhang W., Lu G., Cui C., Liu Y., Li S., Yan W., Xing C., Chi Y. R., Yang Y., Huo F., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 4056—4060 |
| [8] | Zhu Q. L., Li J., Xu Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 10210—10213 |
| [9] | Lu G., Li S., Guo Z., Farha O. K., Hauser B. G., Qi X., Wang Y., Wang X., Han S., Liu X., DuChene J. S., Zhang H., Zhang Q., Chen X., Ma J., Loo S. C., Wei W. D., Yang Y., Hupp J. T., Huo F., Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 310—316 |
| [10] | Sumida K., Rogow D. L., Mason J. A., McDonald T. M., Bloch E. D., Herm Z. R., Bae T. H., Long J. R., Chem. Rev., 2012, 112, 724—781 |
| [11] | Schröder F., Esken D., Cokoja M., van den Berg M. W., Lebedev O. I., van Tendeloo G., Walaszek B., Buntkowsky G., Limbach H. H., Chaudret B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 6119—6130 |
| [12] | Sabo M., Henschel A., Fröde H., Klemm E., Kaskel S., J. Mater. Chem., 2007, 17, 3827—3832 |
| [13] | Proch S., Herrmannsdörfer J., Kempe R., Kern C., Jess A., Seyfarth L., Senker J., Chem. Eur. J., 2008, 14, 8204—8212 |
| [14] | Park Y. K., Choi S. B., Nam H. J., Jung D. Y., Ahn H. C., Choi K., Furukawa H., Kim J., Chem. Commun., 2010, 46, 3086—3088 |
| [15] | Huang Y., Zheng Z., Liu T., Lü J., Lin Z., Li H., Cao R., Catal. Commun., 2011, 14, 27—31 |
| [16] | Hermes S., Schröter M. K., Schmid R., Khodeir L., Muhler M., Tissler A., Fischer R. W., Fischer R. A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2005, 44, 6237—6241 |
| [17] | Esken D., Turner S., Lebedev O. I., van Tendeloo G., Fischer R. A., Chem. Mater., 2010, 22, 6393—6401 |
| [18] | Dhakshinamoorthy A., Garcia H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 5262—5284 |
| [19] | Burtch N. C., Jasuja H., Walton K. S., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 10575—10612 |
| [20] | Bo X. F., Wu P. Y., Liu D. H., Yang Q. Y., Ma Q. T., Lan L., Wang S. H., Zhang Y., Zhong C. L., J. Chem. Ind.Eng.(China), 2014, 65, 1644—1651 |
| (薄晓帆, 吴平易, 刘大欢, 阳庆元, 麻沁甜, 兰玲, 王少华, 张轶, 仲崇立. 化工学报, 2014, 65, 1644—1651) | |
| [21] | Vilhelmsen L. B., Walton K. S., Sholl D. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 12807—12816 |
| [22] | Vilhelmsen L. B., Sholl D. S., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2012, 3, 3702—3706 |
| [23] | Cavka J. H., Jakobsen S., Olsbye U., Guillou N., Lamberti C., Bordiga S., Lillerud K. P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130, 13850—13851 |
| [24] | Wu R., Qian X., Zhou K., Liu H., Yadian B., Wei J., Zhu H., Huang Y., J. Mater. Chem. A,2013, 1, 14294—14299 |
| [25] | Dong W., Feng C., Zhang L., Shang N., Gao S., Wang C., Wang Z., Catal. Lett., 2016, 146, 117—125 |
| [26] | Chen D. L., Wu S., Yang P., He S., Dou L., Wang F. F., J. Phys. Chem.C,2017, 121, 8857—8863 |
| [27] | Larsen A. H., Kleis J., Thygesen K. S., Nørskov J. K., Jacobsen K. W., Phys. Rev.B,2011, 84, 245429 |
| [28] | Wang L. L., Johnson D. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2007, 129, 3658—3664 |
| [29] | Wu H., Chua Y. S., Krungleviciute V., Madhusudan T., Chen P., Yildirim T., Zhou W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(28), 10525—10532 |
| [30] | Tang W., Sanville E., Henkelman G., J. Phys.: Condens.Matter,2009, 21, 084204 |
| [31] | Sanville E., Kenny S. D., Smith R., Henkelman G., J. Comput. Chem., 2007, 28, 899—908 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | LI Hua, YANG Ke, HUANG Junfeng, CHEN Fengjuan. Design and Construction of UiO-66-NH2/wood Composite for Efficient Removal of Trace Heavy Metal Ions from Water [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210701. |
| [4] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [5] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [6] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [7] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [8] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [9] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [10] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [11] | LI Meiyan, CHEN Zijuan, WANG Shuhua, CHEN Chao. Zr-MOF Hollow Nanospheres Supported Ionic Liquid for CO2 Cycloaddition Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2474. |
| [12] | CHENG Xiao, K BORA Debajeet, GLANS Per⁃Anders, GUO Jinghua, LUO Yi. An In-depth Theoretical Study of Ligand Field and Charge Transfer Effects on Co2+2pL2,3-edges X-ray Absorption Spectra [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2197. |
| [13] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [14] | LIU Yang, LI Qingbo, SUN Jie, ZHAO Xian. Direct Synthesis of Graphene on AlN Substrates via Ga Remote Catalyzation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2271. |
| [15] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||