

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2014, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (6): 1300.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20131237
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
GUO Sha, WANG Weina*( ), JIN Lingxia, WANG Shuai, WANG Wenliang
), JIN Lingxia, WANG Shuai, WANG Wenliang
Received:2013-12-17
Online:2014-06-10
Published:2014-04-21
Contact:
WANG Weina
E-mail:wangwn@snnu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
GUO Sha, WANG Weina, JIN Lingxia, WANG Shuai, WANG Wenliang. Mechanistic Studies on CH3CH2O+HCHO Reaction and Rate Constants of Major Channel†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014, 35(6): 1300.
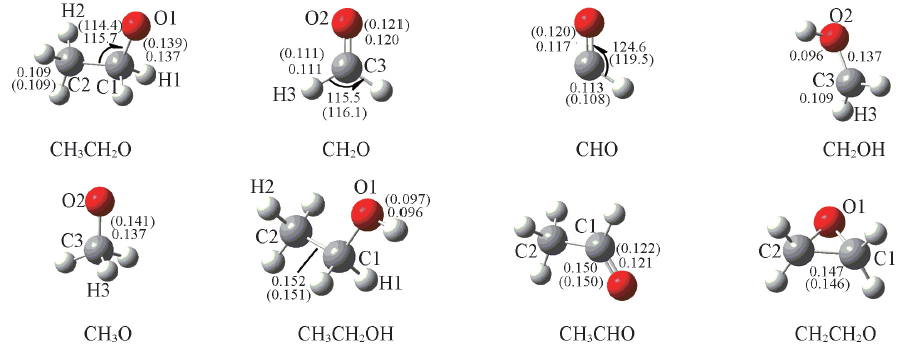
Fig.1 Optimized geometries of the reactants and products of the hydrogen abstraction, at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level Bond lengths(nm) and bond angles(°), the data in the parentheses are experimental values.
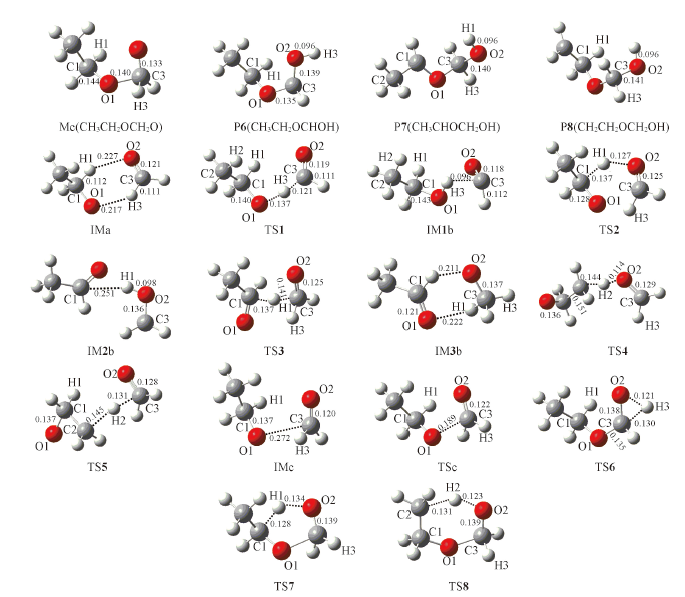
Fig.2 Optimized geometries of intermediates, transition states and the products of the hydrogen migration isomerization at the B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level[bond lengths(nm)]
| Species | Δr | Species | Δr | Species | Δf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | -57.78(-70.50±10.00) | R5 | 103.5(90.67±7.23) | CH3CH2OCH2O | -109.9±4.00 |
| R2 | -34.40 | R6 | -41.48 | CH3CH2OCHOH | -163.8±4.10 |
| R3 | -23.89(-27.40±8.10) | R7 | -20.48 | CH3CHOCH2OH | -142.8±4.00 |
| R4 | 92.95 | R8 | -112.1 | CH2CH2OCH2OH | -234.4±5.00 |
Table 1 Reaction enthalpy(ΔrH298 K0—) for the title reaction, and formation enthalpies (ΔfH(g, M, 298 K)0—) for some species
| Species | Δr | Species | Δr | Species | Δf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | -57.78(-70.50±10.00) | R5 | 103.5(90.67±7.23) | CH3CH2OCH2O | -109.9±4.00 |
| R2 | -34.40 | R6 | -41.48 | CH3CH2OCHOH | -163.8±4.10 |
| R3 | -23.89(-27.40±8.10) | R7 | -20.48 | CH3CHOCH2OH | -142.8±4.00 |
| R4 | 92.95 | R8 | -112.1 | CH2CH2OCH2OH | -234.4±5.00 |
| T/K | kTST | kCVT | kCVT/SCT | T/K | kTST | kCVT | kCVT/SCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 275 | 7.41×10-20 | 1.91×10-20 | 1.43×10-17 | 500 | 3.19×10-17 | 4.15×10-18 | 1.06×10-16 |
| 298 | 2.06×10-19 | 4.86×10-20 | 2.02×10-17 | 550 | 6.54×10-17 | 7.56×10-18 | 1.34×10-16 |
| 325 | 5.66×10-19 | 1.21×10-19 | 2.84×10-17 | 600 | 1.21×10-16 | 1.25×10-17 | 1.64×10-16 |
| 350 | 1.27×10-18 | 2.50×10-19 | 3.73×10-17 | 650 | 2.04×10-16 | 1.92×10-17 | 1.94×10-16 |
| 375 | 2.57×10-18 | 4.67×10-19 | 4.70×10-17 | 700 | 3.25×10-16 | 2.79×10-17 | 2.26×10-16 |
| 400 | 4.78×10-18 | 8.07×10-19 | 5.76×10-17 | 750 | 4.92×10-16 | 3.87×10-17 | 2.59×10-16 |
| 425 | 8.3×10-18 | 1.31×10-18 | 6.90×10-17 | 800 | 7.17×10-16 | 5.17×10-17 | 2.94×10-16 |
| 475 | 2.12×10-17 | 2.93×10-18 | 9.34×10-17 | 1000 | 2.36×10-15 | 1.29×10-16 | 4.49×10-16 |
Table 2 Calculated rate constants kTST, kCVT and kCVT/SCT(cm3·molecule-1·s-1) for major channel R1 in 275—1000 K
| T/K | kTST | kCVT | kCVT/SCT | T/K | kTST | kCVT | kCVT/SCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 275 | 7.41×10-20 | 1.91×10-20 | 1.43×10-17 | 500 | 3.19×10-17 | 4.15×10-18 | 1.06×10-16 |
| 298 | 2.06×10-19 | 4.86×10-20 | 2.02×10-17 | 550 | 6.54×10-17 | 7.56×10-18 | 1.34×10-16 |
| 325 | 5.66×10-19 | 1.21×10-19 | 2.84×10-17 | 600 | 1.21×10-16 | 1.25×10-17 | 1.64×10-16 |
| 350 | 1.27×10-18 | 2.50×10-19 | 3.73×10-17 | 650 | 2.04×10-16 | 1.92×10-17 | 1.94×10-16 |
| 375 | 2.57×10-18 | 4.67×10-19 | 4.70×10-17 | 700 | 3.25×10-16 | 2.79×10-17 | 2.26×10-16 |
| 400 | 4.78×10-18 | 8.07×10-19 | 5.76×10-17 | 750 | 4.92×10-16 | 3.87×10-17 | 2.59×10-16 |
| 425 | 8.3×10-18 | 1.31×10-18 | 6.90×10-17 | 800 | 7.17×10-16 | 5.17×10-17 | 2.94×10-16 |
| 475 | 2.12×10-17 | 2.93×10-18 | 9.34×10-17 | 1000 | 2.36×10-15 | 1.29×10-16 | 4.49×10-16 |
| [1] | Salthammer T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(12), 3320—3327 |
| [2] | Atkinson R., Baulch D. L., Cox R. A., Crowley J. N., Hampson R. F., Hynes R. G., Jenkin M. E., Rossi M. J., Troe J., Atmos. Chem. Phys., 2004, 4(6), 1461—1738 |
| [3] | Gomez A. L., Lewis T. L., Wilkinson S. A., Nizkorodov S. A., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, 42(10), 3582—3587 |
| [4] | Huang S., Shao M., Lu S. H., Liu Y., Chin. Chem. Lett., 2008, 19(5), 573—5769 |
| [5] | Im U., Tayanc M., Yenigun O., Atmos. Res., 2008, 89(4), 382—390 |
| [6] | Wallington T. J., Hurley M. D., Fracheboud J. M., Orlando J. J., Tyndall G. S., Sehested J., Mogelberg T. E., Nielsen O. J., J. Phys. Chem., 1996, 100(46), 18116—18122 |
| [7] | Zhu R. S., Diau E. G. W., Lin M. C., Mebel A. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2001, 105(50), 11249—11259 |
| [8] | Clemitshaw K. C., Williams J., Rattigan O. V., Shallcross D. E., Law K. S., Anthony Cox R., J. Geophys. Res., 1997, 102(2), 117—126 |
| [9] | Leplat N., Dagaut P., Togbe C., Vandooren J., Combust. Flame, 2011, 158(4), 705—725 |
| [10] | Beukes J. A., Anna B. D., Bakken V., Nielsen C. J., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2000, 2(18), 4049—4060 |
| [11] | Bras G. L., Foon R., Combourieu J., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1980, 73(2), 357—361 |
| [12] | Eiteneer B., Yu C. L., Goldenberg M., Frenklach M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 1998, 102(27), 5196—5205 |
| [13] | Frost M. J., Smith I. W. M., J. Chem. Soc. Faraday. Trans., 1990, 86(10), 1751—1756 |
| [14] | Frost M. J., Smith I. W. M., J. Chem. Soc. Faraday. Trans., 1990, 86(10), 1757—1762 |
| [15] | Daele V., Vassalli L., Poulet G., Bras G. L., Int. J. Chem. Kine., 1995, 27(11), 1121—1133 |
| [16] | Setokuchi O., Sato M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106(35), 8124—8132 |
| [17] | Henon E., Bohr F., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2001, 342(5/6), 659—666 |
| [18] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Y., Nanayakkara A., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Revision C.02, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2004 |
| [19] | Anglada J. M., Domingo V. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2005, 109(47), 10786—10794 |
| [20] | Zhang S.W., Truong T. N., VKLab, Version 1.0, University of Utah: Salt Lake City, 2001 |
| [21] | Computational Chemistry Comparison and Benchmark Database, |
| [22] | Lee T. J., Taylor P. R., J. Quantum Chem. Symp., 1989, 36(23), 199—207 |
| [23] | Rienstra-Kiracofe J. C., Allen W. D., Schaefer H. F., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2000, 104(44), 9823—9840 |
| [24] | Gurvich L. V., Veyts I. V., Alcock C. B., Pure. Appl. Chem., 1989, 61(6), 1027—1031 |
| [25] | Ruscic B., Boggs J. E., Burcat A., Csasza A. G., Demaison J., Janoschek R., Martin J. M. L., Morton M. L., Rossi M. J., Stanton J. F., Szalay P. G., Westmoreland P. R., Zabel F., J. Phys. Chem. Ref. Data, 2005, 34(2), 573—655 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | ZHOU Zixuan, YANG Haiyan, SUN Yuhan, GAO Peng. Recent Progress in Heterogeneous Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Methanol [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [3] | YANG Dan, LIU Xu, DAI Yihu, ZHU Yan, YANG Yanhui. Research Progress in Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction Reaction over Gold Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [4] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [5] | SUN Cuihong, LYU Liqiang, LIU Ying, WANG Yan, YANG Jing, ZHANG Shaowen. Mechanism and Kinetics on the Reaction of Isopropyl Nitrate with Cl, OH and NO3 Radicals [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [6] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [7] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [8] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [9] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [10] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [11] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [12] | MENG Fanwei, GAO Qi, YE Qing, LI Chenxi. Potassium Poisoning Mechanism of Cu-SAPO-18 Catalyst for Selective Catalytic Reduction of NOx by Ammonia [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2832. |
| [13] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [14] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [15] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||