

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (5): 892.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190673
• 庆祝《高等学校化学学报》复刊40周年专栏 • 上一篇 下一篇
收稿日期:2019-12-16
出版日期:2020-05-10
发布日期:2020-03-19
通讯作者:
李娟
E-mail:lijuan@fzu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Jingying1,2,CHEN Chen1,2,LI Juan1,*( ),YANG Huanghao1
),YANG Huanghao1
Received:2019-12-16
Online:2020-05-10
Published:2020-03-19
Contact:
Juan LI
E-mail:lijuan@fzu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
从利用物理刺激和生物大分子诱导两个方面综述了人工调控细胞表面受体聚集状态的策略. 前者是利用相应的纳米材料在光、 磁场、 温度等物理刺激作用下实现人工调控受体聚集; 后者则利用包括蛋白/多肽类分子、 核酸在内的生物分子的自组装对其靶向识别的受体进行人工调控. 系统介绍了相关研究领域取得的最新进展, 并阐述和展望了该领域现存的挑战和发展方向.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李婧影, 陈琛, 李娟, 杨黄浩. 人工调控细胞表面受体聚集状态及功能. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(5): 892.
LI Jingying, CHEN Chen, LI Juan, YANG Huanghao. Artificial Regulation of Receptor Clustering and Function on Cell Surface †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(5): 892.
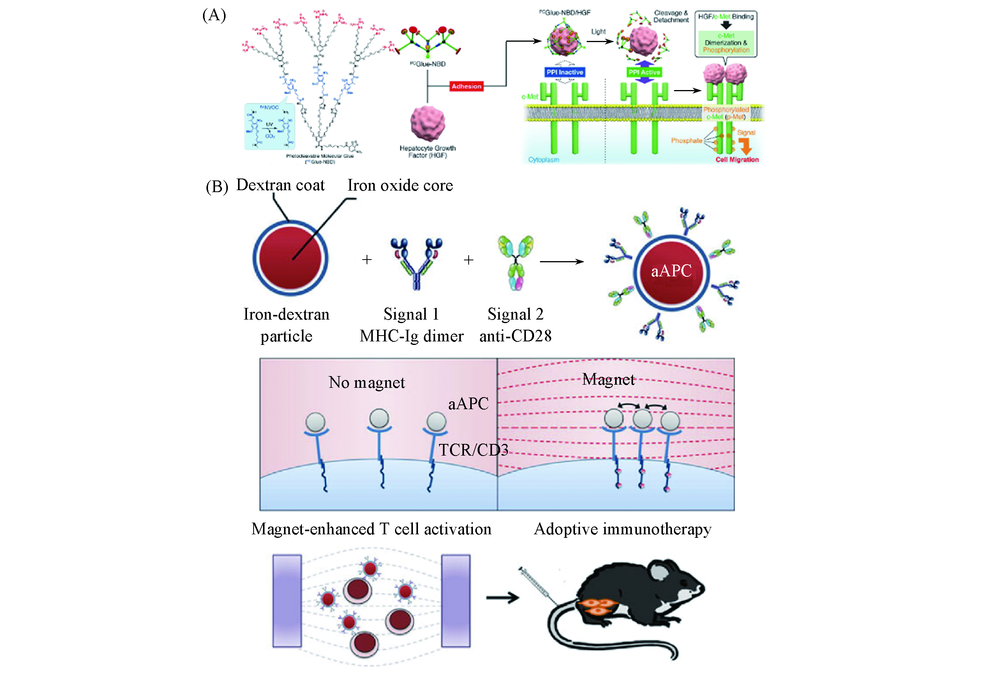
Fig.2 Chemical structure of PCGlue-NBD and schematic illustration of the mechanistic role of PCGlue-NBD for turning off and on Met dimerization caused by the interaction between Met and its ligand HGF(A)[23], schematic representation of nano-aAPC synthesis by coupling MHC-Ig dimers and co-stimulatory anti-CD28 to iron-dextran nanoparticles(B)[31] (A) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society.
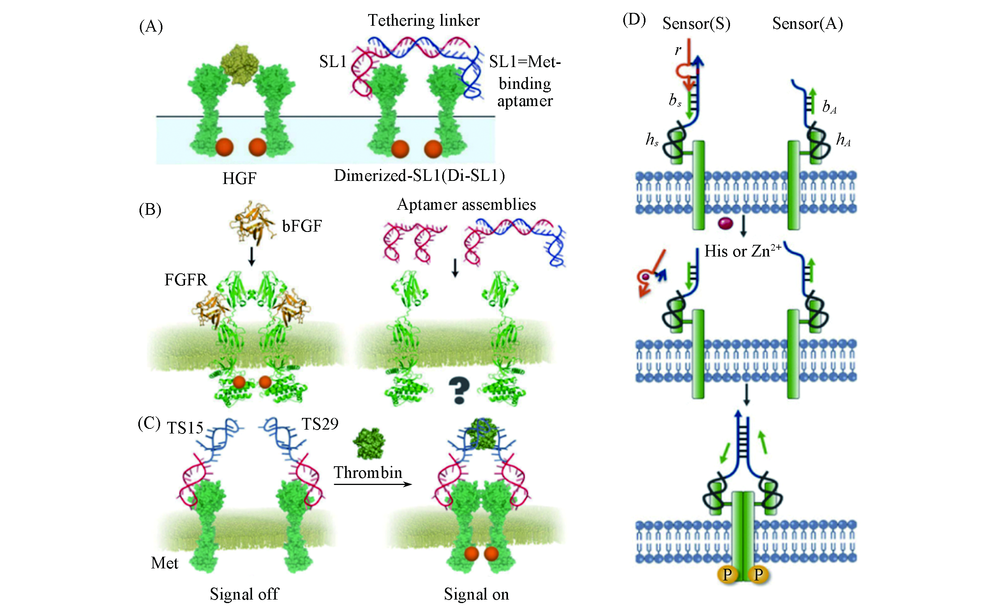
Fig.3 Schematic representation of DNA-based HGF mimetic(A)[49] and FGFR activation induced by FGF(left) or designed aptamer assemblies(right)(B)[50], DRIPaR for inducing thrombin-dependent Met activation, and their influences in the p-Met expression level in A549 cells(C)[51], histidine or Zn2+ DNAzyme-based D-CID of Met activation(D)[52] (A) Copyright 2016, John Wiley and Sons; (B) Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry; (C) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (D) Copyright 2018, John Wiley and Sons.
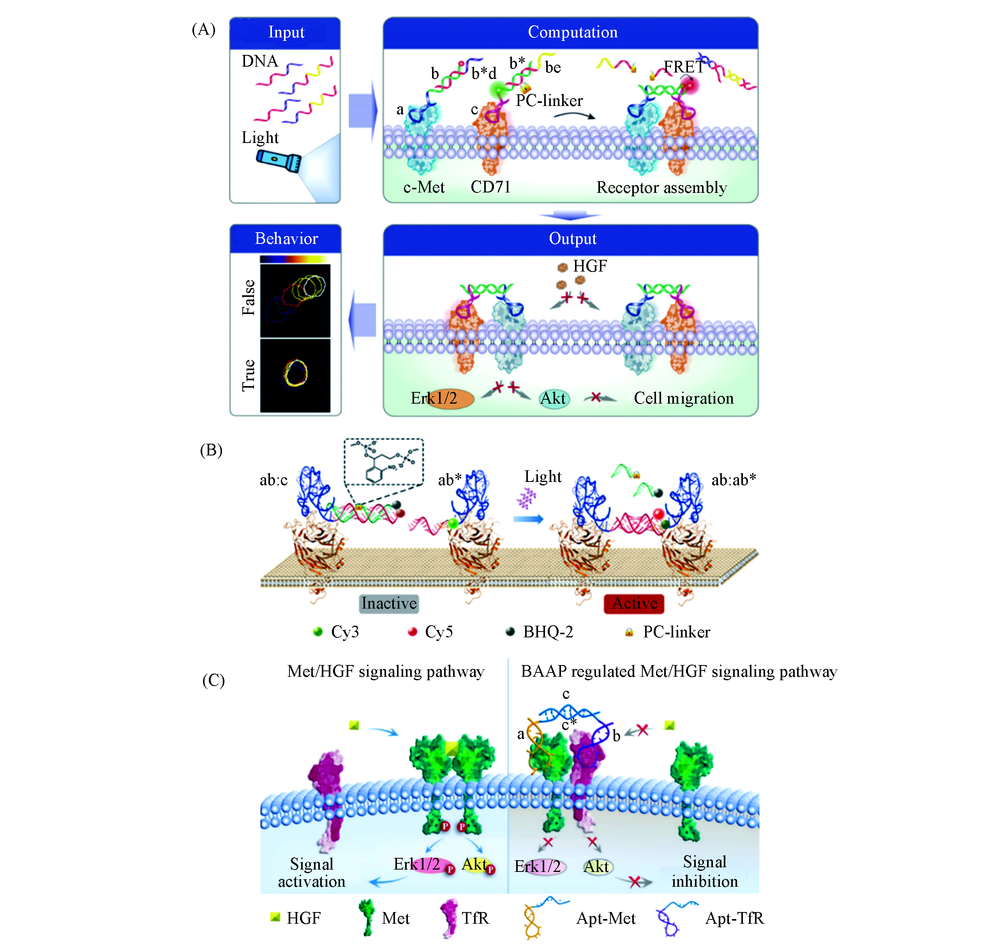
Fig.4 Schematic representation of logic-based aptamer-controlled receptor assembly for modulation of cellular signal transduction(A)[53] and photo-controlled DNA assembly approach for the receptor dimerization and signaling activation(B)[54], BAAP strategy to selectively regulate Met receptor function and downstream signaling pathways(C)[56] (A) Copyright 2019, John Wiley and Sons; (B) Copyright 2018, John Wiley and Sons; (C) Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
| [1] | Bradshaw R. A., Dennis E. A., Handbook of Cell Signaling, Academic Press, Salt Lake City, 2009, 1—384 |
| [2] | Allen S. J., Crown S. E., Handel T. M., Annu. Rev. Immunol., 2007,25(1), 787—820 |
| [3] |
Campbell I. D., Humphries M. J., Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 2011,3(3), a004994
doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a004994 URL pmid: 21421922 |
| [4] | Noriega-Guerra H., Freitas V. M., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2018,19(11), 3300 |
| [5] |
Garcia-Parajo M. F., Cambi A., Torreno-Pina J. A., Thompson N., Jacobson K., J. Cell Sci., 2014,127(23), 4995—5005
doi: 10.1242/jcs.146340 URL pmid: 25453114 |
| [6] |
Heldin C. H., Cell, 1995,80(2), 213—223
doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90404-2 URL pmid: 7834741 |
| [7] |
Zhang K., Gao H., Deng R., Li J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019,58(15), 4790—4799
doi: 10.1002/anie.201809006 URL pmid: 30328227 |
| [8] |
Taylor M. J., Husain K., Gartner Z. J., Mayor S., Vale R. D., Cell, 2017,169(1), 108—119
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.03.006 URL pmid: 28340336 |
| [9] |
Kanchanawong P., Shtengel G., Pasapera A. M., Ramko E. B., Davidson M. W., Hess H. F., Waterman C. M., Nature, 2010,468(7323), 580—584
doi: 10.1038/nature09621 URL pmid: 21107430 |
| [10] |
Iwamoto D. V., Calderwood D. A., Curr. Opin. Cell Biol., 2015,36, 41—47
doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2015.06.009 URL pmid: 26189062 |
| [11] |
Jorissen R. N., Walker F., Pouliot N., Garrett T. P. J., Ward C. W., Burgess A. W., Exp. Cell Res., 2003,284(1), 31—53
doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(02)00098-8 URL pmid: 12648464 |
| [12] |
Hartwell B. L., Martinez-Becerra F. J., Chen J., Shinogle H., Sarnowski M., Moore D. S., Berkland C., Biomacromolecules, 2016,17(3), 710—722
doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.5b01097 URL pmid: 26771518 |
| [13] |
Singh S. S., Jois S. D., Adv. Protein Chem. Struct. Biol., 2018,111, 1—59
doi: 10.1016/bs.apcsb.2017.08.003 URL pmid: 29459028 |
| [14] |
Di Liberto V., Mudo G., Belluardo N ., Neuropharmacology, 2019,152, 67—77
doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.11.018 URL pmid: 30445101 |
| [15] |
Fribourg M., Moreno J. L., Holloway T., Provasi D., Baki L., Mahajan R., Park G., Adney S. K., Hatcher C., Eltit J. M., Ruta J. D., Albizu L., Li Z., Umali A., Shim J., Fabiato A., MacKerell A. D. Jr., Brezina V., Sealfon S. C., Filizola M., Gonzalez-Maeso J., Logothetis D. E., Cell, 2011,147(5), 1011—1023
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.055 URL pmid: 22118459 |
| [16] |
Voss S., Klewer L., Wu Y. W., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2015,28, 194—201
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2015.09.003 URL pmid: 26431673 |
| [17] |
Goglia A. G., Toettcher J. E., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2019,48, 106—113
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.11.010 URL pmid: 30529586 |
| [18] |
Liu Q., Tucker C. L., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2017,40, 17—23
doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2017.05.001 URL pmid: 28527343 |
| [19] |
Beyer H. M., Naumann S., Weber W., Radziwill G., Biotechnol. J., 2015,10(2), 273—283
doi: 10.1002/biot.201400077 URL pmid: 25216399 |
| [20] |
Kim K. S., Seeley R. J., Sandoval D. A., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2018,19(4), 185—196
doi: 10.1038/nrn.2018.8 URL pmid: 29467468 |
| [21] |
Becnel J., Johnson O., Majeed Z. R., Tran V., Yu B., Roth B. L., Cooper R. L., Kerut E. K., Nichols C. D., Cell Rep., 2013,4(5), 1049—1059
doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.08.003 URL pmid: 24012754 |
| [22] |
Li W., Yan Z., Ren J., Qu X., Chem. Soc. Rev, 2018,47(23), 8639—8684
doi: 10.1039/c8cs00053k URL pmid: 30283962 |
| [23] |
Mogaki R., Okuro K., Ueki R., Sando S., Aida T ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019,141(20), 8035—8040
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b02427 URL pmid: 30977371 |
| [24] |
Mogaki R., Okuro K., Aida T ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017,139(29), 10072—10078
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b05151 URL pmid: 28675032 |
| [25] |
Okuro K., Sasaki M., Aida T ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(17), 5527—5530
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b02664 URL pmid: 27087468 |
| [26] |
Yan Z., Qin H., Ren J., Qu X., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,57(35), 11182—11187
doi: 10.1002/anie.201803939 URL pmid: 30035841 |
| [27] |
Liu Z., Liu Y., Chang Y., Seyf H. R., Henry A., Mattheyses A. L., Yehl K., Zhang Y., Huang Z., Salaita K., Nat. Methods, 2016,13(2), 143—146
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3689 URL pmid: 26657558 |
| [28] |
Sniadecki N. J., Endocrinology, 2010,151(2), 451—457
doi: 10.1210/en.2009-0932 URL pmid: 20016028 |
| [29] |
Mannix R. J., Kumar S., Cassiola F., Montoya-Zavala M., Feinstein E., Prentiss M., Ingber D. E., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008,3(1), 36—40
doi: 10.1038/nnano.2007.418 URL pmid: 18654448 |
| [30] |
Seo D., Southard K. M., Kim J., Lee H. J., Farlow J., Lee J., Litt D. B., Haas T., Alivisatos A. P., Cheon J., Gartner Z. J., Jun Y., Cell, 2016,165(6), 1507—1518
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.04.045 URL pmid: 27180907 |
| [31] |
Perica K., Tu A., Richter A., Bieler J. G., Edidin M., Schneck J. P., ACS Nano, 2014,8(3), 2252—2260
doi: 10.1021/nn405520d URL pmid: 24564881 |
| [32] |
Cho M. H., Lee E. J., Son M., Lee J. H., Yoo D., Kim J. W., Park S. W., Shin J. S., Cheon J., Nat. Mater., 2012,11(12), 1038—1043
doi: 10.1038/nmat3430 URL pmid: 23042417 |
| [33] |
Karimi M., Ghasemi A., Sahandi Zangabad P., Rahighi R., Moosavi Basri S. M., Mirshekari H., Amiri M., Shafaei Pishabad Z., Aslani A., Bozorgomid M., Ghosh D., Beyzavi A., Vaseghi A., Aref A. R., Haghani L., Bahrami S., Hamblin M. R., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016,45(5), 1457—1501
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00798d URL pmid: 26776487 |
| [34] | Qiao S., Wang H., Nano Res., 2018,11(10), 5400—5423 |
| [35] |
Qiao S. L., Wang Y., Lin Y. X., An H. W., Ma Y., Li L. L., Wang L., Wang H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016,8(27), 17016—17022
doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b04580 URL pmid: 27348260 |
| [36] |
Wu S., Bellve K. D., Fogarty K. E., Melikian H. E., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2015,112(50), 15480—15485
doi: 10.1073/pnas.1512957112 URL pmid: 26621748 |
| [37] |
Fan J., Wang H. H., Xie S., Wang M., Nie Z., ChemBioChem, 2020,21(3), 282—293
doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900315 URL pmid: 31364788 |
| [38] |
Li J., Mo L., Lu C. H., Fu T., Yang H. H., Tan W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016,45(5), 1410—1431
doi: 10.1039/c5cs00586h URL pmid: 26758955 |
| [39] |
Wang L., Li W., Sun J., Zhang S. Y., Yang S., Li J., Li J., Yang H. H., Anal. Chem., 2018,90(24), 14433—14438
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04015 URL pmid: 30444610 |
| [40] |
Li J., Liu S., Sun L., Li W., Zhang S. Y., Yang S., Li J., Yang H. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(48), 16589—16595
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b08442 URL pmid: 30407002 |
| [41] |
Liang H., Chen S., Li P., Wang L., Li J., Li J., Yang H. H., Tan W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(12), 4186—4190
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b11311 URL pmid: 29522674 |
| [42] |
Wu S., Li J., Liang H., Wang L., Chen X., Jin G., Xu X., Yang H. H., Sci. China Chem., 2016,60(5), 628—634
doi: 10.1007/s11426-016-0351-5 URL |
| [43] |
Zhou J., Rossi J., Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2017,16(3), 181—202
doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.199 URL pmid: 27807347 |
| [44] |
McNamara J. O., Kolonias D., Pastor F., Mittler R. S., Chen L., Giangrande P. H., Sullenger B., Gilboa E., J. Clin. Invest., 2008,118(1), 376—386
doi: 10.1172/JCI33365 URL pmid: 18060045 |
| [45] |
Parekh P., Kamble S., Zhao N., Zeng Z., Portier B. P., Zu Y., Biomaterials, 2013,34(35), 8909—8917
doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.07.099 URL pmid: 23968853 |
| [46] |
Dollins C. M., Nair S., Boczkowski D., Lee J., Layzer J. M., Gilboa E., Sullenger B. A., Chem. Biol., 2008,15(7), 675—682
doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.05.016 URL pmid: 18635004 |
| [47] |
Pratico E. D., Sullenger B. A., Nair S. K., Nucleic Acid Ther., 2013,23(1), 35—43
doi: 10.1089/nat.2012.0388 URL pmid: 23113766 |
| [48] |
Ramaswamy V., Monsalve A., Sautina L., Segal M. S., Dobson J., Allen J. B., Nucleic Acid Ther., 2015,25(5), 227—234
doi: 10.1089/nat.2014.0519 URL pmid: 26125598 |
| [49] |
Ueki R., Ueki A., Kanda N., Sando S., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016,55(2), 579—582
doi: 10.1002/anie.201508572 URL pmid: 26592704 |
| [50] |
Ueki R., Atsuta S., Ueki A., Hoshiyama J., Li J., Hayashi Y., Sando S., Chem. Commun, 2019,55(18), 2672—2675
doi: 10.1039/c8cc08080a URL pmid: 30746545 |
| [51] |
Ueki R., Atsuta S., Ueki A., Sando S ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017,139(19), 6554—6557
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b02411 URL pmid: 28459560 |
| [52] |
Li H., Wang M., Shi T., Yang S., Zhang J., Wang H. H., Nie Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,57(32), 10226—10230
doi: 10.1002/anie.201806155 URL pmid: 29944203 |
| [53] |
Chen S., Xu Z., Yang W., Lin X., Li J., Li J., Yang H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019,58(50), 18186—18190
doi: 10.1002/anie.201908971 URL pmid: 31595614 |
| [54] |
Chen S., Li J., Liang H., Lin X. H., Li J., Yang H. H., Chem. Eur. J., 2018,24(60), 15988—15992
doi: 10.1002/chem.201803868 URL pmid: 30155946 |
| [55] |
Wang M., He F., Li H., Yang S. H., Zhang J. H., Ghosh P., Wang H. H., Nie Z., Nano Lett., 2019,19(4), 2603—2613
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.9b00421 URL pmid: 30907088 |
| [56] |
Wang L., Liang H., Sun J., Liu Y., Li J., Li J., Li J., Yang H ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019,141(32), 12673—12681
doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b05123 URL pmid: 31381313 |
| [57] |
Shaw A., Lundin V., Petrova E., Fordos F., Benson E., Al-Amin A., Herland A., Blokzijl A., Hogberg B., Teixeira A. I., Nat. Methods, 2014,11(8), 841—846
doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3025 URL pmid: 24997862 |
| [58] |
Zhang K., Deng R., Sun Y., Zhang L., Li J., Chem. Sci, 2017,8(10), 7098—7105
doi: 10.1039/c7sc02489d URL pmid: 29147539 |
| [59] |
Ralff M. D., El-Deiry W. S., Expert Rev. Precis. Med. Drug Dev., 2018,3(3), 197—204
doi: 10.1080/23808993.2018.1476062 URL pmid: 30740527 |
| [60] |
Graves J. D., Kordich J. J., Huang T. H., Piasecki J., Bush T. L., Sullivan T., Foltz I. N., Chang W., Douangpanya H., Dang T., O’Neill J. W., Mallari R., Zhao X., Branstetter D. G., Rossi J. M., Long A. M., Huang X., Holland P. M., Cancer Cell, 2014,26(2), 177—189
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2014.04.028 URL pmid: 25043603 |
| [61] |
Gilbreth R. N., Novarra S., Wetzel L., Florinas S., Cabral H., Kataoka K., Rios-Doria J., Christie R. J., Baca M., J. Controlled Release, 2016,234, 104—114
doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.05.041 URL pmid: 27212104 |
| [62] |
Wu H ., Cell, 2013,153(2), 287—292
doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.013 URL pmid: 23582320 |
| [63] |
De Miguel D., Lemke J., Anel A., Walczak H., Martinez-Lostao L., Cell Death Differ., 2016,23(5), 733—747
doi: 10.1038/cdd.2015.174 URL pmid: 26943322 |
| [64] |
De Miguel D., Gallego-Lleyda A., Anel A., Martinez-Lostao L., Leukemia Res., 2015,39(6), 657—666
doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2015.03.019 URL pmid: 25882551 |
| [65] |
Valldorf B., Fittler H., Deweid L., Ebenig A., Dickgiesser S., Sellmann C., Becker J., Zielonka S., Empting M., Avrutina O., Kolmar H., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2016,55(16), 5085—5089
doi: 10.1002/anie.201511894 URL pmid: 26991930 |
| [66] |
Angell Y. M., Bhandari A., Francisco M. N. D., Frederick B. T., Green J. M., Leu K., Leuther K., Sana R., Schatz P. J., Whitehorn E. A., Wright K., Holmes C. P., Discovery and Optimization of a TRAIL R2 Agonist for Cancer Therapy. In Peptides for Youth, Springer, New York, 2009, 101—103
doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-73657-0_45 URL pmid: 19400112 |
| [67] |
Schneider H., Yanakieva D., Macarron A., Deweid L., Becker B., Englert S., Avrutina O., Kolmar H ., ChemBioChem, 2019,20(24), 3006—3012
doi: 10.1002/cbic.201900251 URL pmid: 31206933 |
| [68] |
Ng S., Galipeau J., Stem Cells Transl. Med., 2015,4(1), 66—73
doi: 10.5966/sctm.2014-0145 URL pmid: 25391644 |
| [69] |
Passioura T., Suga H., Chem. Commun, 2017,53(12), 1931—1940
doi: 10.1039/c6cc06951g URL pmid: 28091672 |
| [70] |
Ito K., Sakai K., Suzuki Y., Ozawa N., Hatta T., Natsume T., Matsumoto K., Suga H., Nat. Commun, 2015,6, 6373
doi: 10.1038/ncomms7373 URL pmid: 25758345 |
| [71] | Miao W., Sakai K., Imamura R., Ito K., Suga H., Sakuma T., Yamamoto T., Matsumoto K., Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2018,19(10), 3141 |
| [72] |
Hipolito C. J., Bashiruddin N. K., Suga H., Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 2014,26, 24—31
doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2014.03.001 URL pmid: 24681557 |
| [1] | 王君旸, 刘争, 张茜, 孙春燕, 李红霞. DNA银纳米簇在功能核酸荧光生物传感器中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220010. |
| [2] | 张宏伟, 陈雯, 赵美淇, 马超, 韩云虎. 单原子催化剂在电化学中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220129. |
| [3] | 王瑞洁, 焦小雨, 潘宇, 王训春, 杨洋, 成中军. 透明抗静电多功能超疏水薄膜的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210703. |
| [4] | 郑雪莲, 杨翠翠, 田维全. 全椅式边含薁缺陷石墨烯纳米片的二阶非线性光学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [5] | 丁钦, 张梓轩, 徐培程, 李晓宇, 段莉梅, 王寅, 刘景海. Cu, Ni, Co掺杂对Fe碳纳米管的结构及电催化性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [6] | 董妍红, 鲁新环, 杨璐, 孙凡棋, 段金贵, 郭昊天, 张钦峻, 周丹, 夏清华. 双功能金属有机骨架材料的制备及催化烯烃环氧化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220458. |
| [7] | 袁萌, 赵英杰, 吴雨辰, 江雷. 钙钛矿阵列化组装及其多功能探测器的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220448. |
| [8] | 李然, 张旭东, 穆丽丹, 孙童, 艾刚刚, 沙夜龙, 张玉琦, 王记江. 三联噻吩衍生物功能化SiO2反蛋白石光子晶体荧光薄膜的制备及应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2989. |
| [9] | 符金洲, 王汉伟, 李莹莹, 王超, 李彩彩, 孙庆丰, 李会巧. 微纳米纤维素功能膜在能源与环境领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1407. |
| [10] | 李淑荟, 黄剑莹, 赖跃坤. 绿色环保特殊浸润性纺织品的前沿进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1043. |
| [11] | 窦树珍, 王中舜, 吕男. 硅纳米结构对表面辅助激光解吸/电离质谱检测性能的提高[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1156. |
| [12] | 杨琳燦, 冷雪菲, 韩丽, 李超, 张松波, 雷岚, 马红卫, 李杨. 基于双锂法的炔基功能化热塑性弹性体的合成[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 866. |
| [13] | 王伟, 卢香超, 周立军, 鲁艺珍, 曹阳. 基于二维压电材料功能性器件的设计、 构筑与性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 595. |
| [14] | 彭海月, 汪婷, 李国瑞, 黄静. 黑色素的合成及小分子对其功能的调控[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3357. |
| [15] | 吉采灵, 程兴, 谈洁, 袁荃. 功能化核酸适体的筛选及分子识别应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3457. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||