

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (6): 1128.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190006
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Chibao( ), PAN Qi, CHEN Huashi, LIANG Xing, LÜ Guoling
), PAN Qi, CHEN Huashi, LIANG Xing, LÜ Guoling
Received:2019-01-04
Online:2019-06-10
Published:2019-05-11
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
HUANG Chibao,PAN Qi,CHEN Huashi,LIANG Xing,LÜ Guoling. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Environment-sensitive Probe†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(6): 1128.
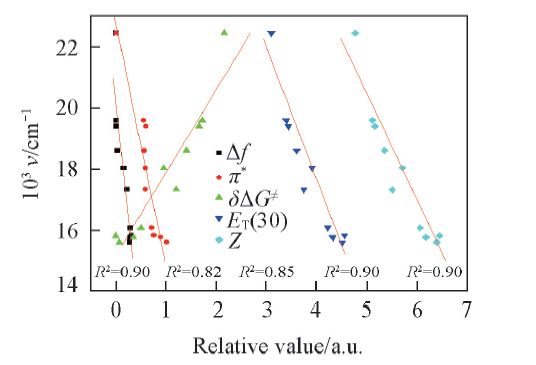
Fig.1 Correlations between the emission maxima of SP in various solvents and selected solvent parameters such as Δf, π*, δΔG≠, ET(30) and Z c(SP)=1 μmol/L, λex(OP)=410 nm.
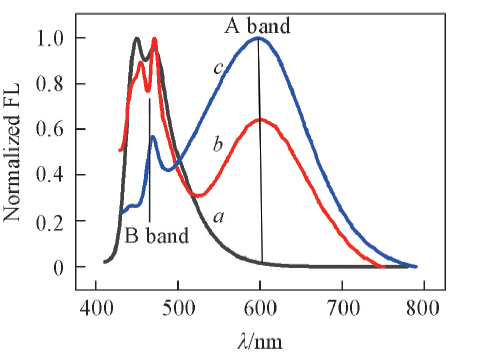
Fig.4 Normalized emission spectra of SP in ethanol at different temperatures c(SP)=3.6 μmol/L, λex(OP)=410 nm, a. 77 K; b. 77—294 K; c. 294 K. No control of the temperature was available when samples at 77 K were warmed up. The exact temperature of spectrum B was unknown, visual inspection showed that was mostly a solution.
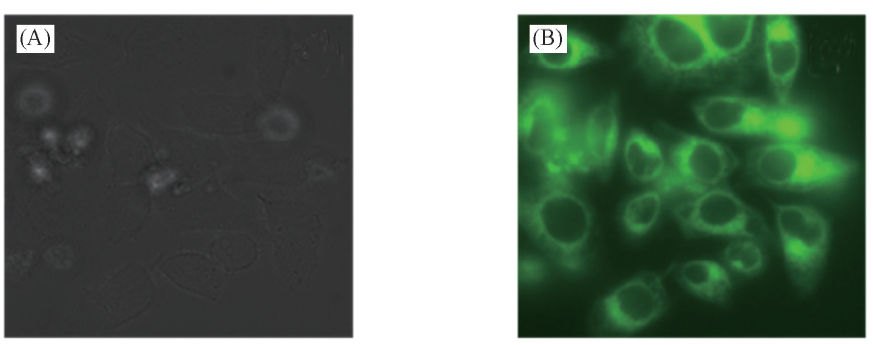
Fig.7 Bright-field(A) and two-photon microscopy(TPM, B) image 1 μmol/L SP-labeled mouse fibroblast two-photon fluorescent images were collected at 550—650 nm, λex=790 nm, replicate experiments 5 times.
| [1] | Luby-Phelps K., Intern. Rev. Cytol., 2000, 192(4), 189-221 |
| [2] | Rohrbach D.H., Timpl R., Molecular and Cellular Aspects of Basement Membranes, Academic Press, San Diego, 1993, 1-448 |
| [3] | Yeagle P.L., The Membranes of Cells, Academic Press, San Diego, 1993, 1-286 |
| [4] | Ohnishi S.T., Ohnishi T., Membrane Abnormalities in Sickle Cell Disease and in Other Red Blood Cell Disorders, CRC Press, Boca Raton, 1994, 1-356 |
| [5] | Reinhart W. H., Biorheology, 2001, 38(2/3), 203-212 |
| [6] | Moriarty P. M., Gibson C. A., Cardiovasc. Rev. Rep.,2003, 24, 321-325 |
| [7] | Uchimura I., Numano F., Diabetes Frontier,1997, 8(1), 33-37 |
| [8] | Simon A., Gariepy J., Chironi G., Megnien J. L., Levenson J., J. Hypertens.,2002, 20(2), 159-169 |
| [9] | Oppenheimer N., Diamant H., Biophys.J.,2009, 96(8), 3041-3049 |
| [10] | Owen D. M., Williamson D., Rentero C., Gaus K., Traffic,2009, 10(8), 962-971 |
| [11] | Frick M., Schmidt K., Nichols B. J., Curr. Biol.,2007, 17(5/6), 462-467 |
| [12] | Luneva O. G., Brazhe N. A., Maksimova N. V., Rodnenkov O. V., Parsina E. Y., Bryzgalova N. Y., Maksimov G. V., Rubin A. B., Orlov S. N., Chazov E. I., Pathophysiology,2007, 14(1), 41-46 |
| [13] | Goodwin J. S., Drake K. R., Remment C. L., Kenworthy A. K., Biophys.J.,2005, 89(2), 1398-1410 |
| [14] | Dibner M. D., Ireland K. A., Koerner L. A., Dexter D. L., Cancer Res.,1985, 45(10), 4998-5003 |
| [15] | Aleardi A. M., Benard G., Augereau O., Malgat M., Talbot J. C., Mazat J. P., Letellier T., Dachary-Prigent J., Solaini G. C., Rossignol R., J. Bioenerg. Biomembr.,2005, 37(4), 207-225 |
| [16] | Hou X., Richardson S. J., Aguilar M. I., Small D. H., Biochemistry,2005, 44(34), 11618-11627 |
| [17] | Ahn J. H., Kim T. Y., Kim Y. J., Han M. W., Yoon T. H., Chung J. W., Diabet.Med.,2006, 23(12), 1339-1343 |
| [18] | Salazar V. B. Y., Salazar V. M. A., Venzor V. C., Negrete A. C., Cabrales P., Diaz J. S., Intaglietta M., Clin. Hemorheol. Microcirc.,2008, 38(2), 67-74 |
| [19] | Kearney-Schwartz A., Virion J. M., Stoltz J. F., Drouin P., Zannad F., Fund. Clin.Pharmacol.,2007, 21, 387-396 |
| [20] | Velcheva I., Antonova N., Dimitrova V., Dimitrov N., Ivanov I., Clin. Hemorheol.Microcirc.,2006, 35(1/2), 155-157 |
| [21] | Bosman G. J. C. G. M.,Bartholomeus I. G. P., de Grip W. J., Gerontology,1991, 37, 95-112 |
| [22] | International Committee for Standardization in Haematology , J. Clin.Pathol., 1984, 37(10), 1147-1152 |
| [23] | Wang S., Boss A. H., Kensey K. R., Rosenson R. S., Clin. Chim.Acta,2003, 332(1/2), 79-82 |
| [24] | Haidekker M. A., Theodorakis E. A., Org. Biomol. Chem.,2007, 5, 1669-1678 |
| [25] | Demchenko P., Mely Y., Duportail G., Klymchenko A. S., Biophys.J.,2009, 96(9), 3461-3470 |
| [26] | Grabowski Z. R., Rotkiewicz K., Rettig W., Chem.Rev.,2003, 103(10), 3899-4031 |
| [27] | Zhong Q. L., Chen Y., Wang Y. H., Chi X. C., Wang Y., Ni M. C., Zhang H. Z., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2017, 33(3), 400-405 |
| [28] | Loutfy R. O., Pure Appl. Chem., 1986, 58(9), 1239-1248 |
| [29] | Levitt J. A., Kuimova M. K., Yahioglu G., Chung P. H., Suhling K., Phillips D., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113(27), 11634-11642 |
| [30] | Bohne C., Ihmels H., Waidelich M., Yihwa C., J. Am. Chem.Soc.,2005, 127(49), 17158-17159 |
| [31] | Uchiyama S., Takehira K., Yoshihara T., Tobita S., Ohwada T., Organic Letters,2006, 8(25), 5869-5872 |
| [32] | Sutharsan J., Lichlyter D., Wright N. E., Dakanali M., Haidekker M. A., Theodorakis E. A., Tetrahedron,2010, 66, 2582-2588 |
| [33] | Xu G. P., Tang Y. H., Lin W. Y., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2018, 34(4), 523-527 |
| [34] | Li H., Pang M. L., Guo X. F., Meng J. B., Chem. Res. Chinese Universities,2015, 31(3), 357-361 |
| [35] | Droumaguet C. L., Mongin O., Werts M. H. V., Blanchard-Desce M., Chem.Commun.,2005, 41(22), 2802-2804 |
| [36] | Strehmel B., Sarker A. M., Detert H., ChemPhysChem,2003, 4, 249-259 |
| [37] | Kim H. M., Jeong B. H., Hyon J. Y., An M. J., Seo M. S., Hong J. H., Lee K. J., Kim C. H., Joo T., Hong S. C., Cho B. R., J. Am. Chem.Soc.,2008, 130(13), 4246-4247 |
| [38] | Kim H. M., Choo H. J., Jung S. Y., Ko Y. G., Park W. H., Jeon S. J., Kim C. H., Joo T., Cho B. R., ChemBioChem,2007, 8(5), 553-559 |
| [39] | Huang C. B., Qu J., Qi J., Yan M., Xu G., Org.Lett.,2011, 13(6), 1462-1465 |
| [40] | Huang C. B., Chen H. S., Zeng B. P., Chen X. Y., Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2015, 43(4), 507-511 |
| (黄池宝,陈华仕,曾伯平,陈晓远. 分析化学, 2015, 43(4), 507-511) | |
| [41] | Huang C. B., Pan Q., Chen X. Y., Zhao G. L., Chen H. S., Liang X., Lv G. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(10),1751—1756 |
| (黄池宝,潘淇,陈晓远,赵光练,陈华仕,梁兴,吕国岭. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(10), 1751-1756) | |
| [42] | Huang C. B., Ding C., Analytica Chimica Acta,2011, 699(2), 198-205 |
| [43] | Huang H., He Q., Lin H., Bai F., Sun Z., Li Q., Polym. Adv.Technol.,2004, 15(1/2), 84-88 |
| [44] | Huang C., Fan J., Peng X., Lin Z., Guo B., Ren A., Cui J., Sun S., J. Photochem. Photobio. A: Chem.,2008, 199(2/3), 144-149 |
| [45] | BakerⅢ T. N., Doherty Jr. W. P., Kelley W. S., Newmeyer W., Rogers Jr J. E., Spalding R. E., Walter R. I., J. Org.Chem.,1965, 30(11), 3714-3718 |
| [46] | Reichardt C., Chem.Rev., 1994, 94(8), 2319-2358 |
| [47] | Kbamlet M. J., Abboud J. L. M., Taft R. W., Prog. Phys. Org.Chem.,1981, 13, 485-630 |
| [48] | Lippert E. Z., Z. Naturforsch.A, 1955, 10(7), 541-545 |
| [49] | Mataga N., Kaifu Y., Koizumi M., Bull. Chem. Soc.Jpn.,1956, 29(4), 465-471 |
| [50] | Platt J. R., J. Chem.Phys., 1949, 17(5), 470-481 |
| [51] | Grabowski Z. R., Rotkiewicz K., Rubaszewska W., Kirlor-Kaminska E., Acta Phys. Pol.A,1978, A54, 767-772 |
| [52] | Huang C. B., Ren A. X., Li H. B., Yang N. F., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2010, 31(11), 2222-2227 |
| (黄池宝,任安祥,李海渤, 阳年发. 高等学校化学学报, 2010, 31(11), 2222-2227) | |
| [53] | Huang C. B., Ren A. X., Acta Chimica Sinica,2007, 65(23),2765—2770 |
| (黄池宝,任安祥. 化学学报, 2007, 65(23), 2765-2770) |
| [1] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [2] | ZHAO Baodong, LIU Yajing, PAN Yongfei, LIU Weixiao, GAO Fulei, WANG Yinglei. Synthesis and Properties of Energetic Plasticizer 2,2-Dinitropropyl Trifluoropropanoate [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2815. |
| [3] | HUANG Chibao, KANG Shuai, PAN Qi, LYU Guoling. Carbazole-derived Dicyanostilbene Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Lipid Raft [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2443. |
| [4] | JIANG Lei, YAN Shengdi, LIN Yu, WU Guozhang. Studies on Viscosity and Chemical Structure Changes in Polycarbonate Melts under Nitrogen Protection [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 884. |
| [5] | LI Mengshuo, ZHANG Jing, LIU Dan, ZHU Yaxian, ZHANG Yong. Interactions of Pyrene with Human Serum Albumin and Bovine Serum Albumin: Microenvironmental Polarity Differences at Binding Sites [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 731. |
| [6] | ZHAO Yuhui, LI Mingle, LONG Saran, FAN Jiangli, PENG Xiaojun. Spectroscopic Characterization of Solvation Effect for a Polarity-Sensitive BDP [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(9): 2018. |
| [7] | YIN Shaoyun, ZHANG Luyin, WANG Zheng, PAN Mei. Glass-like Cuprous Iodide Complexes with Photoluminescence Tuning and Two-photon Emission Properties † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(4): 646. |
| [8] | WU Wenbo,LIU Bin. Two-photon Excitable Photosensitizers with Aggregation-induced Emission and Their Biomedical Applications † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 191. |
| [9] | LI Haocheng, GAO Yuan, XIN Yingchun, ZONG Hua, LIU Huiying, ZHANG Lei, ZHANG Lu. Interfacial Dilational Rheology of Polyether Demulsifiers [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(4): 809. |
| [10] | HUANG Chibao, PAN Qi, CHEN Huashi, LIANG Xing, LÜ Guoling. Triphenylamine-based Dicyanostilbene Type Two-photon Fluorescence Solvatochromic Probe† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(8): 1676. |
| [11] | HUANG Chibao,PAN Qi,CHEN Huashi,LIANG Xing,LÜ Guoling. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Lead Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(5): 897. |
| [12] | WANG Wenqi,LIN Yu,WU Guozhang. High-frequency Specific Dielectric Properties of Carbon Black Filled Rubber Composites† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2320. |
| [13] | MA Haizhu,HAN Wentao,TAO Fei. Effect of Side Groups on Conformational Characteristics of Containing Phosphor, Fluoride, Oxygen and Silane Polymers† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2304. |
| [14] | HUANG Chibao, PAN Qi, CHEN Xiaoyuan, ZHAO Guanglian, CHEN Huashi, LIANG Xing, LÜ Guoling. Dicyanostilbene-derived Two-photon Fluorescence Probe for Mercury Ions† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1751. |
| [15] | LI Juanli, PENG Zenghui, LI Jian, HU Minggang, AN Zhongwei, ZHANG Lu. Synthesis and Properties of Novel Isothiocyanatotolane Liquid Crystals with Terminal Difluorovinyl Substitute† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(10): 1788. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||