

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (2): 292.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20170465
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHAO Guozheng1, FAN Rongrong1, YAN Xilin2,*( ), TANG Wei2, TANG Mingfeng2, JIA Jianfeng1, WU Haishun1
), TANG Wei2, TANG Mingfeng2, JIA Jianfeng1, WU Haishun1
Received:2017-07-14
Online:2018-02-10
Published:2018-01-11
Contact:
YAN Xilin
E-mail:linyxl_306@sina.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHAO Guozheng, FAN Rongrong, YAN Xilin, TANG Wei, TANG Mingfeng, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Periodic DFT Study on Structural Transformations of Crystalline Hydrazinium 5-Nitramino-3,4-dinitropyrazolate Under High Pressures†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 292.
| Method | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | β/(°) | Cell volume/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA/CA-PZ | 0.350(-3.58) | 1.064(-0.56) | 2.218(-2.33) | 92.14(-0.33) | 0.825(-6.36) |
| LDA/CA-PZ-OBS | 0.333(-8.26) | 1.040(-2.80) | 2.161(-4.84) | 88.04(-4.77) | 0.747(-15.21) |
| GGA/PBE | 0.406(11.85) | 1.167(9.07) | 2.392(5.33) | 97.60(5.57) | 1.124(27.58) |
| GGA/PBE-TS | 0.369(1.65) | 1.111(3.83) | 2.327(2.47) | 94.86(2.61) | 0.949(7.72) |
| Exp. | 0.363 | 1.070 | 2.271 | 92.45 | 0.881 |
Table 1 Comparison of relaxed lattice parameters of HNDP with experimental data at ambient conditions*
| Method | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | β/(°) | Cell volume/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA/CA-PZ | 0.350(-3.58) | 1.064(-0.56) | 2.218(-2.33) | 92.14(-0.33) | 0.825(-6.36) |
| LDA/CA-PZ-OBS | 0.333(-8.26) | 1.040(-2.80) | 2.161(-4.84) | 88.04(-4.77) | 0.747(-15.21) |
| GGA/PBE | 0.406(11.85) | 1.167(9.07) | 2.392(5.33) | 97.60(5.57) | 1.124(27.58) |
| GGA/PBE-TS | 0.369(1.65) | 1.111(3.83) | 2.327(2.47) | 94.86(2.61) | 0.949(7.72) |
| Exp. | 0.363 | 1.070 | 2.271 | 92.45 | 0.881 |
| Species | d/nm | Species | Bond angle/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA/CA-PZ | Exp. | LDA/CA-PZ | Exp. | ||
| N6—C2 | 0.136 | 0.136 | C3—C1—N7 | 129.32 | 129.08 |
| C1—C2 | 0.141 | 0.140 | N5—N6—H4 | 119.21 | 123.20 |
| C1—C3 | 0.140 | 0.140 | N13—C2—C1 | 126.27 | 125.86 |
| C3—N5 | 0.132 | 0.131 | O11—N10—C3 | 116.37 | 117.14 |
| N5—N6 | 0.135 | 0.136 | O15—N14—O16 | 121.11 | 119.98 |
Table 2 Experimental and calculated bond lengths and angles for HNDP
| Species | d/nm | Species | Bond angle/(°) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LDA/CA-PZ | Exp. | LDA/CA-PZ | Exp. | ||
| N6—C2 | 0.136 | 0.136 | C3—C1—N7 | 129.32 | 129.08 |
| C1—C2 | 0.141 | 0.140 | N5—N6—H4 | 119.21 | 123.20 |
| C1—C3 | 0.140 | 0.140 | N13—C2—C1 | 126.27 | 125.86 |
| C3—N5 | 0.132 | 0.131 | O11—N10—C3 | 116.37 | 117.14 |
| N5—N6 | 0.135 | 0.136 | O15—N14—O16 | 121.11 | 119.98 |
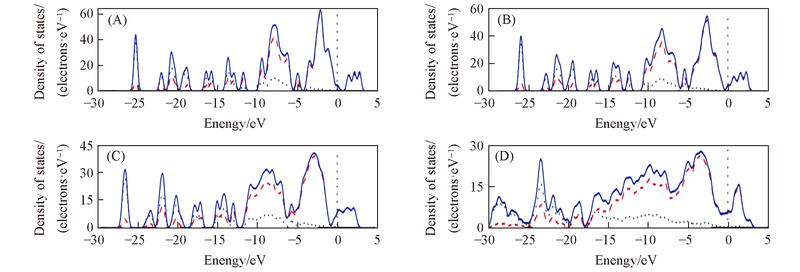
Fig.9 Total DOS of HNDP under different pressuresPressure/Pa: (A) 0; (B) 6; (C) 28; (D) 110. s, p, and total states are shown as dotted, dashed, and solid curves, respectively.
| [1] | Li Y., Huang H. F., Shi Y. M., Yang J., Pan R. M., Lin X. Y., Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23(30), 7353—7360 |
| [2] | Xu Z., Cheng G. B., Yang H. W., Ju X. H., Yin P., Zhang J. H., Shreeve J. M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(21), 5877—5881 |
| [3] | Liu Q., Xiao J. J., Zhang J., Zhao F., He Z. H., Xiao H. M., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(3), 559—566 |
| (刘强, 肖继军, 张将, 赵峰, 何正华, 肖鹤鸣. 高等学校化学学报, 2016,37(3), 559—566) | |
| [4] | Meng L. Y., Lu Z. P., Ma Y., Xue X. G., Nie F. D., Zhang C. Y., Cryst. Growth. Des., 2016, 16(12), 7231—7239 |
| [5] | Qu Y. Y., Zeng Q., Wang J., Ma Q., Li H. Z., Li H. B., Yang G. C., Chem. Eur. J., 2016, 22(35), 12527—12532 |
| [6] | Zhang Q. H., Shreeve J. M., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(20), 10527—10574 |
| [7] | Fischer N., Fischer D., Klapötke T. M., Piercey D. G., Stierstorfer J., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(38), 20418—20422 |
| [8] | Yin P., Parrish D. A., Shreeve J. M., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(14), 4778—4786 |
| [9] | He Z. H., Chen J., Wu Q., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121(15), 8227—8235 |
| [10] | Zhang L., Jiang S. L., Yu Y., Long Y., Zhao H. Y., Peng L. J., Chen J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2016, 120(44), 11510—11522 |
| [11] | Chellappa R. S., Dattelbaum D. M., Coe J. D., Velisavljevic N., Stevens L. L., Liu Z. X., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118(31), 5969—5982 |
| [12] | Wang F., Du H. C., Zhang J. Y., Gong X. D., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(11), 6745—6753 |
| [13] | Wu Q., Zhu W. H., Xiao H. M., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(33), 16830—16839 |
| [14] | Materials Studio 6.0, Accelrys Inc., San Diego, 2012 |
| [15] | Clark S. J., Segall M. D., Pickard C. J., Hasnip P. J., Probert M. J., Refson K., Payne M. C., Z. Kristallogr., 2005, 220(5/6), 567—570 |
| [16] | Vanderbilt D., Phys. Rev. B, 1990, 41(11), 7892—7895 |
| [17] | Kresse G., Furthmuller J., Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54(16), 11169—11186 |
| [18] | Fletcher R., Practical Methods of Optimization, Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1980 |
| [19] | Jeffrey G.A., An Introduction to Hydrogen Bonding, Oxford University Press, New York, 1997 |
| [20] | Segall M. D., Shah R., Pickard C. J., Payne M. C., Phys. Rev. B, 1996, 54(23), 16317—16320 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | TAN Lejian, ZHONG Xuanshu, WANG Jin, LIU Zongjian, ZHANG Aiying, YE Lin, FENG Zengguo. Low Critical Dissolution Temperature Behavior of β⁃Cyclodextrin and Its Application in the Preparation of β⁃Cyclodextrin Sheet Crystal with Ordered Nano⁃channel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [4] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [5] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [6] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [7] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [8] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [9] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [10] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [11] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [12] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| [13] | YING Fuming, JI Chenru, SU Peifeng, WU Wei. λ-DFCAS: A Hybrid Density Functional Complete Active Space Self Consistent Field Method [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2218. |
| [14] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [15] | HU Wei, LIU Xiaofeng, LI Zhenyu, YANG Jinlong. Surface and Size Effects of Nitrogen-vacancy Centers in Diamond Nanowires [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||