

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (9): 1686.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20160270
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Jian, DU Jing, LIU Shuo, YANG Zhongzhi, ZHAO Dongxia*( ), LIU Cui*(
), LIU Cui*( )
)
Received:2016-04-22
Online:2016-09-10
Published:2016-08-23
Contact:
ZHAO Dongxia,LIU Cui
E-mail:zhaodxchem@lnnu.edu.cn;liuc@lnnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Jian, DU Jing, LIU Shuo, YANG Zhongzhi, ZHAO Dongxia, LIU Cui. Theoretical Studies on the Effect of Amino Acid Side Chains on Hydrogen Bonding for G:C in Aqueous Solution†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(9): 1686.
| Hydrogen bond | Length of HB/nm | Angle of HB/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | |
| N—H…N | 0.178—0.220 | 0.182—0.268 | 142.4—178.9 | 120.4—179.8 |
| N—H…O | 0.166—0.204 | 0.177—0.218 | 137.2—179.1 | 126.6—179.8 |
| O—H…N | 0.168—0.213 | 0.168—0.237 | 148.1—155.7 | 145.8—158.6 |
| O—H…O | 0.186 | 0.187 | 149.2 | 151.1 |
Table 1 Geometry structure of complexes in gas and aqueous solution within region 1
| Hydrogen bond | Length of HB/nm | Angle of HB/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | |
| N—H…N | 0.178—0.220 | 0.182—0.268 | 142.4—178.9 | 120.4—179.8 |
| N—H…O | 0.166—0.204 | 0.177—0.218 | 137.2—179.1 | 126.6—179.8 |
| O—H…N | 0.168—0.213 | 0.168—0.237 | 148.1—155.7 | 145.8—158.6 |
| O—H…O | 0.186 | 0.187 | 149.2 | 151.1 |
| Complex | d[N—H…O(upper)]/nm | d[N—H…N(middle)]/nm | d[N—H…O(lower)]/nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | |
| G:C | 0.1764 | 0.1873 | 0.1923 | 0.1926 | 0.1901 | 0.1837 |
| GC1:Arg1 | 0.1928 | 0.1909 | 0.1903 | 0.1919 | 0.1791 | 0.1815 |
| GC1:Arg2 | 0.1928 | 0.1903 | 0.1900 | 0.1918 | 0.1790 | 0.1817 |
| GC1:Arg3 | 0.1924 | 0.1891 | 0.1913 | 0.1922 | 0.1793 | 0.1819 |
| GC1:Arg4 | 0.1918 | 0.1892 | 0.1915 | 0.1925 | 0.1796 | 0.1821 |
| GC1:Asn/Gln2 | 0.1832 | 0.1886 | 0.1938 | 0.1927 | 0.1879 | 0.1828 |
| GC1:Lys1 | 0.1949 | 0.1902 | 0.1902 | 0.1919 | 0.1761 | 0.1811 |
| GC2:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1768 | 0.1863 | 0.1937 | 0.1938 | 0.1929 | 0.1869 |
| GC2:Ser/Thr1 | 0.1776 | 0.1876 | 0.1923 | 0.1924 | 0.1901 | 0.1838 |
| GC3:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1815 | 0.1861 | 0.1915 | 0.1925 | 0.1859 | 0.1842 |
| GC4:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1729 | 0.1883 | 0.1973 | 0.1951 | 0.2009 | 0.1850 |
| GC5:Arg1 | 0.1902 | 0.1880 | 0.1914 | 0.1918 | 0.1817 | 0.1827 |
| GC5:Arg2 | 0.1886 | 0.1878 | 0.1893 | 0.1917 | 0.1799 | 0.1828 |
| GC6:Arg1 | 0.1839 | 0.1881 | 0.1872 | 0.1917 | 0.1751 | 0.1809 |
| GC6:Arg2 | 0.1840 | 0.1882 | 0.1871 | 0.1916 | 0.1753 | 0.1808 |
Table 2 Bond length of hydrogen bond of G:C in gas and aqueous solution within region 2
| Complex | d[N—H…O(upper)]/nm | d[N—H…N(middle)]/nm | d[N—H…O(lower)]/nm | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | Gas | Aqueous | |
| G:C | 0.1764 | 0.1873 | 0.1923 | 0.1926 | 0.1901 | 0.1837 |
| GC1:Arg1 | 0.1928 | 0.1909 | 0.1903 | 0.1919 | 0.1791 | 0.1815 |
| GC1:Arg2 | 0.1928 | 0.1903 | 0.1900 | 0.1918 | 0.1790 | 0.1817 |
| GC1:Arg3 | 0.1924 | 0.1891 | 0.1913 | 0.1922 | 0.1793 | 0.1819 |
| GC1:Arg4 | 0.1918 | 0.1892 | 0.1915 | 0.1925 | 0.1796 | 0.1821 |
| GC1:Asn/Gln2 | 0.1832 | 0.1886 | 0.1938 | 0.1927 | 0.1879 | 0.1828 |
| GC1:Lys1 | 0.1949 | 0.1902 | 0.1902 | 0.1919 | 0.1761 | 0.1811 |
| GC2:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1768 | 0.1863 | 0.1937 | 0.1938 | 0.1929 | 0.1869 |
| GC2:Ser/Thr1 | 0.1776 | 0.1876 | 0.1923 | 0.1924 | 0.1901 | 0.1838 |
| GC3:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1815 | 0.1861 | 0.1915 | 0.1925 | 0.1859 | 0.1842 |
| GC4:Asn/Gln1 | 0.1729 | 0.1883 | 0.1973 | 0.1951 | 0.2009 | 0.1850 |
| GC5:Arg1 | 0.1902 | 0.1880 | 0.1914 | 0.1918 | 0.1817 | 0.1827 |
| GC5:Arg2 | 0.1886 | 0.1878 | 0.1893 | 0.1917 | 0.1799 | 0.1828 |
| GC6:Arg1 | 0.1839 | 0.1881 | 0.1872 | 0.1917 | 0.1751 | 0.1809 |
| GC6:Arg2 | 0.1840 | 0.1882 | 0.1871 | 0.1916 | 0.1753 | 0.1808 |
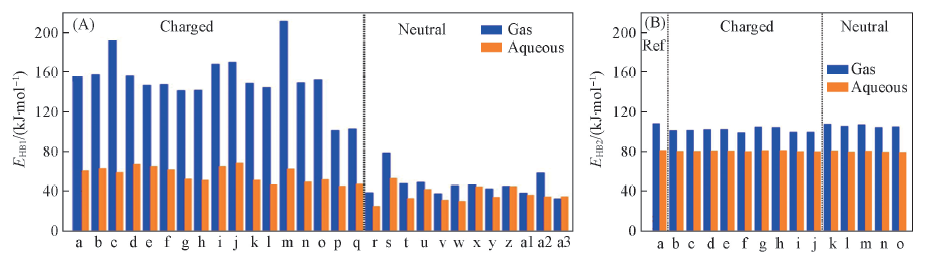
Fig.3 Hydrogen bond energies of complexes (A) EHB1 of the complexes in gas and aqueous solution. (B) EHB2 of G:C of complexes in gas and aqueous solution. a. G1:Arg1; b. G1:Arg2; c. G1:Lys1; d. G3:Asn/Glu1; e. C1:Arg1; f. C1:Arg2; g. C3:Arg1; h. C3:Arg2; i. GC1:Arg1; j. GC1:Arg2; k. GC1:Arg3; l. GC1:Arg4; m. GC1:Lys1; n. GC5:Arg1; o. GC5:Arg2; p. GC6:Arg1; q. GC6:Arg2; r. G1:Asn/Gln2; s. G2:Asn/Gln1; t. G2:Ser/Thr1; u. G4:Asn/Gln1; v. G4:Asn/thr1; w. C2:Ser/Thr1; x. C2:Asn/Gln1; y. GC1:Asn/Gln2; z. GC2:Asn/Gln1; a1. GC2:Ser/Thr1; a2. GC3:Asn/Gln1; a3. GC4:Asn/Gln1. (B) a. G:C; b. GC1:Arg1; c. GC1:Arg2; d. GC1:Arg3; e. GC1:Arg4; f. GC1:Lys1; g. GC5:Arg1; h. GC5:Arg2; i. GC6:Arg1; j. GC6:Arg2; k. GC1:Asn/Gln2; l. GC2:Asn/Gln1; m. GC2:Ser/Thr1; n. GC3:Asn/Gln1; o. GC4:Asn/Gln1.
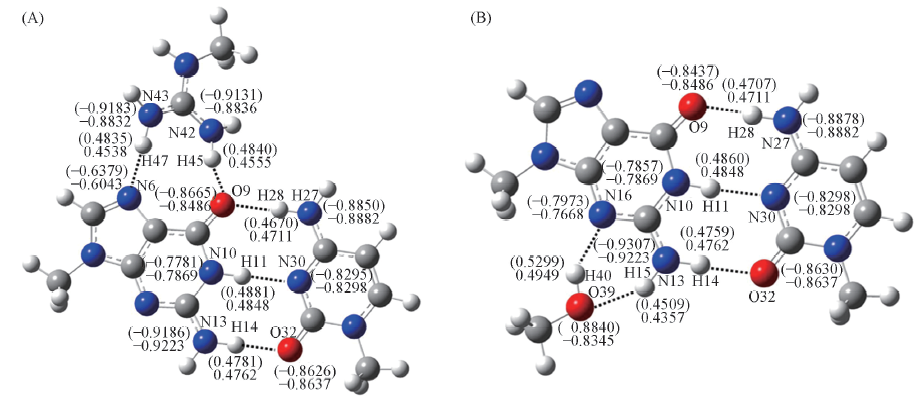
Fig.4 Atomic charges of hydrogen bonds of GC1:Arg1(A) and GC2:Ser/Thr1(B) complexes in aqueous solution Value in parenthesis denotes the atomic charges(e) of forming the triple-body complexes; values without parenthesis are those of G, C and AASC.
| [1] | Malone T., Blumenthal R. M., Cheng X., J. Mol. Biol., 1995, 253(4), 618—632 |
| [2] | Xin L., Zhou C., Yang Z. Q., Liu D. S., Small,2013, 9(18), 3088—3091 |
| [3] | Katie A. W., Jennifer L. K., Nucleic Acids Res., 2014, 42(10), 6726—6741 |
| [4] | Wells R. A., Kellie J. L., Wetmore S. D., J. Phys. Chem. B,2013, 117(36), 10462—10474 |
| [5] | Latimer W. M., Rodebush W. H., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1920, 42(7), 1419—1433 |
| [6] | Buckingham A. D., Del Bene J. E., McDowell S. A. C., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2008, 463(1), 1—10 |
| [7] | Deepa P., Kolandaivel P., Senthilkumar K., Mol. Phys., 2011, 109(16), 1995—2008 |
| [8] | Qiu Z. M., Xia Y. M., Wang H. J., Diao K. S., Struct. Chem., 2010, 1(21), 99—105 |
| [9] | Jones S., Heyningen P., Berman H. M., Thornton J. M., J. Mol. Biol., 1999, 5(287), 877—896 |
| [10] | Shelkovsky V. S., Eur. Phys. J. D, 2002, 20(3), 421—430 |
| [11] | Kumar N. V., Govil G., Biopolymers,1984, 23(10), 1995—2008 |
| [12] | Mandel-Gutfreund Y., Ora S., Hanah M., J. Mol. Bio., 1995, 253(2), 370—382 |
| [13] | Wang C. S., Liu P., Yu N., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2013, 29(6), 1173—1182 |
| (王长生, 刘朋, 于楠. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29(6), 1173—1182) | |
| [14] | Rachael A. W., Kellie J. L., Wetmore S. D., J. Phys. Chem. B,2013, 117(36), 10462—10474 |
| [15] | Huo H. J., Zhao D. X., Yang Z. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2011, 32(12), 2877—2884 |
| (霍红洁, 赵东霞, 杨忠志. 高等学校化学学报,2011, 32(12), 2877—2884) | |
| [16] | Jacopo T., Benedetta M., Roberto C., Chem. Rev., 2005, 105(8), 2999—3093 |
| [17] | Takano Y., Houk K. N., J. Chem. Theory. Comput., 2005, 1(1), 70—77 |
| [18] | Si D., Li H., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(14), 144107 |
| [19] | Paukku Y., Hill G., J. Phys. Chem. A,2011, 115(18), 4804—4810 |
| [20] | Ryoichi F., Masahiro E., Roberto C., J. Chem. Phys., 2014, 140(6), 064114 |
| [21] | Liu C., Zhang Q. H., Gong L. D., Lu L. N., Yang Z. Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2014, 35(12), 2645—2653 |
| (刘翠, 张千慧, 宫利东, 卢丽男, 杨忠志. 高等学校化学学报,2014, 35(12), 2645—2653) | |
| [22] | Czyznikowska Z., Lipkowski P., Góra R. W., Zalesny R., Cheng A. C., J. Phys. Chem. B,2009, 113(33), 11511—11520 |
| [23] | Frisch M. J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Vreven T., Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E., Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N., Kobayashi R., Normand J., Raghavachari K., Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Martin R. L., Morokuma K., Zakrzewski V. G., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Farkas Ö., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cioslowski J., Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision D.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [24] | Glendening E. D., Reed A. E., Carpenter J. E., Weinhold F., NBO Version 3.1 Gaussian 09, Revision D.01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [25] | Liu C., Zhao D. X., Yang Z. Z., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33(4), 379—390 |
| [26] | Seeman N. C., Rosenberg J. M., Rich A., P. Natl. Acad. Sci., 1976, 73(3), 804—808 |
| [1] | MIN Jing, WANG Liyan. 1H NMR Study on the Conformation of Aromatic Amides Limited by Three-center Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220084. |
| [2] | ZHANG Yong, XU Jun, BAO Yu, CUI Shuxun. Quantifying the Degree of Weakening Effect of Nonpolar Organic Solvent on the Strength of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding by Single-molecule Force Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210863. |
| [3] | CUI Shaoli, ZHANG Weijia, SHAO Xueguang, CAI Wensheng. Revealing the Effect of Threonine on the Binding Ability of Antifreeze Proteins with Ice Crystals by Free-energy Calculations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210838. |
| [4] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [5] | GAO Huiling, CAO Zhenzhen, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Monte Carlo Simulation on Self-healing Behaviour of Hydrogen-bonded Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220482. |
| [6] | WANG Le, QIN Liulei, LIU Yang, REN Li, XU Huiting, LIU Zunqi. Synthesis, Structure and Dielectric Properties of One-dimensional Chain Hydrogen Glycine Supramolecular Compound [(Gly)2+(18-crown-6)2(MnCl4)2‒] [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 691. |
| [7] | NI Qingsheng, DU Miao, SHAN Guorong, SONG Yihu, WU Ziliang, ZHENG Qiang. Regulation of Rheological Behavior of Polyvinyl Alcohol Aqueous Solution by One-dimensional Particles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3738. |
| [8] | GONG Shanshan, WU Tong, WANG Guange, HUANG Qing, SU Yuefeng, WU Feng. Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Efficient Recovery of Spent Lithium⁃ion Battery Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3151. |
| [9] | BAI Lan, ZHAI Lei, WANG Changou, HE Minhui, MO Song, FAN Lin. Thermal Expansion Behavior of Amide-containing Polyimide Films with Ultralow Thermal Expansion Coefficient † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 795. |
| [10] | QIN Liulei,LIU Yang,GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi. Synthesis and Switchable Dielectric Properties of an Inorganic-organic Hybrid Complex [H2(DABCO)CuCl4]·H2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 70. |
| [11] | XU Yan,LIU Cui,HAN Chengjuan,PAN Mingyu,SUN Zhaoqi,HAN Bingyu,YANG Zhongzhi. Development of Polarization Force Field for Guanine and Amino Acid Residues Systems† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(2): 288. |
| [12] | XU Yu,HUA Er. Hydrogen Bonding Study on Protic Ionic Liquids Composed of N-Alkyl Ethylenediaminum Cations with Trifluoroacetic Anion† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1954. |
| [13] | OUYANG Shunli, ZHANG Mingzhe, ZHANG Yongzhao, HU Qingcheng, WEI Haiyan, WU Nannan, HUANG Baokun. Raman Spectroscopic Investigation on the Effect of Hydrogen Bond on Molecular Structure in Ternary Aqueous Solution† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(4): 758. |
| [14] | WANG Xingxing, LI Panpan, HE Jinglin, OUYANG Wen, XIAO Hui, YANG Chan, CAO Zhong. Cytosine-rich Oligonucleotide-templated Fluorescent Silver Nanoclusters for Sensitive Assay of S1 Nuclease [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(8): 1334. |
| [15] | HAN Bingyu, LI Yue, LIU Cui. Investigation on the Hydrogen Bonding Interaction Between Amino Acid Side Chains and Base Pairs Containing Oxidized Guanine† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(6): 1068. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||