

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (9): 1818.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190085
• Articles:Inorganic Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
MU Xin,JIANG Shuangshuang,ZHANG Shuhao,REN Hao,SUN Fuxing( )
)
Received:2019-01-29
Online:2019-09-10
Published:2019-07-12
Contact:
SUN Fuxing
E-mail:fxsun@jlu.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
MU Xin, JIANG Shuangshuang, ZHANG Shuhao, REN Hao, SUN Fuxing. Growth and Gas Permeation Properties of SIFSIX-3-Ni Membrane †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(9): 1818.
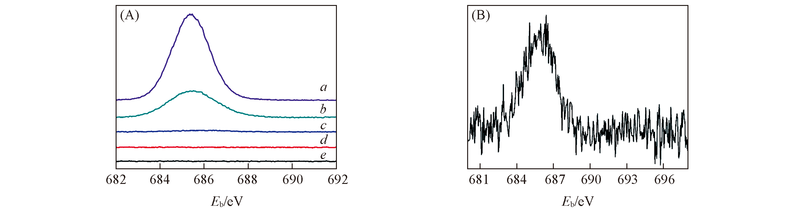
Fig.2 F1s XPS spectra of (NH4)2SiF6 powder(a), SIFSIX-3-Ni membrane(b), glass frit disk treated in(NH4)2SiF6 solution(c), glass frit disk treated in a solution of H2SO4 and H2O2(d) and raw glass-frit disk surface(e)(A) and enlarged pattern of glass frit disk treated in (NH4)2SiF6 solution(B)
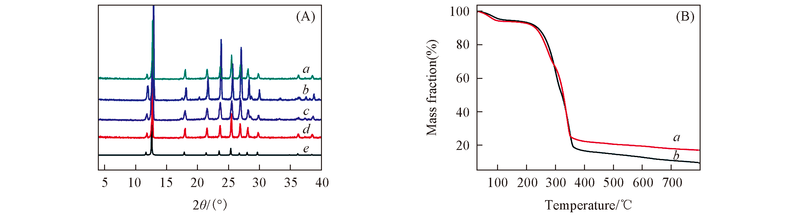
Fig.3 PXRD patterns of SIFSIX-3-Ni membrane(A) and TG analysis of SIFSIX-3-Ni-3 membrane(B) (A) a. activated SIFSIX-3-Ni-3, b. SIFSIX-3-Ni-3, c. SIFSIX-3-Ni-2, d. SIFSIX-3-Ni-1, e. simulated; (B) a. activated, b. as-synthesized.
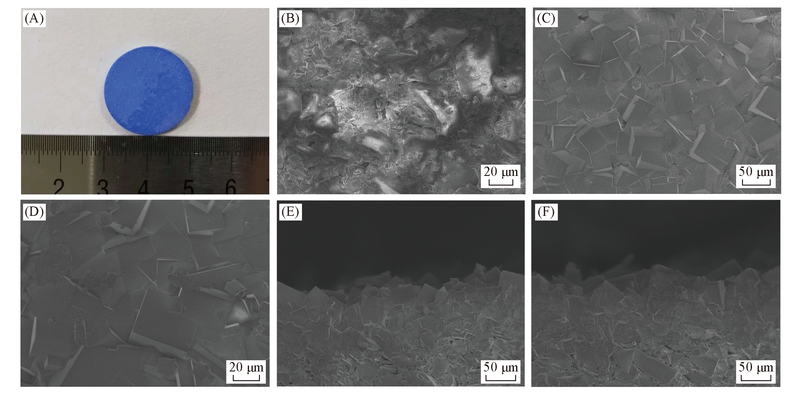
Fig.5 Optical images of SIFSIX-3-Ni-2 membrane(A), SEM images of macroporous glass-frit disk(B), SIFSIX-3-Ni-2 membrane(C, D) and cross-section of the SIFSIX-3-Ni-2 membrane(E, F)
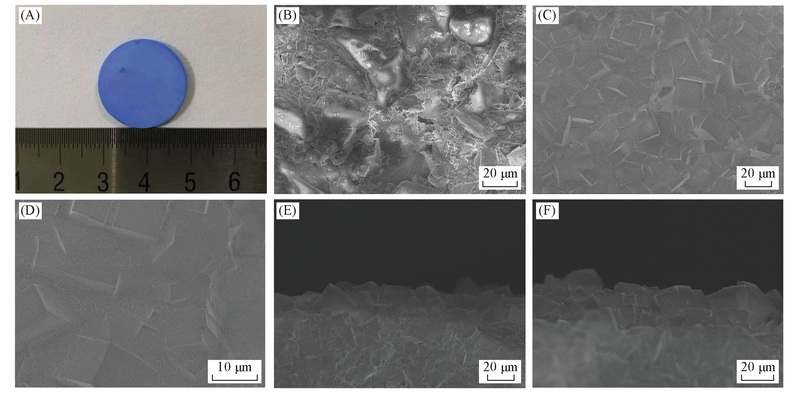
Fig.6 Optical image of SIFSIX-3-Ni-3 membrane(A), SEM images of macroporous glass-frit disk(B), SIFSIX-3-Ni-3 membrane(C, D) and cross-section of the SIFSIX-3-Ni-3 membrane(E, F)
| [1] | Li P., Cheng F. F., Xiong W. W., Zhang Q. C., Li P., Cheng F. F., Xiong W. W., Zhang Q. C., ,Inorg. Chem. Front., 2018, 5( 11), 2693— 2708 |
| [2] | Zhao L., Zhao C. J., ,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016,37( 10), 1763— 1768 |
| (赵仑, 赵长江. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(10), 1763— 1768) | |
| [3] | Li K., He K. H., Li Q. W., Xia B., Wang Q. L., Zhang Y. H., ,. Chem. Res. Chinese Universities 2018, 34( 5), 700— 704 |
| [4] | Liang L. F., Liu C. P., Jiang F. L., Chen Q. H., Zhang L. J., Xue H., Jiang H. L., Qian J. J., Yuan D. Q., Hong M. C., ,. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1233 |
| [5] | Liao P. Q., Huang N. Y., Zhang W. X., Zhang J. P., Chen X. M ., Science 2017, 356( 6343), 1193— 1196 |
| [6] | Lin R. B., Liu S. Y., Ye J. W., Li X. Y., Zhang J. P., ,. Adv. Sci. 2016, 3( 7), 1500434 |
| [7] | Pan M., Zhu Y. X., Wu K., Chen L., Hou Y. J., Yin S. Y., Wang H. P., Fan Y. N., Su C. Y., ,. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56( 46), 14582— 14586 |
| [8] | Simon-Yarza T., Mielcarek A., Couvreur P., Serre C., ,Adv. Mater., 2018, 30( 37), 1707365 |
| [9] | Qiu S. L., Xue M., Zhu G. S., ,. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43( 16), 6116— 6140 |
| [10] | Bétard A., Fischer R. A., ,Chem. Rev., 2012, 112( 2), 1055— 1083 |
| [11] | Liu Y., Ban Y. J., Yang W. S., ,. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29( 31), 1606949 |
| [12] |
Zhang J. L., Zhao Q., Liu J., Sun F. X., ,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2013,34( 4), 771— 775
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20120988 |
|
(张金磊, 赵晴, 刘佳, 孙福兴.高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(4), 771— 775)
doi: 10.7503/cjcu20120988 |
|
| [13] | Duan C. J., Cao Y. M., Jie X. M., Wang L. N., Yuan Q., ,Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2014,35( 7), 1584— 1589 |
| (段翠佳, 曹义鸣, 介兴明, 王丽娜, 袁权. 高等学校化学学报, 2014, 35(7), 1584— 1589) | |
| [14] | Zhang F., Zou X. Q., Gao X., Fan S. J., Sun F. X., Ren H., Zhu G. S., ,. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22( 17), 3583— 3590 |
| [15] | Li Y. S., Liang F. Y., Bux H., Feldhoff A., Yang W. S., Caro J., ,Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2010, 49( 3), 548— 551 |
| [16] | Huang A., Bux H., Steinbach F., Caro J., ,. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49( 29), 4958— 4961 |
| [17] | Kang Z. X., Xue M., Fan L. L., Huang L., Guo L. J., Wei G. Y., Chen B. L., Qiu S. L., ,. Energy Environ. Sci. 2014, 7( 12), 4053— 4060 |
| [18] | Forrest K. A., Pham T., Space B ., CrystEngComm 2017, 19( 24), 3338— 3347 |
| [19] | Nugent P., Belmabkhout Y., Burd S. D., Cairns A. J., Luebke R., Forrest K., Pham P., Ma S. Q., Space B., Wojtas L., Eddaoudi M., Zaworotko M. J ., Nature 2013, 495( 7439), 80— 84 |
| [20] | Fan S. J., Sun F. X., Xie J. J., Guo J., Zhang L. M., Wang C. R., Pan Q. K., Zhu G. S., ,. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1( 37), 11438— 11442 |
| [21] | Gong H. Q., Nguyen T. H., Wang R., Bae T. H., ,J. Membr. Sci., 2015, 495, 169— 175 |
| [22] | Shekhah O., Belmabkhout Y., Adil K., Bhatt P. M., Cairns A. J., Eddaoudi M., ,Chem. Commun., 2015, 51( 71), 13595— 13598 |
| [23] | Cadiau A., Adil K., Bhatt P. M., Belmabkhout Y., Eddaoudi M ., Science 2016, 353( 6295), 137— 140 |
| [24] | Kumar A., Madden D. G., Lusi M., Chen K. J., Daniels E. A., Curtin T., Perry J. J., Zaworotko M. J., ,. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54( 48), 14372— 14377 |
| [25] | Chen K. J., Scott H. S., Madden D. G., Pham T., Kumar A., Bajpai A., Lusi M., Forrest K. A., Space B., Perry J. J., Zaworotko M. J ., Chem. 2016, 1( 5), 753— 765 |
| [26] | Yang L. F., Cui X. L., Yang Q. W., Qian S. H., Wu H., Bao Z. B., Zhang Z. G., Ren Q. L., Zhou W., Chen B. L., Xing H. B., ,. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30( 10), 1705374 |
| [27] | Yin X. J., Zhu G. S., Yang W. S., Li Y. S., Zhu G. Q., Xu R., Sun J. Y., Qiu S. L., Xu R. R., ,. Adv. Mater. 2005, 36( 45), 2006— 2010 |
| [28] | Elsaidi S. K., Mohamed M. H., Simon C. M., Braun E., Pham T., Forrest K. A., Xu W. Q., Banerjee D., Space B., Zaworotko M. J., Thallapally K. J., ,. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8( 3), 2373— 2380 |
| [1] | YANG Qingfeng, LYU Liang, LAI Xiaoyong. Progress on Preparation and Electrocatalytic Application of Hollow MOFs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220666. |
| [2] | ZHU Haotian, JIN Meixiu, TANG Wensi, SU Fang, LI Yangguang. Properties of Transition Metal-biimidazole-Dawson-type Tungstophosphate Hybrid Compounds as Supports for Enzyme Immobilization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220328. |
| [3] | ZHANG Zhinan, CHENG Haiming, TENG Shiyong, ZHANG Ying. Synthesis and Optical Properties of RbPb2Cl5 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220418. |
| [4] | YUAN Meng, ZHAO Yingjie, WU Yuchen, JIANG Lei. Assembly of Perovskite Arrays and Multifunctional Detector Applications [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220448. |
| [5] | ZHANG Qian, LIU Yawei, WANG Fan, LIU Kai, ZHANG Hongjie. High-Resolution in vivo imaging, Diagnosis and Treatment Applications of Rare-Earth-Based Nanomaterials [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220552. |
| [6] | ZHAO Hengzhi, YU Fangzhi, LI Xiangfei, LI Lele. Advances in Biosensing and imaging Based on the Integration of DNA and UCNPs [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 0, (): 20220626. |
| [7] | XING Peiqi, LU Tong, LI Guanghua, WANG Liyan. Controllable Syntheses of Two Cd(II) Metal-organic Frameworks Possessing Related Structures [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220218. |
| [8] | SHAO Wenhui, HU Xin, SHANG Jing, LIN Feng, JIN Liming, QUAN Chunshan, ZHANG Yanmei, LI Jun. Design, Synthesis and Photocatalytic Antibacterial Mechanism of Ag-AgVO3/BiVO4 Composite as a High-efficient and Broad-spectral Antibacterial Agent [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220132. |
| [9] | LI Dan, XIAO Liping, FAN Jie. Inorganic-based Surface Materials with Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Properties and Their Mechanisms of Action [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220301. |
| [10] | ZHANG Taiwen, GUO Jun, ZHANG Dan, YUAN Changmei, QIU Shuangyan. Synthesis, Characterization and Catalytic Oxidation Iodine Ion Performance of trz-Cl-Cu-PMo12 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220215. |
| [11] | WU Yu, LI Xuan, YANG Hengpan, HE Chuanxin. Construction of Cobalt Single Atoms via Double-confinement Strategy for High-performance Electrocatalytic Reduction of Carbon Dioxide [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(9): 20220343. |
| [12] | ZHAO Sheng, HUO Zhipeng, ZHONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Hong, HU Liqun. Preparation of Modified Gadolinium/Boron/Polyethylene Nanocomposite and Its Radiation Shielding Performance for Neutron and Gamma-ray [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [13] | LU Cong, LI Zhenhua, LIU Jinlu, HUA Jia, LI Guanghua, SHI Zhan, FENG Shouhua. Synthesis, Structure and Fluorescence Detection Properties of a New Lanthanide Metal-Organic Framework Material [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220037. |
| [14] | ZHUANG Jiahao, WANG Dingsheng. Current Advances and Future Challenges of Single-atom Catalysis [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220043. |
| [15] | LI Jiafu, ZHANG Kai, WANG Ning, SUN Qiming. Research Progress of Zeolite-encaged Single-atom Metal Catalysts [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220032. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||