

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (3): 559.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150605
刘强1, 肖继军1( ), 张将1, 赵峰2, 何正华2, 肖鹤鸣1(
), 张将1, 赵峰2, 何正华2, 肖鹤鸣1( )
)
收稿日期:2015-07-31
出版日期:2016-03-10
发布日期:2016-01-24
基金资助:
LIU Qiang1, XIAO Jijun1,*( ), ZHANG Jiang1, ZHAO Feng2, HE Zhenghua2, XIAO Heming1,*(
), ZHANG Jiang1, ZHAO Feng2, HE Zhenghua2, XIAO Heming1,*( )
)
Received:2015-07-31
Online:2016-03-10
Published:2016-01-24
Contact:
XIAO Jijun,XIAO Heming
E-mail:xiao_jijun@njust.edu.cn;xiao@mail.njust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
运用分子动力学(MD)方法, 选择凝聚态分子势能优化力场(COMPASS), 对六硝基六氮杂异伍兹烷(ε-CL-20)、 2,4,6-三硝基甲苯(TNT)晶体及其等摩尔比的CL-20/TNT混合炸药和共晶炸药进行不同温度下恒定粒子数等压等温(NPT)系综模拟研究. 结果表明, CL-20/TNT共晶的内聚能密度(CED)和结合能随温度的升高逐渐减小; 共晶的CED比混合炸药的大, 结合能是混合炸药的2倍多, 预示其稳定性明显增强. 对相关函数和局部放大结构显示共晶中组分分子间作用主要来自TNT中H和CL-20中O以及CL-20中H和TNT中O之间形成的氢键. 通过波动法求得的弹性力学性能结果表明, CL-20/TNT共晶的拉伸模量(E)、 体积模量(K)和剪切模量(G)介于ε-CL-20和TNT晶体之间, 且随温度的升高而下降, 符合一般预期; 但共晶炸药的柯西压(C12-C44, Cij弹性系数)、 K/G和泊松比(ν)均比其组分炸药ε-CL-20和TNT高得多, 预示该共晶具有异常高的延展性和弹性伸长, 主要是二组分呈层状交替排列且之间存在较强相互作用所致.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
刘强, 肖继军, 张将, 赵峰, 何正华, 肖鹤鸣. CL-20/TNT共晶炸药的分子动力学研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(3): 559.
LIU Qiang, XIAO Jijun, ZHANG Jiang, ZHAO Feng, HE Zhenghua, XIAO Heming. Molecular Dynamics Simulation on CL-20/TNT Cocrystal Explosive†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3): 559.
| T/K | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 | 0.935 | 1.958 | 2.470 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.94 | 4.521 |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.18) | (0.14) | (0.13) | (0.01) | (0.011) | |
| 195 | 0.872 | 2.216 | 2.452 | 90.02 | 90.02 | 89.99 | 1.86 | 4.739 |
| (0.014) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.36) | (0.25) | (0.22) | (0.01) | (0.016) | |
| 245 | 0.878 | 2.210 | 2.462 | 90.01 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.85 | 4.775 |
| (0.003) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.42) | (0.27) | (0.25) | (0.01) | (0.179) | |
| 295 | 0.882 | 2.208 | 2.473 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.84 | 4.815 |
| (0.007) | (0.020) | (0.010) | (0.44) | (0.31) | (0.31) | (0.01) | (0.023) | |
| 345 | 0.886 | 2.211 | 2.483 | 89.99 | 89.99 | 90.00 | 1.82 | 4.860 |
| (0.008) | (0.021) | (0.011) | (0.49) | (0.34) | (0.33) | (0.01) | (0.024) | |
| 395 | 0.892 | 2.212 | 2.491 | 90.02 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.80 | 4.912 |
| (0.009) | (0.024) | (0.012) | (0.53) | (0.37) | (0.36) | (0.01) | (0.027) | |
| Exp.[ | 0.967 | 1.937 | 2.469 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.91 | 4.626 |
Table 1 Primitive lattice parameters, cell densities and volumes of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures*
| T/K | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | ρ/(g·cm-3) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 95 | 0.935 | 1.958 | 2.470 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.94 | 4.521 |
| (0.004) | (0.009) | (0.005) | (0.18) | (0.14) | (0.13) | (0.01) | (0.011) | |
| 195 | 0.872 | 2.216 | 2.452 | 90.02 | 90.02 | 89.99 | 1.86 | 4.739 |
| (0.014) | (0.011) | (0.007) | (0.36) | (0.25) | (0.22) | (0.01) | (0.016) | |
| 245 | 0.878 | 2.210 | 2.462 | 90.01 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.85 | 4.775 |
| (0.003) | (0.005) | (0.009) | (0.42) | (0.27) | (0.25) | (0.01) | (0.179) | |
| 295 | 0.882 | 2.208 | 2.473 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.84 | 4.815 |
| (0.007) | (0.020) | (0.010) | (0.44) | (0.31) | (0.31) | (0.01) | (0.023) | |
| 345 | 0.886 | 2.211 | 2.483 | 89.99 | 89.99 | 90.00 | 1.82 | 4.860 |
| (0.008) | (0.021) | (0.011) | (0.49) | (0.34) | (0.33) | (0.01) | (0.024) | |
| 395 | 0.892 | 2.212 | 2.491 | 90.02 | 90.01 | 90.00 | 1.80 | 4.912 |
| (0.009) | (0.024) | (0.012) | (0.53) | (0.37) | (0.36) | (0.01) | (0.027) | |
| Exp.[ | 0.967 | 1.937 | 2.469 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 90.00 | 1.91 | 4.626 |
| Sample | T/K | vdW energy/(kJ·cm-3) | Electrostatic energy/(kJ·cm-3) | CED/(kJ·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 0.37(0.01) | 0.54(0.01) | 0.91(0.01) |
| 245 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.52(0.01) | 0.88(0.01) | |
| 295 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.50(0.01) | 0.86(0.01) | |
| 345 | 0.35(0.00) | 0.48(0.01) | 0.83(0.01) | |
| 395 | 0.34(0.00) | 0.47(0.01) | 0.81(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 0.31(0.01) | 0.45(0.01) | 0.76(0.01) |
Table 2 Cohesive energy density(CED) and its components of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures and CL-20/TNT composite at 295 K*
| Sample | T/K | vdW energy/(kJ·cm-3) | Electrostatic energy/(kJ·cm-3) | CED/(kJ·cm-3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 0.37(0.01) | 0.54(0.01) | 0.91(0.01) |
| 245 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.52(0.01) | 0.88(0.01) | |
| 295 | 0.36(0.00) | 0.50(0.01) | 0.86(0.01) | |
| 345 | 0.35(0.00) | 0.48(0.01) | 0.83(0.01) | |
| 395 | 0.34(0.00) | 0.47(0.01) | 0.81(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 0.31(0.01) | 0.45(0.01) | 0.76(0.01) |
| Sample | T/K | Ebind/ (kJ·mol-1) | Nonbond energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | vdW energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Repulsive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Dispersive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Electrostatic energy/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 178.90(0.37) | 178.90(0.37) | 65.73(0.21) | -181.76(0.77) | 247.48(0.65) | 113.17(0.39) |
| 245 | 176.77(0.26) | 176.77(0.26) | 65.94(0.24) | -178.47(0.60) | 244.41(0.63) | 110.83(0.31) | |
| 295 | 174.19(0.30) | 174.19(0.44) | 65.50(0.39) | -176.72(1.32) | 242.22(1.02) | 108.69(0.64) | |
| 345 | 169.43(0.42) | 169.43(0.42) | 64.78(0.26) | -170.80(0.99) | 235.58(0.82) | 104.65(0.34) | |
| 395 | 166.18(0.65) | 166.18(0.65) | 63.82(0.39) | -166.96(1.05) | 230.78(0.85) | 102.36(0.39) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 75.27(0.42) | 75.27(0.42) | 29.66(0.19) | -74.03(0.62) | 103.69(0.68) | 45.61(0.29) |
Table 3 Binding energy and its components of CL-20/TNT cocrystal at different temperatures and CL-20/TNT composite at 295 K*
| Sample | T/K | Ebind/ (kJ·mol-1) | Nonbond energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | vdW energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Repulsive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Dispersive energy/ (kJ·mol-1) | Electrostatic energy/ (kJ·mol-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CL-20/TNT cocrystal | 195 | 178.90(0.37) | 178.90(0.37) | 65.73(0.21) | -181.76(0.77) | 247.48(0.65) | 113.17(0.39) |
| 245 | 176.77(0.26) | 176.77(0.26) | 65.94(0.24) | -178.47(0.60) | 244.41(0.63) | 110.83(0.31) | |
| 295 | 174.19(0.30) | 174.19(0.44) | 65.50(0.39) | -176.72(1.32) | 242.22(1.02) | 108.69(0.64) | |
| 345 | 169.43(0.42) | 169.43(0.42) | 64.78(0.26) | -170.80(0.99) | 235.58(0.82) | 104.65(0.34) | |
| 395 | 166.18(0.65) | 166.18(0.65) | 63.82(0.39) | -166.96(1.05) | 230.78(0.85) | 102.36(0.39) | |
| CL-20/TNT composite | 295 | 75.27(0.42) | 75.27(0.42) | 29.66(0.19) | -74.03(0.62) | 103.69(0.68) | 45.61(0.29) |
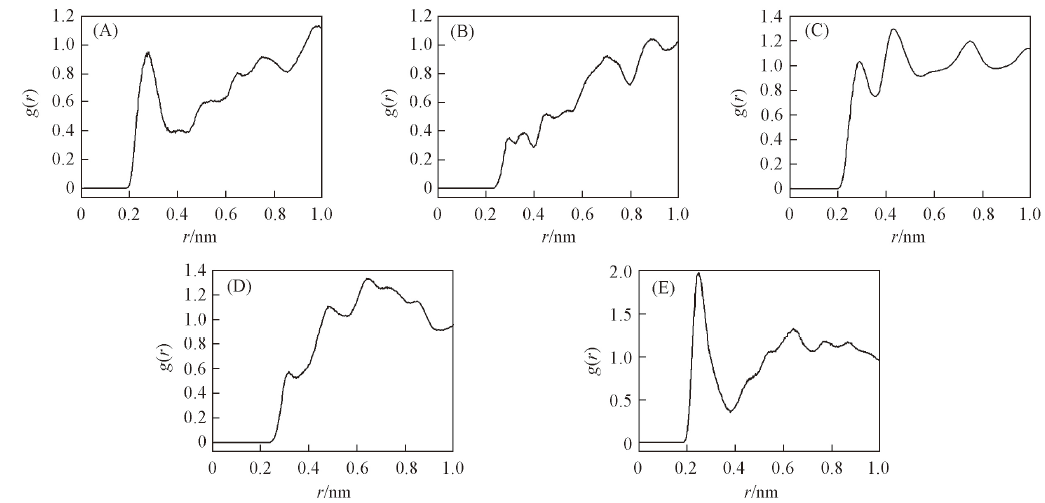
Fig.4 g(r)-r curves of H-O pairs and H-N pairs among CL-20 molecules and between CL-20 and TNT molecules in cocrystal (A) H(2)-O(2); (B) H(2)-N(2); (C) H(1)-O(2); (D) H(1)-N(2); (E) H(2)-O(1).
| Sample | T/K | Mechanical modulus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-C44/GPa | E/GPa | K/GPa | G/GPa | ν | K/G | ||
| ε-CL-20 | 195 | -6.30(0.14) | 19.50(0.08) | 11.44(0.06) | 8.02(0.03) | 0.22(0.00) | 1.43(0.03) |
| 245 | -5.64(0.21) | 18.47(0.09) | 11.30(0.08) | 7.52(0.05) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 295 | -5.08(0.11) | 17.11(0.02) | 10.46(0.08) | 6.96(0.01) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 345 | -5.23(0.10) | 15.93(0.24) | 9.78(0.06) | 6.49(0.11) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.04) | |
| 395 | -4.32(0.07) | 14.93(0.04) | 9.17(0.05) | 6.08(0.02) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT | 195 | 6.49(0.11) | 7.57(0.06) | 9.38(0.09) | 2.77(0.03) | 0.37(0.00) | 3.39(0.05) |
| 245 | 6.26(0.07) | 6.30(0.06) | 8.94(0.07) | 2.28(0.02) | 0.38(0.00) | 3.92(0.06) | |
| 295 | 5.50(0.04) | 5.65(0.07) | 8.20(0.05) | 2.04(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.02(0.06) | |
| 345 | 4.93(0.06) | 5.10(0.14) | 7.59(0.05) | 1.84(0.05) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.14(0.13) | |
| 395 | 4.32(0.06) | 4.58(0.08) | 6.84(0.04) | 1.65(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.15(0.08) | |
| TNT | 195 | -1.51(0.07) | 7.13(0.03) | 7.00(0.04) | 2.68(0.01) | 0.33(0.00) | 2.61(0.02) |
| 245 | -1.47(0.10) | 5.99(0.05) | 6.08(0.08) | 2.24(0.02) | 0.34(0.00) | 2.71(0.02) | |
| 295 | 0.37(0.06) | 5.50(0.04) | 5.99(0.02) | 2.04(0.02) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.93(0.03) | |
| 345 | 0.84(0.14) | 5.43(0.03) | 5.98(0.12) | 2.01(0.01) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.97(0.05) | |
| 395 | |||||||
Table 4 Mechanical properties for ε-CL-20 crystal, CL-20/TNT cocrystal and TNT crystal at different temperatures*
| Sample | T/K | Mechanical modulus | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C12-C44/GPa | E/GPa | K/GPa | G/GPa | ν | K/G | ||
| ε-CL-20 | 195 | -6.30(0.14) | 19.50(0.08) | 11.44(0.06) | 8.02(0.03) | 0.22(0.00) | 1.43(0.03) |
| 245 | -5.64(0.21) | 18.47(0.09) | 11.30(0.08) | 7.52(0.05) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 295 | -5.08(0.11) | 17.11(0.02) | 10.46(0.08) | 6.96(0.01) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.50(0.02) | |
| 345 | -5.23(0.10) | 15.93(0.24) | 9.78(0.06) | 6.49(0.11) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.04) | |
| 395 | -4.32(0.07) | 14.93(0.04) | 9.17(0.05) | 6.08(0.02) | 0.23(0.00) | 1.51(0.01) | |
| CL-20/TNT | 195 | 6.49(0.11) | 7.57(0.06) | 9.38(0.09) | 2.77(0.03) | 0.37(0.00) | 3.39(0.05) |
| 245 | 6.26(0.07) | 6.30(0.06) | 8.94(0.07) | 2.28(0.02) | 0.38(0.00) | 3.92(0.06) | |
| 295 | 5.50(0.04) | 5.65(0.07) | 8.20(0.05) | 2.04(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.02(0.06) | |
| 345 | 4.93(0.06) | 5.10(0.14) | 7.59(0.05) | 1.84(0.05) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.14(0.13) | |
| 395 | 4.32(0.06) | 4.58(0.08) | 6.84(0.04) | 1.65(0.03) | 0.39(0.00) | 4.15(0.08) | |
| TNT | 195 | -1.51(0.07) | 7.13(0.03) | 7.00(0.04) | 2.68(0.01) | 0.33(0.00) | 2.61(0.02) |
| 245 | -1.47(0.10) | 5.99(0.05) | 6.08(0.08) | 2.24(0.02) | 0.34(0.00) | 2.71(0.02) | |
| 295 | 0.37(0.06) | 5.50(0.04) | 5.99(0.02) | 2.04(0.02) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.93(0.03) | |
| 345 | 0.84(0.14) | 5.43(0.03) | 5.98(0.12) | 2.01(0.01) | 0.35(0.00) | 2.97(0.05) | |
| 395 | |||||||
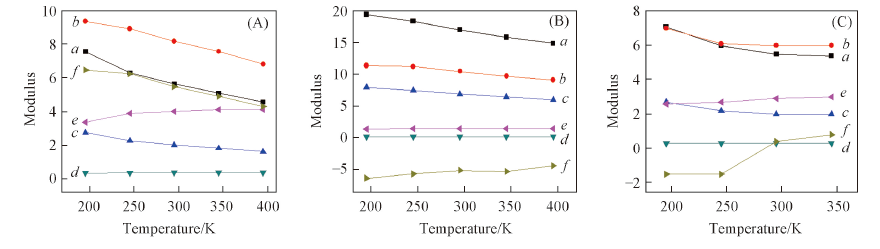
Fig.8 Mechanical properties of CL-20/TNT cocrystal(A), ε-CL-20(B) and TNT(C) crystals vs. temperatureModulus: a. E/GPa; b. K/GPa; c. G/GPa; d. ν; e. K/G; f. C12-C44/GPa.
| [1] | Lara O. F., Espinosa P. G., Supramolecular Chemistry, 2007, 19(8), 553—557 |
| [2] | Stahly G. P., Crystal Growth and Design, 2009, 9(10), 4212—4229 |
| [3] | Ji B. M., Deng D. S., Ma N., Miao S.B., Liu P., Li X. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9), 2114—2122 |
| (吉保明, 邓冬生, 马宁, 苗少斌, 刘鹏, 李贤飞. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(9), 2114—2122) | |
| [4] | Chen J. M., Wu C. B., Lu T. B., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2011, 32(9), 1996—2009 |
| (陈嘉媚, 吴传斌, 鲁统部. 高等学校化学学报, 2011, 32(9), 1996—2009) | |
| [5] | Michael L., Propellant Made with Cocrystals of Cyclotetramethy Lenetetramine and AmmoniumPerchlorate,US 4086110, 1978-04-25 |
| [6] | Levakova I. V., Korobko A. P., Krasheninnikov S. V., Zavodnik V. E., Kristallografiya,1996, 41(6), 963—965 |
| [7] | Jin P. S., Xiao H. D., Qing P. L., Yong Z., Qiao L. B., Yong J. L., Chong H. P., Crystal Growth and Design,2011, 11, 1759—1765 |
| [8] | Wei C. X., Duan X. H., Liu C. J., Liu Y G., Li J. S., Acta Chim. Sinica, 2009, 67(24), 2822—2826 |
| (卫春雪, 段晓惠, 刘成建, 刘永刚, 李金山. 化学学报, 2009, 67(24), 2822—2826) | |
| [9] | Guo C. Y., Zhang H. B., Wang X. C., Sun J., Materials Review, 2012, 26(19), 49—53 |
| (郭长艳, 张浩斌, 王晓川, 孙杰. 材料导报, 2012, 26(19), 49—53) | |
| [10] | Bolton O., Matzger A. J., Angew. Chem. Inter. Ed., 2011, 50(38), 8960—8963 |
| [11] | Yang Z. W., Zhang Y. L., Li H. Z., Zhou X. Q., Nie F. D., Li J. S., Huang H., Chin. J. Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(6), 674—679 |
| (杨宗伟, 张艳丽, 李洪珍, 周小青, 聂福德, 李金山, 黄辉. 含能材料. 2012, 20(6), 674—679) | |
| [12] | Yang Z. W, Huang H., Li H. Z., Zhou X. Q., Li J. S., Nie F. D., Chin. J. Energetic Materials, 2012, 20(2), 256—257 |
| (杨宗伟, 黄辉, 李洪珍, 周小清, 李金山, 聂福德. 含能材料. 2012, 20(2), 256—257) | |
| [13] | Yang Z. W., Li H. Z., Huang H., Zhou X. Q., Li J. S., Nie F. D., Propellants, Explosives Pyrotechnics, 2013, 38(4), 495—501 |
| [14] | Aldoshin S. M., Aliev Z. G., Goncharov T. K., Kazakov A. I., Milekhin Yu. M., Plishkin N. A., Shishov N. I. Russ. Chem. Bull., Int.Ed..2013, 62(6), 1354—1360 |
| [15] | Liu H., Li Q. K., He Y. H., Acta Physica Sinica, 2013, 62(20), 208202 |
| (刘海, 李启楷, 何远航. 物理学报, 2013, 62(20), 208202) | |
| [16] | Ou Y. X., Meng Z., Liu J. Q., Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2007, 26(12), 1690—1694 |
| (欧育湘, 孟征, 刘进全. 化工进展. 2007, 26(12), 1690—1694) | |
| [17] | Xiao H.M., Xu X, J., Qiu L., The Theoretical Design of High Energy Density Material, Science Press, Beijing, 2008, 19—32 |
| (肖鹤鸣, 许晓娟, 邱玲. 高能量密度材料的理论设计, 北京: 科学出版社, 2008, 19—32) | |
| [18] | Xu X. J., Xiao H. M., Ju X. H., Gong X. D., Chinese Journal of Organic Chemistry,2005, 25(5), 536—539 |
| (许晓娟, 肖鹤鸣, 居学海, 贡雪东. 有机化学, 2005, 25(5), 536—539) | |
| [19] | Agrawal J. P., Propellants,Explosives,Pyrotechnics.2005, 30(5), 316—328 |
| [20] | Foltz M. F., Coon C. L., Garcia F., Nichols A. L., Propellants, Explosives Pyrotechnics, 1994, 19(1), 19—25 |
| [21] | Sun H., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(38), 7338—7364 |
| [22] | Xu X. J., Xiao H. M., Xiao J. J., Zhu W., Huang H., Li J. S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(14), 7203—7207 |
| [23] | Xu X. J., Xiao J. J., Huang H., Li J. S., Xiao H. M., Science in China B, Chemistry,2007, 50(6), 737—745 |
| [24] | Zhou Y., Long X. P., Wei X. W., Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2011, 17(11), 3015—3019 |
| [25] | Zhao X. Q., Shi N. C., Chinese Science Bulletin, 1995, 40(23), 2158—2160 |
| (赵信岐, 施倪承. 科学通报, 1995, 40(23), 2158—2160) | |
| [26] | Vrcelj R. M., Sherwood J. N., Kennedy A. R., Gallagher H. G., Gelbrich T., Crystal Growth and Design,2003, 3(6), 1027—1032 |
| [27] | Andersen H. C., J. Chem. Phys., 1980, 72(4), 2384—2393 |
| [28] | Parrinello M., Rahman A., J. Appl. Phys., 1981, 52, 7182—7190 |
| [29] | Xiao J.J.,Zhu W. H., Zhu W., Xiao H. M., Molecular Dynamics Study on High Energy Materials, Science Press, Beijing, 2013, 54—65 |
| (肖继军, 朱卫华, 朱伟, 肖鹤鸣. 高能材料分子动力学, 北京: 科学出版社, 2013, 54—65) | |
| [30] | Pugh S. F., Philosophical Magazine, 1954, A45, 823—843 |
| [31] | Pettifor D. G., Materials Science and Technology, 1992, 8(4), 345—349 |
| [32] | Xiao J. J., Wang W. R., Chen J., Ji G. F., Zhu W., Xiao H. M., Computational and Theoretical Chemistry, 2012, 999, 21—27 |
| [1] | 高志伟, 李军委, 史赛, 付强, 贾钧儒, 安海龙. 基于分子动力学模拟的TRPM8通道门控特性分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220080. |
| [2] | 曾晛阳, 赵熹, 黄旭日. 细胞松弛素B对葡萄糖/质子共转运蛋白GlcPSe的抑制机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210822. |
| [3] | 刘嘉欣, 闵杰, 许华杰, 任海生, 谈宁馨. 基于反应力场分子模拟的乙烯燃烧自由基与氮气相互作用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210834. |
| [4] | 陈瀚翔, 边绍菊, 胡斌, 李武. LiCl-NaCl-KCl-H2O溶液体系渗透压的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210727. |
| [5] | 张志博, 尚涵, 徐文轩, 韩广东, 崔金声, 杨皓然, 李瑞鑫, 张生辉, 徐欢. 氧化石墨烯插层聚β-羟基丁酸酯复合材料的结晶形态与宏观性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210566. |
| [6] | 胡波, 朱昊辰. 双层氧化石墨烯纳米体系中受限水的介电常数[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [7] | 徐欢, 柯律, 唐梦珂, 尚涵, 徐文轩, 张子林, 付亚男, 韩广东, 崔金声, 杨皓然, 高杰峰, 张生辉, 何新建. 液相剪切原位剥离蒙脱土纳米片增强高阻氧聚乳酸[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220316. |
| [8] | 张伶育, 张继龙, 曲泽星. RDX分子内振动能量重分配的动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220393. |
| [9] | 雷晓彤, 金怡卿, 孟烜宇. 基于分子模拟方法预测PIP2在双孔钾通道TREK-1上结合位点的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2550. |
| [10] | 李聪聪, 刘明皓, 韩佳睿, 朱镜璇, 韩葳葳, 李婉南. 基于分子动力学模拟的VmoLac非特异性底物催化活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2518. |
| [11] | 刘沙沙, 张恒, 苑世领, 刘成卜. 脉冲电场O/W乳状液破乳的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2170. |
| [12] | 曾永辉, 言天英. 质子水合结构的振动态密度分析[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1855. |
| [13] | 王献伟, 柯红军, 袁航, 鲁戈舞, 李丽英, 孟祥胜, 宋书林, 王震. 耐高温可溶性聚酰亚胺树脂及其复合材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [14] | 齐人睿, 李明昊, 常浩, 付学奇, 高波, 韩葳葳, 韩璐, 李婉南. 基于拉伸分子动力学模拟的黄嘌呤氧化酶抑制剂解离途径的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 758. |
| [15] | 刘爱清, 徐文生, 徐晓雷, 陈继忠, 安立佳. 高分子/棒状纳米粒子复合物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(3): 875. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||