

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (3): 429.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160775
王睿1, 李一粒1, 凤旭凯1, 宋亮1, 张田雷1( ), 王竹青2, 靳玲侠1, 张强1, 许琼1, 王志银1
), 王竹青2, 靳玲侠1, 张强1, 许琼1, 王志银1
收稿日期:2016-11-08
出版日期:2017-03-10
发布日期:2017-02-23
作者简介:联系人简介: 张田雷, 男, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事理论与计算化学研究. E-mail: 基金资助:
WANG Rui1, LI Yili1, FENG Xukai1, SONG Liang1, ZHANG Tianlei1,*( ), WANG Zhuqing2, JIN Lingxia1, ZHANG Qiang1, XU Qiong1, WANG Zhiyin1
), WANG Zhuqing2, JIN Lingxia1, ZHANG Qiang1, XU Qiong1, WANG Zhiyin1
Received:2016-11-08
Online:2017-03-10
Published:2017-02-23
Contact:
ZHANG Tianlei
E-mail:ztianlei88@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)方法对n(H2O)(n=0,1,2)参与HO2+NOHNO3反应的微观机理和速率常数进行了研究. 结果表明, 由于水分子与HO2形成的复合物(H2O…HO2, HO2…H2O)结合NO与水分子形成的复合物(NO…H2O, ON…H2O)的反应方式具有较高能垒和较低有效速率, 其对HO2+NO
HNO3反应的影响远小于双体水(H2O)2与HO2(或NO)形成复合物然后再与另一分子反应物NO(或HO2)的反应方式, 因此n(H2O)(n=1,2)催化HO2+NO
HNO3反应主要经历了HO2…(H2O)n(n=1,2)+NO和NO…(H2O)n(n=1,2)+HO2 2种反应类型. 由于HO2…(H2O)n(n=1, 2)+NO反应的低能垒和高速率, HO2…(H2O)n(n=1,2)+NO反应优于NO…(H2O)n(n=1,2)+HO2反应. 与此同时, 由于计算温度范围内HO2…H2O+NO反应的有效速率常数比HO2…(H2O)2+NO反应对应的有效速率常数大了10~12数量级, 可推测(H2O)n(n=1,2)催化HO2+NO
HNO3反应主要来自于单个水分子. 此外, 在216.7~298.6 K范围内水分子对HO2+NO
HNO3反应起显著的正催化作用, 且随温度的升高有明显增大的趋势, 在298.2 K时增强因子k'RW1/ktotal达到67.93%, 表明在实际大气环境中水蒸气对HO2+NO
HNO3反应具有显著影响.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
王睿, 李一粒, 凤旭凯, 宋亮, 张田雷, 王竹青, 靳玲侠, 张强, 许琼, 王志银. n(H2O)(n=1,2)在HO2+NOHNO3反应中的催化机制研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(3): 429.
WANG Rui, LI Yili, FENG Xukai, SONG Liang, ZHANG Tianlei, WANG Zhuqing, JIN Lingxia, ZHANG Qiang, XU Qiong, WANG Zhiyin. Catalytic Effect of n(H2O)(n=1,2) on the Reaction of HO2+NOHNO3 †. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(3): 429.
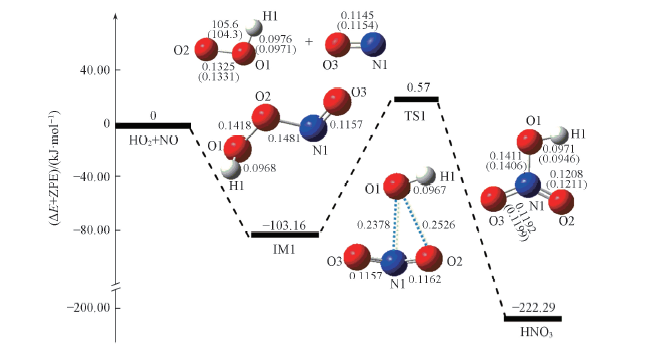
Fig.1 Schematic energy diagrams for the HO2+NO HNO3 reaction Bond lengths are in nm: bond anyels are in deyree. The values in parenthese are the experimental values and taken from Ref. [33].
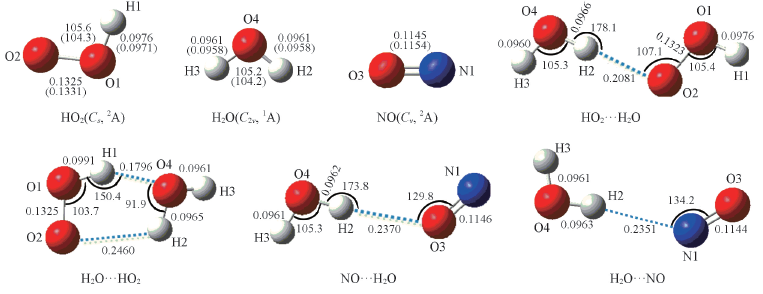
Fig.2 Geometrical parameters for HO2, NO, H2O, H2O…HO2, HO2…H2O, NO…H2O and ON…H2O complexes optimized at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory Bond lengths are in nm, bond angles are in degree. The values in paranthese are the experimental values and taken from Ref.[32].
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O+NO+H2O | 0 | 148.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O…HOO+NO | 10.65 | 121.69 | -39.61 | -32.02 | 1.75 | -28.96 |
| IMW1 | 19.36 | 88.12 | -139.85 | -125.57 | -49.93 | -120.49 |
| TSW1 | 10.94 | 94.59 | -22.68 | -6.89 | 60.68 | -3.62 |
| IMWF1 | 28.94 | 79.91 | -286.55 | -266.43 | -180.55 | -257.62 |
| HOO…H2O+NO | 6.60 | 129.24 | -14.62 | -8.34 | 16.01 | -8.02 |
| IMW2 | 16.05 | 94.65 | -118.16 | -105.26 | -37.75 | -102.11 |
| TSW2 | 12.34 | 87.11 | -0.17 | 5.22 | 82.12 | 12.16 |
| IMWF2 | 24.87 | 91.60 | -254.28 | -235.17 | -163.86 | -229.42 |
| NO…H2O+HOO | 2.49 | 137.10 | -4.69 | -0.85 | 13.69 | -2.21 |
| IMW3 | 15.74 | 95.45 | -114.71 | -101.86 | -35.35 | -98.97 |
| TSW3 | 13.73 | 85.27 | -4.35 | 1.72 | 80.92 | 9.38 |
| IMWF3 | 25.16 | 79.93 | -254.90 | -235.69 | -164.31 | -229.74 |
| H2O…NO+HOO | 2.92 | 129.99 | -6.35 | -4.87 | 18.54 | -3.43 |
| IMW4 | 16.04 | 90.76 | -123.22 | -111.02 | -38.67 | -107.18 |
| TSW4 | 11.90 | 87.65 | -2.10 | 3.82 | 80.05 | 9.79 |
| HNO3+H2O | 20.20 | 108.67 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
Table 1 Zero-point energy(ZPE), entropies(S), relative energies(ΔE, ΔE+ZPE), free energies[ΔG(298 K)] and enthalpies[ΔH(298 K)] for the HO2+NO reaction with a water molecule at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory*
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2O+NO+H2O | 0 | 148.76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| H2O…HOO+NO | 10.65 | 121.69 | -39.61 | -32.02 | 1.75 | -28.96 |
| IMW1 | 19.36 | 88.12 | -139.85 | -125.57 | -49.93 | -120.49 |
| TSW1 | 10.94 | 94.59 | -22.68 | -6.89 | 60.68 | -3.62 |
| IMWF1 | 28.94 | 79.91 | -286.55 | -266.43 | -180.55 | -257.62 |
| HOO…H2O+NO | 6.60 | 129.24 | -14.62 | -8.34 | 16.01 | -8.02 |
| IMW2 | 16.05 | 94.65 | -118.16 | -105.26 | -37.75 | -102.11 |
| TSW2 | 12.34 | 87.11 | -0.17 | 5.22 | 82.12 | 12.16 |
| IMWF2 | 24.87 | 91.60 | -254.28 | -235.17 | -163.86 | -229.42 |
| NO…H2O+HOO | 2.49 | 137.10 | -4.69 | -0.85 | 13.69 | -2.21 |
| IMW3 | 15.74 | 95.45 | -114.71 | -101.86 | -35.35 | -98.97 |
| TSW3 | 13.73 | 85.27 | -4.35 | 1.72 | 80.92 | 9.38 |
| IMWF3 | 25.16 | 79.93 | -254.90 | -235.69 | -164.31 | -229.74 |
| H2O…NO+HOO | 2.92 | 129.99 | -6.35 | -4.87 | 18.54 | -3.43 |
| IMW4 | 16.04 | 90.76 | -123.22 | -111.02 | -38.67 | -107.18 |
| TSW4 | 11.90 | 87.65 | -2.10 | 3.82 | 80.05 | 9.79 |
| HNO3+H2O | 20.20 | 108.67 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
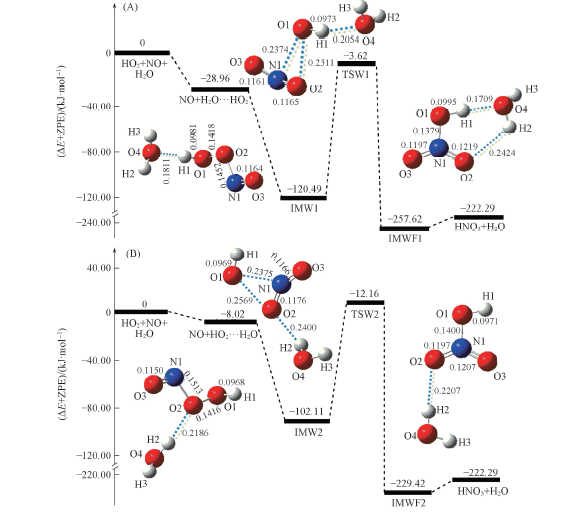
Fig.3 Schematic energy diagrams for H2O…HO2+NO(channel RW1, A) and HO2…H2O+NO(channel RW2, B) reactions at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level
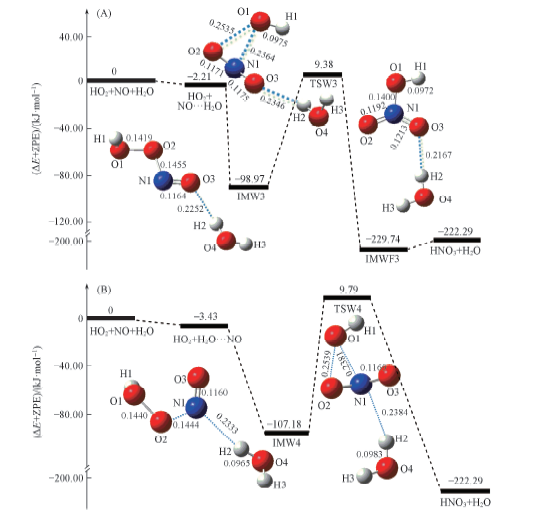
Fig.4 Schematic energy diagrams in the reaction of NO…H2O+HO2(channel RW3, A) and ON…H2O+HO2 (channel RW4, B) at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level
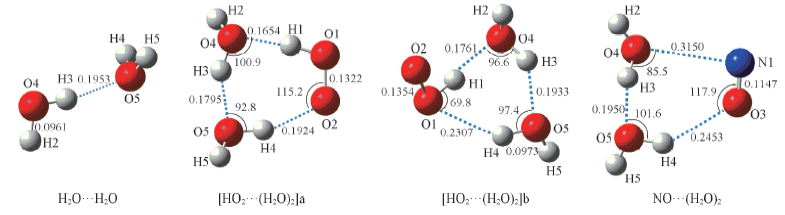
Fig.5 Geometrical parameters for (H2O)2, HO2…(H2O)2 and NO…(H2O)2 complexes optimized at the B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory Bond lengths are in nm, bond angles are in degree.
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HO2+NO+(H2O)2 | 0 | 173.153 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]a+NO | 14.53 | 132.57 | -66.62 | -57.71 | -7.08 | -52.09 |
| IMWW1 | 22.08 | 99.25 | -160.58 | -145.38 | -53.19 | -138.51 |
| TSWW1 | 14.81 | 88.92 | 22.32 | 23.75 | 128.82 | 37.12 |
| IMWWF1 | 30.29 | 94.70 | -308.12 | -287.57 | -189.70 | -277.83 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO | 11.96 | 132.40 | -28.38 | -22.37 | 28.47 | -12.74 |
| IMWW2 | 21.88 | 100.62 | -164.80 | -149.80 | -59.31 | -142.91 |
| TSWW2 | 14.86 | 105.12 | -38.97 | -30.15 | 54.71 | -24.11 |
| IMWWF2 | 28.15 | 101.28 | -296.89 | -276.46 | -186.79 | -268.74 |
| NO…(H2O)2+HO2 | 3.58 | 152.58 | -9.35 | -4.72 | 20.95 | -5.77 |
| IMWW3 | 20.87 | 90.25 | -67.97 | -58.68 | 44.75 | -41.70 |
| TSWW3 | 12.39 | 101.892 | -29.09 | -22.47 | 66.42 | -16.70 |
| HNO3+(H2O)2 | 20.20 | 133.06 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
Table 2 Zero-point energy(ZPE), entropies(S), relative energies[ΔE, Δ(E+ZPE)], free energies[ΔG(298 K)] and enthalpies[ΔH(298 K)] for water dimer-catalyzed the HO2+NO reaction at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p) level of theory
| System | ZPE/ (kJ·mol-1) | S/ (J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔE/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔH/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔG/ (kJ·mol-1) | (ΔE+ZPE)/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HO2+NO+(H2O)2 | 0 | 173.153 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]a+NO | 14.53 | 132.57 | -66.62 | -57.71 | -7.08 | -52.09 |
| IMWW1 | 22.08 | 99.25 | -160.58 | -145.38 | -53.19 | -138.51 |
| TSWW1 | 14.81 | 88.92 | 22.32 | 23.75 | 128.82 | 37.12 |
| IMWWF1 | 30.29 | 94.70 | -308.12 | -287.57 | -189.70 | -277.83 |
| [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO | 11.96 | 132.40 | -28.38 | -22.37 | 28.47 | -12.74 |
| IMWW2 | 21.88 | 100.62 | -164.80 | -149.80 | -59.31 | -142.91 |
| TSWW2 | 14.86 | 105.12 | -38.97 | -30.15 | 54.71 | -24.11 |
| IMWWF2 | 28.15 | 101.28 | -296.89 | -276.46 | -186.79 | -268.74 |
| NO…(H2O)2+HO2 | 3.58 | 152.58 | -9.35 | -4.72 | 20.95 | -5.77 |
| IMWW3 | 20.87 | 90.25 | -67.97 | -58.68 | 44.75 | -41.70 |
| TSWW3 | 12.39 | 101.892 | -29.09 | -22.47 | 66.42 | -16.70 |
| HNO3+(H2O)2 | 20.20 | 133.06 | -242.49 | -229.21 | -179.20 | -222.29 |
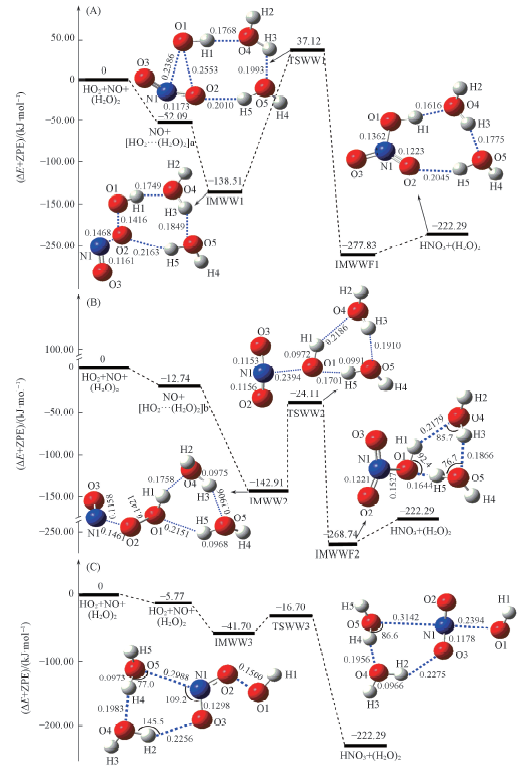
Fig.6 Schematic energy diagrams in the reaction of HO2…(H2O)2+NO(A, B) and NO…(H2O)2+HO2 (channel RWW3, C) at the CCSD(T)/aug-cc-pVTZ//B3LYP/6-311+G(2df,2p)+ZPE level (A) Channel RWW1; (B) channel RWW2.
| h/km | T/K | 1014kR1 | 1013kRW1 | 1015k'RW1 | 1011kRWW2 | 1025k'RWW2 | 1015kRWW3 | 1028k'RWW3 | 1013ktotal | k'RW1/ktotal(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 298.2 | 5.69 | 1.80 | 381 | 1.23 | 566 | 50.5 | 0.178 | 4.38 | 67.93 |
| 0 | 288.2 | 5.76 | 1.68 | 240 | 1.33 | 975 | 38.6 | 1.74 | 2.98 | 58.83 |
| 2 | 275.2 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 243 | 1.50 | 390 | 23.8 | 6.47 | 3.02 | 61.32 |
| 4 | 262.2 | 6.14 | 1.40 | 200 | 1.74 | 220 | 15.6 | 35.3 | 2.61 | 58.73 |
| 6 | 249.3 | 6.48 | 1.29 | 78.1 | 2.06 | 27.0 | 10.8 | 410 | 1.43 | 37.70 |
| 8 | 236.3 | 6.97 | 1.19 | 46.7 | 2.55 | 7.49 | 7.71 | 1010 | 1.16 | 28.15 |
| 10 | 223.3 | 7.72 | 1.12 | 27.2 | 3.29 | 1.85 | 5.72 | 2890 | 1.04 | 19.57 |
| 12 | 216.7 | 8.24 | 1.09 | 9.92 | 3.84 | 0.205 | 4.64 | 947 | 0.923 | 8.36 |
Table 3 Rate constants(cm3·molecule-1·s-1) for the process of HNO3 formation occurring through the reactions of HO2+NO, H2O…HO2+NO, [HO2…(H2O)2]b+NO and NO…(H2O)2+HO2 within the temperature range of 216.7—298.2 K*
| h/km | T/K | 1014kR1 | 1013kRW1 | 1015k'RW1 | 1011kRWW2 | 1025k'RWW2 | 1015kRWW3 | 1028k'RWW3 | 1013ktotal | k'RW1/ktotal(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 298.2 | 5.69 | 1.80 | 381 | 1.23 | 566 | 50.5 | 0.178 | 4.38 | 67.93 |
| 0 | 288.2 | 5.76 | 1.68 | 240 | 1.33 | 975 | 38.6 | 1.74 | 2.98 | 58.83 |
| 2 | 275.2 | 5.91 | 1.53 | 243 | 1.50 | 390 | 23.8 | 6.47 | 3.02 | 61.32 |
| 4 | 262.2 | 6.14 | 1.40 | 200 | 1.74 | 220 | 15.6 | 35.3 | 2.61 | 58.73 |
| 6 | 249.3 | 6.48 | 1.29 | 78.1 | 2.06 | 27.0 | 10.8 | 410 | 1.43 | 37.70 |
| 8 | 236.3 | 6.97 | 1.19 | 46.7 | 2.55 | 7.49 | 7.71 | 1010 | 1.16 | 28.15 |
| 10 | 223.3 | 7.72 | 1.12 | 27.2 | 3.29 | 1.85 | 5.72 | 2890 | 1.04 | 19.57 |
| 12 | 216.7 | 8.24 | 1.09 | 9.92 | 3.84 | 0.205 | 4.64 | 947 | 0.923 | 8.36 |
| [1] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., Phys. Chem. Comm., 2001, 4(25), 127—132 |
| [2] | Wallington T. J., Dagaut P., Kurylo M. J., Chem. Rev., 1992, 92(4), 667—710 |
| [3] | Leu M., J. Chem. Phys., 1979, 70(4), 1662—1666 |
| [4] | Xu W. B., Earth Environ., 1999, 27(3),86—91 |
| (徐文彬. 地球与环境, 1999, 27(3), 86—91) | |
| [5] | Atkinson R., Baulch D. L., Co R. A., Crowley J. N., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2004, 3(6), 1461—1738 |
| [6] | Bardwell M. W., Bacak A., Raventos M. T., Percival C. J., Sanchez-Reyna G., Shallcross D. E., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5(11), 2381—2385 |
| [7] | Zhang J., Donahue N. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(21), 6898—6911 |
| [8] | Lightfoot P. D., Cox R. A., Crowley J. N., Destriau M., Hayman G. D., Jenkin M. E., Atmos. Environ., 1992, 26(10), 1805—1961 |
| [9] | Howard C. J., J. Chem. Phys., 1979, 71(6), 2352—2359 |
| [10] | Butkovskaya N., Le Bras G., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(37), 9047—9053 |
| [11] | Atkinson R., Baulch D. L., Cox R. A., Hampson R. F., Kerr J. A., Rossi M. J., Troe J., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data,1997, 26(6), 1329—1499 |
| [12] | Chakraborty D., Park J., Lin M. C., Chem. Phys., 1998, 231(1), 39—49 |
| [13] | Jemialade A. A., Thrush B. A., J. Chem. Soc., 1990, 86(20), 3355—3363 |
| [14] | Margitan J. J., J. Phys.Chem., 1984, 88(15), 129—130 |
| [15] | Dyke J. M., Jonathan N., Lewis A. E., Mol. Phys., 1983, 50(1), 77—89 |
| [16] | Thrush B. A., Wilkinson J. P. T., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1981, 81(1), 1—3 |
| [17] | Butkovskaya N. I., Kukui A., Pouvesl N., Le Bras G. J., Phys. Chem. A, 2005, 109(29), 6509—6520 |
| [18] | Butkovskaya N., Rayez M. T., Rayez J. C., Kukui A., Le B. G., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 113(42), 11327—11342 |
| [19] | Buszek R. J., Francisco J. S., Anglada J. M., Int. Rev. Phys. Chem., 2011, 30(3), 335—369 |
| [20] | Pfeilsticker K., Lotter A., Peters C., Bosch H., Science,2003, 300(5628), 2078—2080 |
| [21] | Dunn M. E., Pokon E. K., Shields G. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2004, 126(8), 2647—2653 |
| [22] | Vaida V., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(2), 020901 |
| [23] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [24] | Zhang T. L., Yang C., Feng X. K., Kang J., Song L., Lu Y., Wan Z. Y., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18(26), 17414—17427 |
| [25] | Zhang T. L., Wang R., Wang W. L., Min S. T., Xu Q., Wang Z. Y., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2014, 1045, 135—144 |
| [26] | Viegas L. P., Varandas A. J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2016, 120(8), 1560—1568 |
| [27] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., Phys. Chem. Comm., 2003, 6(13), 51—54 |
| [28] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [29] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S., Tomasi S. J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Nanayakkara Y., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Revision D.02, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2004 |
| [30] | Zhang S.W., Truong N. T., VKLab Version1.0, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, 2001 |
| [31] | Si W. J., Zhuo S. P., Ju G. Z., Acta Phys. Chim. Sinica, 2003, 19(10), 974—977 |
| (司维江, 禚淑萍, 居冠之. 物理化学学报, 2003, 19(10), 974—977) | |
| [32] | Chen J.F., Cheng W., Dou Y. L.,J. Mol. Sci., 2016, (6), 515—522 |
| (陈静飞, 成伟, 窦玉龙. 分子科学学报, 2016, (6), 515—522) | |
| [33] | From the NIST Chemistry Webbook, . |
| [34] | Long B., Tan X. F., Long Z. W., Wang Y. B., Ren D. S., Zhang W. J., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2011, 115(24), 6559—6567 |
| [35] | Yung Y. L., DeMore W. B., J. Atmos. Chem., 2001, 39(2), 215—216 |
| [36] | Zhu R. S., Lin M. C., J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119(20), 10667—10677 |
| (Ed.:Y, Z, S) |
| [1] | 姜胜寒, 曹长林, 肖荔人, 杨唐, 钱庆荣, 陈庆华. 基于紫外屏蔽性能的云母/MnO2/TiO2复合半导体微米片的制备及在聚丙烯中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220071. |
| [2] | 周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [3] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [4] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [5] | 高文秀, 吕杰琼, 高永平, 孔长剑, 王雪平, 郭胜男, 娄大伟. 富氮多孔有机聚合物催化制备α⁃氰基肉桂酸乙酯[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220078. |
| [6] | 孙翠红, 吕立强, 刘迎, 王妍, 杨静, 张绍文. 硝酸异丙酯与Cl原子、 OH和NO3自由基反应的机理及动力学[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [7] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [8] | 孟繁伟, 高琦, 叶青, 李晨曦. Cu-SAPO-18催化剂氨选择性催化还原NOx钾中毒机理的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [9] | 陈旺, 胡代花, 刘格歌. 由醋酸去氢表雄酮合成熊去氧胆酸[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2782. |
| [10] | 杨一莹, 朱荣秀, 张冬菊, 刘成卜. 金催化炔基苯并二𫫇英环化合成8-羟基异香豆素的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [11] | 李心怡, 刘永军. 人工设计逆醛缩酶RA95.5-8F催化β-羟基酮C—C裂解的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2306. |
| [12] | 李宜蔚, 申屠江涛, 王静波, 李象远. 燃烧反应机理构建的极小反应网络方法: C1燃料燃烧[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1871. |
| [13] | 田胜侨, 韦美菊. Rh(Ⅱ)催化吲哚衍生物[3+3]环化机理及产物性质分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1899. |
| [14] | 任颖, 李昌华, 王涛, 薛珊珊, 张婷婷, 贾建峰, 武海顺. 钯催化氧化N—H键羰基化反应合成1,3,4⁃噁二唑⁃2(3H)⁃酮杂环化合物机理的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1793. |
| [15] | 齐国栋, 叶晓栋, 徐君, 邓风. 分子筛上糖类催化转化的核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(1): 148. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||