

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (10): 1945.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150327
• Physical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Yanqing1,2, ZHENG Huayan1, ZHANG Riguang1, LI Zhong1,*( ), WANG Baojun1, ZHAO Qiuyong2
), WANG Baojun1, ZHAO Qiuyong2
Received:2015-04-22
Online:2015-10-10
Published:2015-10-09
Contact:
LI Zhong
E-mail:lizhong@tyut.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
ZHANG Yanqing, ZHENG Huayan, ZHANG Riguang, LI Zhong, WANG Baojun, ZHAO Qiuyong. Density Functional Theory Investigation on the Effect of Alkali Metal Cations on the Catalytic Performance for Cu+Y Zeolites in Oxidative Carbonylation of Methanol†[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(10): 1945.
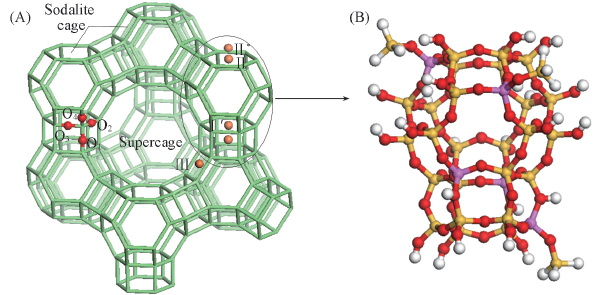
Fig.1 Structure of the faujasite(A) Stereodiagram of the faujasite-framework with cation sites and different crystallographic oxygen positions; (B) the cluster model Y zeolite. Red, yellow, purple, white and orange balls stand for O, Si, Al, H atoms, and cation sites, respectively.
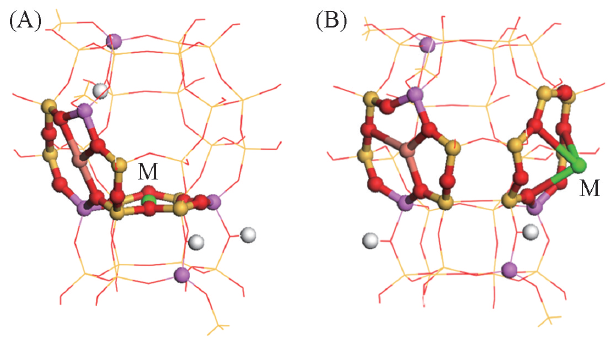
Fig.2 Stable structures of CuMY zeolitesOrange and green balls stand for Cu+ and alkali metal cations, respectively, others see Fig.1. (A) CuMY-Ⅰ'(M=Li, Na, K); (B) CuMY-Ⅱ*(M=Rb, Cs).
| Metal cation | Location | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | q(M)/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Ⅰ' | 605.88 | 0.623 |
| Na+ | Ⅰ' | 525.34 | 0.747 |
| K+ | Ⅰ' | 444.98 | 0.804 |
| Rb+ | Ⅱ* | 387.96 | 0.784 |
| Cs+ | Ⅱ* | 355.92 | 0.860 |
Table 1 Location of alkali metal cations after opti-mization, the net charge[q(M)] and the binding energies(Eb) of metal cations at different sites of Y zeolites
| Metal cation | Location | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | q(M)/e |
|---|---|---|---|
| Li+ | Ⅰ' | 605.88 | 0.623 |
| Na+ | Ⅰ' | 525.34 | 0.747 |
| K+ | Ⅰ' | 444.98 | 0.804 |
| Rb+ | Ⅱ* | 387.96 | 0.784 |
| Cs+ | Ⅱ* | 355.92 | 0.860 |
| Catalyst | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | q(Cu)/e | q(M)/e | Electronic configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuCuY-Ⅰ'[ | 647.39 | 0.393 | 0.340 | 3d9.9534s0.4254p0.229 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 658.63 | 0.385 | 0.617 | 3d9.9524s0.4334p0.230 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 672.20 | 0.367 | 0.758 | 3d9.9424s0.4554p0.235 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 690.10 | 0.340 | 0.821 | 3d9.9314s0.4974p0.233 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 670.70 | 0.343 | 0.783 | 3d9.9414s0.4764p0.239 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ*[ | 673.21 | 0.345 | 0.801 | 3d9.9434s0.4774p0.235 |
Table 2 Binding energies(Eb), net charge [q(Cu/M)] and electronic configurations of Cu+ of CuMY zeolite
| Catalyst | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | q(Cu)/e | q(M)/e | Electronic configuration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuCuY-Ⅰ'[ | 647.39 | 0.393 | 0.340 | 3d9.9534s0.4254p0.229 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 658.63 | 0.385 | 0.617 | 3d9.9524s0.4334p0.230 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 672.20 | 0.367 | 0.758 | 3d9.9424s0.4554p0.235 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 690.10 | 0.340 | 0.821 | 3d9.9314s0.4974p0.233 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 670.70 | 0.343 | 0.783 | 3d9.9414s0.4764p0.239 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ*[ | 673.21 | 0.345 | 0.801 | 3d9.9434s0.4774p0.235 |
| Catalyst | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbed CH3OH | Adsorbed CO | Co-adsorbed CO | Adsorbed CH3O | Co-adsorbed CH3O | Co-adsorbed CO/CH3O | TS | |
| CuCuY-Ⅰ' | 103.17 | 154.40 | 42.35 | 177.32 | 110.10 | 241.11 | 101.80 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 111.61 | 156.47 | 87.56 | 172.35 | 150.11 | 218.49 | 165.75 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 117.28 | 158.25 | 91.46 | 176.66 | 143.42 | 224.25 | 148.69 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 124.29 | 162.37 | 95.15 | 179.79 | 113.17 | 234.61 | 141.98 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 117.88 | 165.34 | 96.98 | 193.58 | 157.53 | 230.12 | 141.77 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ* | 103.17 | 153.66 | 95.89 | 175.11 | 145.62 | 222.59 | 167.19 |
Table 3 Adsorption energies of single CH3OH(CO, CH3O), co-adsorbed CO/CH3O and transition state(TS) involving in CO insertion into CH3O to CH3OCO on CuMY zeolites
| Catalyst | Eads/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adsorbed CH3OH | Adsorbed CO | Co-adsorbed CO | Adsorbed CH3O | Co-adsorbed CH3O | Co-adsorbed CO/CH3O | TS | |
| CuCuY-Ⅰ' | 103.17 | 154.40 | 42.35 | 177.32 | 110.10 | 241.11 | 101.80 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 111.61 | 156.47 | 87.56 | 172.35 | 150.11 | 218.49 | 165.75 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 117.28 | 158.25 | 91.46 | 176.66 | 143.42 | 224.25 | 148.69 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 124.29 | 162.37 | 95.15 | 179.79 | 113.17 | 234.61 | 141.98 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 117.88 | 165.34 | 96.98 | 193.58 | 157.53 | 230.12 | 141.77 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ* | 103.17 | 153.66 | 95.89 | 175.11 | 145.62 | 222.59 | 167.19 |
| Catalyst | q/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3OH | CO | co-adsorbed CO | CH3O | co-adsorbed CH3O | |
| CuCuY-Ⅰ'[ | 0.247 | 0.426 | 0.395 | -0.116 | -0.124 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 0.173 | 0.404 | 0.354 | -0.065 | -0.158 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 0.241 | 0.417 | 0.364 | -0.066 | -0.121 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 0.248 | 0.420 | 0.365 | -0.078 | -0.072 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 0.258 | 0.414 | 0.373 | -0.102 | -0.174 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ*[ | 0.243 | 0.409 | 0.378 | -0.098 | -0.161 |
Table 4 Net charge of single CH3OH(CO, CH3O) and co-adsorbed CO/CH3O on CuMY zeolites
| Catalyst | q/e | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH3OH | CO | co-adsorbed CO | CH3O | co-adsorbed CH3O | |
| CuCuY-Ⅰ'[ | 0.247 | 0.426 | 0.395 | -0.116 | -0.124 |
| CuLiY-Ⅰ' | 0.173 | 0.404 | 0.354 | -0.065 | -0.158 |
| CuNaY-Ⅰ' | 0.241 | 0.417 | 0.364 | -0.066 | -0.121 |
| CuKY-Ⅰ' | 0.248 | 0.420 | 0.365 | -0.078 | -0.072 |
| CuRbY-Ⅱ* | 0.258 | 0.414 | 0.373 | -0.102 | -0.174 |
| CuCsY-Ⅱ*[ | 0.243 | 0.409 | 0.378 | -0.098 | -0.161 |
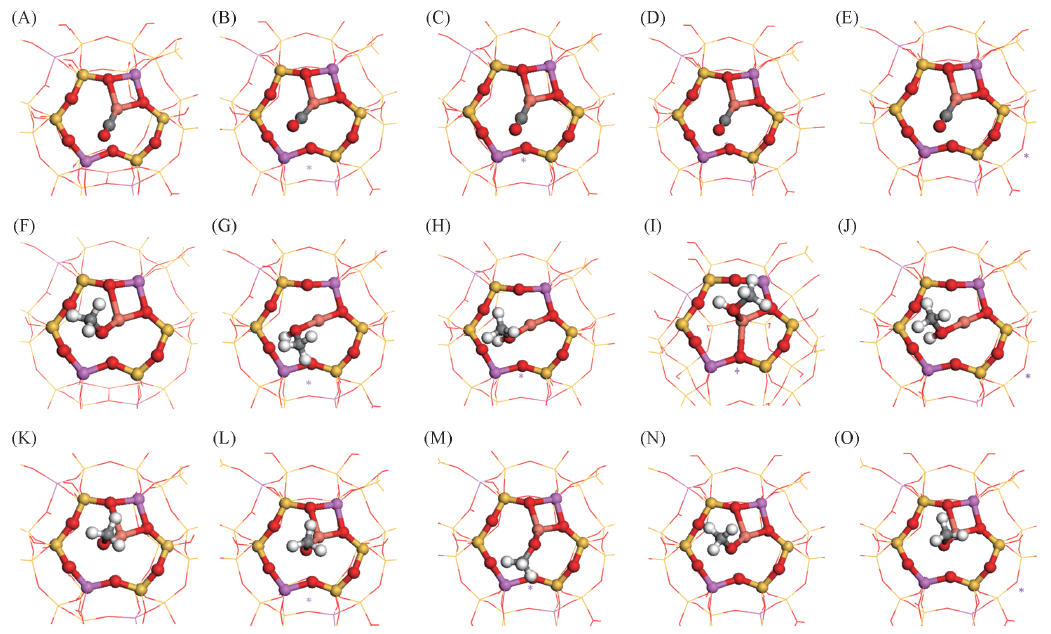
Fig.3 Stable configurations of CO, CH3OH and CH3O adsorbed on CuY and CuMY zeolitesBond lengths are in nm.(A) CO on CuCuY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1148, dCu—C=0.1788; (B) CO on CuLiY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1148, dCu—C=0.1787; (C) CO on CuNaY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1154, dCu—C=0.1784; (D) CO on CuKY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1148, dCu—C=0.1788; (E) CO on CuRbY-Ⅱ* , dC—O=0.1149, dCu—C=0.1786; (F) CH3OH on CuCuY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH4=0.1910; (G) CH3OH on CuLiY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH4=0.1929; (H) CH3OH on CuNaY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH4=0.1919; (I) CH3OH on CuKY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH4=0.2098; (J) CH3OH on CuRbY-Ⅱ*, dCu—OCH4=0.1932; (K) CH3O on CuCuY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH3=0.1810; (L) CH3O on CuLiY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH3=0.1804; (M) CH3O on CuNaY-Ⅰ' , dCu—OCH3=0.1801; (N) CH3O on CuKY-Ⅰ', dCu—OCH3=0.1799; (O) CH3O on CuRbY-Ⅱ* , dCu—OCH3=0.1808.
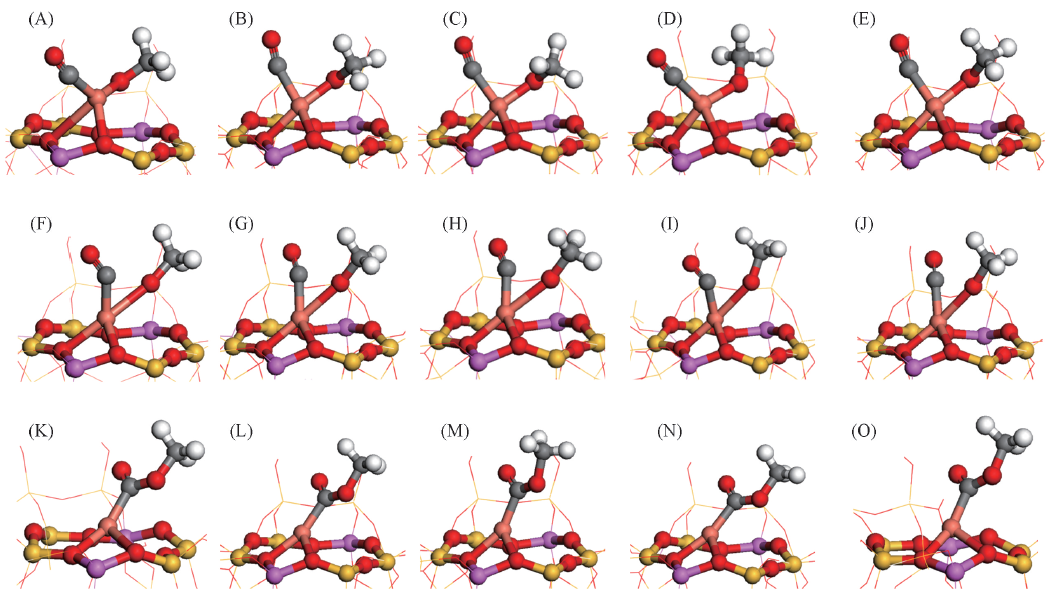
Fig.4 Stable configurations of co-adsorbed CO and CH3O on CuMY zeolitesBond lengths are in nm.(A) CO/CH3O on CuCuY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1145, dCu—O=0.1844, dC—OCH3=0.3312; (B) CO/CH3O on CuLiY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1142, dCu—O=0.1882, dC—OCH3=0.2488; (C) CO/CH3O on CuNaY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1140, dCu—O=0.1879, dC—OCH3=0.2670; (D) CO/CH3O on CuKY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1142, dCu—O=0.1845, dC—OCH3=0.3123; (E) CO/CH3O on CuRbY-Ⅱ* , dC—O=0.1140, dCu—O=0.1889, dC—OCH3=0.2539; (F) TS on CuCuY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1150, dCu—O=0.2356, dC—OCH3=0.2041; (G) TS on CuLiY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1179, dCu—O=0.2298, dC—OCH3=0.1845; (H) TS on CuNaY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1150, dCu—O=0.2353, dC—OCH3=0.1889; (I) TS on CuKY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1193, dCu—O=0.2414, dC—OCH3=0.2012; (J) TS on CuRbY-Ⅱ* , dC—O=0.1180, dCu—O=0.2275, dC—OCH3=0.1858; (K) CH3OCO on CuCuY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1225, dCu—O=0.2817, dC—OCH3=0.1336; (L) CH3OCO on CuLiY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1224, dCu—O=0.2824, dC—OCH3=0.1332; (M) CH3OCO on CuNaY-Ⅰ' , dC—O=0.1224, dCu—O=0.2805, dC—OCH3=0.1332; (N) CH3OCO on CuKY-Ⅰ', dC—O=0.1223, dCu—O=0.2816, dC—OCH3=0.1331; (O) CH3OCO on CuRbY-Ⅱ* , dC—O=0.1220, dCu—O=0.2726, dC—OCH3=0.1339.
| [1] | Keller N., Rebmann G., Keller V., J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem., 2010, 317(1/2), 1—18 |
| [2] | Pacheco M. A., Marshall C.L., Energ. Fuel, 1997, 11(1), 2—29 |
| [3] | Romano U., Tesel R., Maurl M. M., Rebora P., Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 1980, 19(3), 396—403 |
| [4] | Delledonne D., Rivetti F., Romano U., Appl. Catal. A: Gen., 2001, 221(1/2), 241—251 |
| [5] | Richter M., Fait M. J. G., Eckelt R., Schneider M., Radnik J., Heidemann D., Fricke R., J. Catal., 2007, 245(1), 11—24 |
| [6] | Zhang Y. H., Briggs D. N., Smit E. D., Bell A. T., J. Catal., 2007, 251(2), 443—452 |
| [7] | King S.T., J. Catal., 1996, 161(2), 530—538 |
| [8] | Gao Z., He M.Y., Dai Y. Y., Zeolite Catalysis and Separation Technology, China Petrochemical Press, Beijing, 1999 |
| (高滋, 何鸣元, 戴逸云. 沸石催化与分离技术, 北京: 中国石化出版社, 1999) | |
| [9] | Zheng H., Qi J., Zhang R., Li Z., Wang B., Ma X., Fuel Process. Technol., 2014, 128(0), 310—318 |
| [10] | Fu T., Zheng H., Niu Y., Wang R., Li Z., Acta Chimica Sinica, 2011, 69(15), 1765—1772 |
| (付廷俊, 郑华艳, 牛燕燕, 王瑞玉, 李忠. 化学学报,2011, 69(15), 1765—1772) | |
| [11] | Kieger S., Delahay G., Coq B., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2000, 25(1), 1—9 |
| [12] | Zhang Z., Wong T.T., Sachtler W.M.H., J. Catal., 1991, 128(1), 13—22 |
| [13] | Keane M. A., Microporous Mater., 1995, 3(4/5), 385—394 |
| [14] | Seiki T., Nakato A., Nishiyama S., Tsuruya S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2003, 5(17), 3818—3826 |
| [15] | Ren J., Wang D.L., Pei Y.L., Qin Z. F., Lin J.Y., Li Z., 2013, 34(11), 2594—2600 |
| (任军, 王冬蕾, 裴永丽, 秦志峰, 林建英, 李忠. 高等学校化学学报,2013, 34(11), 2594—2600) | |
| [16] | Nam J. K., Choi M. J., Cho D. H., Suh J. K., Kim S. B., J. Mol. Catal. A:Chem., 2013, 370(0), 7—13 |
| [17] | Zhang Y.H., Bell A.T., J. Catal., 2008, 255(2), 153—161 |
| [18] | Delley B., J.Chem.Phys., 2000, 113(18), 7756—7764 |
| [19] | Delley B., J.Chem.Phys., 1990, 92(1), 508—517 |
| [20] | Perdew J. P., Burke K., Ernzerhof M., Phys. Rev. Lett., 1996, 77(18), 3865—3868 |
| [21] | Halgren T.A., Lipscomb W.N., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1977, 49(2), 225—232 |
| [22] | Zheng X., Bell A.T., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2008, 112(13), 5043—5047 |
| [23] | Drake I.J., Zhang Y., Briggs D., Lim B., Chau T., Bell A. T., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110(24), 11654—11664 |
| [24] | Rejmak P., Sierka M., Sauer J., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2007, 9(40), 5446—5456 |
| [25] | Hill J. R., Freeman C.M., Delley B., J. Phys. Chem. A, 1999, 103(19), 3772—3777 |
| [26] | Sierka M., Eichler U., Datka J., Sauer J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1998, 102(33), 6397—6404 |
| [27] | Kim H.S., Bae D., Lim W. T. , Seff K., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2012, 116(16), 9009—9018 |
| [28] | Su H., Kim H. S., Seo S. M., Ko S. O., Suh J. M., Kim G. H., Lim W. T., Bull. Korean Chem. Soc., 2012, 33(8), 2785—2788 |
| [29] | Frising T., Leflaive P., Microporous Mesoporous Mater., 2008, 114(1—3), 27—63 |
| [30] | Berthomieu D., Ducéré J. M., Goursot A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2002, 106(30), 7483—7488 |
| [31] | Palomino G. T., Bordiga S., Zecchina A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2000, 104(36), 8641—8651 |
| [32] | Berthomieu D., Krishnamurty S., Coq B., Delahay G., Goursot A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2001, 105(6), 1149—1156 |
| [33] | Anderson S.A., Root T.W., J. Mol. Catal. A: Chem., 2004, 220(2), 247—255 |
| [34] | Bak J.,Clausen S., Appl. Spectrosc., 1999, 53(6), 697—700 |
| [35] | Zhang R., Song L., Wang B., Li Z., J. Comput. Chem., 2012, 33(11), 1101—1110 |
| [36] | Zhang R., Wang G., Wang B., J. Catal., 2013, 305, 238—255 |
| [37] | Hammond G. S.,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1955, 77(2), 334—338 |
| [1] | HE Hongrui, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Density-functional Theoretical Study on the Interaction of Indium Oxyhydroxide Clusters with Carbon Dioxide and Methane [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | WONG Honho, LU Qiuyang, SUN Mingzi, HUANG Bolong. Rational Design of Graphdiyne-based Atomic Electrocatalysts: DFT and Self-validated Machine Learning [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | LIU Yang, LI Wangchang, ZHANG Zhuxia, WANG Fang, YANG Wenjing, GUO Zhen, CUI Peng. Theoretical Exploration of Noncovalent Interactions Between Sc3C2@C80 and [12]Cycloparaphenylene Nanoring [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [4] | ZHOU Chengsi, ZHAO Yuanjin, HAN Meichen, YANG Xia, LIU Chenguang, HE Aihua. Regulation of Silanes as External Electron Donors on Propylene/butene Sequential Polymerization [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [5] | CHENG Yuanyuan, XI Biying. Theoretical Study on the Fragmentation Mechanism of CH3SSCH3 Radical Cation Initiated by OH Radical [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220271. |
| [6] | WANG Yuanyue, AN Suosuo, ZHENG Xuming, ZHAO Yanying. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies on 5-Mercapto-1,3,4-thiadiazole-2-thione Microsolvation Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [7] | MA Lijuan, GAO Shengqi, RONG Yifei, JIA Jianfeng, WU Haishun. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrogen Storage Properties of Sc, Ti, V-decorated and B/N-doped Monovacancy Graphene [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [8] | ZHONG Shengguang, XIA Wensheng, ZHANG Qinghong, WAN Huilin. Theoretical Study on Direct Conversion of CH4 and CO2 into Acetic Acid over MCu2Ox(M = Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+) Clusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [9] | HUANG Luoyi, WENG Yueyue, HUANG Xuhui, WANG Chaojie. Theoretical Study on the Structures and Properties of Flavonoids in Plantain [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [10] | WANG Jian, ZHANG Hongxing. Theoretical Study on the Structural-photophysical Relationships of Tetra-Pt Phosphorescent Emitters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [11] | HU Wei, LIU Xiaofeng, LI Zhenyu, YANG Jinlong. Surface and Size Effects of Nitrogen-vacancy Centers in Diamond Nanowires [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| [12] | YANG Yiying, ZHU Rongxiu, ZHANG Dongju, LIU Chengbu. Theoretical Study on Gold-catalyzed Cyclization of Alkynyl Benzodioxin to 8-Hydroxy-isocoumarin [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2299. |
| [13] | ZHENG Ruoxin, ZHANG Igor Ying, XU Xin. Development and Benchmark of Lower Scaling Doubly Hybrid Density Functional XYG3 [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [14] | LIU Yang, LI Qingbo, SUN Jie, ZHAO Xian. Direct Synthesis of Graphene on AlN Substrates via Ga Remote Catalyzation [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2271. |
| [15] | LIU Changhui, LIANG Guojun, LI Yanlu, CHENG Xiufeng, ZHAO Xian. Density Functional Theory Study of NH3 Adsorption on Boron Nanotubes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(7): 2263. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||