

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (5): 1063.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20130811
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
TU Guogang, LIU Chao, LIAO Yijing, XIONG Shengtao, LI Shaohua*( )
)
Received:2013-08-22
Online:2014-05-10
Published:2014-04-03
Contact:
LI Shaohua
E-mail:tugg199@yahoo.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
TU Guogang, LIU Chao, LIAO Yijing, XIONG Shengtao, LI Shaohua. Homology Modeling and S1' Binding Pocket Characteristics of MMP-26†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(5): 1063.

Fig.1 Multiple sequence alignment of the MMP-26 catalytic domain with other MMPs^The secondary structure elements were taken from the crystal structure of MMP-1. The residue numbering was based on that of MMP-26. Gaps were indicated by hyphens. The S1' loop region was surrounded by a rectangle: ‘*’, identical residues in all six sequences; ‘:’, similar residues by the definition of CLUSTAL X2.
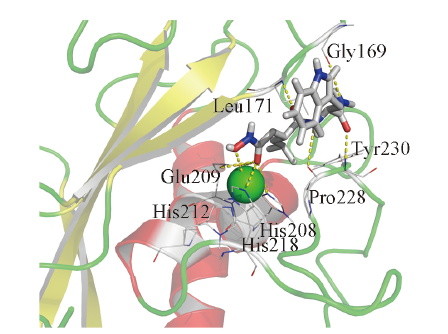
Fig.7 Binding profile of GM6001 and MMP-26^The inhibitor GM6001 is represented as a tube with atoms colored. The residues coordinating the catalytic zinc ion(green sphere) or forming hydrogen bond are represented as sticks. Coordination bonds and hydrogen bonds are represented as yellow dash line.
| [1] | Brinckerhoff C. E., Matrisian L. M., Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 2002, 3(3), 207—214 |
| [2] | Egeblad M., Werb Z., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2002, 2(3), 163—175 |
| [3] | Overall C. M., Mol. Biotech., 2002, 22(1), 51—86 |
| [4] | Park H. I., Ni J., Gerkema F. E., Liu D., Belozerov V. E., Sang Q. X., J. Biol. Chem., 2000, 275(27), 20540—20544 |
| [5] | Uría J. A., López-Otín C., Cancer Res., 2000, 60(17), 4745—4751 |
| [6] | de Coginac A. B., Elson G., Delneste Y., Magistrelli G., Jeannin P., Aubry J. P., Berthier O., Schmitt D., Bonnefoy J. Y., Gauchat J. F., Eur. J. Biochem., 2000, 267(11), 3323—3329 |
| [7] | Marchenko G. N., Ratnikov B. I., Rozanov D. V., Godzik A., Deryugina E. I., Strongin A. Y., Biochem. J., 2001, 359(3), 705—718 |
| [8] | Marchenko G. N., Marchenko N. D., Leng J., Strongin A. Y., Biochem. J., 2002, 363(2), 253—262 |
| [9] | Zhao Y. G., Xiao A. Z., Newcomer R. G., Park H. I., Kang T., Chung L. W., Swanson M. G., Zhau H. E., Kurhanewicz J., Sang Q. X., J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278(17), 15056—15064 |
| [10] | Park H. I., Turk B. E., Gerkema F. E., Cantley L. C., Sang Q. X., J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277(38), 35168—35175 |
| [11] | Fiser A., Do R. K., Sali A., Protein Sci., 2000, 9(9), 1753—1773 |
| [12] | Hess B., Kutzner C., van der Spoel D., Lindahl E. J., Chem. Theory Comput., 2008, 4(3), 435—447 |
| [13] | Morris G. M., Goodsell D. S., Halliday R. S., Huey R., Hart W. E., Belew R. K., Olson A. J., J. Comput. Chem., 1998, 19(14), 1639—1662 |
| [14] | Bowie J. U., Luthy R., Eisenberge D., Science, 1991, 253(5016), 164—170 |
| [15] | Laskowski R. A., MacArthur M. W., Moss D. S., Thornton J. M., J. Appl. Crystallogr., 1993, 26(2), 283—291 |
| [16] | Cheng F. S., Zhang M. Q., Cheng F. J., Sheng J. P., Chen J. Y., Zheng Y. Y., Shen L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2012, 33(8), 1788—1793 |
| (程凡升, 张茂秋, 程凡杰, 生吉萍, 陈婧雨, 郑鄢燕, 申琳.高等学校化学学报, 2012,33(8), 1788—1793) | |
| [17] | van der Spoel D., Buuren A. R. V., Tieleman D. P., Berendsen H. J., J. Biomol. NMR, 1996, 8(3), 229—238 |
| [18] | Hess B., Bekker H., Berendsen H. J. C., Fraaije J. G. E. M., J. Comput. Chem., 1997, 18(12), 1463—1472 |
| [19] | Darden T., York D., Pedersen L., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98(12), 10089—10092 |
| [20] | Zhan D. L., Gao N., Han W. W., Feng Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013, 34(3), 628—633 |
| (詹冬玲, 高楠, 韩葳葳, 冯雁.高等学校化学学报, 2013,34(3), 628—633) | |
| [21] | Park H. I., Jin Y., Hurst D. R., Monroe C. A., Lee S., Schwartz M. A., Sang Q. X., J. Biol. Chem., 2003, 278(51), 51646—51653 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [3] | SHUAI Die, ZHAO Meijuan, CHEN Bingnian, WANG Li. Inhibitory Effect of Four Kinds of Keegin-type Phosphomolybdate on Tyrosinase and Melanin Formation and Its Antioxidant Activities [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3579. |
| [4] | YANG Ju, SU Lijiao, LI Canhua, LU Jiajia, YANG Junli, GU Jie, YANG Li, YANG Lijuan. Host-guest Complexation Behavior of Nardosinone and Water-soluble Phosphate Salt Pillar[6]arene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3099. |
| [5] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [6] | WANG Lianping,LI Qingjie,LIU Xiaoyan,REN Yueying,YANG Xiuwei. Screening of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Fructus Evodiae Alkaloids Based on UFLC-MS/molecular Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 111. |
| [7] | WANG Xiaoxia, MA Litong, NIE Zhihua, WANG Zhengde, CUI Jinlong, ZHAO Wenyuan, SAI Huazheng. Interaction Between Fulvic Acid and Pepsin Investigated by Multispectral and Molecular Docking Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1840. |
| [8] | LIU Zhongcheng, LIU Shifang, ZHANG Su, YANG Yanlei, LI Fei, ZHANG Nan, YUAN Xin, ZHANG Yanfen. Structure Prediction and Screening of Oligonucleotide Aptamers Target Cε3-Cε4 Protein† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 83. |
| [9] | XIN Meiling, CHU Zhenhua, LI Yu. Molecular Modification of Polychlorinated Biphenyl Dihydroxy Derivatives Through Molecular Docking Associated with CoMSIA/HQSAR Models† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 299. |
| [10] | WANG Yan, CHEN Ping, WANG Yunfei, LIU Guiying, YANG Xi, SU Ying, LI Junyang, LIU Weiwei, LIN Lie. Spectral Characterization of the Interaction Between Methamphetamine and Serum Albumin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11): 2507. |
| [11] | DUAN Yongbin, YIN Yan, MENG Fanli, ZHAO Lianhua, LIU Yukun, YUAN Zhe, FENG Yangbo. Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Benzothiazoles as Highly Potent ROCK Inhibitors Through Molecular Docking and Free Energy Calculations† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(9): 1568. |
| [12] | WANG Song, GUAN Shanshan, WAN Yongfeng, SHAN Yaming, ZHANG Hao. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on the Binding Modes of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme with Inhibitory Peptides† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1216. |
| [13] | TANG Qian, SU Jinhong, CAO Hongyu, WANG Lihao, SHI Fei, WANG Ailing, GONG Tingting, JIN Xiaojun, ZHENG Xuefang. Interaction of Pyrimidine Derivatives with Human Serum Albumin† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(11): 1982. |
| [14] | ZHAO Bin, HUO Jingqian, XING Jihong, QI Meng, ZHANG Jinlin, DONG Jingao. Homologous Modeling of Transketolase AtTKL1 and Its Combination with α-Terthienyl in Arabidopsis Thaliana† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(4): 682. |
| [15] | DONG Lu, YI Zhongsheng, WU Zhiwei, WANG Haiyang, ZHANG Aiqian. Mechanism Study on the Interaction Between 2'-Hydroxy-2,4-dibromo Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Based on Spectroscopic Methods and Computional Simulations† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(3): 516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||