

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (5): 1357.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20210013
薛琳琳,吕瑞景,王澳轩,罗加严
收稿日期:2021-01-05
出版日期:2021-05-10
发布日期:2021-05-08
基金资助:
XUE Linlin, LYU Ruijing, WANG Aoxuan, LUO Jiayan( )
)
Received:2021-01-05
Online:2021-05-10
Published:2021-05-08
Contact:
LUO Jiayan
E-mail:jluo@tju.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
可充电镁电池具有理论体积比容量大、 地壳丰度高、 成本低、 环境友好及更为安全等优点, 是未来高能量存储系统发展的重要方向之一. 在大多数传统电解液中, 镁金属负极表面形成的钝化膜会阻碍镁的可逆沉积溶解过程, 从而限制了可充电镁电池的商业化应用. 由于存在成本高、 合成步骤复杂、 离子电导率低及难以同时与正负极兼容等问题, 聚焦于解决镁负级钝化问题的电解液研究陷入瓶颈. 因此, 通过对镁电池负极进行修饰改性, 使其在传统电解液中实现可逆过程是一种具有发展前景的策略. 本文从合金负极及人工界面形成两方面总结了近年来用于可充电镁电池负极改性的策略, 并在分析对比的基础上提出了进一步发展的结论和展望.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
薛琳琳, 吕瑞景, 王澳轩, 罗加严 . 可充电镁电池负极改性策略. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(5): 1357.
XUE Linlin, LYU Ruijing, WANG Aoxuan, LUO Jiayan. Strategies Concerning Anode Modification in Rechargeable Magnesium Batteries. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(5): 1357.
| Metal anode | Electrode potential/V | Gravimetric capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Volumetric capacity/(mA·h·cm-3) | Cost/(USD·kg-1) | Abundance rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | -3.04 | 3862 | 2066 | 19.2 | 33rd |
| Na | -2.71 | 1166 | 1128 | 0.2 | 6th |
| K | -2.93 | 685 | 591 | 1.0 | 7th |
| Mg | -2.37 | 2205 | 3832 | 2.2 | 8th |
| Zn | -0.76 | 820 | 5854 | 2.2 | 25th |
| Ca | -2.87 | 1337 | 2072 | 2.4 | 5th |
| Al | -1.66 | 2980 | 8046 | 1.9 | 3rd |
Table 1 Different properties of various metal anodes
| Metal anode | Electrode potential/V | Gravimetric capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Volumetric capacity/(mA·h·cm-3) | Cost/(USD·kg-1) | Abundance rank |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Li | -3.04 | 3862 | 2066 | 19.2 | 33rd |
| Na | -2.71 | 1166 | 1128 | 0.2 | 6th |
| K | -2.93 | 685 | 591 | 1.0 | 7th |
| Mg | -2.37 | 2205 | 3832 | 2.2 | 8th |
| Zn | -0.76 | 820 | 5854 | 2.2 | 25th |
| Ca | -2.87 | 1337 | 2072 | 2.4 | 5th |
| Al | -1.66 | 2980 | 8046 | 1.9 | 3rd |
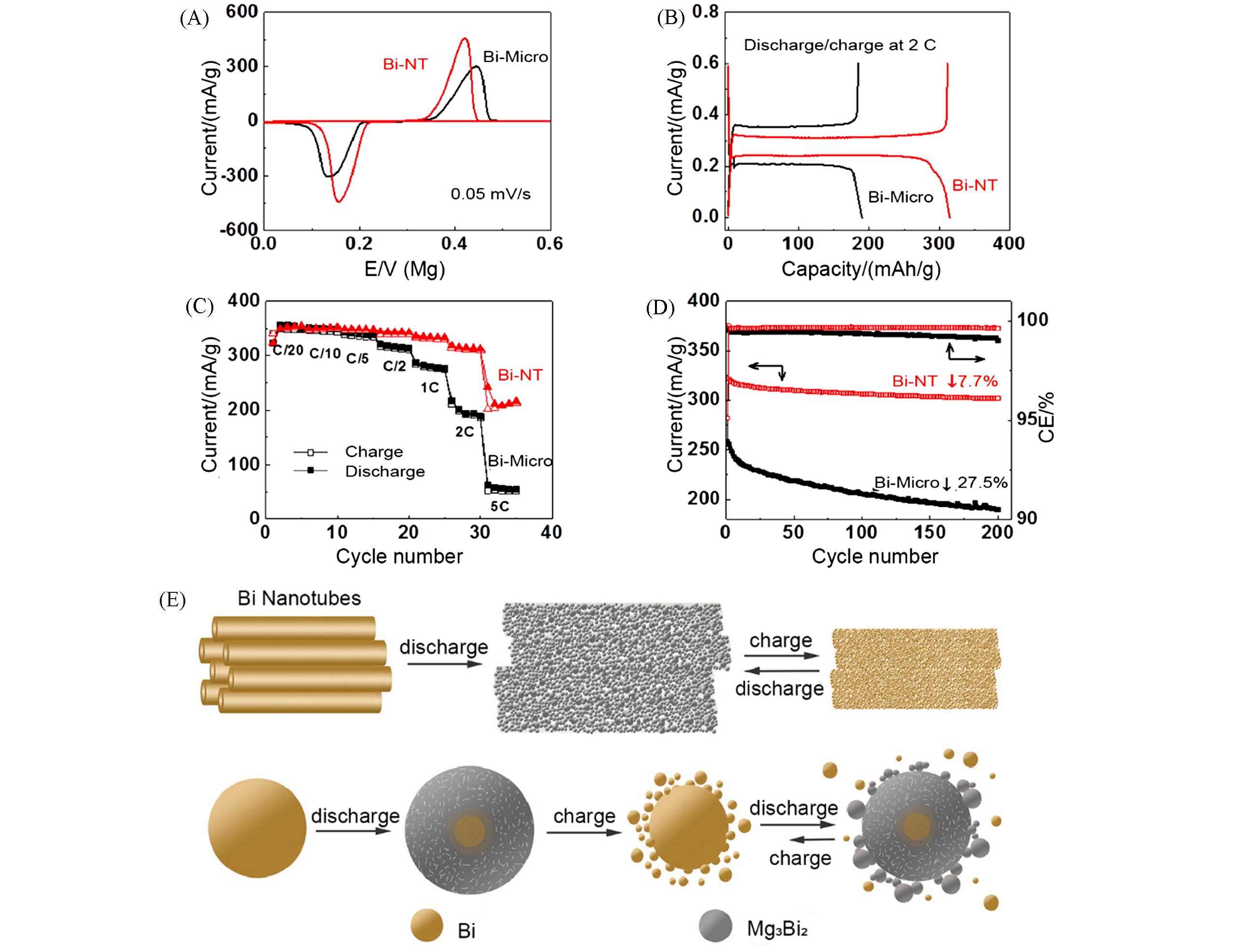
Fig.3 Electrochemical performance and illustration of structural transformation for Bi?Mg alloy anode[41](A) Cyclic voltammograms of Mg2+ insertion/deinsertion in Bi?NT and Bi?micro; (B) discharge/charge profile of a Mg?Bi cell; (C) rate performance of a Mg?Bi cell; (D) cycling stability and Coulombic efficiency of Bi electrode; (E) schematic illustration of the structural transformations of Bi?NT and Bi?micro during the discharge/charge process.Copyright 2013, American Chemical Society.
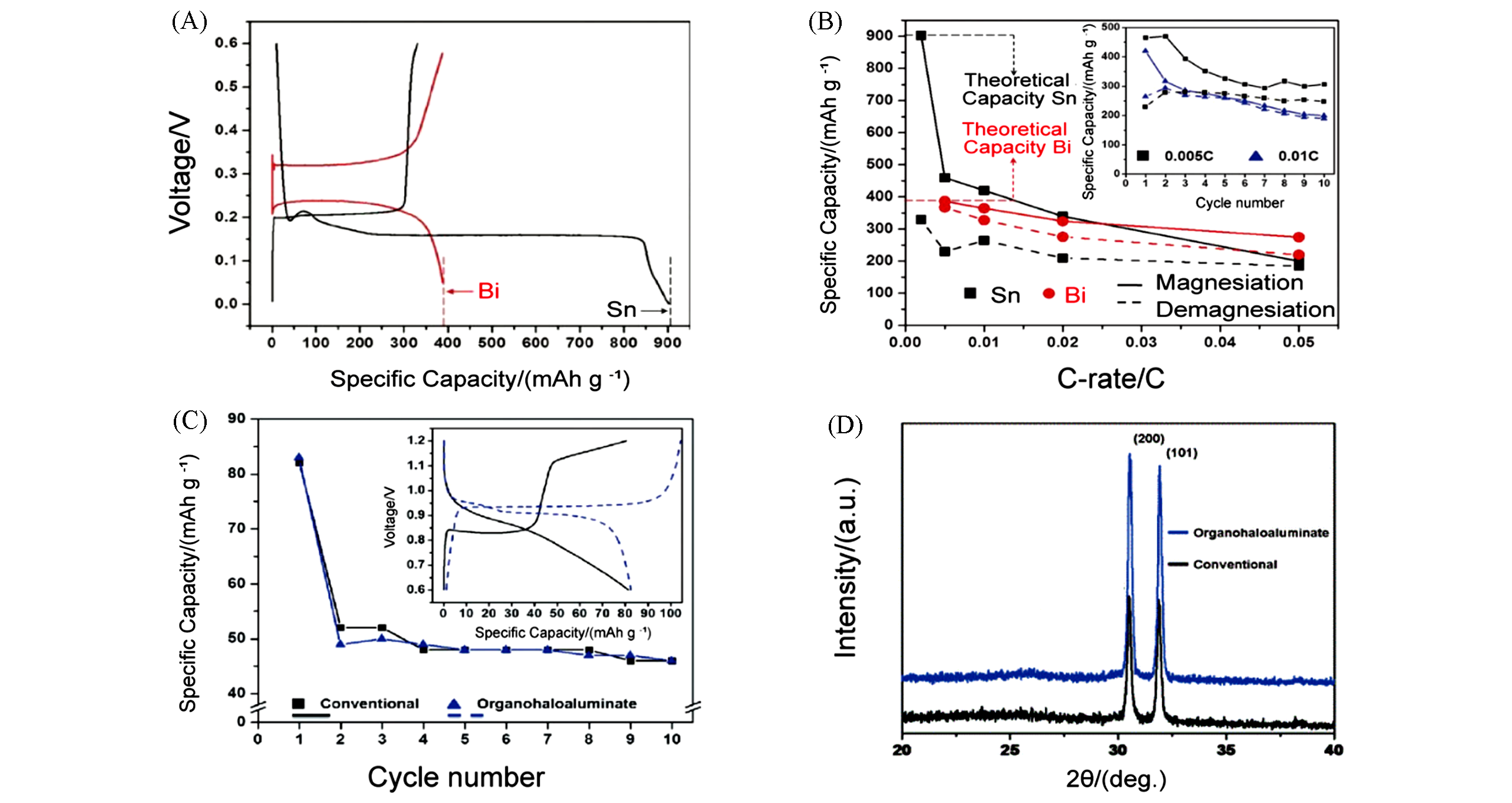
Fig.4 Electrochemical performance and XRD patterns of Sn?Mg alloy anode[48](A) 1st cycle galvanostatic magnesiation/demagnesiation curves for Sn/Mg and Bi/Mg half cells at 0.002C rate(using organohaloaluminate electrolyte); (B) magnesiation/demagnesiation capacities for Sn/Mg and Bi/Mg half?cells at various rates. Inset of (B): 10 cycles of a Sn/Mg half?cell at 0.005C and 0.01C rates in the same electrolyte; (C) the first 10 cycles for [Mo6S8/conventional electrolyte/Mg2Sn] and [Mo6S8/organohaloaluminate electrolyte/Mg2Sn] full?cell. Inset of (C): 1st cycle voltage profiles for each full?cell; (D) XRD patterns of demagnesiated Mg2Sn from organohaloaluminate and conventional electrolytes.Copyright 2013, The Royal Society of Chemistry.
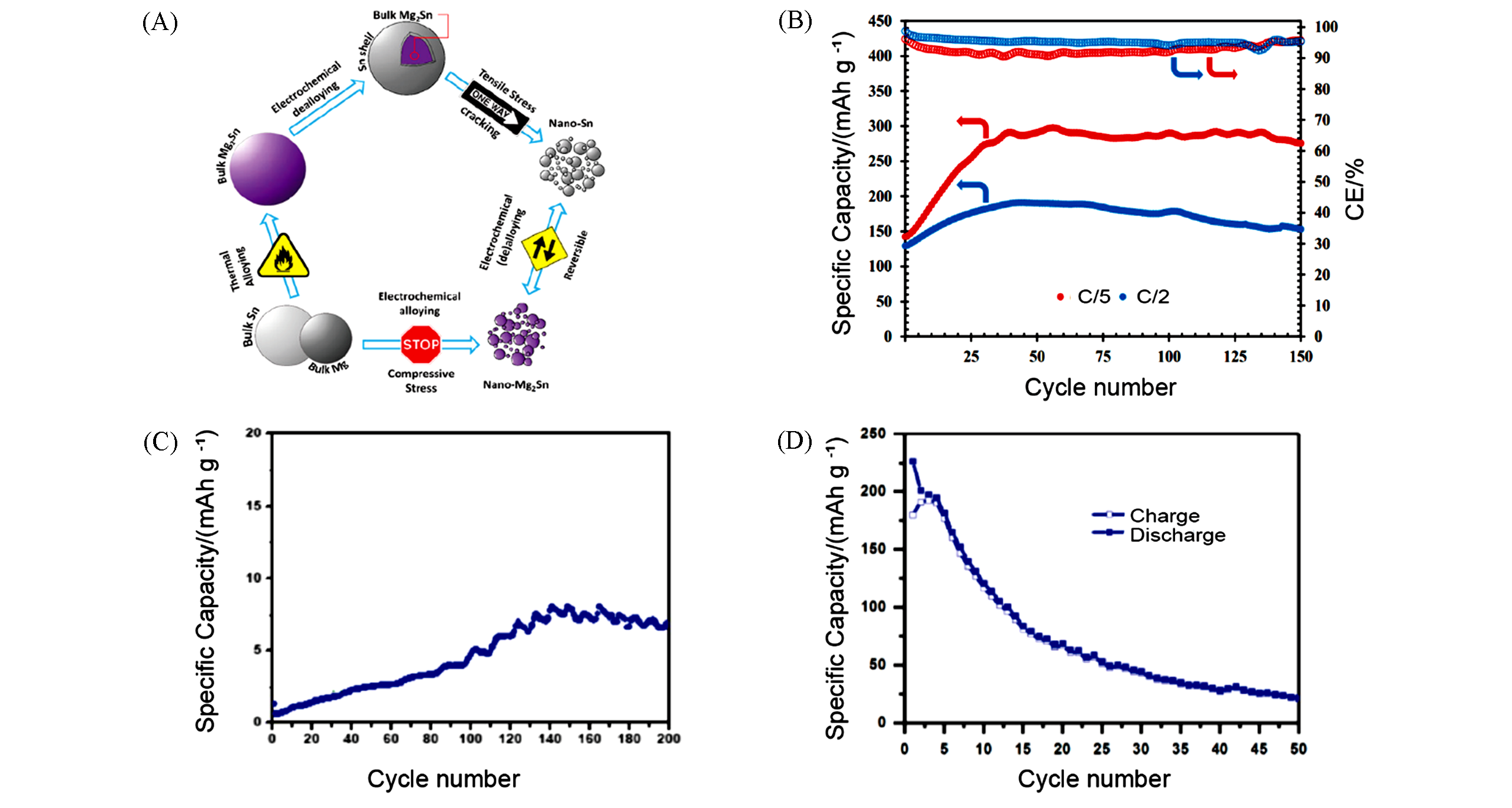
Fig.5 Synthesis process and electrochemical performance of Sn based anode(A) Schematic illustration of process producing nanostructured Sn[50]; (B) capacity retention of Mg2Sn/APC/Mg cells following application of oxidative pulses and past the preconditioning steps at C/5 and C/2[50]; (C) cycling performance of micro?Sn[51]; (D) nano?Sn at C/20 in Mg half?cell using 0.5 mol/L PhMgCl/THF and 0.5 mol/L EtMgCl/THF as electrolyte respectively[51].(A, B) Copyright 2018, American Chemical Society; (C, D) Copyright 2018, MDPI AG.
Alloy element | Theoretical capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Cost/ (USD·kg-1) | Abundance | Reversibility/toxicity/ volume expansion | Conventional electrolyte | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Mg3Bi2 385 | 28.3 | 4.8×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Mg(BH4)2?LiBH4/diglyme | [ | |||||
| Sn | Mg2Sn 900 | 18.0 | 2.2 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic/120% | Mg(TFSI)2/DME | [ |
| Ga | Mg5Ga2 1920 | 2200.0 | 18.0 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Ge | Mg2Ge 1475 | 1200.0 | 1.8 ppm | Almost irreversible/Non?toxic/178% | ― | [ |
| Sb | Mg3Sb2 660 | 4.4 | 0.2 ppm | Almost irreversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/diglyme | [ |
| Si | Mg2Si 3817 | 1.4 | 27.7% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic/216% | ― | [ |
| Pb | Mg2Pb 517 | 0.2 | 14.0 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| In | Mg3In 1400 | 540.0 | 4.9×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| P | Mg2P 3461 | 300.0 | 1000.0 ppm | Maybe reversible/Non?toxic for black P | ― | [ |
| Al | Mg17Al12 2582 | 2.0 | 8.1% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic | ― | [ |
Table 2 Specific properties of representative alloy anodes
Alloy element | Theoretical capacity/ (mA·h·g-1) | Cost/ (USD·kg-1) | Abundance | Reversibility/toxicity/ volume expansion | Conventional electrolyte | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bi | Mg3Bi2 385 | 28.3 | 4.8×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Mg(BH4)2?LiBH4/diglyme | [ | |||||
| Sn | Mg2Sn 900 | 18.0 | 2.2 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic/120% | Mg(TFSI)2/DME | [ |
| Ga | Mg5Ga2 1920 | 2200.0 | 18.0 ppm | Reversible/Non?toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/AN | [ |
| Ge | Mg2Ge 1475 | 1200.0 | 1.8 ppm | Almost irreversible/Non?toxic/178% | ― | [ |
| Sb | Mg3Sb2 660 | 4.4 | 0.2 ppm | Almost irreversible/Toxic | Mg(TFSI)2/diglyme | [ |
| Si | Mg2Si 3817 | 1.4 | 27.7% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic/216% | ― | [ |
| Pb | Mg2Pb 517 | 0.2 | 14.0 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| In | Mg3In 1400 | 540.0 | 4.9×10-2 ppm | Reversible/Toxic | ― | [ |
| P | Mg2P 3461 | 300.0 | 1000.0 ppm | Maybe reversible/Non?toxic for black P | ― | [ |
| Al | Mg17Al12 2582 | 2.0 | 8.1% | Maybe irreversible/Non?toxic | ― | [ |
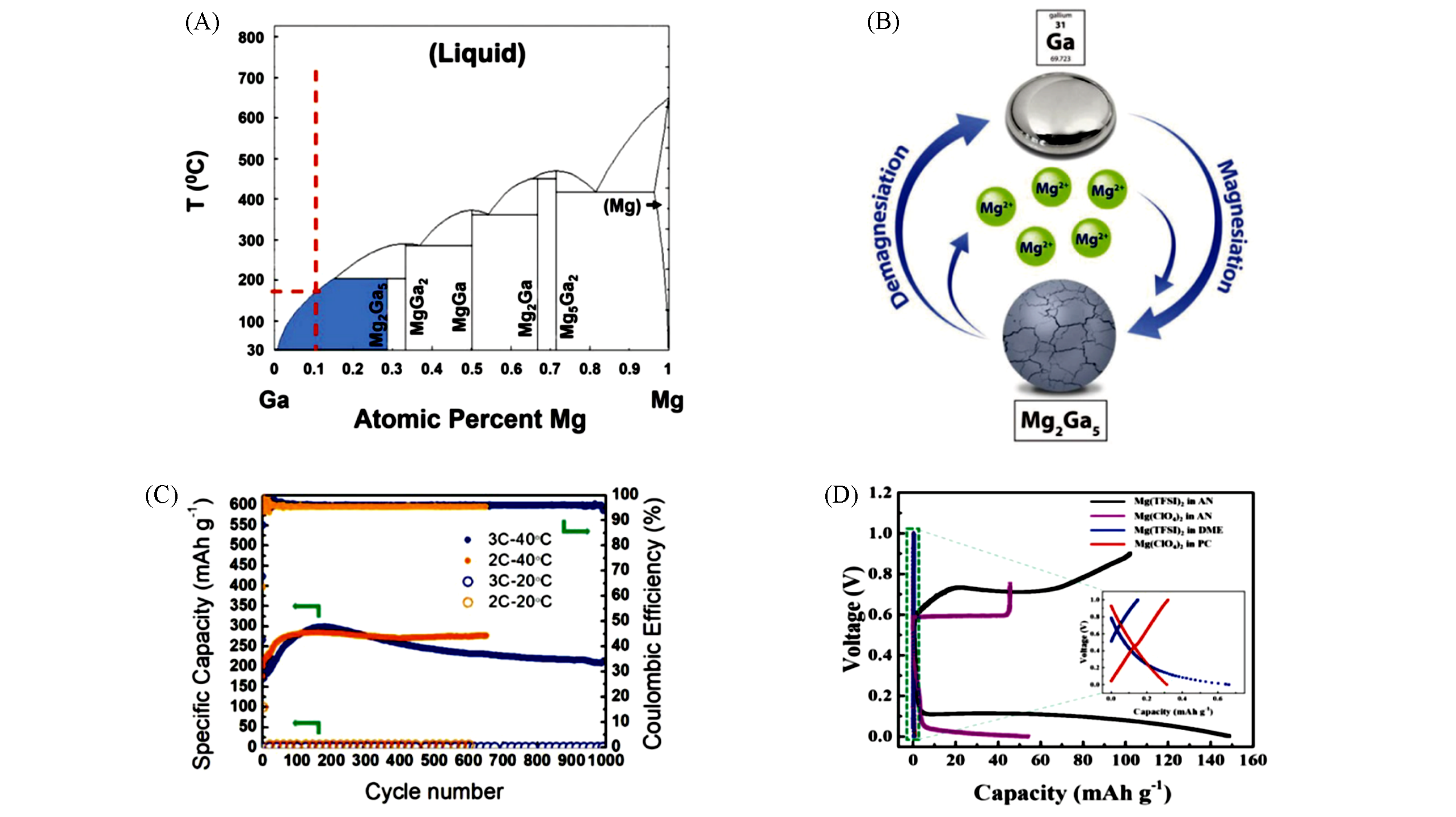
Fig.6 Mechanism and electrochemical performance of Ga?Mg alloy electrodes[61](A) Equilibrium phase diagram of the Mg?Ga system; (B) schematic of the magnesiation and demagnesiation process during which liquid Ga is reversibly converted into solid Mg2Ga5 at constant temperature and pressure; (C) long cycle?life of Mg2Ga5 alloy?type anode operating at 40 ℃ and 3C, 40 ℃ and 2C, 20 ℃ and 3C, 20 ℃ and 2C; (D) investigation of the compatibility of Mg2Ga5 with conventional electrolytes.Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
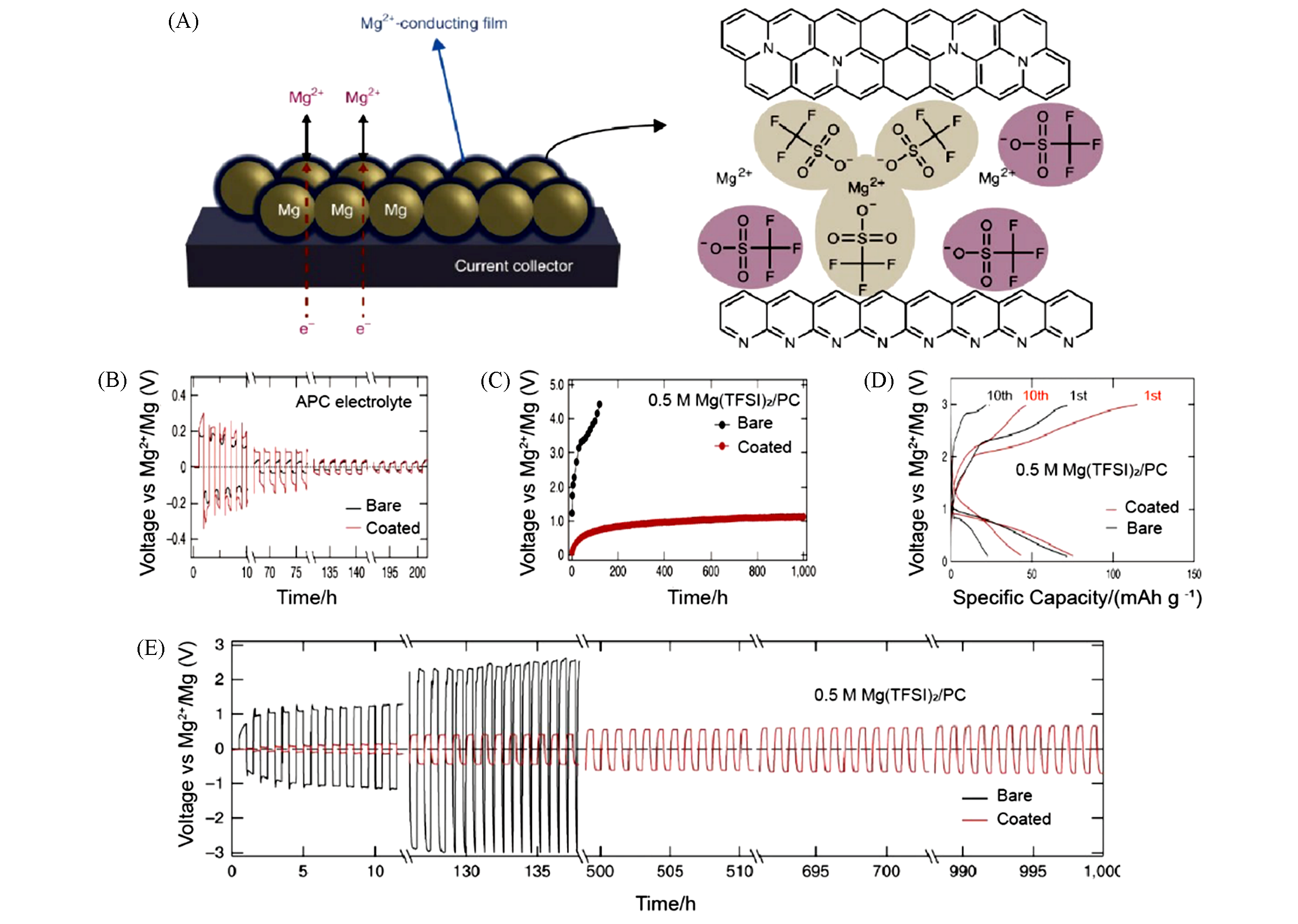
Fig.7 Structure of the interphase and electrochemical performance of coated or bare Mg anodes[64](A) Schematic of a Mg powder electrode coated with the artificial Mg2+?conducting interphase, and the proposed structure for the interphase; (B) reversible Mg deposition/stripping in APC electrolyte; (C) voltage hysteresis versus cycle numbers for symmetric Mg electrodes with 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte; (D) voltage profiles of full cells using V2O5 as cathode in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte; (E) reversible Mg deposition/stripping in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/PC electrolyte.Copyright 2018, Springer Nature.
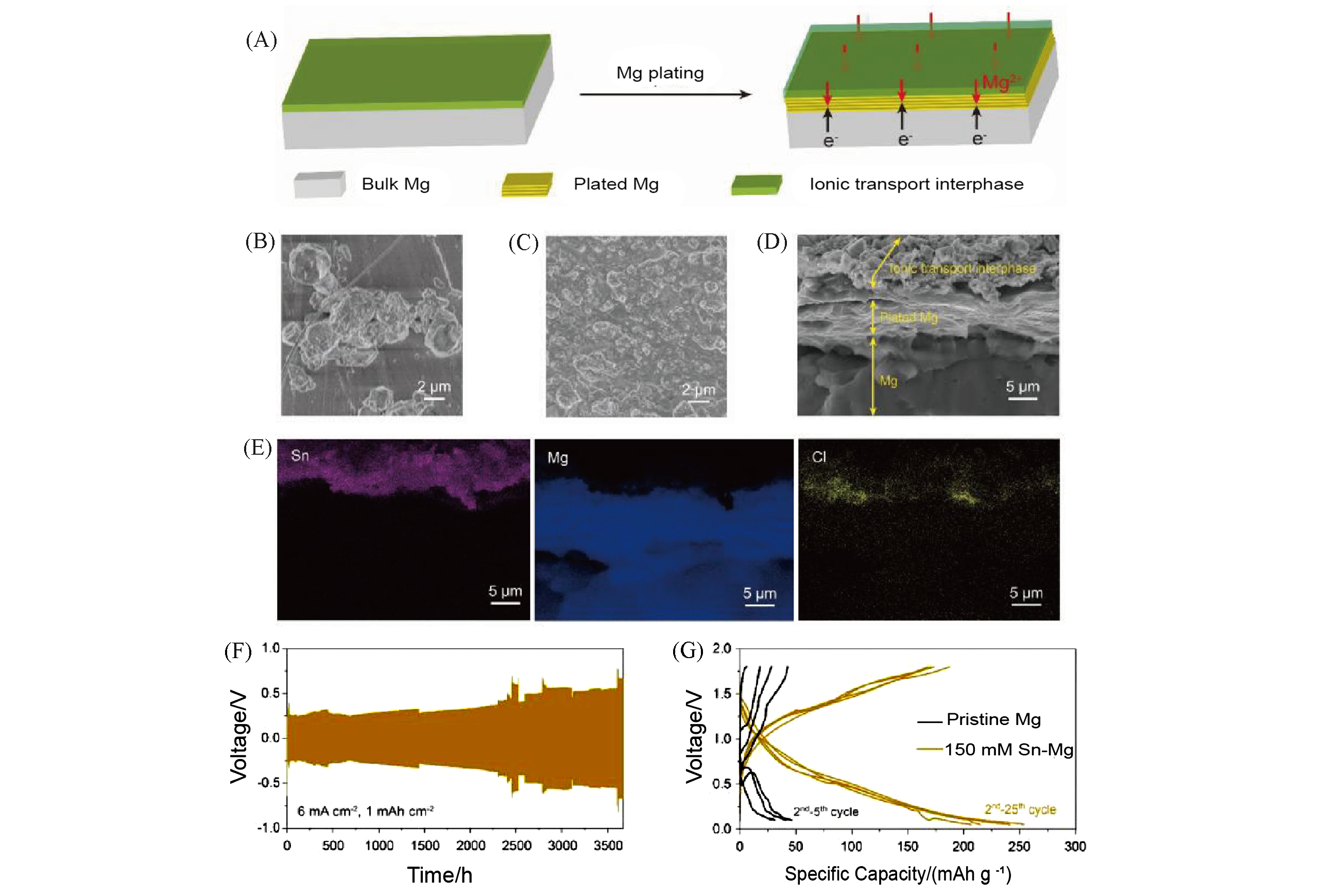
Fig.8 Morphology characterization and electrochemical performance of pristine and Sn based Mg anodes[65](A) Schematic showing the Mg deposition behavior in Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolyte with ionic transport interphase on Mg metal anodes; (B, C) surface views of the pristine Mg anode(0.05 mA/cm2)(B) and modified Mg anode(2 mA/cm2) plated with 2 mA·h/cm2 of Mg(C); (D, E) cross?sectional image for modified Mg anode plated with 2 mA·h/cm2(D) and the corresponding EDS mappings of Sn, Mg and Cl, respectively(E); (F) voltage profiles in symmetric cells with modified Mg anodes at a current density of 6 mA/cm2; (G) galvanos?tatic voltage profiles of the pristine and modified Mg anodes paired with TiS2 cathode at a current density of 10 mA/g.Copyright 2019, Oxford University Press.
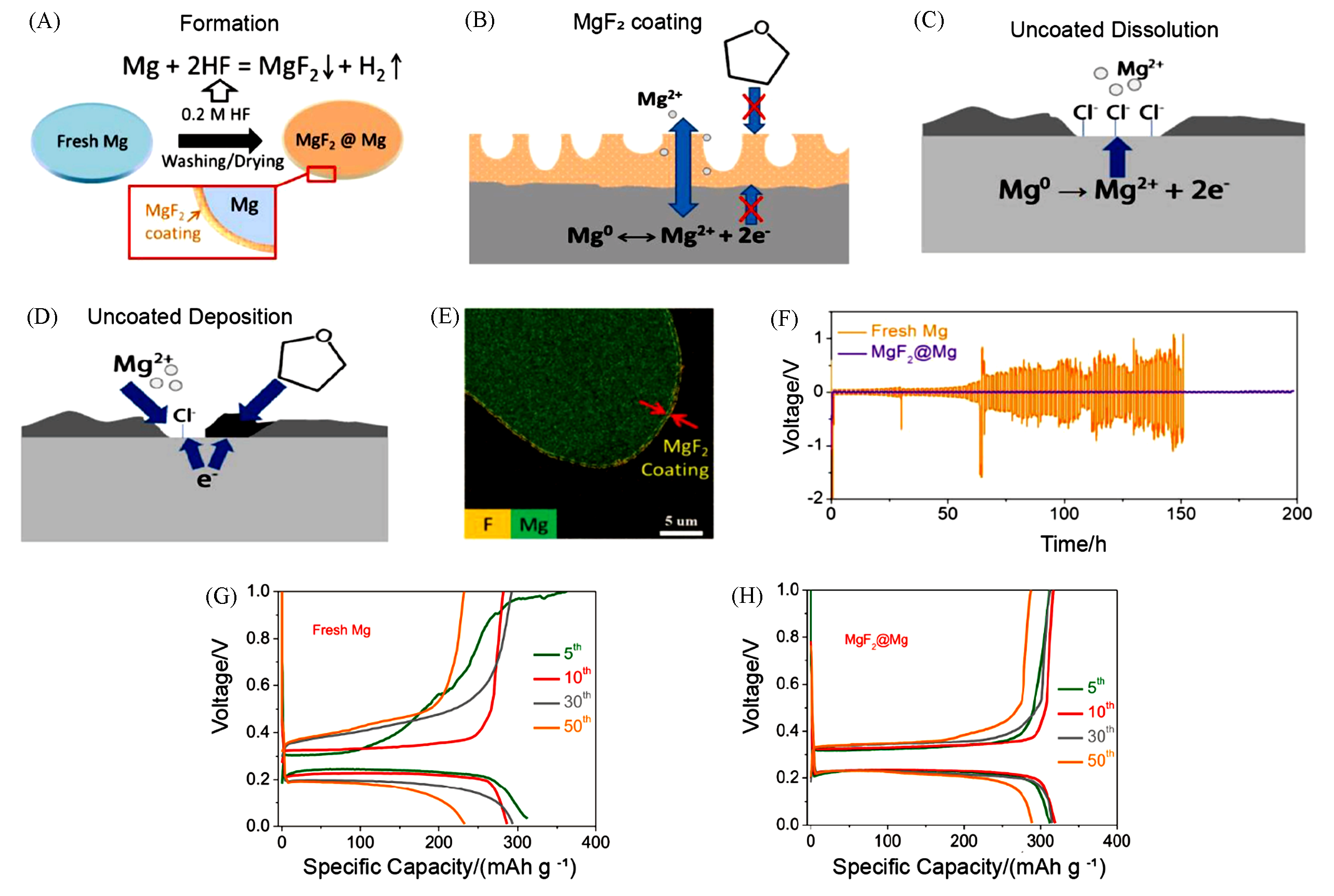
Fig.9 Formation and operating mechanism of MgF2 interphase and electrochemical performance of fresh or coated Mg anodes[66](A) Schematic illustration of the formation process of the MgF2 surface coating; (B) schematic of the operating mechanism of the MgF2 for stripping and deposition of Mg metal; (C, D) schematics of failure mechanism for the Mg metal anode; (E) cross?section EDS mapping of as?prepared MgF2@Mg electrode; (F) voltage profiles of the symmetric cells cycling of fresh Mg and MgF2 coated Mg at current density of 0.25 mA/cm2; (G, H) voltage profiles(with Bi as cathode) of fresh Mg(G) and MgF2@Mg(H) at 120 mA/g.Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
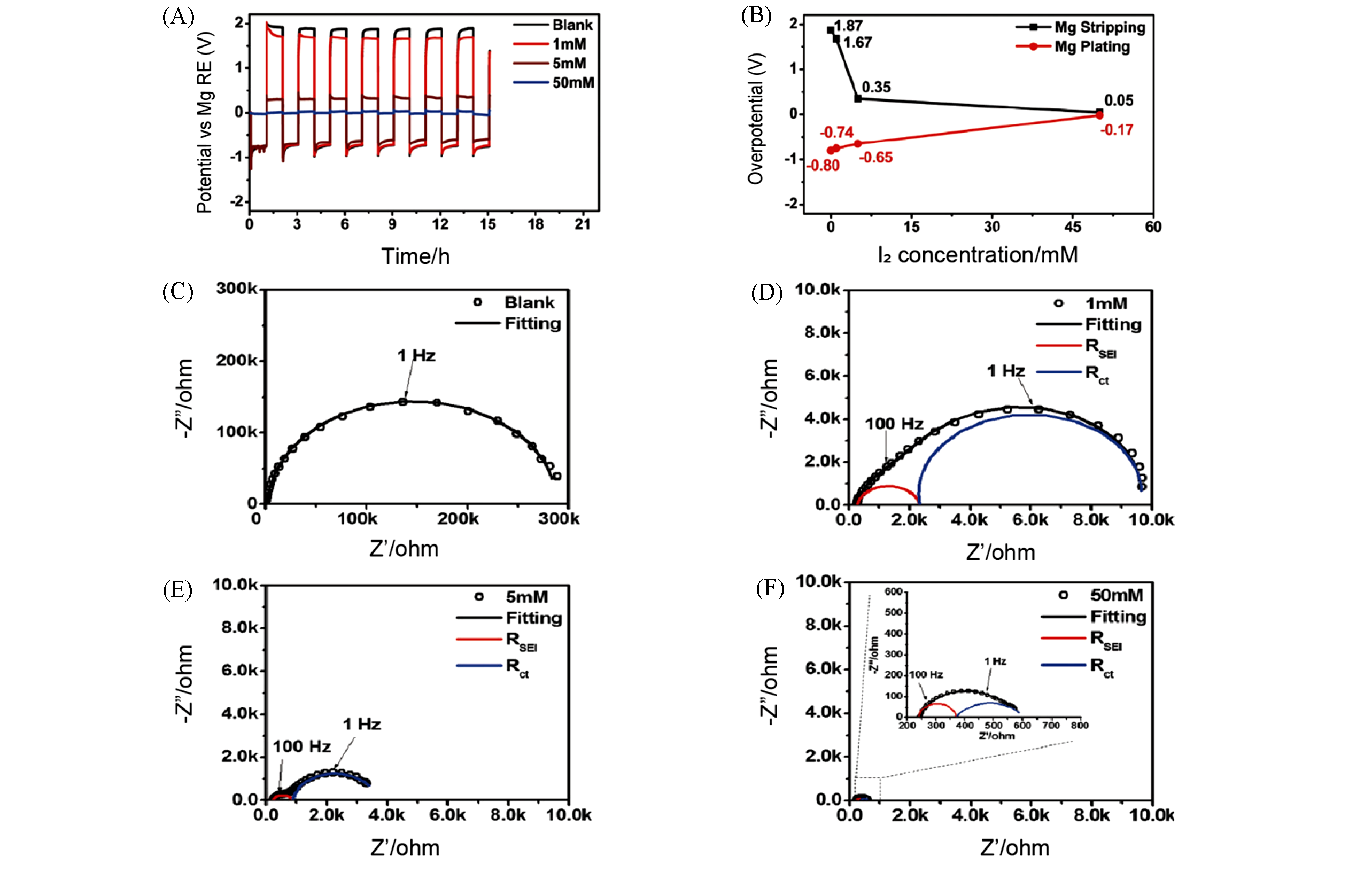
Fig.10 Electrochemical performance of Mg anodes in electrolytes with or without I2 additive[68](A) Potential of Mg electrode during cycling in 0.5 mol/L Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolytes with different amounts of I2 additive; (B) overpotentials for deposition and stripping; (C―F) EIS of Mg electrodes cycled in blank electrolyte and electrolytes with different concentrations of I2 additive.Copyright 2017, Wiley?VCH.
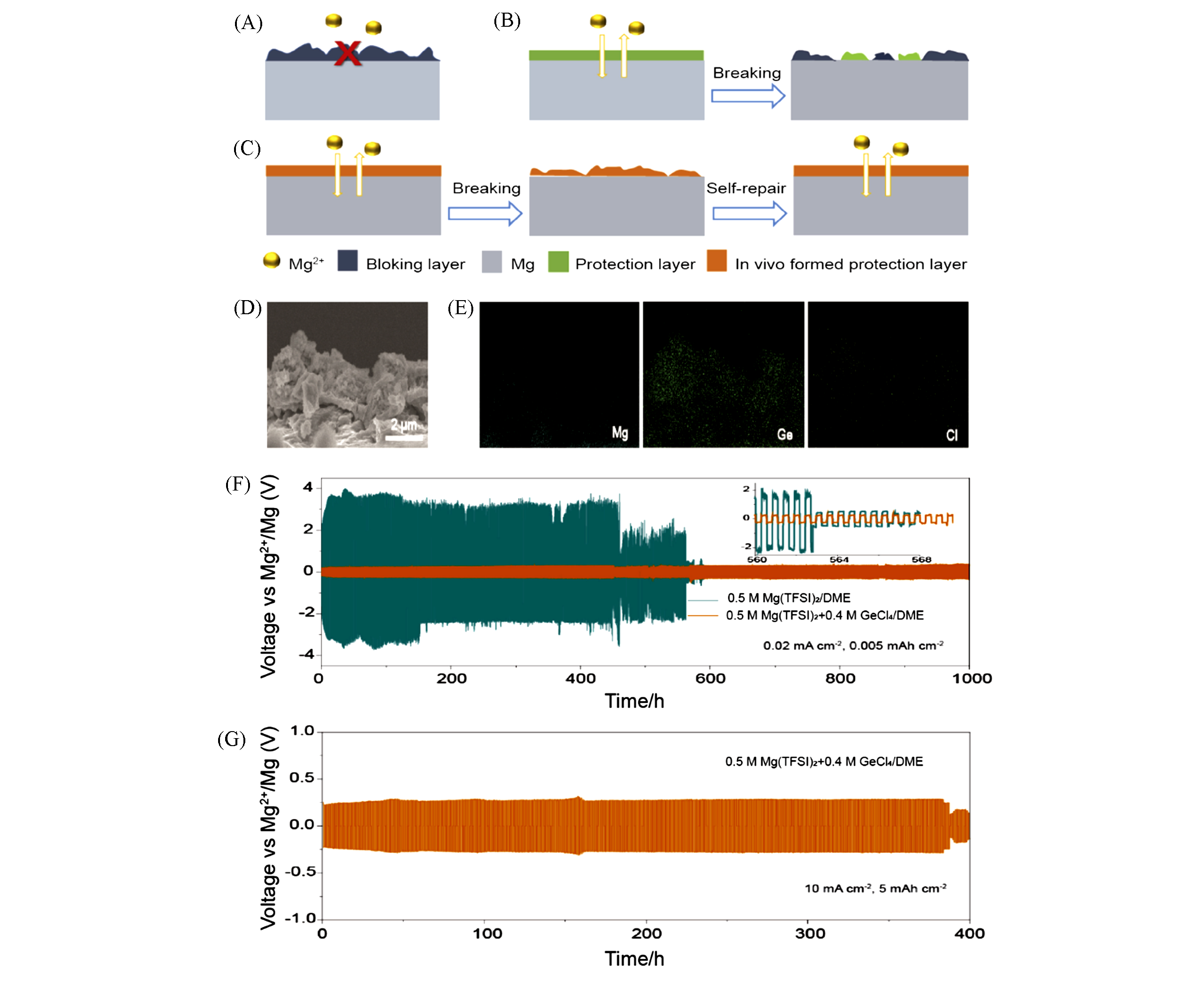
Fig.11 Operating mechanism of interphase and electrochemical performance of anodes in electrolytes with or without GeCl4 additive[69](A) Schematic diagrams showing the passivation layer in blank electrolyte; (B, C) breaking process for protection layer(B) and breaking and self?repair process for in situ?formed protection layer(C) during Mg deposition/stripping in conventional organic electrolyte; (D, E) cross?section SEM image(D) and the corresponding EDX mapping analysis(E) of the Ge?based protection layer; (F, G) voltage responses of symmetric Mg cells under repeated polarization from 1/4 h charge/discharge cycling at 0.02 mA/cm2(F) and 1/2 h charge/discharge cycling at 10 mA/cm2(G).Copyright 2019, Elsevier.
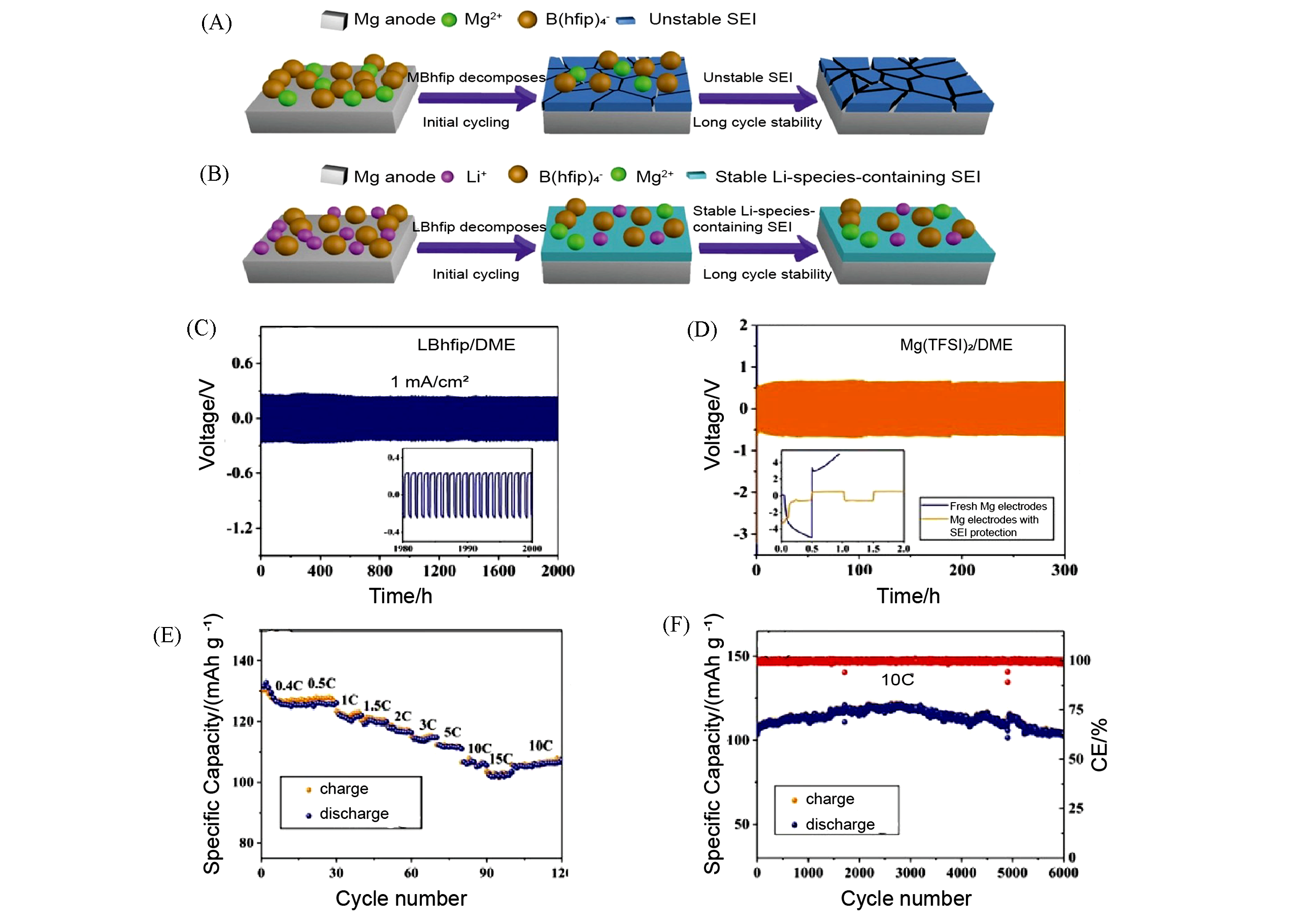
Fig.12 Mechanism of SEI formation and electrochemical performance of anodes in MBhfip/DME or LBhfip/DME electrolyte[70](A, B) The specific mechanism of SEI formation on the Mg anode surface in MBhfip/DME electrolyte(A) and LBhfip/DME electrolyte(B); (C) long?term cycling behavior of the Mg/Mg symmetrical cell(with LBhfip/DME) at the current density of 1.0 mA/cm2; (D) polarization behavior of the Mg/Mg symmetric cell with bare Mg electrodes and SEI protecting Mg electrodes at the current density of 0.1 mA/cm2 in Mg(TFSI)2/DME electrolyte; (E) charge?discharge profiles of Mo6S8/Mg battery(with LBhfip/DME electrolyte) at diffe?rent rates; (F) cycling stability and corresponding Coulombic efficiency of this Mo6S8/Mg battery for 6000 cycles at the rate of 10C.Copyright 2019, Wiley?VCH.
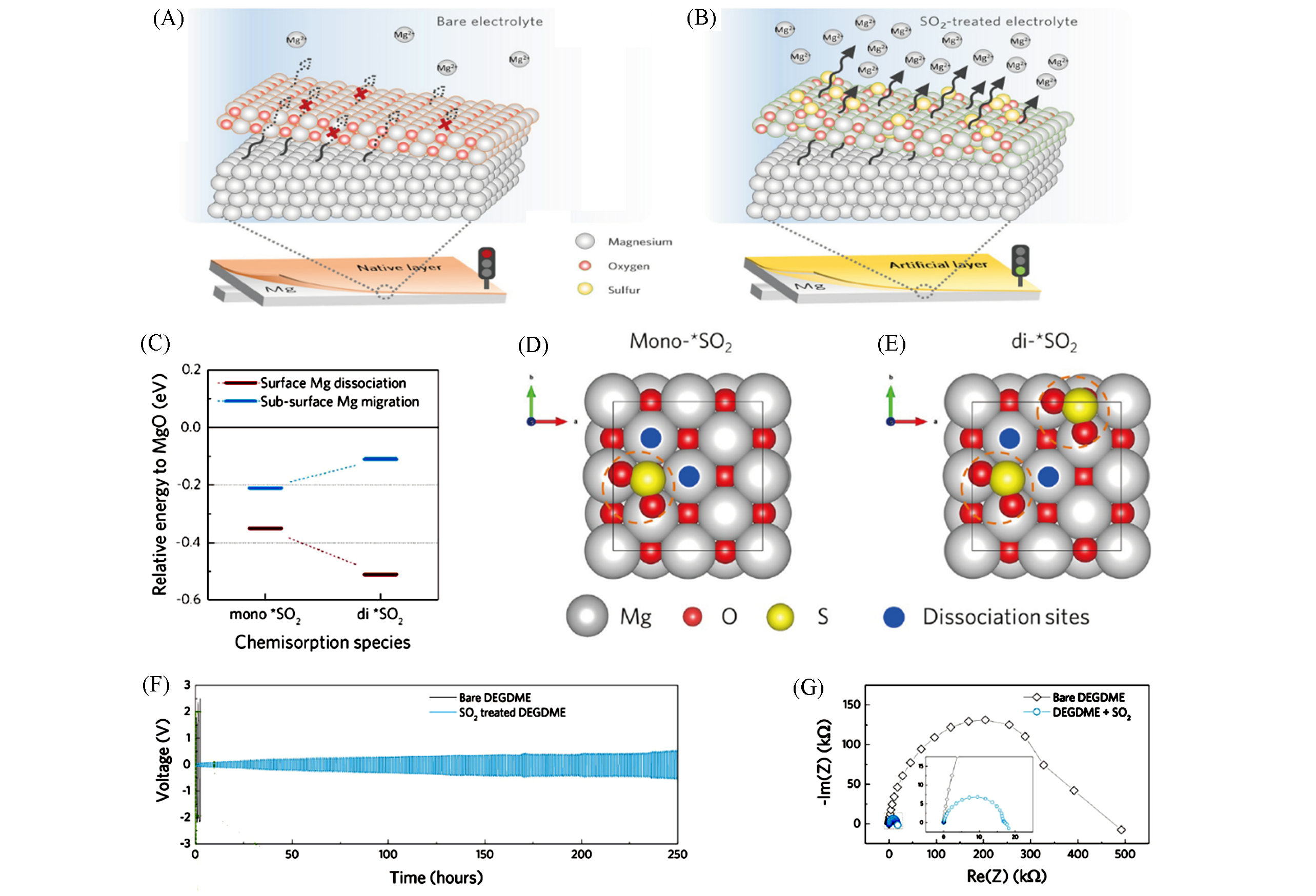
Fig.13 Operating mechanism of the tailored interphase on Mg anode and electrochemical performance in conventional electrolytes[71](A) Native passivation oxide layers on Mg anode; (B) artificial Mg2+?conducting layers tailored by SO2 chemisorption; (C) DFT calculation results for the energetics of Mg dissociation and migration with surface chemisorption structures; (D, E) top view of the calculated models of the mono?(D) and di?SO2 cases(E); (F) galvanostatic voltage profiles of Mg symmetric cells at 0.01 mA/cm2; (G) nyquist plots for Mg symmetric cells.Copyright 2020, American Chemical Society.
| 1 | Armand M., Tarascon J. M., Nature,2008, 451(7179), 652―657 |
| 2 | Noorden R. V., Nature,2014, 507(7490), 26―28 |
| 3 | Schmuch R., Wagner R., Hörpel G., Placke T., Winter M., Nat. Energy,2018, 3(4), 267―278 |
| 4 | Xu K., Chem. Rev.,2004, 104(10), 4303―4417 |
| 5 | Muldoon J., Bucur C. B., Gregory T., Chem. Rev.,2014, 114(23), 11683―11720 |
| 6 | Yang C., Feng J., Lv F., Zhou J., Lin C., Wang K., Zhang Y., Yang Y., Wang W., Li J., Guo S., Adv. Mater.,2018, 30(27), 1800036 |
| 7 | Pramudita J. C., Sehrawat D., Goonetilleke D., Sharma N., Adv. Energy Mater.,2017, 7(24), 1602911 |
| 8 | Liu Y., Gao C., Dai L., Deng Q., Wang L., Luo J., Liu S., Hu N., Small,2020, 16(44), 2004096 |
| 9 | Cui J., Wang A., Li G., Wang D., Shu D., Dong A., Zhu G., Luo J., Sun B., J. Mater. Chem. A,2020, 8(31), 15399―15416 |
| 10 | Leng K., Li G., Guo J., Zhang X., Wang A., Liu X., Luo J., Adv. Funct. Mater.,2020, 30(23), 2001317 |
| 11 | Long Y., Li H., Ye M., Chen Z., Wang Z., Tao Y., Weng Z., Qiao S. Z., Yang Q. H., Energy Storage Mater.,2021, 34, 194―202 |
| 12 | Song H., Su J., Wang C., Adv. Mater.,2021, 33(2), 2170015 |
| 13 | Tian H., Gao T., Li X., Wang X., Luo C., Fan X., Yang C., Suo L., Ma Z., Han W., Wang C., Nat. Commun.,2017, 8(1), 1―8 |
| 14 | Guan X., Wang A., Liu S., Li G., Liang F., Yang Y. W., Liu X., Luo J., Small,2018, 14(37), 1―21 |
| 15 | Attias R., Salama M., Hirsch B., Goffer Y., Aurbach D., Joule,2019, 3(1), 27―52 |
| 16 | Yoo H. D., Shterenberg I., Gofer Y., Gershinsky G., Pour N., Aurbach D., Energy Environ. Sci.,2013, 6(8), 2265―2279 |
| 17 | Kuvancheva A. M., Nauryzbayev M. K., Ishkenov A. R., Kurbatov A. P., Eurasian Chem. Technol. J.,2016, 3(1), 17―27 |
| 18 | Aurbach D., Gizbar H., Schechter A., Chusid O., Gottlieb H. E., Gofer Y., Goldberg I., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2002, 149(2), A115―A121 |
| 19 | Shterenberg I., Salama M., Gofer Y., Levi E., Aurbach D., MRS Bull.,2014, 39(5), 453―460 |
| 20 | Nelson J., Evans W., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2002, 39(1), 82―83 |
| 21 | Lu Z., Schechter A., Moshkovich M., Aurbach D., J. Electroanal. Chem., 1999, 466(2), 203―217 |
| 22 | Aurbach D., Lu Z., Schechter A., Gofer Y., Gizbar H., Turgeman R., Cohen Y., Moshkovich M., Levi E., Nature,2000, 407(6805), 724―727 |
| 23 | Gizbar H., Vestfrid Y., Chusid O., Gofer Y., Gottlieb H., Marks V., Aurbach D., Organometallics,2004, 23(16), 3826―3831 |
| 24 | Aurbach D., Suresh G. S., Levi E., Mitelman A., Mizrahi O., Chusid O., Brunelli M., Adv. Mater.,2007, 19(23), 4260―4267 |
| 25 | Salama M., Shterenberg I., Shimon L. J. W., Keinan⁃Adamsky K., Afri M., Gofer Y., Aurbach D., J. Phys. Chem. C,2017, 121(45), 24909―24918 |
| 26 | Mizrahi O., Amir N., Pollak E., Chusid O., Aurbach D., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2008, 155(2), A103―A109 |
| 27 | Kim H. S., Arthur T. S., Allred G. D., Zajicek J., Newman J. G., Rodnyansky A. E., Oliver A. G., Boggess W. C., Muldoon J., Nat. Commun.,2011, 2(1), 427 |
| 28 | Muldoon J., Bucur C. B., Oliver A. G., Sugimoto T., Matsui M., Kim H. S., Allred G. D., Zajicek J., Kotani Y., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(3), 5941―5950 |
| 29 | Guo Y. S., Zhang F., Yang J., Wang F. F., Hirano S. I., Energy Environ. Sci.,2012, 5(10), 9100―9106 |
| 30 | Mohtadi R., Matsui M., Arthur T. S., Hwang S. J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2012, 124(39), 9918―9921 |
| 31 | Arthur T. S., Glans P. A., Singh N., Tutusaus O., Nie K., Liu Y. S., Mizuno F., Guo J., Alsem D. H., Salmon N. J., Mohtadi R., Chem. Mater.,2017, 29(17), 7183―7188 |
| 32 | Rajput N. N., Qu X., Sa N., Burrell A. K., Persson K. A., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2015, 137(9), 3411―3420 |
| 33 | Connell J. G., Genorio B., Lopes P. P., Strmcnik D., Stamenkovic V. R., Markovic N. M., Chem. Mater.,2016, 28(22), 8268―8277 |
| 34 | Terada S., Mandai T., Suzuki S., Tsuzuki S., Watanabe K., Kamei Y., Ueno K., Dokko K., Watanabe M., J. Phys. Chem. C,2016, 120(3), 1353―1365 |
| 35 | Shterenberg I., Salama M., Yoo H. D., Gofer Y., Park J. B., Sun Y. K., Aurbach D., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2015, 162(13), A7118―A7128 |
| 36 | Arthur T. S., Singh N., Matsui M., Electrochem. Commun.,2012, 16(1), 103―106 |
| 37 | Niu J., Zhang Z., Aurbach D., Adv. Energy Mater.,2020, 10(23), 2000697 |
| 38 | Kravchyk K. V., Piveteau L., Caputo R., He M., Stadie N. P., Bodnarchuk M. I., Lechner R. T., Kovalenko M. V., ACS Nano,2018, 12(8), 8297―8307 |
| 39 | Jung S. C., Han Y. K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2018, 122(31), 17643―17649 |
| 40 | Nayeb⁃Hashemi A. A., Clark J. B., Bull. Alloy Phase Dirgrams,1985, 6(6), 528―533 |
| 41 | Shao Y., Gu M., Li X., Nie Z., Zuo P., Li G., Liu T., Xiao J., Cheng Y., Wang C., Zhang J. G., Liu J., Nano Lett.,2014, 14(1), 255―260 |
| 42 | Yang B., Mo M., Hu H., Li C., Yang X., Li Q., Qian Y., ChemInform,2004, 35(28), 1785―1787 |
| 43 | Liu Z., Lee J., Xiang G., Glass H. F. J., Keyzer E. N., Dutton S. E., Grey C., Chem. Commun., 2017, 53(4), 743―746 |
| 44 | He M., Protesescu L., Caputo R., Krumeich F., Kovalenko M. V., Chem. Mater.,2015, 27(2), 635―647 |
| 45 | Tan Y. H., Yao W. T., Zhang T., Ma T., Lu L. L., Zhou F., Yao H. B., Yu S. H., ACS Nano,2018, 12(6), 5856―5865 |
| 46 | Penki T. R., Valurouthu G., Shivakumara S., Sethuraman V. A., Munichandraiah N., New J. Chem.,2018, 42(8), 5996―6004 |
| 47 | Xu X., Chao D., Chen B., Liang P., Li H., Xie F., Davey K., Qiao S. Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2020, 59(48), 21728―21735 |
| 48 | Singh N., Arthur T. S., Ling C., Matsui M., Mizuno F., Chem. Commun.,2013, 49(2), 149―151 |
| 49 | Wang Z., Su Q., Shi J., Deng H., Yin G. Q., Guan J., Wu M. P., Zhou Y. L., Lou H. L., Fu Y. Q., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces,2014, 6(9), 6786―6789 |
| 50 | Yaghoobnejad Asl H., Fu J., Kumar H., Welborn S. S., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Chem. Mater.,2018, 30(5), 1815―1824 |
| 51 | Nacimiento F., Cabello M., Pérez⁃Vicente C., Alcántara R., Lavela P., Ortiz G. F., Tirado J. L., Nanomaterials,2018, 8(7), 501 |
| 52 | Wang L., Welborn S. S., Kumar H., Li M., Wang Z., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(45), 1―7 |
| 53 | Legrain F., Manzhos S., J. Chem. Phys.,2016, 146(3), 034706 |
| 54 | Malyi O. I., Tan T. L., Manzhos S., J. Power Sources,2013, 233, 341―345 |
| 55 | Periyapperuma K., Tran T. T., Purcell M. I., Obrovac M. N., Electrochim. Acta,2015, 165, 162―165 |
| 56 | Murgia F., Weldekidan E. T., Stievano L., Monconduit L., Berthelot R., Electrochem. Commun.,2015, 60, 56―59 |
| 57 | Hembram K., Jung H., Yeo B. C., Pai S. J., Lee H. J., Lee K. R., Han S. S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2016, 18(31), 21391―21397 |
| 58 | Tran T., Obrovac M., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2011, 158(12), A1411―A1416 |
| 59 | Ho L. T., Appl. Phys. Lett.,1979, 35(5), 409―410 |
| 60 | Cheng Y., Shao Y., Parent L. R., Sushko M. L., Li G., Sushko P. V., Browning N. D., Wang C., Liu J., Adv. Mater.,2015, 27(42), 6598―6605 |
| 61 | Wang L., Welborn S. S., Kumar H., Li M., Wang Z., Shenoy V. B., Detsi E., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(45), 1902086 |
| 62 | Cheng Y., Shao Y., Parent L., Sushko M., Li G., Sushko P., Browning N., Wang C., Liu J., Adv. Mater.,2015, 27(42), 6598―6605 |
| 63 | Niu J., Gao H., Ma W., Luo F., Yin K., Peng Z., Zhang Z., Energy Storage Mater.,2018, 14, 351―360 |
| 64 | Son S. B., Gao T., Harvey S. P., Steirer K. X., Stokes A., Norman A., Wang C., Cresce A., Xu K., Ban C., Nat. Chem.,2018, 10(5), 532―539 |
| 65 | Lv R., Guan X., Zhang J., Xia Y., Luo J., Natl. Sci. Rev.,2020, 7, 333―341 |
| 66 | Li B., Masse R., Liu C., Hu Y., Li W., Zhang G., Cao G., Energy Storage Mater.,2019, 22, 96―104 |
| 67 | Nandiyanto A. B. D., Iskandar F., Ogi T., Okuyama K., Langmuir,2010, 26(14), 12260―12266 |
| 68 | Li X., Gao T., Han F., Ma Z., Fan X., Hou S., Eidson N., Li W., Wang C., Adv. Energy Mater.,2018, 8(7), 1―6 |
| 69 | Zhang J., Guan X., Lv R., Wang D., Liu P., Luo J., Energy Storage Mater.,2020, 26, 408―413 |
| 70 | Tang K., Du A., Dong S., Cui Z., Liu X., Lu C., Zhao J., Zhou X., Cui G., Adv. Mater.,2020, 32(6), 1―7 |
| 71 | Park H., Lim H. K., Oh S. H., Park J., Lim H. D., Kang K., ACS Energy Lett.,2020, 5(12), 3733―3740 |
| 72 | Aziz A., Tominaga Y., Ionics,2018(11), 24, 3475―3481 |
| 73 | Polu A. R., Kumar R., Bull. Mater. Sci.,2011, 34(5), 1063―1067 |
| 74 | Liang Y., Feng R., Yang S., Ma H., Liang J., Chen J., Adv. Mater.,2011, 23(5), 640―643 |
| 75 | Li W., Li C., Zhou C., Ma H., Chen J., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.,2006, 45(36), 6009―6012 |
| 76 | Guo W., Liu S., Guan X., Zhang X., Liu X., Luo J., Adv. Energy Mater.,2019, 9(20), 1900193 |
| 77 | Park B., Schaefer J. L., J. Electrochem. Soc.,2020, 167(7), 070545 |
| 78 | Canepa P., Bo S. H., Sai Gautam G., Key B., Richards W. D., Shi T., Tian Y., Wang Y., Li J., Ceder G., Nat. Commun.,2017, 8(1), 1759 |
| [1] | 孙竹梅 傅杰 李鑫 王海芳 卢静 童天星 朱明飞 王云燕. 电吸附除氯过程电化学阻抗谱及动力学研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220528. |
| [2] | 陈佳琪 程晚亭 温秋慧 韩静茹 马福秋 颜永得 薛云. 活性炭电极的改性及其对Co2+、Mn2+、Ni2+的电吸附性能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220598. |
| [3] | 刘杰, 李金晟, 柏景森, 金钊, 葛君杰, 刘长鹏, 邢巍. 降低直接甲醇燃料电池浓差极化的含磺化碳管阻水夹层的构建[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220420. |
| [4] | 刘坤, 尹远, 耿文强, 夏昊天, 李华. 不同组分过渡金属氧化物催化剂对介质阻挡放电固氮的影响机制[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220278. |
| [5] | 丁钦, 张梓轩, 徐培程, 李晓宇, 段莉梅, 王寅, 刘景海. Cu, Ni, Co掺杂对Fe碳纳米管的结构及电催化性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220421. |
| [6] | 何宇婧, 李佳乐, 王东洋, 王福玲, 肖作旭, 陈艳丽. 锌活化Fe/Co/N掺杂的生物质碳基高效氧还原催化剂[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220475. |
| [7] | 胡平澳 张琪 张会茹. 锂硫电池中硒缺陷WSe2催化性能理论预测[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220595. |
| [8] | 吴钰洁 黄文治 潘俊达 石凯祥 刘全兵. “蛋黄-蛋壳”结构纳米反应器的设计、调控及其在锂硫电池正极中的应用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220619. |
| [9] | 张玲玲 董欢欢 何祥喜 李丽 李林 吴星樵 侴术雷. 中空碳材料用于钠离子电池负极的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220620. |
| [10] | 侯从聪, 王惠颖, 李婷婷, 张志明, 常春蕊, 安立宝. N-CNTs/NiCo-LDH复合材料的制备及电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220351. |
| [11] | 姜宝正, 黄文婷, 刘文宝, 郭荣胜, 徐成俊, 康飞宇. 纳米铜修饰三维锌网电极的制备及锌离子电池负极的电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220257. |
| [12] | 刘坤, 左杰, 李华, 项红甫, 冉从福, 杨明昊, 耿文强. 电子能量对沿面介质阻挡放电等离子体化学产物的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220249. |
| [13] | 王鹏飞, 富文豪, 孙少妮, 曹学飞, 袁同琦. 纤维素纳米晶模板法制备多级孔炭材料及其电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220497. |
| [14] | 胡诗颖 沈佳艳 韩峻山 郝婷婷 李星. CoO纳米颗粒/石墨烯纳米纤维复合材料的制备及其电化学性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 0, (): 20220462. |
| [15] | 任诗杰, 谯思聪, 刘崇静, 张文华, 宋礼. 铂单原子催化剂同步辐射X射线吸收谱的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(9): 20220466. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||