

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (1): 115.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180551
罗伟1, 方镭1, 孟跃2, 薛继龙1, 陈涛1, 夏盛杰1, 倪哲明1( )
)
收稿日期:2018-08-03
出版日期:2019-01-10
发布日期:2018-12-06
作者简介:联系人简介: 倪哲明, 女, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事计算化学及纳米无机光催化材料方面的研究. E-mail: nzm@zjut.edu.cn;夏盛杰, 男, 博士, 副教授, 主要从事无机材料及光催化方面的研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
LUO Wei1, FANG Lei1, MENG Yue2, XUE Jilong1, CHEN Tao1, XIA Shengjie1,*, NI Zheming1,*( )
)
Received:2018-08-03
Online:2019-01-10
Published:2018-12-06
Contact:
XIA Shengjie,NI Zheming
E-mail:xiasj@zjut.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
利用密度泛函理论研究了巴豆醛和肉桂醛分子在Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面的吸附构型以及相关电子性质. 吸附构型与吸附能结果表明, 巴豆醛和肉桂醛在覆盖度为1/25 ML的条件下, 以C=C和C=O双键协同吸附在Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面较为稳定, 且肉桂醛与Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面的吸附能远大于巴豆醛. 由Mulliken电荷布局和差分电荷密度可知, 在吸附过程中肉桂醛分子向Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面上转移的电荷数较巴豆醛更多, 相互作用更大. 由电子态密度分析结果可知, 不饱和醛与Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面的吸附作用主要是由于分子的p轨道电子与催化剂d轨道电子之间的相互作用. 由于苯基的存在使肉桂醛分子在Pt-Ni-Pt(111)面上的吸附更强, 且平行于催化剂表面.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
罗伟, 方镭, 孟跃, 薛继龙, 陈涛, 夏盛杰, 倪哲明. α,β-不饱和醛在Ni-Pt(111)面上吸附的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(1): 115.
LUO Wei,FANG Lei,MENG Yue,XUE Jilong,CHEN Tao,XIA Shengjie,NI Zheming. Theoretical Study on Adsorption of α,β-Unsaturated Aldehydes on Ni-Pt(111) Surface†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(1): 115.
| Molecule | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-(s)-trans | E-(s)-cis | Z-(s)-trans | Z-(s)-cis | |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0 | 8.46 | 10.73 | 14.92 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 0 | 7.82 | 18.64 | 23.07 |
Table 1 Relative energy of unsaturated aldehyde models
| Molecule | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-(s)-trans | E-(s)-cis | Z-(s)-trans | Z-(s)-cis | |
| Crotonaldehyde | 0 | 8.46 | 10.73 | 14.92 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | 0 | 7.82 | 18.64 | 23.07 |
| Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | ||||
| O | top | 47.15 | 69.70 | C=O, C=C | top-hcp | 61.58 | 98.80 |
| bri | 44.81 | 75.99 | top-fcc | 61.37 | 98.52 | ||
| hcp | 44.52 | 85.77 | bri-top | 61.92 | 99.21 | ||
| fcc | 45.20 | 76.33 | bri-bri | 61.50 | 98.82 | ||
| C=C | top | 60.59 | 96.81 | bri-hcp | 58.57 | 98.72 | |
| bri | 61.86 | 98.42 | bri-fcc | 61.92 | 98.61 | ||
| hcp | 61.43 | 97.76 | hcp-top | 61.94 | 99.10 | ||
| fcc | 60.70 | 97.93 | hcp-bri | 61.86 | 98.93 | ||
| C=O | top | 60.96 | 97.81 | hcp-hcp | 61.66 | 98.79 | |
| bri | 61.78 | 96.16 | hcp-fcc | 61.68 | 98.60 | ||
| hcp | 61.60 | 98.54 | fcc-top | 61.60 | 98.70 | ||
| fcc | 60.19 | 97.93 | fcc-bri | 61.71 | 98.80 | ||
| C=O, C=C | top-top | 60.98 | 98.24 | fcc-hcp | 62.32 | 98.38 | |
| top-bri | 61.84 | 98.56 | fcc-fcc | 59.49 | 99.85 | ||
Table 2 Adsorption energy(Eads) of unsaturated aldehyde molecules on Ni-Pt(111) surface
| Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | Species | Adsorption site | Eads /(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | Crotonaldehyde | Cinnamaldehyde | ||||
| O | top | 47.15 | 69.70 | C=O, C=C | top-hcp | 61.58 | 98.80 |
| bri | 44.81 | 75.99 | top-fcc | 61.37 | 98.52 | ||
| hcp | 44.52 | 85.77 | bri-top | 61.92 | 99.21 | ||
| fcc | 45.20 | 76.33 | bri-bri | 61.50 | 98.82 | ||
| C=C | top | 60.59 | 96.81 | bri-hcp | 58.57 | 98.72 | |
| bri | 61.86 | 98.42 | bri-fcc | 61.92 | 98.61 | ||
| hcp | 61.43 | 97.76 | hcp-top | 61.94 | 99.10 | ||
| fcc | 60.70 | 97.93 | hcp-bri | 61.86 | 98.93 | ||
| C=O | top | 60.96 | 97.81 | hcp-hcp | 61.66 | 98.79 | |
| bri | 61.78 | 96.16 | hcp-fcc | 61.68 | 98.60 | ||
| hcp | 61.60 | 98.54 | fcc-top | 61.60 | 98.70 | ||
| fcc | 60.19 | 97.93 | fcc-bri | 61.71 | 98.80 | ||
| C=O, C=C | top-top | 60.98 | 98.24 | fcc-hcp | 62.32 | 98.38 | |
| top-bri | 61.84 | 98.56 | fcc-fcc | 59.49 | 99.85 | ||
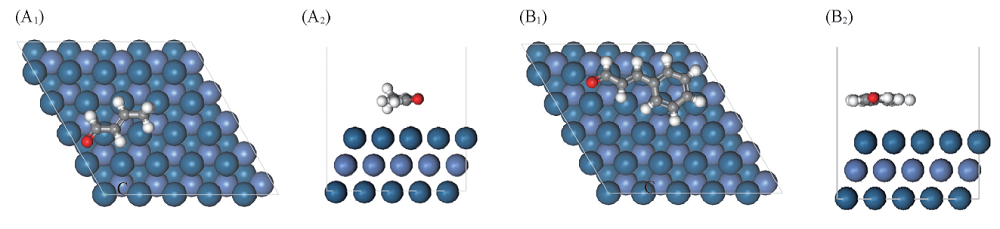
Fig.3 Top(A1, B1) and side(A2, B2) views of the most stable adsorption configuration for crotonaldehyde(A1, A2) and cinnamaldehyde(B1, B2) on Ni-Pt(111) surface
| Crotonaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1271 | 0.1429 | 0.1393 | 0.1481 |
| fcc-hcp | 0.1269 | 0.1435 | 0.1396 | 0.1480 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 |
Table 3 Structure parameters of crotonaldehyde for the most stable adsorption configuration*
| Crotonaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1271 | 0.1429 | 0.1393 | 0.1481 |
| fcc-hcp | 0.1269 | 0.1435 | 0.1396 | 0.1480 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0003 | 0.0001 |
| Cinnamaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm | d5/nm | d6/nm | d7/nm | d8/nm | d9/nm | d10/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1272 | 0.1425 | 0.1404 | 0.1430 | 0.1433 | 0.1407 | 0.1414 | 0.1414 | 0.1408 | 0.1432 |
| fcc-fcc | 0.1270 | 0.1431 | 0.1406 | 0.1434 | 0.1436 | 0.1411 | 0.1416 | 0.1416 | 0.1412 | 0.1434 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 |
Table 4 Structure parameters of cinnamaldehyde for the most stable adsorption configuration*
| Cinnamaldehyde | d1/nm | d2/nm | d3/nm | d4/nm | d5/nm | d6/nm | d7/nm | d8/nm | d9/nm | d10/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Free | 0.1272 | 0.1425 | 0.1404 | 0.1430 | 0.1433 | 0.1407 | 0.1414 | 0.1414 | 0.1408 | 0.1432 |
| fcc-fcc | 0.1270 | 0.1431 | 0.1406 | 0.1434 | 0.1436 | 0.1411 | 0.1416 | 0.1416 | 0.1412 | 0.1434 |
| Δd/nm | 0.0002 | 0.0006 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0003 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 0.0004 | 0.0002 |
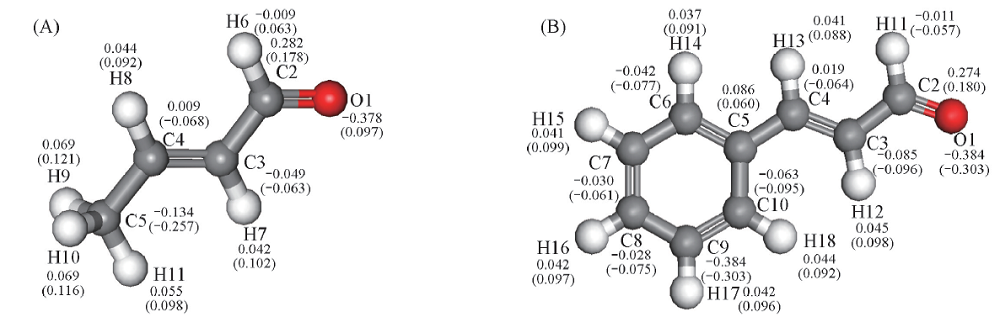
Fig.4 Mulliken charge populations of crotonaldehyde(A) and cinnamaldehyde(B)The values outside the parentheses are the amount of charge of each atom for free molecules. The values in parentheses are the amount of charge of the atom after the adsorption, and the adsorption configuration modes are shown in Fig.3.
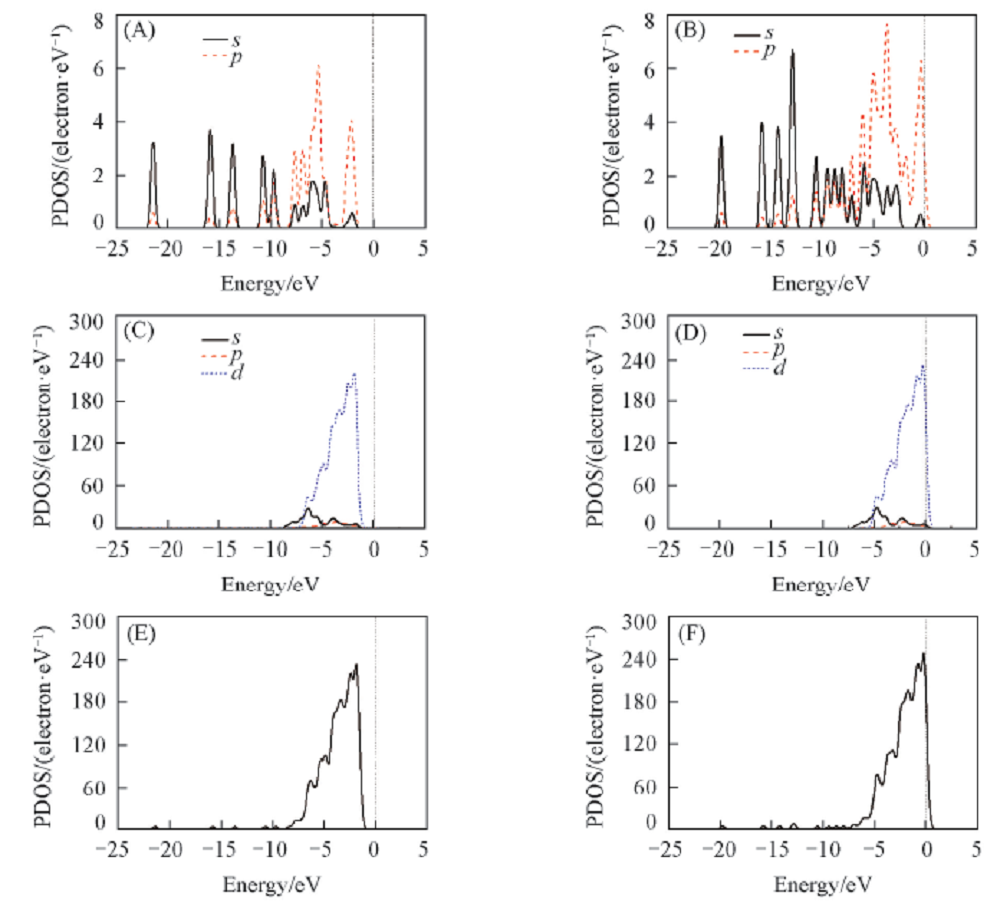
Fig.6 Densities of states of crotonaldehyde(A, C, E) and cinnamaldehyde(B, D, F) for the most stable adsorption configuration(A), (B) Represent the electron density of molecule after adsorption; (C), (D) represent electron density of of Pt-Ni-Pt(111) surface after adsorption; (E), (F) represent total DOS most stable adsorption configuration.
| [1] | Concepción P., Pérez Y., Hernández-Garrido J. C., Fajardo M., Calvino J. J., Corma A., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.,2013,15, 12048—12055 |
| [2] | Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Delbecq F., Sautet P., Krupski A., Becker C., Wandelt K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113, 13947—13967 |
| [3] | Mohr C., Hofmeister H., Radnik J., Claus P., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2003, 125, 1905—1911 |
| [4] | Raj K. J. A., Prakash M. G., Elangovan T., Viswanathan B., Catal. Lett.,2012, 142, 87—94 |
| [5] | Esan D. A., Ren Y., Feng X., Trenary M., J. Phys. Chem. C,2017, 121, 4384—4392 |
| [6] | Luo Q. Q., Wang T., Beller R., Jiao H. J., J. Phys. Chem. C,2013, 117, 12715—12724 |
| [7] | Cao Y. Y., Jiang J. H., Ni Z. M., Xia S. J., Qian M. D., Xue J. L., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2016, 37(7), 1342—1350 |
| (曹勇勇, 蒋军辉, 倪哲明, 夏盛杰, 钱梦丹, 薛继龙. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(7), 1342—1350) | |
| [8] | Myint M. N., Yan Y., Chen J. G., J. Phys. Chem. C,2014, 118, 11340—11349 |
| [9] | Esan D.A., Trenary M.,Top. Catal., 2017, 1—10 |
| [10] | Zanella R., Louis C., Giorgio S., Touroude R., J. Catal.,2004, 223, 328—339 |
| [11] | Ide M. S., Hao B., Neurick M., Davis R. J., ACS Catal.,2012, 2, 671—683 |
| [12] | Liu J., Fan X. F., Sun C. Q., Zhu W. G., Appl. Surf. Sci.,2018, 441, 23—28 |
| [13] | Wang X. J., Li X. J., Liao S. J., Li B. T., Comp. Mater. Sci.,2018, 149, 107—114 |
| [14] | Chen J. G., Menning C. A., Zellner M. B., Surf. Sci. Rep.,2008, 63, 201—254 |
| [15] | Zheng R., Zhu Y., Chen J. G., Chem. Cat. Chem.,2015, 3, 578—581 |
| [16] | Zheng R., Humbert M. P., Zhu Y., Chen J. G., Catalysis Science & Technology,2011, 1, 638—643 |
| [17] | Li X. D., Wan W. M., Kattel S., Chen J. G., Wang T. F., J. Catal.,2016, 344, 148—156 |
| [18] | Murillo L. E., Menning C. A., Chen J. G., J. Catal.,2009, 268, 335—342 |
| [19] | Murillo L. E., Goda A. M., Chen J. G., J. Am. Chem. Soc.,2007, 129, 7101—7105 |
| [20] | Humbert M. P., Chen J. G., J. Catal.,2008, 257, 297—306 |
| [21] | Delbecq F., Sautet P., J. Catal.,2003, 220, 115—126 |
| [22] | Delbecq F., Sautet P., J. Catal.,1995, 152, 217—236 |
| [23] | Liu H. Y., Mei Q. Q., Li S. P., Yang Y. D., Wang Y. Y., Liu H. Z., Zheng L. R., An P. F., Zhang J., Han B. X., Chem. Commun.,2018, 54, 908—911 |
| [24] | Liu C., Luo W., Liu J. H., Sun L., Yang Y., Liu G., Wang F., Zhong W., Guild C., Suib S. L., Catal. Lett.,2018, 148, 1—9 |
| [25] | Perdew J. P., Wang Y., Physical Review B,1992, 45, 13244—13249 |
| [26] | Vigné F., Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Sautet P., Delbecq F., J. Catal.,2010, 275, 129—139 |
| [27] | Qian M. D., Luo W., Ni Z. M., Xia S. J., Xue J. L., Jiang J. H., Chem. J. Chinese Universities,2017, 38(9), 1611—1618 |
| (钱梦丹, 罗伟, 倪哲明, 夏盛杰, 薛继龙, 蒋军辉. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(9), 1611—1618) | |
| [28] | Ni Z.M., Xia M. Y., Shi W., Qian P. P., Acta Phys. Chim. Sin., 2013, 29, 1916—1922 |
| (倪哲明, 夏明玉, 施炜, 钱萍萍. 物理化学学报, 2013, 29, 1916—1922) | |
| [29] | Kang G. J., Ma J., Chen Z. X., Catal. Lett.,2012, 142, 287—293 |
| [30] | Durig J. R., Brown S. C., Kalasinsky V. F., George W. O., Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular Spectoscopy,1976, 32, 807—813 |
| [31] | Groot M. S. D., Lamb J., Proc. Roy. Soc. A,1957, 242, 36—56 |
| [32] | Haubrich J., Loffreda D., Delbecq F., Sautet P., Krupski A., Becker C., Wandelt K., J. Phys. Chem. C,2009, 113, 13947—13967 |
| [33] | Tao J., Yao Z.J., Xue F., Fundamentals of Material Science, Chemical Industry Press, Beijing, 2006, 50—51 |
| (陶杰, 姚正军, 薛烽. 北京:化学工业出版社, 2006, 50—51) | |
| [34] | Liu R. Q., Comput. Theor. Chem., 2013, 1019, 141—145 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 姜宏斌, 代文臣, 张娆, 徐晓晨, 陈捷, 杨光, 杨凤林. Co3O4/UiO-66@α-Al2O3陶瓷膜对VOCs废气的分离催化性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220025. |
| [3] | 戴卫, 侯华, 王宝山. 七氟异丁腈负离子结构与反应活性的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220044. |
| [4] | 郝宏蕾, 孟繁雨, 李若钰, 李迎秋, 贾明君, 张文祥, 袁晓玲. 生物质基氮掺杂多孔炭材料的制备及对水中亚甲基蓝的吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220055. |
| [5] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [6] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 蒋伟, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 香蒲基生物炭的活化及对VOCs吸附的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210824. |
| [7] | 陈潇禄, 袁珍闫, 仲迎春, 任浩. 机械球磨制备三苯胺基PAF-106s及C2烃吸附性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210771. |
| [8] | 孟祥龙, 杨歌, 郭海玲, 刘晨光, 柴永明, 王纯正, 郭永梅. 纳米分子筛的合成及硫化氢吸附性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210687. |
| [9] | 靳科研, 白璞, 李小龙, 张佳楠, 闫文付. 新型Mg-Al吸附剂去除压水堆核电厂废水中高浓度硼[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210516. |
| [10] | 谭乐见, 仲宣树, 王锦, 刘宗建, 张爱英, 叶霖, 冯增国. β-环糊精的低临界溶解温度现象及其在有序纳米孔道片晶制备中的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220405. |
| [11] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [12] | 郑美琪, 毛方琪, 孔祥贵, 段雪. 类水滑石材料在核废水处理领域的应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220456. |
| [13] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [14] | 周成思, 赵远进, 韩美晨, 杨霞, 刘晨光, 贺爱华. 硅烷类外给电子体对丙烯-丁烯序贯聚合的调控作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [15] | 田晓康, 张青松, 杨舒淋, 白洁, 陈冰洁, 潘杰, 陈莉, 危岩. 微生物发酵诱导多孔材料: 制备方法和应用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220216. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||