

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (7): 1500.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20140136
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
JIANG Haiyang, FENG Wei, SUN Yanwei, QI Qiaofang, TIAN Hongwei, LIU Huiling*, HUANG Xuri*( )
)
Received:2014-02-24
Online:2014-07-10
Published:2019-08-01
Contact:
LIU Huiling,HUANG Xuri
E-mail:huangxr@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
JIANG Haiyang, FENG Wei, SUN Yanwei, QI Qiaofang, TIAN Hongwei, LIU Huiling, HUANG Xuri. Theoretical Studies on the Conjugate Addition of 1-Bromonitromethane to Benzylidene Acetone Catalyzed by 9-Amino-9-deoxyepiquinine†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(7): 1500.
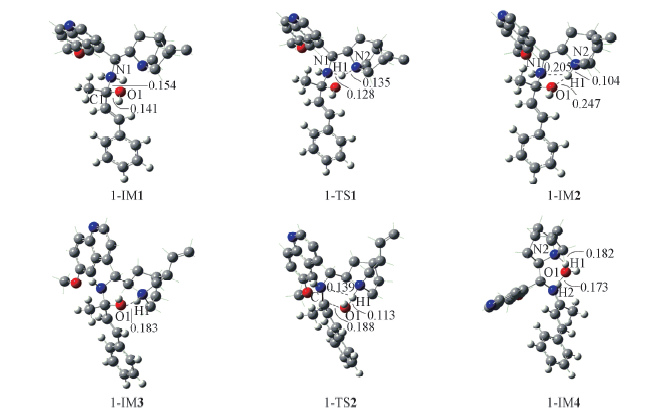
Fig.3 Optimized geometries and selected geometric parameters for the formation of iminium intermediate Some hydrogen atoms of the catalyst not involved in reaction sites are omitted; distances are in nm.
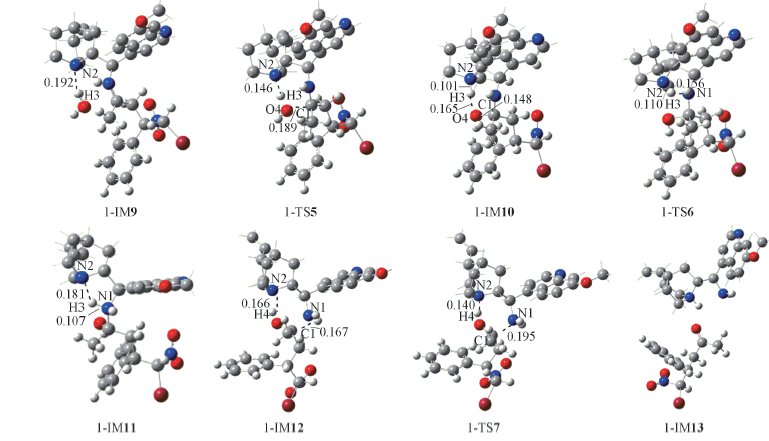
Fig.7 Optimized geometries and selected geometric parameters for the hydrolysis and regeneration of the catalyst Some hydrogen atoms not involved in reaction sites are omitted; distances are in nm.
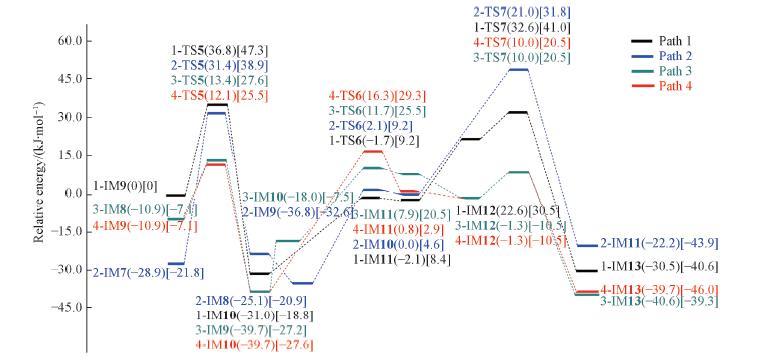
Fig.10 Relative energy profiles for the hydrolysis to obtain the final product for the real reaction system Values of ΔE are given in parentheses and ΔG in brackets.
| [1] | Dalko P. I., Moisan L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2004, 43(39), 5138—5175 |
| [2] | Seayad J., List B., Org. Biomol. Chem., 2005, 3(5), 719—724 |
| [3] | Zhang Q. Y., Zhang D. D., Suo J. J., Li J. Y., Long H. L., Xu L., Chem. J. Chinese Universtities, 2012, 33(7), 1413—1419 |
| (张庆友, 张丹丹, 索净洁, 李静亚, 龙海林, 许禄.高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(7), 1413—1419) | |
| [4] | Pei W., Chem. J. Chinese Universtities, 1998, 19(3), 402—405 |
| (裴文. 高等学校化学学报, 1998, 19(3), 402—405) | |
| [5] | List B.,Chem. Commun., 2006, (8), 819—824 |
| [6] | Xu L.W., Luo J., Lu Y. X.,Chem. Commun., 2009, (14), 1807—1821 |
| [7] | Xie J. W., Chen W., Li R., Zeng M., Du W., Yue L., Chen Y. C., Wu Y., Deng J. G., Angew. Chem., 2007, 119(3), 393—396 |
| [8] | Martin N. J. A., List B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(41), 13368—13369 |
| [9] | Dong L. T., Lu R. J., Du Q. S., Zhang J. M., Xuan Y. N., Yan M., Tetrahedron, 2009, 65(21), 4124—4129 |
| [10] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(4), 2154—2161 |
| [11] | Gonzalez C., Schlegel H. B., J. Phys. Chem., 1990, 94(14), 5523—5527 |
| [12] | Reed A. E., Curtiss L. A., Weinhold F., Chem. Rev., 1988, 88(6), 899—926 |
| [13] | Reed A. E., Weinstock R. B., Weinhold F., J. Chem. Phys., 1985, 83(2), 735—746 |
| [14] | Jones G. O., Li X., Hayden A. E., Houk K. N., Danishefsky S. J., Org. Lett., 2008, 10(18), 4093—4096 |
| [15] | Peles D. N., Thoburn J. D., J. Org. Chem., 2008, 73(8), 3135—3144 |
| [16] | Rehbein J., Hiersemann M., J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74(11), 4336—4342 |
| [17] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Kitao O., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., AlLaham M. A., Peng C. Y., Nanayakkara A., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Revision B. 05, Gaussian Inc., Pittsburgh PA, 2003 |
| [18] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Challacombe M., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 09, Revision A. 1, Gaussian Inc.Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [19] | Oliva C.G., Silva A. M. S., Resende D. I. S. P., Paz F. A. A., Cavaleiro J. A. S.,Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2010, (18), 3449—3458 |
| [20] | Yao C. F., Sun C. X., Yan S. Y., Wu H. H., Prog. Chem., 2008, 20(6), 887—898 |
| (姚成福, 孙彩霞, 闫少宇, 吴海虹. 化学进展, 2008, 20(6), 887—898 ) | |
| [21] | Yang K., Xu M., Huang Z. P., Gan G. L., Chemical Industry of Guangzhou, 2009, 37(3), 51—54 |
| (杨昆, 徐梦, 黄志平, 甘桂莲. 广州化工, 2009, 37(3), 51—54 ) | |
| [22] | Huang H., Jacobsen E. N., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(22), 7170—7171 |
| [23] | Wei S., Yalavov D. A., Tsogoeva S. B., Schmatz S., Catal. Today, 2007, 121(2), 151—157 |
| [24] | Peng F., Shao Z., J. Mol. Catal. A, 2008, 285(1), 1—14 |
| [25] | Xu L.W., Luo J., Lu Y. X.,Chem. Commun., 2009, (14), 1807—1821 |
| [26] | Jiang L., Chen Y. C., Catal. Sci. Technol., 2011, 1(3), 354—365 |
| [27] | Su Z., Lee H. W., Kim C. K., Eur. J. Org. Chem., 2013, 2013(9), 1706—1715 |
| [28] | Wang X. P., Wang X. Z., Wang X. K., Liu Z. Q., Niu J. H., Univ. Chem., 2011, 26(3),33—37(王新平, 王旭珍, 王新葵, 刘泽群, 牛家豪. 大学化学, 2011, 2011, 26(3), 33—37) |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [4] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [5] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [6] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [7] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [8] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [9] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [10] | SHI Ge, XU Qian, DAI Xiao, ZHANG Jie, SHEN Jun, WAN Xinhua. Effect of Aromatic Substituent on Chiral Recognition of Helical Polyacetylene-based Chiral Stationary Phases for High-Performance Liquid Chromatography [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2673. |
| [11] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [12] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [13] | LIU Yang, LI Qingbo, SUN Jie, ZHAO Xian. Direct Synthesis of Graphene on AlN Substrates via Ga Remote Catalyzation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2271. |
| [14] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [15] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||