

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (2): 204.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190620
• 庆祝《高等学校化学学报》复刊40周年专栏 • 上一篇 下一篇
肖宇情1,2,李申慧1,*( ),汤晶1,2,徐君1,邓风1,*(
),汤晶1,2,徐君1,邓风1,*( )
)
收稿日期:2019-12-02
出版日期:2020-02-10
发布日期:2019-12-31
通讯作者:
李申慧,邓风
E-mail:lishenhui@wipm.ac.cn;dengf@wipm.ac.cn
基金资助:
XIAO Yuqing1,2,LI Shenhui1,*( ),TANG Jing1,2,XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,*(
),TANG Jing1,2,XU Jun1,DENG Feng1,*( )
)
Received:2019-12-02
Online:2020-02-10
Published:2019-12-31
Contact:
Shenhui LI,Feng DENG
E-mail:lishenhui@wipm.ac.cn;dengf@wipm.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
金属有机框架材料(MOFs)在绿色能源气体储存、 二氧化碳捕获、 化学分离、 化学传感和多相催化等领域有着广泛的应用前景, 与其分子结构、 动力学行为以及与客体分子的相互作用密切相关. 固体核磁共振(NMR)能提供原子水平的结构距离信息, 能从多个时间尺度反映分子动力学行为, 能通过极化转移揭示主客体相互作用. 本文综述了近年来先进的固体核磁共振方法在研究MOFs的结构、 动力学行为以及主客体相互作用等方面的研究进展. 多核、 多维固体NMR可给出MOFs材料的金属中心以及有机配体的局部配位状态, 变温固体NMR可以反映MOFs的分子柔性以及有机配体在不同温度下的运动模式及速率. 固体NMR还可用来研究MOFs与吸附客体分子(如甲烷、 二氧化碳等)之间的相互作用模式. 通过固体NMR技术获得的结构信息有助于人们理解MOFs材料的构效关系, 并为合理设计新型的MOFs材料提供依据.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
肖宇情,李申慧,汤晶,徐君,邓风. 金属有机框架材料的结构、 动力学行为和主客体相互作用的固体核磁共振研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 204.
XIAO Yuqing,LI Shenhui,TANG Jing,XU Jun,DENG Feng. Solid-state NMR Spectroscopy Studies on Structure, Dynamics and Host-guest Interaction in Metal-organic Framework Materials †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 204.
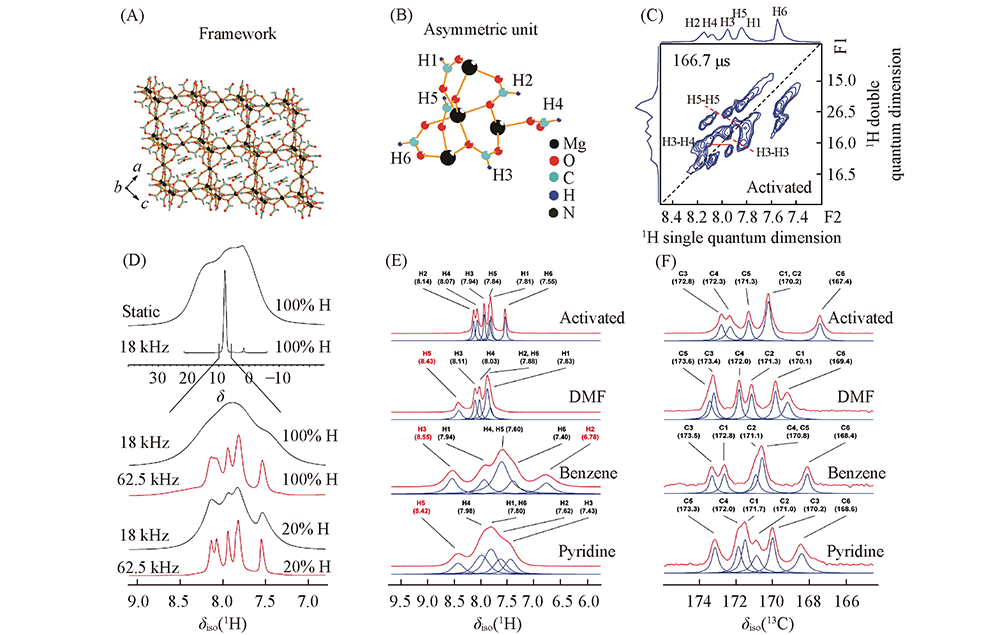
Fig.1 Structural demonstration of α-Mg3(HCOO)6(A), six unequivalent proton and carbon sites in α-Mg3(HCOO)6(B), 2D 1H-1H DQ MAS NMR spectra of α-Mg3(HCOO)6(C), the resolution of 1H MAS NMR spectra of α-Mg3(HCOO)6 largely improved by fast MAS speed and isotopic dilution(D), 1H MAS(E) and 13C CP/MAS(F) NMR spectra of activated α-Mg3(HCOO)6 and α-Mg3(HCOO)6 upon adsorption of DMF, benzene and pyridine[24] Copyright 2015, American Chemical Society.
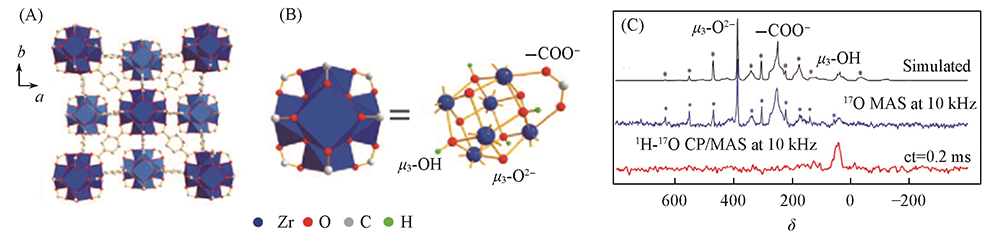
Fig.2 Structural illustration of UiO-66 framework(A), three types of oxygen coordination in UiO-66(B) and 17O MAS and 1H-17O CP/MAS NMR spectra of 17O isotope enriched Zr-UiO-66[33](C) Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
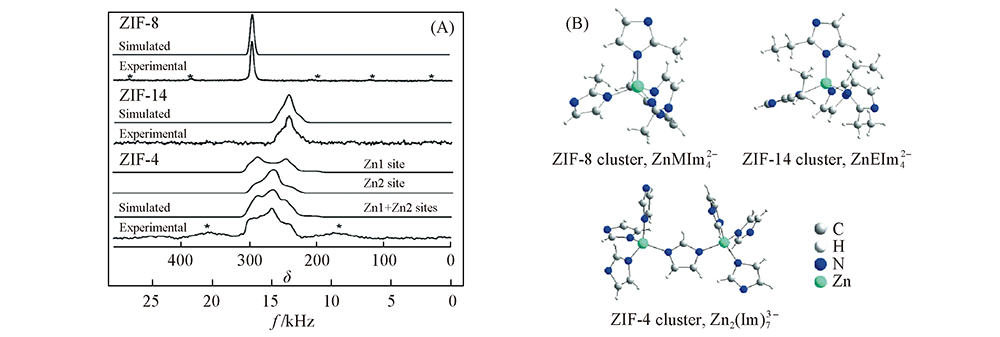
Fig.3 67Zn MAS NMR spectra of ZIF-8, ZIF-14, and ZIF-4 recorded at 21.1 T(A) and model clusters representing the structure of ZIF-8, ZIF-14, and ZIF-4(B)[36] Copyright 2012, John Wiley and sons.
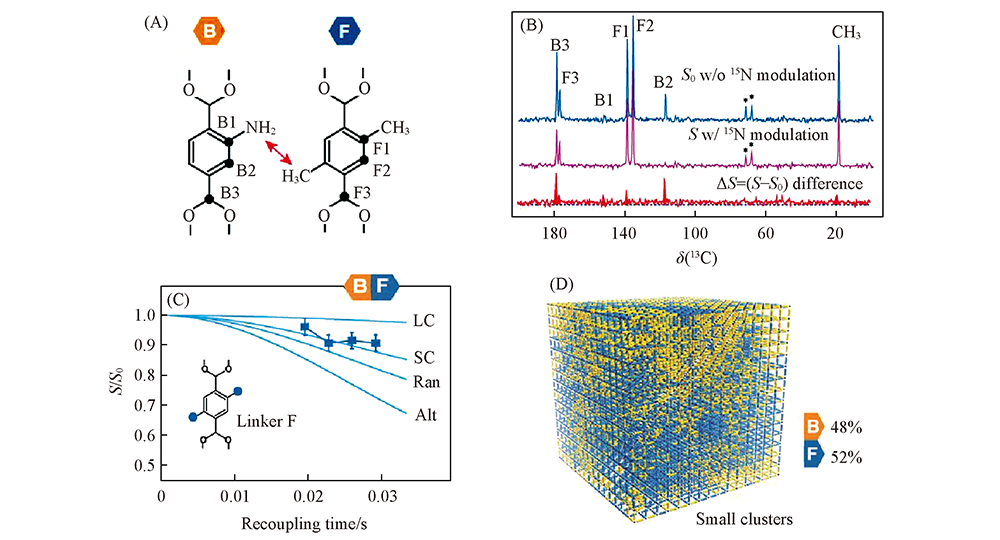
Fig.4 Molecular demostration of MTV-MOF-5-BF(A), 13C NMR spectra extracted from 13C{15N} REDOR experiment(B), 13C{15N} REDOR dephasing ratios and simulation curves using various models(C), and linker apportionment in MTV-MOF-5-BF(D)[45] Copyright 2013, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
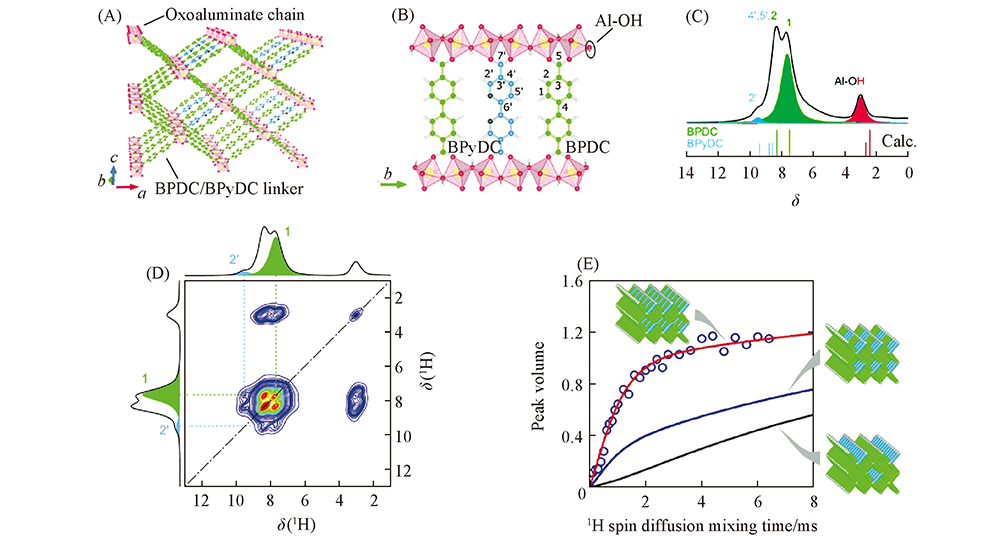
Fig.5 Structure demonstration of ML-DUT-5(A), various proton sites in ML-DUT-5 labled for spectral assignment(B), 1H MAS NMR spectra of ML-DUT-5(C), 1H-1H 2D spin diffusion spectrum of ML-DUT-5(D) and 1H spin diffusion buildup curves of different linker apportionments(E)[47] Copyright 2015, John Wiley and sons.
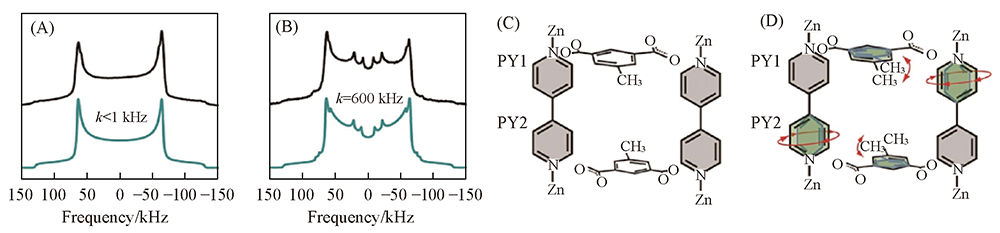
Fig.6 2H NMR spectra of CID-Me at 195 K(A) and 298 K(B) and pore window composed of bpy and 5-Me-ip at 195 K(C) and 296 K(D)[66] Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
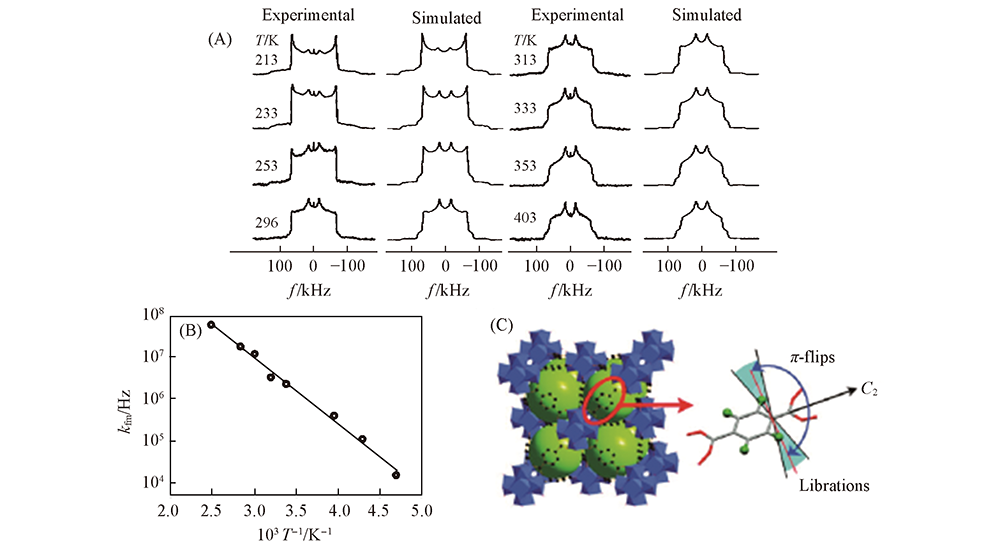
Fig.7 Variable 2H NMR spectra of deuterated 1,4-benzene-dicarboxylate(BDC) linker fragments of UiO-66(Zr)(A), Arrhenius plot for the mean flipping rate constant in UiO-66(B) and rotation of the BDC aromatic rings in UiO-66(C)[70] Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
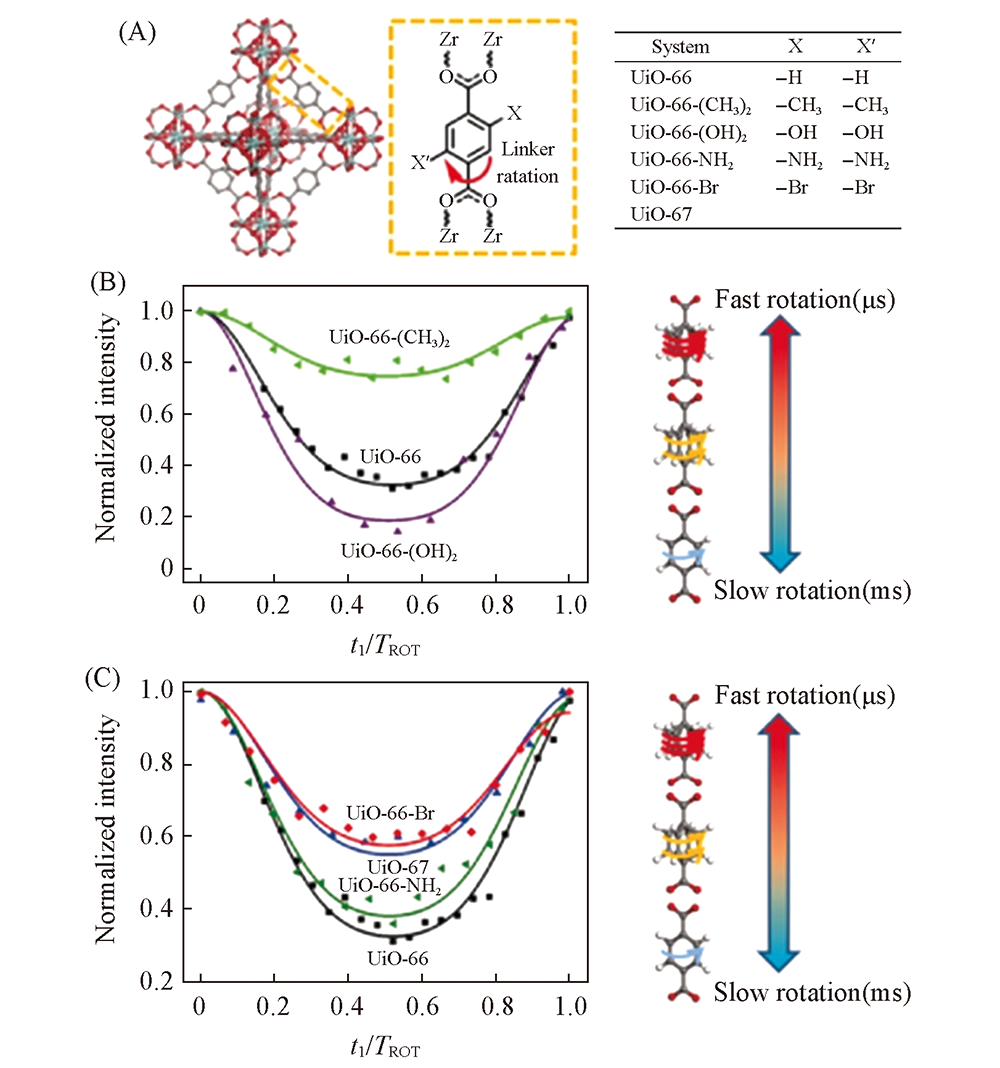
Fig.8 Structural demonstration of UiO-66-X(A), DIPSHIFT dephasing curves and scheme of linker rotation of UiO-66-X(B, C)[78] Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
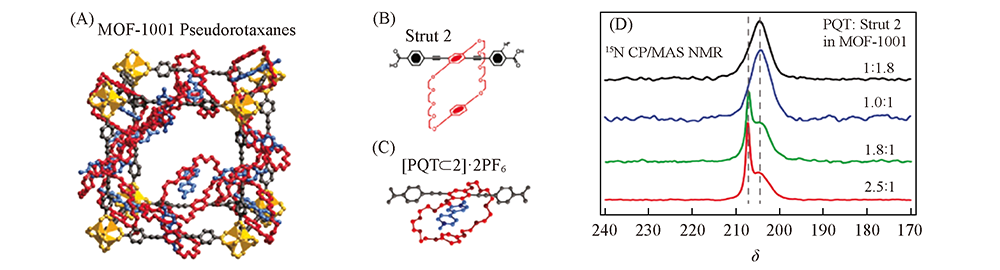
Fig.9 Structural demonstration of MOF-1001 pseudorotaxanes(A), organic linker of MOF-1001(B), PQT2+ adorbed on the organic linker(C) and 15N CP/MAS NMR spectra of MOF-1001 pseudorotaxanes(D)[82] Copyright 2009, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
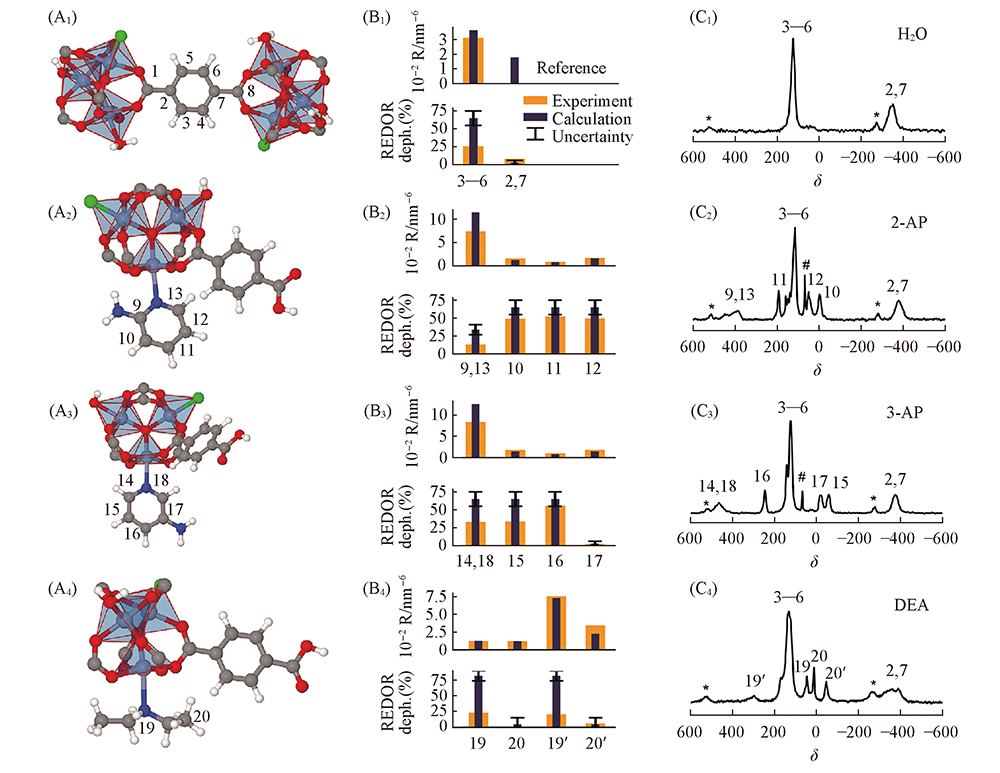
Fig.10 DFT-optimized structural fragments(A1—A4), experimental and calculated distance(B1—B4), 13C MAS NMR spectra(C1—C4) of H2O@Cr-MIL-101(A1—C1), 2-AP@Cr-MIL-101(A2—C2), 3-AP@Cr-MIL-101(A3—C3), and DEA@Cr-MIL-101(A4—C4)[88] Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society.
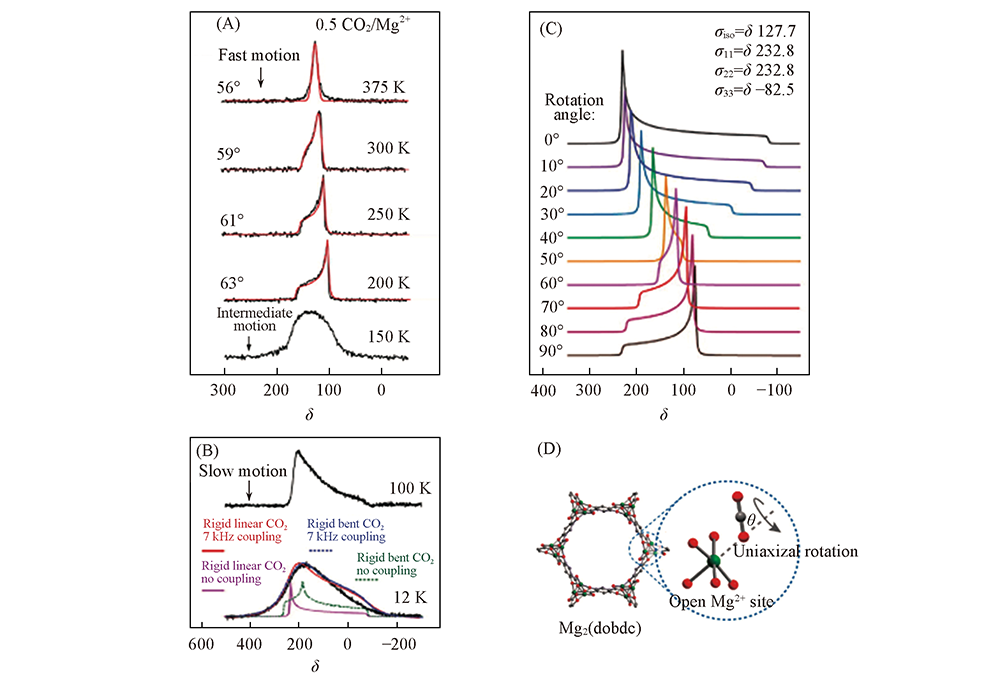
Fig.11 13C CSA powder patterns of 13C-enriched CO2 in Mg2(dobdc) acquried at variable temperature(A, B), 13C lineshapes simulations for CO2 uniaxial rotation(C) and illustration of CO2 uniaxial rotation at the open Mg2+ site in Mg2(dobdc)(D)[94] Copyright 2012, American Chemical Society.
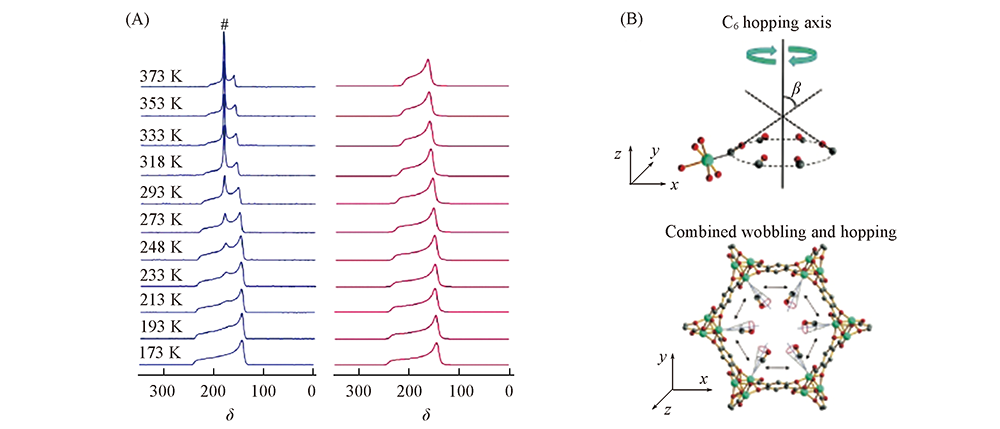
Fig.12 Variable-temperature 13C experimental(left) and simulated(right) NMR spectra of 13CO adsorbed on Mg-MOF-74(A) and schematic diagram illustrating the motions of CO(B) The # symbol denotes the resonance corresponding to mobile, isotropically tumbling CO[105]. Copyright 2016, John Wiley and sons.
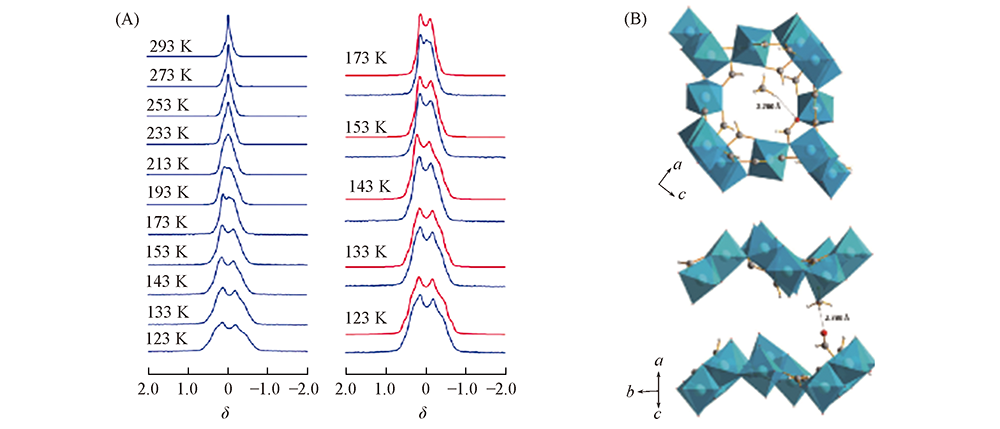
Fig.13 Static variable temperature 2H NMR spectra of CH3D adsorbed within α-Mg3(HCO2)6(A) and DFT-optimized structure of methane-loaded α-Mg3(HCO2)6(B)[109] (A): Left column denotes the experimetal spectra(in blue); right column demonstrates the representive experimental spectra(in blue) and corresponding simulated spectra(in red). Copyright 2018, John Wiley and sons.
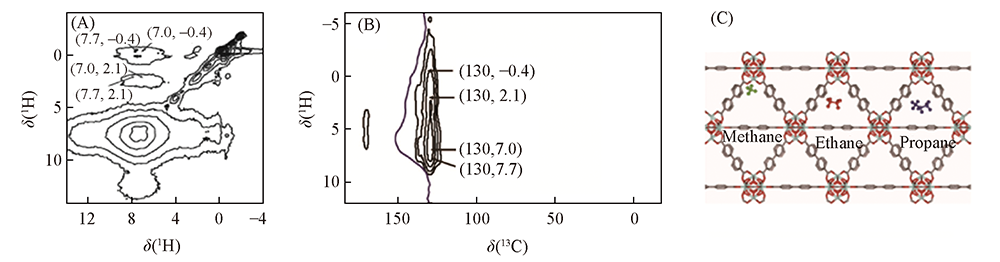
Fig.14 2D 1H-1H spin diffusion HOMCOR NMR spectra(A), 1H-13C HETCOR NMR spectra of UiO-67 upon methane adsorption with a spin diffusion mixing time of 36 ms(B) and schematic model of host-guest interaction between UiO-67 and light alkane(C)[110] Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
| [1] | Furukawa H., Cordova K. E., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2013,341(6149), 974— 989 |
| [2] | Ferey G., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2008,37(1), 191— 214 |
| [3] |
Liu C., Li F., Ma L. P., Cheng H. M., Adv. Mater., 2010,22(8), E28— E62
doi: 10.1002/adma.v22:8 URL |
| [4] | Sumida K., Rogow D. L., Mason J. A., McDonald T. M., Bloch E. D., Herm Z. R., Bae T. H., Long J. R., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 724— 781 |
| [5] |
Kreno L. E., Leong K., Farha O. K., Allendorf M., van Duyne R. P., Hupp J. T., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 1105— 1125
doi: 10.1021/cr200324t URL |
| [6] |
Li J. R., Sculley J., Zhou H. C., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 869— 932
doi: 10.1021/cr200190s URL |
| [7] |
Han Q., Wang Z., Chen X., Mao C., Li H., Yu R., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2019,35(4), 564— 569
doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-8415-z URL |
| [8] | Mu X., Jiang S. S., Zhang S. H., Ren H., Sun F. X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(9), 1818— 1824 |
| ( 穆鑫, 姜双双, 张舒皓, 任浩, 孙福兴 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(9), 1818— 1824) | |
| [9] | Hou J. Y., Hao J. J., Wang Y. Y., Liu J. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(9), 1926— 1931 |
| ( 侯俊英, 郝建军, 王雅雅, 刘敬春 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(9), 1926— 1931) | |
| [10] |
Horcajada P., Gref R., Baati T., Allan P. K., Maurin G., Couvreur P., Ferey G., Morris R. E., Serre C., Chem. Rev., 2012,112(2), 1232— 1268
doi: 10.1021/cr200256v URL |
| [11] |
Lee J., Farha O. K., Roberts J., Scheidt K. A., Nguyen S. T., Hupp J. T., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009,38(5), 1450— 1459
doi: 10.1039/b807080f URL |
| [12] |
Hou J., Hao J., Wang Y., Liu J., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2019,35(5), 860— 865
doi: 10.1007/s40242-019-9133-2 URL |
| [13] |
Zhang Y., Zhang F., Zhang X., Xu Y., Qi X., Quan C., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2018,34(4), 655— 660
doi: 10.1007/s40242-018-7361-5 URL |
| [14] | Wang P. C., Shan L., Fan Y., Wang L., Xu J. N., Wu S. J., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(8), 1655— 1661 |
| ( 王鹏程, 单梁, 范勇, 王莉, 徐家宁, 吴淑杰 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(8), 1655— 1661) | |
| [15] |
Brown S. P., Spiess H. W., Chem. Rev., 2001,101(12), 4125— 4155
doi: 10.1021/cr990132e URL |
| [16] |
Laws D. D., Bitter H. M. L., Jerschow A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2002,41(17), 3096— 3129
doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020902)41:17<>1.0.CO;2-C URL |
| [17] |
Li S., Deng F., Annu. Rep. NMR Spectro., 2013,78, 1— 54
doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-404716-7.00001-8 URL |
| [18] |
Lucier B. E. G., Chen S., Huang Y., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018,51(2), 319— 330
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00357 URL |
| [19] | Sutrisno A., Huang Y ., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2013, 49—50, 1— 11 |
| [20] |
Witherspoon V. J., Xu J., Reimer J. A., Chem. Rev., 2018,118(20), 10033— 10048
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00695 URL |
| [21] |
Marchetti A., Chen J., Pang Z., Li S., Ling D., Deng F., Kong X., Adv. Mater., 2017,29(14), 1605895
doi: 10.1002/adma.v29.14 URL |
| [22] |
Ding S. Y., Dong M., Wang Y. W., Chen Y. T., Wang H. Z., Su C. Y., Wang W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(9), 3031— 3037
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b10754 URL |
| [23] |
Ben T., Ren H., Ma S., Cao D., Lan J., Jing X., Wang W., Xu J., Deng F., Simmons J. M., Qiu S., Zhu G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2009,48(50), 9457— 9460
doi: 10.1002/anie.200904637 URL |
| [24] |
Xu J., Terskikh V. V., Chu Y., Zheng A., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2015,27(9), 3306— 3316
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b00360 URL |
| [25] |
Devautour-Vinot S., Maurin G., Serre C., Horcajada P., da Cunha D. P., Guillerm V., Costa E. d. S., Taulelle F., Martineau C., Chem. Mater., 2012,24(11), 2168— 2177
doi: 10.1021/cm300863c URL |
| [26] |
Loiseau T., Serre C., Huguenard C., Fink G., Taulelle F., Henry M., Bataille T., Ferey G., Chem. Eur. J., 2004,10(6), 1373— 1382
doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1521-3765 URL |
| [27] |
Dawson D. M., Jamieson L. E., Mohideen M. I. H., McKinlay A. C., Smellie I. A., Cadou R., Keddie N. S., Morris R. E., Ashbrook S. E., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013,15(3), 919— 929
doi: 10.1039/C2CP43445H URL |
| [28] |
Tong Y. B., Liu S. X., Zou Y., Xue C., Duan H. B., Liu J. L., Ren X. M., Inorg. Chem., 2016,55(22), 11716— 11726
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b01759 URL |
| [29] |
Li Y., Wu X. P., Jiang N., Lin M., Shen L., Sun H., Wang Y., Wang M., Ke X., Yu Z., Gao F., Dong L., Guo X., Hou W., Ding W., Gong X. Q., Grey C. P., Peng L., Nat. Commun., 2017,8, 581
doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-00603-7 URL |
| [30] |
Wang M., Wu X. P., Zheng S., Zhao L., Li L., Shen L., Gao Y., Xue N., Guo X., Huang W., Gan Z., Blanc F., Yu Z., Ke X., Ding W., Gong X. Q., Grey C. P., Peng L., Sci. Adv., 2015,1(1), e1400133
doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1400133 URL |
| [31] |
Peng L. M., Liu Y., Kim N. J., Readman J. E., Grey C. P., Nat. Mater., 2005,4(3), 216— 219
doi: 10.1038/nmat1332 URL |
| [32] |
Peng L., Stebbins J. F., J. Non-Crys. Solids, 2008,354(27), 3120— 3128
doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2008.01.026 URL |
| [33] |
He P., Xu J., Terskikh V. V., Sutrisno A., Nie H. Y., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(33), 16953— 16960
doi: 10.1021/jp403512m URL |
| [34] |
Bignami G. P. M., Davis Z. H., Dawson D. M., Morris S. A., Russell S. E., McKay D., Parke R. E., Iuga D., Morris R. E., Ashbrook S. E., Chem. Sci., 2018,9(4), 850— 859
doi: 10.1039/C7SC04649A URL |
| [35] |
Mueller M., Hermes S., Kaehler K., van den Berg M. W. E., Muhler M., Fischer R. A., Chem. Mater., 2008,20(14), 4576— 4587
doi: 10.1021/cm703339h URL |
| [36] |
Sutrisno A., Terskikh V. V., Shi Q., Song Z., Dong J., Ding S. Y., Wang W., Provost B. R., Daff T. D., Woo T. K., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2012,18(39), 12251— 12259
doi: 10.1002/chem.201201563 URL |
| [37] |
Xu J., Lucier B. E. G., Sinelnikov R., Terskikh V. V., Staroverov V. N., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2015,21(41), 14348— 14361
doi: 10.1002/chem.201501954 URL |
| [38] |
He P., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Shi Q., Dong J., Chu Y., Zheng A., Sutrisno A., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(41), 23728— 23744
doi: 10.1021/jp5063868 URL |
| [39] |
Xu J., Blaakrneer E. S. M., Lipton A. S., McDonald T. M., Liu Y. M., Smit B., Long J. R., Kentgens A. P. M., Reimert J. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017,121(36), 19938— 19945
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b07809 URL |
| [40] |
Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Chen M., Terskikh V. V., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2018,24(35), 8732— 8736
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.35 URL |
| [41] | Jiang Y., Huang J., Marx S., Kleist W., Hunger M., Baiker A ., J. vPhys. Chem. Lett., 2010,1(19), 2886— 2890 |
| [42] | Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Zheng R., Huang Y., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2017,84, 118— 131 |
| [43] | Deng H., Doonan C. J., Furukawa H., Ferreira R. B., Towne J., Knobler C. B., Wang B., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2010,327(5967), 846— 850 |
| [44] |
Abednatanzi S., Gohari Derakhshandeh P., Depauw H., Coudert F. X., Vrielinck H., van Der Voort P., Leus K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019,48(9), 2535— 2565
doi: 10.1039/C8CS00337H URL |
| [45] |
Kong X., Deng H., Yan F., Kim J., Swisher J. A., Smit B., Yaghi O. M., Reimer J. A., Science, 2013,341(6148), 882— 885
doi: 10.1126/science.1241606 URL |
| [46] | Giovine R., Volkringer C., Trebosc J., Amoureux J. P., Loiseau T., Lafon O., Pourpoint F., Acta Crystallog. C, 2017,73, 176— 183 |
| [47] |
Krajnc A., Kos T., Logar N. Z., Mali G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015,54(36), 10535— 10538
doi: 10.1002/anie.201504426 URL |
| [48] |
Bueken B van Velthoven N., Krajnc A., Smolders S., Taulelle F., Mellot-Draznieks C., Mali G., Bennett T. D., de Vos D., ., Chem. Mater., 2017,29(24), 10478— 10486
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b04128 URL |
| [49] |
Krajnc A., Bueken B., De Vos D., Mali G ., J. Magn. Reson., 2017,279, 22— 28
doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2017.04.008 URL |
| [50] |
Jayachandrababu K. C., Verploegh R. J., Leisen J., Nieuwendaal R. C., Sholl D. S., Nair S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(23), 7325— 7336
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b02754 URL |
| [51] |
Jayachandrababu K. C., Sholl D. S., Nair S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017,139(16), 5906— 5915
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b01660 URL |
| [52] |
Springuel-Huet M. A., Nossov A., Adem Z., Guenneau F., Volkringer C., Loiseau T., Ferey G., Gedeon A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010,132(33), 11599— 11607
doi: 10.1021/ja103105y URL |
| [53] |
Springuel-Huet M. A., Nossov A., Guenneau F., Gedeon A., Chem. Commun., 2013,49(67), 7403— 7405
doi: 10.1039/c3cc43119c URL |
| [54] |
Chen Y. Z., Gu B., Uchida T., Liu J., Liu X., Ye B. J., Xu Q., Jiang H. L., Nat. Commun., 2019,10, 3462
doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11449-6 URL |
| [55] |
Cao W., Wang W. D., Xu H. S., Sergeyev I. V., Struppe J., Wang X., Mentink-Vigier F., Gan Z., Xiao M. X., Wang L. Y., Chen G. P., Ding S. Y., Bai S., Wang W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(22), 6969— 6977
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b02839 URL |
| [56] | Rossini A. J., Zagdoun A., Lelli M., Canivet J., Aguado S., Ouari O., Tordo P., Rosay M., Maas W. E., Coperet C., Farrusseng D., Emsley L., Lesage A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012,51(1), 123— 127 |
| [57] |
Todorova T. K., Rozanska X., Gervais C., Legrand A., Ho L. N., Berruyer P., Lesage A., Emsley L., Farrusseng D., Canivet J., Mellot-Draznieks C., Chem. Eur. J., 2016,22(46), 16531— 16538
doi: 10.1002/chem.201603255 URL |
| [58] |
Guo Z., Kobayashi T., Wang L. L., Goh T. W., Xiao C., Caporini M. A., Rosay M., Johnson D. D., Pruski M., Huang W., Chem. Eur. J., 2014,20(49), 16308— 16313
doi: 10.1002/chem.v20.49 URL |
| [59] |
Kobayashi T., Perras F. A., Goh T. W., Metz T. L., Huang W., Pruski M., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2016,7(13), 2322— 2327
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.6b00860 URL |
| [60] |
Pourpoint F., Thankamony A. S. L., Volkringer C., Loiseau T., Trebosc J., Aussenac F., Carnevale D., Bodenhausen G., Vezin H., Lafon O., Amoureux J. P., Chem. Commun., 2014,50(8), 933— 935
doi: 10.1039/C3CC47208F URL |
| [61] |
Hong M., Zhang Y., Hu F. H., Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2012,63, 1— 24
doi: 10.1146/annurev-physchem-032511-143731 URL |
| [62] |
Rapp A., Schnell I., Sebastiani D., Brown S. P., Percec V., Spiess H. W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003,125(43), 13284— 13297
doi: 10.1021/ja035127d URL |
| [63] |
Fu D. W., Cai H. L., Li S. H., Ye Q., Zhou L., Zhang W., Zhang Y., Deng F., Xiong R. G., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2013,110(25), 257601
doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.257601 URL |
| [64] |
Ye H. Y., Li S. H., Zhang Y., Zhou L., Deng F., Xiong R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014,136(28), 10033— 10040
doi: 10.1021/ja503344b URL |
| [65] |
Ji C., Li S., Deng F., Sun Z., Li L., Zhao S., Luo J ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016,120(48), 27571— 27576
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b09890 URL |
| [66] |
Ferey G., Serre C., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2009,38(5), 1380— 1399
doi: 10.1039/b804302g URL |
| [67] |
Ott L. S., Cline M. L., Deetlefs M., Seddon K. R., Finke R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,127(16), 5758— 5759
doi: 10.1021/ja0423320 URL |
| [68] |
Gonzalez-Nelson A., Coudert F. X., van der Veen M. A., Nanomaterials, 2019,9(3), 330— 365
doi: 10.3390/nano9030330 URL |
| [69] | Inukai M., Tamura M., Horike S., Higuchi M., Kitagawa S., Nakamura K., Angew. Chem. Int.Ed., 2018,57(28), 8687— 8690 |
| [70] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Serre C., Frick B., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(22), 12131— 12136
doi: 10.1021/jp3029193 URL |
| [71] |
Kolokolov D. I., Jobic H., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Devic T., Serre C., Ferey G., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010,49(28), 4791— 4794
doi: 10.1002/anie.201001238 URL |
| [72] |
Gonzalez J., Devi R. N., Tunstall D. P., Cox P. A., Wright P. A., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2005,84(1—3), 97— 104
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2005.04.019 URL |
| [73] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Guillerm V., Serre C., Frick B., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(22), 12131— 12136
doi: 10.1021/jp3029193 URL |
| [74] |
Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Jobic H., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(29), 15978— 15984
doi: 10.1021/jp506010p URL |
| [75] |
Inukai M., Fukushima T., Hijikata Y., Ogiwara N., Horike S., Kitagawa S ., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015,137(38), 12183— 12186
doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b05413 URL |
| [76] |
Eddaoudi M., Kim J., Rosi N., Vodak D., Wachter J., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2002,295(5554), 469— 472
doi: 10.1126/science.1067208 URL |
| [77] |
Deria P., Mondloch J. E., Karagiaridi O., Bury W., Hupp J. T., Farha O. K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43(16), 5896— 5912
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00067F URL |
| [78] |
Damron J. T., Ma J., Kurz R., Saalwaechter K., Matzger A. J., Ramamoorthy A., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018,57(28), 8678— 8681
doi: 10.1002/anie.v57.28 URL |
| [79] |
Li S. H., Pourpoint F., Trebosc J., Zhou L., Lafon O., Shen M., Zheng A. M., Wang Q., Amoureux J. P., Deng F., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014,5(17), 3068— 3072
doi: 10.1021/jz501389z URL |
| [80] |
Xu J., Wang Q., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019,52(8), 2179— 2189
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00125 URL |
| [81] |
Zheng A., Li S., Liu S. B., Deng F., Acc. Chem. Res., 2016,49(4), 655— 663
doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.6b00007 URL |
| [82] |
Li Q., Zhang W., Miljanic O. S., Sue C. H., Zhao Y. L., Liu L., Knobler C. B., Stoddart J. F., Yaghi O. M., Science, 2009,325(5942), 855— 859
doi: 10.1126/science.1175441 URL |
| [83] |
Xu X., Li S., Liu Q., Liu Z., Yan W., Zhao L., Zhang W., Zhang L., Deng F., Cong H., Deng H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019,11(1), 973— 981
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b19211 URL |
| [84] |
Nandy A., Forse A. C., Witherspoon V. J., Reimer J. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2018,122(15), 8295— 8305
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b12628 URL |
| [85] | Tang J., Li S., Chui Y., Xiao Y., Xu J., Deng F., Magn. Reson. Chem., 2020, DOI: 10.1002/mrc.4923 |
| [86] |
Wack J., Siegel R., Ahnfeldt T., Stock N., Mafra L., Senker J ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(39), 19991— 20001
doi: 10.1021/jp4063252 URL |
| [87] |
Li S., Li J., Tang J., Deng F ., Solid State Nucl. Magn. Reson., 2018,90, 1— 6
doi: 10.1016/j.ssnmr.2017.12.004 URL |
| [88] |
Wittmann T., Mondal A., Tschense C. B. L., Wittmann J. J., Klimm O., Siegel R., Corzilius B., Weber B., Kaupp M., Senker J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(6), 2135— 2144
doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b10148 URL |
| [89] |
Tang J., Li S., Chu Y., Xiao Y., Xu J., Deng F ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(39), 24062— 24070
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b06332 URL |
| [90] |
Khan A. H., Peikert K., Hoffmann F., Fröba M., Bertmer M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(7), 4299— 4307
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11919 URL |
| [91] |
Gul-E-Noor F Jee B., Pöppl A., Hartmann M., Himsl D., Bertmer M., ., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2011,13(17), 7783— 7788
doi: 10.1039/c0cp02848g URL |
| [92] |
Gul-E-Noor F., Michel D., Krautscheid H., Haase J., Bertmer M., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2013,180, 8— 13
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2013.06.033 URL |
| [93] |
Fu Y., Kang Z. Z., Yin J. L., Cao W. C., Tu Y. Q., Wang Q., Kong X. Q., Nano Lett., 2019,19(3), 1618— 1624
doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04518 URL |
| [94] |
Kong X., Scott E., Ding W., Mason J. A., Long J. R., Reimer J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012,134(35), 14341— 14344
doi: 10.1021/ja306822p URL |
| [95] |
Chen M., Chen S., Chen W., Lucier B. E. G., Zhang Y., Zheng A., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2018,30(11), 3613— 3617
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b00681 URL |
| [96] |
Wang W. D., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Wang W., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2014,5(19), 3360— 3365
doi: 10.1021/jz501729d URL |
| [97] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Huang Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016,18(12), 8327— 8341
doi: 10.1039/C5CP04984A URL |
| [98] |
Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Boyle P. D., Huang Y., Chem. Mater., 2016,28(16), 5829— 5846
doi: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.6b02239 URL |
| [99] |
Lu Y., Lucier B. E. G., Zhang Y., Ren P., Zheng A., Huang Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017,19(8), 6130— 6141
doi: 10.1039/C7CP00199A URL |
| [100] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., McKenzie S. M., Arhangelskis M., Morris A. J., Friscic T., Reid J. W., Terskikh V. V., Chen M., Huang Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018,10(34), 28582— 28596
doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b08562 URL |
| [101] |
Desveaux B. E., Wong Y. T. A., Lucier B. E. G., Terskikh V. V., Boyle P. D., Jiang S., Huang Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(29), 17798— 17807
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b03221 URL |
| [102] |
Sin M., Kavoosi N., Rauche M., Pallmann J., Paasch S., Senkovska I., Kaskel S., Brunner E ., Langmuir, 2019,35(8), 3162— 3170
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03554 URL |
| [103] |
McDonald T. M., Mason J. A., Kong X., Bloch E. D., Gygi D., Dani A., Crocella V., Giordanino F., Odoh S. O., Drisdell W. S., Vlaisavljevich B., Dzubak A. L., Poloni R., Schnell S. K., Planas N., Lee K., Pascal T., Wan L. F., Prendergast D., Neaton J. B., Smit B., Kortright J. B., Gagliardi L., Bordiga S., Reimer J. A., Long J. R., Nature, 2015,519(7543), 303— 308
doi: 10.1038/nature14327 URL |
| [104] |
Forse A. C., Milner P. J., Lee J. H., Redfearn H. N., Oktawiec J., Siegelman R. L., Martell J. D., Dinakar B., Porter-Zasada L. B., Gonzalez M. I., Neaton J. B., Long J. R., Reimer J. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018,140(51), 18016— 18031
doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b10203 URL |
| [105] | Lucier B. E. G., Chan H., Zhang Y., Huang Y., Eur.J. Inorg. Chem., 2016,2016(13/14), 2017— 2024 |
| [106] |
Gul-E-Noor F Mendt M., Michel D., Poeppl A., Krautscheid H., Haase J., Bertmer M., ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013,117(15), 7703— 7712
doi: 10.1021/jp400869f URL |
| [107] |
Wong Y. T. A., Babcock T. K., Chen S., Lucier B. E. G., Huang Y., Langmuir, 2018,34(51), 15640— 15649
doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02205 URL |
| [108] |
He Y. B., Zhou W., Qian G. D., Chen B. L., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014,43(16), 5657— 5678
doi: 10.1039/C4CS00032C URL |
| [109] |
Zhang Y., Lucier B. E. G., Fischer M., Gan Z., Boyle P. D., Desveaux B., Huang Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2018,24(31), 7866— 7881
doi: 10.1002/chem.v24.31 URL |
| [110] |
Li J., Li S., Zheng A., Liu X., Yu N., Deng F ., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017,121(26), 14261— 14268
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.7b04611 URL |
| [111] |
Wehring M., Gascon J., Dubbeldam D., Kapteijn F., Snurr R. Q., Stallmach F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010,114(23), 10527— 10534
doi: 10.1021/jp102212w URL |
| [112] |
Chmelik C., Freude D., Bux H., Haase J., Micropor. Mesopor. Mat., 2012,147(1), 135— 141
doi: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2011.06.009 URL |
| [113] |
Freude D., Dvoyashkina N., Arzumanov S. S., Kolokolov D. I., Stepanov A. G., Chmelik C., Jin H., Li Y., Kaerger J., Haase J., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019,123(3), 1904— 1912
doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b11673 URL |
| [114] |
Pantatosaki E., Megariotis G., Pusch A. K., Chmelik C., Stallmach F., Papadopoulos G. K., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012,116(1), 201— 207
doi: 10.1021/jp207771s URL |
| [115] |
Ramsahye N. A., Gao J., Jobic H., Llewellyn P. L., Yang Q., Wiersum A. D., Koza M. M., Guillerm V., Serre C., Zhong C. L., Maurin G., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014,118(47), 27470— 27482
doi: 10.1021/jp509672c URL |
| [116] |
Berens S., Chmelik C., Hillman F., Kaerger J., Jeong H. K., Vasenkov S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2018,20(37), 23967— 23975
doi: 10.1039/C8CP04889D URL |
| [1] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | 李志光, 齐国栋, 徐君, 邓风. Sn-Al-β分子筛酸性在葡萄糖转化反应中作用的固体NMR研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220138. |
| [3] | 姜宏斌, 代文臣, 张娆, 徐晓晨, 陈捷, 杨光, 杨凤林. Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3陶瓷膜对VOCs废气的分离催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [4] | 曾晛阳, 赵熹, 黄旭日. 细胞松弛素B对葡萄糖/质子共转运蛋白GlcPSe的抑制机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [5] | 刘嘉欣, 闵杰, 许华杰, 任海生, 谈宁馨. 基于反应力场分子模拟的乙烯燃烧自由基与氮气相互作用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [6] | 张小玉, 薛冬萍, 杜宇, 蒋粟, 魏一帆, 闫文付, 夏会聪, 张佳楠. MOF衍生碳基电催化剂限域催化O2还原和CO2还原反应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210689. |
| [7] | 李华, 杨科, 黄俊峰, 陈凤娟. UiO-66-NH2/wood的设计构筑及高效去除水中微量重金属离子性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210701. |
| [8] | 陈瀚翔, 边绍菊, 胡斌, 李武. LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O溶液体系渗透压的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [9] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [10] | 张伶育, 张继龙, 曲泽星. RDX分子内振动能量重分配的动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [11] | 王婕, 霍海燕, 王洋, 张仲, 刘术侠. 铜箔上原位合成NENU-n系列多酸基MOFs的通用策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210557. |
| [12] | 莫宗文, 张学文, 周浩龙, 周东东, 张杰鹏. 一种多孔配位聚合物的氢键协同客体响应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210576. |
| [13] | 柳雪广, 杨晓珊, 马菁菁, 刘伟生. 铕基金属有机框架材料从混合染料中选择性分离亚甲基蓝[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210715. |
| [14] | 王美银, 黄道丰, 陈欣, 周俊夫, 任远航, 叶林, 岳斌, 贺鹤勇. 介孔磷钨酸铯盐的液相组装及酸性研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2734. |
| [15] | 雷晓彤, 金怡卿, 孟烜宇. 基于分子模拟方法预测PIP2在双孔钾通道TREK-1上结合位点的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||