

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (10): 20220290.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220290
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHOU Chengsi1, ZHAO Yuanjin1, HAN Meichen1, YANG Xia2, LIU Chenguang1, HE Aihua1( )
)
Received:2022-04-29
Online:2022-10-10
Published:2022-05-24
Contact:
HE Aihua
E-mail:ahhe@qust.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290.
| ED | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔE(kJ/mol) | -165.72 | -164.50 | -158.77 | -158.23 |
| ΔG(kJ/mol) | -104.06 | -97.11 | -87.74 | -85.68 |
Table 1 Adsorption energy of electron donor on carrier
| ED | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ΔE(kJ/mol) | -165.72 | -164.50 | -158.77 | -158.23 |
| ΔG(kJ/mol) | -104.06 | -97.11 | -87.74 | -85.68 |
| ED | Name | Structure | Electron density[ | Volume[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Dimethyl dimethoxysilane | 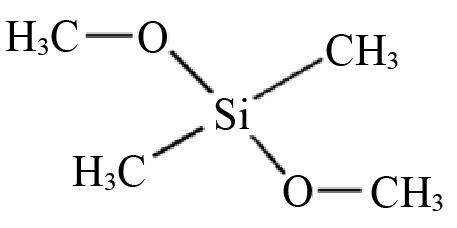 | 0.6802 | 0.1201 |
| D2 | Dibutyl dimethoxysilane | 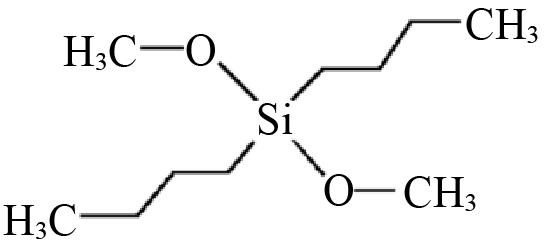 | 0.6892 | 0.2221 |
| D3 | Diphenyl dimethoxysilane | 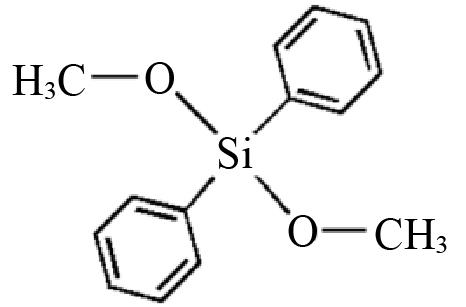 | 0.6969 | 0.2312 |
| D4 | Dicyclopentyl dimethoxysilane | 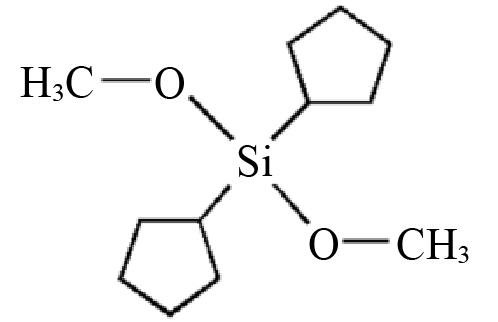 | — | — |
Table 2 Structures and parameters of electron donors
| ED | Name | Structure | Electron density[ | Volume[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| D1 | Dimethyl dimethoxysilane |  | 0.6802 | 0.1201 |
| D2 | Dibutyl dimethoxysilane |  | 0.6892 | 0.2221 |
| D3 | Diphenyl dimethoxysilane |  | 0.6969 | 0.2312 |
| D4 | Dicyclopentyl dimethoxysilane |  | — | — |
| Run | ED | n(ED)/n(Ti) | CA/ (kg?gTi-1?h-1) | Mass fraction(%) | [C*]/[Ti] (%) | kp/ (L?mol-1·s-1) | GPC | DSC f | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aP b | MiPP c | iPP d | iPB e | 10-4Mw | Mw/Mn | Tm,PB/℃ | Xc,PB(%) | Tm,PP/℃ | Xc,PP(%) | ||||||
| PP1 | No | 0 | 28.7 | 7.6 | 10.5 | 81.9 | — | 22.2 | 141.6 | 64 | 9.2 | — | — | 160.1 | 34.7 |
| PP2 | D1 | 5 | 23.0 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 81.4 | — | 16.4 | 154.3 | 73 | 7.6 | — | — | 159.1 | 34.1 |
| PP3 | D1 | 10 | 22.4 | 8.3 | 7.6 | 84.1 | — | 15.7 | 156.9 | 77 | 6.5 | — | — | 160.1 | 35.4 |
| PP4 | D1 | 15 | 24.4 | 12.6 | 9.1 | 78.3 | — | 16.3 | 163.5 | 74 | 6.6 | — | — | 159.4 | 30.9 |
| PP5 | D1 | 20 | 16.3 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 86.3 | — | 14.2 | 125.8 | 82 | 6.6 | — | — | 159.4 | 32.4 |
| PP6 | D2 | 5 | 18.9 | 1.8 | 13.8 | 84.4 | — | 13.6 | 152.6 | — | — | — | — | 161.9 | 44.4 |
| PP7 | D2 | 10 | 19.8 | 3.2 | 10.0 | 86.8 | — | 13.9 | 155.9 | 76 | 5.6 | — | — | 163.5 | 43.9 |
| PP8 | D2 | 15 | 17.0 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 92.5 | — | 11.8 | 157.8 | — | — | — | — | 162.2 | 41.2 |
| PP9 | D2 | 20 | 14.4 | 1.4 | 7.4 | 91.2 | — | 10.6 | 148.9 | — | — | — | — | 162.7 | 32.6 |
| PP10 | D3 | 5 | 20.5 | 3.0 | 8.6 | 88.4 | — | 15.6 | 143.8 | — | — | — | — | 163.4 | 43.1 |
| PP11 | D3 | 10 | 19.9 | 2.8 | 7.3 | 89.9 | — | 14.6 | 150.0 | 71 | 5.8 | — | — | 164.5 | 46.9 |
| PP12 | D3 | 15 | 18.6 | 2.8 | 6.7 | 90.5 | — | 13.0 | 157.4 | — | — | — | — | 164.0 | 42.4 |
| PP13 | D3 | 20 | 18.5 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 92.0 | — | 13.2 | 152.9 | — | — | — | — | 163.6 | 45.7 |
| PP18 | D4 | 5 | 19.3 | 2.5 | 7.7 | 89.8 | — | 15.3 | 138.4 | 82 | 12.8 | — | — | 161.5 | 46.5 |
| PP19 | D4 | 10 | 18.3 | 1.8 | 7.5 | 90.7 | — | 13.8 | 146.1 | 113 | 9.4 | — | — | 163.3 | 48.3 |
| PP20 | D4 | 15 | 20.0 | 1.7 | 7.3 | 91.0 | — | 13.3 | 165.6 | 126 | 9.0 | — | — | 162.9 | 48.7 |
| PP21 | D4 | 20 | 18.2 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 92.8 | — | 12.6 | 158.8 | 122 | 8.7 | — | — | 163.4 | 48.8 |
| PBA1 | N0 | 0 | 41.9 | 6.1 | — | 73.1 | 20.8 | 5.8 | — | 103 | 6.5 | 98.8 | 1.9 | 152.5 | 42.1 |
| PBA2 | D2 | 10 | 34.7 | 3.7 | — | 66.6 | 29.7 | 5.0 | — | 91 | 6.7 | 101.9 | 12.0 | 154.1 | 42.9 |
| PBA3 | D3 | 10 | 30.9 | 2.6 | — | 83.0 | 14.4 | 4.3 | — | 76 | 5.5 | 102.6 | 3.3 | 154.6 | 44.9 |
| PBA4 | D4 | 10 | 31.8 | 3.2 | — | 85.2 | 11.6 | 3.1 | — | 111 | 5.2 | 107.6 | 38.1 | 154.9 | 37.1 |
Table 3 Summary for the olefin polymerizations and polymer characterization catalyzed by the TiCl4/MgCl2/ID-AlEt3-ED system a
| Run | ED | n(ED)/n(Ti) | CA/ (kg?gTi-1?h-1) | Mass fraction(%) | [C*]/[Ti] (%) | kp/ (L?mol-1·s-1) | GPC | DSC f | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| aP b | MiPP c | iPP d | iPB e | 10-4Mw | Mw/Mn | Tm,PB/℃ | Xc,PB(%) | Tm,PP/℃ | Xc,PP(%) | ||||||
| PP1 | No | 0 | 28.7 | 7.6 | 10.5 | 81.9 | — | 22.2 | 141.6 | 64 | 9.2 | — | — | 160.1 | 34.7 |
| PP2 | D1 | 5 | 23.0 | 9.6 | 9.0 | 81.4 | — | 16.4 | 154.3 | 73 | 7.6 | — | — | 159.1 | 34.1 |
| PP3 | D1 | 10 | 22.4 | 8.3 | 7.6 | 84.1 | — | 15.7 | 156.9 | 77 | 6.5 | — | — | 160.1 | 35.4 |
| PP4 | D1 | 15 | 24.4 | 12.6 | 9.1 | 78.3 | — | 16.3 | 163.5 | 74 | 6.6 | — | — | 159.4 | 30.9 |
| PP5 | D1 | 20 | 16.3 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 86.3 | — | 14.2 | 125.8 | 82 | 6.6 | — | — | 159.4 | 32.4 |
| PP6 | D2 | 5 | 18.9 | 1.8 | 13.8 | 84.4 | — | 13.6 | 152.6 | — | — | — | — | 161.9 | 44.4 |
| PP7 | D2 | 10 | 19.8 | 3.2 | 10.0 | 86.8 | — | 13.9 | 155.9 | 76 | 5.6 | — | — | 163.5 | 43.9 |
| PP8 | D2 | 15 | 17.0 | 1.5 | 6.0 | 92.5 | — | 11.8 | 157.8 | — | — | — | — | 162.2 | 41.2 |
| PP9 | D2 | 20 | 14.4 | 1.4 | 7.4 | 91.2 | — | 10.6 | 148.9 | — | — | — | — | 162.7 | 32.6 |
| PP10 | D3 | 5 | 20.5 | 3.0 | 8.6 | 88.4 | — | 15.6 | 143.8 | — | — | — | — | 163.4 | 43.1 |
| PP11 | D3 | 10 | 19.9 | 2.8 | 7.3 | 89.9 | — | 14.6 | 150.0 | 71 | 5.8 | — | — | 164.5 | 46.9 |
| PP12 | D3 | 15 | 18.6 | 2.8 | 6.7 | 90.5 | — | 13.0 | 157.4 | — | — | — | — | 164.0 | 42.4 |
| PP13 | D3 | 20 | 18.5 | 1.6 | 6.4 | 92.0 | — | 13.2 | 152.9 | — | — | — | — | 163.6 | 45.7 |
| PP18 | D4 | 5 | 19.3 | 2.5 | 7.7 | 89.8 | — | 15.3 | 138.4 | 82 | 12.8 | — | — | 161.5 | 46.5 |
| PP19 | D4 | 10 | 18.3 | 1.8 | 7.5 | 90.7 | — | 13.8 | 146.1 | 113 | 9.4 | — | — | 163.3 | 48.3 |
| PP20 | D4 | 15 | 20.0 | 1.7 | 7.3 | 91.0 | — | 13.3 | 165.6 | 126 | 9.0 | — | — | 162.9 | 48.7 |
| PP21 | D4 | 20 | 18.2 | 1.8 | 5.4 | 92.8 | — | 12.6 | 158.8 | 122 | 8.7 | — | — | 163.4 | 48.8 |
| PBA1 | N0 | 0 | 41.9 | 6.1 | — | 73.1 | 20.8 | 5.8 | — | 103 | 6.5 | 98.8 | 1.9 | 152.5 | 42.1 |
| PBA2 | D2 | 10 | 34.7 | 3.7 | — | 66.6 | 29.7 | 5.0 | — | 91 | 6.7 | 101.9 | 12.0 | 154.1 | 42.9 |
| PBA3 | D3 | 10 | 30.9 | 2.6 | — | 83.0 | 14.4 | 4.3 | — | 76 | 5.5 | 102.6 | 3.3 | 154.6 | 44.9 |
| PBA4 | D4 | 10 | 31.8 | 3.2 | — | 85.2 | 11.6 | 3.1 | — | 111 | 5.2 | 107.6 | 38.1 | 154.9 | 37.1 |
| 1 | Busico V., Corradini P., Martino L. D., Proto A., Sauino V., Makromol. Chem., 1985, 186(6), 1279—1288 |
| 2 | Kashiwa N., Polym. J., 1980, 12(9), 603—608 |
| 3 | Zhang H. X., Lee Y. J., Park J. R., Lee D. H., Yoon K. B., Makromol. Res., 2011, 19(6), 622—628 |
| 4 | Garoff T., Virkkunen V., Jääskeläinen P., Vestberg T., Eur. Polym. J., 2003, 39(8), 1679—1685 |
| 5 | Ma Z. L., Wang L., Wang W. Q., Feng L. F., Gu X. P., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2005, 95(3), 738—742 |
| 6 | Taniike T., Terano M., Macromol. Rapid. Commun., 2007, 28(18/19), 1918—1922 |
| 7 | Monaco G., Toto M., Guerra G., Piemontesi F., Cavallo L., Macromolecules, 2000, 33(24), 8953—8962 |
| 8 | Brambilla L., Zerbi G., Fabrizio P., Nascetti S., Morini G., J. Mol. Catal. A⁃Chem., 2007, 263(1/2), 103—111 |
| 9 | D’Amore M., Thushara K. S., Piovano A., Causà M., Bordiga S., Groppo E., ACS Catal., 2016, 6(9), 5786—5796 |
| 10 | Bahri⁃Laleh N., Hanifpour A., Mirmohammadi S. A., Poater A., Nekoomanesh⁃Haghighi M., Talarico G., Cavallo L., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2018, 84, 89—114 |
| 11 | Stukalov D. V., Zakharov V. A., Potapov A. G., Bukatov G. D., J. Catal., 2009, 266(1), 39—49 |
| 12 | D’Amore M., Credendino R., Budzelaar P. H. M., Causá M., Busico V., J. Catal., 2012, 286, 103—110 |
| 13 | Bazhenov A., Linnolahti M., Pakkanen T. A., Denifl P., Leinonen T., J. Phys. Chem. C., 2014, 118(9), 4791—4796 |
| 14 | Bazhenov A. S., Denifl P., Leinonen T., Pakkanen A., Linnolahti M., Pakkanen T. A., J. Phys. Chem. C., 2014, 118(48), 27878—27883 |
| 15 | Kuklin M. S., Bazhenov A. S., Denifl P., Lenonen T., Linnolahti M., Pakkanen T. A., Surf. Sci., 2015, 635, 5—10 |
| 16 | Nikolaeva M., Matsko M., Zakharov V., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2018, 135(23), 46291 |
| 17 | Alshaiban A., Soares J. B. P., Macromol. React. Eng., 2012, 6(6/7), 265—274 |
| 18 | Alshaiban A., Soares J. B. P., Macromol. React. Eng., 2013, 7(3/4), 135—145 |
| 19 | Alshaiban A., Soares J. B. P., Macromol. React. Eng., 2014, 8(10), 723—735 |
| 20 | Weng Y. H., Jiang B. Y., Fu Z. H., Fan Z. Q., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2018, 135(32), 46605 |
| 21 | Wondimagegn T., Ziegler T., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(1), 1027—1033 |
| 22 | Zhou Q., Zheng T., Li H. Y., Li Q., Zhang Y., Zhang L. Y., Hu Y. L., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2014, 53(46), 17929—17936 |
| 23 | Khatri V., Sahoo U., Kaur S., Rani R., Singh G., Kapur G. S., Kashyap H. K., New. J. Chem., 2020, 44(17), 6845—6852 |
| 24 | Shen X. R., Fu Z. S., Hu J., Wang Q., Fan Z. Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(29), 15174—15182 |
| 25 | Ren H. G., Yang M., Zhang B. J., Ren X. F., Liu B. Y., Wang Y. J., Kim Il., Macromol. Res., 2012, 20(9), 985—989 |
| 26 | He A. H., Zheng W. P., Shi Y. W., Liu G. Q., Yao W., Huang B. C., Polym Int., 2012, 61(10), 1575—1581 |
| 27 | He A. H., Shi Y. W., Liu G. Q., Yao W., Huang B. C., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2012, 30(5), 632—641 |
| 28 | Jiang B. Y., Shao H. F., Nie H. R., He A. H., Polym. Chem., 2015, 6(17), 3315—3323 |
| 29 | Zheng W. P., Dua D. L., He A. H., Ma Y. P., Shao H. F., Liu C. G., Hsiao B. S., Mater. Today Commun., 2020, 23, 100868 |
| 30 | Zheng W. P., Han M. C., Zhao Y. J., Shao H. F., He A. H., Polym. Test., 2021, 94, 107011 |
| 31 | Zheng W. P., He A. H., Liu C. G., Shao H. F., Wang R. G., Polymer, 2020, 21, 122998 |
| 32 | Peng W., Qi P. Y., Dong K. X., He A. H., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2020, 78(12), 1418—1425 |
| 彭伟, 戚佩瑶, 董凯旋, 贺爱华. 化学学报, 2020, 78(12), 1418—1425 | |
| 33 | Zheng W. P., Zhao Y. J., Han M. C., Zhou C. S., He A. H., Polymer, 2021, 228, 123925 |
| 34 | Ma Y. P., Zhang N., Zheng W. P., Liu C. G., He A. H., Chinese J. Polym. Sci., 2020, 38(12), 1382—1391 |
| 35 | Ma Y. P., He A. H., Liu C. G., Polymer, 2021, 228, 123901 |
| 36 | Ma Y. P., Zhang N., Zheng W. P., Xiao W. J., Liu C. G., He A. H., Shao H. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(12), 2851—2860 |
| 马亚萍, 张宁, 郑伟平, 肖玮佳, 刘晨光, 贺爱华, 邵华锋. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(12), 2851—2860 | |
| 37 | Nie H. R., Xiao W. J., Ma Y. P., Liu C. G., He A. H., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2019, 58, 6919—6924 |
| 38 | Xu Y., Ma Y. P., Liu C. G., Men Y. F., He A. H., Polymer, 2019, 182, 121817—121822 |
| 39 | Jiang B. Y., Shao H. F., Nie H. R., He A. H., Polym. Chem., 2015, 6(17), 3315—3323 |
| 40 | Qiao Y. N., Wang Q., Men Y. F., Macromolecules, 2016, 49(10),5126—5136 |
| 41 | Wunderlich B., Polym. Eng. Sci., 1978, 18(6), 431—436 |
| 42 | Shen X. R., Hu J., Fu Z. S., Lou J. Q., Fan Z. Q., Catal. Commun., 2013, 30, 66—69 |
| 43 | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega Millam N. J., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R. E., Stratmann O., Yazyev A. J., Austin R., Cammi C., Pomelli J. W., Ochterski R., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision A.1, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| 44 | Breuza E., Antinucci G., Budzelaar P. H. M., Busico V., Correa A., Ehm C., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018, 122(16), 9046—9053 |
| 45 | Okano T., Chida K., Furuhashi H., Nakano A., Ueki S., Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal., 1990, 56, 177—183 |
| [1] | FAN Jianling, TANG Hao, QIN Fengjuan, XU Wenjing, GU Hongfei, PEI Jiajing, CEHN Wenxing. Nitrogen Doped Ultra-thin Carbon Nanosheet Composited Platinum-ruthenium Single Atom Alloy Catalyst for Promoting Electrochemical Hydrogen Evolution Process [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220366. |
| [2] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [3] | JIANG Shenghan, CAO Changlin, XIAO Liren, YANG Tang, QIAN Qingrong, CHEN Qinghua. Preparation of Composite Semiconductor Micro-sheets with UV Shielding Performance and Its Application in Polypropylene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [4] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [5] | FAN Xiaoyong, ZHU Yongqiang, WU Yan, ZHANG Shuai, XU Lei, GOU Lei, LI Donglin. Three-dimensional Porous Sn-Zn Alloy Towards Uniform Zn Plating/stripping [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210861. |
| [6] | LI Weihui, LI Haobo, ZENG Cheng, LIANG Haoyue, CHEN Jiajun, LI Junyong, LI Huiqiao. Hot-pressed PVDF-based Difunctional Protective Layer for Lithium Metal Anodes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210629. |
| [7] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [8] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [9] | JIANG Baozheng, HUANG Wenting, LIU Wenbao, GUO Rongsheng, XU Chengjun, KANG Feiyu. Preparation of Nano-copper Modified Three-dimensional Zinc Mesh Electrode and Its Performance as Anode for Zinc-ion Batteries [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220257. |
| [10] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [11] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [12] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [13] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [14] | LIANG Xuejing, ZHAO Fulai, WANG Yu, ZHANG Yichao, WANG Yaling, FENG Yiyu, FENG Wei. Preparation and Photoelectric Properties of Germanium Sulphoselenide Photodetector [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2661. |
| [15] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||