

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 20240167.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20240167
乐鑫1,3, 贾庭芳2, 陈瑶1,3, 周远柱1,3, 曲佳菲1,3, 李聪1,3, 申静1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-03
出版日期:2025-01-10
发布日期:2024-07-08
通讯作者:
申静
E-mail:shenjing611@163.com
作者简介:第一联系人:共同第一作者.
基金资助:
YUE Xin1,3, JIA Tingfang2, CHEN Yao1,3, ZHOU Yuanzhu1,3, QU Jiafei1,3, LI Cong1,3, SHEN Jing1,3( )
)
Received:2024-04-03
Online:2025-01-10
Published:2024-07-08
Contact:
SHEN Jing
E-mail:shenjing611@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
为了提高现有复合树脂材料在近红外光下的固化效果和生物相容性, 合成了一种无细胞毒性的稀土上转换纳米粒子(RE UCNPs)掺杂的口腔复合树脂材料. 荧光光谱分析结果表明, 该RE UCNPs在808 nm近红外光激发下发射出450~475 nm的可见光, 可被光引发剂樟脑醌(CQ)有效吸收. 研究结果表明, 将该RE UCNPs掺入树脂基质中, 可增强树脂单体的固化性能、 机械性能和单体转化率, 并具备良好的生物相容性. 当该口腔复合树脂材料中含有1%(质量分数)樟脑醌/甲基丙烯酸二甲氨基乙酯(CQ/DMAEMA)和4%(质量分数)RE UCNPs时, 在808 nm近红外光的照射下实现了最佳的固化效果, 并可掺杂质量分数为40%的改性SiO2无机填料以获得较好的机械强度. RE UCNPs掺杂的口腔复合树脂材料在近红外光照射下具有较好的固化效果和生物相容性, 为龋病治疗提供了一个有前途的替代方案.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
乐鑫, 贾庭芳, 陈瑶, 周远柱, 曲佳菲, 李聪, 申静. 稀土上转换纳米粒子掺杂口腔复合树脂材料的近红外光固化. 高等学校化学学报, 2025, 46(1): 20240167.
YUE Xin, JIA Tingfang, CHEN Yao, ZHOU Yuanzhu, QU Jiafei, LI Cong, SHEN Jing. Near-infrared Light Curing of Dental Resin Composite Doped with Rare Earth Upconversion Nanoparticles. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2025, 46(1): 20240167.
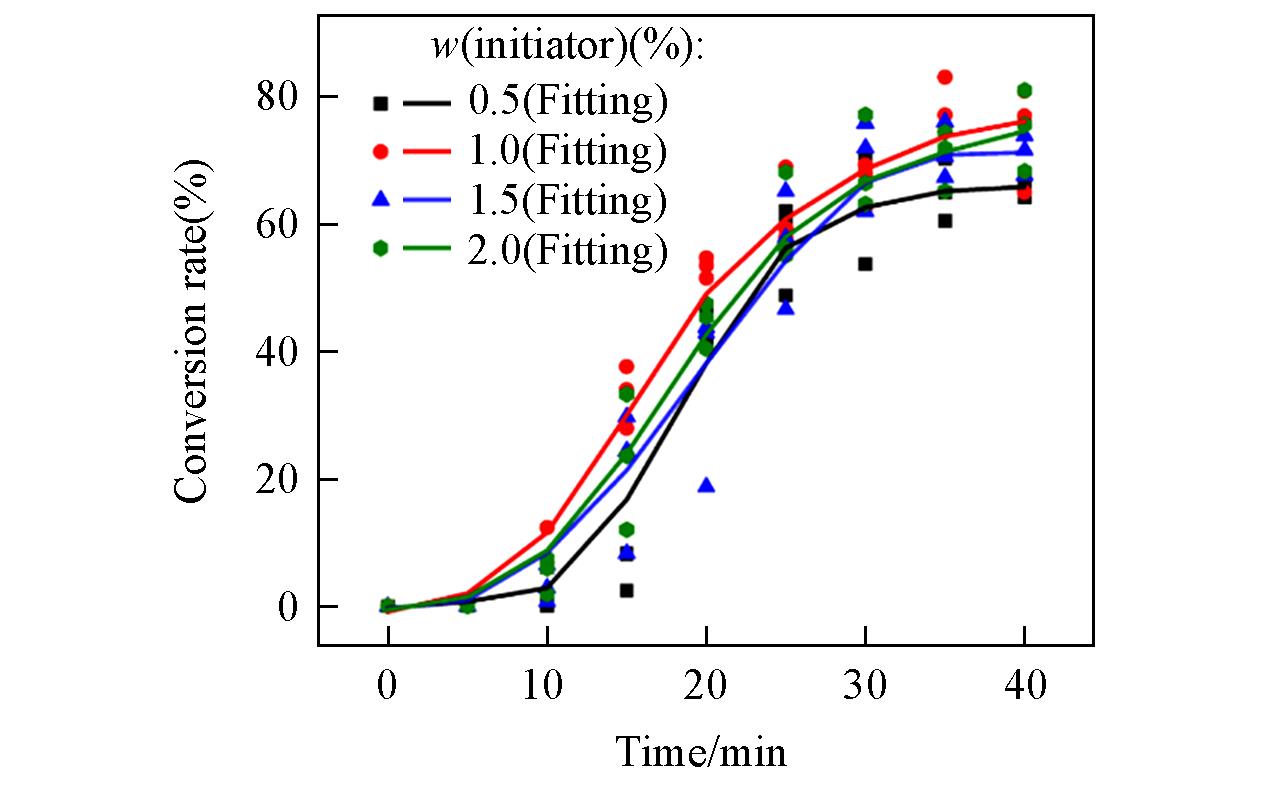
Fig.4 Conversion rate of 808 nm near⁃infrared light cured resin containing 2%(mass fraction) RE UCNPs at different initiator concentrations under different irradiation times
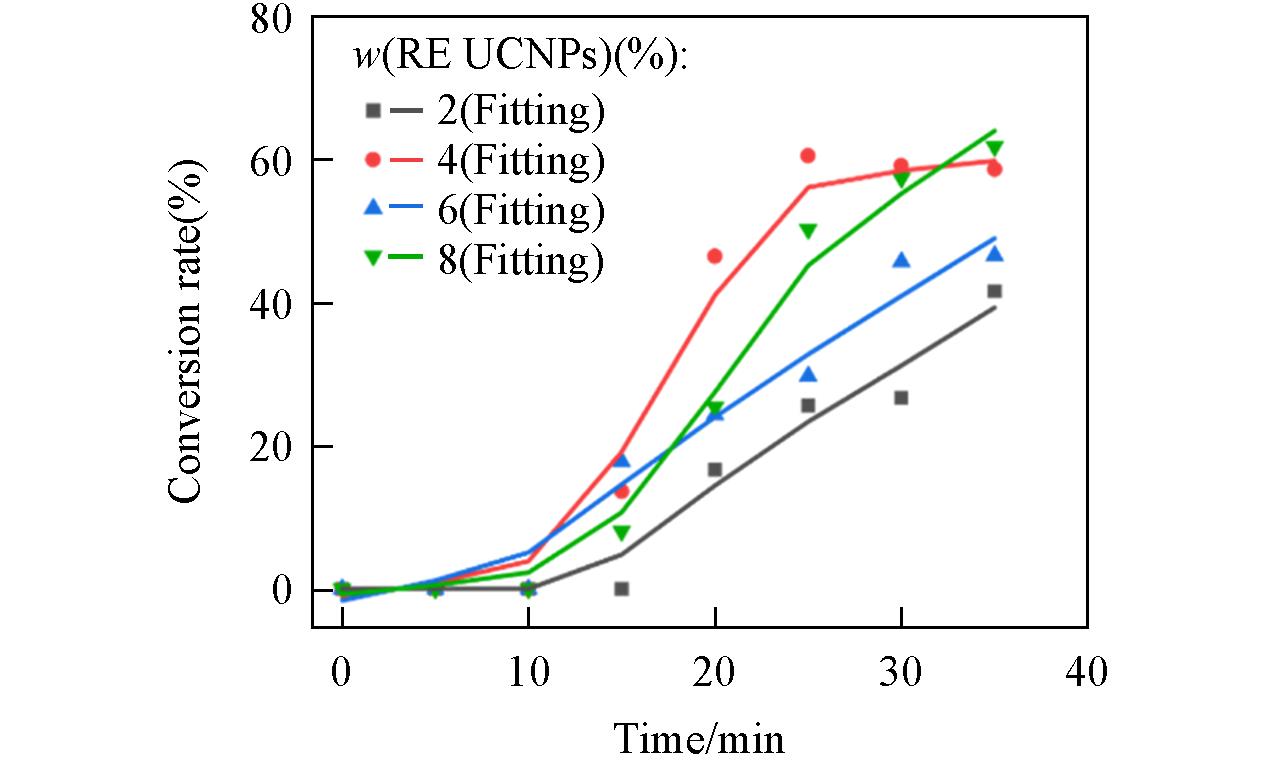
Fig.5 Conversion rate of 808 nm near⁃infrared light cured resin containing 1%(mass fraction) initiator and different RE UCNPs concentrationds under different irradiation times
| 1 | Vos T., Abajobir A. A., Abate K. H., The Lancet, 2017, 390(10100), 1211—1259 |
| 2 | Northridge M. E., Kumar A., Kaur R., Annu. Rev. Public Health, 2020, 41, 513—535 |
| 3 | Kassebaum N. J., Bernabé E., Dahiya M., BhandariB., Murray C. J. L., MarcenesM., J. Dent. Res., 2015, 94(5), 650—658 |
| 4 | Bowen R. L., J. Am. Dent. Assoc., 1963, 66(1), 57—64 |
| 5 | Holmstrup P., J. Oral Pathol. Med., 1991, 20(1), 1—7 |
| 6 | Eltahlah D., Lynch C. D., Chadwick B. L., Blum I. R., Wilson N. H. F., J. Dent., 2018, 72, 1—7 |
| 7 | Makvandi P., Jamaledin R., Jabbari M., Blum I. M., Wilson N. H. F., Dent. Mater., 2018, 34(6), 851—867 |
| 8 | Sevkusic M., Schuster L., Rothmund L., Dettinger K., Kirsten M. M. R., Landhuyt L. V., Durner J., Högg C., Reichl F., Dent. Mater., 2014, 30(6), 619—631 |
| 9 | Randolph L. D., Palin W. M., Bebelman S., Devaux J., Gallez B., Leloup G., Leprince J. G., Dent. Mater., 2014, 30(5), 594—604 |
| 10 | Chang M. C., Chen L. I., Chan C. P., Lee J. J., Wang T. M., Yang T. T., Lin P. S., Lin H. J., Chang H. H., Jeng J. H., Biomaterials, 2010, 31(32), 8164—8171 |
| 11 | Demarco F. F., Corrêa M. B., Cenci M. S., Moraes R. R., Opdam N. J. M., Dent. Mater., 2012, 28(1), 87—101 |
| 12 | Collares K., Opdam N. J. M., Laske M.,Bronkhorst E. M., DeMarco F. F., Correa M. B., Huysmans M., J. Dent. Res., 2017, 96(10), 1092—1099 |
| 13 | Qvist V., Dent. Caries: Dis. Clin. Manage., 2008, 2, 444—455 |
| 14 | Podgórski M., Dent. Mater., 2011, 27(8), 748—754 |
| 15 | Walters N. J., Xia W., Salih V., Ashley P. F., Young A. M., Dent. Mater., 2016, 32(2), 264—277 |
| 16 | Pérez⁃Mondragón A. A., Cuevas⁃Suárez C. E., Castillo O. R. S., González⁃López J. A., Herrera⁃González A. M., Mater. Sci. Eng. C, 2018, 93, 80—87 |
| 17 | Herrera⁃González A. M., González⁃López J. A., Cuevas⁃Suárez C. E., Polym. Compos., 2018, 39, E342—E350 |
| 18 | Wang X., Huyang G., Palagummi S. V.,Liu X., Skrtic D., Beauchamp C., Bowen R., Sun J., Dent. Mater., 2018, 34(2), 228—237 |
| 19 | He J., Garoushi S., Säilynoja E., Vallittu P., Lassila L., Dent. Mater., 2019, 35(4), 627—635 |
| 20 | Faria⁃e⁃Silva A. L., Dos Santos A., Tang A., Girotto E. M., Pfeifer C. S., Dent. Mater., 2018, 34(9), 1351—1358 |
| 21 | Bai X., Lin C., Wang Y., Ma J., Wang X., Yao X., Tang B., Dent. Mater., 2020, 36(6), 794—807 |
| 22 | Mirjalili A., Zamanian A., Hadavi S. M. M., J. Compos. Mater., 2019, 53(23), 3217—3228 |
| 23 | Finlayson L., Barnard I. R. M., McMillan L., Ibbotson S. H., Brown C. T. A., Eadie E., Wood K., Photochem. Photobiol., 2022, 98(4), 974—981 |
| 24 | Mallidi S., Anbil S., Bulin A. L., Obaid G., Ichikawa M., Hasan T., Theranostics, 2016, 6(13), 2458 |
| 25 | Anderson R. R., Parrish J. A., J. Invest. Dermatol., 1981, 77(1), 13—19 |
| 26 | Xue P., Bisoyi H. K., Chen Y., Zeng H., Yang J., Yang X., Lv P., Zhang X., Priimagi A., Wang L., Xu X., Li Q., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(7), 3390—3396 |
| 27 | Chen Y., Valenzuela C., Zhang X., Yang X., Wang L., Feng W., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 3036 |
| 28 | Ma S., Xue P., Valenzuela C., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2024, 34(7), 2309899 |
| 29 | Stevens L. M., Tagnon C., Page Z. A., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2022, 14(20), 22912—22920 |
| 30 | Strehmel B., Schmitz C., Bromme T., J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol., 2016, 29(1), 111—121 |
| 31 | McKenzie T. G., Fu Q., Uchiyama M., Satoh K., Xu J., Boyer C., Kamigaito M., Qiao G. G., Adv. Sci., 2016, 3(9), 1500394 |
| 32 | Shanmugam S., Xu J., Boyer C., Angew. Chem., 2016, 128(3), 1048—1052 |
| 33 | Liu H., Huang K., Valiev R. R., Laser Photon. Rev., 2018, 12(1), 1700144 |
| 34 | Li H., Wang X., Ohulchanskyy T. Y., Chen G. Y., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(6), 2000678 |
| 35 | Zhao H. Z., Yu F. Z., Li X. F., Li L. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(12), 20220626 |
| 赵恒智, 余方志, 李翔菲, 李乐乐. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(12), 20220626 | |
| 36 | Liu X., Wang Y., Li X., Yi Z., Deng R., Liang R., Xie X., Loong D., Song S., Fan D., All A., Zhang H., Huang L., Liu X., Nat. Commun., 2017, 8(1), 899 |
| 37 | Kang F., He J., Sun T., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(36), 1701842 |
| 38 | Yang J., Zhang X., Zhang X., Adv. Mater., 2021, 33(14), 2004754 |
| 39 | Wu S., Butt H. J., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(6), 1208—1226 |
| 40 | Wu S., Blinco J. P., Barner⁃Kowollik C., Chem. Eur. J., 2017, 23(35), 8325—8332 |
| 41 | Wang L., Dong H., Li Y., Xue C., Sun L. D., Yan C. H., Li Q., Adv. Mater.(Deerfield Beach, Fla.), 2015, 27(12), 2065—2069 |
| 42 | Wang L., Dong H., Li Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(12), 4480—4483 |
| 43 | Qiu Y., Yang Y., Valenzuela C., Adv. Opt. Mater., 2022, 10(9), 2102475 |
| 44 | Zhu J., Zhang Q., Yang T., Liu Y., Liu R., Nat. Commun., 2020, 11(1), 3462 |
| 45 | Zhao Y., Zhu J., He W., Liu Y., Sang X. X., Liu R., Nat. Commun., 2023, 14(1), 2381 |
| 46 | Li Z., Zou X., Shi F., Liu R., Yagci Y., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10(1), 3560 |
| 47 | Uo M., Kudo E., Okada A., J. Photopolym. Sci. Technol., 2009, 22(5), 551—554 |
| 48 | Stepuk A., Mohn D., Grass R. N., Zehnder M., Krämer K. W., Pellé F., Ferrier A., Stark W. J., Dent. Mater., 2012, 28(3), 304—311 |
| 49 | Fan Y., Liu L., Zhang F., Nano Today, 2019, 25, 68—84 |
| 50 | Zou Y., Zhao Y., Zhu R., Liu R., Macromolecules, 2022, 55, 2075—2084 |
| [1] | 曾湘楚, 叶雨婷, 武哲, 韦瑞松, 刘欢. pH介导铜络合物活化过一硫酸盐选择性氧化水体四环素的分子内电子转移机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(12): 20240337. |
| [2] | 曾湘楚 丁以宣 武哲 汪艳平 刘牧. 原位Cu络合调控类芬顿氧化强化水体痕量喹诺酮的选择性净化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20240358. |
| [3] | 胡文馨, 赵莹, 杜丹阳, 张红丹, 程鹏. ZSM-5封装Pt-La双金属催化剂的制备及对异丁烷裂解反应的催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(10): 20240244. |
| [4] | 张丽媛, 王查斯娜, 胡井香, 詹传郎. 离子掺杂调控双钙钛矿量子点发光性能的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(9): 20240126. |
| [5] | 宋宇航, 刘湛, 吕佳敏, 余申, 李小云, 孙明慧, 陈丽华, 苏宝连. 等级孔结构协同Fe改性提升ZSM-5分子筛催化苯甲醇烷基化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(5): 20240095. |
| [6] | 孟庆华, 史超. 分子筛型声学增强材料的储存耐候性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(3): 20230474. |
| [7] | 冀超, 李文, 张丽荣, 华佳, 刘云凌. 一例Eu-MOF材料的构筑及对Fe3+与硝基芳香族爆炸物的荧光检测性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(2): 20230455. |
| [8] | 杨玉婷, 丛明晓, 景晓飞, 刘佳. 低成本季铵盐类多孔材料的合成及氨气吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2024, 45(1): 20230438. |
| [9] | 孔祥宇, 廖力, 卢灿忠, 方千荣. 共价有机框架-杂多酸复合材料用于非均相催化烯烃环氧化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(12): 20230282. |
| [10] | 戚刚刚, 孟祥举. 中国沸石分子筛基础研究近年来的突破性进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230227. |
| [11] | 张宗洋, 李玉平, 张若茜, 刘宇峰, 陈泽, 韩丽娜, 韩培德. L沸石晶间转化快速合成SSZ-13沸石及其中空结构形成机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(10): 20230034. |
| [12] | 杨颖楠, 孙启明. EAB分子筛的合成及在甲醇制烯烃反应中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230119. |
| [13] | 汪梦蕾, 巩建晓, 夏云生. 纳米超粒子的水相制备及生物医学应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230020. |
| [14] | 张璐, 邹云鹤, 徐中胜, 刘云. 中空结构纳米材料在生物医学领域的应用: 现状与展望[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(8): 20230134. |
| [15] | 张小玉, 曲干, 薛冬萍, 闫文付, 张佳楠. 碳基催化剂用于电催化氧还原生产H2O2的研究进展: 策略、 计算及实际应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2023, 44(5): 20220775. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||