

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 2189.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150595
收稿日期:2015-07-30
出版日期:2015-11-10
发布日期:2015-10-10
作者简介:联系人简介: 李全松, 男, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事光化学和高能材料的理论计算. E-mail:基金资助:
CHI Weijie, TIAN Meng, LI Quansong*( ), LI Zesheng*(
), LI Zesheng*( )
)
Received:2015-07-30
Online:2015-11-10
Published:2015-10-10
Contact:
LI Quansong,LI Zesheng
E-mail:liquansong@bit.edu.cn;zeshengli@bit.edu.cn
摘要:
为了寻找兼具优异爆轰性能和良好热力学及动力学稳定性的高能材料, 本文设计了15个硝基尿酸化合物, 运用密度泛函理论, 对其性质进行了研究. 通过半经验的K-J方程和比冲量预测了其爆炸性能, 结果表明, 所设计分子的爆热、 分子密度、 爆炸速率和爆炸压强同硝基取代基数目之间存在较强的线性关系. 三硝基尿酸和四硝基尿酸衍生物的爆炸速率超过了8.0 km/s, 爆炸压强超过了30 GPa, 并且大多数衍生物的比冲量要高于目前经常使用的炸药黑索金. 通过计算N—NO2键的解离能、 特征落高、 分子的自由空间预判了衍生物的稳定性和撞击感度, 结果显示, 绝大多数分子有大于80 kJ/mol的键解离能. 本文的理论结果可以为实验上设计合成新的高能材料提供一些有用的信息.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
迟伟杰, 田萌, 李全松, 李泽生. 多硝基尿酸衍生物含能性质的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(11): 2189.
CHI Weijie, TIAN Meng, LI Quansong, LI Zesheng. Computational Studies on Energetic Performance of Polynitro-substituted Uric Acid Derivatives. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(11): 2189.
| Compound | HOFg/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHsub/ (kJ·mol-1) | HOFs/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHcomb / (kJ·g-1) | Compound | HOFg/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHsub/ (kJ·mol-1) | HOFs/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHcomb / (kJ·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | -513.96 | 101.97 | -615.92 | -8.36 | U24 | -436.23 | 110.54 | -546.77 | -6.61 |
| U2 | -529.67 | 109.81 | -639.48 | -8.25 | U34 | -422.47 | 106.60 | -529.07 | -6.68 |
| U3 | -550.33 | 99.51 | -649.84 | -8.20 | U123 | -336.94 | 116.09 | -453.03 | -5.47 |
| U4 | -530.90 | 101.32 | -632.22 | -8.28 | U124 | -320.26 | 119.48 | -439.74 | -5.51 |
| U12 | -420.53 | 112.64 | -533.17 | -6.67 | U134 | -307.40 | 115.58 | -422.98 | -5.57 |
| U13 | -441.04 | 106.18 | -547.21 | -6.61 | U234 | -313.71 | 113.92 | -427.63 | -5.55 |
| U14 | -418.24 | 108.65 | -526.90 | -6.69 | U1234 | -196.07 | 124.71 | -320.78 | -4.73 |
| U23 | -449.42 | 108.26 | -557.69 | -6.57 |
Table 1 Calculated heat of formation(HOFs) and the specific enthalpy(ΔHcomb) of combustion of the title compounds at B3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level
| Compound | HOFg/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHsub/ (kJ·mol-1) | HOFs/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHcomb / (kJ·g-1) | Compound | HOFg/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHsub/ (kJ·mol-1) | HOFs/ (kJ·mol-1) | ΔHcomb / (kJ·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | -513.96 | 101.97 | -615.92 | -8.36 | U24 | -436.23 | 110.54 | -546.77 | -6.61 |
| U2 | -529.67 | 109.81 | -639.48 | -8.25 | U34 | -422.47 | 106.60 | -529.07 | -6.68 |
| U3 | -550.33 | 99.51 | -649.84 | -8.20 | U123 | -336.94 | 116.09 | -453.03 | -5.47 |
| U4 | -530.90 | 101.32 | -632.22 | -8.28 | U124 | -320.26 | 119.48 | -439.74 | -5.51 |
| U12 | -420.53 | 112.64 | -533.17 | -6.67 | U134 | -307.40 | 115.58 | -422.98 | -5.57 |
| U13 | -441.04 | 106.18 | -547.21 | -6.61 | U234 | -313.71 | 113.92 | -427.63 | -5.55 |
| U14 | -418.24 | 108.65 | -526.90 | -6.69 | U1234 | -196.07 | 124.71 | -320.78 | -4.73 |
| U23 | -449.42 | 108.26 | -557.69 | -6.57 |
| Compound | Q / (kJ·mol-1) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | D / (k·ms-1) | P/GPa | Compound | Q / (kJ·mol-1) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | D / (k·ms-1) | P/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 488.64 | 1.83 | 6.19 | 18.66 | U24 | 811.13 | 1.97 | 7.59 | 28.19 |
| U2 | 462.21 | 1.93 | 6.33 | 20.28 | U34 | 827.53 | 1.92 | 7.49 | 26.96 |
| U3 | 450.59 | 1.87 | 6.17 | 18.76 | U123 | 1057.23 | 1.97 | 8.28 | 33.11 |
| U4 | 470.36 | 1.90 | 6.28 | 19.66 | U124 | 1067.70 | 1.98 | 8.31 | 33.42 |
| U12 | 823.73 | 1.95 | 7.57 | 27.86 | U134 | 1080.93 | 1.99 | 8.38 | 34.08 |
| U13 | 810.72 | 1.94 | 7.51 | 27.32 | U234 | 1077.26 | 1.98 | 8.33 | 33.52 |
| U14 | 829.54 | 1.89 | 7.43 | 26.35 | U1234 | 1266.12 | 2.00 | 8.86 | 37.93 |
| U23 | 801.02 | 1.94 | 7.50 | 27.26 | RDX | 1591.03 | 1.81 | 8.75 | 34.00 |
Table 2 Calculated detonation properties of the title compounds and reference compound RDX
| Compound | Q / (kJ·mol-1) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | D / (k·ms-1) | P/GPa | Compound | Q / (kJ·mol-1) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | D / (k·ms-1) | P/GPa |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 488.64 | 1.83 | 6.19 | 18.66 | U24 | 811.13 | 1.97 | 7.59 | 28.19 |
| U2 | 462.21 | 1.93 | 6.33 | 20.28 | U34 | 827.53 | 1.92 | 7.49 | 26.96 |
| U3 | 450.59 | 1.87 | 6.17 | 18.76 | U123 | 1057.23 | 1.97 | 8.28 | 33.11 |
| U4 | 470.36 | 1.90 | 6.28 | 19.66 | U124 | 1067.70 | 1.98 | 8.31 | 33.42 |
| U12 | 823.73 | 1.95 | 7.57 | 27.86 | U134 | 1080.93 | 1.99 | 8.38 | 34.08 |
| U13 | 810.72 | 1.94 | 7.51 | 27.32 | U234 | 1077.26 | 1.98 | 8.33 | 33.52 |
| U14 | 829.54 | 1.89 | 7.43 | 26.35 | U1234 | 1266.12 | 2.00 | 8.86 | 37.93 |
| U23 | 801.02 | 1.94 | 7.50 | 27.26 | RDX | 1591.03 | 1.81 | 8.75 | 34.00 |
| Compound | N | Tc | Is | Compound | N | Tc | Is |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.0270 | 9766.7 | 16.24 | U24 | 0.0271 | 7627.1 | 14.39 |
| U2 | 0.0270 | 9641.4 | 16.13 | U34 | 0.0271 | 7703.1 | 14.46 |
| U3 | 0.0270 | 9586.3 | 16.09 | U123 | 0.0272 | 6266.9 | 13.06 |
| U4 | 0.0270 | 9680.0 | 16.17 | U124 | 0.0272 | 6314.7 | 13.11 |
| U12 | 0.0271 | 7685.5 | 14.44 | U134 | 0.0272 | 6375.1 | 13.17 |
| U13 | 0.0271 | 7625.2 | 14.38 | U234 | 0.0272 | 6358.4 | 13.16 |
| U14 | 0.0271 | 7712.5 | 14.47 | U1234 | 0.0273 | 5720.7 | 12.50 |
| U23 | 0.0271 | 7580.3 | 14.34 | RDX | 14.13 |
Table 3 Calculated Is and the corresponding parameters for the title compounds and RDX
| Compound | N | Tc | Is | Compound | N | Tc | Is |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.0270 | 9766.7 | 16.24 | U24 | 0.0271 | 7627.1 | 14.39 |
| U2 | 0.0270 | 9641.4 | 16.13 | U34 | 0.0271 | 7703.1 | 14.46 |
| U3 | 0.0270 | 9586.3 | 16.09 | U123 | 0.0272 | 6266.9 | 13.06 |
| U4 | 0.0270 | 9680.0 | 16.17 | U124 | 0.0272 | 6314.7 | 13.11 |
| U12 | 0.0271 | 7685.5 | 14.44 | U134 | 0.0272 | 6375.1 | 13.17 |
| U13 | 0.0271 | 7625.2 | 14.38 | U234 | 0.0272 | 6358.4 | 13.16 |
| U14 | 0.0271 | 7712.5 | 14.47 | U1234 | 0.0273 | 5720.7 | 12.50 |
| U23 | 0.0271 | 7580.3 | 14.34 | RDX | 14.13 |
| Compound | BO | ΔE/eV | BDE /(kJ·mol-1) | Compound | BO | ΔE/eV | BDE /(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.83 | 3.80 | 188.18 | U24 | 0.92 | 3.78 | 101.16 |
| U2 | 0.89 | 4.53 | 100.76 | U34 | 0.83 | 3.80 | 73.44 |
| U3 | 0.97 | 3.60 | 117.91 | U123 | 0.84 | 3.97 | 87.32 |
| U4 | 0.93 | 3.36 | 81.46 | U124 | 0.90 | 3.77 | 91.85 |
| U12 | 0.88 | 4.42 | 101.05 | U134 | 0.79 | 3.80 | 64.50 |
| U13 | 0.96 | 3.69 | 118.49 | U234 | 0.82 | 4.05 | 88.00 |
| U14 | 0.80 | 3.34 | 70.73 | U1234 | 0.79 | 4.05 | 88.51 |
| U23 | 0.85 | 3.87 | 85.84 | RDX | 0.98 | 5.97 | 160.41 |
Table 4 Calculated bond order(BO), HOMO-LUMO energy gap(ΔE), and BDE of the title compounds and RDX at UB3LYP/6-31G(d,p) level
| Compound | BO | ΔE/eV | BDE /(kJ·mol-1) | Compound | BO | ΔE/eV | BDE /(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.83 | 3.80 | 188.18 | U24 | 0.92 | 3.78 | 101.16 |
| U2 | 0.89 | 4.53 | 100.76 | U34 | 0.83 | 3.80 | 73.44 |
| U3 | 0.97 | 3.60 | 117.91 | U123 | 0.84 | 3.97 | 87.32 |
| U4 | 0.93 | 3.36 | 81.46 | U124 | 0.90 | 3.77 | 91.85 |
| U12 | 0.88 | 4.42 | 101.05 | U134 | 0.79 | 3.80 | 64.50 |
| U13 | 0.96 | 3.69 | 118.49 | U234 | 0.82 | 4.05 | 88.00 |
| U14 | 0.80 | 3.34 | 70.73 | U1234 | 0.79 | 4.05 | 88.51 |
| U23 | 0.85 | 3.87 | 85.84 | RDX | 0.98 | 5.97 | 160.41 |
| Compound | ΔV/nm3 | h50/cm | Compound | ΔV/nm3 | h50/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.028 | 21.0 | U24 | 0.028 | 38.6 |
| U2 | 0.026 | 28.2 | U34 | 0.031 | 33.4 |
| U3 | 0.024 | 48.2 | U123 | 0.034 | 21.0 |
| U4 | 0.023 | 49.3 | U124 | 0.033 | 25.7 |
| U12 | 0.029 | 23.2 | U134 | 0.033 | 22.5 |
| U13 | 0.027 | 30.3 | U234 | 0.030 | 26.5 |
| U14 | 0.032 | 35.5 | U1234 | 0.035 | 20.2 |
| U23 | 0.029 | 37.9 | RDX | 0.046 | 26.0 |
Table 5 Calculated impact sensitivity(h50) and the free space per molecule(ΔV) of the investigated molecules and RDX
| Compound | ΔV/nm3 | h50/cm | Compound | ΔV/nm3 | h50/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| U1 | 0.028 | 21.0 | U24 | 0.028 | 38.6 |
| U2 | 0.026 | 28.2 | U34 | 0.031 | 33.4 |
| U3 | 0.024 | 48.2 | U123 | 0.034 | 21.0 |
| U4 | 0.023 | 49.3 | U124 | 0.033 | 25.7 |
| U12 | 0.029 | 23.2 | U134 | 0.033 | 22.5 |
| U13 | 0.027 | 30.3 | U234 | 0.030 | 26.5 |
| U14 | 0.032 | 35.5 | U1234 | 0.035 | 20.2 |
| U23 | 0.029 | 37.9 | RDX | 0.046 | 26.0 |
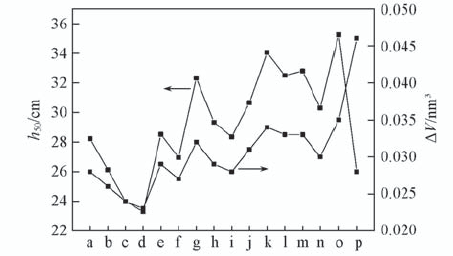
Fig.2 Calculated ΔV and h50 of the designed molecules and RDX a. U1; b. U2; c. U3; d. U4; e. U12; f. U13; g. U14; h. U23; i. U24; j. U34; k. U123; l. U124; m. U134; n. U234; o. U1234; p. RDX.
| [1] | Zhang J., Zhang Q., Vo T. T., Parrish D. A., Shreeve J. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(4), 1697—1704 |
| [2] | Bian C., Zhang M., Li C., Zhou Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(1), 163—169 |
| [3] | Rice B. M., Larentzos J. P., Byrd E. F., Weingarten N. S., J. Chem. Theory. Comput., 2015, 11(2), 392—405 |
| [4] | Huynh M. H. V., Hiskey M. A., Chavez D. E., Naud D. L., Gilardi R. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005, 127(36), 12537—12543 |
| [5] | Yin P., Parrish D. A., Shreeve J. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(14), 4778—4786 |
| [6] | Chavez D. E., Hiskey M. A., J. Energ. Mater., 1999, 17(4), 357—377 |
| [7] | Malow M., Wehrstedt K. D., Neuenfeld S., Tetrahedron. Lett., 2007, 48(7), 1233—1235 |
| [8] | Lesnikovich A., Ivashkevich O., Levchik S., Balabanovich A., Gaponik P., Kulak A., Thermochim. Acta, 2002, 388(1), 233—251 |
| [9] | Korkin A. A., Balkova A., Bartlett R. J., Boyd R. J., von Rague Schleyer P., J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(14), 5702—5714 |
| [10] | Simões P., Pedroso L., Matos Beja A., Silva M. R., MacLean E., Portugal A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(1), 150—158 |
| [11] | Li C., Liang L., Wang K., Bian C., Zhang J., Zhou Z., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(42), 18097—18105 |
| [12] | Sikder A., Sikder N., J. Hazard. Mater., 2004, 112(1), 1—15 |
| [13] | Liu Y., Gong X., Wang L., Wang G., Xiao H., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2011, 115(9), 1754—1762 |
| [14] | Pan Y., Zhu W., Xiao H., J. Mol. Model., 2012, 18(7), 3125—3138 |
| [15] | Chi W., Li L., Li B., Wu H., Struct. Chem., 2012, 23(6), 1837—1841 |
| [16] | Chi W., Li B., Wu H., Struct. Chem., 2013, 24(2), 375—381 |
| [17] | Chi W. J., Li Z. S., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(10), 7766—7772 |
| [18] | Chi W., Wang X., Li B., Wu H., J. Mol. Model., 2012, 18(9), 4217—4223 |
| [19] | Guo Y. Y., Chi W. J., Li Z. S., Li Q. S., RSC Adv., 2015, 5(48), 38048—38055 |
| [20] | Liu X. F., Xu W. G., Lu S. X., Chem. J. Chinese. Universities, 2009, 30(7), 1406—1409 |
| [21] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A., Vreven T. Jr., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S., Tomasi S. J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Nanayakkara Y., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2009 |
| [22] | Zhang X., Zhu W., Xiao H., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2009, 114(1), 603—612 |
| [23] | Chen Z., Xiao J., Xiao H., Chiu Y., J. Phys. Chem. A, 1999, 103(40), 8062—8066 |
| [24] | |
| [25] | Politzer P., Murray J. S., Edward Grice M., Desalvo M., Miller E., Mol. Phys., 1997, 91(5), 923—928 |
| [26] | Byrd E. F., Rice B. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2006, 110(3), 1005—1013 |
| [27] | Rice B. M., Pai S. V., Hare J., Combust. Flame, 1999, 118(3), 445—458 |
| [28] | Kamlet M., Jacobs S., J. Chem. Phys., 1968, 48, 23—35 |
| [29] | Bulat F. A., Toro-Labbé A., Brinck T., Murray J. S., Politzer P., J. Mol. Model., 2010, 16(11), 1679—1691 |
| [30] | Wei T., Zhu W., Zhang J., Xiao H., J. Hazard. Mater., 2010, 179(1), 581—590 |
| [31] | He P., Zhang J. G., Wang K., Yin X., Zhang T. L., J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80(11), 5643—5651 |
| [32] | Ghule V. D., Jadhav P. M., Patil R. S., Radhakrishnan S., Soman T., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2010, 114(1), 498—503 |
| [33] | Ghule V. D., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2012, 116(37), 9391—9397 |
| [34] | Chi W. J., Li L. L., Li B. T., Wu H. S., J. Mol. Model., 2012, 18(8), 3695—3704 |
| [35] | Ma Q., Jiang T., Zhang X., Fan G., Wang J., Huang J., J. Phys. Org. Chem., 2015, 28(1), 31—39 |
| [36] | Politzer P., Murray J. S., Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater., 2011, 8(3), 209—220 |
| [37] | Hoffmann R., J. Chem. Soc., 1969, 5, 240—241 |
| [38] | Liu H., Wang F., Wang G. X., Gong X. D., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33(22), 1790—1796 |
| [39] | Fan X. W., Ju X. H., Xiao H. M., Qiu L., J. Mol. Struct: Theochem., 2006, 801(1), 55—62 |
| [40] | Owens F., J. Mol. Struct: Theochem., 1996, 370(1), 11—16 |
| [41] | Ravi P., Mol. Phys., 2015, 113(7), 647—655 |
| [42] | Fried L. E., Manaa M. R., Pagoria P. F., Simpson R. L., Ann. Rev. Mater. Res., 2001, 31(1), 291—321 |
| [43] | Politzer P., Murray J. S., J. Mol. Struct., 1996, 376(1), 419—424 |
| [44] | Pospíšil M., Vávra P., Concha M. C., Murray J. S., Politzer P., J. Mol. Model., 2011, 17(10), 2569—2574 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [4] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [5] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [6] | 周成思, 赵远进, 韩美晨, 杨霞, 刘晨光, 贺爱华. 硅烷类外给电子体对丙烯-丁烯序贯聚合的调控作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [7] | 黄罗仪, 翁约约, 黄旭慧, 王朝杰. 车前草中黄酮类成分结构和性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [8] | 钟声广, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 电中性团簇MCu2Ox(M=Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+)上甲烷和二氧化碳直接合成乙酸的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [9] | 马丽娟, 高升启, 荣祎斐, 贾建峰, 武海顺. Sc, Ti, V修饰B/N掺杂单缺陷石墨烯的储氢研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [10] | 郑若昕, 张颖, 徐昕. 低标度XYG3双杂化密度泛函的开发与测评[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [11] | 王建, 张红星. 四配位铂磷光发射体结构与光物理性质关系的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [12] | 胡伟, 刘小峰, 李震宇, 杨金龙. 金刚石纳米线氮空位色心的表面与尺寸效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| [13] | 杨一莹, 朱荣秀, 张冬菊, 刘成卜. 金催化炔基苯并二𫫇英环化合成8-羟基异香豆素的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [14] | 应富鸣, 计辰儒, 苏培峰, 吴玮. 基于完全活性空间自洽场的杂化多组态密度泛函方法λ-DFCAS[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [15] | 刘昌辉, 梁国俊, 李妍璐, 程秀凤, 赵显. NH3在硼纳米管表面吸附的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||