

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (6): 1274.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180166
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LU Tong, WANG Chunyang, ZHU Zhihui, JIANG Wei, HUO Mingnan, LI Fei*( )
)
Received:2018-03-04
Online:2018-06-10
Published:2018-05-16
Contact:
LI Fei
E-mail:feili@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LU Tong, WANG Chunyang, ZHU Zhihui, JIANG Wei, HUO Mingnan, LI Fei. Polyethyleneimine Functionalized Graphene Oxide Against hIAPP Amyloid Aggregation†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(6): 1274.
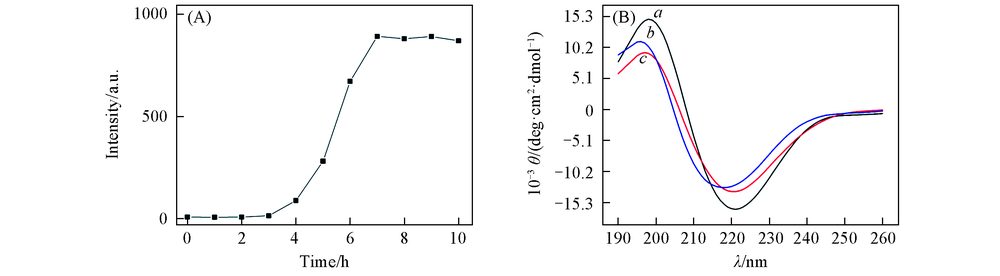
Fig.3 Kinetics of hIAPP aggregation as monitored by the thioflavin T fluorescence(A) and far-UV CD spectra of hIAPP in the absence(a) and presence of GO(b) and GO-PEI(c)(B)
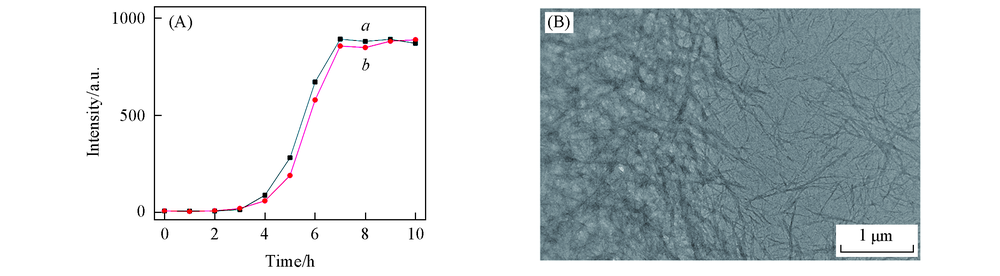
Fig.5 Kinetics of hIAPP aggregation as monitored by the thioflavin T fluorescence(A) in the absence(a) and presence of PEI(b) and TEM image(B) of hIAPP in the presence of PEI
| Sample | Diameter(DLS)/nm | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|
| GO | 200—600 | -10.5 |
| GO-PEI | 150—300 | 50.1 |
Table 1 Hydrodynamic diameter and Zeta potential of GO and GO-PEI
| Sample | Diameter(DLS)/nm | Zeta potential/mV |
|---|---|---|
| GO | 200—600 | -10.5 |
| GO-PEI | 150—300 | 50.1 |

Fig.7 AFM images of hIAPP(A) and mixed with GO-PEI at the incubation time of 0 h(B), 5 h(C) and 8 h(D)All images were recorded after the mixtures were further incubated for 10 h.
| [1] | Soto C., FEBS Lett., 2001, 498, 204—207 |
| [2] | Soto C., Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 2003, 4, 49—60 |
| [3] | Chiti F., Dobson C .M., Annu. Rev. Biochem., 2006, 75, 333—366 |
| [4] | Westermark P., Andersson A., Westermark G.T., Physiological Reviews, 2011, 91, 795—826 |
| [5] | Kahn S. E., Andrikopoulos S., Verchere C. B., Diabetes, 1999, 48, 241—253 |
| [6] | Lorenzo A., Razzaboni B., Weir G. C., Yankner B. A., Nature, 1994, 368, 756—760 |
| [7] | Brender J. R., Salamekh S., Ramamoorthy A., Accounts of Chemical Research, 2011, 4, 454—462 |
| [8] | Westermark P., Wernstedt C., Wilander E., Hayden D. W., O’Brien T. D., Johnson K. H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1987, 84, 3881—3885 |
| [9] | De Toma A. S., Salamekh S., Ramamoorthy A., Lim M. H., Chemical Society Reviews, 2012, 41, 608—621 |
| [10] | Pithadia A. S., Bhunia A., Sribalan R., Padmini V., Fierke C. A., Ramamoorthy A., Chem. Commun., 2016, 52, 942—945 |
| [11] | Cheng B., Gong H., Li X., Sun Y., Zhang X., Chen H., Liu X., Zheng L., Huang K., Biochem. Biophys. Res.Commun., 2012, 419, 495—499 |
| [12] | Wang L., Lei L., Li Y., Wang L., Li F., FEBS Lett., 2014, 588, 884—891 |
| [13] | Tatarek-Nossol M., Yan L. M., Schmauder A., Tenidis K., Westermark G., Kapurniotu A., Chem. Biol., 2005, 12, 797—809 |
| [14] | Yan L. M., Tatarek-Nossol M., Velkova A., Kazantzis A., Kapurniotu A., Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006, 103, 2046—2051 |
| [15] | Wang L., Zhu S. J., Lu T., Zhang G. J., Xu J., Song Y. B., Li Y., Wang L. P., Yang B., Li F., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, 4913—4921 |
| [16] | Liu G., Men P., Kudo W., Perry G., Smith M.A., Neuroscience Letters, 2009, 455, 187—190 |
| [17] | Kong B., Zhu A., Ding C., Zhao X., Li B., Tian Y., Advanced Materials, 2012, 24, 5844—5848 |
| [18] | Welsher K., Liu Z., Sherlock S. P., Robinson J. T., Chen Z., Daranciang D., Dai H., Nat. Nanotechnol., 2009, 4, 773—780 |
| [19] | Jeong J., Cho M., Lim Y. T., Song N. W., Chung B. H., Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48, 5296—5299 |
| [20] | Zhu S., Zhang J., Tang S., Qiao C., Wang L., Wang H., Liu X., Li B., Li Y., Yu W., Wang X., Sun H., Yang B., Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22, 4732—4740 |
| [21] | Georgakilas V., Tiwari J. N., Kemp K. C., Perman J. A., Bourlinos A. B., Kim K. S., Zboril R., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 5464—5519 |
| [22] | Wang C., Wang X., Lu T., Liu F., Guo B., Wen N., Du Y., Lin H., Tang J., Zhang L., RSC Adv., 2016, 6, 22461—22468 |
| [23] | Mahmoudi M ., Akhavan O., Ghavami M., Rezaee F., Ghiasi S.M. A., Nanoscale, 2012, 4, 7322—7325 |
| [24] | Li M., Yang X. J., Ren J. S., Qu K. G., Qu X. G., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24, 1722—1728 |
| [25] | Li Q., Liu L., Zhang S., Xu M., Wang X., Wang C., Besenbacher F., Dong M., Chem. Eur. J., 2014, 20, 7236—7240 |
| [26] | Liu Y., Xu L., Dai W., Dong H., Wen Y., Zhang X., Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 19060—19065 |
| [27] | Nedumpully-Govindan P., Gurzov E. N., Chen P., Pilkington E. H., Stanley W. J., Litwak S. A., Davis T. P., Ke P. C., Ding F., Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18, 94—100 |
| [28] | Liu J., Yang Z., Li H., Gu Z., Garate J. A., Zhou R., J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 141, 22D520 |
| [29] | Lin C. Y., Cheng Y. S., Liao T. Y., Lin C., Chen Z. T., Twu W. I., Wang C. W., Tan D. T., Liu R. S., Tu P., Chen R. P. Y., Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 2016, 53, 1053—1067 |
| [30] | Georgieva J. V., Kalicharan D., Couraud P. O., Romero I. A., Weksler B., Hoekstra D., Zuhorn I. S., Molecular Therapy, 2011, 19, 318—325 |
| [31] | Loftus L. T., Li H. F., Gray A. J., Hirata-Fukae C., Stoica B. A., Futami J., Yamada H., Aisen P. S., Matsuoka Y., Neuroscience, 2006, 139, 1061—1067 |
| [32] | Futami J., Kitazoe M., Maeda T., Nukui E., Sakaguchi M., Kosaka J., Miyazaki M., Kosaka M., Tada H., Seno M., Sasaki J., Huh N. H., Namba M., Yamada H., J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2005, 99, 95—103 |
| [33] | Murata H., Futami J., Kitazoe M., Kosaka M., Tada H., Seno M., Yamada H., J. Biosci. Bioeng., 2008, 105, 34—38 |
| [34] | O’Connor D. M., Boulis N. M., Trends in Molecular Medicine, 2015, 21, 504—512 |
| [35] | Hudry E., Van Da D., Kulik W., De Deyn P. P., Stet F. S., Ahouansou O., Benraiss A., Delacourte A., Bougnères P., Aubourg P., Cartier N., Molecular Therapy, 2010, 18, 44—53 |
| [36] | Morton G. J., Niswender K. D., Rhodes C. J., Myers M. G., Blevins J. E., Baskin D. G., Schwartz M. W., Endocrinology, 2003, 144, 2016—2024 |
| [37] | Zhang L., Lu Z., Zhao Q., Huang J., Shen H., Zhang Z., Small, 2011, 7, 460—464 |
| [38] | Feng L., Zhang S., Liu Z., Nanoscale, 2011, 3, 1252—1257 |
| [39] | Chen B., Liu M., Zhang L., Huang J., Yao J., Zhang Z., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21, 7736—7741 |
| [40] | Hummers W. S., Offeman R. E., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1958, 80, 1339 |
| [41] | Biancalana M., Koide S., Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2010, 1804, 1405—1412 |
| [42] | Batzli K. M., Love B. J., Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2015, 48, 359—364 |
| [43] | Jaikaran E. T. A. S., Higham C. E., Serpell L. C., Zurdo J., Gross M., Clark A., Fraser P. E., FEBS Letters, 2001, 308, 515—525 |
| [44] | Higham C. E., Jaikaran E. T. A. S., Fraser P. E., Gross M., Clark A., FEBS Letters, 2000, 470, 55—60 |
| [45] | Ferreira S. T., Vieira M. N. N., De Felice F. G., IUMB Life, 2007, 59, 332—345 |
| [46] | Hardy J., Selkoe D.J., Science, 2002, 297, 353—356 |
| [47] | Glabe C. G., Kayed R., Neurology, 2006, 66(Suppl.), S74—S78 |
| [1] | HUAN Xinyu, LAI Ganqiang, HUANG Yue, YANG Caiguang. Research Progress on Chemical Intervention of N6-methyladenosine Modification [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(Album-4): 20220340. |
| [2] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [3] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [4] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [5] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [6] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [7] | ZHU Deshuai, ZHAO Jianying, YANG Zhenghui, GUO Haiquan, GAO Lianxun. Graphene Oxide/Polyimide Composites with High Energy Storage Density Based on Multilayer Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2694. |
| [8] | LI Peihong, ZHANG Chunling, DAI Xueyan, SUI Yanlong. Progress of Graphene Oxide/Polymer Composite Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1694. |
| [9] | MIAO Weijun, WU Feng, WANG Yong, WANG Zongbao. In⁃situ Study of the Epitaxial Crystallization of PCL/RGO at High Shear Rate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 910. |
| [10] | HUANG Dongxue, ZHANG Ying, ZENG Ting, ZHANG Yuanyuan, WAN Qijin, YANG Nianjun. Transition Metal Sulfides Hybridized with Reduced Graphene Oxide for High-Performance Supercapacitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 643. |
| [11] | YE Chenghao, LIANG Heng, LI Enmin, XU Liyan, LI Peng, CHEN Guanghui. High-throughput Virtual Screening of CDK2/Cyclin A2 Target Inhibitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3135. |
| [12] | WANG Bowei, MA Rui, WU Fan, LIU Zhihui, LI Lingfeng, ZHANG Xiao, LIU Dingkun, YANG Nan, LI Meihui, YANG Defeng, SUN Qi. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide-sodium Alginate-chitosan Composite Scaffold [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2099. |
| [13] | ZHANG Weiguo, FAN Songhua, WANG Hongzhi, YAO Suwei. Synthesis of Self-assembled α-Fe2O3/Graphene Hydrogel for Supercapacitors with Promising Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1850. |
| [14] | CHEN Yantian, QIE Hantong, ZHANG Yinjie, ZHOU Caiji, TAN Xiao, LIN Aijun. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported Zero-valent Iron and Its Treatment of TNT Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1836. |
| [15] | ZHANG Xiaofei, WU Lie, LI Shanshan, ZHU Manyu, CHENG Xiaowei, JIANG Xiu’e. Effect of Phase Behavior of Phospholipids on Lipid Membrane Damage Induced by Graphene Oxide † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 661. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||