

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 643.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200641
• Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Dongxue1, ZHANG Ying1, ZENG Ting1( ), ZHANG Yuanyuan1, WAN Qijin1(
), ZHANG Yuanyuan1, WAN Qijin1( ), YANG Nianjun2(
), YANG Nianjun2( )
)
Received:2020-09-01
Online:2021-02-10
Published:2020-12-01
Contact:
YANG Nianjun
E-mail:tingzeng1201@outlook.com;qijinwan@wit.edu.cn;nianjun.yang@uni-siegen.de
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Dongxue, ZHANG Ying, ZENG Ting, ZHANG Yuanyuan, WAN Qijin, YANG Nianjun. Transition Metal Sulfides Hybridized with Reduced Graphene Oxide for High-Performance Supercapacitors[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 643.
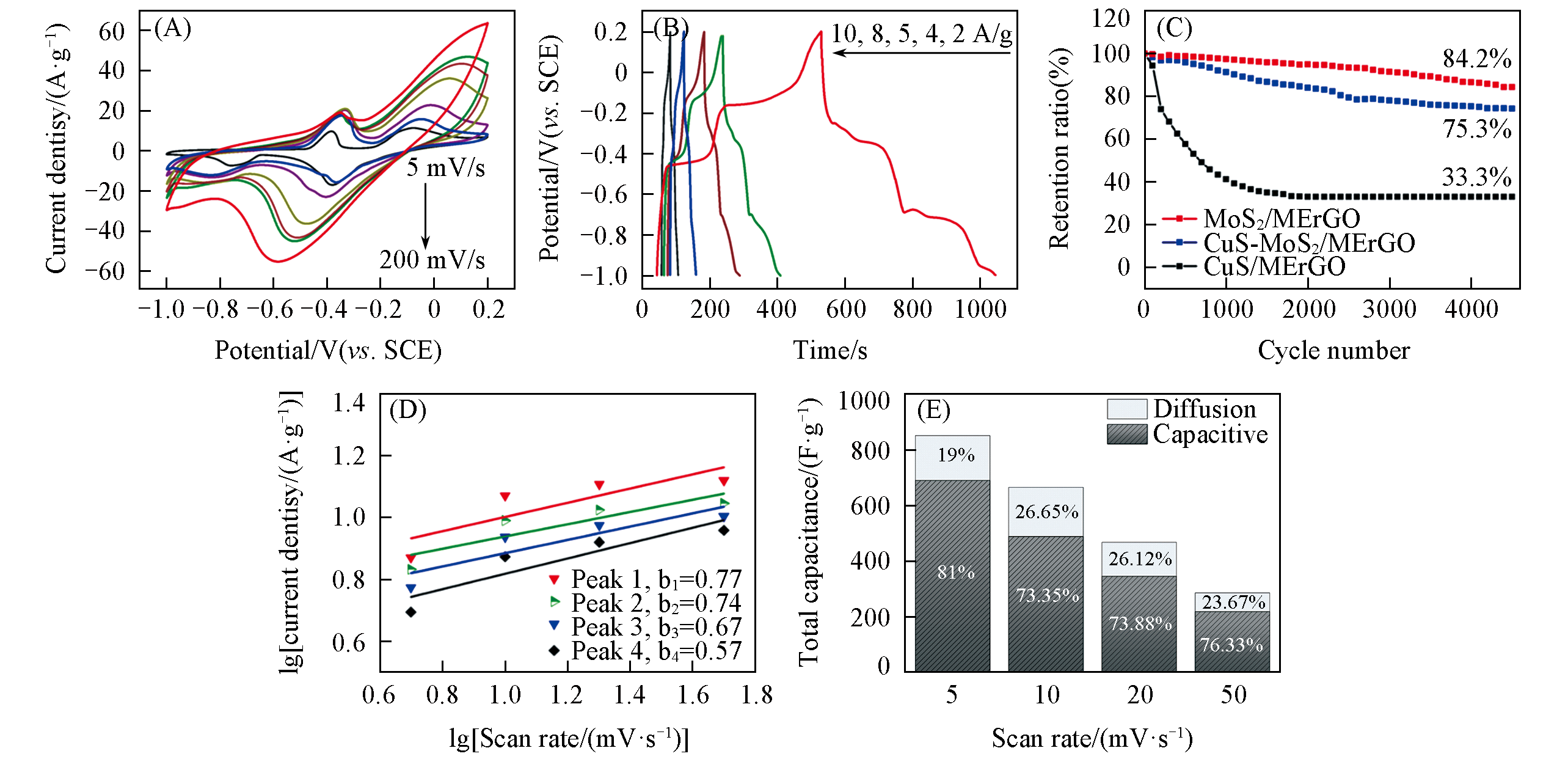
Fig.3 CVs at different scan rates(A), GCD curves at different current densities(B), the capacitance retention as a function of charging/discharging cycles(C), variation of the logarithms of scan rates with those of corresponding peak currents in(A)(D) and contribution ratios of faradaic and capacitive processes during the charge storage processes(E) of the CuS?MoS2/MErGO hybrid
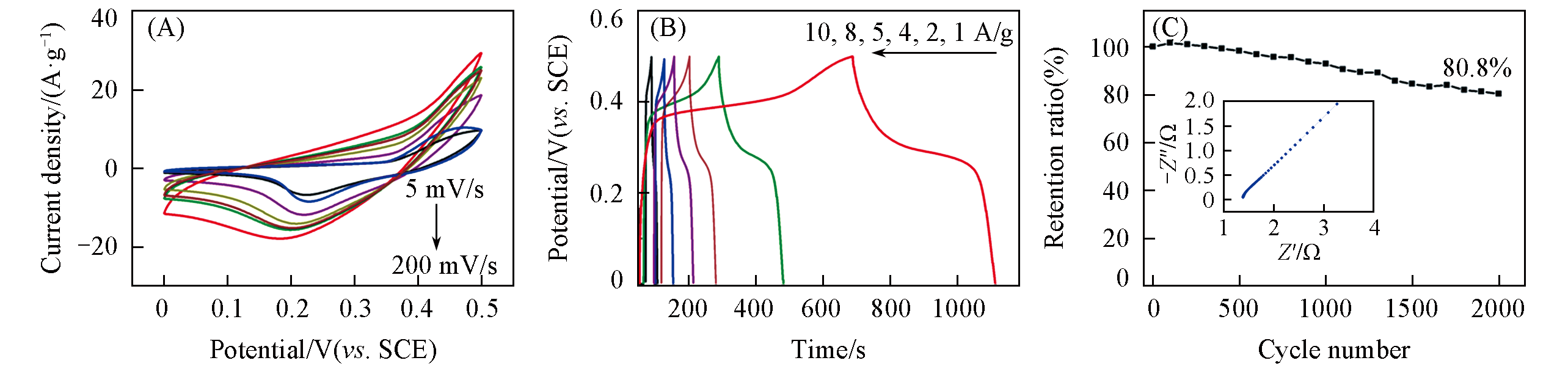
Fig.4 CVs at different scan rates(A), GCD curves at different current densities(B) and the capacitance retention(C) of the NiS/MErGO hybrid(C) The inset is the Nyquist plot.
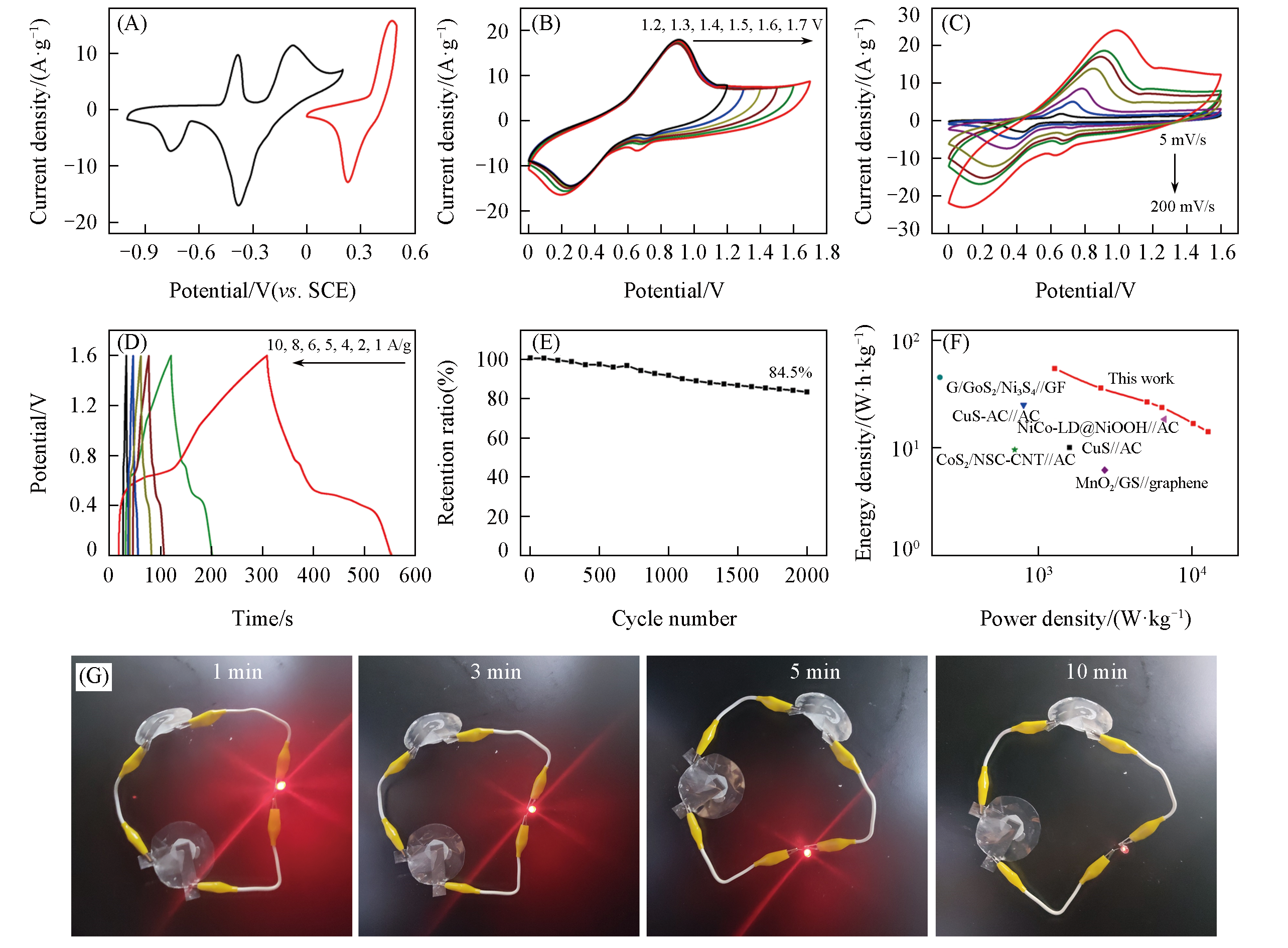
Fig.5 CVs of the positive and negative electrodes at a scan rate of 5 mV/s(A), CVs at a scan rate of 100 mV/s within altered cell voltages(B), CVs at different scan rates(C), GCD curves at different current densities(D), the capacitance retention over 2000 cycles(E), comparison of the Ragone plot of this device with other reported devices(F) and demonstration of LED lighting at different charging times(G) of the CuS?MoS2/MErGO//NiS/MErGO ASC device
| 29 | Hussain S., Patil S. A., Memon A. A., Vikraman D., Naqvi B. A., Jeong S. H., Kim H. S., Kim H. S., Jung J., Solar Energy, 2018, 171, 122—129 |
| 30 | Pan Z. H., Cao F., Hu X., Ji X. H., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7, 8984—8992 |
| 31 | Liu D. Q., Li Q. W., Zhao H. Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 11471—11478 |
| 32 | Ma Y. X., Hao J., Liu H. Y., Shi W. H., Lian J. S., J. Solid State Chem., 2020, 282, 121088 |
| 33 | Ikkurthi K. D., Rao S. S., Ahn J. W., Sunesh C. D., Kim H. J., Dalton Trans., 2019, 48, 578—586 |
| 34 | Shit S., Chhetri S., Jang W., Murmu N. C., Koo H., Samanta P., Kuila T., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 27712—27722 |
| 35 | Chen F., Wang H., Ji S., Linkov V., Wang R., Mater. Today Energy, 2019, 11, 211—217 |
| 36 | Naz R., Imtiaz M., Liu Q. L., Yao L. L., Abbas W., Li T. F., Zada I., Yuan Y., Chen W. S., Gu, J. J., Carbon,2019, 152, 697—703 |
| 37 | Huo J. H., Xue Y. J., Zhang X. J., Guo S. W., Electrochimica Acta, 2018, 292, 639—645 |
| 38 | Li X. F., Zhou K. X., Zhou J. Y., Shen J. F., Ye M. X., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2018, 34, 2342—2349 |
| 39 | Liu J., Xu Y. G., Kong L. B., Ionics, 2020, 20, 4499—4510 |
| 40 | Wang R. H., Xu C. H., Lee J. M., Nano Energy, 2016, 19, 210—221 |
| 41 | Rao S. S., Durga I. K., Kundakarla N., Punnoose D., Gopi C. V. V. M., Reddy A. E., Jagadeesh M., Kim H. J., New J. Chem., 2017, 41, 10037—10047 |
| 42 | Jiang D., Liang H., Yang W., Liu Y., Cao X., Zhang J., Li C., Liu J., Gooding J. J., Carbon, 2019, 146, 557—567 |
| 43 | Wang G., Zhang M., Lu L., Xu H., Xiao Z., Liu S., Gao S., Yu Z., Chemnanomat., 2018, 4, 964—971 |
| 44 | Liang H. Y., Lin J. H., Jia H. N., Chen S. L., Qi J. L., Cao J., Lin T. S., Fei W. D., Feng J. C., J. Power Sources, 2018, 378, 248—254 |
| 45 | Fu W., Han W., Zha H., Mei J., Li Y., Zhang Z., Xie E., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2016, 18, 24471—24476 |
| 46 | Lei K., Ling J., Zhou J., Zou H., Yang W., Chen S., Mater. Res. Bull., 2019, 116, 59-66 |
| 47 | Wu S., Chen W., Yan L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2, 2765—2772 |
| 48 | Zhu Y. R., Li J. Y., Yun X. R., Zhao G. G., Ge P., Zou G. Q., Liu Y., Hou H. S., Ji X. B., Nanomicro Lett., 2020, 12, 16 |
| 49 | Zou K. Y., Cai P., Wang B. W., Liu C., Li J. Y., Qiu T. Y., Zou G. Q., Hou H. S., Ji X. B., Nanomicro Lett., 2020, 12, 121 |
| 50 | Zou K. Y., Liu Y. C., Jiang Y. F., Yu C. Y., Yue M. L., Li Z. X., Inorg. Chem., 2017, 56, 6184—6196 |
| 1 | Aneke M., Wang M. H., Applied Energy, 2016, 179, 350—377 |
| 2 | Koohi⁃Fayegh S., Rosen M. A., J. Energy Storage, 2020, 27, 101047 |
| 3 | Poonam, Sharma K., Arora A., Tripathi S. K., J. Energy Storage, 2019, 21, 801—825 |
| 4 | Kouchachvili L., Yaici W., Entchev E., J. Power Sources, 2018, 374, 237—248 |
| 5 | Dubey R., Guruviah V., Ionics, 2019, 25, 1419—1445 |
| 6 | Geng P. B., Zheng S. S., Tang H., Zhu R. M., Zhang L., Cao S., Xue H. G., Pang H., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1703259 |
| 7 | Xu X., Liu W., Kim Y., Cho J., Nano Today, 2014, 9, 604—630 |
| 8 | Lu Y., Liu X. M., Wang W. X., Cheng J. B., Yan H. L., Tang C. C., Kim J. K., Luo Y. S., Sci. Rep., 2015, 5, 16584 |
| 9 | Xiao Y. H., Su D. C., Wang X. Z., Wu S. D., Zhou L. M., Shi Y., Fang S. M., Cheng H. M., Li F., Adv.Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1800930 |
| 10 | Yu X. Y., Yu L., Lou X. W., Small Methods, 2017, 1, 1600020 |
| 11 | Weng Q. H., Wang X., Wang X. B., Zhang C., Jiang X. F., Bando Y., Golberg D., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 3097—3102 |
| 12 | Yoo H. D., Li Y. F., Liang Y. L., Lan Y. C., Wang F., Yao Y., Chemnanomat., 2016, 2, 688—691 |
| 13 | Li X. X., Chen G. F., Xiao K., Li N., Ma T. Y., Liu Z. Q., Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 255, 153—159 |
| 14 | Zhang D., Sun W. P., Zhang Y., Dou Y. H., Jiang Y. Z., Dou S. X., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26, 7479—7485 |
| 15 | Yuan H., Kong L., Li T., Zhang Q., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2017, 28, 2180—2194 |
| 16 | Akhavan O., Carbon, 2010, 48, 509—519 |
| 17 | Savaram K., Li M. J., Tajima K., Takai K., Hayashi T., Hall G., Garfunkel E., Osipov V., He H. X., Carbon, 2018, 139, 861—871 |
| 18 | Khai T. V., Kwak D. S., Kwon Y. J., Cho H. Y., Huan T. N., Chung H., Ham H., Lee C., Dan N. V., Tung N. T., Kim H. W., Chem. Eng. J., 2013, 232, 346—355 |
| 19 | Cai L., He J. F., Liu Q. H., Yao T., Chen L., Yan W. S., Hu F. C., Jiang Y., Zhao Y. D., Hu T. D., Sun Z. H., Wei S. Q., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 2622—2627 |
| 20 | Guo J. X., Zhang X. Q., Sun Y. F., Zhang X. H., Tang L., Zhang X., J. Power Sources, 2017, 355, 31—35 |
| 21 | Fang Y. J., Guan B. Y., Luan D. Y., Lou X. W., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 7739—7743 |
| 22 | Wang Y., Chen Z. X., Lei T., Ai Y. F., Peng Z. K., Yan X. Y., Li H., Zhang J. J., Wang Z. M. M., Chueh Y. L., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8, 1703453 |
| 23 | Li Y., Gao J., Zhang F., Qian Q., Liu Y., Zhang G., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2018, 6, 15523-15529 |
| 24 | Shao Y., El⁃Kady M. F., Sun J., Li Y., Zhang Q., Zhu M., Wang H., Dunn B., Kaner R. B., Chem. Rev., 2018, 118, 9233—9280 |
| 25 | Chen P. C., Shen G., Shi Y., Chen H., Zhou C., ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 4403—4411 |
| 26 | Rattana T., Chaiyakun S., Witit⁃anun N., Nuntawong N., Chindaudom P., Oaew S., Kedkeaw C., Limsuwan P., Procedia Engineering, 2012, 32, 759—764 |
| 27 | Thangappan R., Kalaiselvam S., Elayaperumal A., Jayavel R., Arivanandhan M., Karthikeyan R., Hayakawa Y., Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 2637—2646 |
| 28 | Ludwig J., An L., Pattengale B., Kong Q. Y., Zhang X. Y., Xi P. X., Huang J. E., J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2015, 6, 2671—2675 |
| [1] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [2] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [3] | LIANG Yu, LIU Huan, GONG Lige, WANG Chunxiao, WANG Chunmei, YU Kai, ZHOU Baibin. Synthesis and Supercapacitor Properties of Biimidazole-modified {SiW12O40} Hybrid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(1): 20210556. |
| [4] | WEI Yuchen, WU Tingting, YANG Lei, JIN Biyu, LI Hongqiang, HE Xiaojun. Preparation and Supercapacitive Performance of Naphthalene-based Interconnected Porous Carbon Nanocapsules [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2852. |
| [5] | ZHANG Nan, HAN Kuo, LI Yue, WANG Chunru, ZHAO Feng, HAN Dongxue, NIU Li. Core-shell Heterostructure Construction Between Thiospinel CuCo2S4 and MoS2 for Improved Hydrogen Evolution Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1307. |
| [6] | MIAO Weijun, WU Feng, WANG Yong, WANG Zongbao. In⁃situ Study of the Epitaxial Crystallization of PCL/RGO at High Shear Rate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 910. |
| [7] | SHA Huiwen, MA Weiting, ZHOU Xiaojuan, SONG Weixing. One-step Preparation and Applications of Laser Induced Three-dimensional Reticular Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 607. |
| [8] | CHEN Minghua, LI Hongwu, FAN He, LI Yu, LIU Weiduo, XIA Xinhui, CHEN Qingguo. Research Progress of Two-dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenides in Supercapacitors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 539. |
| [9] | ZHANG Weiguo, FAN Songhua, WANG Hongzhi, YAO Suwei. Synthesis of Self-assembled α-Fe2O3/Graphene Hydrogel for Supercapacitors with Promising Electrochemical Properties [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(8): 1850. |
| [10] | GUAN Fanglan,LI Xin,ZHANG Qun,GONG Yan,LIN Ziyu,CHEN Yao,WANG Lejun. Fabrication and Capacitance Performance of Laser-machined RGO/MWCNT/CF In-plane Flexible Micro-supercapacitor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 300. |
| [11] | LI Botian,SHAO Wei,XIAO Da,ZHOU Xue,DONG Junwei,TANG Liming. Polypyrrole Nanowire Gels Based on Templating Fabrication and Their Energy Storage and Electrochemical Sensing Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 183. |
| [12] | LIU Ben,ZHANG Xingying,CHEN Shaoyun,HU Chenglong. Preparation and Electrochemical Energy Storage Performance of One Dimensional Orderly Polyaniline Nanowires Array† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(3): 498. |
| [13] | LIU Hao,ZHAO Dingxuan,GONG Guodong,ZHANG Zhuxin,JIA Tuo,CHEN Hanzhe. Effect of Temperature on Morphology and Supercapacitor Performance of Carbon Nano-spheres† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 18. |
| [14] | LI Long,HU Hongli,DING Shujiang. Facile Synthesis of Scale-like CoMn2O4 Nanosheets on Reduced Graphene Oxide for Supercapacitors† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 2010. |
| [15] | NIE Guangdi, ZHU Yun, TIAN Di, WANG Ce. Research Progress in the Electrospun Nanofiber-based Supercapacitor Electrode Materials† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7): 1349. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||