

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 20230497.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20230497
收稿日期:2023-12-06
出版日期:2024-04-10
发布日期:2024-03-04
通讯作者:
温良英
E-mail:cquwen@cqu.edu.cn
基金资助:
CHEN Rong1, WEN Liangying1( ), YUE Dong1, YANG Zhongqing2
), YUE Dong1, YANG Zhongqing2
Received:2023-12-06
Online:2024-04-10
Published:2024-03-04
Contact:
WEN Liangying
E-mail:cquwen@cqu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
基于密度泛函理论的第一性原理从头计算方法, 建立了Cl2和O2在TiC(100)表面的共吸附模型. 通过分析吸附能、 电荷密度和偏态密度(PDOS)等参数, 研究了Cl2和O2在TiC(100)表面的反应机理, 发现解离后的Cl原子和O原子与TiC(100)表面的原子均成键, 从而破坏了Ti—C键. Cl2分子在吸附过程中充当电子的受体, 得到与之成键的Ti原子贡献的电子, O2分子在吸附过程中也充当电子的受体, 得到C原子贡献的电子. TiC(100)表面在吸附分子后, Ti—C成键轨道上电子占据数变少, 反键轨道上电子占据数增多, Ti原子与C原子之间的成键作用减弱. 同时, Ti3d与Cl3s, Cl3p发生轨道重叠杂化作用, O2p轨道和C2p轨道存在较强的共振峰, Cl原子和O原子与TiC表面相互作用强烈.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
陈荣, 温良英, 岳东, 杨仲卿. Cl2和O2在TiC(100)表面共吸附行为的密度泛函理论分析. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(4): 20230497.
CHEN Rong, WEN Liangying, YUE Dong, YANG Zhongqing. Density Functional Theory Analysis of Coadsorption Behavior of Cl2 and O2 on TiC(100) Surface. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2024, 45(4): 20230497.
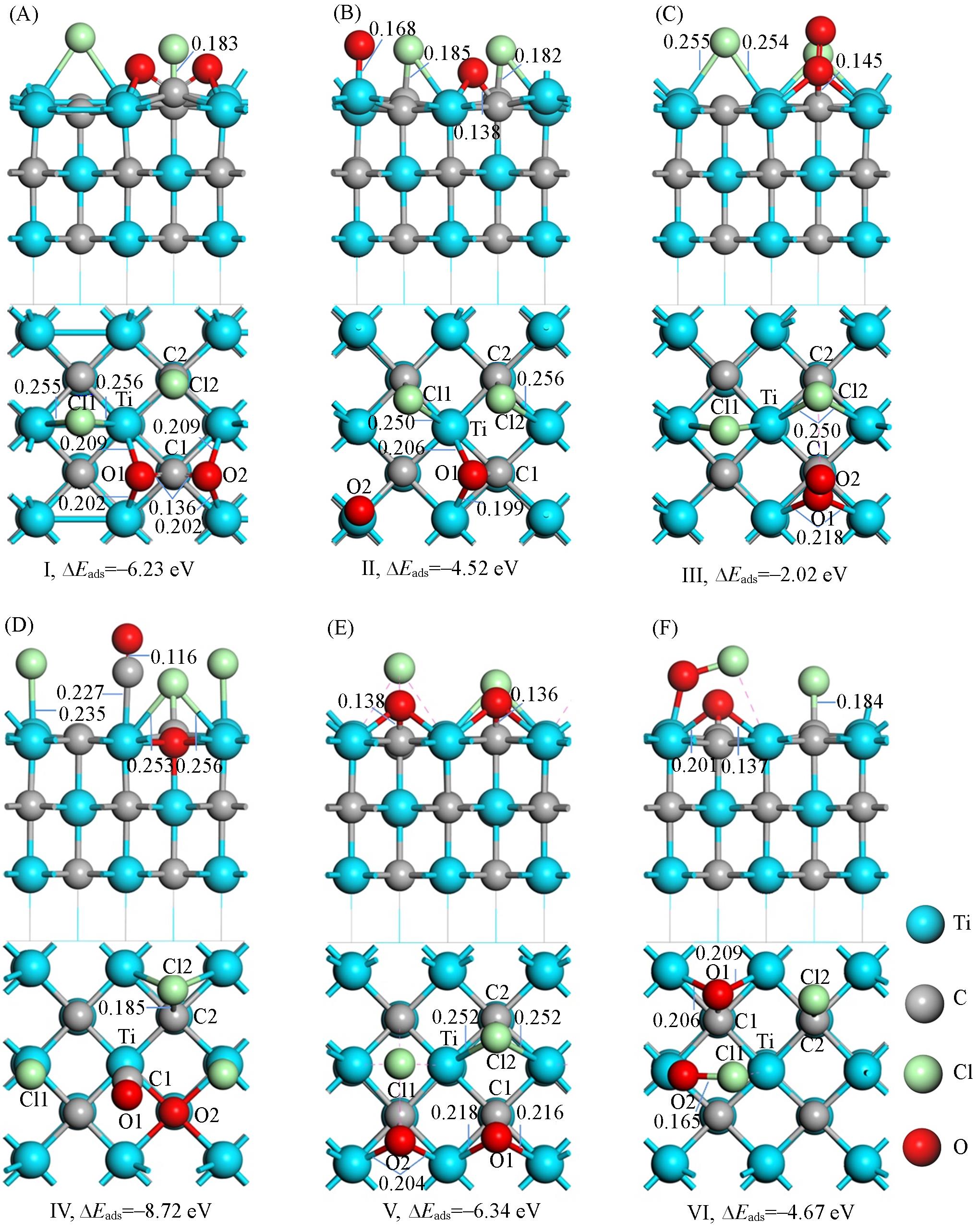
Fig.3 Adsorption structure of Cl2 and O2 molecules on TiC(100) clean surface(A)—(F) Represent adsorption structures I—VI, respectively. The upper part of each small image is a side view, and the lower part is a top view. The dotted pink line represents the role of van der Waals force. For clarity, the chlorine atoms in the Cl2 molecule are denoted as Cl1 and Cl2, the oxygen atoms in O2 are denoted as O1 and O2, the carbon atoms bonded to O are denoted as C1, and the carbon atoms bonded to Cl are denoted as C2. Bond lengths are in nm.
| Structure | C1-Ti | C1-O1 | Ti-O1 | Cl1-Ti | Cl2-C2 | O1-O2 | Cl1-Cl2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | |
| TiC(100) clean surface | 0.42 | 0.217 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| I | 0.01 | 0.231 | 0.65 | 0.136 | 0.13 | 0.209 | 0.37 | 0.256 | 0.30 | 0.183 | -0.16 | 0.221 | — | 0.332 |
| II | 0.04 | 0.214 | 0.63 | 0.138 | 0.12 | 0.206 | 0.13 | 0.250 | 0.33 | 0.182 | -0.03 | 0.284 | — | 0.302 |
| III | 0.33 | 0.223 | 0.48 | 0.145 | — | 0.309 | 0.08 | 0.250 | 0.33 | 0.182 | 0.25 | 0.143 | — | 0.328 |
| IV | 0.27 | 0.227 | 1.31 | 0.116 | 0.27 | 0.218 | — | 0.400 | 0.31 | 0.185 | — | 0.368 | — | 0.320 |
| V | 0.35 | 0.226 | 0.66 | 0.136 | — | 0.304 | 0.10 | 0.252 | 0.28 | 0.186 | — | 0.307 | — | 0.322 |
| VI | 0.36 | 0.223 | 0.65 | 0.137 | — | 0.311 | — | 0.362 | 0.33 | 0.184 | -0.02 | 0.294 | — | 0.362 |
Table 1 Bond population(p) and bond length(d) of Cl2 and O2 molecule coadsorbed on TiC(100) clean surface*
| Structure | C1-Ti | C1-O1 | Ti-O1 | Cl1-Ti | Cl2-C2 | O1-O2 | Cl1-Cl2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | p | d/nm | |
| TiC(100) clean surface | 0.42 | 0.217 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| I | 0.01 | 0.231 | 0.65 | 0.136 | 0.13 | 0.209 | 0.37 | 0.256 | 0.30 | 0.183 | -0.16 | 0.221 | — | 0.332 |
| II | 0.04 | 0.214 | 0.63 | 0.138 | 0.12 | 0.206 | 0.13 | 0.250 | 0.33 | 0.182 | -0.03 | 0.284 | — | 0.302 |
| III | 0.33 | 0.223 | 0.48 | 0.145 | — | 0.309 | 0.08 | 0.250 | 0.33 | 0.182 | 0.25 | 0.143 | — | 0.328 |
| IV | 0.27 | 0.227 | 1.31 | 0.116 | 0.27 | 0.218 | — | 0.400 | 0.31 | 0.185 | — | 0.368 | — | 0.320 |
| V | 0.35 | 0.226 | 0.66 | 0.136 | — | 0.304 | 0.10 | 0.252 | 0.28 | 0.186 | — | 0.307 | — | 0.322 |
| VI | 0.36 | 0.223 | 0.65 | 0.137 | — | 0.311 | — | 0.362 | 0.33 | 0.184 | -0.02 | 0.294 | — | 0.362 |
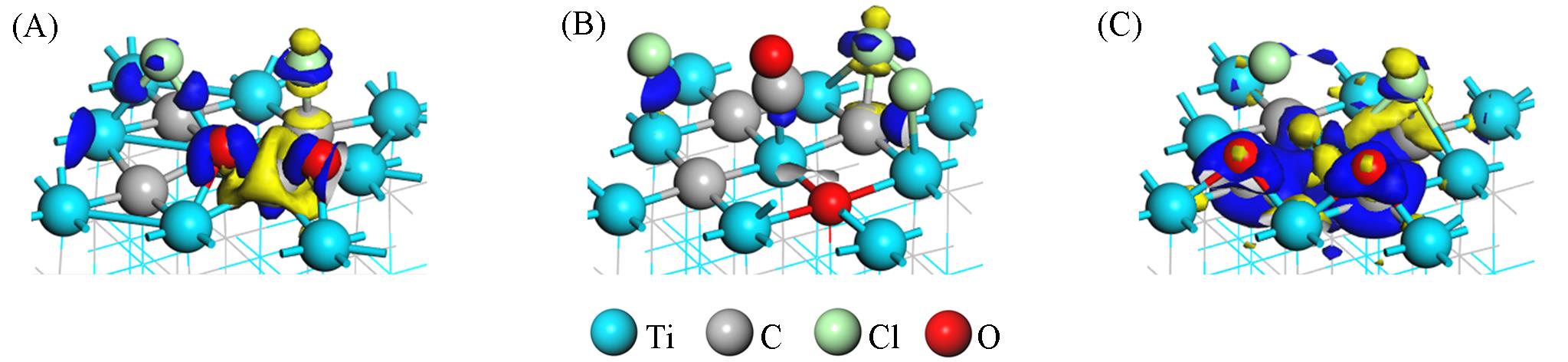
Fig.4 Differential charge density of adsorption sturctures I(A), IV(B) and V(C) of Cl2 and O2 molecules coadsorb on TiC(100) clean surfaceThe blue area and yellow area represent the charge accumulation and loss, respectively. The value of the isosurface is 0.008 nm.
| Structure | Charge(Ti)/e | Charge(C1)/e | Charge(C2)/e | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3s(4s) | 3p(4p) | 3d | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | |
TiC(100) clean surface | 2.00(0.28) | 6.00(0.40) | 2.57 | 11.25 | 0.75 | 1.56 | 3.19 | 4.75 | -0.75 | 1.56 | 3.19 | 4.75 | -0.75 |
| I | 2.00(0.21) | 6.00(0.42) | 2.55 | 11.18 | 0.82 | 1.26 | 2.93 | 4.19 | -0.19 | 1.52 | 3.22 | 4.74 | -0.74 |
| IV | 2.00(0.22) | 6.00(0.47) | 2.54 | 11.23 | 0.77 | 1.46 | 2.23 | 3.69 | 0.31 | 1.54 | 3.20 | 4.74 | -0.74 |
| V | 2.00(0.23) | 6.00(0.44) | 2.58 | 11.25 | 0.75 | 1.41 | 3.08 | 4.49 | -0.49 | 1.52 | 3.21 | 4.73 | -0.73 |
Table 2 Mulliken charge analysis of Cl2 and O2 molecules coadsorb on TiC(100) clean surface
| Structure | Charge(Ti)/e | Charge(C1)/e | Charge(C2)/e | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3s(4s) | 3p(4p) | 3d | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | |
TiC(100) clean surface | 2.00(0.28) | 6.00(0.40) | 2.57 | 11.25 | 0.75 | 1.56 | 3.19 | 4.75 | -0.75 | 1.56 | 3.19 | 4.75 | -0.75 |
| I | 2.00(0.21) | 6.00(0.42) | 2.55 | 11.18 | 0.82 | 1.26 | 2.93 | 4.19 | -0.19 | 1.52 | 3.22 | 4.74 | -0.74 |
| IV | 2.00(0.22) | 6.00(0.47) | 2.54 | 11.23 | 0.77 | 1.46 | 2.23 | 3.69 | 0.31 | 1.54 | 3.20 | 4.74 | -0.74 |
| V | 2.00(0.23) | 6.00(0.44) | 2.58 | 11.25 | 0.75 | 1.41 | 3.08 | 4.49 | -0.49 | 1.52 | 3.21 | 4.73 | -0.73 |
| Structure | Charge(Cl1)/e | Charge(Cl2)/e | Charge(O1)/e | Charge(O2)/e | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | |
| Cl | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| O | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| I | 1.94 | 5.32 | 7.26 | -0.26 | 1.94 | 4.98 | 6.92 | 0.08 | 1.85 | 4.5 | 6.35 | -0.35 | 1.85 | 4.61 | 6.46 | -0.46 |
| IV | 1.94 | 5.44 | 7.38 | -0.38 | 1.94 | 4.99 | 6.93 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 4.45 | 6.28 | -0.28 | 1.85 | 4.80 | 6.65 | -0.65 |
| V | 1.95 | 5.38 | 7.33 | -0.33 | 1.94 | 4.95 | 6.89 | 0.11 | 1.86 | 4.63 | 6.49 | -0.49 | 1.86 | 4.59 | 6.45 | -0.45 |
Table 3 Mulliken charge analysis of Cl2 and O2 molecules coadsorbed on TiC(100) clean surface
| Structure | Charge(Cl1)/e | Charge(Cl2)/e | Charge(O1)/e | Charge(O2)/e | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 3s | 3p | q | Δq | 2s | 2p | q | Δq | |
| Cl | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | 2 | 5 | 7 | 0 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| O | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 0 |
| I | 1.94 | 5.32 | 7.26 | -0.26 | 1.94 | 4.98 | 6.92 | 0.08 | 1.85 | 4.5 | 6.35 | -0.35 | 1.85 | 4.61 | 6.46 | -0.46 |
| IV | 1.94 | 5.44 | 7.38 | -0.38 | 1.94 | 4.99 | 6.93 | 0.07 | 1.83 | 4.45 | 6.28 | -0.28 | 1.85 | 4.80 | 6.65 | -0.65 |
| V | 1.95 | 5.38 | 7.33 | -0.33 | 1.94 | 4.95 | 6.89 | 0.11 | 1.86 | 4.63 | 6.49 | -0.49 | 1.86 | 4.59 | 6.45 | -0.45 |
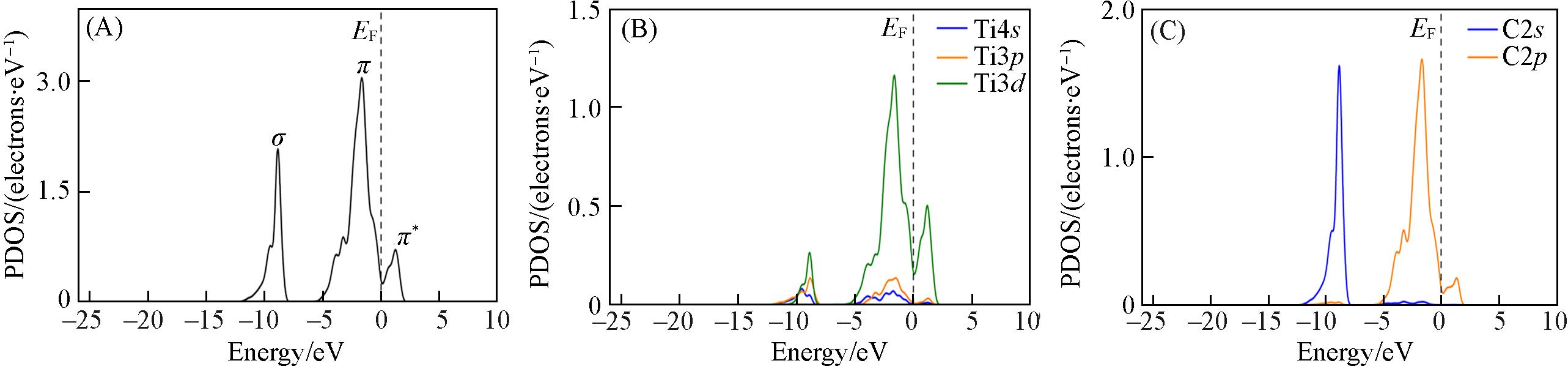
Fig.5 Partial density of states(PDOSs) of Ti—C bond(A) , Ti(B) and C(C) atoms of TiC(100) clean surfaceThe dotted line at energy=0 eV indicates the Fermi energy level.
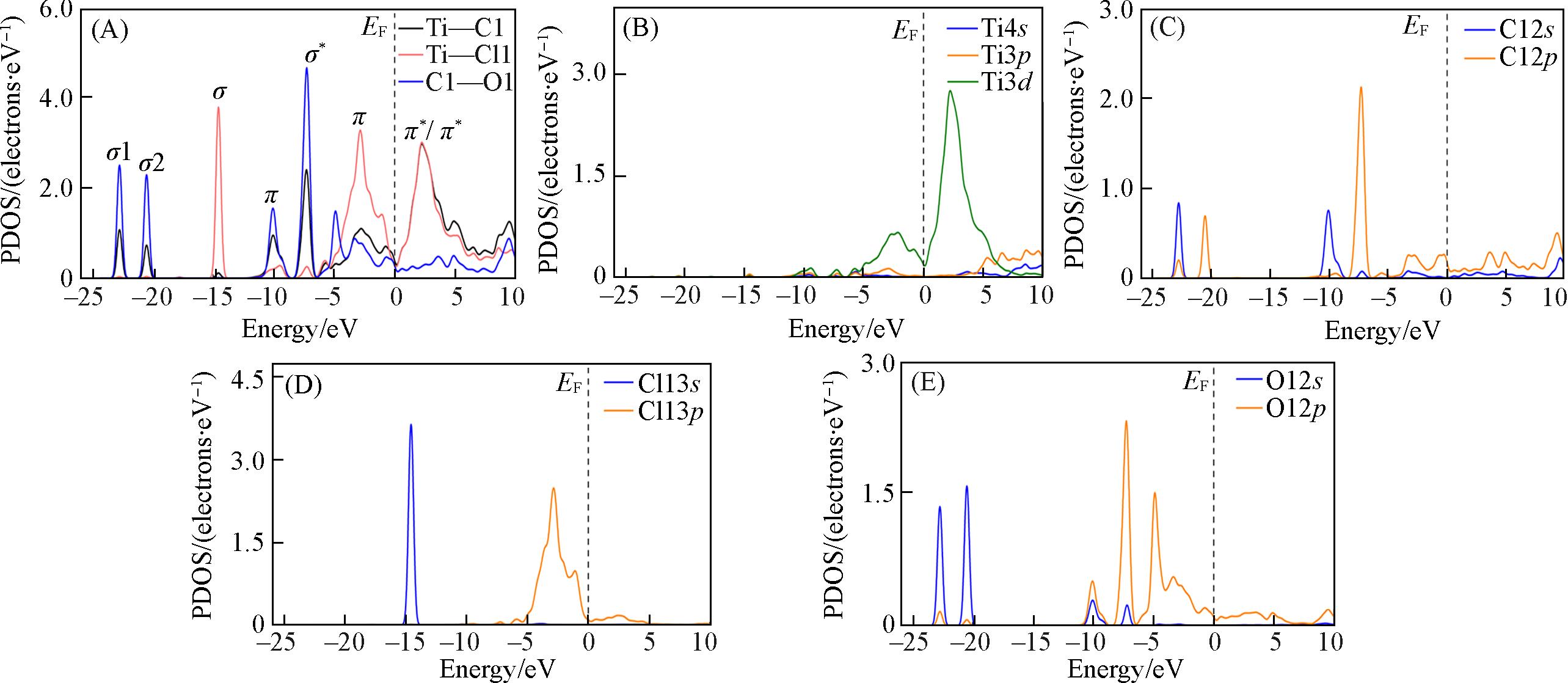
Fig.6 PDOSs of co⁃adsorption structure I of Cl2 and O2 molecules on TiC(100) surfaceThe dashed line at energy=0 eV indicates the Fermi level. (A)—(E) represent the state density diagram of Ti—C, Ti—Cl and C—O bonds, Ti, C, Cl, O atoms, respectively.
| 1 | Zhu F. X., Ma S. G., Ma Z. S., Qi L. H., Peng W. X., Li K. H., Qiu K. H., J. Mater. Res. Technol., 2023, 23, 2703—2718 |
| 2 | Shi J. J., Qiu Y. C., Yu B., Xie X. K., Dong J. J., Hou C. L., Li J. Z., Liu C. S., JOM, 2022, 74(2), 654—667 |
| 3 | Lu P., Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2013, 34(3), 33—38 |
| 陆平. 钢铁钒钛, 2013, 34(3), 33—38 | |
| 4 | Li L., Light Metals, 2021, (10), 42—48 |
| 李亮. 轻金属, 2021, (10), 42—48 | |
| 5 | Zhang Y., Wang H. B., Liu X., J. New Industrialization, 2018, 8(8), 124—127 |
| 张月, 王海波, 刘湘. 新型工业化, 2018, 8(8), 124—127 | |
| 6 | Huang J. X., Yang Y. J., Lu P., Liu S. L., Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2011, 32(4), 12—15, 50 |
| 黄家旭, 杨仰军, 陆平, 刘森林. 钢铁钒钛, 2011, 32(4), 12—15, 50 | |
| 7 | Huang J. X., Long F. H., Zhao Q. E., Liu Y. D., Light Metals, 2022, (1), 51—55 |
| 黄家旭, 龙飞虎, 赵青娥, 刘亚东. 轻金属, 2022, (1), 51—55 | |
| 8 | Peng Y., Titanium Industry Progress, 2005, 22(6), 45—49 |
| 彭毅. 钛工业进展, 2005, 22(6), 45—49 | |
| 9 | Liu X. H., Study on High⁃temperature Carbonization and Low⁃temperature Chlorination on Modified Titanium Bearing Blast Furnace Slag, Northeastern University, Shenyang, 2009 |
| 刘晓华. 改性含钛高炉渣高温碳化低温氯化的研究, 沈阳: 东北大学, 2009 | |
| 10 | Yue D., Wen L. Y., Chen R., Wang J. X., Yang Y. J., Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(5), 1—8 |
| 岳东, 温良英, 陈荣, 王建鑫, 杨仰军. 钢铁钒钛, 2023, 44(5), 1—8 | |
| 11 | Wen L. Y., Qin J., Zhao Y., Shi S. Y., Yang F., Zhang S. F., Yang Z. Q., JOM, 2020, 72(10), 3483—3490 |
| 12 | Zhao Y., Chen R., Yue D., Wen L. Y., Zhang S. F., Yang Z. Q., New. J. Chem., 2023, 47(5), 2264—2272 |
| 13 | Pavlova T. V., Andryushechkin B. V., Zhidomirov G. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2016, 120(5), 2829—2836 |
| 14 | Ilyasov V. V., Pham K. D., Ershov I. V., Nguyen C. V., Hieu N. N., Comp. Mater. Sci., 2016, 124, 344—352 |
| 15 | Fang L. H., First⁃principles Study on TiC Bulk and Surfaces Properties and AI/TiC Interfaces Properties, Shandong University, Jinan, 2011 |
| 房立红. TiC体性质、 表面性质以及AI/TiC界面性质的第一原理研究, 济南: 山东大学, 2011 | |
| 16 | Zaima S., Shibata Y., Adachi H., Oshima C., Otani S., Aono M., Ishizawa Y., Surf. Sci., 1985, 157(2), 380—392 |
| 17 | Pinto H. M., Coutinho J., Ramos M. M. D., Vaz F., Marques L., Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2009, 165(3), 194—197 |
| 18 | Fang L. H., Wang L., Gong J. H., Dai H. S., Miao D. Z., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2010, 20(5), 857—862 |
| 19 | Wang L., Fang L. H., Gong J. H., Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China, 2012, 22(1), 170—174 |
| 20 | Asara G. G., Feria L., Florez E., Ricart J. M., Liu P., Rodriguez J. A., Illas F., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2011, 115(45), 22495—22504 |
| 21 | Wang S. Y., Zhang X. L., Zhang Y. X., Mao J. J., Yang Z. X., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, 19(39), 27116—27122 |
| 22 | Vines F., Sousa C., Illas F., Liu P., Rodriguez J. A., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(45), 16982—16989 |
| 23 | Xia Y. B., Wang Y., Guo X. T., Yang X. W., Yang Z. X., J. Atom. Molec. Phys., 2023, 40(2), 37—42 |
| 夏雅兵, 王雁, 郭笑天, 杨新伟, 杨宗献. 原子与分子物理学报, 2023, 40(2), 37—42 | |
| 24 | Ruberto C., Lundqvist I. B., Phys. Rev. B, 2007, 75(23), 235438 |
| 25 | Ilyasov V. V., Pham K. D., Holodova O. M., Ershov I. V., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2015, 351(Oct.1), 433—444 |
| 26 | Yue D., Wen L. Y., Chen R., Wang J. X., Yang Z. Q., Surf. Sci., 2024, 739, 122384 |
| 27 | Zhong H., Wen L. Y., Zou C., Zhang S. F., Bai C. G., Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 2015, 46(5), 2288—2295 |
| 28 | Wang Z. M., Li Y. Q., Dou Y. P., Li K. J., Yu W. H., Sheng P. C., Molecules, 2023, 28(16), 5971 |
| 29 | Wang Y., Yang Z. X., J. Chem. Phys., 2018, 149(5), 054705 |
| 30 | Victor V. I., Khang D. P., Igor V. E., Nguyen N. H., Chuong V. N., J. Electron Spectrosc., 2018, 222, 142—148 |
| 31 | Delley B., J. Chem. Phys., 1990, 92(1), 508—517 |
| 32 | Perdew J. P., Burke K., Ernzerhof M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77(18), 3865—3868 |
| 33 | Ramalho J. P. P., Gomes J. B. R., Illas F., RSC Adv., 2013, 3(32), 13085—13100 |
| 34 | Grimme S., J. Comput. Chem., 2006, 27(15), 1787—1799 |
| 35 | Yang Y., Lu H., Yu C., Chen J. M., J. Alloy. Compd., 2009, 485(1/2), 542—547 |
| 36 | Chen K. Y., Zhao L. R., J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2007, 68(9), 1805—1811 |
| 37 | Liu Y. Z., Jiang Y. H., Zhou R., Feng J., J. Alloy. Compd., 2014, 582, 500—504 |
| 38 | Nakamura K., Yashima M., Mater. Sci. Eng. B, 2008, 148(1—3), 69—72 |
| 39 | Dunand A., Flack H. D., Yvon K., Phys. Rev. B, 1985, 31(4), 2299—2315 |
| 40 | Segall M. D., Shah R., Pickard C. J., Payne M. C., Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54(23), 16317—16320 |
| 41 | Yu Y. X., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2019, 123(1), 205—213 |
| 42 | Pang X. Z., Yang J. B., Pang M. J., He J. X., Yang W. C., Qin H. Q., Zhan Y. Z., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2019, 470, 1064—1070 |
| 43 | Demaison J., Császár A. G., J. Mol. Struct., 2012, 1023, 7—14 |
| [1] | 陈晴晴, 李江涛, 黄欣蓉, 顾芳, 王海军. 氢键流体中Janus粒子的过量熵[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(2): 20230443. |
| [2] | 富忠恒, 陈翔, 姚楠, 余乐耕, 沈馨, 张睿, 张强. 固态电解质锂离子输运机制研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220703. |
| [3] | 彭辛哲, 葛娇阳, 王访丽, 余国静, 冉雪芹, 周栋, 杨磊, 解令海. 基于苯并噻吩平面格的张力与重组能的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(2): 20220313. |
| [4] | 郭昊天, 鲁新环, 孙凡棋, 陶艺元, 段金贵, 张望, 周丹, 夏清华. 纳米球型Mo-MOF材料的调控合成及催化硫醚选择性氧化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230408. |
| [5] | 张海平, 孔雪, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. C18环基过渡金属(Os, Ir)单原子对甲烷C—H的活化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(11): 20230259. |
| [6] | 冯林雁, 胡晓波, 闫苗, 苗常青, 陈瑞, 郭谨昌, 王迎进. 平面十二配位MB8C4(M=Ca, Sr, Ba)分子轮团簇的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230281. |
| [7] | 刘建芳, 赵浩成, 梁芳楠, 尤雪瑞, 周琨. 化学剥离碳化钛纳米片辅助合成可控尺寸的银纳米线[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230009. |
| [8] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [9] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [10] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [11] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [12] | 周成思, 赵远进, 韩美晨, 杨霞, 刘晨光, 贺爱华. 硅烷类外给电子体对丙烯-丁烯序贯聚合的调控作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [13] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [14] | 钟声广, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 电中性团簇MCu2Ox(M=Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+)上甲烷和二氧化碳直接合成乙酸的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [15] | 黄罗仪, 翁约约, 黄旭慧, 王朝杰. 车前草中黄酮类成分结构和性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||