

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 96.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180589
马玉聪1, 樊保民1( ), 郝华2, 吕金玉1, 冯云皓3, 杨彪1
), 郝华2, 吕金玉1, 冯云皓3, 杨彪1
收稿日期:2018-08-23
出版日期:2019-01-10
发布日期:2018-12-20
作者简介:联系人简介: 樊保民, 男, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事超分子化学与腐蚀电化学方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
MA Yucong1, FAN Baomin1,*( ), HAO Hua2, LÜ Jinyu1, FENG Yunhao3, YANG Biao1
), HAO Hua2, LÜ Jinyu1, FENG Yunhao3, YANG Biao1
Received:2018-08-23
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2018-12-20
Contact:
FAN Baomin
E-mail:fanbaomin@btbu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
应用分子动力学模拟明确了以β-环糊精(β-CyD)为主体、 十八胺(ODA)为客体的分子组装体(CDDA)的最优空间构型, 并采用动态失重、 电化学极化与阻抗测试结合扫描电子显微镜、 原子力显微镜、 接触角、 X射线光电子能谱(XPS)与衰减全反射红外光谱(ATR-FTIR)等表面分析手段, 研究了CDDA对Q235碳钢在蒸汽凝结水中的缓蚀机理. 结果显示, CDDA的4种构型可共存于组装体系内; 35 ℃下, 添加1 mmol/L CDDA对碳钢的缓蚀率达94.1%; 添加CDDA不改变腐蚀机理, 但可同时抑制电化学反应的阴、 阳极过程, 并显著提升极化阻抗, 属于阳极抑制为主的混合型缓蚀剂. XPS和ATR-FTIR结果均表明, CDDA在碳钢/溶液界面释放客体ODA, 并由其自发吸附组装形成疏水膜, 吸附过程符合Langmuir等温式. 分子动力学模拟与量子化学计算结果支持上述ODA释放并于金属表面组装成膜的推断.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
马玉聪, 樊保民, 郝华, 吕金玉, 冯云皓, 杨彪. 十八胺基分子组装体在碳钢表面的作用机理与模拟. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 96.
MA Yucong,FAN Baomin,HAO Hua,LÜ Jinyu,FENG Yunhao,YANG Biao. Experimental and Theoretical Studies of Action Mechanism of an Octadecylamine-based Molecular Assembly on Mild Steel†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 96.
| pH | Conductivity/ (μS·cm-1) | Concentration of dissolved oxygen/(mg·L-1) | Concentration of Na+/ (μg·L-1) | Concentration of Cl-/ (μg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.89 | 108.32 | 2.11 | 66.13 | 129.19 |
Table 1 Water parameters of the sampled condensate water at 25 ℃
| pH | Conductivity/ (μS·cm-1) | Concentration of dissolved oxygen/(mg·L-1) | Concentration of Na+/ (μg·L-1) | Concentration of Cl-/ (μg·L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5.89 | 108.32 | 2.11 | 66.13 | 129.19 |
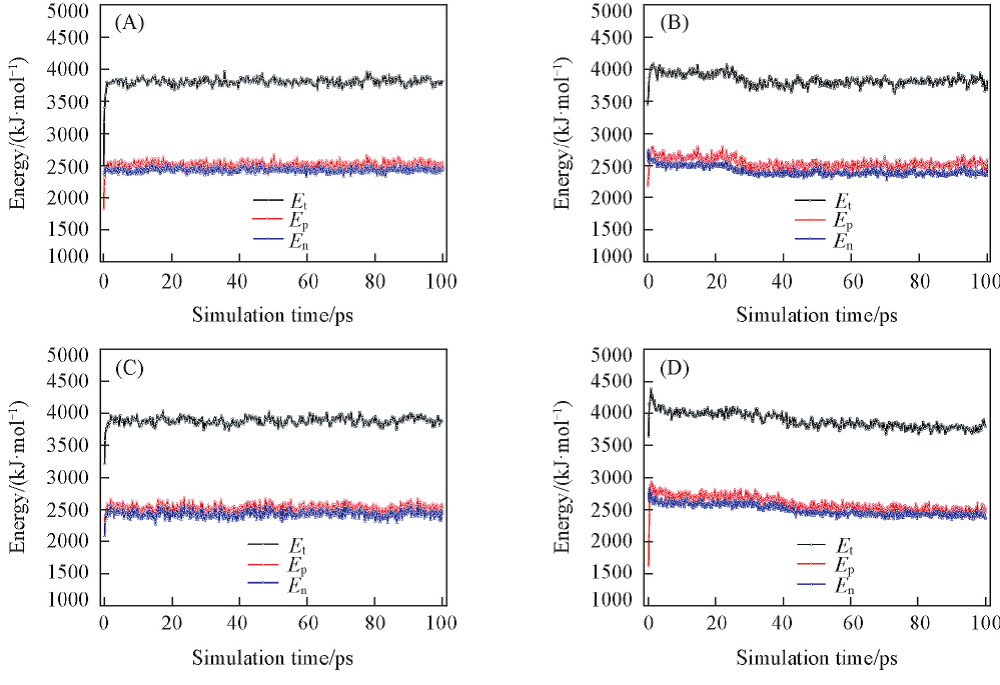
Fig.2 Calculated energies of CDDA for different configurations(A) Wide towards narrow; (B) wide towards wide; (C) narrow towards narrow; (D) narrow towards wide.
| Configuration | Et/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | En/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wide towards narrow | 3820.59 | 2534.28 | 2444.70 |
| Wide towards wide | 3828.99 | 2562.72 | 2420.12 |
| Narrow towards narrow | 3830.92 | 2497.26 | 2464.99 |
| Narrow towards wide | 3815.06 | 2518.11 | 2402.59 |
Table 2 Equilibrium values of total energy(Et), potential energy(Ep) and non-bond energy(En) for different spatial configurations of CDDA
| Configuration | Et/(kJ·mol-1) | Ep/(kJ·mol-1) | En/(kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wide towards narrow | 3820.59 | 2534.28 | 2444.70 |
| Wide towards wide | 3828.99 | 2562.72 | 2420.12 |
| Narrow towards narrow | 3830.92 | 2497.26 | 2464.99 |
| Narrow towards wide | 3815.06 | 2518.11 | 2402.59 |
| Temperature/℃ | c(CDDA)/(mol·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1 | |
| 35 | 0.118 | 0.021(82.2) | 0.013(89.0) | 0.011(90.7) | 0.009(92.4) | 0.007(94.1) |
| 45 | 0.153 | 0.030(80.4) | 0.021(86.3) | 0.016(89.5) | 0.013(91.5) | 0.010(93.5) |
| 55 | 0.202 | 0.055(72.8) | 0.044(78.2) | 0.028(86.1) | 0.021(89.6) | 0.018(91.1) |
| 65 | 0.210 | 0.064(69.5) | 0.052(75.2) | 0.041(80.5) | 0.030(85.7) | 0.022(89.5) |
| 75 | 0.233 | 0.082(64.8) | 0.061(73.8) | 0.048(79.4) | 0.040(82.8) | 0.033(85.8) |
Table 3 Corrosion rates(g·m-2·h-1) of Q235 steel with various concentrations of CDDA in condensate water under preset temperatures along with the corresponding corrosion efficiencies(ηw, %) in the brackets
| Temperature/℃ | c(CDDA)/(mol·L-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.05 | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 1 | |
| 35 | 0.118 | 0.021(82.2) | 0.013(89.0) | 0.011(90.7) | 0.009(92.4) | 0.007(94.1) |
| 45 | 0.153 | 0.030(80.4) | 0.021(86.3) | 0.016(89.5) | 0.013(91.5) | 0.010(93.5) |
| 55 | 0.202 | 0.055(72.8) | 0.044(78.2) | 0.028(86.1) | 0.021(89.6) | 0.018(91.1) |
| 65 | 0.210 | 0.064(69.5) | 0.052(75.2) | 0.041(80.5) | 0.030(85.7) | 0.022(89.5) |
| 75 | 0.233 | 0.082(64.8) | 0.061(73.8) | 0.048(79.4) | 0.040(82.8) | 0.033(85.8) |
| c(CDDA)/(mmol·L-1) | Ecorr/mV | Jcorr/(μA·cm-2) | βa/(mV·dec-1) | βc/(mV·dec-1) | ηp(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -538.02 | 29.89 | 69.28 | -504.45 | —— |
| 0.05 | -495.82 | 4.90 | 222.47 | -462.29 | 83.6 |
| 0.1 | -490.06 | 2.36 | 253.04 | -484.93 | 92.1 |
| 0.3 | -492.89 | 2.01 | 252.97 | -481.25 | 93.3 |
| 0.6 | -478.53 | 1.94 | 258.49 | -478.06 | 93.5 |
| 1 | -462.73 | 1.88 | 251.29 | -479.89 | 93.7 |
Table 4 Electrochemical parameters and inhibition efficiencies for Q235 steel derived from cathodic and anodic polarization measurements
| c(CDDA)/(mmol·L-1) | Ecorr/mV | Jcorr/(μA·cm-2) | βa/(mV·dec-1) | βc/(mV·dec-1) | ηp(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -538.02 | 29.89 | 69.28 | -504.45 | —— |
| 0.05 | -495.82 | 4.90 | 222.47 | -462.29 | 83.6 |
| 0.1 | -490.06 | 2.36 | 253.04 | -484.93 | 92.1 |
| 0.3 | -492.89 | 2.01 | 252.97 | -481.25 | 93.3 |
| 0.6 | -478.53 | 1.94 | 258.49 | -478.06 | 93.5 |
| 1 | -462.73 | 1.88 | 251.29 | -479.89 | 93.7 |
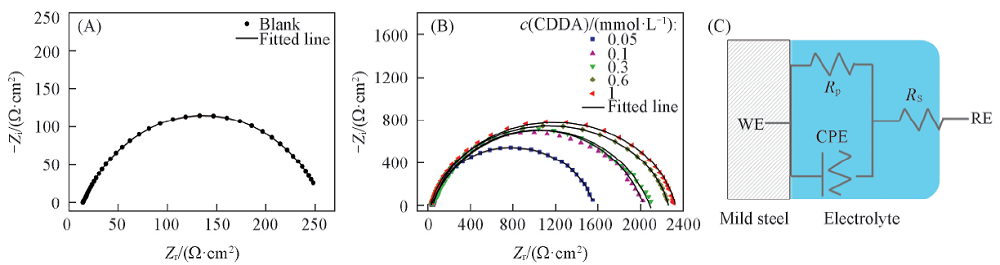
Fig.4 Impedance spectra for Q235 steel in the condensate water at 35 ℃ without(A) and with(B) various concentrations of CDDA in Nyquist form along with the equivalent electric circuit(C)WE: working electrode; RE: reference electrode.
| c(CDDA)/(mmol·L-1) | Rp/(Ω·cm2) | Cdl/(μF·cm-2) | n | ηE(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 255.21 | 223.53 | 0.79 | 243.93 | —— |
| 0.05 | 1589.18 | 83.55 | 0.82 | 1598.41 | 84.7 |
| 0.1 | 1999.30 | 72.18 | 0.77 | 2003.76 | 87.8 |
| 0.3 | 2060.62 | 50.49 | 0.80 | 2079.39 | 88.3 |
| 0.6 | 2265.85 | 30.42 | 0.81 | 2289.16 | 89.3 |
| 1 | 2330.47 | 27.40 | 0.83 | 2358.32 | 89.7 |
Table 5 Impedance parameters for Q235 steel in the condensate water with various concentrations of CDDA
| c(CDDA)/(mmol·L-1) | Rp/(Ω·cm2) | Cdl/(μF·cm-2) | n | ηE(%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 255.21 | 223.53 | 0.79 | 243.93 | —— |
| 0.05 | 1589.18 | 83.55 | 0.82 | 1598.41 | 84.7 |
| 0.1 | 1999.30 | 72.18 | 0.77 | 2003.76 | 87.8 |
| 0.3 | 2060.62 | 50.49 | 0.80 | 2079.39 | 88.3 |
| 0.6 | 2265.85 | 30.42 | 0.81 | 2289.16 | 89.3 |
| 1 | 2330.47 | 27.40 | 0.83 | 2358.32 | 89.7 |
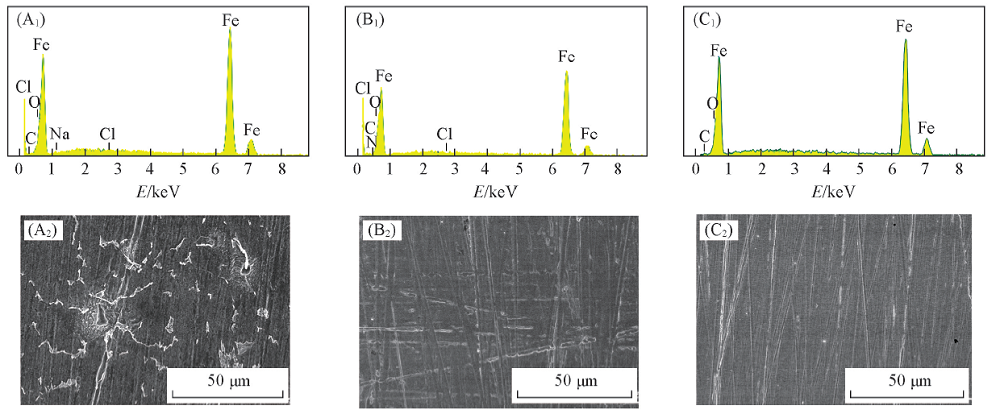
Fig.5 EDX spectra(A1—C1) and surface morphologies(A2—C2) of Q235 steel before and after immersion in condensate water for 72 h (A1, A2) Without CDDA; (B1, B2) with 1 mmol/L CDDA; (C1, C2) freshly polished.
Fig.6 Two-dimension AFM images(A1—C1) and sectional analyses(A2—C2) of Q235 steel surface before and after immersion in condensate water at 35 ℃ for 72 h(A1, A2) Without inhibitor; (B1, B2) with 1 mmol/L CDDA; (C1, C2) freshly polished.
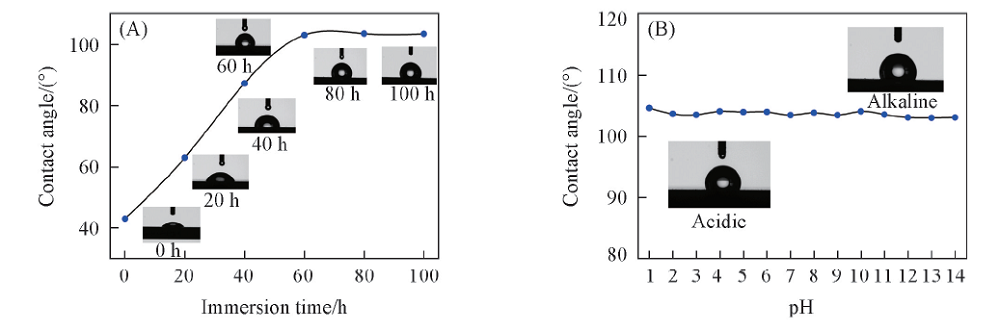
Fig.7 Variation of contact angles for Q235 steel after immersion in condensate water containing 1 mmol/L CDDA with different time(A) and under different pH values after 72 h immersion(B)
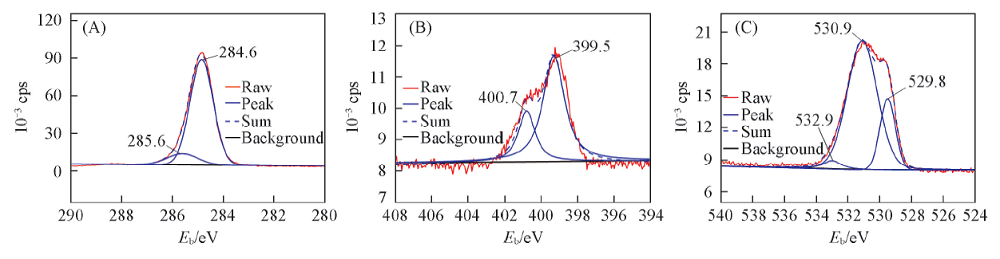
Fig.8 XPS deconvoluted spectra of major elements on Q235 steel after immersion in condensate water with 1 mmol/L CDDA at 35 ℃ for 72 h(A) C1s; (B) N1s; (C) O1s.
| Atom | Atom | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.019 | 0.004 | C11 | 0.022 | 0.005 |
| C2 | 0.010 | 0 | C12 | 0.023 | 0.008 |
| C3 | 0.019 | 0.001 | C13 | 0.030 | 0.011 |
| C4 | 0.024 | 0.002 | C14 | 0.031 | 0.017 |
| C5 | 0.028 | 0 | C15 | 0.032 | 0.025 |
| C6 | 0.027 | 0.002 | C16 | 0.059 | 0.038 |
| C7 | 0.027 | 0.001 | C17 | 0.091 | 0.058 |
| C8 | 0.026 | 0.002 | C18 | 0.121 | 0.223 |
| C9 | 0.013 | 0.003 | N19 | 0.015 | 0.367 |
| C10 | 0.022 | 0.004 |
Table 6 Condensed Fukui indices of ODA*
| Atom | Atom | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 0.019 | 0.004 | C11 | 0.022 | 0.005 |
| C2 | 0.010 | 0 | C12 | 0.023 | 0.008 |
| C3 | 0.019 | 0.001 | C13 | 0.030 | 0.011 |
| C4 | 0.024 | 0.002 | C14 | 0.031 | 0.017 |
| C5 | 0.028 | 0 | C15 | 0.032 | 0.025 |
| C6 | 0.027 | 0.002 | C16 | 0.059 | 0.038 |
| C7 | 0.027 | 0.001 | C17 | 0.091 | 0.058 |
| C8 | 0.026 | 0.002 | C18 | 0.121 | 0.223 |
| C9 | 0.013 | 0.003 | N19 | 0.015 | 0.367 |
| C10 | 0.022 | 0.004 |
| [1] | Fan B. M., Wei B. Y., Hao H., Feng Y. H., Yang B., Mater. Sci. Forum,2018, 913, 424—438 |
| [2] | Fan B. M., Wei G., Zhang Z., Qiao N., Corros. Sci., 2014, 83, 75—85 |
| [3] | Zhu Y., Free M. L., Woollam R., Durnie W., Prog. Mater. Sci., 2017, 90, 159—223 |
| [4] | Cao S. A., Hu J. Y., Xie J. L., Liang Q. Q., Yin L., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater., 2013, 60(1), 14—19 |
| [5] | Kolesnichenko I. V., Anslyn E. V., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2017, 46(9), 2385—2390 |
| [6] | Fang R. C., Zhang H. C., Yang L. L., Wang H. T., Tian Y., Zhang X., Jiang L., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(50), 16372—16379 |
| [7] | Yu H., Li C., Yuan B., Li L., Wang C., Corros. Sci., 2017, 120, 231—238 |
| [8] | Yang L. H., Wan Y. X., Qin Z. L., Xu Q. J., Min Y. L., Corros. Sci., 2018, 130, 85—94 |
| [9] | Fan B. M., Wei G., Zhang Z., Qiao N., Anti-Corros. Methods Mater.,2014, 61(2), 104—111 |
| [10] | Chasoglou D., Hryha E., Norell M., Nyborg L., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 268, 496—506 |
| [11] | Solomon M. M., Gerengi H., Umoren S. A., Essien N. B., Essien U. B., Kaya E., Carbohyd. Polym., 2018, 181, 43—55 |
| [12] | Obot I. B., Macdonald D. D., Gasem Z. M., Corros.Sci., 2015, 99, 1—30 |
| [13] | Feng X. G., Lu X. Y., Zuo Y., Zhuang N., Chen D., Corros.Sci., 2016, 103, 223—229 |
| [14] | Wang T. Y., Zou C. J., Li D. X., Chen Z. L., Liu Y., Li X. K., Li M., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2015, 31(12), 2294—2302 |
| (王太杨, 邹长军, 李代禧, 陈正隆, 刘圆, 李小可, 李明. 物理化学学报, 2015, 31(12), 2294—2302) | |
| [15] | Kannan P., Rao T. S., Rajendran N., J. Colloid Interf. Sci.,2018, 512, 618—628 |
| [16] | Liu L. F., Liu J. X., Zhang J., You L., Yu L. J., Qiao G. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(3), 537—541 |
| (刘林法, 刘金祥, 张军, 尤龙, 于立军, 乔贵民. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(3), 537—541) | |
| [17] | Kan W. H., Chen L. R., Jiang Q. H., Wang Z., Surf. Tech.,2015, 44(4), 127—131 |
| (阚伟海, 陈莉荣, 姜庆宏, 王哲. 表面技术, 2015, 44(4), 127—131) | |
| [18] | He Z.G., Technology of Cyclodextrin Inclusion, People’s Medical Publishing House, Beijing, 2007, 24 |
| (何仲贵. 环糊精包合物技术, 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2007, 24) | |
| [19] | Al Omari M. M., Zughul M. B., Davies J. E. D., Badwan A. A., J. Solution Chem., 2009, 38(6), 669—683 |
| [20] | Tian H. W., Li W. H., Hou B. R., Wang D. P., Corros. Sci., 2017, 117, 43—58 |
| [21] | Messali M., Larouj M., Lgaz H., Rezki N., Al-Blewi F. F., Aouad M. R., Chaouiki A., Salghi R., Chung I. M., J. Mol. Struct., 2018, 1168, 39—48 |
| [22] | Sigircik G., Yildirim D., Tuken T., Corros. Sci., 2017, 120, 184—193 |
| [23] | Shaban S. M., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(46), 39784—39800 |
| [24] | Zhang C., Zhao J. M., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2014, 30(4), 677—685 |
| (张晨, 赵景茂. 物理化学学报, 2014, 30(4), 677—685) | |
| [25] | Tian H. W., Li W. H., Liu A., Gao X., Han P., Ding R., Yang C. Z., Wang D. P., Corros. Sci., 2018, 131, 1—16 |
| [26] | Hsu C. H., Mansfeld F., Corrosion,2001, 57(9), 747—748 |
| [27] | Mendonca G. L. F., Costa S. N., Freire V. N., Casciano P. N. S., Correia A. N., de Lima-Neto P., Corros. Sci., 2017, 115, 41—55 |
| [28] | Dong S. G., Gao Y. B., Guan Z. C., Wang H. P., Wang X., Du R. G., Song G. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2018, 39(6), 1260—1266 |
| (董士刚, 高颖波, 官自超, 王海鹏, 王霞, 杜荣归, 宋光铃. 高等学校化学学报. 2018, 39(6), 1260—1266) | |
| [29] | Zhang D. Q., Tang Y. M., Qi S. J., Dong D. W., Cang H., Lu G., Corros. Sci, 2016, 102, 517—522 |
| [30] | Hassan M. M., Barker H., Collie S., Prog. Org. Coat., 2015, 78, 249—255 |
| [31] | Hu K., Zhuang J., Ding J. T., Ma Z., Wang F., Zeng X. G., Corros. Sci., 2017, 125, 68—76 |
| [32] | Zarrouk A., Hammouti B., Lakhlifi T., Traisnel M., Vezin H., Bentiss F., Corros. Sci., 2015, 90, 572—584 |
| [33] | Benali O., Larabi L., Traisnel M., Gengembre L., Harek Y., Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253(14), 6130—6139 |
| [34] | Gao X., Zhao C. C., Lu H. F.,Gao F, Ma H.Y., Electrochim. Acta,2014, 150, 188—196 |
| [35] | Xu C. H., Wang J. C., Wan L., Lin J. J., Wang X. B., J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21(28), 10463—10471 |
| [36] | Jamil D. M., Al-Okbi A. K., Al-Baghdadi S. B., Al-Amiery A. A., Kadhim A., Gaaz T. S., Kadhum A. A. H., Mohamad A. B., Chem. Cent. J., 2018, 12(1), 7—15 |
| [37] | Avazbaeva Z., Sung W., Lee J., Phan M. D., Shin K., Vaknin D., Kim D., Langmuir,2015, 31(51), 13753—13758 |
| [1] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | 曾晛阳, 赵熹, 黄旭日. 细胞松弛素B对葡萄糖/质子共转运蛋白GlcPSe的抑制机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | 刘嘉欣, 闵杰, 许华杰, 任海生, 谈宁馨. 基于反应力场分子模拟的乙烯燃烧自由基与氮气相互作用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [4] | 陈瀚翔, 边绍菊, 胡斌, 李武. LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O溶液体系渗透压的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [5] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [6] | 张伶育, 张继龙, 曲泽星. RDX分子内振动能量重分配的动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [7] | 雷晓彤, 金怡卿, 孟烜宇. 基于分子模拟方法预测PIP2在双孔钾通道TREK-1上结合位点的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [8] | 李聪聪, 刘明皓, 韩佳睿, 朱镜璇, 韩葳葳, 李婉南. 基于分子动力学模拟的VmoLac非特异性底物催化活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [9] | 刘沙沙, 张恒, 苑世领, 刘成卜. 脉冲电场O/W乳状液破乳的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [10] | 曾永辉, 言天英. 质子水合结构的振动态密度分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [11] | 刘爱清, 徐文生, 徐晓雷, 陈继忠, 安立佳. 高分子/棒状纳米粒子复合物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| [12] | 齐人睿, 李明昊, 常浩, 付学奇, 高波, 韩葳葳, 韩璐, 李婉南. 基于拉伸分子动力学模拟的黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制剂解离途径的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [13] | 李康明, 李延赛, 易阳杰, 徐雷涛, 叶姣, 欧晓明, 李建明, 胡艾希. 5-吡唑甲酰胺类衍生物的设计、 合成与生物活性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 716. |
| [14] | 肖宇情,李申慧,汤晶,徐君,邓风. 金属有机框架材料的结构、 动力学行为和主客体相互作用的固体核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(2): 204. |
| [15] | 朱玉荃, 赵晓婕, 钟嫄, 陈子茹, 鄢红, 段雪. 类水滑石材料主客体插层结构的构筑及特性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(11): 2287. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||