

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (4): 632.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180733
• Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Bing1, WANG Xuemin1, BAI Fengying1,*( ), LIU Shuqing2,*(
), LIU Shuqing2,*( )
)
Received:2018-10-29
Online:2019-04-03
Published:2019-04-10
Contact:
BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing
E-mail:baifengying2003@163.com;Lsqsmz@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
LI Bing,WANG Xuemin,BAI Fengying,LIU Shuqing. Synthesises, Structures and Antibacterial Activities of a Series of Rare Earth Nitrogen Heterocyclic Complexes†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 632.
| Formula | C44H32N7O7Gd | Dc/(g·cm-3) | 1.477 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 928.02 | F(000) | 1860 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | μ(Mo Kα)/mm-1 | 1.647 |
| Space group | P2(1)/n | θ range/(°) | 1.67—28.25 |
| a/nm | 1.3501(9) | Reflections collected | 25661 |
| b/nm | 1.3404(9) | Independent reflections[I>2σ(I)] | 9477 |
| c/nm | 2.3208(16) | Parameter | 532 |
| α/(°) | 90 | Goodness of fit | 1.090 |
| β/(°) | 96.4260(10) | Ra(Rb) | 0.0741(0.1145)b |
| γ/(°) | 90 | w | 0.1981(0.2259)b |
| V/nm3 | 4.1739(5) | Δρ/(e·nm-3) | 1626, -611 |
| Z | 4 |
Table 1 Crystal data and structure refinement for complex 2
| Formula | C44H32N7O7Gd | Dc/(g·cm-3) | 1.477 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 928.02 | F(000) | 1860 |
| Crystal system | Monoclinic | μ(Mo Kα)/mm-1 | 1.647 |
| Space group | P2(1)/n | θ range/(°) | 1.67—28.25 |
| a/nm | 1.3501(9) | Reflections collected | 25661 |
| b/nm | 1.3404(9) | Independent reflections[I>2σ(I)] | 9477 |
| c/nm | 2.3208(16) | Parameter | 532 |
| α/(°) | 90 | Goodness of fit | 1.090 |
| β/(°) | 96.4260(10) | Ra(Rb) | 0.0741(0.1145)b |
| γ/(°) | 90 | w | 0.1981(0.2259)b |
| V/nm3 | 4.1739(5) | Δρ/(e·nm-3) | 1626, -611 |
| Z | 4 |
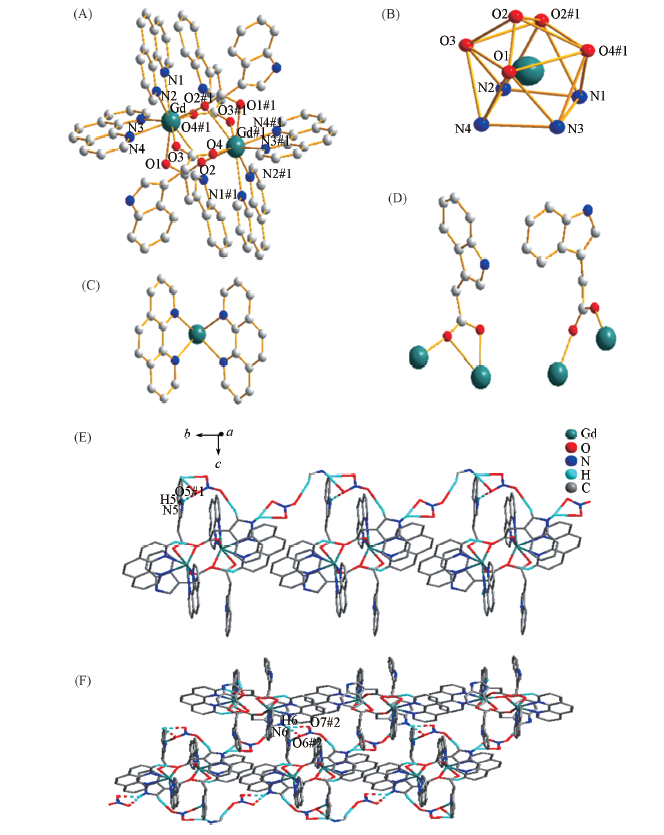
Fig.2 Crystal structure of complex 2(A) Coordination environment of the Gd(Ⅲ) ion(dimer configuration); (B) single-capped quadrilateral inverse prism geometry of Cd(Ⅲ); (C) coordination mode of ligand 1,10-phenanthroline; (D) coordination mode of ligand indole acetic acid; (E) 1D hydrogen-bonded chain along b axis(#1: -x+1, -y+1, -z+1); (F) 2D hydrogen bond network on the surface of bc(#2: 3/2-x, -1/2+y, 1/2-z). All H atoms except for the hydrogen bonds are omitted for clarity.
| [1] | He Q. Z., Yang X. F., Qian X. P., Yu X. B., Wang Z. M., J. Chin. Rare Earth. Soc., 2002, 20(S3), 1—5 |
| (何其庄, 杨小飞, 钱秀萍, 余锡宾, 王则民. 中国稀土学报, 2002, 20(S3), 1—5) | |
| [2] | Zhu Z. L., Liu J. W., Da W. Y., Xu J. P., Song Y. M.,Chemistry Bulletin,2009, 72(1),59—64 |
| (朱早龙, 刘景旺, 达文燕, 许军鹏, 宋玉民. 化学通报, 2009, 72(1), 59—64) | |
| [3] | Yang J., Zhang H., Wang J. C., Wu Y. P., Chinese Rare Earths,2009, 30(1), 35—39 |
| (杨军, 张赫, 王甲辰, 伍艳平. 稀土, 2009, 30(1), 35—39) | |
| [4] | Yang J., Zhang H., Wang J. C., Wu Y. P., J. Chin. Rare Earth. Soc., 2007, 25(S1), 77—81 |
| (杨军,张赫, 王甲辰, 伍艳平. 中国稀土学报, 2007, 25(S1), 77—81) | |
| [5] | Li X. F., Feng X. Q., Zhang. H. W., Yang S., Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2015, 39(1), 62—67 |
| (李小芳, 冯小强, 张宏伟, 杨声. 稀有金属,2015, 39(1), 62—67) | |
| [6] | Liu M.Y., Xiao S. X., Liu H., Yin Z. W., Food & Machinery,2012, 28(6), 112—116 |
| (刘美艳, 肖圣雄, 刘浩, 尹智伟. 食品与机械, 2012, 28(6), 112—116) | |
| [7] | Li X., Bai J. C., Inner Mongolia Petrochemical Industry,2017, 43(11), 25—27 |
| (李欣, 白剑臣. 内蒙古石油化工, 2017, 43(11), 25—27) | |
| [8] | Wang H. J., Xue J. X., Liu W., Diao H. P., Chem.Res.,2017, 28(3), 326—330 |
| (王浩江, 薛晶鑫, 刘文, 刁海鹏. 化学研究, 2017, 28(3), 326—330) | |
| [9] | Jiang J. H., Xiao S. X., Xiao H. Y., Liu H., Yin Z. W., Li Q. G., Chinese Rare Earths,2013, 34(3), 69—73 |
| (蒋建宏, 肖圣雄, 肖航英, 刘浩, 尹智伟, 李强国. 稀土, 2013, 34(3), 69—73) | |
| [10] | Bai F. Y., Lv X., Liu S. Q., Li X. T., J. Chin. Inorg.Chem.,2011, 27(7), 1261—1264 |
| (白凤英., 吕晓., 刘淑清., 李晓天.无机化学学报, 2011, 27(7), 1261—1264) | |
| [11] | Wang W., Synthesis and Properties of 1,10-Phenanthroline Metal Complexes, Chongqing University,Chongqing, 2012 |
| (王维. 1,10-邻菲罗啉金属配合物的合成及性质的研究, 重庆: 重庆大学, 2012) | |
| [12] | Zhang H.M., Hydrothermal Synthesis and Structural Characterization of o-Phenanthroline and Derivative Complexes., Shanxi University,Taiyuan, 2006 |
| (张红梅. 邻菲罗啉及衍生物配合物的水热合成与结构表征, 太原: 山西大学, 2006) | |
| [13] | Deng H.K., Study on the Catalytic 1,4-1,2-Addition Reaction of 1,10-Phenanthroline with Hydrogen Phosphite(Phosphate) Catalyzed by Nickel., Xiamen University,Xiamen, 2013 |
| (邓洪癸. 镍催化1,10-菲罗啉与氢亚磷(膦)酸酯的串联1,4-1,2-加成反应研究, 厦门: 厦门大学, 2013) | |
| [14] | Kumar R. S., Arunachalam S., European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2009, 44(5), 1878—1883 |
| [15] | Yang Y., Gao K. X., Wu Y., Liu X. G., Biotechnology Bulletin,2016, 32(8), 14—21 |
| (杨扬, 高克祥, 吴岩, 刘晓光. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(8), 14—21) | |
| [16] | Cui F. G., Biology Teaching, 2011, 36(8), 71—72 |
| (崔凤国. 生物学教学, 2011, 36(8), 71—72) | |
| [17] | Zhang X. M., Wang H. J., Wang H. B., J. Chin.Ecol.,2017, 36(4),1097—1105 |
| (张雪梅, 王海娟, 王宏镔. 生态学杂志, 2017, 36(4), 1097—1105) | |
| [18] | Xu X.L., Crystal Structure and Fluorescence Properties of Complexes Constructed by Indole Acetic Acid, Zhengzhou University,Zhangzhou, 2011 |
| (薛旭玲. 由吲哚乙酸构筑的配合物的晶体结构和荧光性能的研究, 郑州: 郑州大学, 2011) | |
| [19] | Ren Y. X., Tang L., Wu Y. F., Wang D. J., Wu Y. P., Fu F.,J. Chin. Inorg.Chem.,2012, 28(8), 1729—1735 |
| (任宜霞, 唐龙, 武玉飞, 王丹军, 吴亚盘, 付峰. 无机化学学报, 2012, 28(8), 1729—1735) | |
| [20] | Bai F. Y., Wang X. M., Qu C. Q., Wang Y., Xing Y. H., J. Chin. Inorg.Chem.,2018, 34(4), 639—646 |
| (白凤英, 王学敏, 曲长庆, 王玉, 邢永恒. 无机化学学报, 2018, 34(4), 639—646) | |
| [21] | Sheldrick G.M., SHELX-97, Program for Crystal Structure Refinement, University of Göttingen, Göttingen, 1997 |
| [22] | Wang Z. N., Xu X. T., Lv X., Bai F.Y., RSC Adv.,2015, 5(126), 104263—104274 |
| [23] | Wu D. L., Liu G. J., Li Z., Li A. M., Yin H., Zhu S. Q., Chen Z. Q., Wu Y. H., Jouranal of Synthetic Crystals,2016, 45(3) 569—573 |
| [1] | LIU Qingqing, WANG Pu, WANG Yongshuai, ZHAO Man, DONG Huanli. Synthesis and Topochemical Polymerization Study of Naphthalene/perylene Imides Substituted Diacetylene Derivatives [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220091. |
| [2] | SHI Naike, ZHANG Ya, SANSON Andrea, WANG Lei, CHEN Jun. Uniaxial Negative Thermal Expansion and Mechanism in Zn(NCN) [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220124. |
| [3] | ZHOU Yonghui, LI Yao, WU Yuxuan, TIAN Jing, XU Longquan, FEI Xu. Synthesis of A Novel Photoluminescence Self-healing Hydrogel [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210606. |
| [4] | HU Haocheng, LI Wenli, ZHANG Jianing, LIU Yubo. Extraction, Structure Characterization and Biological Activities of Oligosaccharides from Auricularia heimuer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2465. |
| [5] | YUE Shengli, WU Guangbao, LI Xing, LI Kang, HUANG Gaosheng, TANG Yi, ZHOU Huiqiong. Research Progress of Quasi-two-dimensional Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(6): 1648. |
| [6] | TIAN Xia,YANG Fuqun,YUAN Wei,ZHAO Lei,YAO Lei,ZHEN Xiaoli,HAN Jianrong,LIU Shouxin. Synthesis, Structure and Recognition Properties of Macrocyclic Crown Ethers with Oxadiazole † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 490. |
| [7] | LIU Dongmei,SU Yajing,LI Shanshan,XU Qiwei,LI Xia. Transition Metal Coordination Polymers Constructed by 4-(4-Carboxyphenoxy)isophthalic Acid: Synthesis, Crystal Structure, Fluorescence Sensing and Photocatalysis † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 253. |
| [8] | QIN Liulei,LIU Yang,GUAN Xiaoqin,ZHENG Xiaoyuan,ZHANG Ziyu,LIU Zunqi. Synthesis and Switchable Dielectric Properties of an Inorganic-organic Hybrid Complex [H2(DABCO)CuCl4]·H2O † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(1): 70. |
| [9] | MAO Long, LIU Yuejun, FAN Shuhong. Preparation and Properties of Polypyrrole Modified Layered Clay/poly(ε-caprolactone) Antibacterial Nanocomposites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(8): 1726. |
| [10] | LI Pu,CHEN Ying,XIA Rongjiao,GUO Tao,ZHANG Min,JIANG Shichun,ANG Xu,HE Ming,XUE Wei. Synthesis and Biological Activities of Myricetin Derivatives Containing Quinoxaline† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(5): 909. |
| [11] | WANG Dongmei,LIU Zihua,LI Guanghua,LIU Yunling,LI Chunxia. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescent Property of Indium-based Bimetallic Metal-organic Frameworks† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(9): 1886. |
| [12] | WAN Jinlin, WU Shouqun, GAN Yiyuan, MENG Jiao, WANG Zhenchao*, OUYANG Guiping*. Synthesis and Antibacterial Activities Evaluation of Chalconesemicarbazone Derivatives Bearing 1,3,4-Thiadiazole Moiety† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1683. |
| [13] | JIA Yunjing, SHI Wensi, HU Feiliu, ZHU Huajie, LIU Li, MA Zhengyue. Cytotoxic Activity of Trichothecene Compounds and Derivatives from Myrothecium sp.† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1668. |
| [14] |
TIAN Huan, ZHANG Menglong, WANG Lisha, TONG Bihai, ZHAO Zhuo.
Synthesis of 4,13-Dithio Benzene and-18-Crown-6 and Its Selective Extractability on A |
| [15] | ZHU Lei,HAN Junyan,CHANG Haizhen,QIU Yuyuan,ZHANG Yanan,PENG Danni,HU Wei,MIAO Shaobin. Different Pathways for the Cyclocondensation Reactions of 1,2-Diamine and 1,2-Diketone† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(12): 2686. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||