

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2017, Vol. 38 ›› Issue (7): 1216.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170007
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Song1, GUAN Shanshan1,2, WAN Yongfeng1, SHAN Yaming2, ZHANG Hao1,*( )
)
Received:2017-01-05
Online:2017-07-10
Published:2017-06-20
Contact:
ZHANG Hao
E-mail:stringbell@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
WANG Song, GUAN Shanshan, WAN Yongfeng, SHAN Yaming, ZHANG Hao. Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study on the Binding Modes of Angiotensin-converting Enzyme with Inhibitory Peptides†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(7): 1216.
| Simulation system | Simulation time/ns | Number of solvent molecules | Number of counter ions | Number of Cl-/Zn2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-domain-RIGLF | 100 | 27191 | 12 Na+ | 2/1 |
| C-domain-AHEPVK | 100 | 27187 | 13 Na+ | 2/1 |
Table 1 Simulation information of two complex systems
| Simulation system | Simulation time/ns | Number of solvent molecules | Number of counter ions | Number of Cl-/Zn2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-domain-RIGLF | 100 | 27191 | 12 Na+ | 2/1 |
| C-domain-AHEPVK | 100 | 27187 | 13 Na+ | 2/1 |
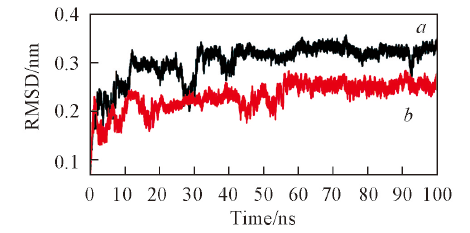
Fig.1 RMSD of backbone Cα atoms of C-domain-RIGLF(a) and N-domain-AHEPVK(b) with respect to their initial structures as function of time during 100 ns
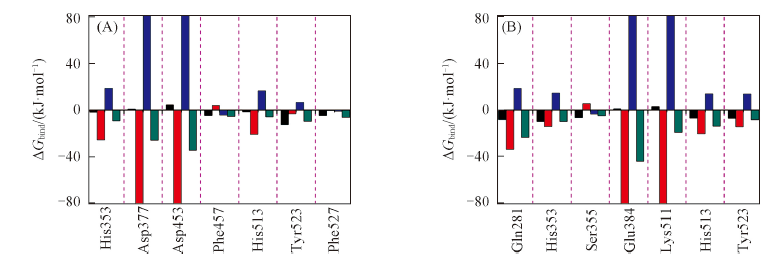
Fig.3 Decomposition of the binding energy on per residue basis on two systems C-domain-RIGLF(A) and C-domain-AHEPVK(B) : the total binding energy contribution form per
| Energy component | C-domain-RIGLF | C-domain-AHEPVK |
|---|---|---|
| ΔEvdw/(kJ·mol-1) | -240.91 | -252.80 |
| ΔEele/(kJ·mol-1) | -2371.28 | -1906.96 |
| ΔEMM/(kJ·mol-1) | -2612.19 | -2159.72 |
| ΔGele,sol/(kJ·mol-1) | -41.49 | -41.11 |
| ΔGnonpolar,sol/(kJ·mol-1) | 2419.64 | 1944.06 |
| ΔGsol/(kJ·mol-1) | 2378.14 | 1902.94 |
| (Δ | -2412.77 | -1948.08 |
| (Δ | 2178.73 | 1691.26 |
| ΔGtotal/(kJ·mol-1) | -234.04 | -256.82 |
Table 2 Calculated energy components, binding free energy of C-domain-RIGLF and C-domain-AHEPVK*
| Energy component | C-domain-RIGLF | C-domain-AHEPVK |
|---|---|---|
| ΔEvdw/(kJ·mol-1) | -240.91 | -252.80 |
| ΔEele/(kJ·mol-1) | -2371.28 | -1906.96 |
| ΔEMM/(kJ·mol-1) | -2612.19 | -2159.72 |
| ΔGele,sol/(kJ·mol-1) | -41.49 | -41.11 |
| ΔGnonpolar,sol/(kJ·mol-1) | 2419.64 | 1944.06 |
| ΔGsol/(kJ·mol-1) | 2378.14 | 1902.94 |
| (Δ | -2412.77 | -1948.08 |
| (Δ | 2178.73 | 1691.26 |
| ΔGtotal/(kJ·mol-1) | -234.04 | -256.82 |
| [1] | Tanzadehpanah H., Asoodeh A., Saberi M. R., Chamani J., Innov. Food Sci. Emerg., 2013, 18, 212—219 |
| [2] | Pihlanto A., Virtanen T., Korhonen H., Int. Dairy. J., 2010, 20(1), 3—10 |
| [3] | Masuyer G., Akif M., Czarny B., Beau F., Schwager S. L., Sturrock E. D., Isaac R. E., Dive V., Acharya K. R., FEBS J., 2014, 281(3), 943—956 |
| [4] | Hu J., Igarashi A., Kamata M., Nakagawa H., J. Biol. Chem., 2001, 276(51), 47863—47868 |
| [5] | Geng X. R., Tian G. T., Zhang W. W., Zhao Y. C., Zhao L. Y., Wang H. X., Ng T. B., Scientific Reports,2016, 6, 24130 |
| [6] | Iwaniak A., Minkiewicz P., Darewicz M., Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F., 2014, 13(2), 114—134 |
| [7] | Conrad N., Schwager S. L. U., Carmona A. K., Sturrock E. D., Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2016, 481, 111—116 |
| [8] | Feng S. M., Limwachiranon J., Luo Z. S., Shi X. D., Ru Q. M., International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2016, 51, 1610—1617 |
| [9] | Orona-Tamayo D., Valverde M. E., Nieto-Rendon B., Paredes-López O., LWT-Food Science and Technology,2015, 64(1), 236—242 |
| [10] | Forghani B., Zarei M., Ebrahimpour A., Philip R., Bakar J., Hamid A. A., Saari N., Journal of Functional Foods,2016, 20, 276—290 |
| [11] | Norris R., O'Keeffe M. B., Poyarkov A., FitzGerald R. J., Food Chemistry,2015, 188, 210—217 |
| [12] | Gangopadhyay N., Wynne K., O'Connor P., Gallagher E., Brunton N. P., Rai D. K., Hayes M., Food Chemistry,2016, 203, 367—374 |
| [13] | Lau C. C., Abdullah N., Shuib A. S., Aminudin N., Food Chem., 2014, 148, 396—401 |
| [14] | Morris G. M., Huey R., Lindstrom W., Sanner M. F., Belew R. K., Goodsell D. S., Olson A. J., J. Comput. Chem., 2009, 30(16), 2785—2791 |
| [15] | Qian M.D., Shan Y. M., Guan S. S., Zhang H., Wang S., Han W. W., Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2016, 56,2024—2034 |
| [16] | Hou X., Du J., Zhang J., Du L., Fang H., Li M., Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,2013, 53(1), 188—200 |
| [17] | Masuyer G., Schwager S. L., Sturrock E. D., Isaac R. E., Acharya K. R., Scientific Reports,2012, 2, 717 |
| [18] | Guan S. S., Han W. W., Zhang H., Wang S., Shan Y. M., Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics,2016, 34(1), 15—28 |
| [19] | Discovery Studio 2.5, Accelrys Inc.: San Diego, CA., 2009 |
| [20] | Wang X., Wu S., Xu D., Xie D., Guo H., Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,2011, 51(5), 1074—1082 |
| [21] | Hess B., Kutzner C., van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2008, 4(3), 435—447 |
| [22] | Hornak V., Abel R., Okur A., Strockbine B., Roitberg A., Simmerling C.,Proteins,2006, 65(3), 712—725 |
| [23] | Hess B., van der Vegt N. F. A.,J. Phys. Chem.B,2006, 110(35), 17616—17626 |
| [24] | Berendsen H. J. C., Postma J. P. M., van Gunsteren W. F., DiNola A., Haak J. R., J. Chem. Phys., 1984, 81(8), 3684—3690 |
| [25] | Darden T., York D., Pedersen L., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98(12), 10089—10092 |
| [26] | Chen X. G., Zhao X. J., Wang S., Wang L. P., Li W., Sun C. C., Acta Chim. Sinica,2013, 71(02), 199—204 |
| (陈晓光, 赵晓杰, 王嵩, 王丽萍, 李惟, 孙家锺.化学学报, 2013, 71(02), 199—204) | |
| [27] | Wang S., Zhao X., Zheng Q. C., Huang X. R., Sun C. C., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2009, 30(8), 1641—1644 |
| (王嵩, 赵熹, 郑清川, 黄旭日, 孙家锺.高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(8), 1641—1644) | |
| [28] | Case D. A., Cheatham Ⅲ T. E., Darden T., Gohlke H., Luo R., Merz K. M. Jr., Onufriev A., Simmerling C., Wang B., Woods R. J., J. Comput. Chem., 2005, 26(16), 1668—1688 |
| [29] | Case D.A., Darden T., Cheatham Ⅲ T. E., Simmerling C., Wang J. M., Duke R. E., Luo R., Crowley M., Walker R., Zhang W., Merz K. M. Jr., Wang B., Hayik S., Roitberg A., Seabra G., Kolossváry I., Wong K. F., Paesani F., Vanicek J., Wu X. W., Brozell S. R., Steinbrecher T., Gohlke H., Yang L. J., Tan C. H., Mongan J., Hornak V., Cui G. L., Mathews D. H., Seetin M. G., Sagui C., Babin V., Kollman P. A., AMBER 10, University of California,San Francisco, 2008 |
| [30] | Pearlman D. A., Case D. A., Caldwell J. W., Ross W. S., Cheatham Ⅲ T. E., DeBol S., Ferguson D., Seibel G., Kollman P., Comp. Phys. Commun., 1995, 91, 1—41 |
| [31] | Weik M., Ravelli R. B. G., Kryger G., McSweeney S., Raves M. L., Harel M., Gros P., Silman I., Kroon J., Sussman J. L., P. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA,2000, 97(2), 623—628 |
| [32] | Obradovic Z., Peng K., Vucetic S., Radivojac P., Dunker A. K., Proteins,2005, 61(S7), 176—182 |
| [1] | GAO Zhiwei, LI Junwei, SHI Sai, FU Qiang, JIA Junru, AN Hailong. Analysis of Gating Characteristics of TRPM8 Channel Based on Molecular Dynamics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [3] | ZHANG Mi, TIAN Yafeng, GAO Keli, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of the Physicochemical Properties of Trifluoromethanesulfonyl Fluoride Dielectrics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220424. |
| [4] | LEI Xiaotong, JIN Yiqing, MENG Xuanyu. Prediction of the Binding Site of PIP2 in the TREK-1 Channel Based on Molecular Modeling [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [5] | LI Congcong, LIU Minghao, HAN Jiarui, ZHU Jingxuan, HAN Weiwei, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study of the Catalytic Activity of VmoLac Non-specific Substrates Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [6] | ZENG Yonghui, YAN Tianying. Vibrational Density of States Analysis of Proton Hydration Structure [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [7] | QI Renrui, LI Minghao, CHANG Hao, FU Xueqi, GAO Bo, HAN Weiwei, HAN Lu, LI Wannan. Theoretical Study on the Unbinding Pathway of Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitors Based on Steered Molecular Dynamics Simulation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [8] | LIU Aiqing, XU Wensheng, XU Xiaolei, CHEN Jizhong, AN Lijia. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polymer/rod Nanocomposite [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [9] | SHUAI Die, ZHAO Meijuan, CHEN Bingnian, WANG Li. Inhibitory Effect of Four Kinds of Keegin-type Phosphomolybdate on Tyrosinase and Melanin Formation and Its Antioxidant Activities [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3579. |
| [10] | YANG Ju, SU Lijiao, LI Canhua, LU Jiajia, YANG Junli, GU Jie, YANG Li, YANG Lijuan. Host-guest Complexation Behavior of Nardosinone and Water-soluble Phosphate Salt Pillar[6]arene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3099. |
| [11] | ZHANG Aiqin, WANG Man, SHEN Gangyi, JIN Jun. Interactions Between Polybrominated Diphenyl Ethers and Human Serum Albumin Using SPR and Molecular Docking [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2054. |
| [12] | WANG Lianping,LI Qingjie,LIU Xiaoyan,REN Yueying,YANG Xiuwei. Screening of Cholinesterase Inhibitors in Fructus Evodiae Alkaloids Based on UFLC-MS/molecular Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 111. |
| [13] | QU Siying, XU Qin. Different Roles of Some Key Residues in the S4 Pocket of Coagulation Factor Xa for Rivaroxaban Binding † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1918. |
| [14] | WANG Xiaoxia, MA Litong, NIE Zhihua, WANG Zhengde, CUI Jinlong, ZHAO Wenyuan, SAI Huazheng. Interaction Between Fulvic Acid and Pepsin Investigated by Multispectral and Molecular Docking Simulation † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1840. |
| [15] | MA Yucong, FAN Baomin, WANG Manman, YANG Biao, HAO Hua, SUN Hui, ZHANG Huijuan. Two-step Preparation of Trazodone and Its Corrosion Inhibition Mechanism for Carbon Steel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1706. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||