

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 20240035.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240035
收稿日期:2024-01-19
出版日期:2024-05-10
发布日期:2024-03-18
通讯作者:
黄昊
E-mail:huanghao@dlut.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Shuo1, ZHAO Liuyang1, HUANG Hao1( ), WU Aimin1, LI Aikui2
), WU Aimin1, LI Aikui2
Received:2024-01-19
Online:2024-05-10
Published:2024-03-18
Contact:
HUANG Hao
E-mail:huanghao@dlut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理计算探究了高价元素Mo取代Mn稳定层状富锂锰基材料氧离子框架机制. Mo掺杂将体积变化率从‒2.95%降至‒0.53%, 改善了锂化前后的晶格畸变. 空位形成能及巴德电荷分析结果表明, 7种氧空位形成能均明显提升, 且第一配位氧平均巴德电荷从1.13 e升至1.18 e, 抑制了不稳定氧析出; 锂化前后氧原子巴德电荷改变量从0.51 e降至0.11 e, 表明循环前后的体系均具有良好的氧框架稳定性. 通过差分电荷密度计算, 发现Mo能够在Li去除后提供电荷补偿, 而且Mo掺杂后锂离子迁移速率得到了提升, 最低势垒从0.55 eV降至0.42 eV. 为高价元素掺杂锂离子电池正极材料奠定了坚实的理论依据.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
张硕, 赵刘洋, 黄昊, 吴爱民, 李爱魁. 基于第一性原理高价元素Mo稳定层状富锂锰基材料的氧框架机制. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(5): 20240035.
ZHANG Shuo, ZHAO Liuyang, HUANG Hao, WU Aimin, LI Aikui. Oxygen Framework Mechanism of Layered Lithium-rich Manganese-based Materials Stabilized by High-valent Element Mo Based on First-principles Calculations. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(5): 20240035.
| Atom | Bader charge(pristine)/e | Bader charge(Mo⁃doped)/e |
|---|---|---|
| O1 | 1.18 | 1.22 |
| O2 | 1.12 | 1.20 |
| O3 | 1.16 | 1.18 |
| O4 | 1.17 | 1.18 |
| O5 | 1.03 | 1.15 |
| O6 | 1.09 | 1.15 |
| Average bader charge | 1.13 | 1.18 |
Table 1 Bader charge of O atoms in MnO6 of Li1.2Mn0.6Ni0.2O2 and Li1.2Mn0.56Ni0.2Mo0.04O2
| Atom | Bader charge(pristine)/e | Bader charge(Mo⁃doped)/e |
|---|---|---|
| O1 | 1.18 | 1.22 |
| O2 | 1.12 | 1.20 |
| O3 | 1.16 | 1.18 |
| O4 | 1.17 | 1.18 |
| O5 | 1.03 | 1.15 |
| O6 | 1.09 | 1.15 |
| Average bader charge | 1.13 | 1.18 |
| Oxygen vacancy | Ef(Pristine)/eV | Ef(Mo⁃doped)/eV | Oxygen vacancy | Ef(Pristine)/eV | Ef(Mo⁃doped)/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 2.40 | 3.51 | Ⅴ | 1.83 | 3.51 |
| Ⅱ | 1.55 | 2.12 | Ⅵ | 1.95 | 2.12 |
| Ⅲ | 0.85 | 2.41 | Ⅶ | 0.95 | 1.52 |
| Ⅳ | 1.75 | 2.83 |
Table 2 Oxygen vacancy formation energy corresponding to different oxygen vacancy sites*
| Oxygen vacancy | Ef(Pristine)/eV | Ef(Mo⁃doped)/eV | Oxygen vacancy | Ef(Pristine)/eV | Ef(Mo⁃doped)/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ | 2.40 | 3.51 | Ⅴ | 1.83 | 3.51 |
| Ⅱ | 1.55 | 2.12 | Ⅵ | 1.95 | 2.12 |
| Ⅲ | 0.85 | 2.41 | Ⅶ | 0.95 | 1.52 |
| Ⅳ | 1.75 | 2.83 |
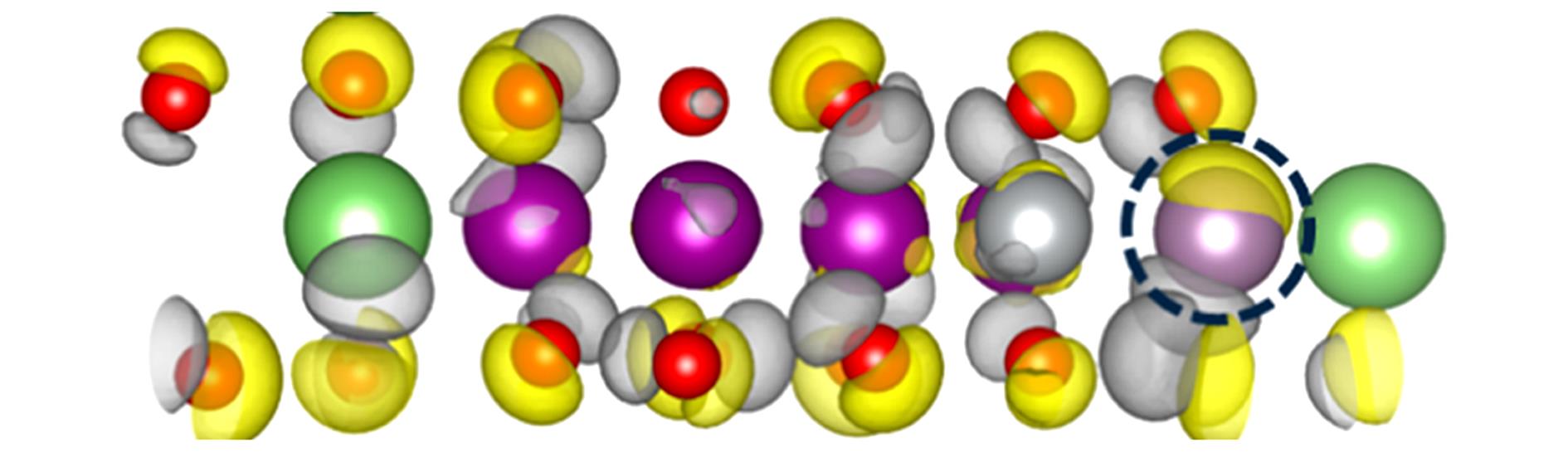
Fig.11 Charge density differences between Li1.2Mn0.56Ni0.2Mo0.04O2 and Mn0.56Ni0.2Mo0.04O2The isosurface level is 0.2, yellow and gray represent charge accumulation and loss, respectively.
| Sample | Path | dO—O/nm | Ea/eV | Sample | Path | dO—O/nm | Ea/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine | 1⁃2 | 0.2619 | 0.77 | Mo⁃doped | 1⁃2 | 0.2631 | 0.65 |
| 2⁃3 | 0.2619 | 0.55 | 2⁃3 | 0.2631 | 0.42 | ||
| 3⁃4 | 0.2619 | 0.82 | 3⁃4 | 0.2631 | 0.58 |
Table 3 Li slab distance(do—o) of the corresponding path and the activation barrier(Ea) of pristine and Mo-doped systems
| Sample | Path | dO—O/nm | Ea/eV | Sample | Path | dO—O/nm | Ea/eV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine | 1⁃2 | 0.2619 | 0.77 | Mo⁃doped | 1⁃2 | 0.2631 | 0.65 |
| 2⁃3 | 0.2619 | 0.55 | 2⁃3 | 0.2631 | 0.42 | ||
| 3⁃4 | 0.2619 | 0.82 | 3⁃4 | 0.2631 | 0.58 |
| 1 | Chen H., Hu Q., Huang Z., Wang Z., Guo H., Li X., Ceram. Int., 2016, 42(1), 263—269 |
| 2 | He Z., Wang Z., Chen H., Huang Z., Li X., Guo H., Wang R., J. Power Sources, 2015, 299, 334—341 |
| 3 | Liu Y., Wang Q. L., Xing Q. W., Tian C. G., Yan Y. S., Ming R. D., Ai C., Ionics, 2015, 21(10), 2725—2733 |
| 4 | Luo K., Roberts M. R., Hao R., Guerrini N., Pickup D.M., Liu Y. S., Edström K., Guo J., Chadwick A. V., Duda L. C., Bruce P. G., Nature Chem., 2016, 8(7), 684—691 |
| 5 | Armstrong A. R., Holzapfel M., Novák P., Johnson C. S., Kang S. H., Thackeray M. M., Bruce P. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2006, 128(26), 8694—8698 |
| 6 | Yu D. Y. W., Yanagida K., Kato Y., Nakamura H., J. Electrochem. Soc., 2009, 156(6), A417 |
| 7 | Li B., Xia D., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(48), 1701054 |
| 8 | Cui S. L., Gao M. Y., Li G. R., Gao X. P., Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(4), 2003885 |
| 9 | Zhuo H., Zhang A., Huang X., Wang J., Zhuang W., Inorg. Chem. Frontiers, 2021, 8(21), 4590—4609 |
| 10 | He W., Guo W., Wu H., Lin L., Liu Q., Han X., Xie Q., Liu P., Zheng H., Wang L., Yu X., Peng D. L., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(50), 2005937 |
| 11 | Yin Z., Zhu H., Huang Y., Luo D., Ren Y., Lan S., Liu Q., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2022, 10(37), 19387—19411 |
| 12 | Mondal S., Zhang Z., Islam A. N. M. N., Andrawis R., Gamage S., Aghamiri N. A., Wang Q., Zhou H., Rodolakis F., Tran R., Kaur J., Chen C., Ong S. P., Sengupta A., Abate Y., Roy K., Ramanathan S., Adv. Intelligent Systems, 2022, 4(10), 2200069 |
| 13 | Mondal S., Venkataraman V., Appl. Phys. Lett., 2019, 114(17), 173502 |
| 14 | Mondal S., Paul T., Ghosh A., Venkataraman V., IEEE Electron Device Lett., 2020, 41(5), 717—720 |
| 15 | Chen L. D., Zou W., Wu L., Xia F. J., Hu Z. Y., Li Y., Su B. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6), 1329—1336 |
| 陈良丹, 邹伟, 吴亮, 夏凡杰, 胡执一, 李昱, 苏宝连. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(6), 1329—1336 | |
| 16 | Qiu J. X., Jiang Q., Gao Y. K., Peng J. Q., Duan Z. H., Lu X. Y., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10), 2238—2244 |
| 邱家欣, 江奇, 高艺珂, 彭俊棋, 段志虹, 卢晓英. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10), 2238—2244 | |
| 17 | Yang J. Y., Li Y. J., Lu D., Chen Y. F., Sun W. W., Zheng C. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(7), 1495—1500 |
| 杨金戈, 李宇杰, 陆地, 陈宇方, 孙巍巍, 郑春满. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(7), 1495—1500 | |
| 18 | Jiang W., Zhang C., Feng Y., Wei B., Chen L., Zhang R., Ivey D. G., Wang P., Wei W., Energy Storage Mater., 2020, 32, 37—45 |
| 19 | Nayak P. K., Grinblat J., Levi M., Levi E., Kim S., Choi J. W., Aurbach D., Adv. Energy Mater., 2016, 6(8), 1502398 |
| 20 | Ha M., Hajibabaei A., Kim D. Y., Singh A. N., Yun J., Myung C. W., Kim K. S., Adv. Energy Mater., 2022, 12(30), 2201497 |
| 21 | Choi A., Lim J., Kim H. J., Jung S. C., Lim H. W., Kim H., Kwon M. S., Han Y. K., Oh S. M., Lee K. T., Adv. Energy Mater., 2018, 8(11), 1702514 |
| 22 | Yu R., Wang X., Fu Y., Wang L., Cai S., Liu M., Lu B., Wang G., Wang D., Ren Q., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2016, 4(13), 4941—4951 |
| 23 | Wang Y., Yu W., Zhao L., Wu A., Li A., Dong X., Huang H., Electrochimica Acta, 2023, 462, 142664 |
| 24 | Nie L., Wang Z., Zhao X., Gao T., Zhang Y., Dong L., Kim F., Nano Lett., 2021, 21(19), 8370—8377 |
| 25 | Chen J., Zou G., Deng W., Huang Z., Gao X., Liu C., Yin S., Liu H., Deng X., Tian Y., Adv. Functional Mater., 2020, 30(46), 2004302 |
| 26 | Yu W., Wang Y., Wu A., Li A., Qiu Z., Dong X., Dong C., Huang H., Green Energy Environment, 2024, 9(1), 138—151 |
| 27 | Dong S., Zhou Y., Hai C., Zeng J., Sun Y., Shen Y., Li X., Ren X., Sun C., Zhang G., J. Power Sources, 2020, 462, 228185 |
| 28 | Gao Y., Ma J., Wang X., Lu X., Bai Y., Wang Z., Chen L., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(13), 4811—4818 |
| 29 | Yan H., Li B., Yu Z., Chu W., Xia D., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(13), 7155—7163 |
| 30 | Yan H. J., Li B., Jiang N., Xia D. G., Acta Phys.⁃Chim. Sin., 2017, 33(9), 1781—1788 |
| 鄢慧君, 李彪, 蒋宁, 夏定国. 物理化学学报, 2017, 33(9), 1781—1788 | |
| 31 | Wang Z. Q., Chen Y. C., Ouyang C. Y., Phys. Lett. A, 2014, 378(32/33), 2449—2452 |
| 32 | Li B., Yan H., Ma J., Yu P., Xia D., Huang W., Chu W., Wu Z., Adv. Functional Mater., 2014, 24(32), 5112—5118 |
| 33 | Dianat A., Seriani N., Bobeth M., Cuniberti G., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(32), 9273—9280 |
| 34 | Park N. Y., Kim S. B., Kim M. C., Han S. M., Kim D. H., Kim M. S., Sun Y. K., Adv. Energy Mater., 2023, 13(34), 2301530 |
| 35 | Li Q., Ning D., Wong D., An K., Tang Y., Zhou D., Schuck G., Chen Z., Zhang N., Liu X., Nature Commun., 2022, 13(1), 1123 |
| 36 | Yu W., Zhao L., Wang Y., Huang H., Zhang S., Li H., Liu X., Dong X., Wu A., Li A., J. Alloys Compounds, 2023, 947, 169481 |
| 37 | Paulus A., Hendrickx M., Mayda S., Batuk M., Reekmans G., Holst M., Elen K., Abakumov A. M., Adriaensens P., Lamoen D., Partoens B., Hadermann J., Van Bael M. K., Hardy A., ACS Appl. Energy Mater., 2023, 6(13), 6956—6971 |
| 38 | Moradi Z., Heydarinasab A., Pajoum Shariati F., Int. J. Quantum Chem., 2020, 121(4), e26458 |
| 39 | Yang K., Geng M. M., Ye J., Gao Y. X., Zhong J. J., Electronic Components Mater., 2019, 38(3), 7—15 |
| 杨凯, 耿萌萌, 叶俊, 高运兴, 钟健健. 电子元件与材料, 2019, 38(3), 7—15 | |
| 40 | Kong W., Wong D., An K., Zhang J., Chen Z., Schulz C., Xu Z., Liu X., Adv. Functional Mater., 2022, 32(31), 2202679 |
| 41 | Seo D. H., Lee J., Urban A., Malik R., Kang S., Ceder G., Nature Chem., 2016, 8(7), 692—697 |
| 42 | Guo W., Zhang Y., Lin L., Liu Y., Fan M., Gao G., Wang S., Sa B., Lin J., Luo Q., Qu B., Wang L., Shi J., Xie Q., Peng D. L., Small, 2023, 19(21), 2300175 |
| 43 | Wang L., Maxisch T., Ceder G., Chem. Mater., 2007, 19(3), 543—552 |
| 44 | Lai Y., Xie H., Li P., Li B., Zhao A., Luo L., Jiang Z., Fang Y., Chen S., Ai X., Adv. Mater., 2022, 34(47), 2206039 |
| 45 | Kang K., Ceder G., Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 74(9), 094105 |
| 46 | Ning F., Xu B., Shi J., Wu M., Hu Y., Ouyang C., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(33), 18428—18434 |
| 47 | Geng K. Q., Yang M. Q., Meng J. X., Zhou L. F., Wang Y. Q., Dmytro S., Zhang Q., Zhong S. W., Ma Q. X., Tungsten, 2022, 4(4), 323—335 |
| [1] | 陈荣, 温良英, 岳东, 杨仲卿. Cl2和O2在TiC(100)表面共吸附行为的密度泛函理论分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(4): 20230497. |
| [2] | 张晋恺, 李佳莉, 刘晓明, 母瀛. 共价有机骨架在高性能锂离子电池负极材料中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(3): 20230523. |
| [3] | 陈晴晴, 李江涛, 黄欣蓉, 顾芳, 王海军. 氢键流体中Janus粒子的过量熵[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(2): 20230443. |
| [4] | 富忠恒, 陈翔, 姚楠, 余乐耕, 沈馨, 张睿, 张强. 固态电解质锂离子输运机制研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220703. |
| [5] | 孙昭宇, 赵经纬, 刘军. 高比能锂离子电池高电压电解液的设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220743. |
| [6] | 贺汝涵, 黎浩, 韩方, 陈奥渊, 麦立强, 周亮. 锂离子电池硅基负极界面工程的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220748. |
| [7] | 彭辛哲, 葛娇阳, 王访丽, 余国静, 冉雪芹, 周栋, 杨磊, 解令海. 基于苯并噻吩平面格的张力与重组能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220313. |
| [8] | 胡诗颖, 沈佳艳, 韩峻山, 郝婷婷, 李星. CoO纳米颗粒/石墨烯纳米纤维复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220462. |
| [9] | 张海平, 孔雪, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. C18环基过渡金属(Os, Ir)单原子对甲烷C—H的活化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230259. |
| [10] | 周惠, 朱帅波, 王际童, 乔文明, 余子舰, 张寅旭. 氮掺杂碳包覆rGO-纳米硅的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230354. |
| [11] | 冯林雁, 胡晓波, 闫苗, 苗常青, 陈瑞, 郭谨昌, 王迎进. 平面十二配位MB8C4(M=Ca, Sr, Ba)分子轮团簇的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230281. |
| [12] | 毕如一, 赵吉路, 王江艳, 于然波, 王丹. 中空多壳层CoFe2O4的制备及锂离子电池性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220453. |
| [13] | 赵霄朗, 杨梅, 王江艳, 王丹. 富锂正极材料结构设计和表面调控的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(1): 20220263. |
| [14] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [15] | 贾洋刚, 邵霞, 程婕, 王朋朋, 冒爱琴. 赝电容控制型钙钛矿高熵氧化物La(Co0.2Cr0.2Fe0.2Mn0.2Ni0.2)O3负极材料的制备及储锂性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220157. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||