

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (1): 70.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190310
• Articles:Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
QIN Liulei,LIU Yang( ),GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi(
),GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi( )
)
Received:2019-05-30
Online:2020-01-10
Published:2019-11-04
Contact:
Yang LIU,Zunqi LIU
E-mail:daidaishu85@163.com;zunqi85@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
QIN Liulei,LIU Yang,GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi. Synthesis and Switchable Dielectric Properties of an Inorganic-organic Hybrid Complex [H2(DABCO)CuCl4]·H2O †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 70.
| Temperature | 100 K | 294 K |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C6H16Cl4CuN2O | C6H16Cl4CuN2O |
| Formula weight | 336.18 | 336.18 |
| Crystal size | 0.13 mm×0.12 mm×0.11 mm | 0.13 mm×0.12 mm×0.11 mm |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/c |
| a/nm | 0.91929(2) | 0.93180(11) |
| b/nm | 0.93404(3) | 0.94267(13) |
| c/nm | 1.42687(3) | 1.44795(19) |
| α/(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| β/(°) | 93.568(2) | 93.379(11) |
| γ/(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| V/nm3 | 1.22281(5) | 1.2696(3) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Dc/(g·cm-3) | 1.834 | 1.766 |
| F(000) | 684 | 684 |
| μ/mm-1 | 2.631 | 2.534 |
| Reflections collected | 11298 | 16181 |
| Independent reflections | 6549 | 6379 |
| Measured 2θ range/(°) | 1.000—24.992 | 0.885—25.242 |
| Rint | 0.0240 | 0.0339 |
| R[I>2σ(I)]a | 0.0262 | 0.0451 |
| wR(all data)b | 0.0592 | 0.0829 |
| GOF | 1.068 | 1.047 |
| Temperature | 100 K | 294 K |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical formula | C6H16Cl4CuN2O | C6H16Cl4CuN2O |
| Formula weight | 336.18 | 336.18 |
| Crystal size | 0.13 mm×0.12 mm×0.11 mm | 0.13 mm×0.12 mm×0.11 mm |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P21/c | P21/c |
| a/nm | 0.91929(2) | 0.93180(11) |
| b/nm | 0.93404(3) | 0.94267(13) |
| c/nm | 1.42687(3) | 1.44795(19) |
| α/(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| β/(°) | 93.568(2) | 93.379(11) |
| γ/(°) | 90.00 | 90.00 |
| V/nm3 | 1.22281(5) | 1.2696(3) |
| Z | 4 | 4 |
| Dc/(g·cm-3) | 1.834 | 1.766 |
| F(000) | 684 | 684 |
| μ/mm-1 | 2.631 | 2.534 |
| Reflections collected | 11298 | 16181 |
| Independent reflections | 6549 | 6379 |
| Measured 2θ range/(°) | 1.000—24.992 | 0.885—25.242 |
| Rint | 0.0240 | 0.0339 |
| R[I>2σ(I)]a | 0.0262 | 0.0451 |
| wR(all data)b | 0.0592 | 0.0829 |
| GOF | 1.068 | 1.047 |
| Cu1—Cl1 | 0.22855(6) | Cu1—Cl4 | 0.22417(6) | Cu1—Cl2 | 0.22476(6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1—Cl3 | 0.22313(6) | N2—C2 | 0.14810(3) | N2—C4 | 0.14870(3) |
| N2—C6 | 0.14800(3) | N1—C1 | 0.15010(3) | N1—C3 | 0.15000(3) |
| N1—C5 | 0.15030(3) | C1—C2 | 0.15260(3) | C3—C4 | 0.15140(4) |
| C5—C6 | 0.15110(3) | ||||
| Cl4—Cu1—Cl1 | 131.98(2) | Cl4—Cu1—Cl2 | 98.96(2) | Cl2—Cu1—Cl1 | 95.38(2) |
| Cl3—Cu1—Cl1 | 101.13(2) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl4 | 99.45(2) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl2 | 136.09(3) |
| C2—N2—C4 | 109.50(2) | C6—N2—C2 | 110.10(2) | C6—N2—C4 | 109.90(2) |
| C1—N1—C3 | 110.93(18) | C1—N1—C5 | 109.66(17) | C3—N1—C5 | 109.23(17) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.09(18) | N1—C3—C4 | 108.48(19) | N1—C5—C6 | 108.12(19) |
| N2—C2—C1 | 109.60(2) | N2—4—C3 | 109.50(2) | N2—C6—C5 | 110.13(19) |
| Cu1—Cl1 | 0.22855(6) | Cu1—Cl4 | 0.22417(6) | Cu1—Cl2 | 0.22476(6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1—Cl3 | 0.22313(6) | N2—C2 | 0.14810(3) | N2—C4 | 0.14870(3) |
| N2—C6 | 0.14800(3) | N1—C1 | 0.15010(3) | N1—C3 | 0.15000(3) |
| N1—C5 | 0.15030(3) | C1—C2 | 0.15260(3) | C3—C4 | 0.15140(4) |
| C5—C6 | 0.15110(3) | ||||
| Cl4—Cu1—Cl1 | 131.98(2) | Cl4—Cu1—Cl2 | 98.96(2) | Cl2—Cu1—Cl1 | 95.38(2) |
| Cl3—Cu1—Cl1 | 101.13(2) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl4 | 99.45(2) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl2 | 136.09(3) |
| C2—N2—C4 | 109.50(2) | C6—N2—C2 | 110.10(2) | C6—N2—C4 | 109.90(2) |
| C1—N1—C3 | 110.93(18) | C1—N1—C5 | 109.66(17) | C3—N1—C5 | 109.23(17) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.09(18) | N1—C3—C4 | 108.48(19) | N1—C5—C6 | 108.12(19) |
| N2—C2—C1 | 109.60(2) | N2—4—C3 | 109.50(2) | N2—C6—C5 | 110.13(19) |
| Cu1—Cl1 | 0.22942(7) | Cu1—Cl4 | 0.22497(7) | Cu1—Cl2 | 0.22573(7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1—Cl3 | 0.22389(7) | N2—C2 | 0.14870(3) | N2—C4 | 0.14820(3) |
| N2—C6 | 0.14900(3) | N1—C1 | 0.15100(3) | N1—C3 | 0.14980(3) |
| N1—C5 | 0.14990(3) | C1—C2 | 0.15230(4) | C3—C4 | 0.15090(4) |
| C5—C6 | 0.15120(4) | ||||
| Cl4—Cu1—Cl1 | 131.65(3) | Cl4—Cu1—Cl2 | 99.17(3) | Cl2—Cu1—Cl1 | 95.45(3) |
| Cl3—Cu1—Cl1 | 100.93(3) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl4 | 99.71(3) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl2 | 135.94(3) |
| C2—N2—C6 | 109.60(2) | C4—N2—C2 | 109.80(2) | C4—N2—C6 | 110.00(2) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 110.60(19) | C3—N1—C1 | 109.92(19) | C3—N1—C5 | 109.34(19) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.15(19) | N1—C5—C6 | 108.40(2) | N1—C3—C4 | 108.60(2) |
| N2—C2—C1 | 109.50(2) | N2—C4—C3 | 109.90(2) | N2—C6—C5 | 109.90(2) |
| Cu1—Cl1 | 0.22942(7) | Cu1—Cl4 | 0.22497(7) | Cu1—Cl2 | 0.22573(7) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu1—Cl3 | 0.22389(7) | N2—C2 | 0.14870(3) | N2—C4 | 0.14820(3) |
| N2—C6 | 0.14900(3) | N1—C1 | 0.15100(3) | N1—C3 | 0.14980(3) |
| N1—C5 | 0.14990(3) | C1—C2 | 0.15230(4) | C3—C4 | 0.15090(4) |
| C5—C6 | 0.15120(4) | ||||
| Cl4—Cu1—Cl1 | 131.65(3) | Cl4—Cu1—Cl2 | 99.17(3) | Cl2—Cu1—Cl1 | 95.45(3) |
| Cl3—Cu1—Cl1 | 100.93(3) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl4 | 99.71(3) | Cl3—Cu1—Cl2 | 135.94(3) |
| C2—N2—C6 | 109.60(2) | C4—N2—C2 | 109.80(2) | C4—N2—C6 | 110.00(2) |
| C5—N1—C1 | 110.60(19) | C3—N1—C1 | 109.92(19) | C3—N1—C5 | 109.34(19) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 108.15(19) | N1—C5—C6 | 108.40(2) | N1—C3—C4 | 108.60(2) |
| N2—C2—C1 | 109.50(2) | N2—C4—C3 | 109.90(2) | N2—C6—C5 | 109.90(2) |
| D—H…A | d(D—H)/nm | d(H…A)/nm | d(D…A) /nm | ∠D—H…A/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1…Cl1j | 0.0980 | 0.2372 | 0.3188 | 140.21 |
| N1—H1…Cl2i | 0.0980 | 0.2746 | 0.3398 | 124.43 |
| N2—H2…O1k | 0.0980 | 0.2146 | 0.2902 | 133.82 |
| O1—H1D…Cl1i | 0.0850 | 0.2313 | 0.3152 | 168.94 |
| O1—H1C…Cl2j | 0.0850 | 0.2487 | 0.3287 | 158.42 |
| O1—H1C…Cl4i | 0.0850 | 0.2797 | 0.3311 | 120.54 |
| O1—H1C…O1i | 0.0850 | 0.3460 | 0.3020 | 52.59 |
| D—H…A | d(D—H)/nm | d(H…A)/nm | d(D…A) /nm | ∠D—H…A/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1…Cl1j | 0.0980 | 0.2372 | 0.3188 | 140.21 |
| N1—H1…Cl2i | 0.0980 | 0.2746 | 0.3398 | 124.43 |
| N2—H2…O1k | 0.0980 | 0.2146 | 0.2902 | 133.82 |
| O1—H1D…Cl1i | 0.0850 | 0.2313 | 0.3152 | 168.94 |
| O1—H1C…Cl2j | 0.0850 | 0.2487 | 0.3287 | 158.42 |
| O1—H1C…Cl4i | 0.0850 | 0.2797 | 0.3311 | 120.54 |
| O1—H1C…O1i | 0.0850 | 0.3460 | 0.3020 | 52.59 |
| D—H…A | d(D—H)/nm | d(H…A)/nm | d(D…A) /nm | ∠D—H…A/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1…Cl1j | 0.0980 | 0.2411 | 0.3229 | 140.72 |
| N1—H1…Cl2i | 0.0980 | 0.2774 | 0.3440 | 125.79 |
| N2—H2…O1k | 0.0980 | 0.2194 | 0.2954 | 134.63 |
| O1—H1D…Cl1i | 0.0850 | 0.2347 | 0.3187 | 169.78 |
| O1—H1C…Cl2j | 0.0850 | 0.2538 | 0.3337 | 156.90 |
| O1—H1C…Cl4 i | 0.0850 | 0.2825 | 0.3362 | 122.79 |
| O1—H1C…O1i | 0.0850 | 0.3481 | 0.3053 | 53.53 |
| D—H…A | d(D—H)/nm | d(H…A)/nm | d(D…A) /nm | ∠D—H…A/(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1…Cl1j | 0.0980 | 0.2411 | 0.3229 | 140.72 |
| N1—H1…Cl2i | 0.0980 | 0.2774 | 0.3440 | 125.79 |
| N2—H2…O1k | 0.0980 | 0.2194 | 0.2954 | 134.63 |
| O1—H1D…Cl1i | 0.0850 | 0.2347 | 0.3187 | 169.78 |
| O1—H1C…Cl2j | 0.0850 | 0.2538 | 0.3337 | 156.90 |
| O1—H1C…Cl4 i | 0.0850 | 0.2825 | 0.3362 | 122.79 |
| O1—H1C…O1i | 0.0850 | 0.3481 | 0.3053 | 53.53 |
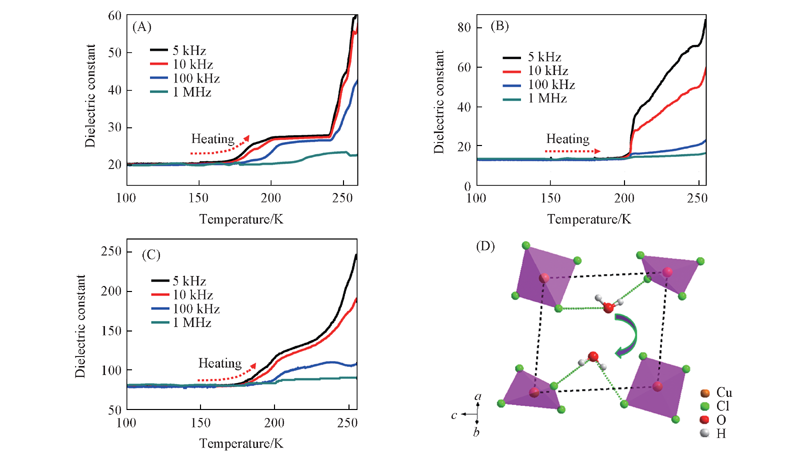
Fig.7 Anisotropic dielectric constants of compound 1 along a-(A), b-(B), c-axes(C) from 100 K to 260 K at 5 kHz—1 MHz up heating and variation of hydrogen bond distance in ac-plane(D)
| [1] |
Hang T., Zhang W., Ye H. Y ., Xiong R. G., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011,40(7), 3577— 3598
doi: 10.1039/c0cs00226g URL pmid: 21509354 |
| [2] |
Yu G. J., Ji C. M.,Song C.,Luo J. H., Chin. Sci. Bull., 2014, 59(31), 3080—3085
doi: 10.1360/N972014-00582 URL |
|
( 余国建, 姬成敏, 宋琤, 罗军华. 科学通报, 2014,59(31), 3080— 3085)
doi: 10.1360/N972014-00582 URL |
|
| [3] |
Ye H. Y ., Cai H. L.,Ge J. Z.,Xiong R. G., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2012,17, 159— 162
doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2011.12.040 URL |
| [4] |
Kozlova S. G ., Mirzaeva I. V.,Ryzhikov M. R., Coordin. Chem. Rev., 2018,376, 62— 74
doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2018.07.008 URL |
| [5] | Yang J., Tao J. Y., Xing G. X.,Meng T.,Yuan X. M.,Du L. T.,Xu L.,Xu H. J., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2018, 34(7), 1312—1318 |
| ( 杨剑, 陶家宇, 幸国香, 孟婷, 袁雪梅, 杜丽婷, 徐莉, 徐海军. 无机化学学报, 2018,34(7), 1312— 1318) | |
| [6] |
Zhang Y., Liao W. Q ., Fu D. W.,Ye H. Y.,Liu C. M.,Chen Z. N.,Xiong R. G., Adv. Mater., 2015,27, 3942— 3946
doi: 10.1002/adma.201501026 URL pmid: 26011784 |
| [7] | Rhaiem T. B ., Boughzala H., Acta Cryst., 2014,E70, m178 |
| [8] | Wang F. M ., Acta Cryst., 2009,E65, m575 |
| [9] | Zhang R. F., Shi W.,Cheng P., Chinese J. Inorg. Chem., 2008, 24(8), 1272—1277 |
| ( 张瑞凤, 师唯, 程鹏. 无机化学学报, 2008,24(8), 1272— 1277) | |
| [10] | Li Z., Li R., Li X., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11), 2363—2371 |
| ( 李铮, 李睿, 李夏. 高等学校化学学报, 2018,39(11), 2363— 2371) | |
| [11] |
Li Q., Shi P. P ., Ye Q.,Wang H. T.,Wu D. H.,Ye H. Y.,Fu D. W.,Zhang Y., Inorg. Chem., 2015,54(22), 10642— 10647
doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5b01437 URL pmid: 26512411 |
| [12] |
Zhang Y., Liao W. Q ., Ye H. Y.,Fu D. W.,Xiong R. G., Cryst. Growth Des., 2013,13(9), 4025— 1030
doi: 10.1021/cg400829d URL |
| [13] |
Sun Z. H ., Wang X. Q.,Luo J. H.,Zhang S. Q.,Yuan D. Q.,Hong M. C., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2013,1(14), 2561— 2567
doi: 10.1039/c3tc30166d URL |
| [14] | Song W., Wang L. Q., Zeng S. L.,Wang L.,Fan Y.,Xu J. N., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(7), 1406—1411 |
| ( 宋伟, 王力群, 曾双利, 王莉, 范勇, 徐家宁 . 高等学校化学学报, 2018,39(7), 1406— 1411) | |
| [15] |
Shi X. J ., Luo J. H.,Sun Z. H.,Li S. G.,Ji C. G.,Li L. N.,Han L.,Zhang S. Q.,Yuan D. Q.,Hong M. C., Cryst. Growth Des., 2013,13(5), 2081— 2086
doi: 10.1021/cg400146b URL |
| [16] |
Han X. B ., Hu P.,Shi C.,Zhang W., J. Mol. Struct., 2017,1127, 372— 376
doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2016.07.113 URL |
| [17] | Liao W. Q ., Zhou Q. Q.,Zhang Y., Acta Cryst., 2013,C69, 380— 383 |
| [18] |
Li L. H ., Zhao W. Y.,Deng S. Y.,Ma L. F.,Chen L. Z., Inorg. Chem. Commun., 2018,92, 125— 130
doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2018.04.022 URL |
| [19] |
Ji Q., Li L. H ., Deng S. Y.,Cao X. X.,Chen L. Z., Dalton. Trans., 2018,47(16), 5630— 5638
doi: 10.1039/c8dt00623g URL pmid: 29619459 |
| [20] |
Chen C. H ., Xu G. C., Cryst Eng Comm., 2015,18(4), 1— 20
doi: 10.1039/C6CE90001A URL |
| [21] |
Chen L. Z ., Huang D. D.,Pan Q. J.,Ge J. Z., RSC. Adv., 2015,5(18), 13488— 13494
doi: 10.1039/C4RA12690D URL |
| [22] |
Chen L. Z ., Huang D. D.,Ge J. Z.,Pan Q. J., J. Mol. Struct., 2014,1072, 307— 312
doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2014.05.041 URL |
| [23] |
Zhang W., Chen L. Z ., Xiong R. G.,Nakamura T.,Huang S. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2009,131(35), 12544— 12545
doi: 10.1021/ja905399x URL pmid: 19685869 |
| [24] |
Chen T. L ., Sun Z. H.,Zhao S. G.,Ji C. M.,Luo J. H., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016,4, 266— 271
doi: 10.1039/C5TC03278D URL |
| [25] |
Shi P. P ., Ye Q.,Li Q.,Wang H. T.,Fu D. W.,Zhang Y.,Xiong R. G., Chem. Mater., 2014,26(20), 6042— 6049
doi: 10.1021/jp312396q URL pmid: 23594107 |
| [26] |
Chen X., Zhou H., Chen Y. Y ., Yuan A. H., Cryst Eng Comm., 2011,13, 5666— 5669
doi: 10.1039/c1ce05699a URL |
| [27] |
Wang X. L ., Zhou L.,Ye Q.,Geng F. J.,Ye H. Y.,Fu D. W.,Zhang Y., RSC. Adv., 2016,6(78), 74117— 74123
doi: 10.1039/C6RA14157A URL |
| [28] |
Ye H. Y ., Ge J. Z.,Tang Y. Y.,Li P. F.,Zhang Y.,You Y. M.,Xiong R. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016,138(40), 13175— 13178
doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b08817 URL pmid: 27681367 |
| [29] | Rhaiem T. B ., Boughzala H., Acta Cryst., 2015,E71, 498— 501 |
| [30] |
Wang Y., Shi C., Han X. B ., Polyhedron., 2017,133, 132— 136
doi: 10.1016/j.poly.2017.05.015 URL |
| [31] |
Zhang Y., Zhang W., Li S. H ., Ye Q.,Cai H. L.,Deng F.,Xiong R. G.,Huang S. D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012,134, 11044— 11049
doi: 10.1021/ja3047427 URL |
| [1] | MIN Jing, WANG Liyan. 1H NMR Study on the Conformation of Aromatic Amides Limited by Three-center Hydrogen Bonds [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220084. |
| [2] | LIU Qingqing, WANG Pu, WANG Yongshuai, ZHAO Man, DONG Huanli. Synthesis and Topochemical Polymerization Study of Naphthalene/perylene Imides Substituted Diacetylene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220091. |
| [3] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [4] | ZHANG Yong, XU Jun, BAO Yu, CUI Shuxun. Quantifying the Degree of Weakening Effect of Nonpolar Organic Solvent on the Strength of Intramolecular Hydrogen Bonding by Single-molecule Force Spectroscopy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210863. |
| [5] | CUI Shaoli, ZHANG Weijia, SHAO Xueguang, CAI Wensheng. Revealing the Effect of Threonine on the Binding Ability of Antifreeze Proteins with Ice Crystals by Free-energy Calculations [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210838. |
| [6] | HU Bo, ZHU Haochen. Dielectric Constant of Confined Water in a Bilayer Graphene Oxide Nanosystem [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210614. |
| [7] | GAO Huiling, CAO Zhenzhen, GU Fang, WANG Haijun. Monte Carlo Simulation on Self-healing Behaviour of Hydrogen-bonded Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220482. |
| [8] | YUE Shengli, WU Guangbao, LI Xing, LI Kang, HUANG Gaosheng, TANG Yi, ZHOU Huiqiong. Research Progress of Quasi-two-dimensional Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1648. |
| [9] | WANG Le, QIN Liulei, LIU Yang, REN Li, XU Huiting, LIU Zunqi. Synthesis, Structure and Dielectric Properties of One-dimensional Chain Hydrogen Glycine Supramolecular Compound [(Gly)2+(18-crown-6)2(MnCl4)2‒] [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 691. |
| [10] | NI Qingsheng, DU Miao, SHAN Guorong, SONG Yihu, WU Ziliang, ZHENG Qiang. Regulation of Rheological Behavior of Polyvinyl Alcohol Aqueous Solution by One-dimensional Particles [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3738. |
| [11] | GONG Shanshan, WU Tong, WANG Guange, HUANG Qing, SU Yuefeng, WU Feng. Screening of Deep Eutectic Solvent Based on Efficient Recovery of Spent Lithium⁃ion Battery Cathode Materials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(10): 3151. |
| [12] | BAI Lan, ZHAI Lei, WANG Changou, HE Minhui, MO Song, FAN Lin. Thermal Expansion Behavior of Amide-containing Polyimide Films with Ultralow Thermal Expansion Coefficient † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 795. |
| [13] | TIAN Xia,YANG Fuqun,YUAN Wei,ZHAO Lei,YAO Lei,ZHEN Xiaoli,HAN Jianrong,LIU Shouxin. Synthesis, Structure and Recognition Properties of Macrocyclic Crown Ethers with Oxadiazole † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 490. |
| [14] | LIU Dongmei,SU Yajing,LI Shanshan,XU Qiwei,LI Xia. Transition Metal Coordination Polymers Constructed by 4-(4-Carboxyphenoxy)isophthalic Acid: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Fluorescence Sensing and Photocatalysis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 253. |
| [15] | LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||