

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 445.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200605
收稿日期:2020-08-27
出版日期:2021-02-10
发布日期:2020-11-27
通讯作者:
闻利平
E-mail:wen@mail.ipc.ac.cn
基金资助:
XIN Weiwen1,2, WEN Liping1,2( )
)
Received:2020-08-27
Online:2021-02-10
Published:2020-11-27
Contact:
WEN Liping
E-mail:wen@mail.ipc.ac.cn
摘要:
在河水与海水的交界处实现渗透能提取与捕获是解决未来能源危机的重要方式之一. 渗透能因为储量大, 容易获取以及绿色可持续的优势受到广泛关注. 反向电渗析技术是一种能够有效捕获渗透能的方法之一, 目前已经得到了深入的研究与发展. 离子交换膜是反向电渗析技术转换渗透能的关键组件, 其性能的优异程度决定能量转换效率的高低. 常见的膜材料主要是高分子聚合物及其改性化合物, 最近一些二维材料如石墨烯、 氧化石墨烯、 二硫化钼、 各种框架材料及其改性复合物因优异的选择性离子传输、 纳米级通道、 丰富的表面功能基团以及可修饰性成为捕获渗透能的重要膜材料. 本文综合评述了二维材料作为离子传输通道的类型以及相应的传输机理; 例举了二维材料及其复合物的设计方案和在渗透能转换方面的具体应用; 最后提出了目前二维材料在渗透能转换领域中面临的挑战以及未来的发展方向.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
辛伟闻, 闻利平. 二维材料用于渗透能转换的研究进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 445.
XIN Weiwen, WEN Liping. Two-dimensional Materials for Osmotic Energy Conversion. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(2): 445.
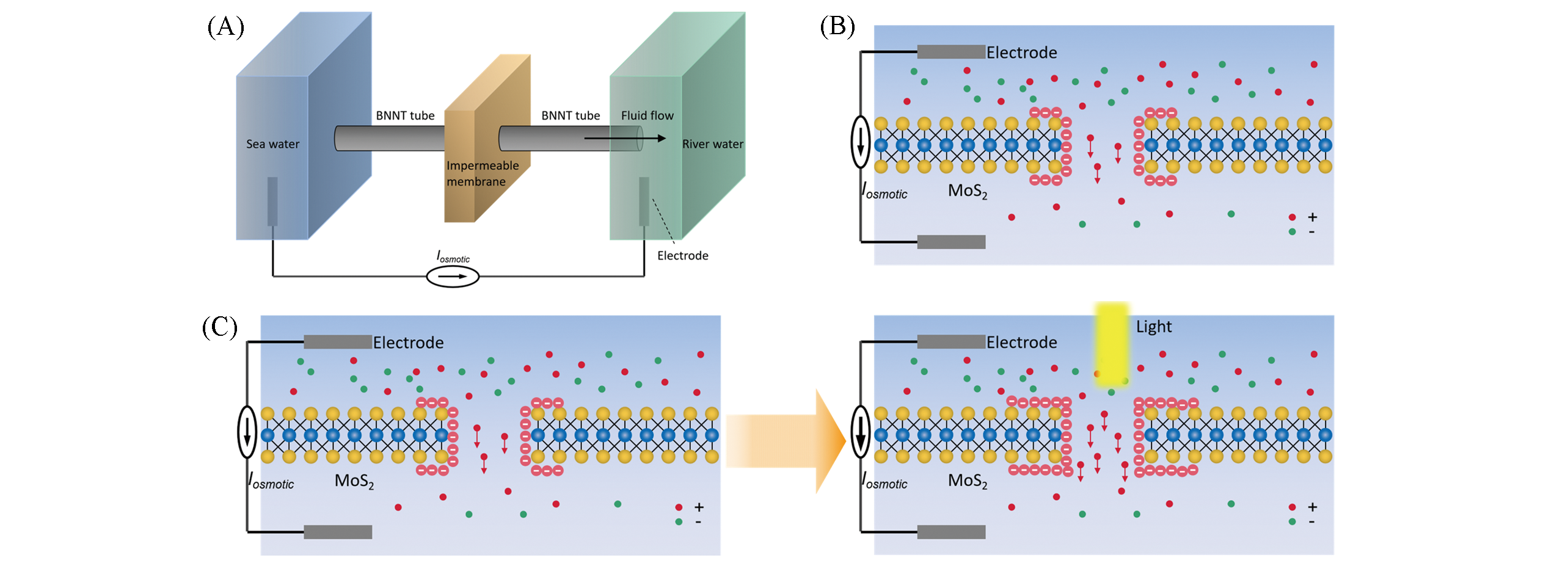
Fig.2 Different single?nanopore or single?channel for osmotic energy harvesting(A) Giant osmotic energy conversion measured in a single transmembrane boron nitride(BN) nanotube[15]. Copyright 2013, Springer Nature. (B) Single?layer molybdenum disulfide(MoS2) with single?nanopore as osmotic generator for osmotic energy capture[16]. Copyright 2016, Springer Nature. (C) Light?enhanced osmotic energy generation using MoS2 Nanopore[45]. Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
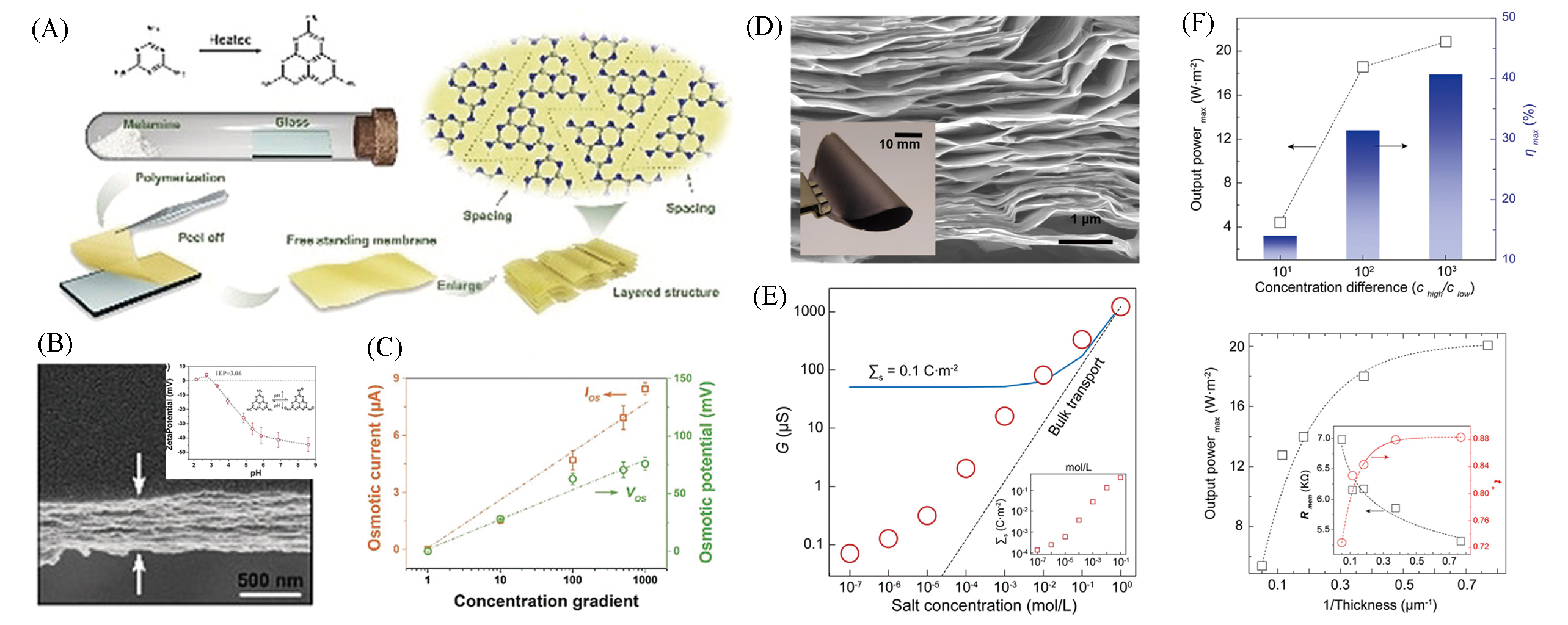
Fig.3 Up?scaling properties of multilayer 2D nanoporous membranes(A) Fabrication process of carbon nitride(C3N4) membrane using the vapor?deposition polymerization; (B) the cross?section of the freestanding multilayered C3N4 membrane and surface character; (C) the pure osmotic potential and current as a function of salt gradient for the C3N4 membrane[20]. Copyright 2018, Wiley?VCH. (D) Flexible two? dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXene membranes; (E) high ionic conductance of MXene membrane under different salt concentration; (F) osmotic energy conversion under different concentration gradients and thickness for MXene membrane[50]. Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
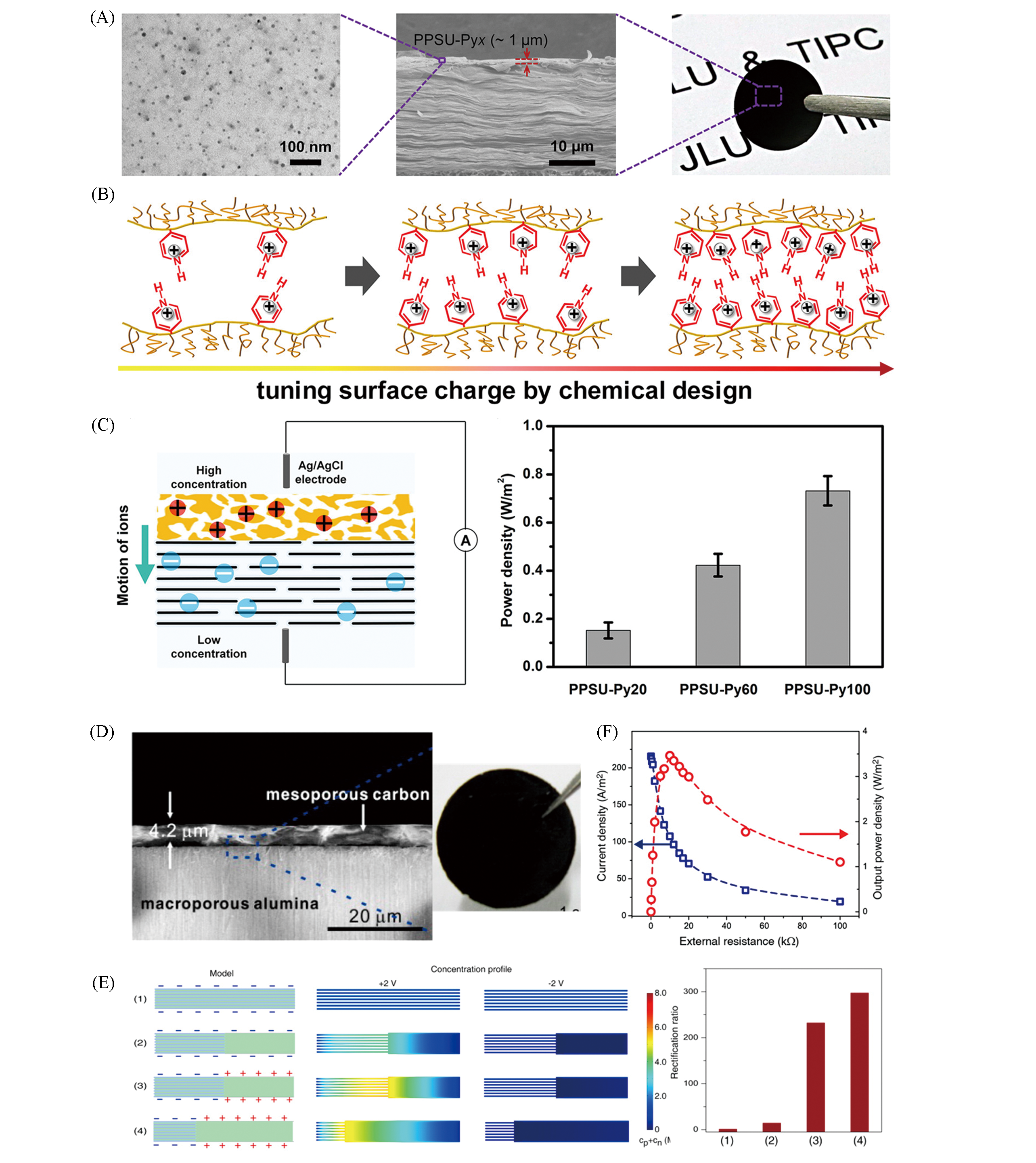
Fig.4 Heterojunction 2D membranes for enhanced ion transport and osmotic energy conversion(A) SEM images and photo of heterogeneous GO/polymer polyphenylsulfone pyridine(PPSU?Py) membrane; (B) tunable charge density of the polymer membrane by monitoring the charged monomer proportion of the copolymer; (C) application for energy conversion with increasing the proportion of pyridine groups in composite membranes[57]. Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society. (D) SEM image and photo of the membrane of mesoporous carbon layer on the top of a macroporous alumina membrane; (E) numerical simulation of the ion transport behaviors in heterojunction channels; (F) generated power translated to the external circuit and supplied an electronic load[62]. Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society. (E) The calculated ion concentration profile inside the nanochannels indicates that the ultrahigh ionic rectification results[the right image of (E)] from the remarkable ion concentration enrichment at positive voltage bias and depletion at negative voltage bias. Among four types of 2D configuration, symmetric nanochannels do not rectify ionic current(1). By sequentially introducing structural(2), electrostatic(3), and length(4) asymmetries, the rectification ratio is increased step wisely. (F) By mixing artificial seawater(0.5 mol/LNaCl) and river water(0.01 mol/LNaCl), the output power density reaches its peak value of up to 3.46 W/m2.
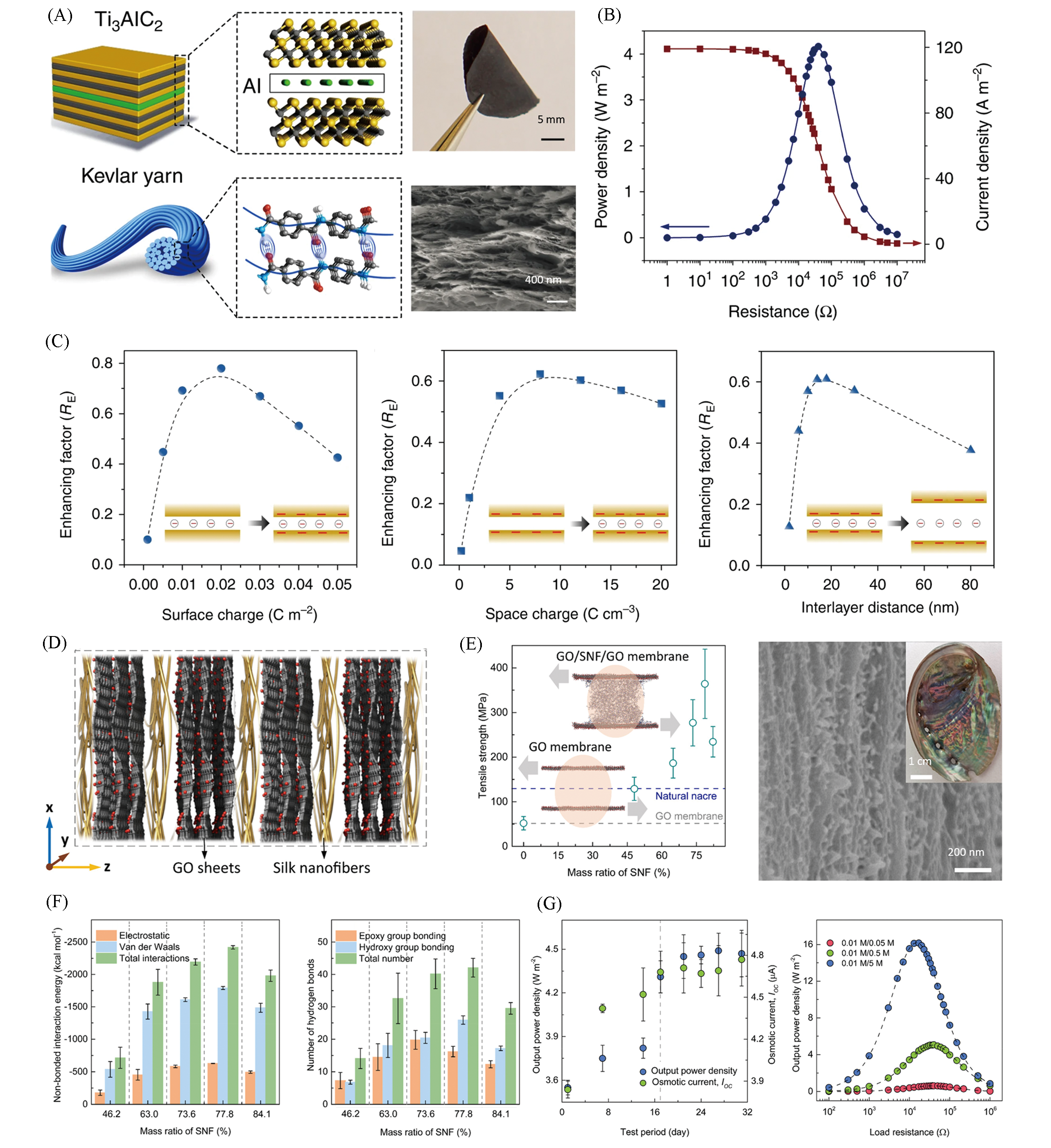
Fig.5 Homogeneous composite membrane for high?performance osmotic energy conversion(A) Fabrication of the MXene/Kevlar nanofiber composite membrane; (B) the power output by mixing natural sea water and river water by using the membrane; (C) continuum?based theoretical simulation for showing the influence of the surface charge on the enhancing factor with the space charge of -4 C/cm3, the influence of the space charge on the enhancing factor with the surface charge of -0.04 C/m2, and the relationship between the interlayer distance of 2D channel and the enhancing factor[65]. Copyright 2019, Springer Nature. (D) The biomimetic nacre?like multilayer assembly of the graphene oxide/silk nanofiber/graphene oxide(GO/SNF/GO) membrane; (E) tensile strength curves of different composite membranes, and SEM image evidencing the sandwich?like architecture of the composite membrane; (F) MD simulations of the calculated nonbonded interaction energy between GO and SNF with different mass ratios and the hydrogen bonds between GO and SNF with different mass ratios; (G) output power density and osmotic current as a function of test period[4]. Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society. (E) The dashed blue and gray lines indicate the corresponding values of natural nacre(130 MPa) and GO membrane, respectively. The inset shows two models for stretching, where the SNF serves as the lock function for crosslinking GO sheets. (G) The corresponding output power densities all obtain a maximum value at a moderate resistance.
| 1 | Logan B. E., Elimelech M., Nature,2012, 488(7411), 313—319 |
| 2 | Cipollina A., Micale G., Tamburini A., Tedesco M., Gurreri L., Veerman J., Grasman S., Sustainable Energy from Salinity Gradients,2016, 135—180 |
| 3 | Zhang Z., Kong X. Y., Xiao K., Liu Q., Xie G., Li P., Ma J., Tian Y., Wen L., Jiang L., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2015, 137(46), 14765—14772 |
| 4 | Xin W., Xiao H., Kong X. Y., Chen J., Yang L., Niu B., Qian Y., Teng Y., Jiang L., Wen L., ACS Nano,2020, 14, 9701—9710 |
| 5 | Dlugole P., Gambier A., Nijmeijer K., Wessling M., Environ. Sci. Technol.,2009, 43(17), 6888—6894 |
| 6 | Yip N. Y., Elimelech M., Environ. Sci. Technol.,2012, 46(9), 5230—5239 |
| 7 | Hu J., Xu S., Wu X., Wu D., Jin D., Wang P., Leng Q., Energy Convers. Manag.,2019, 183, 803—815 |
| 8 | Mei Y., Liu L., Lu Y. C., Tang C. Y., Environ. Sci. Technol.,2019, 53(8), 4640—4647 |
| 9 | Vermaas D. A., Saakes M., Nijmeijer K., Environ. Sci. Technol.,2011, 45(16), 7089—7095 |
| 10 | Macha M., Marion S., Nandigana V. V. R., Radenovic A., Nat. Rev. Mater.,2019, 4(9), 588—605 |
| 11 | Siria l., Bocquet M. L., Bocquet L., Nat. Rev. Chem.,2017, 1, 0091 |
| 12 | Li R., Jiang J., Liu Q., Xie Z., Zhai J., Nano Energy,2018, 53, 643—649 |
| 13 | Fu Y., Guo X., Wang Y., Wang X., Xue J., Nano Energy,2019, 57, 783—790 |
| 14 | Lee K. H., Park H., Eom W., Kang D. J., Noh S. H., Han T. H., J. Mater. Chem. A,2019, 7(41), 23727—23732 |
| 15 | Siria A., Poncharal P., Biance A. L., Fulcrand R., Blase X., Purcell S. T., Bocquet L., Nature,2013, 494(7438), 455—458 |
| 16 | Feng J., Graf M., Liu K., Ovchinnikov D., Dumcenco D., Heiranian M., Nandigana V., Aluru N. R., Kis A., Radenovic A., Nature,2016, 7615, 197—200 |
| 17 | Guo Y., Huang H., Li Z., Wang X., Li P., Deng Z., Peng X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2019, 11(38), 35496—35500 |
| 18 | Ji J., Kang Q., Zhou Y., Feng Y., Chen X., Yuan J., Guo W., Wei Y., Jiang L., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2017, 27(2), 1603623 |
| 19 | Perez M. D. B., Nicolai A., Delarue P., Meunier V., Drndic M., Senet P., Appl. Phys. Lett.,2019, 114(2), 023107 |
| 20 | Xiao K., Giusto P., Wen L., Jiang L., Antonietti M., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2018, 57(32), 10123—10126 |
| 21 | Gao J., Feng Y., Guo W., Jiang L., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2017, 46(17), 5400—5424 |
| 22 | Walker M. I., Ubych K., Saraswat V., Chalklen E. A., Braeuninger⁃Weimer P., Caneva S., Weatherup R. S., Hofmann S., Keyser U. F., ACS Nano,2017, 11(2), 1340—1346 |
| 23 | Grosjean B., Pean C., Siria A., Bocquet L., Vuilleumier R., Bocquet M. L., J. Phys. Chem. Lett.,2016, 7(22), 4695—4700 |
| 24 | He Z., Zhou J., Lu X., Corry B., ACS Nano,2013, 7, 10148—10157 |
| 25 | Sun P., Zheng F., Zhu M., Song Z., Wang K., Zhong M., Wu D., Little R. B., Xu Z., Zhu H., ACS Nano,2014, 8(1), 850—859 |
| 26 | Xin W., Zhang Z., Huang X., Hu Y., Zhou T., Zhu C., Kong X. Y., Jiang L., Wen L., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10(1), 3876—3885 |
| 27 | Chen J., Xin W., Kong X. Y., Qian Y., Zhao X., Chen W., Sun Y., Wu Y., Jiang L., Wen L., ACS Energy Lett.,2019, 5(3), 742—748 |
| 28 | Zhao Y., Wang J., Kong X. Y., Xin W., Zhou T., Qian Y., Yang L., Pang J., Jiang L., Wen L., Natl. Sci. Rev.,2020, 7(8), 1349—1359 |
| 29 | Zhang Z., Sui X., Li P., Xie G., Kong X., Xiao K., Gao L., Wen L., Jiang L., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2017, 139(26), 8905—8914 |
| 30 | Sui X., Zhang Z., Zhang Z., Wang Z., Li C., Yuan H., Gao L., Wen L., Fan X., Yang L., Zhang X., Jiang L., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2016, 55(42), 13056—13060 |
| 31 | Zhang Z., Kong X. Y., Xiao K., Xie G., Liu Q., Tian Y., Zhang H., Ma J., Wen L., Jiang L., Adv. Mater.,2016, 28, 144—150 |
| 32 | Cheng L. J., Guo L. J., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2010, 39(3), 923—938 |
| 33 | Farimani A. B., Min K., Aluru N. R., ACS Nano,2014, 8(8), 7914—7922 |
| 34 | Fanget A., Traversi F., Khlybov S., Granjon P., Magrez A., Forro L., Radenovic A., Nano Lett.,2014, 14(1), 244—249 |
| 35 | Heerema S. J., Dekker C., Nat. Nanotechnol.,2016, 11(2), 127—136 |
| 36 | Traversi F., Raillon C., Benameur S. M., Liu K., Khlybov S., Tosun M., Krasnozhon D., Kis A., Radenovic A., Nat. Nanotechnol.,2013, 8(12), 939—945 |
| 37 | Joshi R. K., Carbone P., Wang F. C., Kravets V. G., Su Y., Grigorieva I. V., Wu H. A., Geim A. K., Nair R. R., Science,2014, 343(6172), 752—754 |
| 38 | Esfandiar A., Radha B., Wang F. C., Yang Q., Hu S., Garaj S., Nair R. R., Geim A. K., Gopinadhan K., Science,2017, 358(6362), 511—513 |
| 39 | Chen L., Shi G., Shen J., Peng B., Zhang B., Wang Y., Bian F., Wang J., Li D., Qian Z., Xu G., Liu G., Zeng J., Zhang L., Yang Y., Zhou G., Wu M., Jin W., Li J., Fang H., Nature,2017, 550(7676), 380—383 |
| 40 | Abraham J., Vasu K. S., Williams C. D., Gopinadhan K., Su Y., Cherian C. T., Dix J., Prestat E., Haigh S. J., Grigorieva I. V., Carbone P., Geim A. K., Nair R. R., Nat. Nanotechnol.,2017, 12(6), 546—550 |
| 41 | Cheng C., Jiang G., Simon G. P., Liu J. Z., Li D., Nat. Nanotechnol.,2018, 13(8), 685—690 |
| 42 | Rollings R. C., Kuan A. T., Golovchenko J. A., Nat. Commun.,2016, 7, 11408 |
| 43 | Razmjou A., Asadnia M., Hosseini E., Habibnejad Korayem A., Chen V., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10(1), 5793 |
| 44 | Yang P., Liu K., Chen Q., Li J., Duan J., Xue G., Xu Z., Xie W., Zhou J., Energy Environ. Sci.,2017, 10(9), 1923—1927 |
| 45 | Graf M., Lihter M., Unuchek D., Sarathy A., Leburton J. P., Kis A., Radenovic A., Joule,2019, 3(6), 1549—1564 |
| 46 | Jia Z., Wang B., Song S., Fan Y., Renewable Sustainable Energy Rev.,2014, 31, 91—100 |
| 47 | Kim D., Duan C., Chen Y., Majumdar A., Microfluid. Nanofluid.,2010, 9(6), 1215—1224 |
| 48 | Ouyang W., Wang W., Zhang H., Wu W., Li Z., Nanotechnology,2013, 24(34), 345401 |
| 49 | Ries L., Petit E., Michel T., Diogo C. C., Gervais C., Salameh C., Bechelany M., Balme S., Miele P., Onofrio N., Voiry D., Nat. Mater.,2019, 18(10), 1112—1117 |
| 50 | Hong S., Ming F., Shi Y., Li R., Kim I. S., Tang C. Y., Alshareef H. N., Wang P., ACS Nano,2019, 13(8), 8917—8925 |
| 51 | Hong S., Constans C., Surmani Martins M. V., Seow Y. C., Guevara Carrio J. A., Garaj S., Nano Lett.,2017, 17(2), 728—732 |
| 52 | Raidongia K., Huang J., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2012, 134(40), 16528—16531 |
| 53 | Shan Y. P., Tiwari P. B., Krishnakumar P., Vlassiouk I., Li W. Z., Wang X. W., Darici Y., Lindsay S. M., Wang H. D., Smirnov S., He J., Nanotechnology,2013, 24(49), 495102 |
| 54 | Konkena B., Vasudevan S., J. Phys. Chem. Lett.,2012,3(7), 867—872 |
| 55 | Guo W., Cao L., Xia J., Nie F. Q., Ma W., Xue J., Song Y., Zhu D., Wang Y., Jiang L., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2010, 20(8), 1339—1344 |
| 56 | Schoch R. B., Han J., Renaud P., Rev. Mod. Phys.,2008, 80(3), 839—883 |
| 57 | Zhu X., Zhou Y., Hao J., Bao B., Bian X., Jiang X., Pang J., Zhang H., Jiang Z., Jiang L., ACS Nano,2017, 11(11), 10816—10824 |
| 58 | Zhang Y., Zhang S., Chung T. S., Environ. Sci. Technol.,2015, 49(16), 10235—10242 |
| 59 | Cervera J., Schiedt B., Ramirez P., Europhys. Lett.,2005, 71(1), 35—41 |
| 60 | White H. S., Bund A., Langmuir,2008, 24, 2212—2218 |
| 61 | Wang J., Zhang M., Zhai J., Jiang L., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2014, 16(1), 23—32 |
| 62 | Gao J., Guo W., Feng D., Wang H., Zhao D., Jiang L., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2014, 136(35), 12265—12272 |
| 63 | Zhang Z., Wen L., Jiang L., Chem. Soc. Rev.,2017, 47(2), 322—356 |
| 64 | Wu Y., Xin W., Kong X. Y., Chen J., Qian Y., Sun Y., Zhao X., Chen W., Jiang L., Wen L., Mater. Horiz.,2020, 7(10), 2702—2709 |
| 65 | Zhang Z., Yang S., Zhang P., Zhang J., Chen G., Feng X., Nat. Commun.,2019, 10(1), 2920—2928 |
| 66 | Ling S., Jin K., Kaplan D. L., Buehler M. J., Nano Lett.,2016, 16, 3795—3800 |
| 67 | Rockwood D. N., Preda R. C., Yücel T., Wang X. Q., Lovett M. L., Kaplan D. L., Nat. Protoc.,2011, 6(10), 1612—1620 |
| 68 | Zhang Z., He L., Zhu C., Qian Y., Wen L., Jiang L., Nat. Commun.,2020, 11(1), 875 |
| 69 | Zhu X., Hao J., Bao B., Zhou Y., Zhang H., Pang J., Jiang Z., Jiang L., Sci. Adv.,2018, 4, eaau1665 |
| 70 | Chen C., Liu D., He L., Qin S., Wang J., Razal J. M., Kotov N. A., Lei W., Joule,2020, 4(1), 247—261 |
| [1] | 李威, 罗飘, 黄廉湛, 崔志明. 基于聚苯乙烯磺酸的锂金属负极界面保护层的设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220166. |
| [2] | 张义超, 赵付来, 王宇, 王亚玲, 沈永涛, 冯奕钰, 封伟. 基于多层二硒化钨的高性能场效应晶体管的实验优化和理论模拟[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220113. |
| [3] | 张弛, 孙福兴, 朱广山. 双金属同构金属-有机框架材料CAU-21-Al/M的合成、 氮气吸附及复合膜性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210578. |
| [4] | 汪灿, 王殿宇, 苗伟宁, 田野. 基于超亲水纳米通道的智能可控微反应器[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1276. |
| [5] | 王伟, 卢香超, 周立军, 鲁艺珍, 曹阳. 基于二维压电材料功能性器件的设计、 构筑与性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 595. |
| [6] | 林生晃, 傅年庆, 鲍桥梁. 单元素二维材料及其衍生物作为电荷传输层在太阳能电池中应用的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 412. |
| [7] | 陈晓煜, 于然波. 纳米二硫化钼的掺杂及催化电解水产氢的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 475. |
| [8] | 邓亚茜, 吴志坦, 吕伟, 陶莹, 杨全红. 二维材料的凝胶化及电化学储能应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 380. |
| [9] | 余强敏, 张致远, 罗雨婷, 李洋, 成会明, 刘碧录. 金属性二维过渡金属硫化物的溶剂热合成及电催化析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 654. |
| [10] | 史江维, 孟楠楠, 郭亚梅, 于一夫, 张兵 . 二维材料用于电催化析氢的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 492. |
| [11] | 董其政, 翟锦. 基于二维材料的仿生纳流体通道在能量转化中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 432. |
| [12] | 陈明华, 李宏武, 范鹤, 李誉, 刘威铎, 夏新辉, 陈庆国. 二维过渡金属硫族化合物在超级电容器中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(2): 539. |
| [13] | 解忱, 陈娜, 杨雁冰, 袁荃. 核酸适体功能化的二维材料场效应晶体管传感器研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(11): 3406. |
| [14] | 张鑫, 赵付来, 王宇, 梁雪静, 冯奕钰, 封伟. 碲化锗场效应晶体管的制备及电学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(9): 2032. |
| [15] | 任文, 张国立, 闫涵, 胡兴华, 李焜, 王景凤, 李瑞琦. 超疏水聚苯胺/聚四氟乙烯复合膜的制备及油-水乳液分离性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2020, 41(4): 846. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||