

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (4): 1114.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200636
收稿日期:2020-09-01
出版日期:2021-04-10
发布日期:2021-02-03
通讯作者:
安琪
E-mail:an@cugb.edu.cn
基金资助:Received:2020-09-01
Online:2021-04-10
Published:2021-02-03
Contact:
AN Qi
E-mail:an@cugb.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
压电现象在新能源开发、 传感、 医药材料设计及可穿戴电子设备中具有广泛的潜在应用, 并受到普遍重视. 在压电材料中, 聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)及其共聚物因具有良好的柔韧性、 易加工性、 稳定性和生物相容性等优点而备受关注. 本文综合评述了近年来在制备工艺和材料复合两个维度提高PVDF基压电材料输出性能的研究进展. 在研究PVDF压电性原理的基础上, 阐释了流延法、 静电纺丝法、 拉丝法及纳米限域策略等工艺和添加小分子、 高分子、 石墨类粒子及无机纳米粒子等复合策略提升其压电性能的机理. 这些制备工艺的提高和填料的掺杂有助于偶极子的排列和高β相的形成. 最后, 对目前存在的一些挑战进行了概述和讨论, 并对PVDF基材料的发展前景提出展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
张淑婷, 安琪. 高性能聚偏氟乙烯基柔性压电材料的设计策略进展. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1114.
ZHANG Shuting, AN Qi. Progress on the Design and Fabrication of High Performance Piezoelectric Flexible Materials Based on Polyvinylidene Fluoride. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(4): 1114.
| Technical characteristic | Device | Morphological characteristic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tape?casting | Normal pressure and temperature Simple | Glass substrate, vacuum drying oven | Flat |
Electrospinning | In situ electrochemistry Mechanical stretching | Electrospinning equipment | Nanofibers Flexible Thinner |
| Dehydrofluorination | Chemical modification Form planar chain conformation | Vacuum drying oven, hot?plate | Thermal stability Composability |
Nanoconfinement effect | Forming in the template Structure preferential crystallization to β phase Enhance ferroelectric characteristics | Vacuum drying oven, ultrasonic instrument, high voltage electrostatic field | Forming materials with nanostructure characteristics Such as nanotubes or porous structures |
Orientation method | The orientation is parallel to the direction of the external force Transformation of α form to β form | Vacuum drying oven, ultrathin slicer, wire drawing equipment | High aspect ratio Uniform cross?sectional area |
Table 1 Preparation characteristics of PVDF-based polymer
| Technical characteristic | Device | Morphological characteristic | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tape?casting | Normal pressure and temperature Simple | Glass substrate, vacuum drying oven | Flat |
Electrospinning | In situ electrochemistry Mechanical stretching | Electrospinning equipment | Nanofibers Flexible Thinner |
| Dehydrofluorination | Chemical modification Form planar chain conformation | Vacuum drying oven, hot?plate | Thermal stability Composability |
Nanoconfinement effect | Forming in the template Structure preferential crystallization to β phase Enhance ferroelectric characteristics | Vacuum drying oven, ultrasonic instrument, high voltage electrostatic field | Forming materials with nanostructure characteristics Such as nanotubes or porous structures |
Orientation method | The orientation is parallel to the direction of the external force Transformation of α form to β form | Vacuum drying oven, ultrathin slicer, wire drawing equipment | High aspect ratio Uniform cross?sectional area |
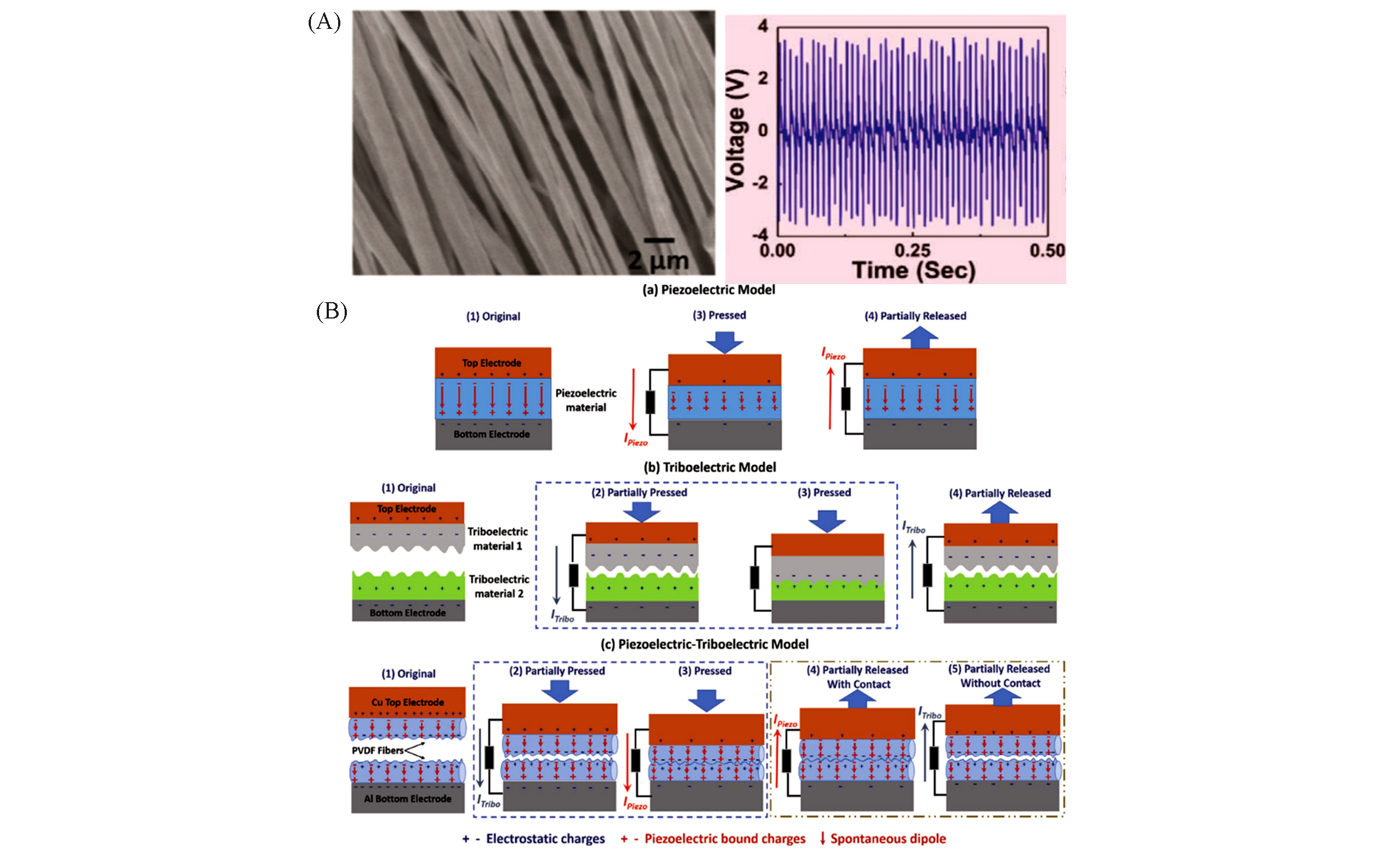
Fig.3 FESEM image of bundles of electro?spinned PVDF fibers presenting output voltages(A) and illustrative models for elucidating the electrical conversion mechanisms(B)[78]Copyright 2020, Wiley?VCH.
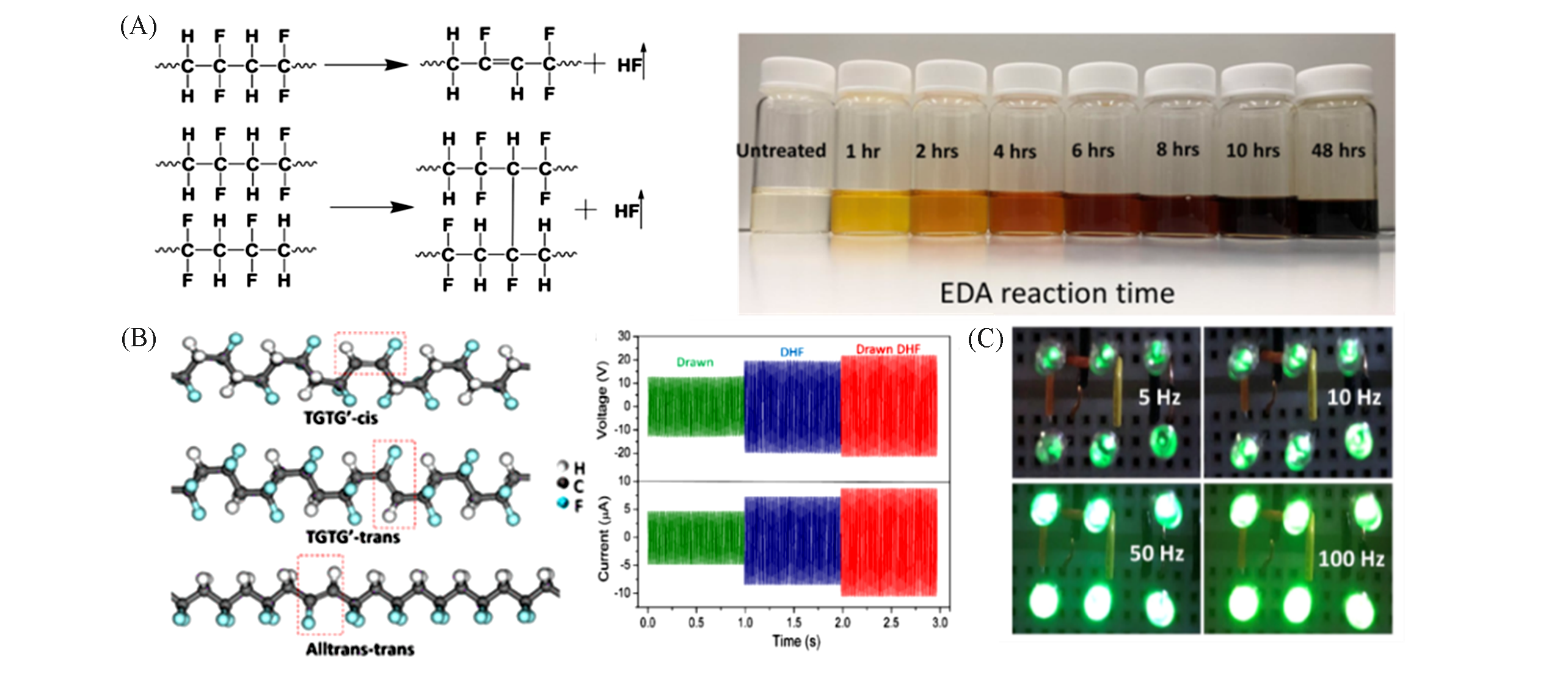
Fig.4 Structure scheme of dehydrofluorinated PVDF and digital photos of reaction mixture after varying reaction period(A), three possible molecular conformations of double bond units and open circuit voltage and short circuit current from the dehydrofluorinated PVDF(B) and digitalimages of dehydro?uorinated PVDF materials lightening LED array(C)[82]Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
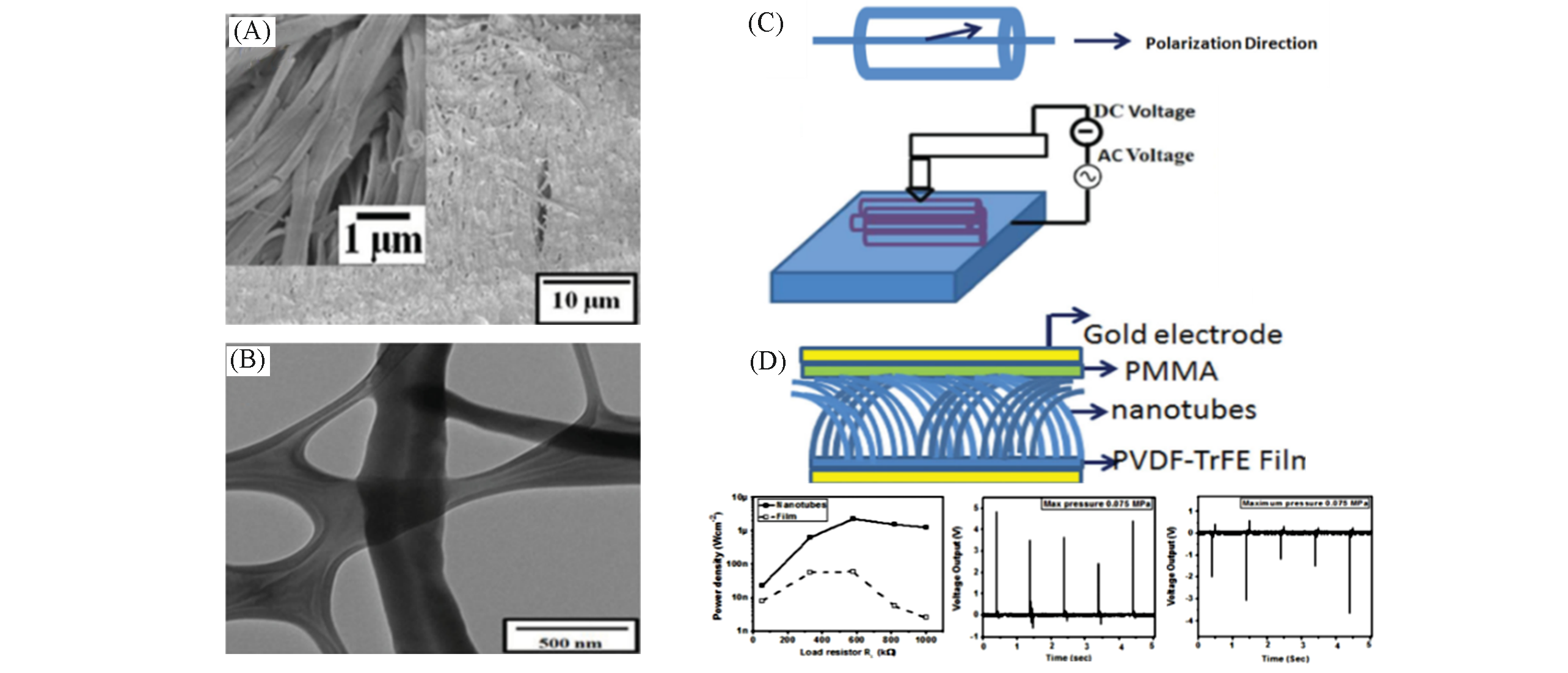
Fig.5 SEM and TEM images of PVDF nanotubes from AAO templates(A), schematic of polarization axis orientation in nanotubes(B), schematic of nanotubes orientation while measuring piezoelectric coef?cient and polarization switching(C), energy harvesting performance of the nanotubes(D)[86]Copyright 2014, Wiley?VCH.
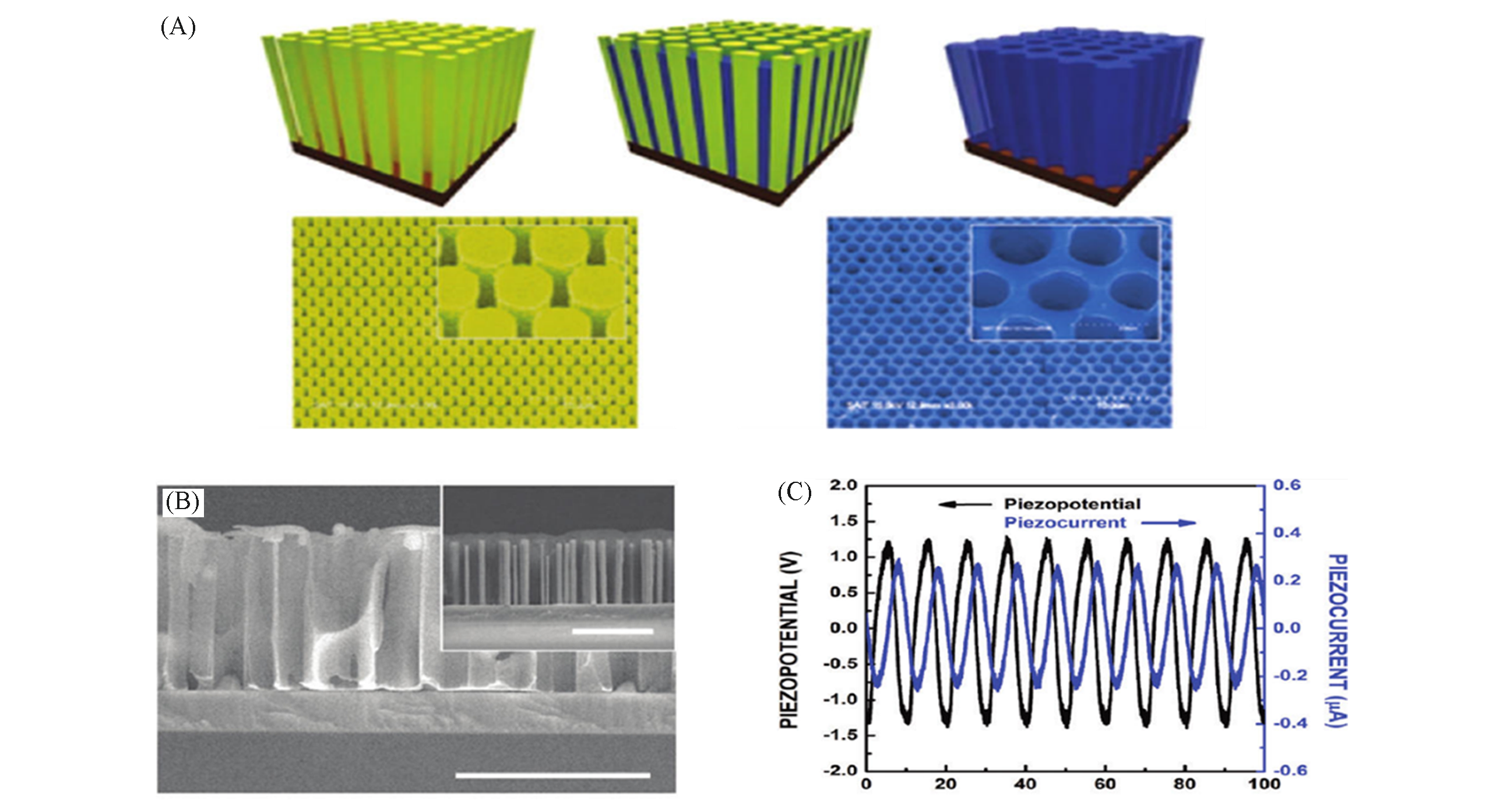
Fig.6 Schematic depiction of the fabrication process(A), cross section SEM images(B) and piezoelectric potential/current obtained from the porous PVDF nanostructures(C)[89]Copyright 2011, American Chemical Society.
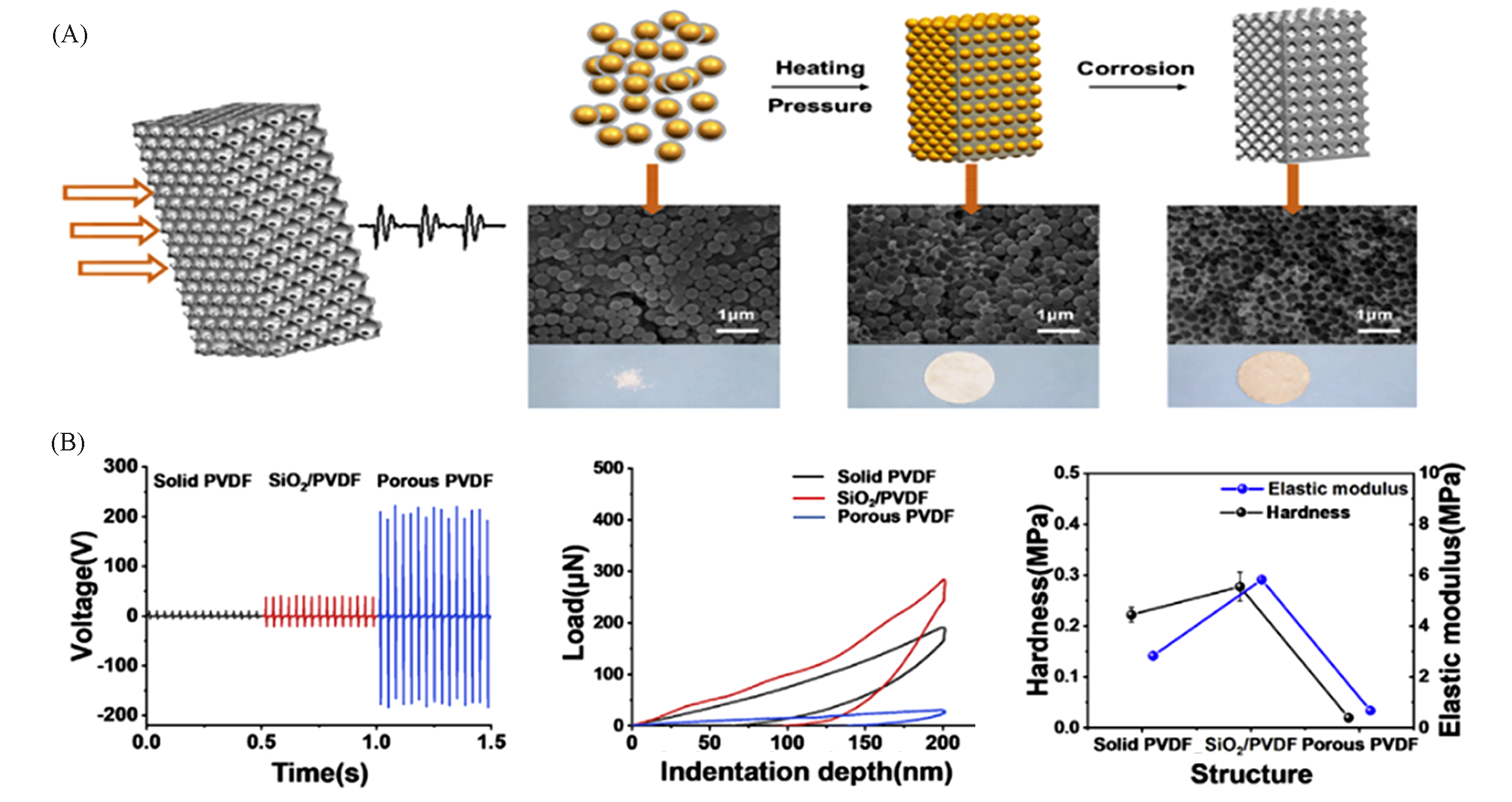
Fig.7 Schematic diagram of fabricating porous materials from reverse opal template and cross?section SEM images(A) and voltage and mechanical properties of solid PVDF blocks and porous blocks(B)[93]Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
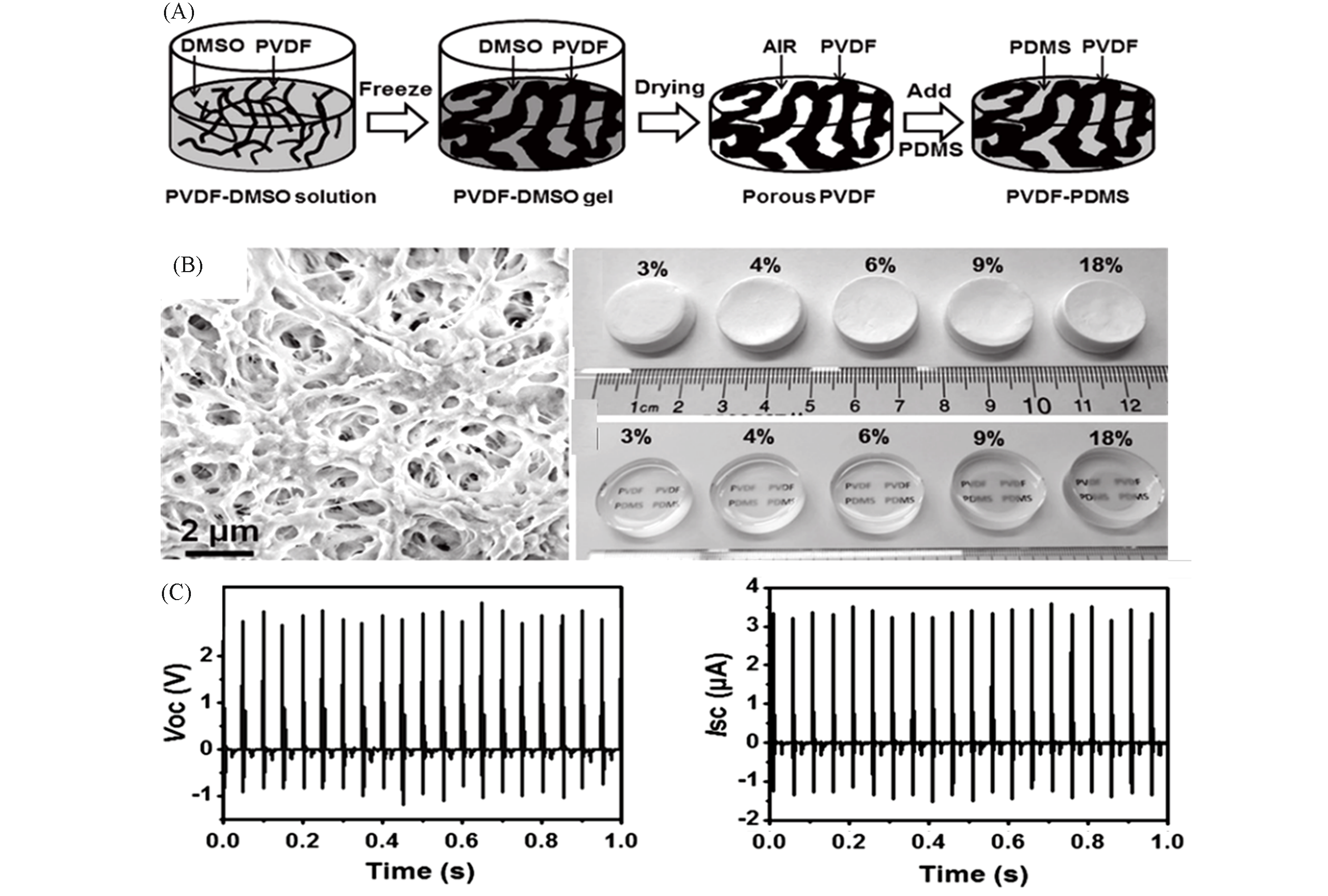
Fig.8 Schematic procedure of preparing mesoporous PVDF?PDMS composite film(A), SEM image and digital photos of porous PVDF(B) and piezoelectric output voltage and current profiles of 4% PVDF?PDMS NG slab(C)[97]Copyright 2016, Wiley?VCH.
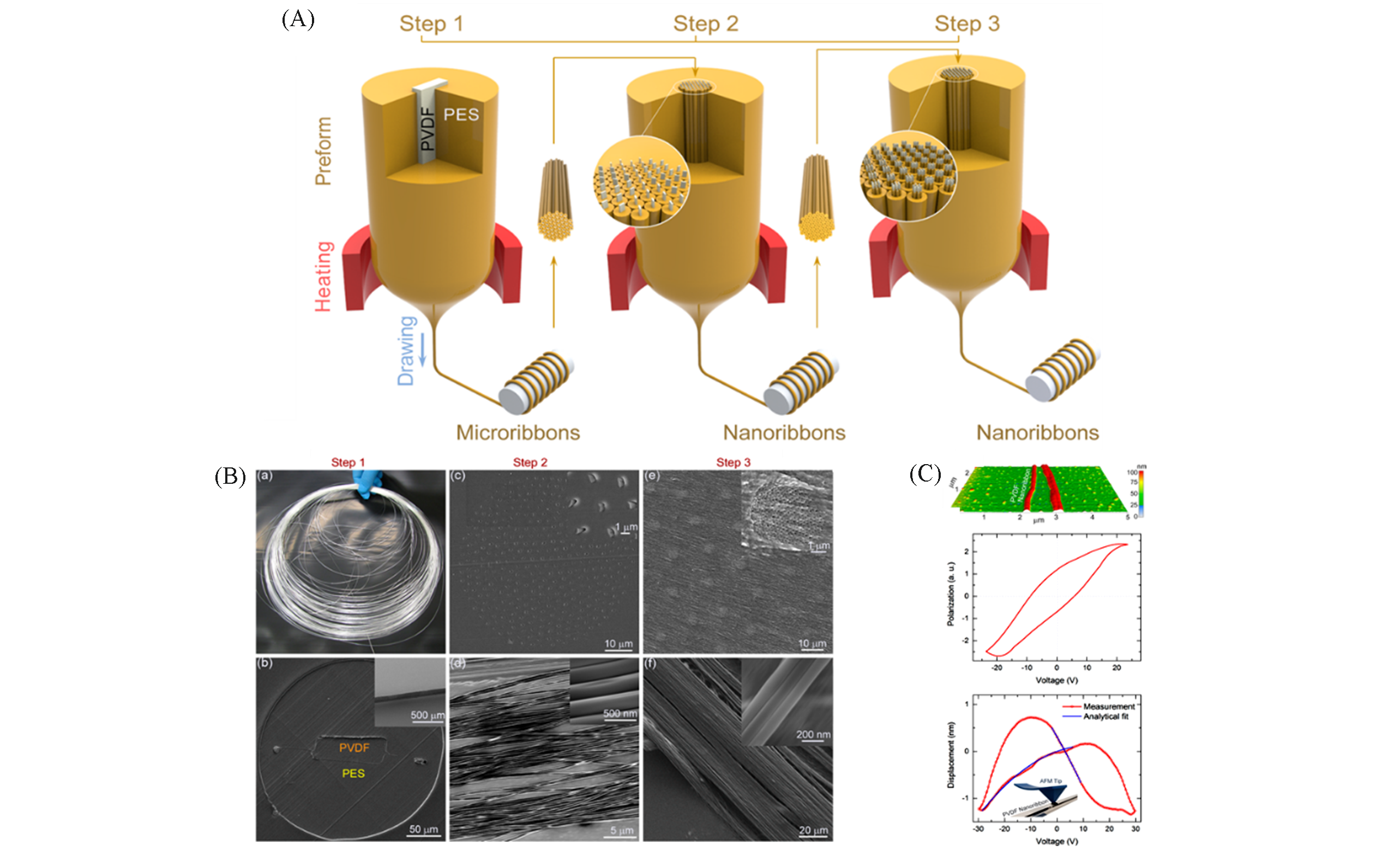
Fig.9 An iterative ?ber drawing scheme achieving nanometer structures(A), SEM micrographs of PVDF in each drawing step(B), AFM and Hysteresis loop(C) of PVDF nanoribbon[98]Copyright 2014, American Chemical Society.
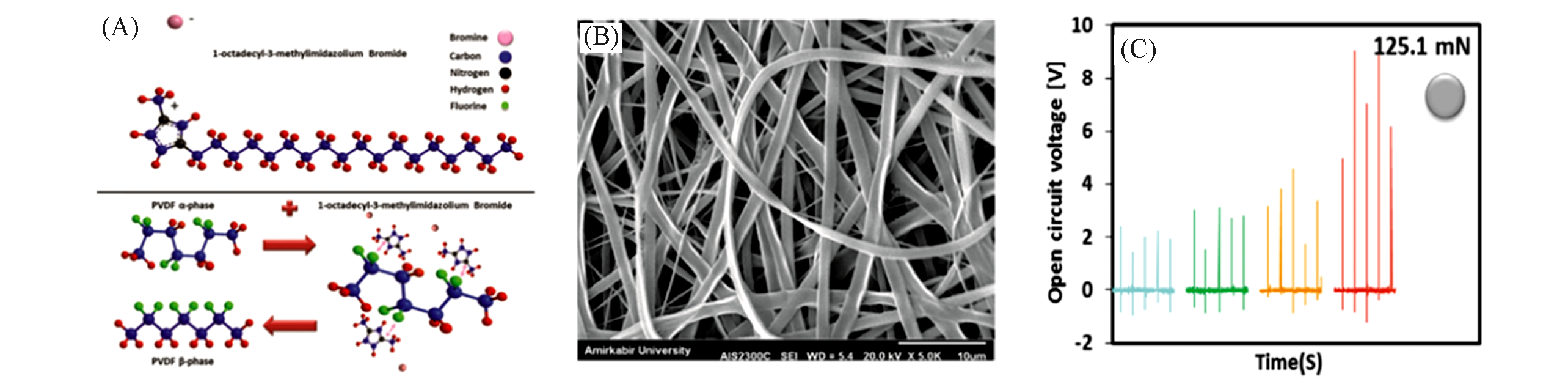
Fig.11 Chemical structure of ILS and their interaction with the PVDF polymer chain fracture(A), SEM image of ILS/PVDF(B) and the output voltage in the electrospun PVDF?based piezo?sensor(C)[106]Copyright 2020, Wiley?VCH.
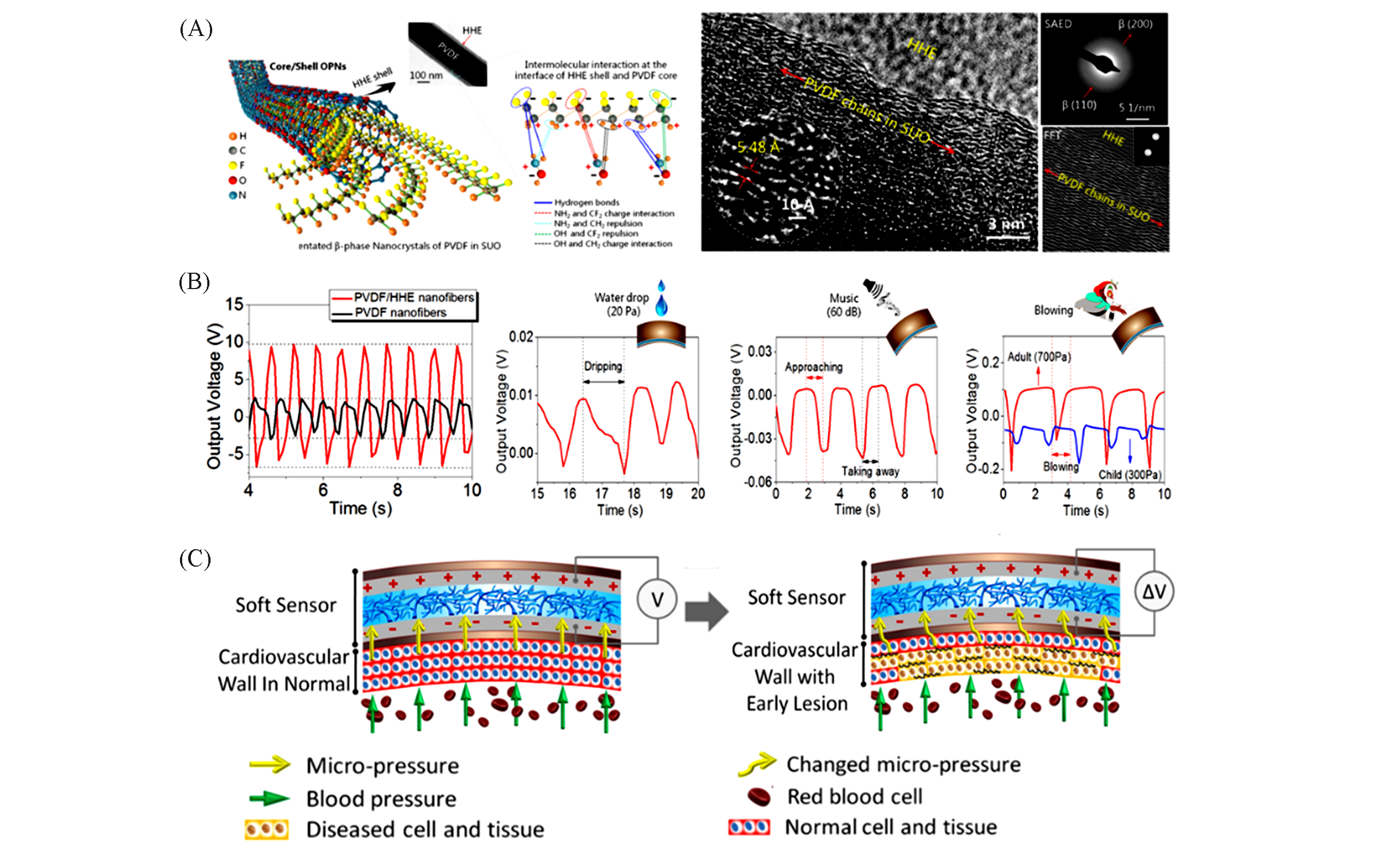
Fig.12 Molecular structure and characterization of the core/shell HHE/PVDF?OPNs with spatial self?orientated β?phase nanocrystals(A), piezoelectric properties of HHE/PVDF?OPNs soft sensor and their electrical performance(B), schematic of the working principle of the sensor for sensing micropressure changes(C) [113]Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
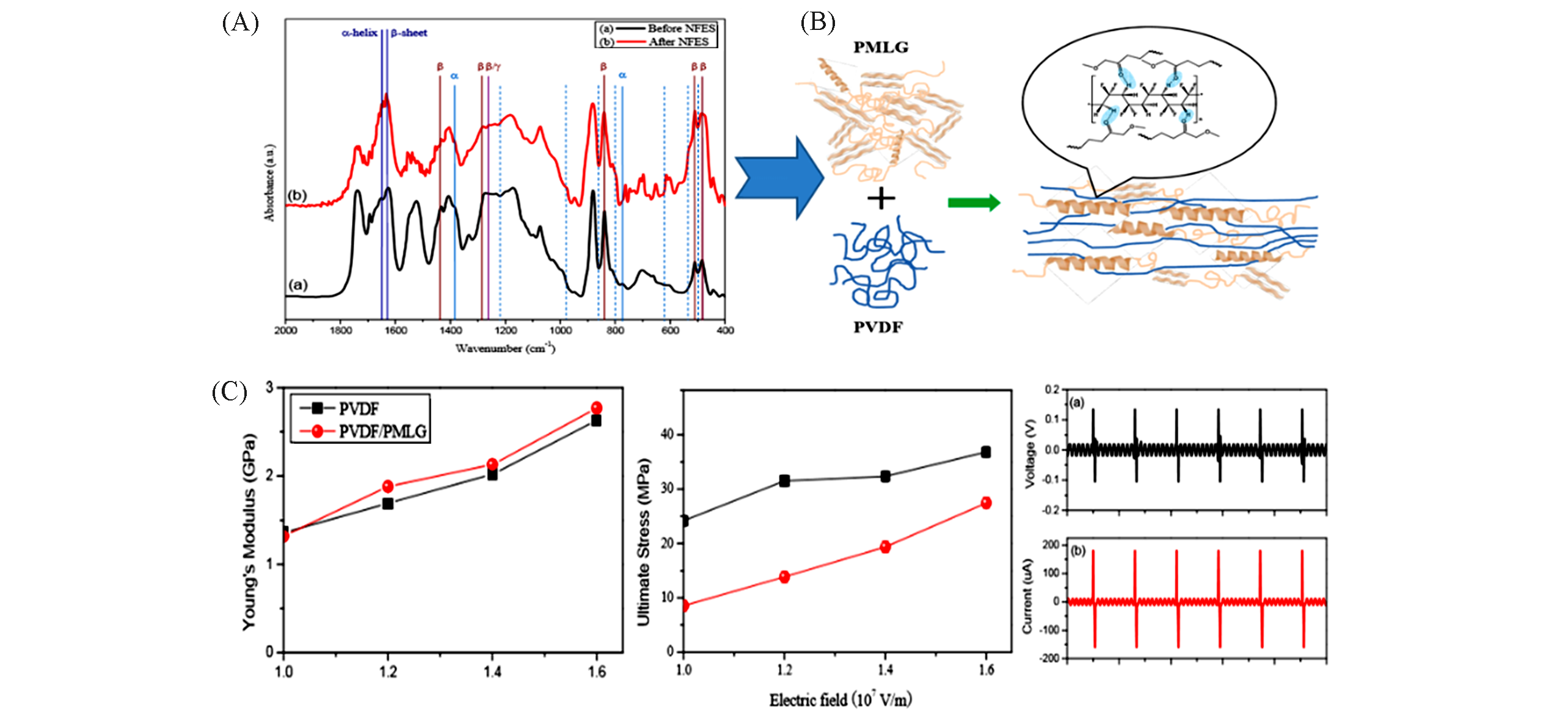
Fig.13 FTIR spectra of PMLG/PVDF composite fibers indicating intermolecular interactions(A), illustrative conformation changes and intermolecular interactions between PVDF and PMLG fibers upon compositing(B), Young’s modulus, ultimate stress and piezoelectric properties of PMLG/PVDF fibers(C)[117]Copyright 2015, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
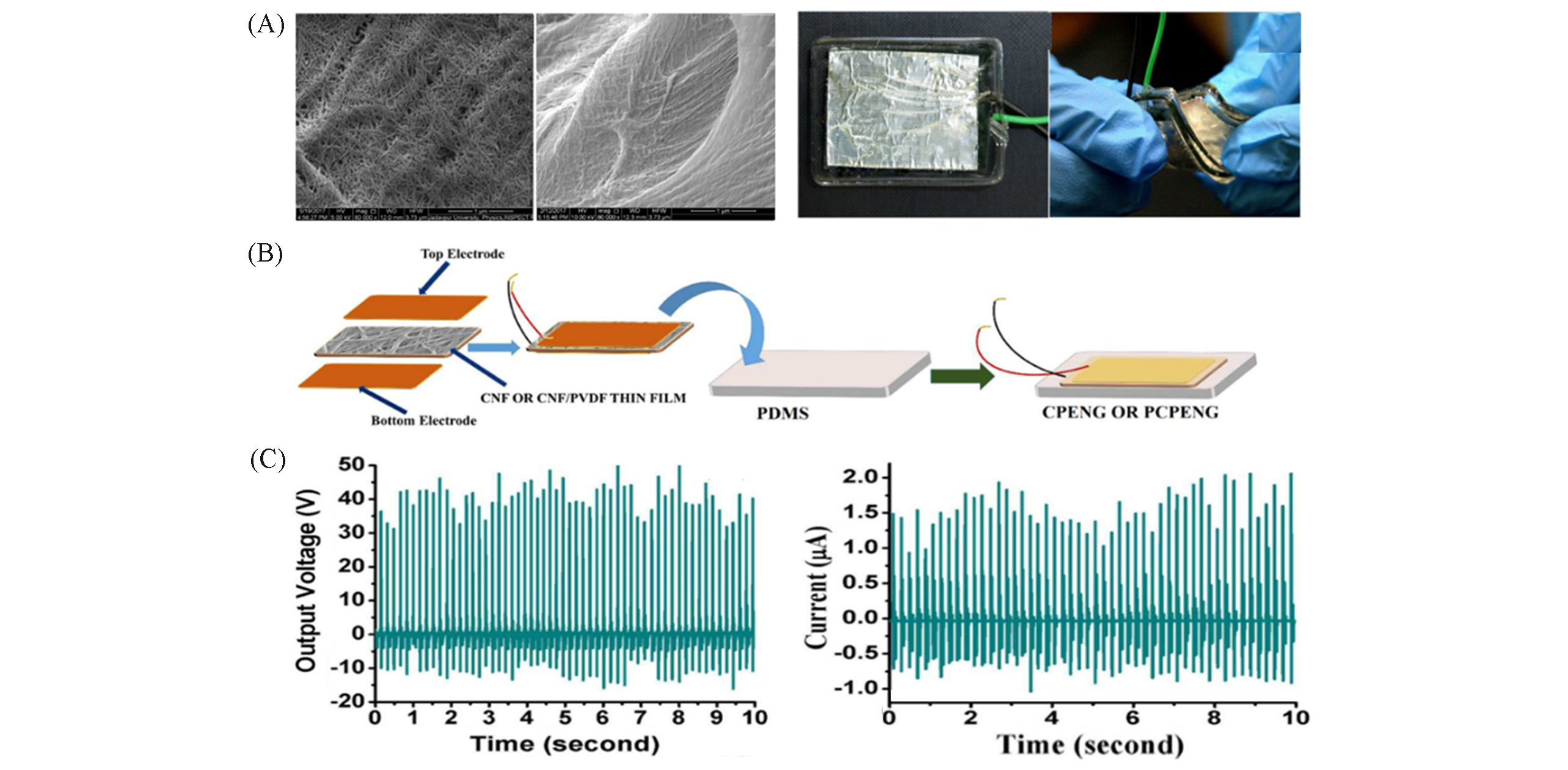
Fig.14 FESEM micrograph of CNF and PCNF thin film, and digital photograph of PCPENG(A), schematic image of CNF/PVDF?based device fabrication(B), output performance of CPENG and PCPENG(C) [120]Copyright 2018, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
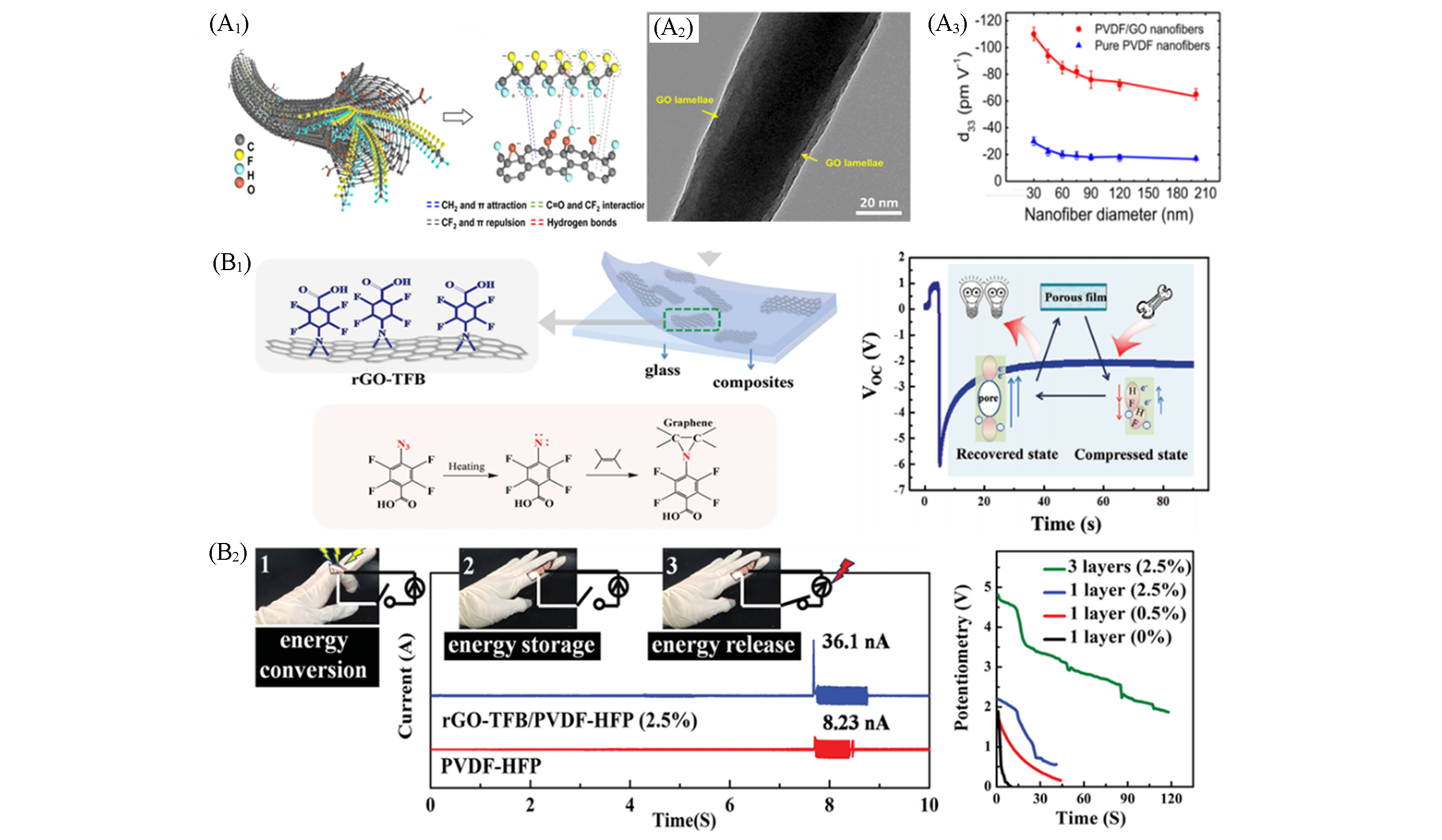
Fig.15 Threedimensional molecular model for the GO/PVDF nano?ber(A1), illustrative structural trait of chemically modified rGO and PVDF?HFP composite and the energy conversion process within the materials upon deformation(A2) and diameter?dependent characteristics of the GO/PVDF and pure PVDF nano?bers(A3)[129], rGO?TFB/PVDF nanocomposite and the mechanism of reaction between TFB and graphene(B1) and output currents/voltages measurements by ?nger?bending motion(B2)[130](A) Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society; (B) Copyright 2015, Wiley?VCH.

Fig.16 Mechanism of chain extension produced by electrospinning and mechanical drawing(A), TEM image showing oriented MWCNT in the PVDF nano?bers(B), and dependence of the remanent polarization on the MWCNT content for the electrospun PVDF membranes(C)[134]Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
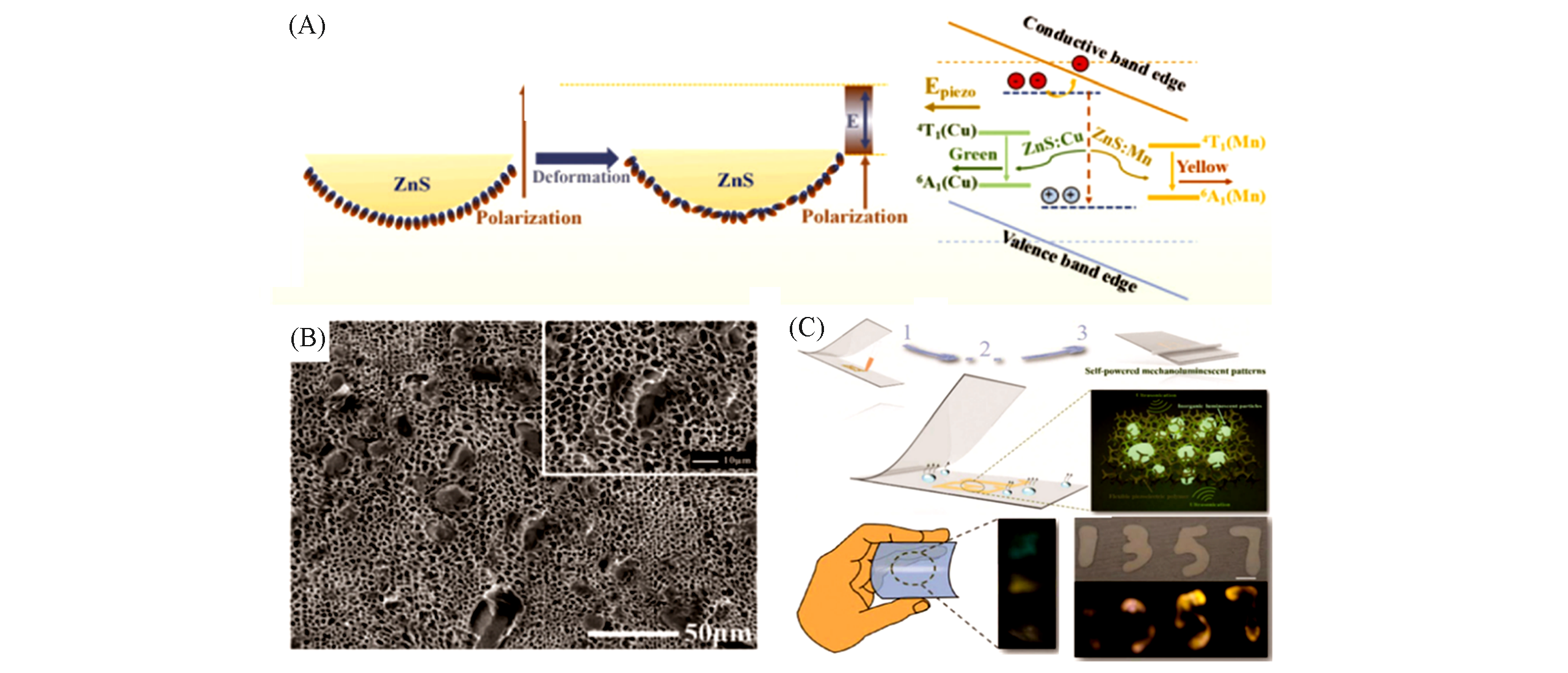
Fig.17 Schematic illustration of the illumination mechanism of ZnS in PVDF?HFP matrix(A), SEM image of the composite porous ZnS/PVDF?HFP ?lm(B), and the schematic illustration of the preparative process of the ZnS/PVDF?HFP composite patterns(C) [131]Copyright 2018, the Royal Society of Chemistry.
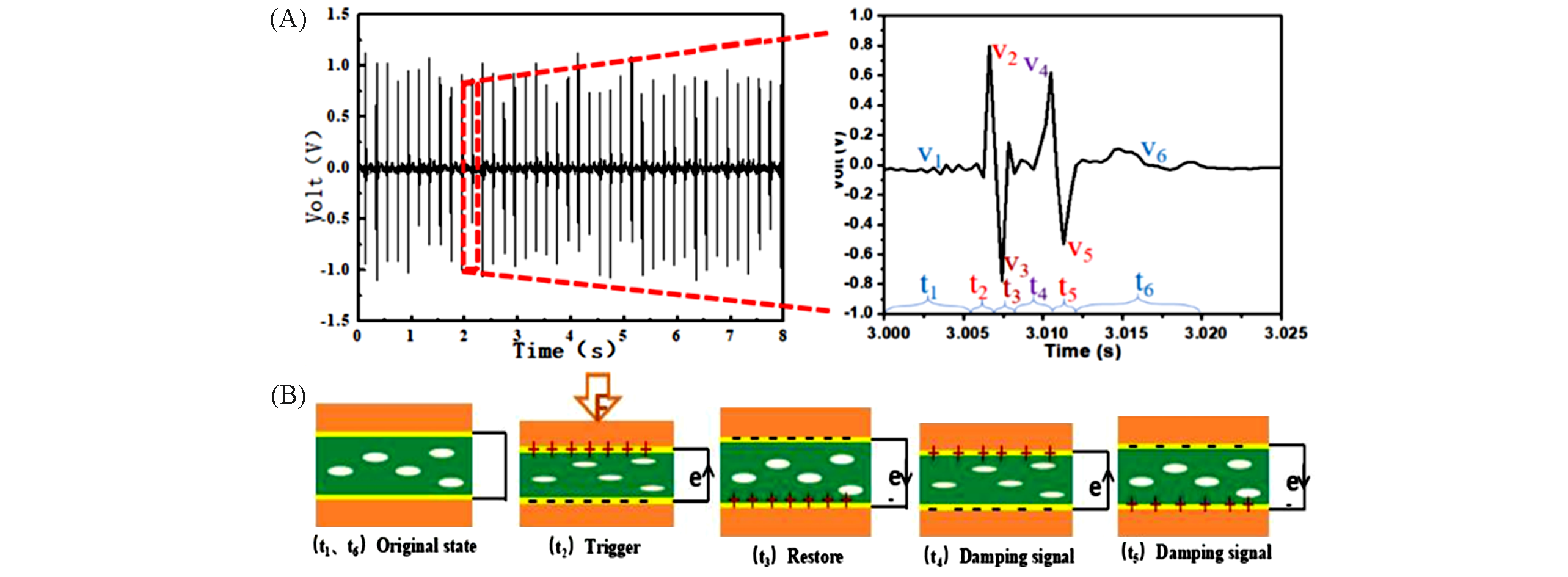
Fig.18 Output voltage of the BiCl3/PVDF piezoelectric nanogenerator(A) and schematic diagram of working mechanism during one vibration cycle(B) [145]Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
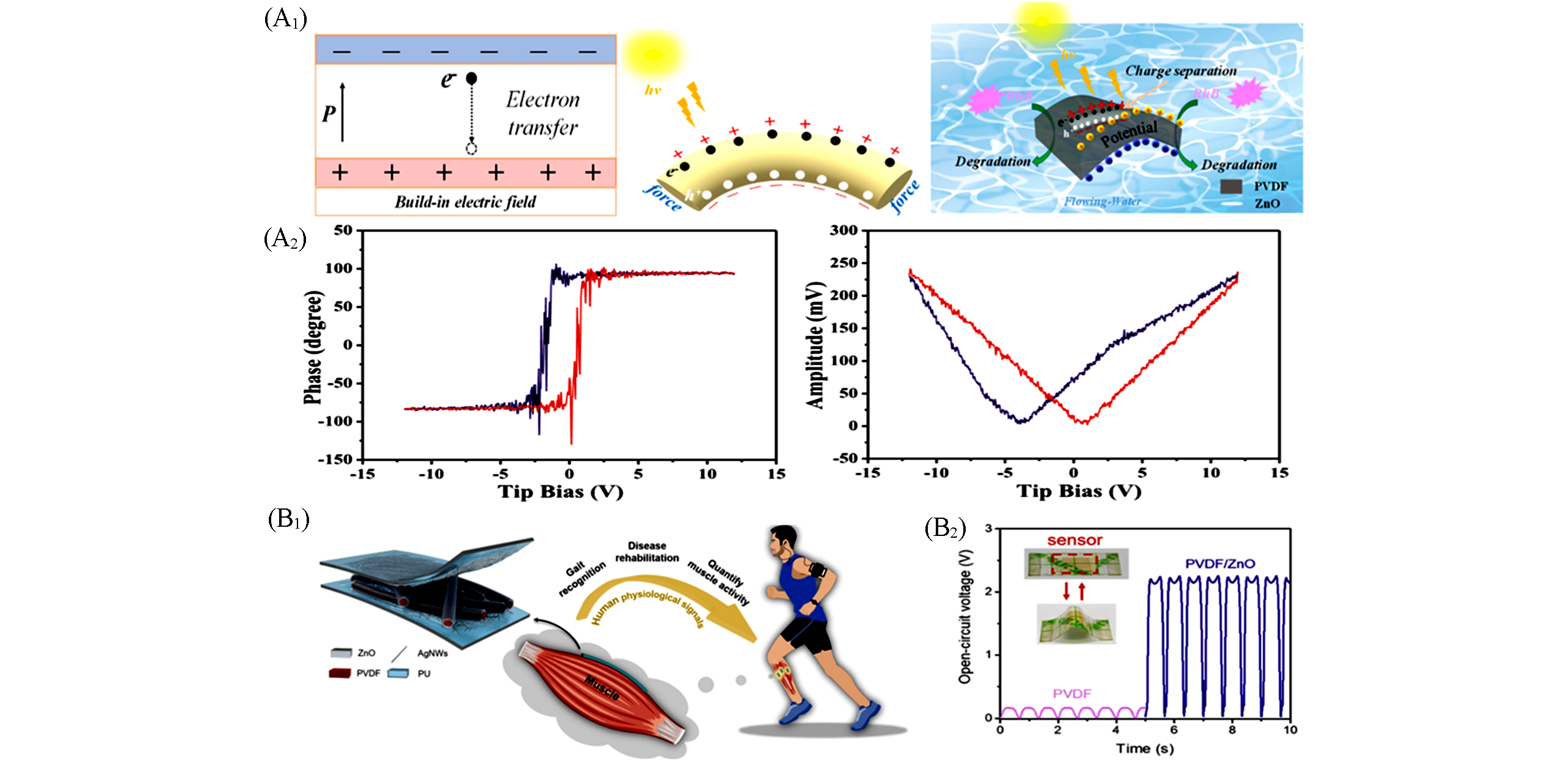
Fig.20 Mechanism of bi?piezoelectric ZnO/PVDF structure(A1), piezoelectric hysteresis and butter?y loops of the ZnO/PVDF piezoelectric ?lm(A2)[155], the schematic diagram of the three?dimensional hierarchically interlocked ZnO/PVDF fibers?based PME for muscle behavior monitoring(B1) and corresponding open?circuit voltage(B2) [156](A) Copyright 2020, Elsevier; (B) Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
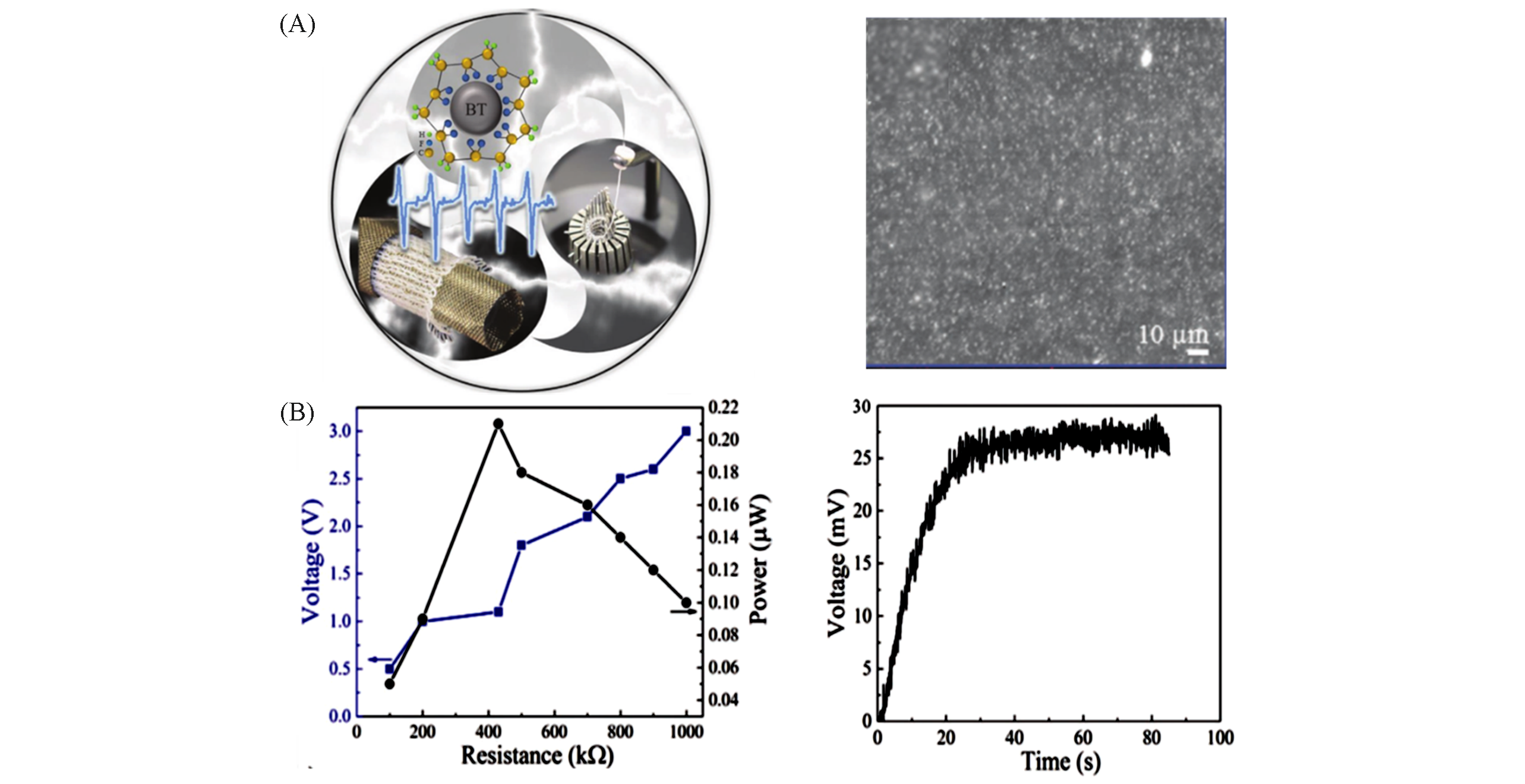
Fig.21 Schematic illustration of the fabrication of the wearable knitted energy generator from nanostructured hybrid PVDF/BT fibers and cross?section SEM image of BT/PVDF(A), voltage output and power dependence on the load resistance of the braided BT/PVDF and charging 10 μF capacitor(B)[159]Copyright 2020, Wiley?VCH.
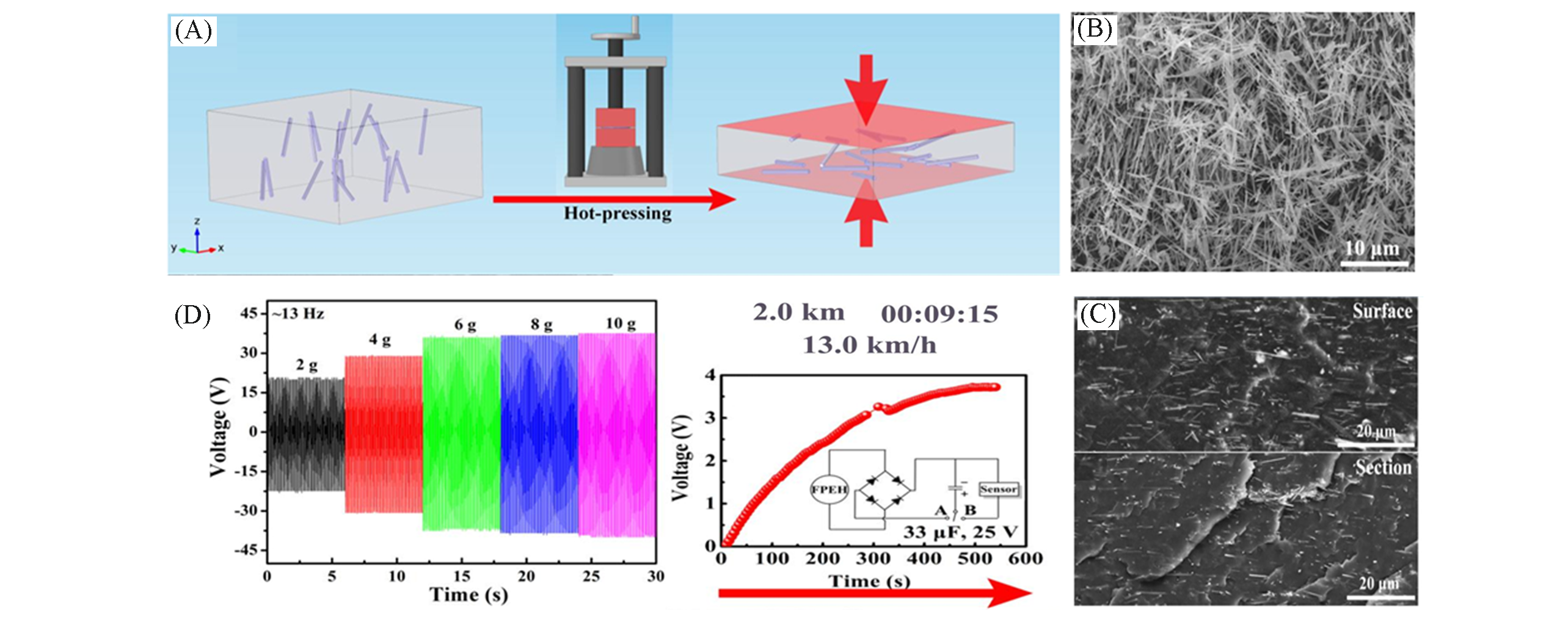
Fig.22 Schematic diagram of hot?pressing process for building textured BT2/PVDF composite(A), SEM image of BT2 products(B), SEM images of the surface and freeze?fractured cross section of the hot?pressed BT2/PVDF(C), the output voltage of the BT2/PVDF FPEHs with different BT2 content(D)[162]Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
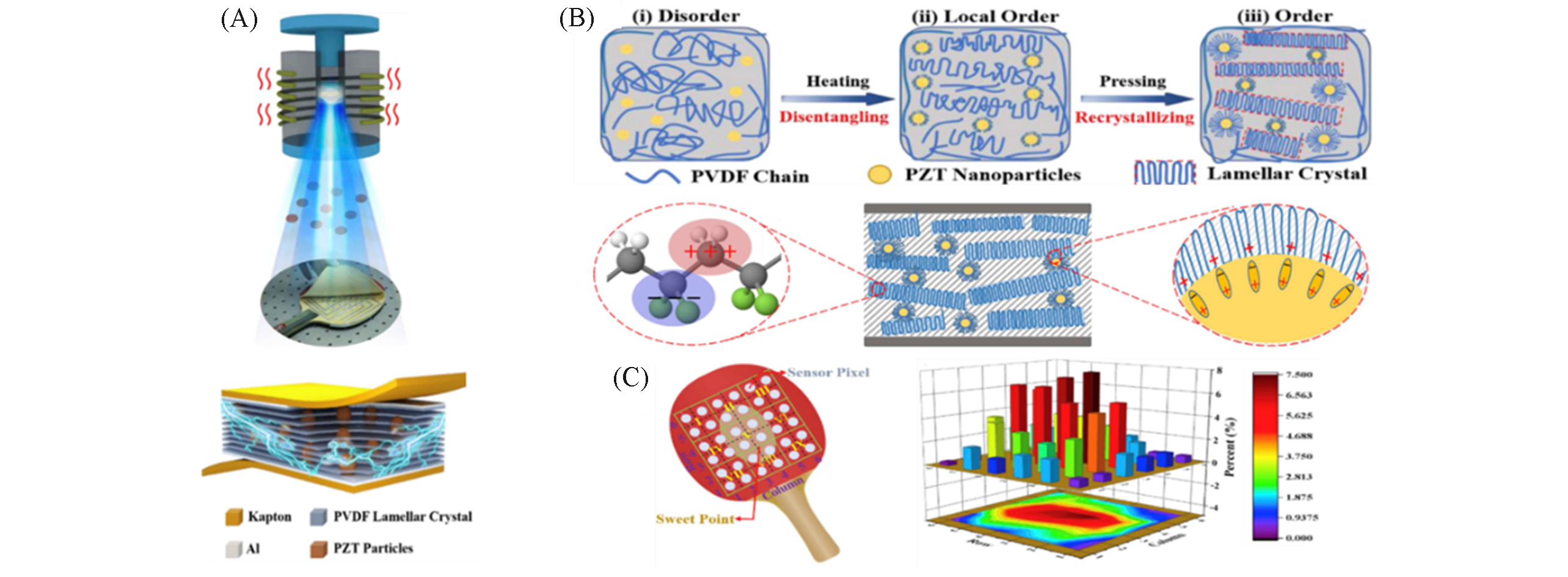
Fig.23 Fabrication process of the piezocomposite and general illustration of the smart racket(A), conception of preparing β?phase lamellar crystal(B) and the distribution of the sensor pixeland point on the racket and electrical potential distribution caused by hits(C)[174]Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
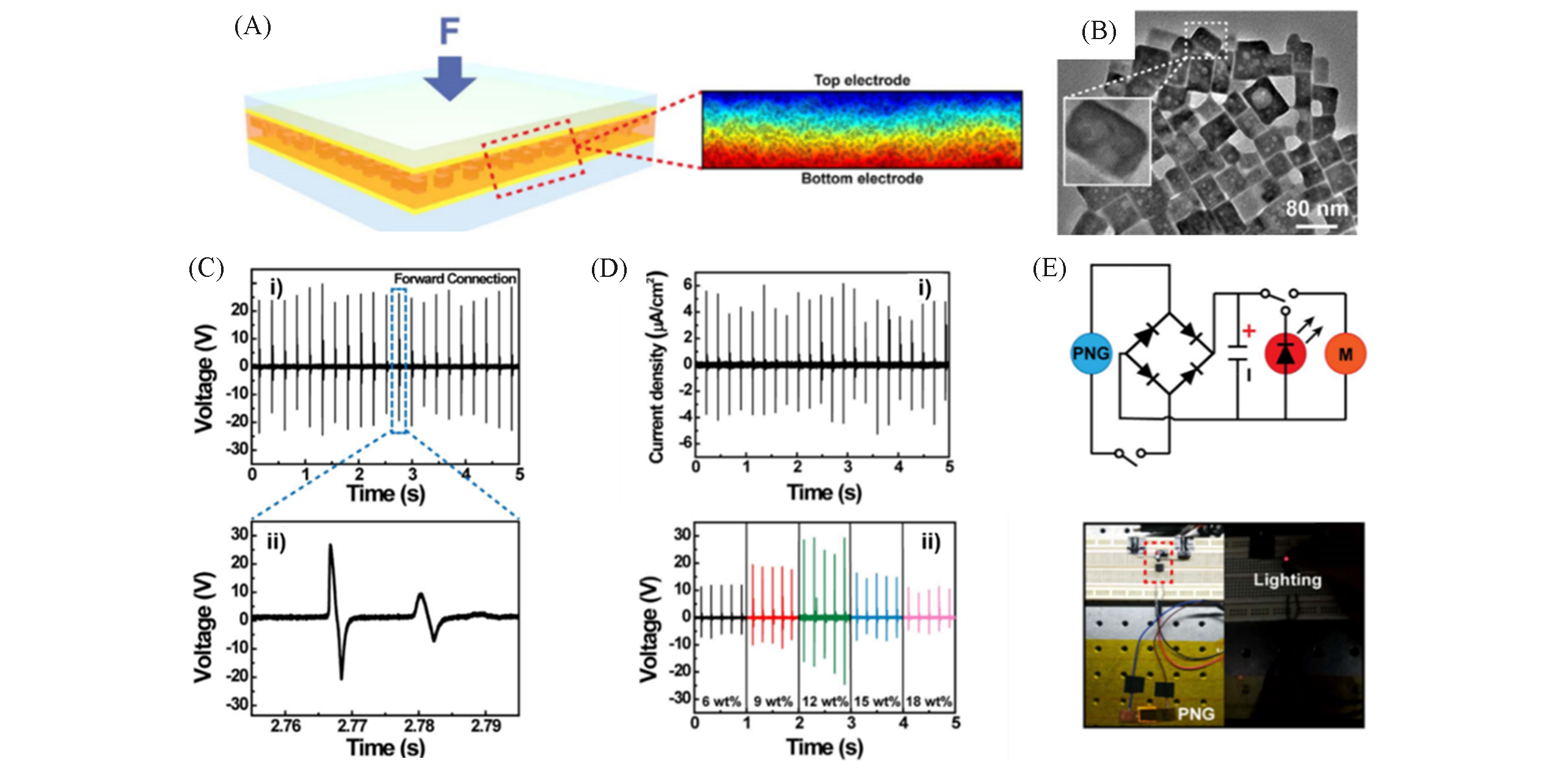
Fig.24 Schematic diagram presenting the structure of the FAPbBr3 NPs/PVDF composite?based nanogenerator(A), SEM image of FAPbBr3 NPs(B), piezoelectric output voltage of the FAPbBr3 NPs/PVDF composite?based nanogenerator(C), the output current density and the output voltage of the FAPbBr3 NPs/PVDF composite?based nanogenerator(D) and schematic circuit diagram of LED driving, capacitor charging and voltage measuring by a multimeter(E)[181]Copyright 2017, Elsevier.
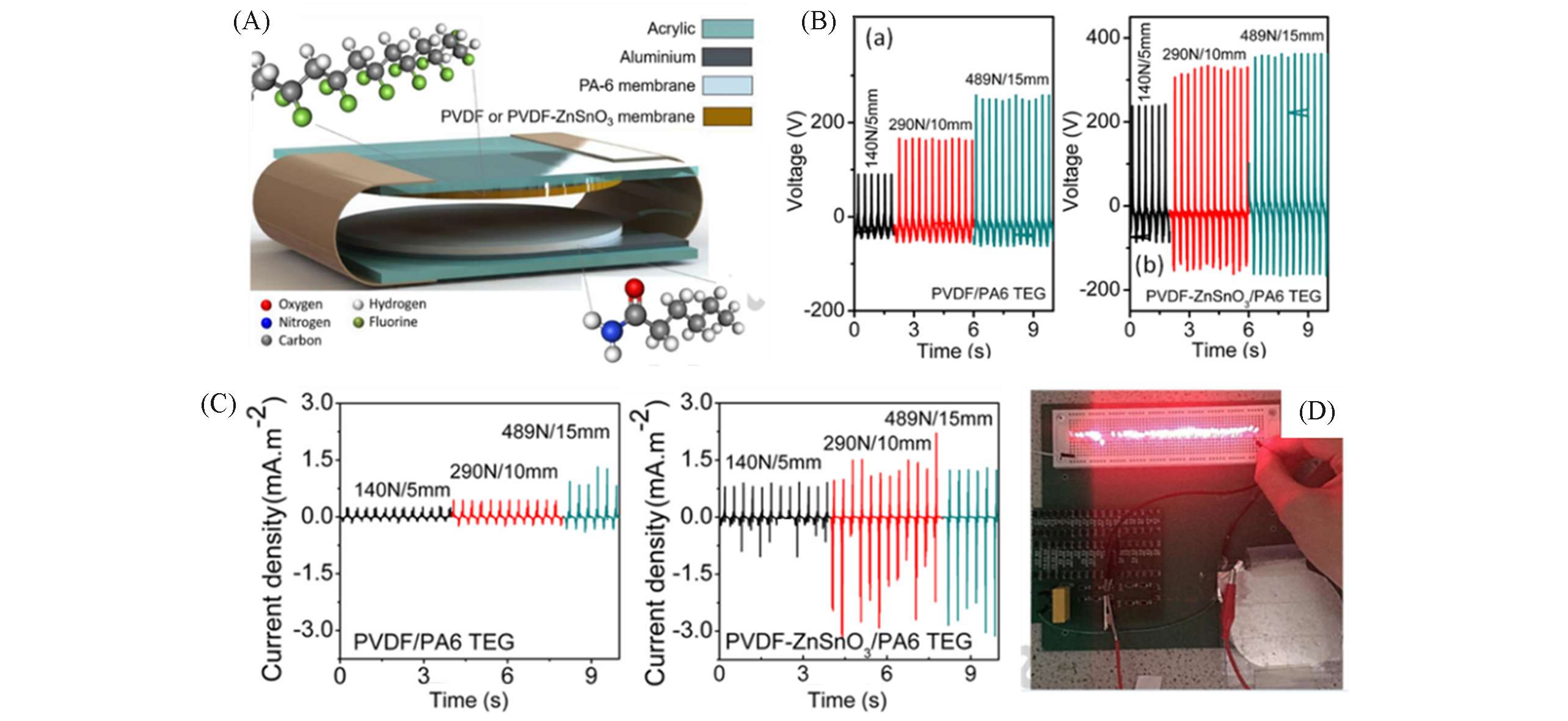
Fig.25 Structure of the TEG showing the position of the various components(A), open circuit voltage(Voc) values(B) and short circuit current values(C) of the TEGs, full brightness achieved for the LEDs via the discharge of the 1 μF capacitor(D)[190]Copyright 2016, Elsevier.
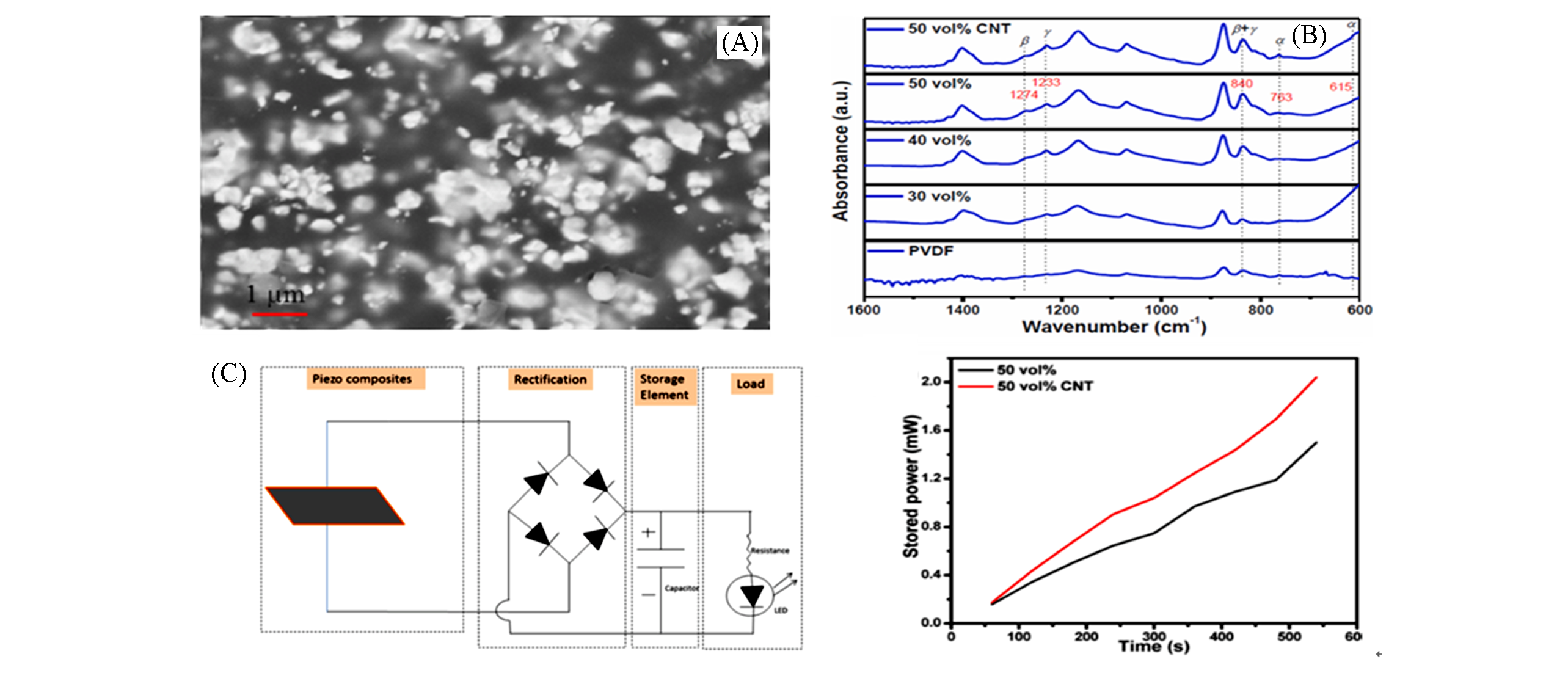
Fig.26 FESEM micrographs of CNT composite films(A), FTIR?ATR spectra of the composite films(B), circuit diagram for rectification of AC voltage and time dependent stored power in CNT films(C)[199]Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
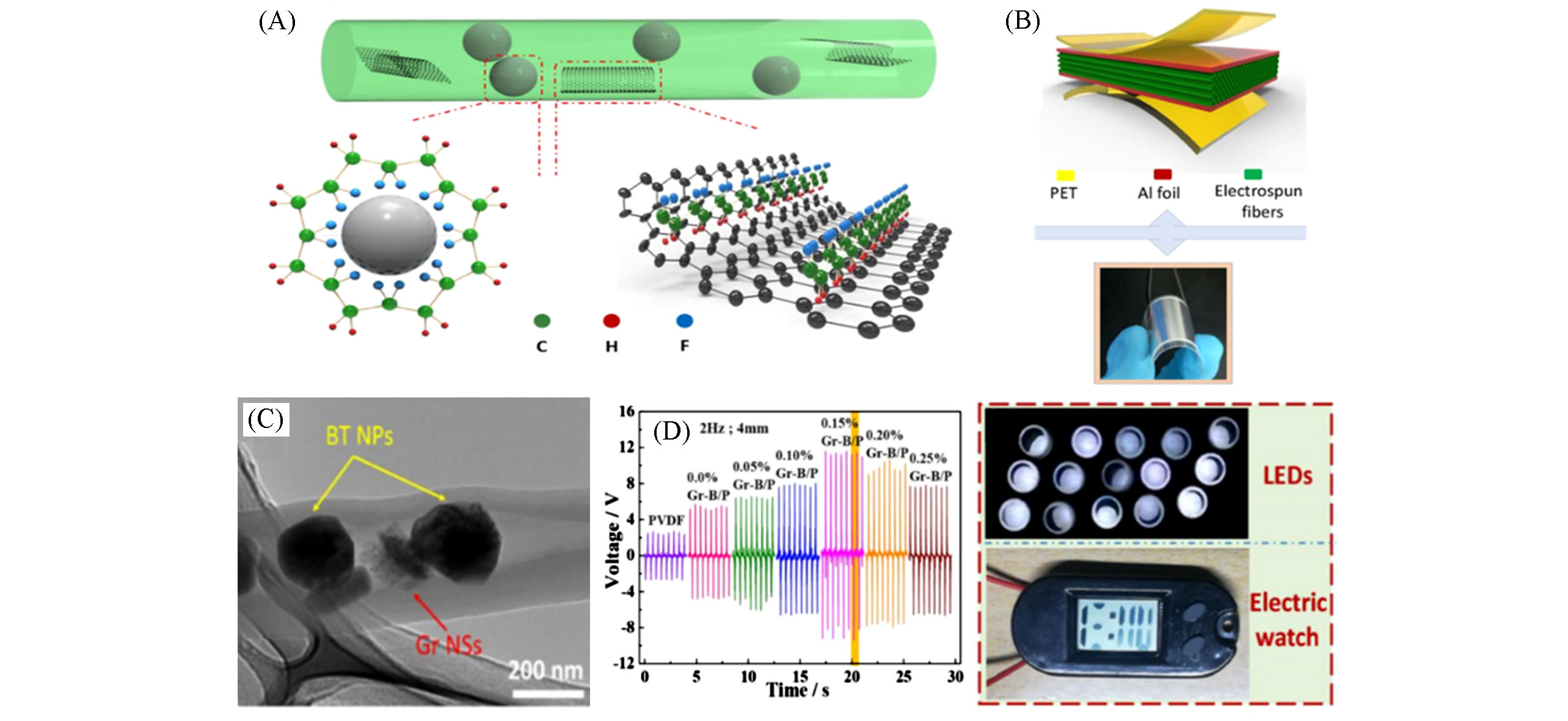
Fig.27 Mechanism diagram of β phase formation on BT nanoparticles and graphene nanosheets in the nanocomposite fiber(A), schematic structure of a PENG and the digital photo showing its flexibility(B), TEM images of Gr?BT/PVDF(C) and output voltages of nanocomposite fibers PENG(D)[202]Copyright 2018, Elsevier.
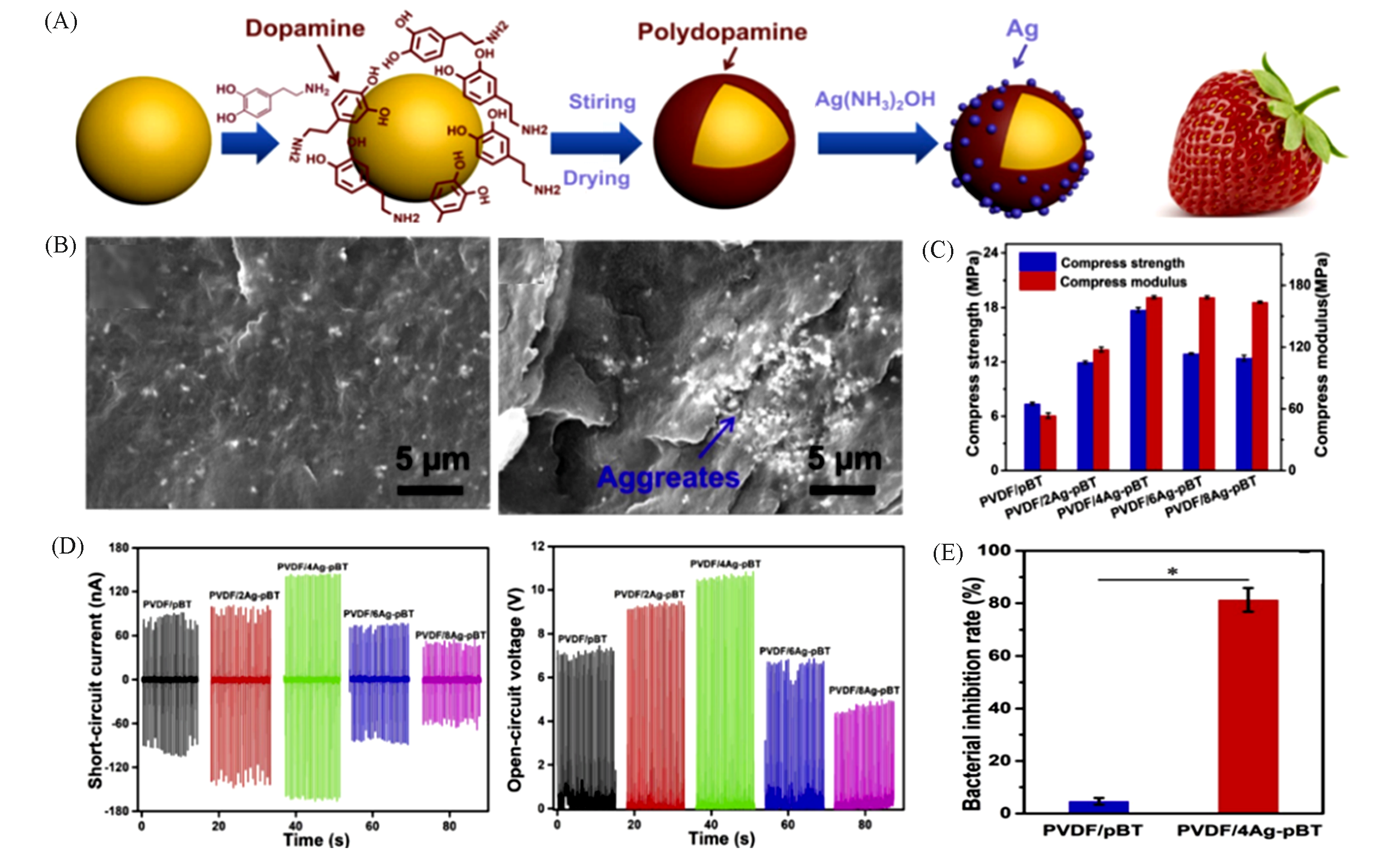
Fig.28 Preparation process and reaction mechanism diagrams(A), cryo?fracture surfaces of composite scaffolds containing with pB(B), corresponding compress strength and modulus of composite scaffolds(C), short?circuit currents open?circuit voltages of composite(D) and bacterial inhibition rate(E)[213]Copyright 2020, Elsevier.
| 1 | Li X. M., Luo C. D., Fu Q. Y., Zhou C. P., Ruelas M., Wang Y. S., He J. X., Wang Y. Y., Zhang Y. S., Zhou J. H., Adv. Mater., 2020,32(21), e2000060 |
| 2 | Huang T., Zhang Y. J., He P., Wang G., Xia X. X., Ding G. Q., Tao T. H., Adv. Mater., 2020, 32(10), e1907336 |
| 3 | Liu L. Q., Yang X. Y., Zhao L. L., Xu W. K., Wang J. W., Yang Q. M., Tang Q. W., Nano Energy, 2020, 73, 104797 |
| 4 | Fu Y. M., He H. X., Zhao T. M., Dai Y. T., Han W. X., Ma J., Xing L. L., Zhang Y., Xue X. Y., Nano Lett., 2018, 10(4), 76—88 |
| 5 | An S., Jo H. S., Li G., Samuel E., Yoon S. S., Yarin A. L., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2020, 30(25), 1—14 |
| 6 | Liu Q. X., Liu Z. G., Li C. G., Xie K. W., Zhu P., Shao B. Q., Zhang J. M., Yang J. L., Zhang J., Wang Q., Guo C. F., Adv. Sci., 2020, 7(10), 2000348 |
| 7 | Kim J., Byun S., Lee S., Ryu J., Cho S., Oh C., Kim H., No K., Ryu S., Lee Y. M., Hong S., Nano Energy, 2020,75, 104992 |
| 8 | Syu M. H., Guan Y. J., Lo W. C., Fuh Y. K., Nano Energy,2020, 76, 105029 |
| 9 | Wang J., Jiang J. F., Zhang C. C., Sun M. Y., Han S. W., Zhang R. T., Liang N., Sun D. H., Liu H., Nano Energy, 2020, 76, 105050 |
| 10 | Zhang S. T., Yu P., Zhang Y., Ma Z. Q., Teng K. X., Hu X. T., Lu L. M., Zhang Y. H., Zhao Y. T., An Q., ChemistrySelect, 2020,5(22), 6715—6722 |
| 11 | Chen L., Di C. G., Chen X. G., Li Z. Z., Luo J., Bioengineered, 2017, 8(1), 78—84 |
| 12 | Sohn A., Lee J. H., Yoon H. J., Lee H. H., Kim S. W., Nano Energy, 2020, 74, 104840 |
| 13 | Zabek D., Seunarine K., Spacie C., Bowen C., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter.,2017,9(10), 9161—9167 |
| 14 | Choi M. H., Yan S. C., Materials Letters, 2018, 223, 73—77 |
| 15 | Huang X. Z., Zhang X., Jiang H. R., RSC Adv., 2016, 6(99), 96490—96494 |
| 16 | He H. X., Fu Y. M., Zang W. L., Wang Q., Xing L. L., Zhang Y., Xue X. Y., Nano Energy, 2017, 31, 37—48 |
| 17 | Han W. X., Zhang L. L., He H. X., Liu H. M., Xing L. L., Xue X. Y., Nanotechnology, 2018, 29(25), 255501 |
| 18 | Han W. X., He H. X., Zhang L. L., Dong C. Y., Zeng H., Dai Y. T., Xing L. L., Zhang Y., Xue X. Y., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(35), 29526—29537 |
| 19 | He H. X., Zeng H., Fu Y. M., Han W. X., Dai Y. T., Xing L. L., Zhang Y., Xue X. Y., Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(36), 9624—9630 |
| 20 | He H. X., Dong C. Y., Fu Y. M., Han W. X., Zhao T. M., Xing L. L., Xue X. Y., Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2018, 267, 392—402 |
| 21 | Dong C. Y., Fu Y. M., Zang W. L., He H. X., Xing L. L., Xue X. Y., Appl. Sur. Sci., 2017, 416, 424—431 |
| 22 | Xue X. Y., Qu Z., Fu Y. M., Yu B. W., Xing L. L., Zhang Y., Nano Energy, 2016, 26, 148—156 |
| 23 | Li N., Yi Z. R., Ma Y., Xie F., Huang Y., Tian Y. W., Dong X. X., Liu Y., Shao X., Li Y., Jin L., Liu J. Q., Xu Z. Y., Yang B., Zhang H., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(3), 2822—2830 |
| 24 | Arakawa M., Kudo K., Kobayashi K., Kanai H., Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2019, 286, 146—151 |
| 25 | Sato S., Yamada K., Inagaki N., Med. Biol. Eng. Comput., 2006, 44(5), 353—362 |
| 26 | Choi Y. S., Kim S. K., Williams F., Calahorra Y., Elliott J. A., Kar⁃Narayan S., Chem. Commun(Camb), 2018, 54(50), 6863—6866 |
| 27 | Qiu C. R., Wang B., Zhang N., Zhang S. J., Liu J. F., Walker D., Wang Y., Tian H., Shrout T. R., Xu Z., Chen L. Q., Li F., Nature, 2020, 577(7790), 350—354 |
| 28 | Carvalho E. O., Fernandes M. M., Padrao J., Nicolau A., Marques⁃Marchan J., Asenjo A., Gama F. M., Ribeiro C., Lanceros⁃Mendez S., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2019, 11(30), 27297—27305 |
| 29 | Schurzig D., Schwarzendahl S., Wallaschek J., van Drunen W. J., Rau T. S., Lenarz T., Majdani O., Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,2018, 56(5), 733—747 |
| 30 | Sun Y., Liu D. L., Li Q., Shim J., He W. H., Fang H. J., Yan Q. F., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter.,2018, 10(15), 12847—12853 |
| 31 | Liu B. H., Liu X, Li P, Li F., Shen B., Zhai J. W., RSC Adv., 2017, 7(66), 41788—41795 |
| 32 | Wojtaś M., Kinzhybalo V., Bdikin I., Kholkin A. L., Crystal Growth & Design, 2019,19(5), 2583—2593 |
| 33 | Huang S. Y, Zeng J. T, Zheng L. Y., Man Z. Y., Ruan X. Z., Shi X., Li G. R., Ceramics International, 2020, 46(5), 6212—6216 |
| 34 | Chen Y. J., Brahma S., Liu C. P., Huang J. L., Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 728, 1248—1253 |
| 35 | Bell A. J., Shepley P. M., Li Y., Acta Materialia, 2020, 195,292—303 |
| 36 | Kamano Y., Tabata Y., Uji H., Kimura S., RSC Adv., 2019, 9(7), 3618—3624 |
| 37 | Dong X. X., Majzoubi M., Choi M., Ma Y. T., Hu M. Q., Jin L., Xu Z. K., Uchino K. J., Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2017, 256, 77—83 |
| 38 | Shin D. H., Cho J. H., Sensors(Basel), 2018, 18(6), 1694—1705 |
| 39 | Chang W. Y, Chung C. C., Yuan Z. Y., Chang C. H., Tian J., Viehland D., Li J. F., Jones J. L., Jiang X. N., Acta Materialia, 2018, 143, 166—173 |
| 40 | Wang D. Z., Shi P., Li X. M., Zhou P., Zhao K. P., Wei Y. L., Jiang C. Y., Liang J. S., Dorey R. A., Ceramics International, 2018, 44(12), 14258—14263 |
| 41 | Choi I., Lee S. J., Kim J. C., Kim Y. G., Hyeon D. Y., Hong K. S., Suh J., Shin D., Jeong H. Y., Park K., Appl. Sur. Sci., 2020, 511, 145614 |
| 42 | Sinha N., Goel S., Joseph A. J., Yadav H., Batra K., Gupta M. K., Kumar B., Ceramics International, 2018, 44(7), 8582—8590 |
| 43 | Tandon B., Kamble P., Olsson R. T., Blaker J. J., Cartmell S. H., Molecules, 2019, 24(10), 1903 |
| 44 | Lu L. J., Ding W. Q., Liu J. Q., Yang B., Nano Energy, 2020, 78,105251 |
| 45 | Fan F. R., Tang W., Wang Z. L., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(22), 4283—4305 |
| 46 | Lou Z., Li L., Wang L. L., Shen G. Z., Small, 2017, 13(45), 1701791 |
| 47 | Chen X., Han X., Shen Q. D., Advanced Electronic Materials, 2017, 3(5), 1600460 |
| 48 | Wang X. M., Sun F. Z., Yin G. C., Wang Y. T., Liu B., Dong M. D., Sensors(Basel), 2018, 18(2), 330—346 |
| 49 | Sun H., Tian H., Yang Y., Xie D., Zhang Y. C., Liu X., Ma S., Zhao H. M., Ren T. L., Nanoscale, 2013, 5(13), 6117—6123 |
| 50 | Yan J. H., Han Y. H, Xia S. H., Wang X., Zhang Y. Y., Yu J. Y., Ding B., Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(51), 1907919 |
| 51 | Jin L., Ma S. Y., Deng W. L., Yan C., Yang T., Chu X., Tian G., Xiong D., Lu J.,Yang W. Q., Nano Energy, 2018, 50, 632—638 |
| 52 | Ryu J., Kim J., Oh J., Lim S., Sim J. Y., Jeon J. S., No K., Park S., Hong S., Nano Energy, 2019, 55, 348—353 |
| 53 | Andrew J. S., Clarke D. R., Langmuir, 2008, 24, 670—672 |
| 54 | Zhang Y., Wang Y., Deng Y., Li M., Bai J. B., ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2012, 4(1), 65—68 |
| 55 | Thakur P., Kool A., Bagchi B., Hoque N. A., Das S., Nandy P., Phys. Chem., 2015, 17(19), 13082—13091 |
| 56 | Chang C., Tran V. H., Wang J., Fuh Y. K., Lin L., Nano Lett., 2010, 10(2), 726—731 |
| 57 | Ren Y., Wang Y., Zhang W. L, Yan X., Huang B. X., RSC Advances, 2019, 9, 29760 |
| 58 | Salimi A., Yousefi A. A., Polymer Testing, 2003, 22(6), 699—704 |
| 59 | Sencadas V., Moreira M. V., Lanceros M. S., Pouzada A. S., Gregório F. R., Materials Science Forum, 2006, 514—516 |
| 60 | Wang X., Qiao B. B., Tan S. B., Zhu W. W., Zhang Z. C., Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2020, 8(33), 11426—11440 |
| 61 | Wang H., Chen Q. S., Xia W., Qiu X. L., Cheng Q., Zhu G. D., Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2018, 135(22), 46324 |
| 62 | Gomes J., Serrado Nunes J., Sencadas V., Lanceros M. S., Smart Materials and Structures, 2010,19(6), 065010 |
| 63 | Kochervinski V. V., Crystallography Reports, 2003, 48(4), 649—675 |
| 64 | Lee C., Tarbutton J. A., Smart Materials and Structures, 2014, 23(9), 095044 |
| 65 | Martins P., Costa C. M., Benelmekki M., Botelho G., Lanceros⁃Mendez S., CrystEngComm, 2012, 14(8), 2807—2811 |
| 66 | Wang F. P., Lack A., Xie Z. L., Frübing P., Taubert A., Gerhard R., Applied Physics Letters, 2012, 100(6), 062903 |
| 67 | Fang J., Wang X. G., Lin T., Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(30), 11088—11091 |
| 68 | Mandal D., Yoon S., Kim K. J., Macromol Rapid Commun, 2011, 32(11), 831—837 |
| 69 | Shao H., Fang J., Wang H. X,, Lang C. H., Lin T., ACS Appl. Mater Interfaces, 2015, 7(40), 22551—22557 |
| 70 | Hansen B. J., Liu Y., Yang R., Wang Z. L., American Chemical Society, 2010, 4(7), 3647—3652 |
| 71 | Pi Z. Y., Zhang J. W., Wen C. Y., Zhang Z. B., Wu D. P., Nano Energy, 2014, 7, 33—41 |
| 72 | Yun H. G., Zhou X. J., Zhu H. R., Zhang M. Y., Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 585, 138—147 |
| 73 | Teo W. E., Ramakrishna S., Nanotechnology, 2006, 17(14), R89—R106 |
| 74 | Liang Y. Y., Zhao J., Huang Q. L., Hu P., Xiao C. F., Journal of Membrane Science, 2021, 618, 118709 |
| 75 | Hoe Z. Y., Chang C. C., Chen J. J., Yen C. K., Wang S. Y., Kao Y. H., Li W. M., Chen W. F., Pan C. T., Sensors(Basel), 2020, 20(17), E4873 |
| 76 | Lei T. P., Cai X. M., Wang X, Yu L. K., Hu X. W., Zheng G. F., Lv W. L., Wang L. Y., Wu D. Z., Sun D. H., Lin L. W., RSC Advances, 2013, 3(47), 24952—24958 |
| 77 | Chang J. Y., Dommer M., Chang C., Lin L. W., Nano Energy, 2012, 1(3), 356—371 |
| 78 | Yousry Y. M., Yao K., Mohamed A. M., Liew W. H., Chen S. T., Ramakrishna S., Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 30(25), 1—9 |
| 79 | Ahmed A., Jia Y. M., Huang Y., Khoso N. A., Deb H., Fan Q. G., Shao J. Z., Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30, 14007—14021 |
| 80 | Sharma T., Naik S., Langevine J., Gill B., Zhang J. X., IEEE Trans. Biomed Eng., 2015, 62(1), 188—195 |
| 81 | Li D. H., Liao M. Y., Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2018, 152, 116—125 |
| 82 | Lin J. J., Malakooti M. H., Sodano H. A., ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2020, 12(19), 21871—21882 |
| 83 | Lutkenhaus J. L., Mcennis K., Serghei A., Russell T. P., Macromolecules, 2010, 43(8), 3844—3850 |
| 84 | Cauda V., Torre B., Falqui A., Canavese G., Stassi S., Bein T., Pizzi M., Chemistry of Materials, 2012, 24(21), 4215—4221 |
| 85 | Guan F. X., Pan J. L., Wang J., Wang Q., Zhu L., Macromolecules, 2010, 43(1), 384—392 |
| 86 | Bhavanasi V., Kusuma D. Y., Lee P. S., Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(16), 1400723 |
| 87 | Lefki K., Dormans G. J. M., Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 76(3), 1764—1767 |
| 88 | Wang Z. L., Song J. H., Science, 2006, 312(5774), 242—246 |
| 89 | Cha S., Kim S. M., Kim H., Ku J., Sohn J. I., Park Y. J., Song B. G., Jung M. H., Lee E. K., Choi B. L., Park J. J., Wang Z. L., Kim J. M., Kim K., Nano Letter, 2011, 11(12), 5142—5147 |
| 90 | Cui C. M., Wang X. Z., Yi Z. R., Yang B., Wang X. L., Chen X., Liu J. Q., Yang C. S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(4), 3652—3659 |
| 91 | Zhang G. Z., Zhao P., Zhang X. S., Han K., Zhao T. K., Zhang Y., Jeong C. K., Jiang S. G., Zhang S. L., Wang Q., Energy & Environmental Science, 2018, 11(8), 2046—2056 |
| 92 | Chun J. S., Kim J. W., Jung W. S., Kang C. Y., Kim S. W., Wang Z. L., Baik J. M., Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(10), 3006—3012 |
| 93 | Zheng J. Q., Wang Y. M., Yu Z. H., Fu Y., Chen D., Zhao P., Zhou H. M., Nano Energy, 2019, 64,103957 |
| 94 | Mao Y. C., Zhao P., Mcconohy G., Yang H., Tong Y. X., Wang X. D., Advanced Energy Materials, 2014, 4(7), 1301624 |
| 95 | Chen D. J., Zhang J. X., Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(19), 193901 |
| 96 | Tong W. S., Zhang Y. H., Huang H. W., Xiao K., Yu S. X., Zhou Y., Liu L. P., Li H. T., Liu L, Huang T., Li M., Zhang Q., Du R. F., An Q., Nano Energy, 2018, 53, 513—523 |
| 97 | Zhang Z. Y., Yao C. H., Yu Y. H., Hong Z. L., Zhi M. J., Wang X. D., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(37), 6760—6765 |
| 98 | Kanik M., Aktas O., Sener S. H., Durgun E., Bayindir M., ACS Nano, 2004, 18(9), 9311—9323 |
| 99 | Guo Z. W., Nilsson E., Rigdahl M.,Hagström B., Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2013, 130(4), 2603—2609 |
| 100 | Barber P., Balasubramanian S., Anguchamy Y., Gong S. S., Wibowo A., Gao H. S., Ploehn H., ZurLoye H. C., Materials, 2009, 2(4), 1697—1733 |
| 101 | Kim P., Doss N. M., Tillotson J. P., Hotchkiss P. J., Pan M. J., Li J. Y., Calame J. P., ACS Nano, 2009, 3(9), 2581—2592 |
| 102 | Li J. J., Seok S. I., Chu B. J., Dogan F., Zhang Q. M., Wang Q., Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(2), 217—221 |
| 103 | Schmitz P., Kolek M., Pyschik M., Jalkanen K., Nowak S., Winter M., Bieker P., Chemistry Select, 2017, 2(21), 6052—6056 |
| 104 | Pandey G. P., Liu T., Hancock C., Li Y. H., Sun X. Z. S., Li J., Journal of Power Sources, 2016, 328, 510—519 |
| 105 | Gadilohar B. L., Shankarling G. S., Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 227, 234—261 |
| 106 | Mahdavi V. A., Yousefzadeh M., Kowsari E., Latifi M., Macromolecular Materials and Engineering, 2020, 305(3), 1900796 |
| 107 | Mejri R., Dias J. C., Hentati S. B., Martins M. S., Costa C. M., Lanceros M. S., Journal of Non⁃Crystalline Solids, 2016, 453, 8—15 |
| 108 | Gregorio R., Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2006, 100(4), 3272—3279 |
| 109 | Cai X. M., Lei T. P., Sun D. H., Lin L. W., RSC Advances, 2017, 7(25), 15382—15389 |
| 110 | Meira R. M., Correia D. M., Ribeiro S., Costa P., Gomes A. C., Gama F. M., Lanceros⁃Méndez S. , Ribeiro C., ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2019, 1(10), 2649—2658 |
| 111 | Lang C. H., Fang J., Shao H., Ding X., Lin T., Nat. Commun, 2016, 7, 11108 |
| 112 | Chen D., Wang C., Chen W., Chen Y., Zhang J. X., Biosens Bioelectron, 2015, 74, 1047—1052 |
| 113 | Li T., Feng Z. Q., Qu M., Yan K., Yuan T., Gao B., Wang T., Dong W., Zheng J., ACS Nano, 2019, 13(9), 10062—10073 |
| 114 | Graham R. L., Golab J. T., Yeager D. L., The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1988, 88(4), 2572—2581 |
| 115 | Sharma M., Sharma K., Bose S., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117(28), 8589—8602 |
| 116 | Cho S., Lee J. S., Jang J., ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2015, 7(18), 9668—9681 |
| 117 | Pan C. T., Yen C. K., Wu H. C., Lin L. W., Lu Y. S., Huang J. C., Kuo S. W., Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(13), 6835—6843 |
| 118 | Pan C. T., Yen C. K., Lin L. W., Lu Y. S., Li H. W., Huang J. C., Kuo S. W., RSC Advances, 2014, 4(41), 21563—21570 |
| 119 | Yee W. A., Kotaki M., Liu Y., Lu X. H., Polymer, 2007, 48(2), 512—521 |
| 120 | Hoque N. A., Thakur P., Biswas P., Saikh M. M., Roy S., Bagchi B., Das S., Ray P. P., Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018, 6(28), 13848—13858 |
| 121 | Dreyer D. R., Park S., Bielawski C. W., Ruoff R. S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2010, 39(1), 228—240 |
| 122 | Borini S., White R., Wei D., Astley M., Haque S., Spigone E., Harris N., Kivioja J., Tapani R., ACS Nano, 2013, 7(12), 11166—11173 |
| 123 | Zhan D., Ni Z. H., Chen W., Sun L., Luo Z. Q., Lai L. F., Yu T., Wee A. T., Shen Z. X., Carbon, 2011, 49(4), 1362—1366 |
| 124 | He P., Gu H. Y., Wang G., Yang S. W., Ding G. Q., Liu Z., Xie X. M., Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(20), 8578—8582 |
| 125 | Geim A. K., Novoselov K. S., Nature Materials, 2007, 6, 183—191 |
| 126 | Bhavanasi V., Kumar V., Parida K., Wang J., Lee P. S., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(1), 521—529 |
| 127 | El A. M., Arrakhiz F. Z., Vaudreuil S., Essassi E. M., Qaiss A., Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(19), 7668—7677 |
| 128 | Yu J. H., Jiang P. K., Wu C., Wang L. C., Wu X. F., Polymer Composites, 2011, 32(10), 1483—1491 |
| 129 | Liu X., Ma J., Wu X. M., Lin L. W., Wang X. H., ACS Nano, 2017, 11(2), 1901—1910 |
| 130 | Tong W. S., Zhang Y. H., Zhang Q., Luan X. L., Lv F. Z., Liu L. P., An Q., Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(45), 7029—7037 |
| 131 | Li H. T., Zhang Y. H., Dai H., Tong W. S., Zhou Y., Zhao J. F., An Q., Nanoscale, 2018, 10(12), 5489—5495 |
| 132 | Tong W. S., Zhang Y. H., Zhang Q., Luan X. L., Duan Y., Pan S. F., Lv F. Z., An Q., Carbon, 2015, 94, 590—598 |
| 133 | Patil A. M., An X. W., Li. S. S., Yue X. Y., Du. X., Yoshida A., Hao X. G., Abudula A., Guan G. Q., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 403, 126411 |
| 134 | Ahn Y. J., Lim J. Y., Hong S. M., Lee J., Ha J., Choi H. J., Seo Y., The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(22), 11791—11799 |
| 135 | Wu L. K., Yuan W. F., Hu N., Wang Z. C., Chen C. L., Qiu J. H., Ying J., Li Y., Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2014, 47(13), 135302 |
| 136 | Yu L., Cebe P., Polymer, 2009, 50(9), 2133—2141 |
| 137 | Moon J. S., Song S., Lee S. K., Choi B., Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102(5), 051110—051114 |
| 138 | Jeong S. M., Song S., Joo K., Kim J., Hwang S. H., Jeong J., Kim H., Energy Environ. Sci., 2014, 7(10), 3338—3346 |
| 139 | Fang H. J., Wang X. D., Li Q., Peng D. F., Yan Q. F., Pan C. F., Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(18), 1600829 |
| 140 | Wang X., Zhang H., Yu R., Dong L., Peng D., Zhang A., Zhang Y., Liu H., Pan C., Wang Z. L., Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(14), 2324—2331 |
| 141 | Kamal C. S., Mishra R. K., Patel D. K., Rao K. R., Sudarsan V., Vatsa R. K., Materials Research Bulletin, 2016, 81, 127—133 |
| 142 | Ummartyotin S., Bunnak N., Juntaro J., Sain M., Manuspiya H., Solid State Sciences, 2012, 14(3), 299—304 |
| 143 | Wang Q. P, Jiang S. L.,, Zhang Y. Y., Zhang G. Z., Xiong L. Y., Polymer Bulletin, 2010, 66(6), 821—830 |
| 144 | Wang Q. Q., Jiang S. L., Zhang Y. Y., Zhang G. Z., Xiong L. Y., Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2010, 22(7), 849—853 |
| 145 | Chen C., Bai Z. K., Cao Y. Z., Dong M. C., Jiang K. K., Zhou Y. S., Tao Y. Z., Gu S. J., Xu J., Yin X. Z., Xu W. L., Composites Science and Technology, 2020, 192, 108100 |
| 146 | Fu R. F., Chen S., Lin Y., Zhang S. H., Jiang J., Li Q. B., Gu Y. C., Materials Letters, 2017, 187, 86—88 |
| 147 | Dhakras D., Borkar V., Ogale S., Jog J., Nanoscale, 2012, 4(3), 752—756 |
| 148 | Pratihar S., Medda S. K., Sen S., Polymer Composites, 2020, 41(8), 3351—3363 |
| 149 | Wang W., Sun H. S., Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2020, 137(36), 49070 |
| 150 | Jeon N. J., Noh J. H., Kim Y. C., Yang W. S., Ryu S., Seok S. I., Nat. Mater., 2014, 13(9), 897—903 |
| 151 | Zhang Y., Liu C. H., Liu J. B., Xiong J., Liu J. Y., Zhang K., Liu Y., Peng M. Z., Yu A. F., Zhang A. H., Zhang Y., Wang Z. W., Zhai J. Y., Wang Z. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8(2), 1381—1387 |
| 152 | Thakur P., Kool A., Hoque N. A., Bagchi B., Khatun F., Biswas P., Brahma D., Roy S., Banerjee S., Das S., Nano Energy, 2018, 44, 456—467 |
| 153 | Anand A., Bhatnagar M. C., Materials Today Energy,2019, 13, 293—301 |
| 154 | Deng W. L., Yang T., Jin L., Yan C., Huang H. C., Chu X., Wang Z. X., Xiong D., Tian G., Gao Y. Y., Zhang H. T., Yang W. Q., Nano Energy, 2019, 55, 516—525 |
| 155 | Wu W., Yin X., Dai B. Y., Kou J. H., Ni Y., Lu C. H., Applied Surface Science, 2020, 517,146119 |
| 156 | Yang T., Pan H., Tian G., Zhang B. B., Xiong D., Gao Y. Y., Yan C., Chu X., Chen N. J., Zhong S., Zhang L., Deng W. L., Yang W. Q., Nano Energy, 2020, 72, 104706 |
| 157 | Guo W., Tan C., Shi K., Li J., Wang X. X., Sun B., Huang X., Long Y. Z., Jiang P., Nanoscale, 2018, 10(37), 17751—17760 |
| 158 | Wu J., Qin N., Bao D. H., Nano Energy, 2018, 45, 44—51 |
| 159 | Mokhtari F., Spinks G. M., Fay C., Cheng Z. X., Raad R., Xi J. T., Foroughi J., Advanced Materials Technologies, 2020, 5(4), 1900900 |
| 160 | Fu J., Hou Y. D., Gao X., Zheng M. P., Zhu M. K., Nano Energy, 2018, 52, 391—401 |
| 161 | Zhu N., West A. R., Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 2010, 93(1), 295—300 |
| 162 | Fu J., Hou Y. D., Gao X., Zheng M. P., Zhu M. K., Nano Energy, 2018, 52, 391—401 |
| 163 | Zhang M., Gao T., Wang J. S., Liao J. J., Qiu Y. Q., Xue H., Shi Z., Xiong Z. X., Chen L. F., Nano Energy, 2015, 11, 510—517 |
| 164 | Rorvik P. M., Grande T., Einarsrud M. A., Adv. Mater., 2011, 23(35), 4007—4034 |
| 165 | Koc M., Parali L., San O., Polymer Testing, 2020, 90, 106695 |
| 166 | Chen X., Xu S. Y., Yao N., Xu W. H., Shi Y., Applied Physics Letters, 2009, 95(6), 069902(1) |
| 167 | Ponnamma D., Chamakh M. M., Deshmukh K., Basheer A. M., Erturk A., Sharma P., Al⁃Maadeed M. A., In Smart Polymer Nanocomposites, 2017, 77—93 |
| 168 | Wang Y., Santiago⁃Avilés J. J., Integrated Ferroelectrics, 2011, 126(1), 60—76 |
| 169 | Won S. S., Seo H., Kawahara M., Glinsek S., Lee J., Kim Y., Jeong C. K., Kingon A. I., Kim S. H., Nano Energy, 2019, 55, 182—192 |
| 170 | Cai X. M., Huang X. J., Zheng Z. Y., Xu J. B., Tang X. C., Lei T. P., Journal of Macromolecular Science, Part B, 2016, 56(2), 75—82 |
| 171 | Sultana A., Sadhukhan P., Mehebub A. M., Das S., Ranjan M. T., Mandal D., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 10, 4121—4130 |
| 172 | Merlini C., Pegoretti A., Araujo T.o M., Ramoa S. D. A. S., Schreiner W. H., Barra G. M. D., Synthetic Metals, 2016, 213, 34—41 |
| 173 | Negar C., Ramin K., Ali A. Y., Farhad G., Ceramics International, 2020, 46(12), 19669—19681 |
| 174 | Tian G., Deng W. L., Gao Y. Y., Xiong D., Yan C., He X. B., Yang T., Jin L., Chu X., Zhang H. T., Yan W., Yang W. Q., Nano Energy, 2019, 59, 574—581 |
| 175 | Zhao Y. X., Zhu K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2016, 45(3), 655—689 |
| 176 | Frost J. M., Butler K. T., Brivio F., Hendon C. H., van Schilfgaarde M., Walsh A., Nano Lett., 2014, 14(5), 2584—2590 |
| 177 | Martins P., Lopes A. C., Lanceros⁃Mendez S., Progress in Polymer Science, 2014, 39(4), 683—706 |
| 178 | Sultana A., Sadhukhan P., Alam M. M., Das S., Middya T. R., Mandal D., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10(4), 4121—4130 |
| 179 | Bodnár E., Grifoll J., Rosell⁃Llompart J., Journal of Aerosol Science, 2018, 125, 93—118 |
| 180 | Li Y., Xu M. H., Xia Y. S., Wu J. M., Sun X. K., Wang S., Hu G. H., Xiong C. X., Chemical Engineering Journal, 2020, 388, 124205 |
| 181 | Ding R., Zhang X. L., Chen G., Wang H. L., Kishor R., Xiao J. X., Gao F., Zeng K. Y., Chen X. D., Sun X. W., Zheng Y. J., Nano Energy, 2017, 37, 126—135 |
| 182 | Niu Y. J., Yu K., Bai Y. Y., Xiang F., Wang H., RSC Advances, 2015, 5(79), 64596—64603 |
| 183 | Wu M. J., Xu C., Zhang Y., Wang Z. L., ACS Nano, 2012, 6(5), 4335—4340 |
| 184 | Bairagi S., Ali S. W., Energy, 2020, 198, 117385 |
| 185 | Wang G., Xi Y., Xuan H. X., Liu R. C., Chen X., Cheng L., Nano Energy, 2015, 18, 28—36 |
| 186 | Alam M. M., Ghosh S. K., Sultana A., Mandal D., Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(16), 165403 |
| 187 | Wu J. M., Xu C., Zhang Y., Yang Y., Zhou Y., Wang Z. L., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(45), 6094—6099 |
| 188 | Han S. W., Chen D., Wang J., Liu Z., Liu F., Chen Y. K., Ji Y. C., Pang J. B., Liu H., Wang J. G., Nano Energy, 2020, 72, 104688 |
| 189 | Inaguma Y., Sakurai D., Aimi A., Yoshida M., Katsumata T., Mori D., Yeon J., Halasyamani P. S., Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2012, 195,115—119 |
| 190 | Soin N., Zhao P. F., Prashanthi K., Chen J. K., Ding P., Zhou E. P., Shah T., Ray S. C., Tsonos C., Thundat T., Siores E., Luo J. K., Nano Energy, 2016, 30, 470—480 |
| 191 | Kim H. J., Kim Y. J., Materials & Design, 2018, 151, 133—140 |
| 192 | Guan X. C., Zhang Y. D., Li H., Ou J. P., Sensors and Actuators A: Physical, 2013, 194, 228—231 |
| 193 | Zhang Y. Y., Zhang J. P., Gao J. X., Li H., Wang E. P., Hu X., Journal of Electroceramics, 2014, 34(2/3), 216—220 |
| 194 | Zhang L. I. N., Cheng Z. Y., Journal of Advanced Dielectrics, 2012, 01(04), 389—406 |
| 195 | Karan S. K., Mandal D., Khatua B. B., Nanoscale, 2015, 7(24), 10655—10666 |
| 196 | Karan S. K., Das A. K., Bera R., Paria S., Maitra A., Shrivastava N. K., Khatua B. B., RSC Advances, 2016, 6(44), 37773—37783 |
| 197 | Gong H. Y., Li Z. J., Zhang Y. Y., Fan R. H., Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2009, 29(10), 2013—2019 |
| 198 | Sakamoto W. K., Marin F. P., Das⁃Gupta D. K., Sensors and Actuators A, 2002, 100, 165—174 |
| 199 | Pal A., Sasmal A., Manoj B., Rao D. S. D. P., Haldar A. K., Sen S., Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2020, 244, 122639 |
| 200 | Park K. I., Lee M., Liu Y., Moon S., Hwang G. T., Zhu G., Kim J. E., Kim S. O., Kim D. K., Wang Z. L., Lee K. J., Adv. Mater., 2012, 24(22), 2999—3004, |
| 201 | Wang X. L., Shi G. Q., Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(3), 790—823 |
| 202 | Shi K. M., Sun B., Huang X. Y., Jiang P. K., Nano Energy, 2018, 52, 153—162 |
| 203 | Karan S. K., Bera R., Paria S., Das A. K., Maiti S., Maitra A., Khatua B. B., Advanced Energy Materials, 2016, 6(20), 1601016 |
| 204 | Kang H. B., Han C. S., Pyun J. C., Ryu W. H., Kang C. Y., Cho Y. S., Composites Science and Technology, 2015, 111, 1—8 |
| 205 | Ponnamma D., Parangusan H., Tanvir A., Alma'adeed M. A. A., Materials & Design, 2019, 184, 108176 |
| 206 | Teka A., Bairagi S., Shahadat M., Joshi M., Ziauddin A. S., Wazed A. S., Polymers for Advanced Technologies, 2018, 29(9), 2537—2544 |
| 207 | Parangusan H., Ponnamma D., Almaadeed M. A. A., Soft Matter, 2018, 14(43), 8803—8813 |
| 208 | Parangusan H., Ponnamma D., Al⁃Maadeed M. A. A., Sci. Rep., 2018, 8(1), 754 |
| 209 | Bairagi S., Ali S. W., International Journal of Energy Research, 2020, 44(7), 5545—5563 |
| 210 | Chen W. H., Duan W. F., Liu Y., Wang Q., Qi F. W., Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(47), 21531—21541 |
| 211 | Choi S., Shin G., Appl. Ergon., 2018, 70, 1—5 |
| 212 | Hu D. W., Yao M. G., Fan Y., Ma C. R., Fan M. J., Liu M., Nano Energy, 2019, 55, 288—304 |
| 213 | Shuai C. J., Liu G. F., Yang Y. W., Qi F. W., Peng S. P., Yang W. J., He C. X., Wang G. Y., Qian G. W., Nano Energy, 2020, 74, 104825 |
| 214 | Shuai C. J., Yang W. J., Yang Y. W., Pan H., He C. X., Qi F. W., Xie D. Q., Liang H. X., Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(1), 015404 |
| 215 | Gao C. D., Yao M., Shuai C. J., Peng S. P., Deng Y. W., Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(11), 2608—2617 |
| 216 | Jia N., Xing Q., Liu X., Sun J., Xia G., Huang W., Song R., J. Colloid Interface Sci., 2015, 453, 169—176 |
| 217 | Tong W. S., An Q., Wang Z. H., Li Y. N., Tong Q. W., Li H. T., Zhang Y., Zhang Y. H.,Advanced Materials, 2020, 32(39), 2003087 |
| 218 | Yu X., Zhao Z. H., Sun D. H., Ren N., Yu J. H., Yang R. Q., Liu H., Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2018, 227, 470—476 |
| 219 | Chen G. H., Ji S. Z., Sang Y. H., Chang S. J., Wang Y. N., Hao P., Claverie J., Liu H., Yu G. W., Nanoscale, 2015, 7(7), 3117—3125 |
| [1] | 赵盛, 霍志鹏, 钟国强, 张宏, 胡立群. 改性钆/硼/聚乙烯纳米复合材料的制备及对中子和伽马射线的屏蔽性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220039. |
| [2] | 于鹏东, 关兴华, 王冬冬, 辛志荣, 石强, 殷敬华. 新型光、 热双响应形状记忆聚合物的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220085. |
| [3] | 赵君禹, 王春博, 王成杨, 张克, 丛冰, 杨岚, 赵晓刚, 陈春海. 导热膨胀石墨/聚醚酰亚胺复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210800. |
| [4] | 储瑶, 王烁, 张子诺, 王艺博, 蔡以兵. 铜粒子负载泡沫基相变复合材料的制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210619. |
| [5] | 李伟辉, 李浩博, 曾诚, 梁昊樾, 陈佳俊, 李俊勇, 李会巧. 热压法构筑锂负极聚偏氟乙烯基双功能保护层的研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210629. |
| [6] | 李淑蓉, 王琳, 陈玉贞, 江海龙. 金属-有机框架材料在液相催化化学制氢中的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(1): 20210575. |
| [7] | 高晓乐, 王家信, 李志芳, 李艳春, 杨冬花. 复合材料NiOx-ZSM-5的制备及微生物电解池催化析氢性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2886. |
| [8] | 李占峰, 刘本学, 刘晓婵, 王新强, 张晶, 于诗摩, 赵新富, 张新恩, 伊希斌. 氧化锆湿凝胶中乙酰丙酮配体的脱除机理及气凝胶复合材料的制备[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2904. |
| [9] | 赵凌云, 黄汉雄, 罗杜宇, 苏逢春. 复合材料柔软性对倒金字塔微结构阵列传感器性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2953. |
| [10] | 魏敏敏, 袁泽, 闾敏, 马辉, 谢小吉, 黄岭. 稀土掺杂上转换纳米颗粒-金属有机骨架复合材料的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2313. |
| [11] | 王献伟, 柯红军, 袁航, 鲁戈舞, 李丽英, 孟祥胜, 宋书林, 王震. 耐高温可溶性聚酰亚胺树脂及其复合材料[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2041. |
| [12] | 高翼飞, 肖长发, 冀大伟, 黄阳正. 熔融纺丝-拉伸法制备PVDF中空纤维膜及其油-水分离性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2065. |
| [13] | 杨思娴, 钟文钰, 李超贤, 苏秋瑶, 许炳佳, 何谷平, 孙丰强. 聚苯胺纳米线/SnO2复合光催化材料的光化学制备与性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 1942. |
| [14] | 丁嘉乐, 金兰, 崔增多, 张海博, 张云鹤, 姜振华. 具有双交联网络结构的纳米复合材料的制备及介电性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(6): 2015. |
| [15] | 巴智晨, 梁大鑫, 谢延军. MXenes复合材料的发展: 界面调控及结构设计[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(4): 1225. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
