

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (9): 1954.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180309
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Received:2018-04-23
Online:2018-09-07
Published:2018-06-26
Contact:
HUA Er
E-mail:huaer0101@hotmail.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
XU Yu,HUA Er. Hydrogen Bonding Study on Protic Ionic Liquids Composed of N-Alkyl Ethylenediaminum Cations with Trifluoroacetic Anion†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1954.
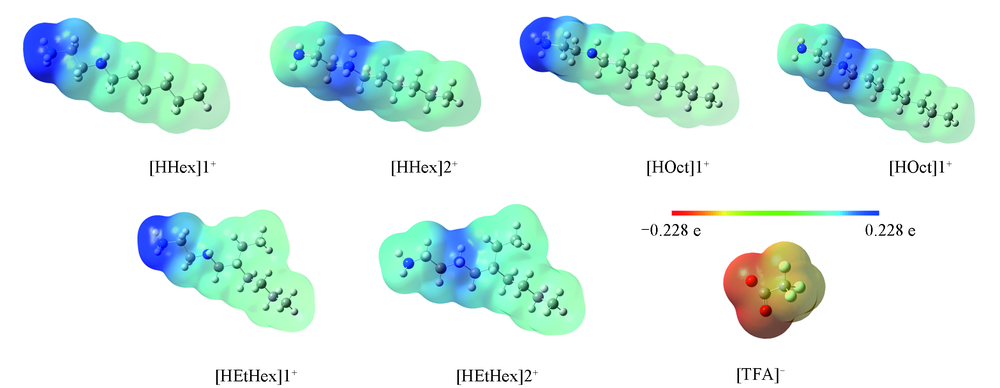
Fig.1 Electrostatic potential surface of [HAlkyl]+ cations and [TFA]- anion at the M06-2X/ 6-311G(d,p) level N: Blue; O: red; H: white; C: gray; F: light blue.
| Structure | ΔEint/(kJ∙mol-1) | BSSE/(kJ∙mol-1) | Δ | ΔEHB/(kJ∙mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | -539.40 | 83.85 | -519.36 | -81.55 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | -528.86 | 113.80 | -501.66 | -71.00 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | -501.62 | 123.64 | -472.04 | -75.23 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | -501.16 | 131.17 | -469.82 | -74.81 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | -510.74 | 107.32 | -485.09 | -84.35 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | -534.84 | 84.31 | -514.72 | -77.28 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | -521.70 | 126.11 | -491.58 | -64.14 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | -497.02 | 124.22 | -467.31 | -74.98 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | -496.77 | 130.79 | -465.51 | -74.73 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | -506.18 | 106.69 | -480.70 | -84.14 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | -539.65 | 70.21 | -522.87 | -81.55 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | -529.07 | 113.26 | -502.00 | -70.92 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | -481.45 | 132.01 | -449.91 | -69.79 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | -490.62 | 144.47 | -456.06 | -78.91 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | -499.78 | 115.60 | -472.16 | -88.12 |
Table 1 Interaction energy(ΔEint) and H-Bonding energies(ΔEHB) calculated for [HAlkyl][TFA] ion pairs at the M06-2X/6-311G(d,p) level*
| Structure | ΔEint/(kJ∙mol-1) | BSSE/(kJ∙mol-1) | Δ | ΔEHB/(kJ∙mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | -539.40 | 83.85 | -519.36 | -81.55 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | -528.86 | 113.80 | -501.66 | -71.00 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | -501.62 | 123.64 | -472.04 | -75.23 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | -501.16 | 131.17 | -469.82 | -74.81 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | -510.74 | 107.32 | -485.09 | -84.35 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | -534.84 | 84.31 | -514.72 | -77.28 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | -521.70 | 126.11 | -491.58 | -64.14 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | -497.02 | 124.22 | -467.31 | -74.98 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | -496.77 | 130.79 | -465.51 | -74.73 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | -506.18 | 106.69 | -480.70 | -84.14 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | -539.65 | 70.21 | -522.87 | -81.55 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | -529.07 | 113.26 | -502.00 | -70.92 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | -481.45 | 132.01 | -449.91 | -69.79 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | -490.62 | 144.47 | -456.06 | -78.91 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | -499.78 | 115.60 | -472.16 | -88.12 |
| Structure | Charge transfer | E(2)/(kJ∙mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 256.23 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H2—O2) | 233.89 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 271.58 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 240.50 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O1) | 288.78 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 254.64 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H1—O1) | 213.55 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 273.26 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 246.44 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 285.85 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 243.76 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H1—O1) | 233.68 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 301.75 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 283.21 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O1) | 328.70 |
Table 2 Significant natural bond orbital interactions of the ion pairs and their second order stabilization energies E(2) calculated at the M06-2X/6-311G(d,p) level
| Structure | Charge transfer | E(2)/(kJ∙mol-1) |
|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 256.23 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H2—O2) | 233.89 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 271.58 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 240.50 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O1) | 288.78 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 254.64 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H1—O1) | 213.55 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 273.26 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 246.44 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 285.85 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | LP(N1)→BD*(Hp—O2) | 243.76 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | LP(N1)→BD*(H1—O1) | 233.68 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 301.75 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O2) | 283.21 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | LP(N2)→BD*(H7—O1) | 328.70 |
| Structure | BCP | ρc/a.u. | ▽2ρc/a.u. | G(r)/a.u. | V(r)/a.u. | H(r)/a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0743 | 0.0878 | 0.0486 | -0.0753 | -0.0267 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | O2—H2…N1 | 0.0699 | 0.0905 | 0.0459 | -0.0693 | -0.0233 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0834 | 0.0758 | 0.0526 | -0.0863 | -0.0337 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0754 | 0.0820 | 0.0481 | -0.0757 | -0.0276 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | O1—H7…N2 | 0.0857 | 0.0690 | 0.0530 | -0.0888 | -0.0358 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0745 | 0.0843 | 0.0483 | -0.0756 | -0.0273 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | O1—H1…N1 | 0.0635 | 0.0910 | 0.0420 | -0.0612 | -0.0192 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | O2—Hp…N2 | 0.0838 | 0.0752 | 0.0528 | -0.0868 | -0.0340 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | O2—Hp…N2 | 0.0768 | 0.0804 | 0.0487 | -0.0774 | -0.0286 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0852 | 0.0671 | 0.0524 | -0.0881 | -0.0357 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0743 | 0.0841 | 0.0482 | -0.0753 | -0.0271 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | O1—H1…N1 | 0.0698 | 0.0905 | 0.0459 | -0.0692 | -0.0233 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0888 | 0.0633 | -0.0923 | -0.0885 | -0.1808 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0840 | 0.0705 | 0.0519 | -0.0861 | -0.0343 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | O1—H7…N2 | 0.0937 | 0.0501 | 0.0555 | -0.0985 | -0.0430 |
Table 3 Properties of the electron density of bond critical points for the intermolecular interactions in configurations [HAlkyl][TFA] calculated at the M06-2X/6-311G(d,p) level*
| Structure | BCP | ρc/a.u. | ▽2ρc/a.u. | G(r)/a.u. | V(r)/a.u. | H(r)/a.u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [HHex][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0743 | 0.0878 | 0.0486 | -0.0753 | -0.0267 |
| [HHex][TFA]S2 | O2—H2…N1 | 0.0699 | 0.0905 | 0.0459 | -0.0693 | -0.0233 |
| [HHex][TFA]S3 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0834 | 0.0758 | 0.0526 | -0.0863 | -0.0337 |
| [HHex][TFA]S4 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0754 | 0.0820 | 0.0481 | -0.0757 | -0.0276 |
| [HHex][TFA]S5 | O1—H7…N2 | 0.0857 | 0.0690 | 0.0530 | -0.0888 | -0.0358 |
| [HOct][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0745 | 0.0843 | 0.0483 | -0.0756 | -0.0273 |
| [HOct][TFA]S2 | O1—H1…N1 | 0.0635 | 0.0910 | 0.0420 | -0.0612 | -0.0192 |
| [HOct][TFA]S3 | O2—Hp…N2 | 0.0838 | 0.0752 | 0.0528 | -0.0868 | -0.0340 |
| [HOct][TFA]S4 | O2—Hp…N2 | 0.0768 | 0.0804 | 0.0487 | -0.0774 | -0.0286 |
| [HOct][TFA]S5 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0852 | 0.0671 | 0.0524 | -0.0881 | -0.0357 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S1 | O2—Hp…N1 | 0.0743 | 0.0841 | 0.0482 | -0.0753 | -0.0271 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S2 | O1—H1…N1 | 0.0698 | 0.0905 | 0.0459 | -0.0692 | -0.0233 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S3 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0888 | 0.0633 | -0.0923 | -0.0885 | -0.1808 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S4 | O2—H7…N2 | 0.0840 | 0.0705 | 0.0519 | -0.0861 | -0.0343 |
| [HEtHex][TFA]S5 | O1—H7…N2 | 0.0937 | 0.0501 | 0.0555 | -0.0985 | -0.0430 |
| [1] | Wilkes J. S., Green Chem., 2002, 4, 73—80 |
| [2] | Ohno H., Yoshizawa M., Solid State Ionics., 2002, 154, 303—309 |
| [3] | Prathibha P., Nilanjan P., Ajay M., J. Surfact Deterg., 2017, 20, 1321—1335 |
| [4] | Amarasekara A. S., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116(10), 6133—6183 |
| [5] | Greaves T. L., Drummond C., J. Chem. Rev., 2008, 108, 206—237 |
| [6] | Hua E., Wang H., J. Mol. Liq., 2016, 220, 649—656 |
| [7] | Takemura S., Kawakami S., Harada M., Iida M., Inorg. Chem., 2014, 53(18), 9667—9678 |
| [8] | Li C. P., Li Z., Zou B. X., Liu Q. S., Liao X. X., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2013, 29, 2157—2161 |
| (李长平, 李琢, 邹本雪, 刘青山, 刘晓霞. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29, 2157—2161) | |
| [9] | Yu G. H., Li X., Feng C., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2015, 1067, 7—12 |
| [10] | Cramer C. J., Truhlar D. G., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2009, 11, 10757—10816 |
| [11] | Li W., Zhang J., Qi C. S., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2015, 31, 1690—1698 |
| (李巍, 张静, 戚传松. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31, 1690—1698) | |
| [12] | Boys S. F., Bernardi F., Mol. Phys., 1970, 19, 553—566 |
| [13] | Bader R.F. W., Atom in Molecules: A Quantum Theory, Oxford University Press, New York, 1990 |
| [14] | Li X. H., Yin G. X., Zhang X. Z., J. Molstruc: Theochem., 2010, 957, 61—65 |
| [15] | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Keith T., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2013 |
| [16] | Bader R. F. W., AIM2000 Program Package, Ver. 2.0, McMaster University, Hamilton, 2002 |
| [17] | Shakourian-Fard M., Jamshidi Z., Bayat A., Fattahi A., J. Fluorine Chem., 2013, 153, 96—100 |
| [18] | Seyedhosseini B., Izadyar M., Housaindokht M. R., J. Mol. Liq., 2014, 200, 439—447 |
| [19] | Hossein R., Khatereh G., J. Mol. Liq., 2015, 209, 14—24 |
| [20] | Hikari W., Hiroyuki D., Soshi S., Masaru M., Kenta F., Ryo K., Yasuo K., Yasuhiro U., J. Mol. Liq., 2016, 217, 35—42 |
| [21] | Sebastian B. C. L., Martin R., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 7473—7486 |
| [22] | Wu Y., Zhang T. T., Yu N., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2009, 25(8), 1689—1696 |
| (吴阳, 张甜甜, 于宁. 物理化学学报, 2009, 25(8), 1689—1696) | |
| [23] | Hunt P. A., Ashworth C. R., Matthews R. P., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 1257—1288 |
| [24] | Chen X., Zhang Y., Yu F., Wang H., J. Solution Chem., 2010, 39, 1341—1349 |
| [25] | Lu R., Qu Z., Lin J., J. Mol. Liq., 2013, 180, 207—214 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [4] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [5] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [6] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [7] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [8] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [9] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [10] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [11] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [12] | HU Wei, LIU Xiaofeng, LI Zhenyu, YANG Jinlong. Surface and Size Effects of Nitrogen-vacancy Centers in Diamond Nanowires [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| [13] | YANG Yiying, ZHU Rongxiu, ZHANG Dongju, LIU Chengbu. Theoretical Study on Gold-catalyzed Cyclization of Alkynyl Benzodioxin to 8-Hydroxy-isocoumarin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [14] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [15] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||
