

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2026, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 20250343.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20250343
收稿日期:2025-11-07
出版日期:2026-01-10
发布日期:2025-12-01
作者简介:朱有亮, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事软物质体系的介观尺度分子模拟方法和软件方面的研究. E-mail: youliangzhu@jlu.edu.cn基金资助:
XU Jiaqi, SHI Rui, ZHU Youliang( ), LU Zhongyuan(
), LU Zhongyuan( )
)
Received:2025-11-07
Online:2026-01-10
Published:2025-12-01
Supported by:摘要:
相较于一维和三维高分子, 二维高分子的理论框架还不完备, 特别是柔性二维高分子, 其独特的构象特征及由此产生的物理性质尚缺乏系统的理论解释, 是当前高分子科学中亟待深入研究的核心科学问题之一. 本文综合评述了柔性二维高分子在理论与计算机模拟方面的研究进展, 首先回顾了20世纪80年代关于系连膜的早期理论研究. 这些研究通过分子动力学模拟, 揭示了自回避相互作用将导致二维网络在热力学极限下展现为平坦构象, 而不会发生预期的皱缩转变. 在此基础上, 进一步阐述了21世纪以来该领域的重要突破: 计算机模拟不仅验证了二维高分子平衡构象与输运性质(如特性黏度)的标度关系, 还通过引入可调网格模型, 在理论上统一了长期存在争议的平坦与皱缩构象, 揭示了两者共存的物理机制; 同时, 建立了从平坦、 多级折叠直至塌缩的完整构象演化路径. 最后, 展望了该领域在精准制备有序柔性网络及利用理论指导智能响应材料设计等方面面临的机遇与挑战.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
徐嘉琦, 施睿, 朱有亮, 吕中元. 柔性二维高分子: 高分子的新维度. 高等学校化学学报, 2026, 47(1): 20250343.
XU Jiaqi, SHI Rui, ZHU Youliang, LU Zhongyuan. Flexible Two-dimensional Polymers: a New Dimension in Polymer. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2026, 47(1): 20250343.
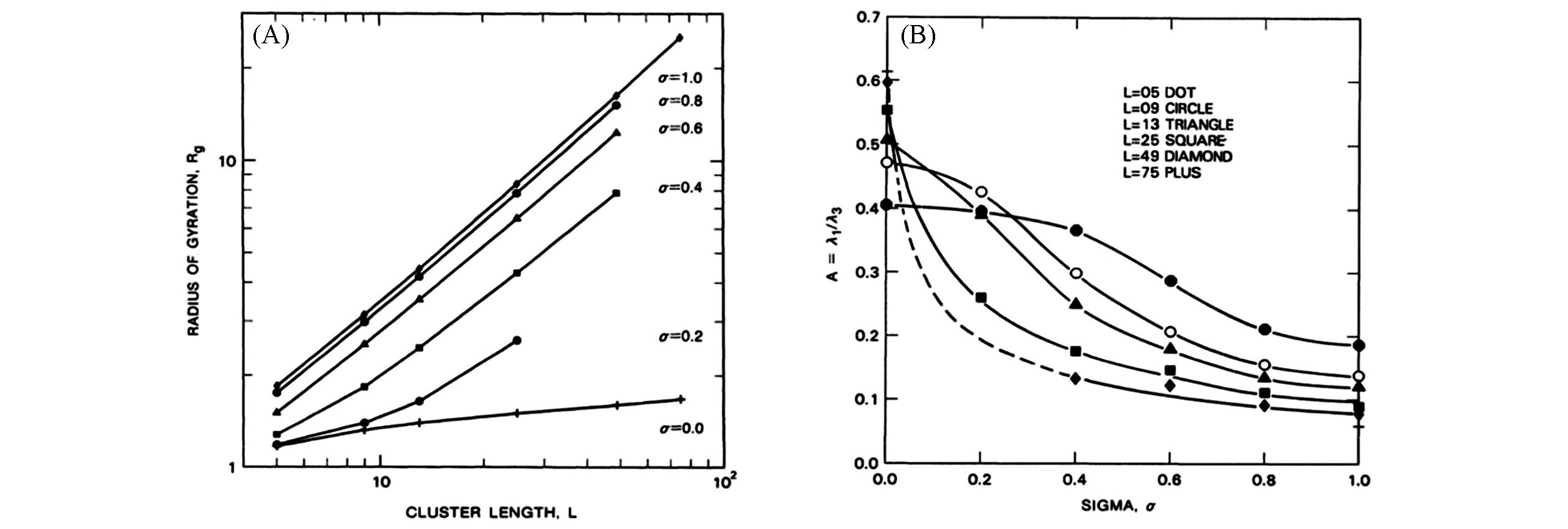
Fig.3 Lg⁃lg plot of the radius of gyration(Rg) of tethered membranes for various values of the parameter σ(A), the shape parameter A=λ1/λ2 plotted as a function of σ for various L(B)[52](A) Straight-line segments are drawn through the data points and have slope equal to the effective exponent ν(L), which, for all σ≠0, increases with L and is consistent with the asymptotic value ν(∞)=1. (B) As discussed in the text, we believe this shows that tethered membranes with σ ≥ 0.2 are asymptotically flat and suggests that the same conclusion holds for all σ>0.
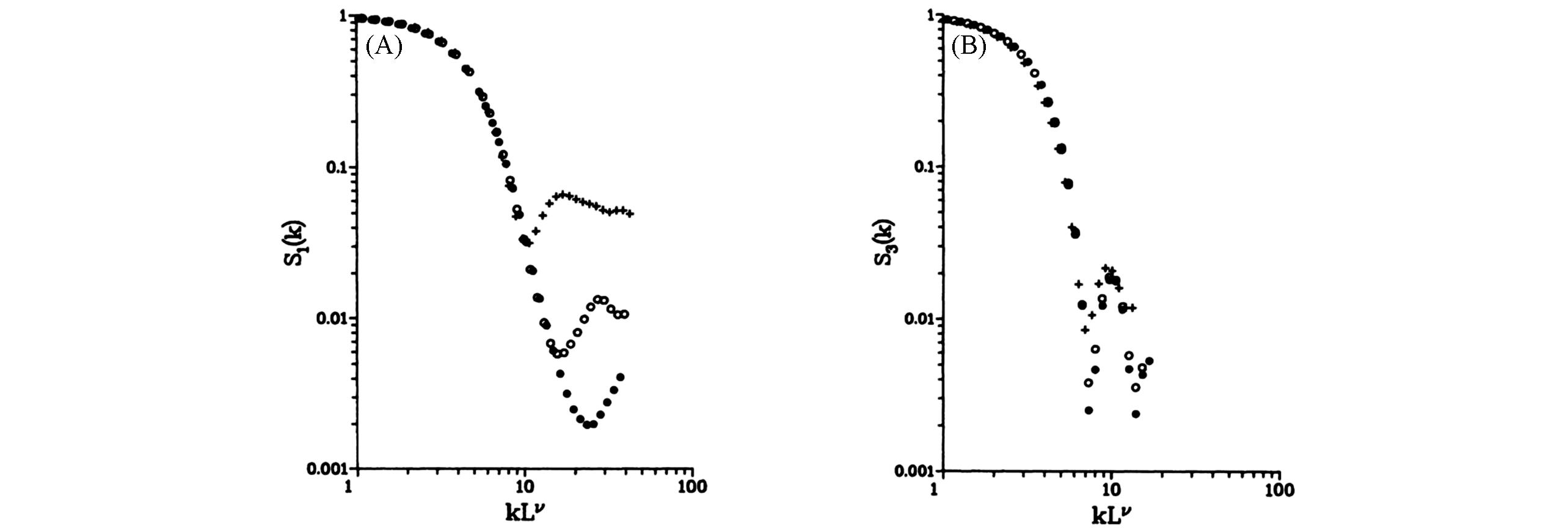
Fig.4 “Perpendicular” structure factor S₁(k) for wave vectors in the direction of the eigenvector corresponding to the smallest eigenvalue of the inertia tensor plotted as a function of the scaled variable kLv with ν=0.65(A), the in⁃plane structure factor S3(k)(with k in the direction of the eigenvector corresponding to the largest eigenvalue of the inertia tensor) plotted as a function of the scaled variable kLv with ν=0.975(B)[46](A) Crosses, L=5(total number of particles, N=19); open circles, L=11(N=91); filled circles, L=19(N=271).(B) Symbols correspond to the same membrane sizes as in (A).
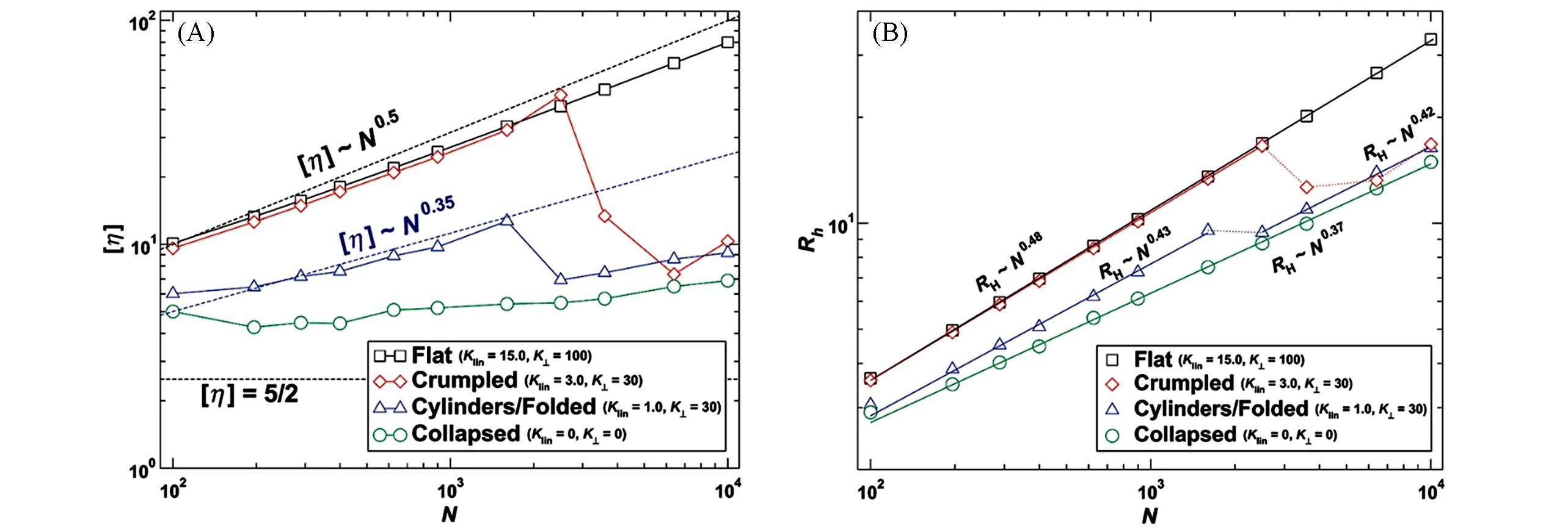
Fig.7 Intrinsic viscosity[η] as a function of sheet size(A) and hydrodynamic radius(Rh) as a function of sheet size(B)[53]Copyright 2010, American Chemical Society.
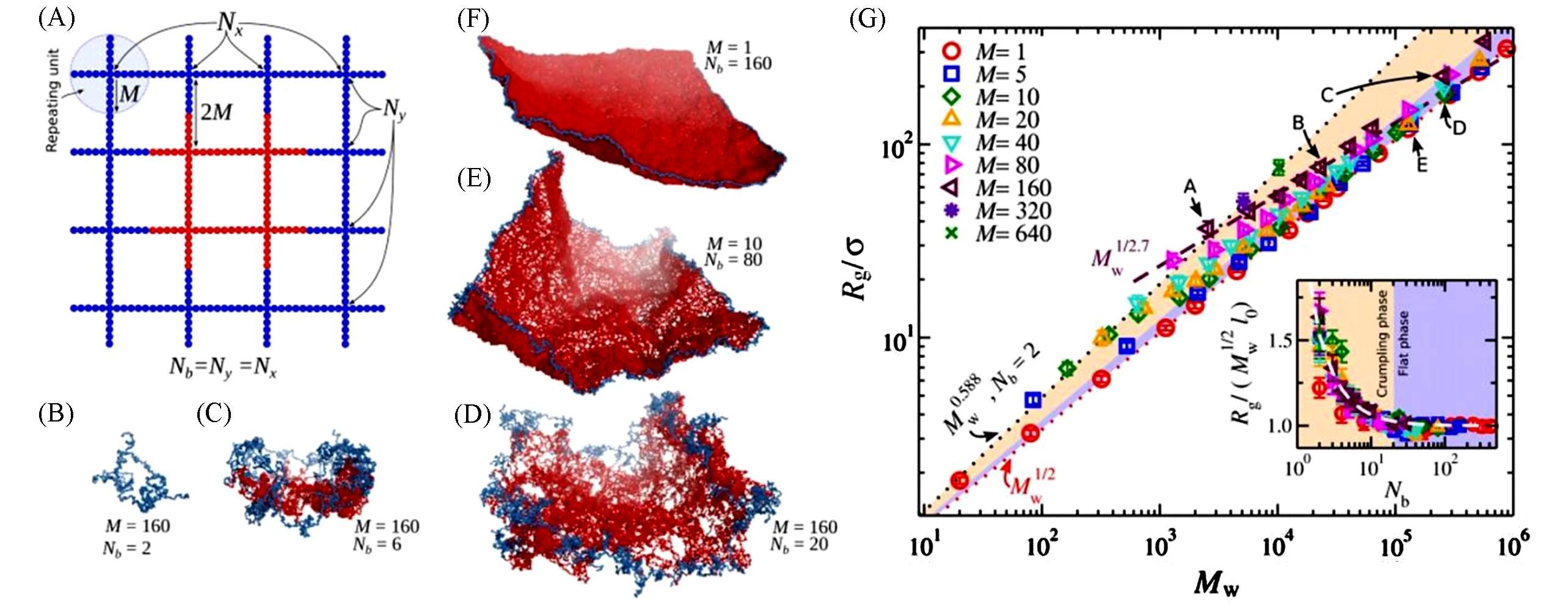
Fig.8 Schematic of a regular 2D polymer network having Nb=4 branches in each direction(A), the structures of 2D polymer networks at different Nb shown respectively(B—F) and radius of gyration Rg of 2D polymer networks as a function of molecular mass Mw(G)[54](A) Screenshots of typical equilibrated 2D polymer networks are also presented. For clarity, the repeating units located at the edge of the polymer network are in blue and for the units in the middle in red. (G) The highlighted regimes approximately outline the emergence of crumpling(pale yellow) and flat sheet regimes(pale blue). The dotted lines are power laws with an exponent of 0.588 and 1/2 and the dashed line is a power law with an exponent of 1/2.7; all lines are guides for the eye. The uncertainty estimates correspond to two standard deviations. Inset: Rg normalized by Mw and l0 as a function of Nb. The dashed line is Rg≈l0Mw1/2(1.3/Nb1.3+1). Here, l0 is a prefactor dependent on the mesh size M.
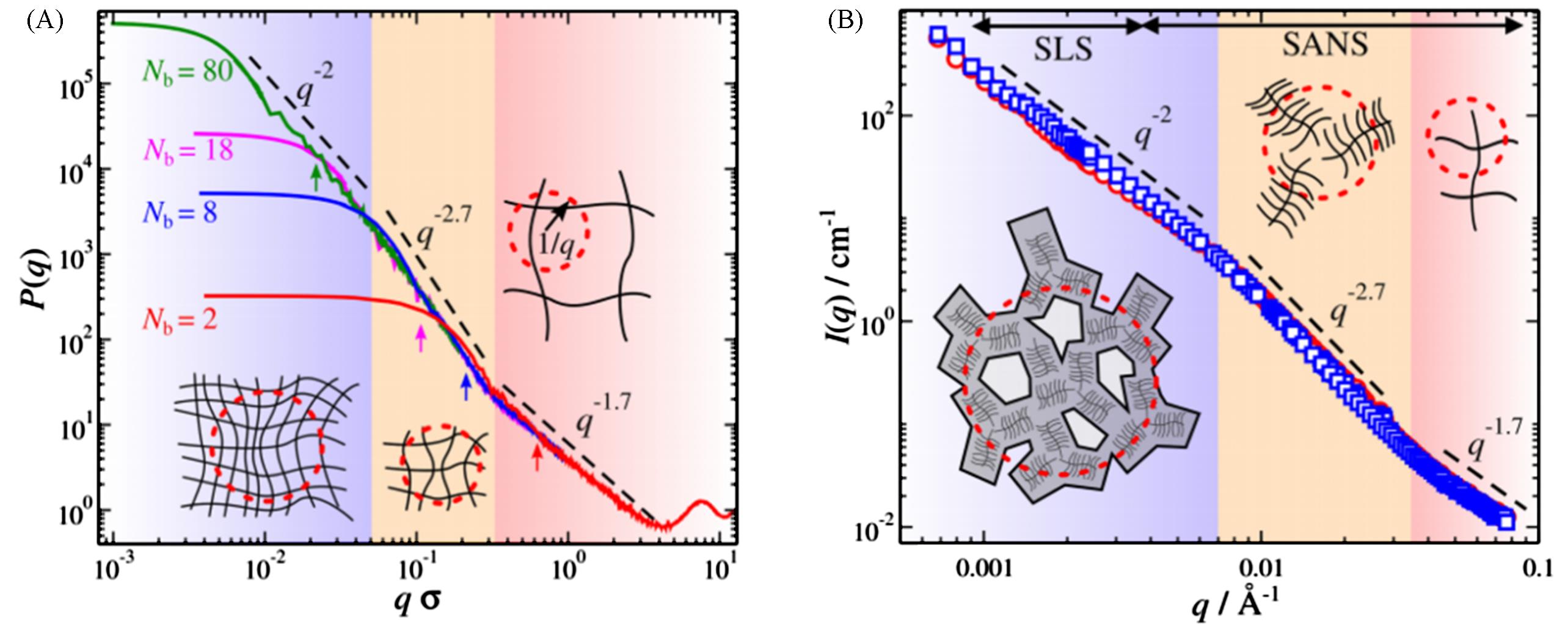
Fig.9 Form factor P(q) of polymer networks having chain length M=20 based on our simulation model(A), combined static light scattering(SLS) and small angle neutron scattering(SANS) measurements of the scattering from 0.1%(mass fraction) aggrecan solutions with no salt(circles) and 100 mmol/L CaCl2(squares)(B)[54]Copyright 2023, American Physical Society
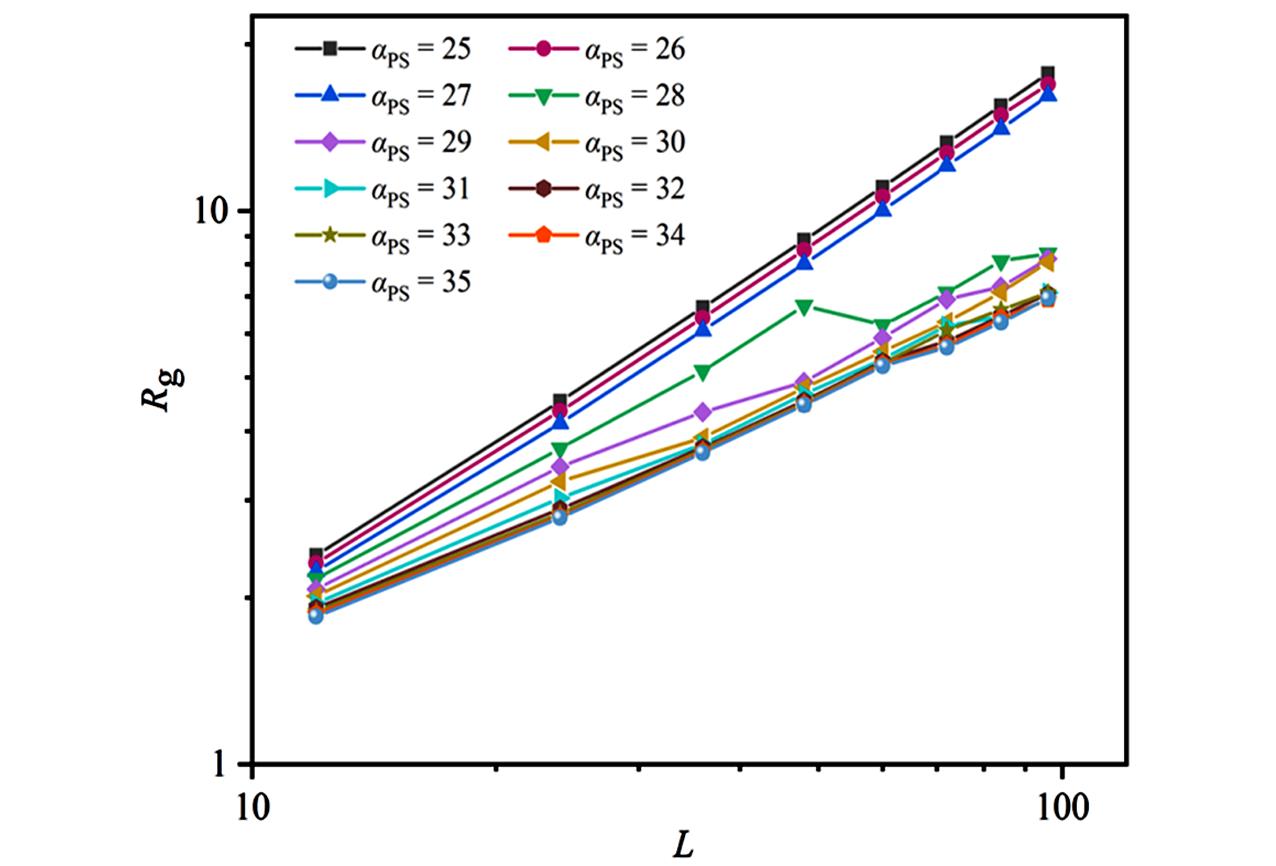
Fig.11 Lg⁃lg plot of the relationship between the radius of gyration Rg and the size of the 2D polymer L under different solvent conditions[55]Copyright 2024, AIP Publishing.
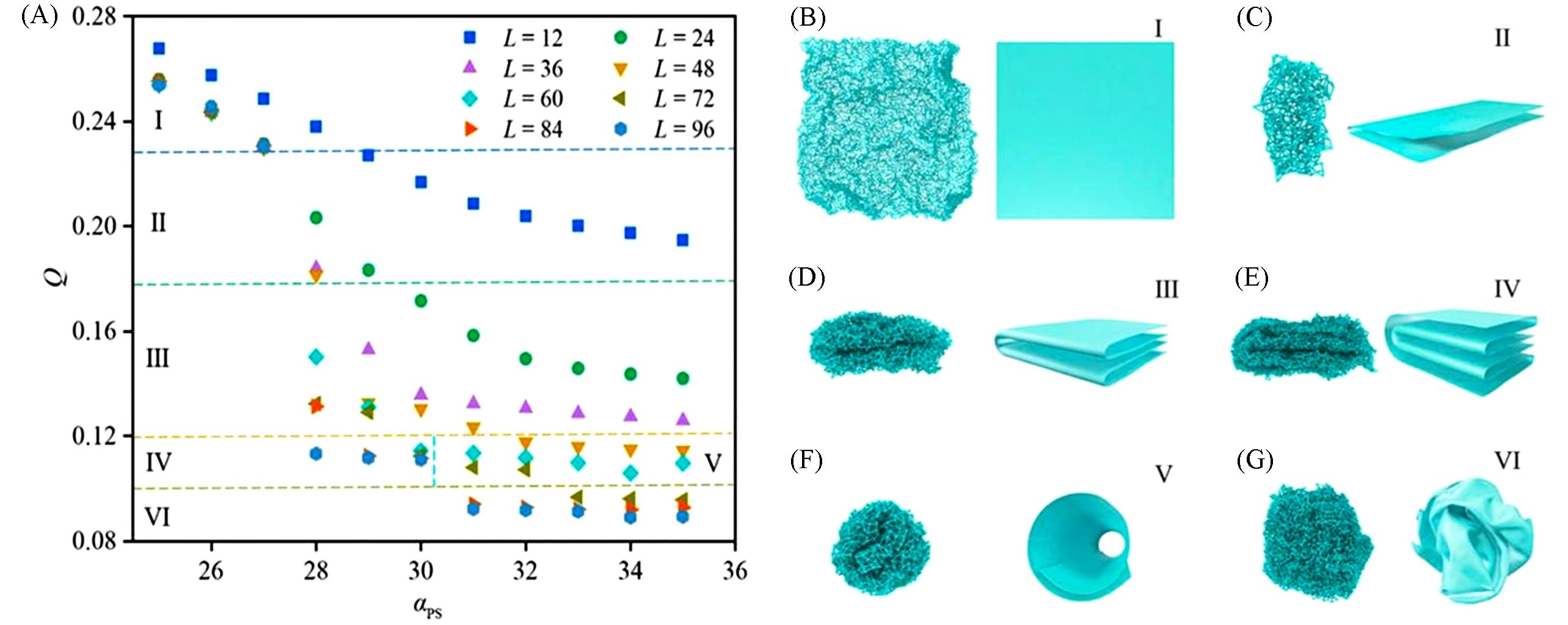
Fig.12 Relationship between the shape parameter(Q) and the solvent condition(αPS) with the different size of the 2D polymer(A), αPS=25.0, snapshot and schematic structure of a 2D polymer with size L=96(B), αPS=29.0, snapshots and schematic structures showcasing 2D polymers with sizes L=24, 72, and 96 in equilibrium states, respectively(C—E), αPS=35.0, snapshots and schematic structures for 2D polymers with L=60 and 96, respectively(F, G)[55]Copyright 2024, AIP Publishing.
| [1] | Staudinger H., Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges., 1920, 53, 1073 |
| [2] | Anguita J. V., Smith C. T. G., Stute T., Funke M., Delkowski M., Silva S. R. P., Nat. Mater., 2020, 19, 474 |
| [3] | Taub A., de Moor E., Luo A., Matlock D. K., Speer J. G., Vaidya U., Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2019, 49, 327 |
| [4] | Tran H., Feig V. R., Liu K., Zheng Y., Bao Z. N., Macromolecules, 2019, 52, 3965 |
| [5] | Charles A. P. R., Jin T. Z., Mu R., Wu Y., Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf., 2021, 20, 6027 |
| [6] | Pfitzner A. K., Von Filseck J. M., Roux A., Trends Cell Biol., 2021, 31, 856 |
| [7] | Zhao X., Chen X., Yuk H., Lin S., Liu X., Parada G., Chem. Rev., 2021, 121, 4309 |
| [8] | Rubinstein M., Colby R. H., Polymer Physics, Oxford University Press, New York, 2003 |
| [9] | Sakamoto J., van Heijst J., Lukin O., Schlüter A. D., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009, 48, 1030 |
| [10] | Li Z., Tang M., Jiang C., Bai R., Bai W., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2018, 39, 1700880 |
| [11] | Kuehl V. A., Yin J., Duong P. H., Mastorovich B., Newell B., Li⁃Oakey K. D., Parkinson B. A., Hoberg J. O., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 18200—18207 |
| [12] | Rodenas T., Luz I., Prieto G., Seoane B., Miro H., Corma A., Kapteijn F., Llabrés i Xamena F. X., Gascon J., Nat. Mater., 2015, 14, 48—55 |
| [13] | Huang N., Wang P., Addicoat M. A., Heine T., Jiang D., Angew. Chem., 2017, 129, 5064—5068 |
| [14] | Li C., Wang Y., Zou Y., Zhang X., Dong H., Hu W., Angew. Chem., 2020, 132, 9489—9493 |
| [15] | Wang S., Wang Q., Shao P., Han Y., Gao X., Ma L., Yuan S., Ma X., Zhou J., Feng X., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 4258—4261 |
| [16] | Roman H. E., Polymers, 2024, 16, 3400 |
| [17] | Haldar S., Roy K., Nandi S., Chakraborty D., Puthusseri D., Gawli Y., Ogale S., Vaidhyanathan R., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1702170 |
| [18] | Lim E. L., Wei Z. H., Mater. Futures, 2023, 2, 027501 |
| [19] | Hadi M. K., Wang X., Peng Y., Sangaraju S., Ran F., PS&T, 2024, 1, 366—412 |
| [20] | Li Z., Lin Z., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2021, 13, 45130 |
| [21] | Ren Y., Xu Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2024, 53, 1823 |
| [22] | Zhao R., Liu G., Koko P., Wang M., Feng X., Org. Chem. Front., 2025, 12, 2457 |
| [23] | Payamyar P., King B. T., Öttinger H. C., Schlüter A. D., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 18—34 |
| [24] | Kissel P., Erni R., Schweizer W. B., Rossell M. D., King B. T., Bauer T., Götzinger S., Schlüter A. D., Sakamoto J., Nat. Chem., 2012, 4, 287—291 |
| [25] | Bhola R., Payamyar P., Murray D. J., Kumar B., Teator A. J., Schmidt M. U., Hammer S. M., Saha A., Sakamoto J., Schlüter A. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135, 14134—14141 |
| [26] | Kory M. J., Wörle M., Weber T., Payamyar P., van de Poll S. W., Dshemuchadse J., Trapp N., Schlüter A. D., Nat. Chem., 2014, 6, 779—784 |
| [27] | Novoselov K. S., Geim A. K., Morozov S. V., Jiang D. E., Zhang Y., Dubonos S. V., Grigorieva I. V., Firsov A. A., Science, 2004, 306, 666—669 |
| [28] | Côté A. P., Benin A. I., Ockwig N. W., O'Keeffe M., Matzger A. J., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2005, 310, 1166—1170 |
| [29] | Liu K., Wang L., Dong R., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2020, 8, 10696—10718 |
| [30] | Schlüter A. D., Payamyar P., Öttinger H. C., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2016, 37, 1638—1650 |
| [31] | Evans A. M., Strauss M. J., Corcos A. R., Hirani Z., Ji W., Hamachi L. S., Aguilar-Enriquez X., Chavez A. D., Smith B. J., Dichtel W. R., Chem. Rev., 2021, 122, 442—564 |
| [32] | Ren Y., Xu Y., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2024, 53, 1823—1869 |
| [33] | Servalli M., Schlüter A. D., Annu. Rev. Mater. Res., 2017, 47, 361—389 |
| [34] | Wang C., Zhang Z., Zhu Y., Yang C., Wu J., Hu W., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34, e2102290 |
| [35] | Liu C., Wang Z., Zhang L., Dong Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2022, 144, 18784—18789 |
| [36] | Li Y., Gao H., Yu H., Jiang K., Yu H., Yang Y., Song Y., Zhang W., Shi H., Lu Z., Sci. Adv., 2019, 5, eaaw9120 |
| [37] | Gao H. M., Zhao L., Liu K., Lu Z. Y., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2021, 12, 2340—2347 |
| [38] | Nelson D., Piran T., Weinberg S., Phys. Rev. B, 2004, 74, 9 |
| [39] | Hwa T., Kokufuta E., Tanaka T., Phys. Rev. A, 1991, 44, R2235 |
| [40] | Spector M., Naranjo E., Chiruvolu S., Zasadzinski J., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1994, 73, 2867 |
| [41] | Radzihovsky L., Toner J., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1995, 75, 4752 |
| [42] | Paczuski M., Kardar M., Nelson D. R., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1988, 60, 2638 |
| [43] | Liu D., Plischke M., Phys. Rev. A, 1992, 45, 7139 |
| [44] | Kantor Y., Kremer K., Phys. Rev. E, 1993, 48, 2490 |
| [45] | Bowick M., Falcioni M., Thorleifsson G., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1997, 79, 885 |
| [46] | Plischke M., Boal D., Phys. Rev. A, 1988, 38, 4943—4945 |
| [47] | Kantor Y., Kardar M., Nelson D. R., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1986, 57, 791 |
| [48] | Kantor Y., Nelson D. R., Phys. Rev. A, 1987, 36, 4020 |
| [49] | Kantor Y., Nelson D. R., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1987, 58, 2774 |
| [50] | Kantor Y., Kardar M., Nelson D. R., Phys. Rev. A, 1987, 35, 3056 |
| [51] | Boal D., Levinson E., Liu D., Plischke M., Phys. Rev. A, 1989, 40, 3292—3300 |
| [52] | Abraham F. F., Rudge W. E., Plischke M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1989, 62, 1757—1759 |
| [53] | Knauert S. T., Douglas J. F., Starr F. W., Macromolecules, 2010, 43, 3438—3445 |
| [54] | Chremos A., Horkay F., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2023, 131, 138101 |
| [55] | Xu J. Q., Shi R., Zhu Y. L., Lu Z. Y., J. Chem. Phys., 2024, 161, 161101 |
| [56] | Xu J. L., Guo S. H., Zhen M. L., Yu Z. C., Zhu Y. L., Milano G., Lu Z. Y., MGE Advances, 2025, 3, e70019 |
| [1] | 沈宇豪, 田泽民, 李伟, 纪亦轩, 颜应文. 构象结构对于顺式-1,3-双甲基环己烷二级加氧反应影响的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(3): 20240458. |
| [2] | 郑笑函, 祝佳怡, 李晓蕾, 郝强, 王长生. 发展可极化键偶极模型快速预测环肽分子构象稳定性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(10): 20250173. |
| [3] | 刘奇, 刘沫毅, 董思雨, 王学重, 何运良. 利格列汀多晶型研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230400. |
| [4] | 韦晚霞, 周先敏, 董馨韵, 刘铁峰, 谢聪, 程靖宇, 陈建平, 陆鑫, 冯凯, 周印华. 交联PEDOT∶F空穴传输层提升柔性有机光伏电池性能的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(7): 20230069. |
| [5] | 苗桂美, 陈隆旋, 公丕文, 韩吉姝, 赵瑞阳, 刘福胜. 一种光致相变型偶氮苯基柔性光热转换器件的制备及性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230256. |
| [6] | 刘建芳, 赵浩成, 梁芳楠, 尤雪瑞, 周琨. 化学剥离碳化钛纳米片辅助合成可控尺寸的银纳米线[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230009. |
| [7] | 骆鑫妍, 贾若男, 向勇, 张晓琨. 可拉伸聚合物基复合固体电解质研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220149. |
| [8] | 闵婧, 王力彦. 利用三中心氢键限制芳酰胺构象的核磁共振氢谱分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220084. |
| [9] | 闫文卿, 张则尧, 李彦. 碳纳米管透明导电薄膜的可控制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210626. |
| [10] | 矫龙, 代学民, 牟建新, 杜志军, 王汉夫, 董志鑫, 邱雪鹏. 柔性OLED用高耐热聚酰亚胺薄膜的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220390. |
| [11] | 莫宗文, 张学文, 周浩龙, 周东东, 张杰鹏. 一种多孔配位聚合物的氢键协同客体响应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210576. |
| [12] | 赵凌云, 黄汉雄, 罗杜宇, 苏逢春. 复合材料柔软性对倒金字塔微结构阵列传感器性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2953. |
| [13] | 曹美琦, 刘霞, 崔树勋. 不同液体环境下聚丙烯酰胺的单分子力学[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2982. |
| [14] | 薛谨, 曹小卫, 刘依帆, 王敏. 纸质空心金纳米笼SERS传感器的制备及对非小细胞肺癌患者痰液中miRNAs的快速高灵敏检测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2393. |
| [15] | 张鋆, 刘忆旋, 杜晓慧, 杨辉. 基于高黏附可拉伸高分子材料的人机交互界面[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1093. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||