

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 2272.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180170
收稿日期:2018-03-04
出版日期:2018-09-29
发布日期:2018-09-29
作者简介:联系人简介: 尤静林, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事分子光谱和无机结构研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
YANG Yejin, YOU Jinglin*( ), WANG Jian, WANG Min, HE Yingxia, WU Zhidong
), WANG Jian, WANG Min, HE Yingxia, WU Zhidong
Received:2018-03-04
Online:2018-09-29
Published:2018-09-29
Contact:
YOU Jinglin
E-mail:jlyou@staff.shu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
运用原位高温拉曼光谱技术研究了KHSO4从室温至550 ℃的相变过程, 分别基于密度泛函理论及量子化学从头算分析KHSO4晶体和K2S2O7熔体的分子振动和拉曼光谱散射活性, 对拉曼光谱特征峰进行归属, 并获取KHSO4与K2S2O7熔体团簇特征振动的拉曼散射截面, 建立特征峰面积与物种浓度的直观关系, 并通过Factsage数据库研究KHSO4分解过程的热力学性能. 结果表明, 210 ℃下KHSO4链状结构向二聚体结构转换, KHSO4由正交α相变为单斜β相; 220-550 ℃分解为K2S2O7, 由平衡常数K计算得到反应焓ΔH=(72.59±2.40) kJ/mol.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
杨冶金, 尤静林, 王建, 王敏, 何莹霞, 吴志东. 硫酸氢钾及其熔体结构的原位高温拉曼光谱与分解热力学研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2272.
YANG Yejin,YOU Jinglin,WANG Jian,WANG Min,HE Yingxia,WU Zhidong. In-situ High Temperature Raman Spectroscopic and Decomposition Thermodynamic Study of the Structure of Potassium Hydrogen Sulfate and Its Melt†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2272.
| Raman shifta/cm-1 | Structureb | Vibrational mode | Raman shifta/cm-1 | Structureb | Vibrational mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 412 | s | D | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 871 | m | C | S—OH symmetric vibration(νs S—OH) |
| 444 | s | D | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 1004 | s | C | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 450 | s | C | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 1028 | s | D | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 570 | m | C+D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1164 | w | C | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
| 580 | s | D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1224 | w | D | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
| 588 | s | C | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1239 | w | D | O—H deformation(δOH) |
| 597 | s | D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1250 | w | D | O—H bending(γOH) |
| 615 | m | C+D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1284 | w | D | O—S—O asymmetric vibration(νas O—S—O) |
| 854 | s | D | S—OH symmetric vibration(νs S—OH) | 1337 | w | C | O—S—O asymmetric vibration(νas O—S—O) |
Table 1 Assignment of major vibrational modes of KHSO4 at ambient temperature
| Raman shifta/cm-1 | Structureb | Vibrational mode | Raman shifta/cm-1 | Structureb | Vibrational mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 412 | s | D | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 871 | m | C | S—OH symmetric vibration(νs S—OH) |
| 444 | s | D | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 1004 | s | C | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 450 | s | C | S—OH bending(βS—OH) | 1028 | s | D | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 570 | m | C+D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1164 | w | C | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
| 580 | s | D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1224 | w | D | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
| 588 | s | C | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1239 | w | D | O—H deformation(δOH) |
| 597 | s | D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1250 | w | D | O—H bending(γOH) |
| 615 | m | C+D | O—S—O deformation(δO—S—O) | 1284 | w | D | O—S—O asymmetric vibration(νas O—S—O) |
| 854 | s | D | S—OH symmetric vibration(νs S—OH) | 1337 | w | C | O—S—O asymmetric vibration(νas O—S—O) |
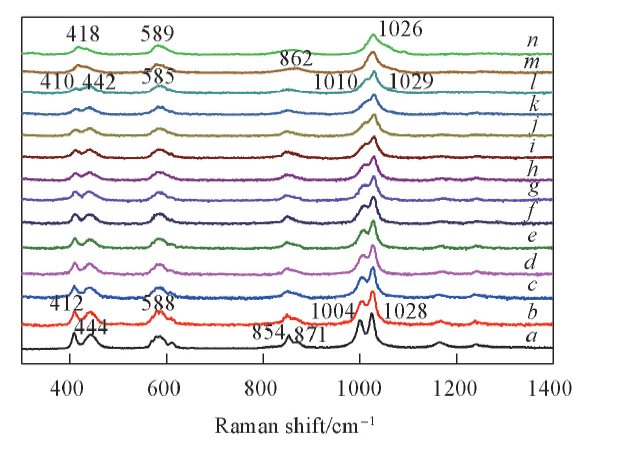
Fig.3 Temperature dependent Raman spectra of KHSO4 in the frequency range of 300—1400 cm-1 from ambient temperature to 220 ℃Temperature/℃: a. r. t.; b. 100; c. 110; d. 120; e. 130; f. 140; g. 150; h. 160; i. 170; j. 180; k. 190; l. 200; m. 210; n. 220.
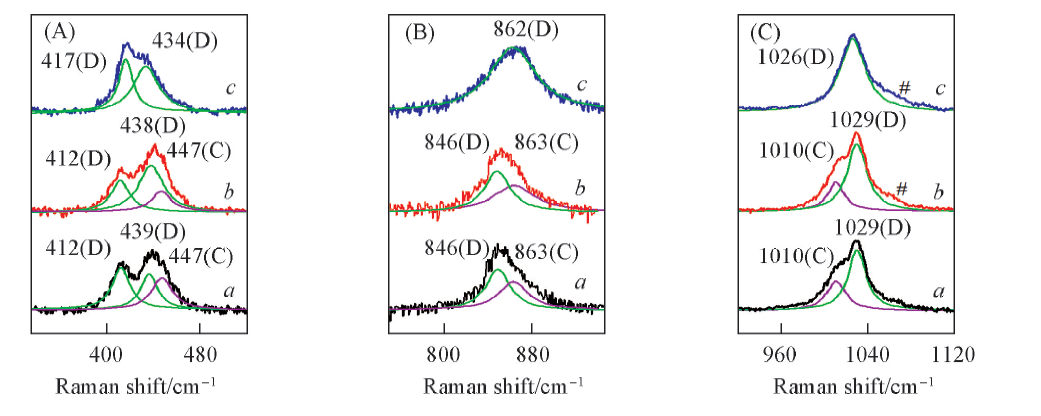
Fig.5 In-situ Raman spectra of the molten KHSO4 at 190 ℃(a), 200 ℃(b) and 210 ℃(c) along with the deconvolution of the bands of melts(D: dimer, C: chain)(A) βS—OH; (B) νs S—OH; (C) νs S—O. # Represents Raman characteristic band of K2S2O7 decomposed from trace KHSO4.
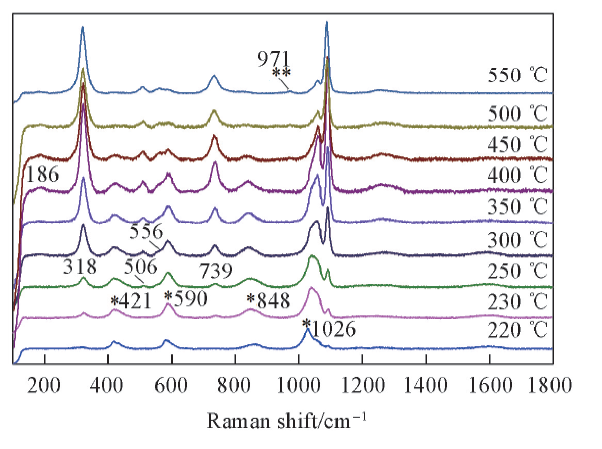
Fig.6 Temperature dependent Raman spectra of KHSO4-K2S2O7 in the frequency range of 100—1800 cm-1 from 220 ℃ to 550 ℃* and ** represent νs S—O of KHSO4 and νs S—O of K2SO4, respectively.
| Raman shift/cm-1 | Vibrational mode | Raman shift/cm-1 | Vibrational mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 186w | S—O swing vibration(ρS—O) | 739m | S—O—S symmetric vibration(νs S—O—S) |
| 318s | S—O—S deformation(δS—O—S) | 971w** | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 506w | S—O—S bending(βS—O—S) | 1060w* | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 556w | S—O deformation(δO—S) | 1090s | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 590w | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
Table 2 Raman vibrational mode assignments of K2S2O7-K2SO4 melt at 550 ℃
| Raman shift/cm-1 | Vibrational mode | Raman shift/cm-1 | Vibrational mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| 186w | S—O swing vibration(ρS—O) | 739m | S—O—S symmetric vibration(νs S—O—S) |
| 318s | S—O—S deformation(δS—O—S) | 971w** | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 506w | S—O—S bending(βS—O—S) | 1060w* | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 556w | S—O deformation(δO—S) | 1090s | S—O symmetric vibration(νs S—O) |
| 590w | S—O deformation(δS—O) |
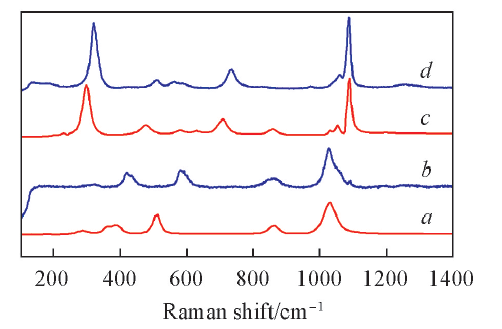
Fig.7 Experimental and calculated Raman spectra at 220 and 550 ℃The scaling factor is 0.92 and the Lorentzian smearing is 15 cm-1. a. Calculated Raman spectrum of KHSO4 cluster; b. KHSO4(l) experimental Raman spectrum at 220 ℃; c. calculated Raman spectrum of K2S2O7 cluster; d. K2S2O7(l) experimental Raman spectrum at 550 ℃.
| Temperature/℃ | lnK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 230 | 13196 | 623 | 0.9762 | 0.0238 | -3.6884 |
| 250 | 23750 | 2448 | 0.9494 | 0.0506 | -2.8792 |
| 300 | 13689 | 5287 | 0.8335 | 0.1665 | -1.4282 |
| 350 | 11894 | 11403 | 0.6684 | 0.3316 | -0.2983 |
| 400 | 9676 | 15741 | 0.5430 | 0.4570 | 0.4383 |
| 450 | 5423 | 17596 | 0.3733 | 0.6267 | 1.5036 |
| 500 | 1180 | 6022 | 0.2748 | 0.7252 | 2.2624 |
| 550 | 834 | 8331 | 0.16208 | 0.8380 | 3.4632 |
Table 3 Raman characteristic band area at 1060, 1090 cm-1 (AHSO4-, AS2O72-), molar fraction of HSO4-, S2O72-(xHSO4-, xS2O72-) and lnK from 230 ℃ to 550 ℃
| Temperature/℃ | lnK | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 230 | 13196 | 623 | 0.9762 | 0.0238 | -3.6884 |
| 250 | 23750 | 2448 | 0.9494 | 0.0506 | -2.8792 |
| 300 | 13689 | 5287 | 0.8335 | 0.1665 | -1.4282 |
| 350 | 11894 | 11403 | 0.6684 | 0.3316 | -0.2983 |
| 400 | 9676 | 15741 | 0.5430 | 0.4570 | 0.4383 |
| 450 | 5423 | 17596 | 0.3733 | 0.6267 | 1.5036 |
| 500 | 1180 | 6022 | 0.2748 | 0.7252 | 2.2624 |
| 550 | 834 | 8331 | 0.16208 | 0.8380 | 3.4632 |
| System | Δ (kJ·mol-1) | Tfus/K | ΔfusH/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ttrans/K | ΔtransH/ (kJ·mol-1) | Cp/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | T/K | Cp/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | T/K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KHSO4 | -1163.00 | 495 | 18.00 | 442 | 2.10(α→β) | -62.50+0.56T | 298—488 | 287.00 | 488—545 |
| 453 | 4.00(β→γ) | ||||||||
| K2S2O7 | -1997.96 | 419 | 21.20 | 591 | 21.80(s1→s2) | 134.7+0.177T | 298—590 | 260.40 | 590—692 |
| H2O | 285.83 | 500 | 40.86 | — | — | 2.47×10-6T3- | 298—500 | -5.52×10-7T2 + | 500—1000 |
| 3.19×10-3T2+ | 0.016T+ | ||||||||
| 1.52T+ | 1107.27T-1- | ||||||||
| 3848757.66T-2- | 27999.32T-2+ | ||||||||
| 203.12 | 25.78 |
Table 4 Thermodynamic properties of KHSO4, K2S2O7 and H2O*
| System | Δ (kJ·mol-1) | Tfus/K | ΔfusH/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ttrans/K | ΔtransH/ (kJ·mol-1) | Cp/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | T/K | Cp/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | T/K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KHSO4 | -1163.00 | 495 | 18.00 | 442 | 2.10(α→β) | -62.50+0.56T | 298—488 | 287.00 | 488—545 |
| 453 | 4.00(β→γ) | ||||||||
| K2S2O7 | -1997.96 | 419 | 21.20 | 591 | 21.80(s1→s2) | 134.7+0.177T | 298—590 | 260.40 | 590—692 |
| H2O | 285.83 | 500 | 40.86 | — | — | 2.47×10-6T3- | 298—500 | -5.52×10-7T2 + | 500—1000 |
| 3.19×10-3T2+ | 0.016T+ | ||||||||
| 1.52T+ | 1107.27T-1- | ||||||||
| 3848757.66T-2- | 27999.32T-2+ | ||||||||
| 203.12 | 25.78 |
| [1] | Najafpour M.M., MoghaddamN. J., New Journal of Chemistry, 2017, 41(5), 1—16 |
| [2] | Busnardo R.G., Busnardo N. G., Salvato G. N., Afonso J. C., Hazardous Materials, 2007, 139(2), 391—398 |
| [3] | Paulino J.F., Busnardo N. G., Afonso J. C., Hazardous Materials, 2008, 150(3), 843—849 |
| [4] | Pérez M., Ruiz D., Autino J., Sathicq A., Romanelli G., Comptes Rendus Chimie, 2016, 19(5), 551—555 |
| [5] | Parry G.S., Glasser L., Crystalline, 1960, 113(1—6), 57—64 |
| [6] | Goypiron A., de Villepin J., Novak A., Raman Spectroscopy, 1980, (9), 297—303 |
| [7] | Bukleski M., Vladimir V., Vladimir P., Vibrational Spectroscopy, 2011, 57(1), 15—22 |
| [8] | Matsuo Y., Ferroelectrics, 2004, 302(1), 85—90 |
| [9] | Hamma H., Rasmussen S.B., Rogez J., Elbelghiti M. A., Eriksen K. M., Fehrmann R., Thermochemica Acta, 2006, 440(2), 200—204 |
| [10] | Hatem G., Eriksen K.M., Fehrmann R., Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2002, 68(1), 25—30 |
| [11] | Swain D., Bhadram V.S., Pradhan G. K., Venkataprasad, Bhat S. V., Narayana C., Rao C. N. R., Physical Chemistry, 2010, 114(37), 10040—10044 |
| [12] | Periasamy A., Muruganand S., Palaniswamy M., Rasayan Journal of Chemistry, 2009, 2(4), 9781—9789 |
| [13] | Sharon M., Kalia A.K., Solid State Chemistry, 1980, 31(3), 295—303 |
| [14] | Fehramnn R., Hansen N.H., Bjerrum N. J., Inorganic Chemistry, 1983, 22(26), 4009—4014 |
| [15] | Walrafen G.E., Irish D. E., Young T. F., Chemical Physics, 1962, 37(3), 662—670 |
| [16] | Swain D., Row T.N., Inorganic Chemistry, 2008, 47(19), 8613—8615 |
| [17] | Knudsen C.B., Kalampounias A. G., Fehrmann R., Boghosian S., Physical Chemistry B, 2008, 112(38), 11996—12000 |
| [18] | Dey B., Jain Y.S., Verma A. L., Raman Spectroscopy, 1982, 13(3), 209—212 |
| [19] | Merinov B.V., Solid State Ionics, 1996, 84(1/2), 89—96 |
| [20] | Eriksen K.M., Fehrmann R., Hatem G., Escard M. G., Lapina O. B., Mastikhin V. M., Physical Chemistry, 1996, 100(25), 10771—10778 |
| [21] | You J.L., Novel High Temperature Raman Spectroscopic Techniques, Spectral Calculation and Their Application in Micro-structure Study of Inorganic Materials, Shanghai University,Shanghai, 2006 |
| (尤静林. 高温拉曼光谱创新技术、 光谱计算和在无机化合物微结构研究中的应用,上海: 上海大学, 2006) | |
| [22] | Li S.P., Wu G. M., Zheng X. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2004, 25(8), 1495—1498 |
| (李少鹏, 吴光明, 郑旭明. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(8), 1495—1498) | |
| [23] | Kalampounias A.G., Boghosian S., Applied Spectroscopy, 2009, 63(9), 1050—1056 |
| [24] | Hatem G., Eriksen K.M., Fehrmann R., Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2002, 68(1), 25—30 |
| [25] | Hatem G., Eriksen K.M., Escard M. G., Fehrmann R., Catalysis, 2002, 19(3), 323—331 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [3] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [4] | 王坤, 邹星礼, 曹战民, 李重河, 鲁雄刚. 多重短程有序准化学模型: 有序原子对的对立与统一[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220391. |
| [5] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [6] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [7] | 周成思, 赵远进, 韩美晨, 杨霞, 刘晨光, 贺爱华. 硅烷类外给电子体对丙烯-丁烯序贯聚合的调控作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [8] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [9] | 黄罗仪, 翁约约, 黄旭慧, 王朝杰. 车前草中黄酮类成分结构和性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [10] | 钟声广, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 电中性团簇MCu2Ox(M=Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+)上甲烷和二氧化碳直接合成乙酸的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [11] | 马丽娟, 高升启, 荣祎斐, 贾建峰, 武海顺. Sc, Ti, V修饰B/N掺杂单缺陷石墨烯的储氢研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [12] | 刘昌辉, 梁国俊, 李妍璐, 程秀凤, 赵显. NH3在硼纳米管表面吸附的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [13] | 应富鸣, 计辰儒, 苏培峰, 吴玮. 基于完全活性空间自洽场的杂化多组态密度泛函方法λ-DFCAS[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [14] | 郑若昕, 张颖, 徐昕. 低标度XYG3双杂化密度泛函的开发与测评[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [15] | 王建, 张红星. 四配位铂磷光发射体结构与光物理性质关系的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||