

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (12): 2255.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170348
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Rongbin1, TONG Sai1, YANG Jinmei1, TANG Xiannong1, HUANG Chuanqing1, WANG Xuewen1, FENG Gang1, CAI Jianxin2,*( )
)
Received:2017-06-06
Online:2017-12-10
Published:2017-11-21
Contact:
CAI Jianxin
E-mail:cjx@ncu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Rongbin, TONG Sai, YANG Jinmei, TANG Xiannong, HUANG Chuanqing, WANG Xuewen, FENG Gang, CAI Jianxin. Graphene Supported Nickel Catalyst for Methanation of Carbon Dioxide†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(12): 2255.
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | 2θ/(°) | Interlayer distancea/nm | Crystallite size/nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiOb | Nic | ||||
| GO | 60 | 11 | 0.81 | ||
| RGO | 463 | 24 | 0.37 | ||
| Ni/RGO | 316 | 24.9 | 0.35 | 4.1 | 5.3 |
| CNTs | 334 | 26 | |||
| Ni/CNTs | 149 | 26 | 4.0 | 8.9 | |
| AC | 868.6 | 23.7 | |||
| Ni/AC | 739 | 24.8 | 6.1 | 11.6 | |
Table 1 Specific surface area, interlayer distance and NiO crystallite size of the samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | 2θ/(°) | Interlayer distancea/nm | Crystallite size/nm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiOb | Nic | ||||
| GO | 60 | 11 | 0.81 | ||
| RGO | 463 | 24 | 0.37 | ||
| Ni/RGO | 316 | 24.9 | 0.35 | 4.1 | 5.3 |
| CNTs | 334 | 26 | |||
| Ni/CNTs | 149 | 26 | 4.0 | 8.9 | |
| AC | 868.6 | 23.7 | |||
| Ni/AC | 739 | 24.8 | 6.1 | 11.6 | |
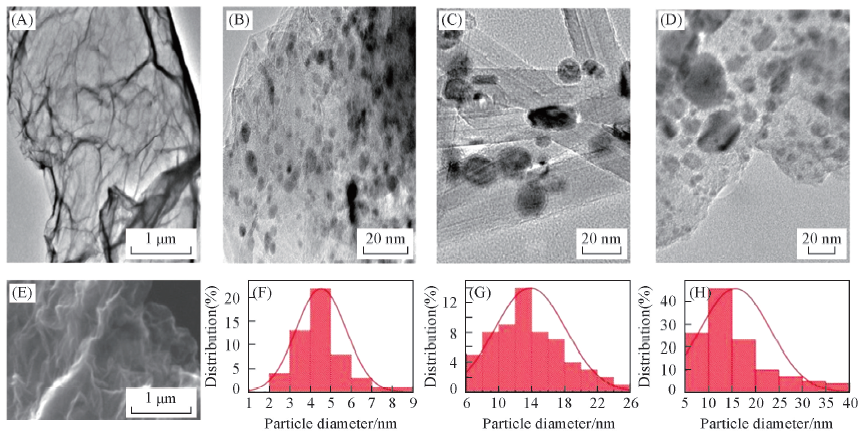
Fig.4 TEM images of RGO(A), Ni/RGO(B), Ni/CNTs(C) and Ni/AC(D), the SEM image of RGO(E) and the particle diameter distribution of Ni/RGO(F), Ni/CNTs(G) and Ni/AC(H)
| Sample | Ni particle sizea/nm | TO | Ni dispersionc(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni/RGO | 23.7 | 5.3 | 0.0659 | 18.9 |
| Ni/CNTs | 13.5 | 8.9 | 0.0630 | 11.2 |
| Ni/AC | 7.8 | 11.6 | 0.0474 | 8.6 |
Table 2 Comparison of catalytic performance of Ni/AC, Ni/CNTs and Ni/RGO in methanation reaction
| Sample | Ni particle sizea/nm | TO | Ni dispersionc(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni/RGO | 23.7 | 5.3 | 0.0659 | 18.9 |
| Ni/CNTs | 13.5 | 8.9 | 0.0630 | 11.2 |
| Ni/AC | 7.8 | 11.6 | 0.0474 | 8.6 |
| [1] | Li L., Zhao N., Wei W., Sun Y. H., Fuel,2013, 108, 112—130 |
| [2] | Sabatier P., Senderens J. B., Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci., 1902, 134, 514—516 |
| [3] | Hashimoto K., Yamasaki M., Meguro S., Sasaki T., Katagiri H., Izumiya K., Kumagai N., Habazaki H., Akiyama E., Asami K., Corros. Sci., 2002, 44(2), 371—386 |
| [4] | Aresta M., Dibenedetto A., Angelini A., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(3), 1709—1742 |
| [5] | Su X., Xu J. H., Liang B. L., Duan H. M., Hou B. L., Huang Y. Q., J. Energ. Chem., 2016, 25, 553—565 |
| [6] | Zhen W., Li B., Lu G., Ma J., Chem. Commun. (Cambridge UK), 2015, 51(9), 1728—1731 |
| [7] | Chang F. W., Kuo M. S., Tsay M. T., Hsieh M. C., Appl. Catal. A, 2003, 247, 309—320 |
| [8] | Iijima S., Nature, 1991, 354, 56—58 |
| [9] | Wang H., Shi Y. L., Li Z. X., Zhang W. G., Yao S. W., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2014, 30(4), 650—655 |
| [10] | Wang C., Zhai P., Zhang Z. C., Zhou Y., Zhang J. K., Zhang H., Shi Z. J., Han R. P. S., Huang F. Q., Ma D., J. Catal., 2016, 334, 42—51 |
| [11] | Ding C., Wei W. L., Sun H. J., Ding J. H., Ren J. S., Qu X. G., Carbon,2014, 79, 615—622 |
| [12] | Cao W., Ma Y. R., Zhou W., Guo L., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2015, 31(4), 508—513 |
| [13] | Bong S., Kim Y. R., Kim I., Woo S., Uhm S., Lee J., Kim H., J. Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 12(1), 129—131 |
| [14] | Yang H.F., Shan C. S., Li F. H., Han D. X., Zhang Q. X., Niu L.,Chem. Commun., 2009, (26), 3880—3882 |
| [15] | Singh S. K., Singh M. K., Kulkarni P. P., Sonkar V. K., Gracio J. J. A., Dash D., J. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(3), 2731—2740 |
| [16] | Yin J., Ding S. M., Zeng L., Xia H., Chen C., Zhang N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4), 720—724 |
| (尹洁, 丁顺民, 曾乐, 夏辉, 陈超, 张宁. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(4), 720—724) | |
| [17] | Wen Z. L., Yang S. D., Song Q. J., Hao L., Zhang X. G., Acta Phys-Chim. Sin., 2010, 26, 1570—1574 |
| (温祝亮, 杨苏东, 宋启军, 郝亮, 张校刚. 物理化学学报, 2010, 26, 1570—1574) | |
| [18] | Hu X. F., Yang W., Wang N., Luo S. Z., Chu W., Adv. Mater. Res., 2014, 924, 217—226 |
| [19] | Peigney A., Laurent C., Flahaut E., Bacsa R., Rousset A., Carbon,2001, 39, 507—514 |
| [20] | Wang Y., Ben T., Qiu S. L.,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6), 1042—1049 |
| (王昀, 贲腾, 裘式纶. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(6), 1042—11049) | |
| [21] | Subrahmanyam K., Vivekchand S., Govindaraj A., Rao C., J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18, 1517—1523 |
| [22] | Zhang Y., Qiu Y. R., Chem. Ind. Eng. Prog., 2010, 5, 918—921 |
| (张煜, 邱运仁. 化工进展, 2010, 5, 918—921) | |
| [23] | Le M. C., Van K. L., Nguyen T. H. T., Nguyen N. H., J. Chem., 2017, 2017, 1—11 |
| [24] | Yuan Q. H., Zeng X. S., Liu Y., Luo L., Wu J. B., Wang Y. C., Zhou G. H., Carbon,2016, 96, 843—855 |
| [25] | Pan C. G., Ye L. Q., Wang J. H., Bao L. X., Que Y. S., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities, 2013, 29(5), 941—946 |
| [26] | Tian Y., Liu Y. X., Pang F., Wang F. L., Zhang X., Colloids Surf. A, 2015, 464, 96—103 |
| [27] | Yang X. Y., Wang X. B., Li J., Yang J., Wan L., Wang J. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(9), 1902—1907 |
| (杨旭宇, 王贤宝, 李静, 杨佳, 万丽, 王敬超. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(9), 1902—1907) | |
| [28] | Liu G., Wang Y. J., Qiu F. Y., Li L., Jiao L. F., Yuan H. T., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 22542—22549 |
| [29] | Qin Z. F., Ren J., Miao M. Q., Li Z., Lin J. Y., Xie K. C., Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 164, 18—30 |
| [1] | WANG Ruina, SUN Ruifen, ZHONG Tianhua, CHI Yuwu. Fabrication of a Dispersible Large-sized Graphene Quantum Dot Assemblies from Graphene Oxide and Its Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence Behaviors [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220161. |
| [2] | ZHAO Runyao, JI Guipeng, LIU Zhimin. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction over Pyrrole Nitrogen-coordinated Single-atom Copper Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220272. |
| [3] | YAN Jiasen, HAN Xianying, DANG Zhaohan, LI Jiangang, HE Xiangming. Preparation and Performance of Paraffin/Expanded Graphite/Graphene Composite Phase Change Heat Storage Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220054. |
| [4] | CAO Lei, CHEN Meijun, YUAN Gang, CHANG Gang, ZHANG Xiuhua, WANG Shengfu, HE Hanping. Solution-gated Graphene Field Effect Transistor Sensor Based on Crown Ether Functionalization for the Detection of Mercury Ion [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210688. |
| [5] | ZHENG Xuelian, YANG Cuicui, TIAN Weiquan. The Second Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Azulene-defect Graphene Nanosheets with Full Armchair Edge [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [6] | GAO Jing, HE Wentao, WANG Xinxin, XIANG Yushu, LONG Lijuan, QIN Shuhao. Preparation of DOPO Derivative Modified Carbon Nanotubes and Their Effect on Flame Retardancy of Polylactic Acid [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210670. |
| [7] | ZHANG Zhibo, SHANG Han, XU Wenxuan, HAN Guangdong, CUI Jinsheng, YANG Haoran, LI Ruixin, ZHANG Shenghui, XU Huan. Self-Assembly of Graphene Oxide at Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Microparticles Toward High-performance Intercalated Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [8] | YANG Junge, GAO Chengqian, LI Boxin, YIN Dezhong. Preparation of High Thermal Conductivity Phase Change Monolithic Materials Based on Pickering Emulsion Stabilized by Surface Modified Graphene Oxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210593. |
| [9] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [10] | YU Bin, CHEN Xiaoyan, ZHAO Yue, CHEN Weichang, XIAO Xinyan, LIU Haiyang. Graphene Oxide-based Cobalt Porphyrin Composites for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210549. |
| [11] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [12] | DING Qin, ZHANG Zixuan, XU Peicheng, LI Xiaoyu, DUAN Limei, WANG Yin, LIU Jinghai. Effects of Cu, Ni and Co Hetroatoms on Constructions and Electrocatalytic Properties of Fe-based Carbon Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [13] | LIU Jie, LI Jinsheng, BAI Jingsen, JIN Zhao, GE Junjie, LIU Changpeng, XING Wei. Constructing a Water-blocking Interlayer Containing Sulfonated Carbon Tubes to Reduce Concentration Polarization in Direct Methanol Fuel Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [14] | HOU Congcong, WANG Huiying, LI Tingting, ZHANG Zhiming, CHANG Chunrui, AN Libao. Preparation and Electrochemical Properties of N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH Composite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [15] | XU Xiaojian, LI Bo, LIN Mengxiao, ZHAN Shuo. Vacuum Freeze Drying to Prepare Porous Carbon Based Composite Membranes for Efficient Solar Steam Generation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220361. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||