

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (9): 1926.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140426
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHENG Huayan, ZHANG Riguang*( ), LI Zhong
), LI Zhong
Received:2014-05-08
Online:2014-09-10
Published:2014-07-14
Contact:
ZHANG Riguang
E-mail:zhangriguang@tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHENG Huayan, ZHANG Riguang, LI Zhong. Theoretical Studies on the Interaction of CO and CH3O on CuCl(111) Surface for Methanol Oxidative Carbonylation†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(9): 1926.
| Method | R(C—O)/nm | BDE/(kJ·mol-1) | v(C—O)/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GGA-BLYP | 0.1143 | 1091.24 | 2128 |
| Expt. | 0.1128[ | 1076.38±0.67 [ | 2138[ |
Table 1 Bond length(R), stretching frequency(ν) and bond dissociation energy(BDE) for free CO molecule
| Method | R(C—O)/nm | BDE/(kJ·mol-1) | v(C—O)/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GGA-BLYP | 0.1143 | 1091.24 | 2128 |
| Expt. | 0.1128[ | 1076.38±0.67 [ | 2138[ |
| Mode | Site | R(C—O)/ nm | R(Cu—C)/ nm | R(Cu—O)/ nm | ∠C—O—Cl(Cu)/ (°) | ∠O—C—Cu(Cl)/ (°) | q(CO) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO(O-down) | Top | 0.1145 | 0.3905 | 179.72 | -0.005 | 11.23 | ||
| Cl-site | 0.1145 | 0.4383 | 179.52 | -0.005 | 10.90 | |||
| Hollow | 0.1146 | 0.4135 | 179.82 | -0.005 | 11.14 | |||
| Bridge | 0.1145 | 0.4152 | 174.94 | -0.004 | 11.12 | |||
| CO(C-down) | Top | 0.1153 | 0.1905 | 172.50 | 0.079 | 84.47 | ||
| Hollow | 0.1158 | 0.2816 | 179.95 | -0.093 | 18.97 |
Table 2 Predicted geometrical parameter, adsorption energies and Mulliken charge at four selected sites
| Mode | Site | R(C—O)/ nm | R(Cu—C)/ nm | R(Cu—O)/ nm | ∠C—O—Cl(Cu)/ (°) | ∠O—C—Cu(Cl)/ (°) | q(CO) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO(O-down) | Top | 0.1145 | 0.3905 | 179.72 | -0.005 | 11.23 | ||
| Cl-site | 0.1145 | 0.4383 | 179.52 | -0.005 | 10.90 | |||
| Hollow | 0.1146 | 0.4135 | 179.82 | -0.005 | 11.14 | |||
| Bridge | 0.1145 | 0.4152 | 174.94 | -0.004 | 11.12 | |||
| CO(C-down) | Top | 0.1153 | 0.1905 | 172.50 | 0.079 | 84.47 | ||
| Hollow | 0.1158 | 0.2816 | 179.95 | -0.093 | 18.97 |
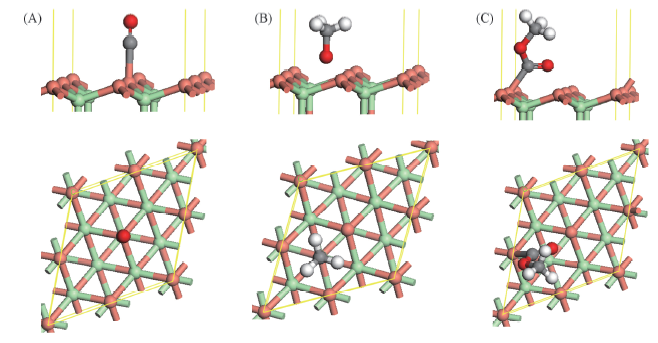
Fig.2 Optimized structure of CO, CH3O and CH3OCO at the top site of CuCl(111) surface (A) CO; (B) CH3O; (C) CH3OCO. Green balls represent Cl atoms, orange balls represent Cu atoms, grey balls represent C atoms, white balls represent H atom, red balls represent O atoms.
| Site | R(C—O)/nm | R(Cu—O)/nm | ∠C—O—Cu/(°) | ∠O—C—Cl/(°) | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hollow | 0.1431 | 0.2508 | 179.723 | -0.423 | 218.02 | |
| Top | 0.1390 | 0.1930 | 175.751 | -0.380 | 184.12 |
Table 3 Predicted geometrical parameter, adsorption energies and Mulliken charge of CH3O
| Site | R(C—O)/nm | R(Cu—O)/nm | ∠C—O—Cu/(°) | ∠O—C—Cl/(°) | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hollow | 0.1431 | 0.2508 | 179.723 | -0.423 | 218.02 | |
| Top | 0.1390 | 0.1930 | 175.751 | -0.380 | 184.12 |
| Site | R(C nm | R(C—O)/ nm | R( nm | R[Cu—C (nearest)]/nm | ∠O—C—O/ (°) | ∠C—O—C/ (°) | q(CH3OCO) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | 0.1258 | 0.1481 | 0.1367 | 0.2046 | 118.350 | 117.837 | 0.171 | 219.59 |
| Bridge | 0.1259 | 0.1480 | 0.1368 | 0.2045 | 118.164 | 117.846 | 0.170 | 219.54 |
| Cl-site | 0.1257 | 0.1480 | 0.1368 | 0.2052 | 118.517 | 117.887 | 0.171 | 219.27 |
| Hollow | 0.1260 | 0.1482 | 0.1369 | 0.2055 | 117.773 | 117.611 | 0.171 | 218.72 |
Table 4 Predicted geometrical parameter, Mulliken charge and adsorption energy of CH3OCO at different adsorption sites
| Site | R(C nm | R(C—O)/ nm | R( nm | R[Cu—C (nearest)]/nm | ∠O—C—O/ (°) | ∠C—O—C/ (°) | q(CH3OCO) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Top | 0.1258 | 0.1481 | 0.1367 | 0.2046 | 118.350 | 117.837 | 0.171 | 219.59 |
| Bridge | 0.1259 | 0.1480 | 0.1368 | 0.2045 | 118.164 | 117.846 | 0.170 | 219.54 |
| Cl-site | 0.1257 | 0.1480 | 0.1368 | 0.2052 | 118.517 | 117.887 | 0.171 | 219.27 |
| Hollow | 0.1260 | 0.1482 | 0.1369 | 0.2055 | 117.773 | 117.611 | 0.171 | 218.72 |
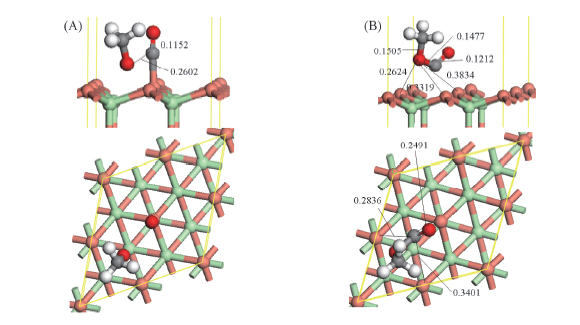
Fig.3 Optimized co-adsorbed structure of CO+CH3O and the corresponding transition state for CO interaction with CH3O to CH3OCO over CuCl(111) surface (A) CO+CH3O; (B) TS1. Bond lengths are in nm.
| Absorption | Molecule | R(C—O)/ nm | R(Cu—C)/ nm | R(Cu—O)/ nm | ∠C—O—Cl/ (°) | ∠O—C—Cu/ (°) | q(X) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ecads/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eint/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-adsorption | CO | 0.1152 | 0.1918 | 174.247 | 0.212 | 89.74 | 294.92 | 2.89 | ||
| CH3O | 0.1425 | 0.2443 | 164.351 | -0.410 | 208.07 | |||||
| Single adsorption | CO | 0.1153 | 0.1905 | 175.502 | 0.186 | 84.47 | | | ||
| CH3O | 0.1431 | 0.2508 | 179.723 | -0.423 | 218.02 | | |
Table 5 Comparisons of theoretical calculation results between(CO+CH3O)/CuCl(111) co-adsorption and CO/CuCl(111) as well as CH3O/CuCl(111) single adsorption
| Absorption | Molecule | R(C—O)/ nm | R(Cu—C)/ nm | R(Cu—O)/ nm | ∠C—O—Cl/ (°) | ∠O—C—Cu/ (°) | q(X) | Eads/ (kJ·mol-1) | Ecads/ (kJ·mol-1) | Eint/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co-adsorption | CO | 0.1152 | 0.1918 | 174.247 | 0.212 | 89.74 | 294.92 | 2.89 | ||
| CH3O | 0.1425 | 0.2443 | 164.351 | -0.410 | 208.07 | |||||
| Single adsorption | CO | 0.1153 | 0.1905 | 175.502 | 0.186 | 84.47 | | | ||
| CH3O | 0.1431 | 0.2508 | 179.723 | -0.423 | 218.02 | | |
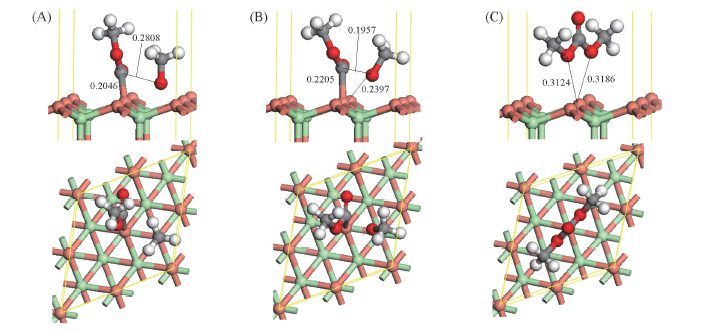
Fig.4 Optimized co-adsorbed structure of CH3OCO and CH3O and the corresponding transition state for CH3OCO interaction with CH3O to DMC over CuCl(111) surface (A) CH3OCO+CH3O; (B) TS2; (C) DMC. Bond lengths are in nm.
| [1] | Wang X., Chen W. K., Sun B. Z., Lu C. M., Chin. J. Inorg. Chem., 2007, 23(5), 807—812 |
| (王霞, 陈文凯, 孙宝珍, 陆春梅. 无机化学学报, 2007, 23(5), 807—812) | |
| [2] | Didziulis S. V., Butcher K. D., Cohen S. L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1989, 111(18), 7110—7123 |
| [3] | Solomon E. I., Jones P. M., May J. A., Chem. Rev., 1993, 93(8), 2623—2644 |
| [4] | Vissokov G. P., Catal. Today, 2004, 89(1/2), 213—221 |
| [5] | Vissokov G. P., Catal. Today, 2004, 89(1/2), 223—231 |
| [6] | Behrens M., Studt F., Kasatkin I., Kühl S., Hävecker M., Abild-Pedersen F., Zander S., Girgsdies F., Kurr P., Kniep B. L., Tovar M., Fischer R. W., Nørskov J. K., Schlögl R., Science,2012, 336(6083), 893—897 |
| [7] | Jia M. J., Zhang W. X., Wu T. H., J. Mol. Catal. A,2002, 185(1/2), 151—157 |
| [8] | Ren J., Wang D. L., Pei Y. L., Qin Z. F., Lin J. Y., Li Z., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(11), 2594—2600 |
| (任军, 王冬蕾, 裴永丽, 秦志峰, 林建英, 李忠. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(11), 2594—2600) | |
| [9] | Huang S., Chen P., Yan B., Wang S., Shen Y., Ma X., Ind. Eng. Chem. Res., 2013, 52(19), 6349—6356 |
| [10] | Ren J., Liu S. S., Li Z., Xie K. C., Catal. Commun., 2011, 12(5), 357—361 |
| [11] | Romano U., Tesel R., Mauri M. M., Rebora P., Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 1980, 19(3), 396—403 |
| [12] | King S. T., J. Catal., 1996, 161(2), 530—538 |
| [13] | King S. T., Catal. Today, 1997, 33(1), 173—182 |
| [14] | Li Z., Meng F. H., Ren J., Zheng H. Y., Xie K. C., Chin. J. Catal., 2008, 29(7), 643—648 |
| (李忠, 孟凡会, 任军, 郑华艳, 谢克昌. 催化学报, 2008, 29(7), 643—648) | |
| [15] | Anderson S. A., Manthata S., Root T. W., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2005, 280(2), 117—124 |
| [16] | Anderson S. A., Root T. W., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2004, 220(2), 247—255 |
| [17] | Anderson S. A., Root T. W., J. Catal., 2003, 217(2), 396—405 |
| [18] | Zhang Y. H., Bell A. T., J. Catal., 2008, 255(2), 153—161 |
| [19] | He C. Z., Wang H., Huai L. Y., Liu J. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(4), 946—951 |
| (何朝政, 王会, 淮丽媛, 刘靖尧. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(4), 946—951) | |
| [20] | Wang L. P., Han P. D., Hao Y. Y., Zhang Z. X., Xu B. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2012, 33(3), 569—574 |
| (王丽平, 韩培德, 郝玉英, 张竹霞, 许并社. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(3), 569—574) | |
| [21] | Ni Z. M., Shi W., Xia M. Y., Xue J. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2013, 34(10), 2353—2362 |
| (倪哲明, 施炜, 夏明玉, 薛继龙. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(10), 2353—2362) | |
| [22] | Zheng X. B., Bell A. T., J. Phys. Chem. C,2008, 112(13), 5043—5047 |
| [23] | Wang X., Chen W. K., Lu C. H., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2008, 254(15), 4421—4431 |
| [24] | Wang X., Chen W. K., Xu X. L., Lu C. M., Chin. J. Catal., 2007, 28(8), 696—702 |
| (王霞, 陈文凯, 徐香兰, 陆春梅. 催化学报, 2007, 28(8), 696—702) | |
| [25] | Baenziger N. C., Modak S. L., Fox C. L., Jnr. Acta Crystallogr. C,1983, 39(12), 1620—1623 |
| [26] | Casarin M., Tondello E., Vittadini A., Inorg. Chim. Acta,1995, 235(1), 151—158 |
| [27] | Lin J. Y., Jones P., Guckert J., Sokomon E. I., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1991, 113(22), 8312—8326 |
| [28] | Wang X., Deng Z. P., Sun B. Z., Xu X. L., Chen W. K., J. Mol. Catal.(China), 2007, 21(5), 463—468 |
| (王霞, 邓昭浦, 孙宝珍, 徐香兰, 陈文凯. 分子催化, 2007, 21(5), 463—468) | |
| [29] | Delley B., J. Chem. Phys., 1990, 92(1), 508—517 |
| [30] | Delley B., J. Chem. Phys., 2000, 113(18), 7756—7764 |
| [31] | Delley B., J. Chem. Phys., 1990, 100(15), 6107—6110 |
| [32] | Shao J. X., Chen X. L., Yang X. D., Zhang F. P., Ge S. H., J. At. Mol. Phys., 2006, 23(1), 80—84 |
| (邵菊香, 程新路, 杨向东, 张芳沛, 葛素红. 原子与分子物理学报, 2006, 23(1), 80—84) | |
| [33] | Luo Y.R., Handbook of Bond Dissociation Energies in Organic Compounds, Science Press, Beijing, 2005, 209 |
| (罗渝然. 化学键能数据手册, 北京: 科学出版社, 2005, 209) | |
| [34] | Sun B. Z., Chen W. K., Zheng J. D., Lu C. H., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2008, 255(5), 3141—3148 |
| [35] | Liu Z. P., Hu P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2001, 123(50), 12596—12604 |
| [36] | Mao J. H., Ni Z. M., Pan G. X., Xu Q., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2008, 24(11), 2059—2064 |
| (毛江洪, 倪哲明, 潘国祥, 胥倩. 物理化学学报, 2008, 24(11), 2059—2064 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WANG Lijun, LI Xin, HONG Song, ZHAN Xinyu, WANG Di, HAO Leiduan, SUN Zhenyu. Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction to CO by Tuning CdO-Carbon Black Interface [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220317. |
| [3] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [4] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [5] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [6] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [7] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [8] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [9] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [10] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [11] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [12] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [13] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [14] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [15] | HU Wei, LIU Xiaofeng, LI Zhenyu, YANG Jinlong. Surface and Size Effects of Nitrogen-vacancy Centers in Diamond Nanowires [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||