

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 20210566.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210566
• Polymer Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Zhibo1, SHANG Han1, XU Wenxuan1, HAN Guangdong2, CUI Jinsheng2, YANG Haoran3, LI Ruixin4, ZHANG Shenghui1, XU Huan1( )
)
Received:2021-08-11
Online:2022-02-10
Published:2021-11-19
Contact:
XU Huan
E-mail:hihuan@cumt.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566.
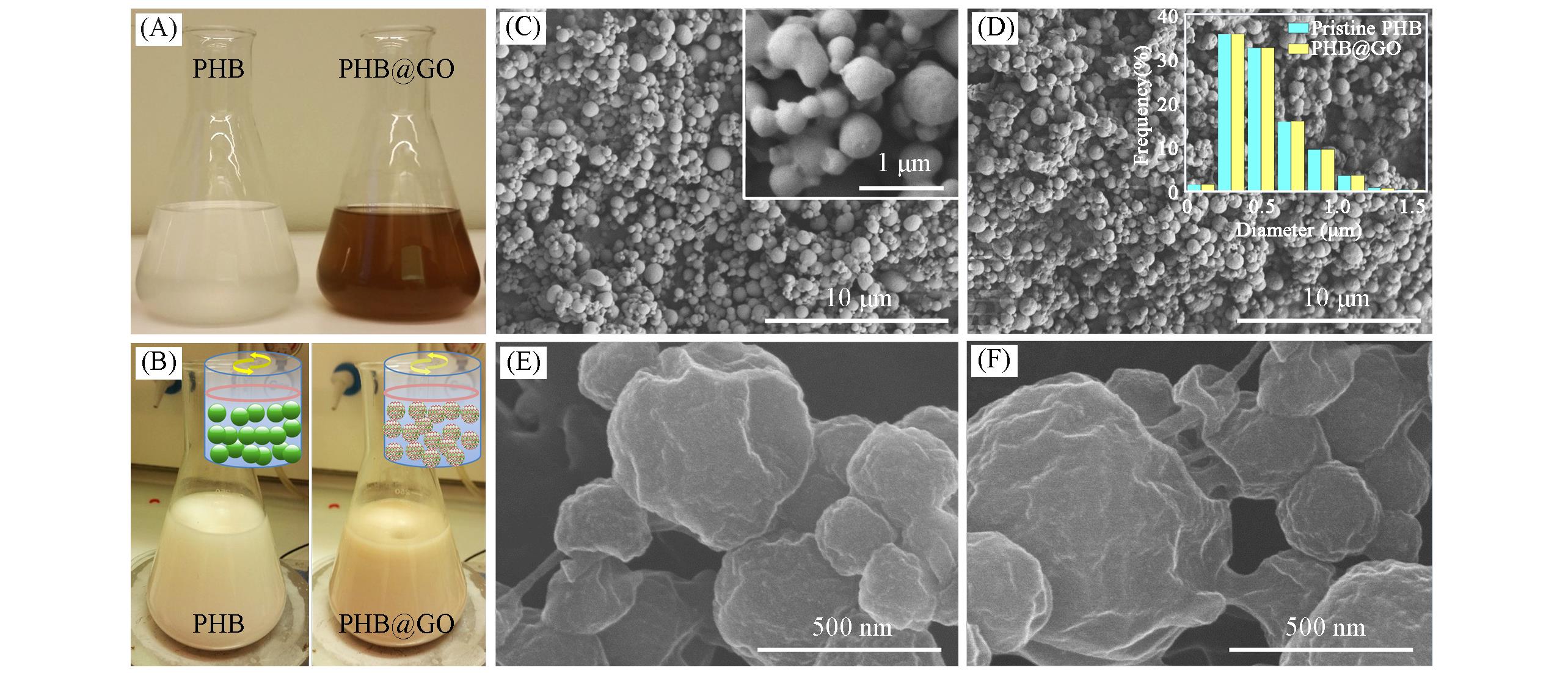
Fig.1 Digital photos of the aqueous solutions before(A) and after(B) mechanical stirring and SEM images of pristine PHB microparticles(C) and PHB@GO hybrids(D—F)
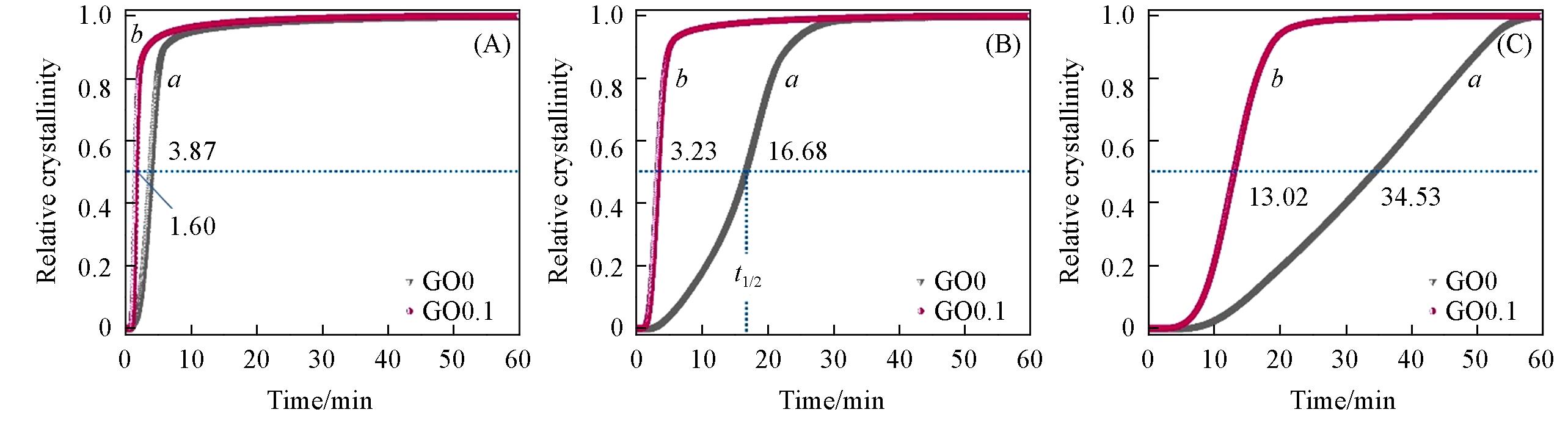
Fig.3 Plots of relative crystallinity versus the crystallization time for GO0(a) and GO0.1(b) during isothermal crystallization at 100(A), 110(B) and 120 ℃(C)The values of half-time crystallization(t1/2) are marked.
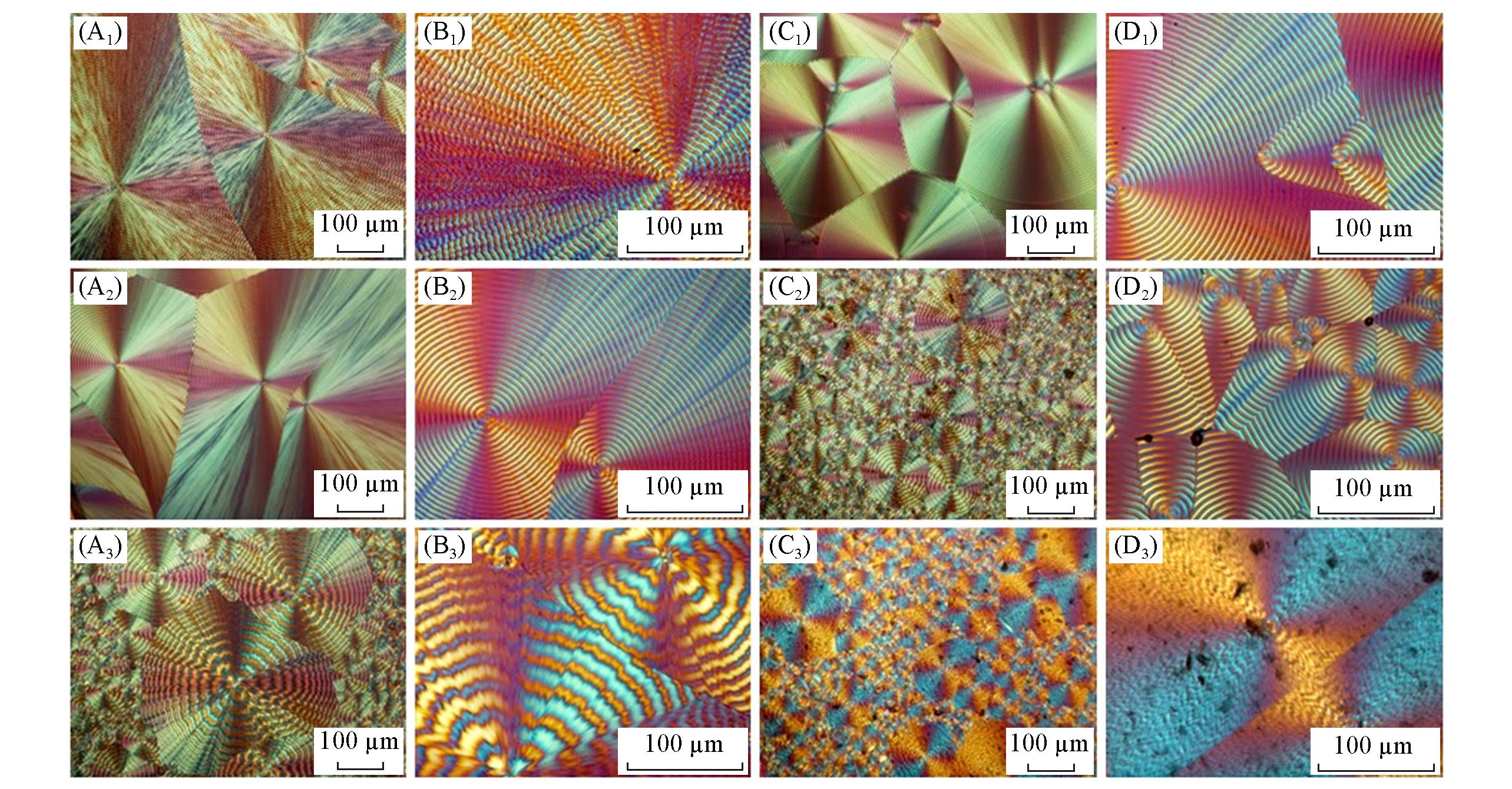
Fig.5 POM images of GO0(A1—A3, B1—B3) and GO0.1(C1—C3, D1—D3) after non?isothermal melt crystallization with a cooling rate of 5(A1—D1), 10(A2—D2) and 20 ℃/min(A3—D3)
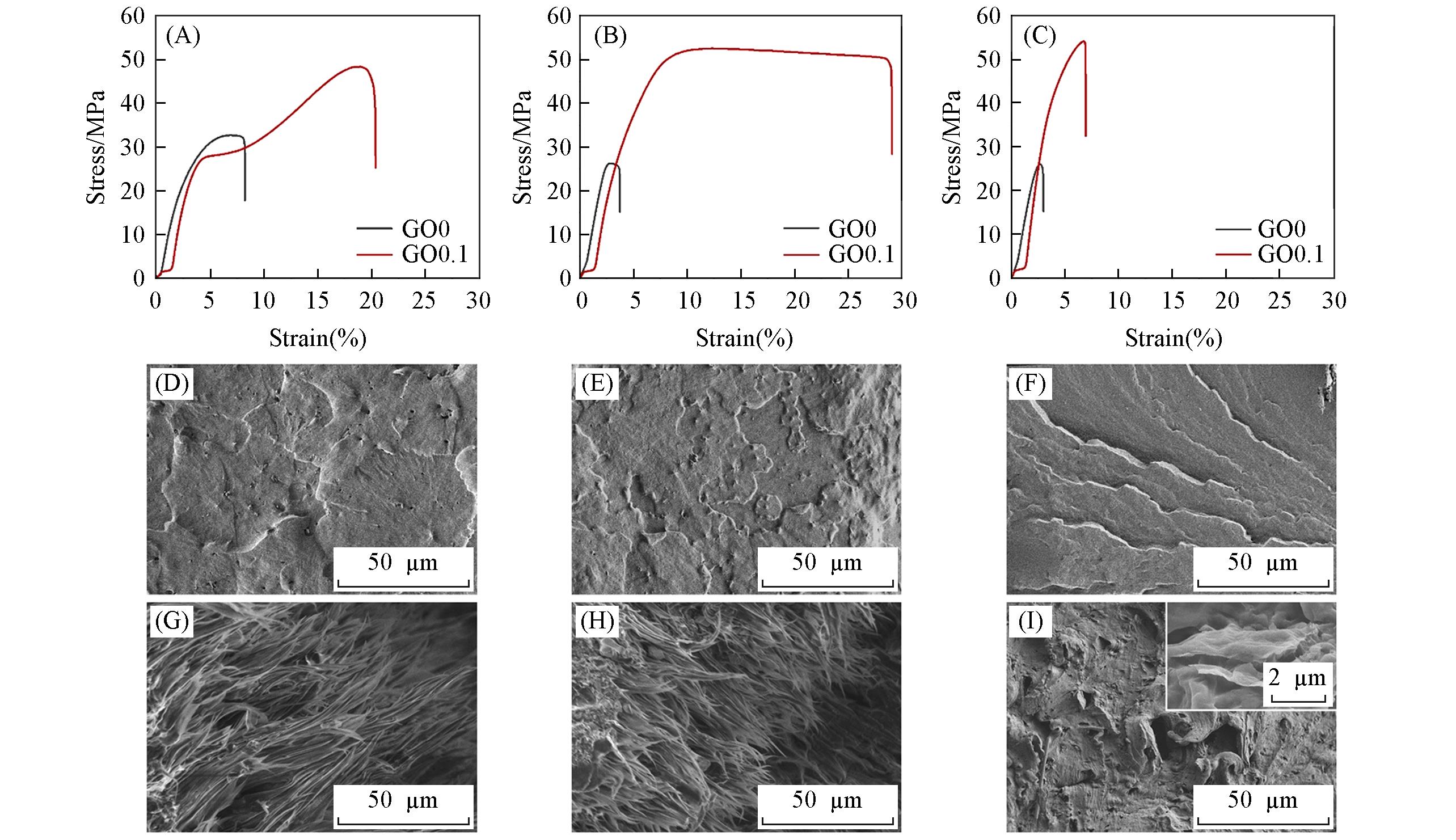
Fig.6 Typical stress?strain curves of GO0 and GO0.1(A—C) with different crosshead speed and SEM images of fracture surfaces after tensile failure of GO0(D—F) and GO0.1(G—I) with different crosshead speed
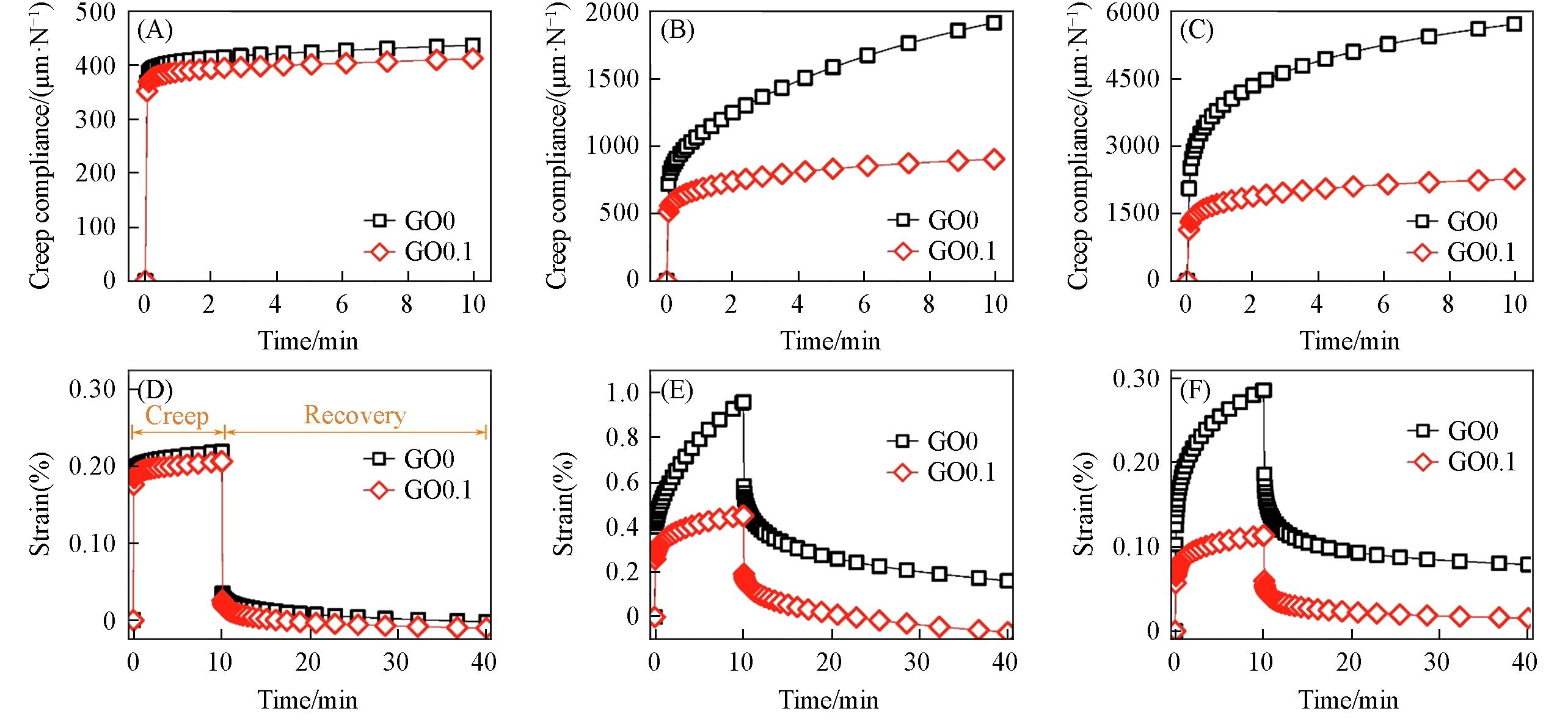
Fig.7 DMA?measured creep compliance?time curves(A—C) and creep and creep-recovery curves(D—F) of GO/PHB composites at 25 ℃(A, D), 60 ℃(B, E) and 100 ℃(C, F)
| 1 | Sudesh K., Abe H., Doi Y., Prog. Polym. Sci., 2000, 25(10), 1503—1555 |
| 2 | Luo Z., Wu Y. L., Li Z., Loh X. J., Biotechnol. J., 2019, 14(12), 1900283 |
| 3 | Lemoigne M., Bull. Soc. Chim. Biol., 1926, 8, 770—782 |
| 4 | Asran A. S., Razghandi K., Aggarwal N., Michler G. H., Groth T., Biomacromolecules., 2010, 11(12), 3413—3421 |
| 5 | Follain N., Chappey C., Dargent E., Chivrac F., Crétois R., Marais S., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2014. 118(12), 6165—6177 |
| 6 | Gazzano M., Focarete M. L., Riekel C., Scandola M., Biomacromolecules, 2000, 1(4), 604—608 |
| 7 | Abe H., Kikkawa Y., Iwata T., Aoki H., Akehata T., Doi Y., Polymer, 2000, 41(3), 867—874 |
| 8 | Ding G., Liu J., Colloid Polym. Sci.,2013, 291(6), 1547—1554 |
| 9 | Seoane I. T., Fortunati E., Puglia D., Cyras V. P., Manfredi L. B., Polym. Int., 2016, 65(9), 1046—1053 |
| 10 | Puente J. A. S., Esposito A., Chivrac F., Dargent E., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 128(5), 2586—2594 |
| 11 | S. de O. Patrício P., Pereira F. V., dos Santos M. C., de Souza P. P., Roa J. P. B., Orefice R. L., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2013, 127(5), 3613—3621 |
| 12 | Manikandan N. A., Pakshirajan K., Pugazhenthi G., Int. J. Biol. Macromol.,2020, 154, 866—877 |
| 13 | Wang Y., Cheng, Y., Chen J., Wu D., Qiu Y., Yao X., Zhou Y., Chen C., Polymer, 2015. 67, 216—226 |
| 14 | Sun X., Sun H., Li H., Peng H., Adv. Mater., 2013. 25(37), 5153—5176 |
| 15 | Zhou S. Y., Yang B., Li Y., Gao X. R., Ji X., Zhong G. J., Li Z. M., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2017, 5(27), 14377—14386 |
| 16 | Ogura K., Rehm B. H. A., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29(37), 1901893 |
| 17 | Xu H., Wu D., Yang X., Xie L., Macromolecules, 2015, 48(7), 2127—2137 |
| 18 | Xu H., Feng Z. X., Xie L., ACS Sustainable. Chem. Eng., 2016, 4(1), 334—349 |
| 19 | Huang Y. F., Wang Z. G., Yin H. M., Xu J. Z., Chen Y., Lei J., Zhu L., Gong F., Li Z. M., ACS Appl. Nano. Mater., 2018, 1(7), 3312—3320 |
| 20 | Jia L. C., Yan D. X., Jiang X., Pang H., Gao J. F., Ren P. G., Li Z. M., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2018, 57(35), 11929—11938 |
| 21 | Bordes P., Pollet E., Bourbigot S., Avérous L., Macromol. Chem. Phys.,2008, 209(14), 1473—1484 |
| 22 | Bragança F. D. C., Valadares L. F., Leite C. A. D. P., Galembeck F., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(13), 3334—3342 |
| 23 | Merritt S. M. J., Wemyss A. M., Farris S., Patole S., Patias G., Haddleton D. M., Shollock B., Wan C., ACS Appl. Polym. Mater., 2020, 2(2), 725—731 |
| 24 | Xu P., Wang Q., Yu M., Yang W., Weng Y., Dong W., Chen M., Wang Y., Ma P., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2021, 184, 797—803 |
| 25 | Ma H., Wei Z., Zhou S., Zhu H., Tang J., Yin J., Yue J., Yang J., Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2020, 165, 1562—1573 |
| 26 | Panaitescu D. M., Ionita E. R., Nicolae C. A., Gabor A. R., Ionita M. D., Trusca R., Lixandru B. E., Codita I., Dinescu G., Polymers, 2018. 10(11), 1249 |
| 27 | Peng S., An Y., Chen C., Fei B., Zhuang Y., Dong L., Eur. Polym. J., 2003, 39(7), 1475—1480 |
| 28 | Chen J., Xu C., Wu D., Pan K., Qian A., Sha Y., Wang L., Tong W., Carbohydr. Polym., 2015, 134, 508—515 |
| 29 | Lugito G., Woo E. M., Hsieh Y. T., Macromolecules, 2015, 48(21), 7953—7967 |
| 30 | Woo E. M., Lugito G., Eur. Polym. J.,2015, 71, 27—60 |
| 31 | Luo S., Cao J., McDonald A. G., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2016, 4(6), 3465—3476 |
| 32 | Wang S., Chen W., Xiang H., Yang J., Zhou Z., Zhu M., Polymers, 2016, 8(8), 273 |
| 33 | Wang X., Chen Z., Chen X., Pan J., Xu K., J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2010, 117(2), 838—848 |
| 34 | Abdelwahab M. A., Flynn A., Chiou B. S., Imam S., Orts W., Chiellini E., Polym. Degrad. Stab., 2012, 97(9), 1822—1828 |
| 35 | Zheng T., Clemons C. M., Pilla S., ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8(2), 814—822 |
| 36 | Xu H., Xie L., Chen J. B., Jiang X., Hsiao B. S., Zhong G. J., Fu Q., Li Z. M., Mater. Horiz., 2014, 1, 546—552 |
| 37 | Xu H., Xie L., Li J., Hakkarainen M., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9(33), 27972—27983 |
| 38 | Xu H., Bai Y., Xie L., Li J., Hakkarainen M., ACS. Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2017, 5(12), 11607—11617 |
| 39 | Wei L., Stark N. M., McDonald A. G., Green Chem.,2015, 17(10), 4800—4814 |
| 40 | Kai D., Zhang K., Liow S. S., Loh X. J., ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2019, 2(1), 127—134 |
| 41 | Wei L., McDonald A. G., Stark N. M., Biomacromolecules,2015, 16(3), 1040—1049 |
| [1] | LUO Xinyan, JIA Ruonan, XIANG Yong, ZHANG Xiaokun. Progress on the Stretchable Composite Solid Polymer Electrolytes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220149. |
| [2] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [3] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [4] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [5] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [6] | XU Huan, KE Lyu, TANG Mengke, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, ZHANG Zilin, FU Yanan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, GAO Jiefeng, ZHANG Shenghui, HE Xinjian. In⁃situ Liquid Exfoliation of Montmorillonite Nanosheets in Poly(lactic acid) to Resist Oxygen Permeation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [7] | ZHU Deshuai, ZHAO Jianying, YANG Zhenghui, GUO Haiquan, GAO Lianxun. Graphene Oxide/Polyimide Composites with High Energy Storage Density Based on Multilayer Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2694. |
| [8] | LI Peihong, ZHANG Chunling, DAI Xueyan, SUI Yanlong. Progress of Graphene Oxide/Polymer Composite Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1694. |
| [9] | WANG Xianwei, KE Hongjun, YUAN Hang, LU Gewu, LI Liying, MENG Xiangsheng, SONG Shulin, WANG Zhen. High Temperature Resistant and Soluble Polyimide Resins and Their Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [10] | MIAO Weijun, WU Feng, WANG Yong, WANG Zongbao. In⁃situ Study of the Epitaxial Crystallization of PCL/RGO at High Shear Rate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 910. |
| [11] | HUANG Dongxue, ZHANG Ying, ZENG Ting, ZHANG Yuanyuan, WAN Qijin, YANG Nianjun. Transition Metal Sulfides Hybridized with Reduced Graphene Oxide for High-Performance Supercapacitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 643. |
| [12] | WANG Peng, MAO Dan, WAN Jiawei, QI Qi, DU Jiang, WANG Dan. Effect of Hollow Multi-shelled TiO2 on Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3218. |
| [13] | WANG Bowei, MA Rui, WU Fan, LIU Zhihui, LI Lingfeng, ZHANG Xiao, LIU Dingkun, YANG Nan, LI Meihui, YANG Defeng, SUN Qi. Preparation and Characterization of Graphene Oxide-sodium Alginate-chitosan Composite Scaffold [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2099. |
| [14] | ZHANG Weiguo, FAN Songhua, WANG Hongzhi, YAO Suwei. Synthesis of Self-assembled α-Fe2O3/Graphene Hydrogel for Supercapacitors with Promising Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1850. |
| [15] | CHEN Yantian, QIE Hantong, ZHANG Yinjie, ZHOU Caiji, TAN Xiao, LIN Aijun. Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide Supported Zero-valent Iron and Its Treatment of TNT Wastewater [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1836. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||