

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (6): 20220044.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20220044
收稿日期:2022-01-18
出版日期:2022-06-10
发布日期:2022-03-04
通讯作者:
王宝山
E-mail:baoshan@whu.edu.cn
基金资助:
DAI Wei, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan( )
)
Received:2022-01-18
Online:2022-06-10
Published:2022-03-04
Contact:
WANG Baoshan
E-mail:baoshan@whu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
新型环保绝缘气体七氟异丁腈(C4)在高压输电应用中备受关注. 本文采用多种高精度量子化学理论方法研究了C4吸附电子后形成C4-负离子的结构、 光谱、 寿命以及与CO2的反应机理和动力学. 结果表明, 电子进入C≡N的π*反键轨道, 通过弯曲C—C=N形成C4-负离子, 绝热电子亲合能的最佳预测值为0.30 eV. 在 0~2 eV范围内C4-具有显著的光电子吸收峰, 亚稳态C4-负离子经约9 kJ/mol能垒断裂C—F键生成稳定的长寿命[F...(CF3)2CCN]-中间体. C4-+CO2反应存在进攻F或CN上的C和N 3种复合-解离机理, 在电气应用条件下, 以CO2进攻氰基CN途径为主, 诱发负电荷从CN向CO2转移.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
戴卫, 侯华, 王宝山. 七氟异丁腈负离子结构与反应活性的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220044.
DAI Wei, HOU Hua, WANG Baoshan. Theoretical Investigations on the Electronic Structures and Reactivity of Heptafluoro-iso-butyronitrile Anion. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(6): 20220044.
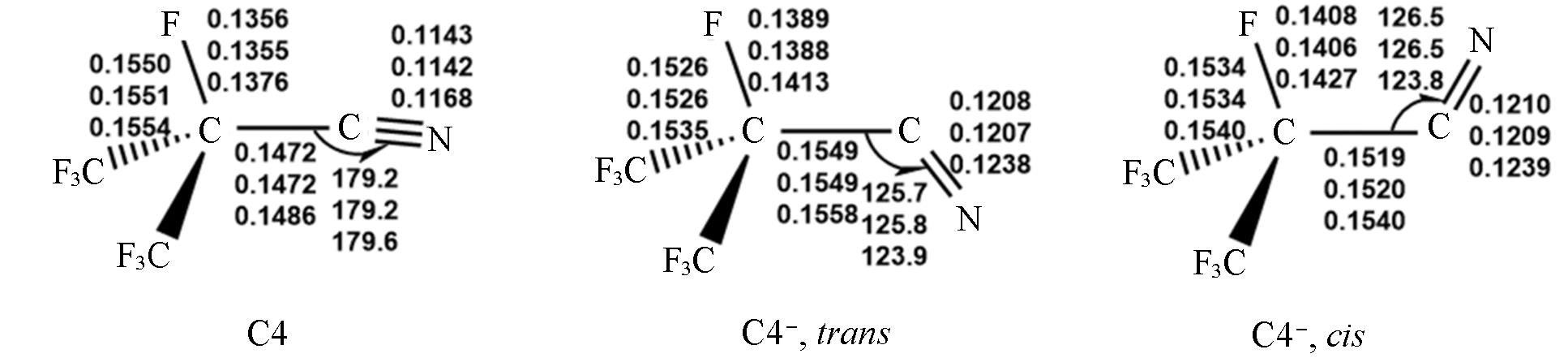
Fig.1 Optimized geometrical parameters of neutral C4 and two C4- anions in either trans or cis conformationFrom top to bottom: M06-2X/AVTZ, M06-2X/AVQZ, and CCSD/AVTZ. Bond distances are in nm and angles are in degrees.
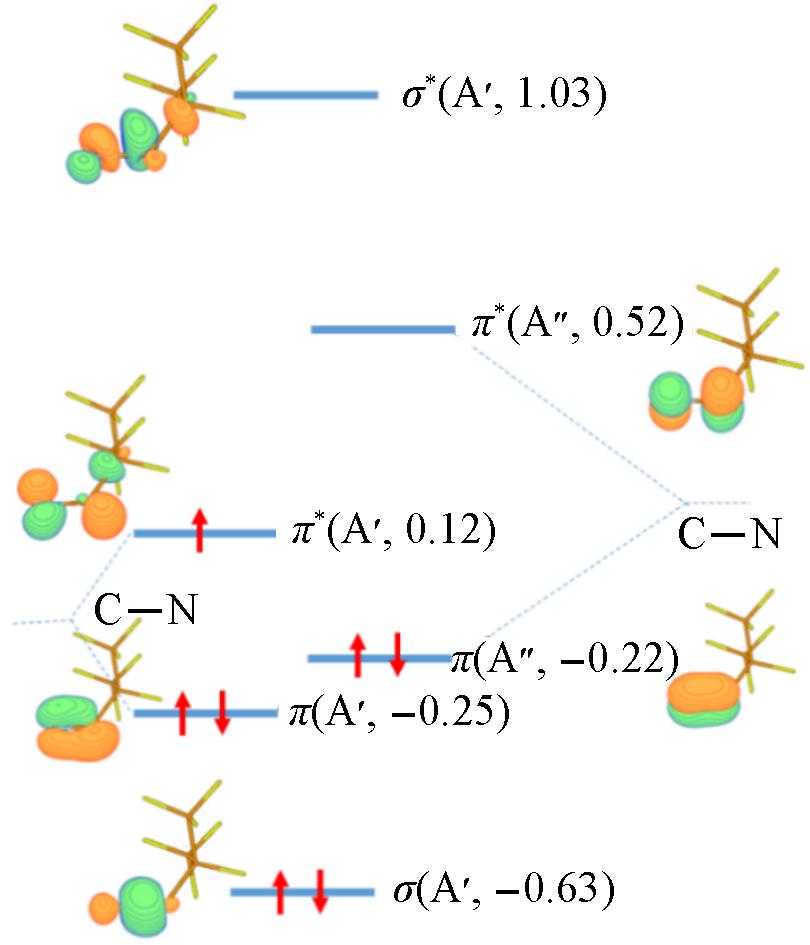
Fig.2 Molecular orbitals of C4- calculated at the CASSCF(7e, 7o)/AVTZ levelSymmetry and orbital energy(in a.u.) are shown in parenthesis. Isovalue=0.1.
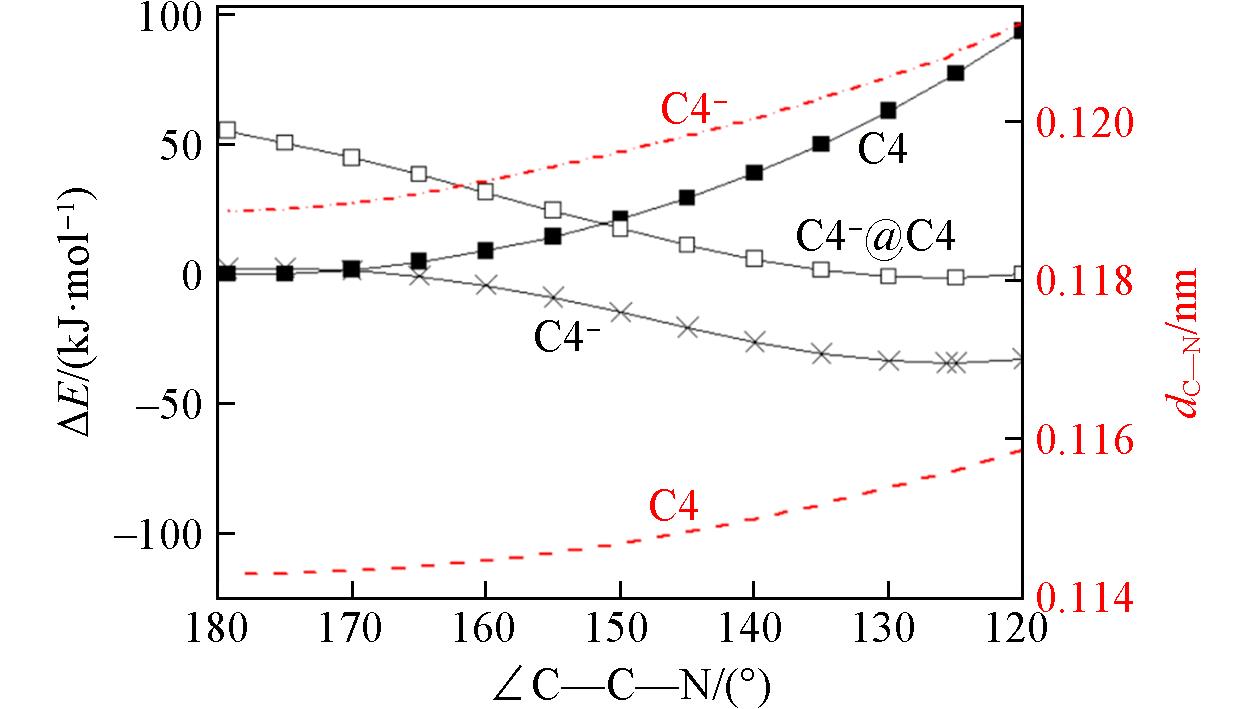
Fig.3 Energetic profiles for both C4 and C4- along the C—C≡N bending coordinates calculated at the M06?2X/AVTZ levelSolid squares: partially optimized C4 molecule with the fixed C—C—N angles. Open squares: single-point energy of C4- at the optimized C4 geometries. Crosses: partially optimized C4- anion with the fixed C—C—N angles. The CN bond lengths in C4 and C4- are shown as dashed and dash-dotted lines, respectively.
| Species | EA/eV | VAE/eV | VDE/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| M06?2X/AVTZ | 0.36(0.18) | -0.57(-0.82) | 1.50(1.29) |
| ROCBS?Q | 0.22(0.22) | -0.74(-0.50) | 1.21(1.47) |
| RCCSD(T)/CBS( | 0.21(0.22) | -0.59(-0.49) | 1.18(1.44) |
| RCCSD(T)/CBS( | 0.21(0.22) | -0.56(-0.47) | 1.18(1.45) |
| RCCSD(T)?F12/VDZ?F12 | 0.18(0.17) | -0.75(-0.73) | 1.11(1.37) |
| RCCSD(T)?F12/VTZ?F12 | 0.21(0.20) | -0.67(-0.66) | 1.16(1.41) |
Table 1 Electron affinity of C4 calculated at various levels of theory*
| Species | EA/eV | VAE/eV | VDE/eV |
|---|---|---|---|
| M06?2X/AVTZ | 0.36(0.18) | -0.57(-0.82) | 1.50(1.29) |
| ROCBS?Q | 0.22(0.22) | -0.74(-0.50) | 1.21(1.47) |
| RCCSD(T)/CBS( | 0.21(0.22) | -0.59(-0.49) | 1.18(1.44) |
| RCCSD(T)/CBS( | 0.21(0.22) | -0.56(-0.47) | 1.18(1.45) |
| RCCSD(T)?F12/VDZ?F12 | 0.18(0.17) | -0.75(-0.73) | 1.11(1.37) |
| RCCSD(T)?F12/VTZ?F12 | 0.21(0.20) | -0.67(-0.66) | 1.16(1.41) |
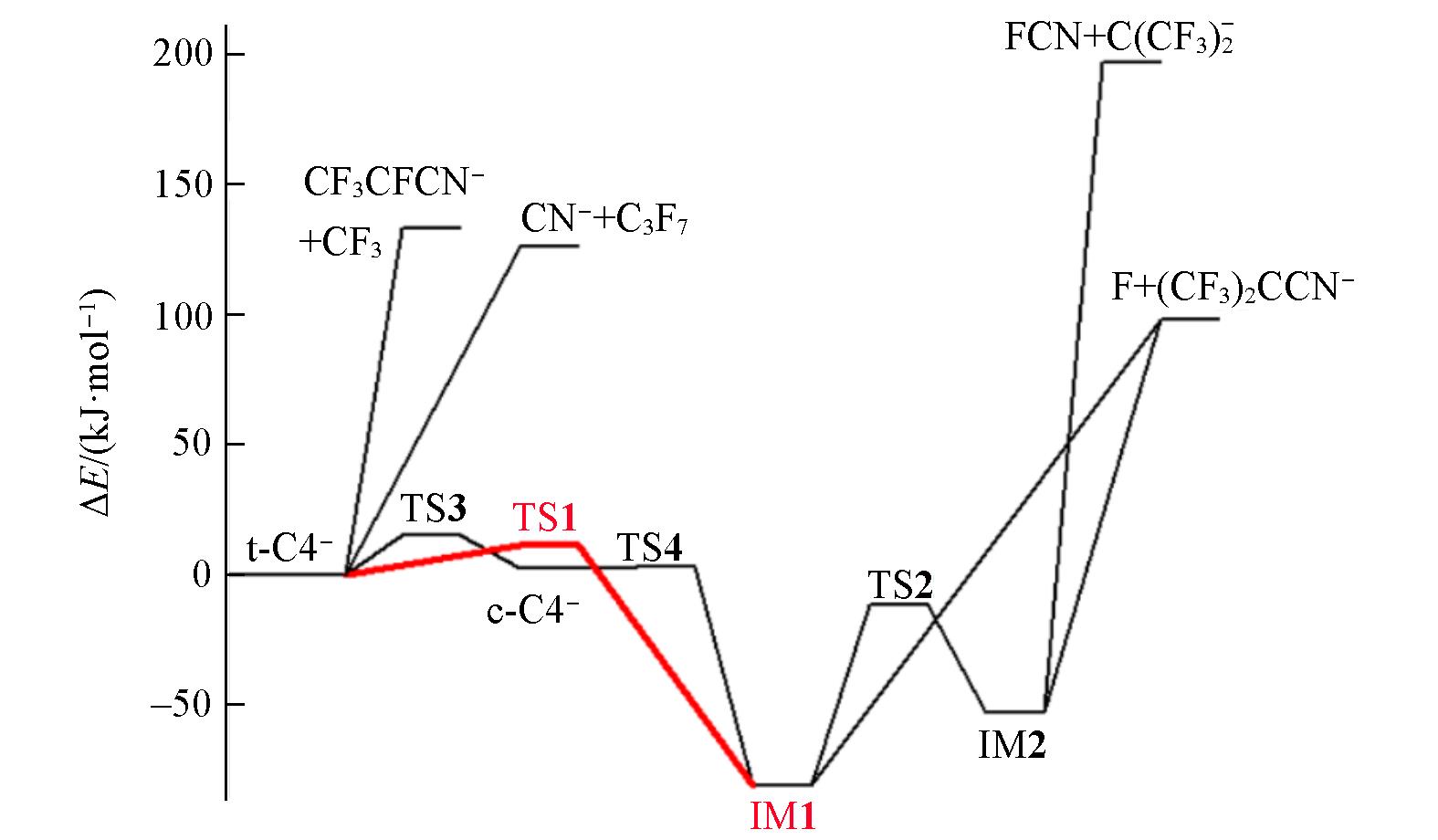
Fig.4 Energetic reaction paths for decomposition of C4- anion calculated at the ROCBS?Q+ZPE//M06?2X/AVTZ level of theoryNote that only the anionic product channels with lower energies are included.
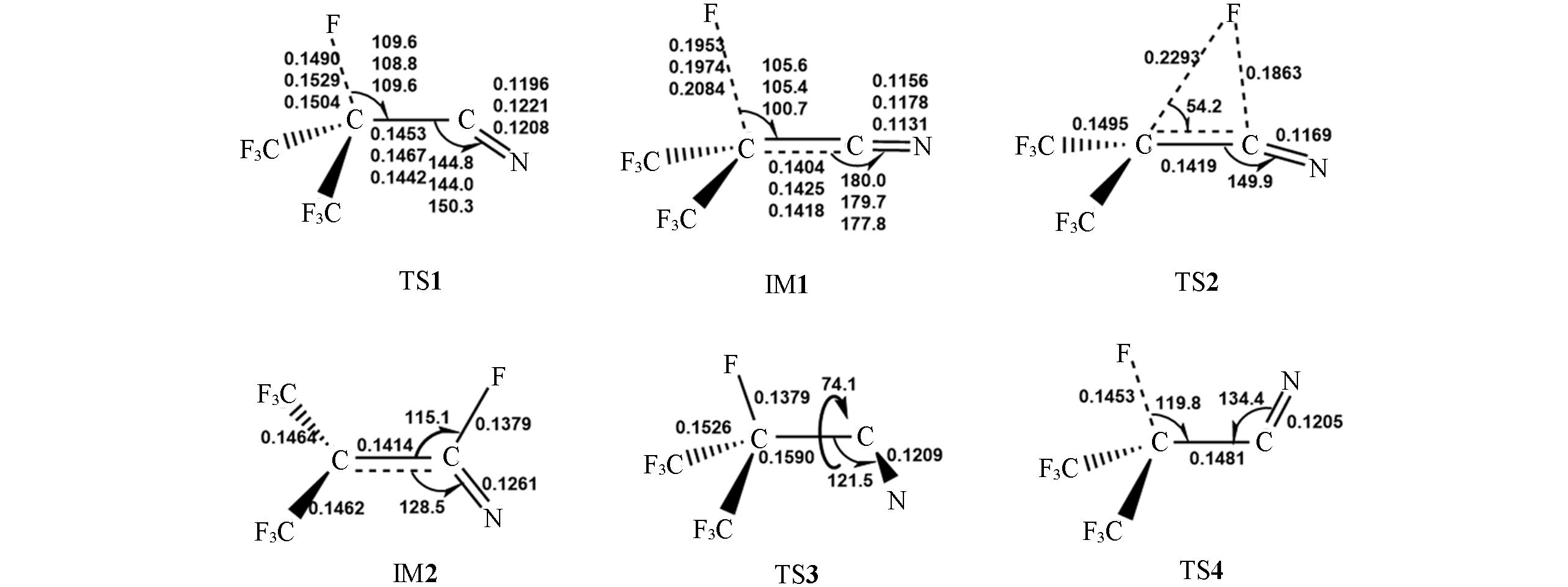
Fig.5 Optimized geometries of the transition states(TS) and intermediates(IM) involved in the decomposition of C4- anion at the M06?2X/AVTZ levelFor TS1 and IM1, the CCSD/AVTZ and CASSCF(7e,7o)/AVTZ optimized geometrical parameters are shown as the 2nd and the 3rd entries, respectively, for the sake of comparison. Bond distances are in nm and angles are in degrees.
| Species | ΔZPE/(kJ·mol-1) | Relative energy/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M06?2X/AVTZ | RCCSD(T)/CBS | ROCBS?Q | RCCSD(T)?F12A/ VDZ?F12 | RCCSD(T)?F12A/ VTZ?F12 | ||
| TS1 | -3.43 | 11.25 | 13.72(12.51) | 11.59(9.92) | 12.68(11.76) | 12.76(11.92) |
| IM1 | 0.21 | -75.94 | -75.69(-76.57) | -80.83(-81.38) | -77.86(-78.66) | -77.66(-78.58) |
| F+(CF3)2CCN- | -5.10 | 92.59 | 91.76 | 98.11 | 91.21 | 92.01 |
| TS2 | -2.59 | 1.55 | -11.30 | -11.38 | -13.26 | -13.01 |
| IM2 | 0.88 | -59.79 | -53.39 | -52.51 | -54.10 | -53.72 |
| FCN+C(CF3)2- | -8.49 | 185.14 | 187.82 | 196.94 | 185.64 | 186.15 |
| TS3 | -0.84 | 15.02 | 15.82 | 15.69 | 15.65 | 15.77 |
| C4-, cis | -0.75 | 3.72 | 3.68 | 3.10 | 3.72 | 3.85 |
| TS4 | -1.84 | 4.39 | 4.81 | 3.14 | 4.39 | 4.60 |
| CF3CFCN-+CF3 | -6.86 | 117.40 | 122.38 | 133.13 | 120.29 | 120.12 |
| CN-+C3F7 | -6.32 | 120.79 | 114.06 | 126.48 | 114.35 | 115.48 |
Table 2 ZPE corrections(ΔZPE) and relative energies for the species involved in the decomposition of C4- anion calculated at various levels of theory with respect to trans-C4- conformation*
| Species | ΔZPE/(kJ·mol-1) | Relative energy/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M06?2X/AVTZ | RCCSD(T)/CBS | ROCBS?Q | RCCSD(T)?F12A/ VDZ?F12 | RCCSD(T)?F12A/ VTZ?F12 | ||
| TS1 | -3.43 | 11.25 | 13.72(12.51) | 11.59(9.92) | 12.68(11.76) | 12.76(11.92) |
| IM1 | 0.21 | -75.94 | -75.69(-76.57) | -80.83(-81.38) | -77.86(-78.66) | -77.66(-78.58) |
| F+(CF3)2CCN- | -5.10 | 92.59 | 91.76 | 98.11 | 91.21 | 92.01 |
| TS2 | -2.59 | 1.55 | -11.30 | -11.38 | -13.26 | -13.01 |
| IM2 | 0.88 | -59.79 | -53.39 | -52.51 | -54.10 | -53.72 |
| FCN+C(CF3)2- | -8.49 | 185.14 | 187.82 | 196.94 | 185.64 | 186.15 |
| TS3 | -0.84 | 15.02 | 15.82 | 15.69 | 15.65 | 15.77 |
| C4-, cis | -0.75 | 3.72 | 3.68 | 3.10 | 3.72 | 3.85 |
| TS4 | -1.84 | 4.39 | 4.81 | 3.14 | 4.39 | 4.60 |
| CF3CFCN-+CF3 | -6.86 | 117.40 | 122.38 | 133.13 | 120.29 | 120.12 |
| CN-+C3F7 | -6.32 | 120.79 | 114.06 | 126.48 | 114.35 | 115.48 |
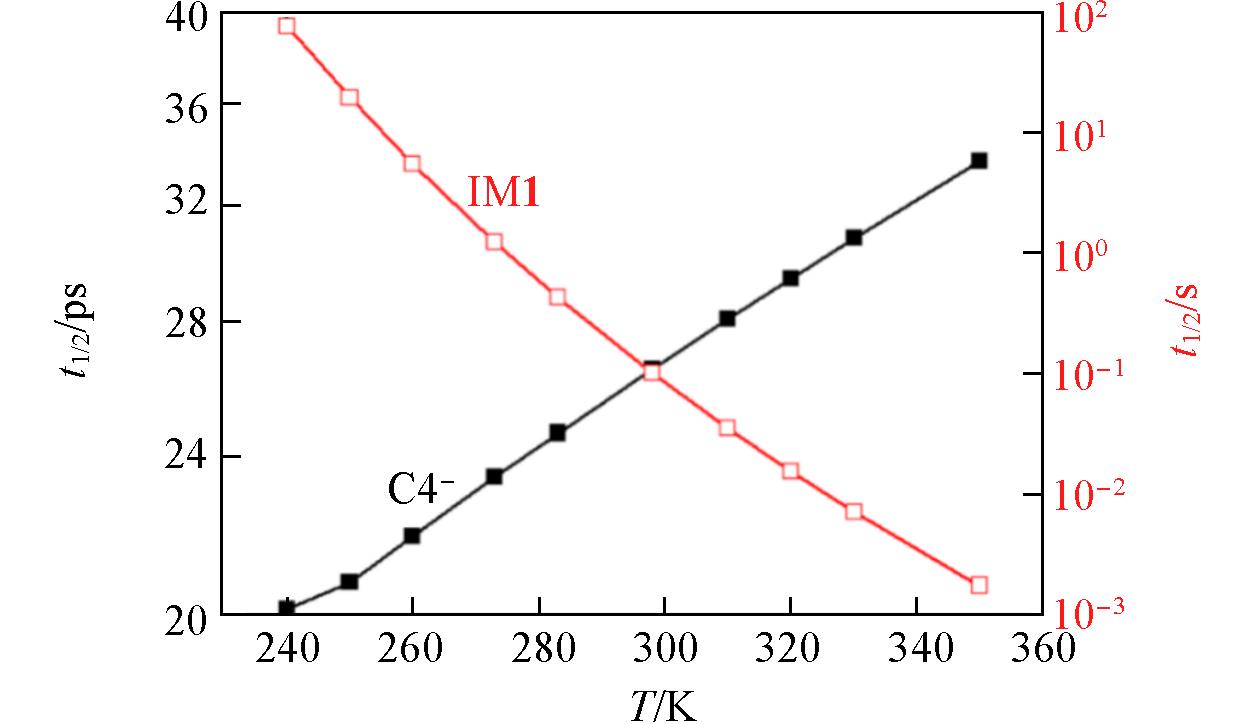
Fig.6 Half?lifetime(t1/2) of C4- and IM1 anions at 0.5 MPa of CO2 bath gasThe geometries and energetics obtained at the ROCBS-Q//M06-2X/AVTZ level of theory were employed.
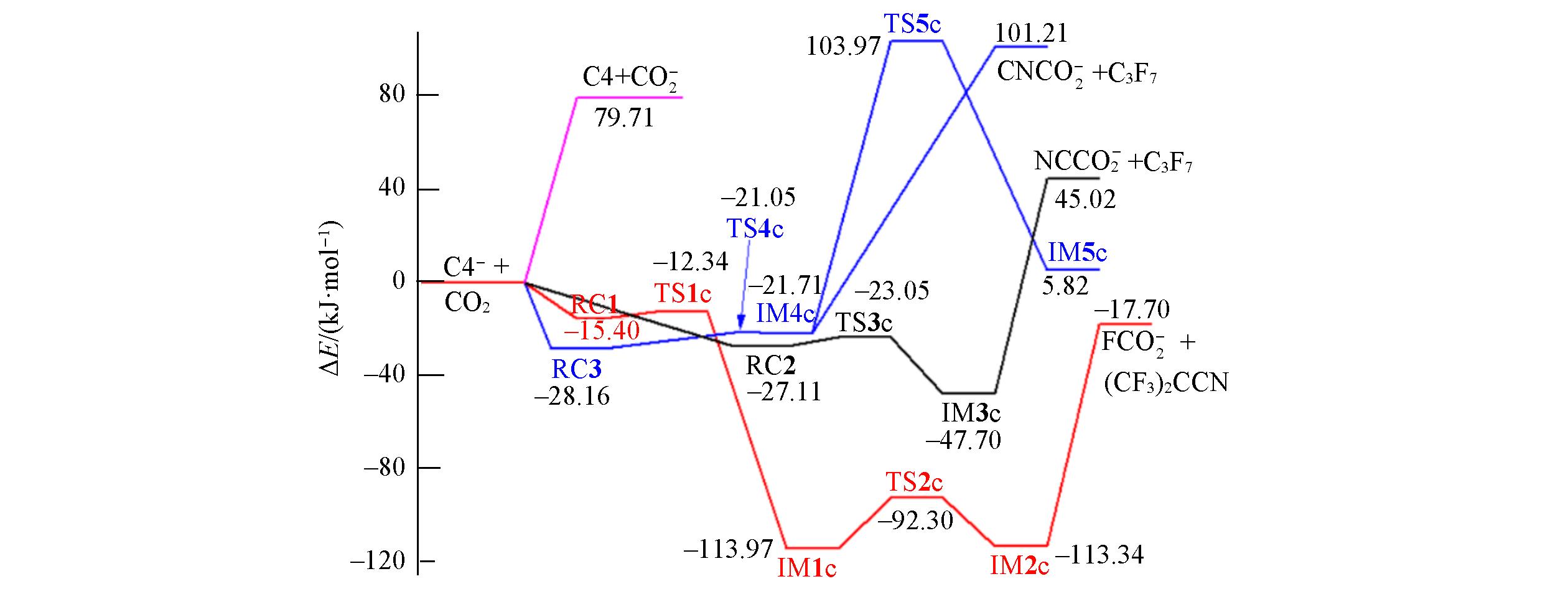
Fig.9 Energetic reaction paths for the C4-+CO2 reaction calculated at the ROCBS?Q+ZPE//M06?2X/AVTZ level of theoryNote that only the anionic product channels with lower energies are included.
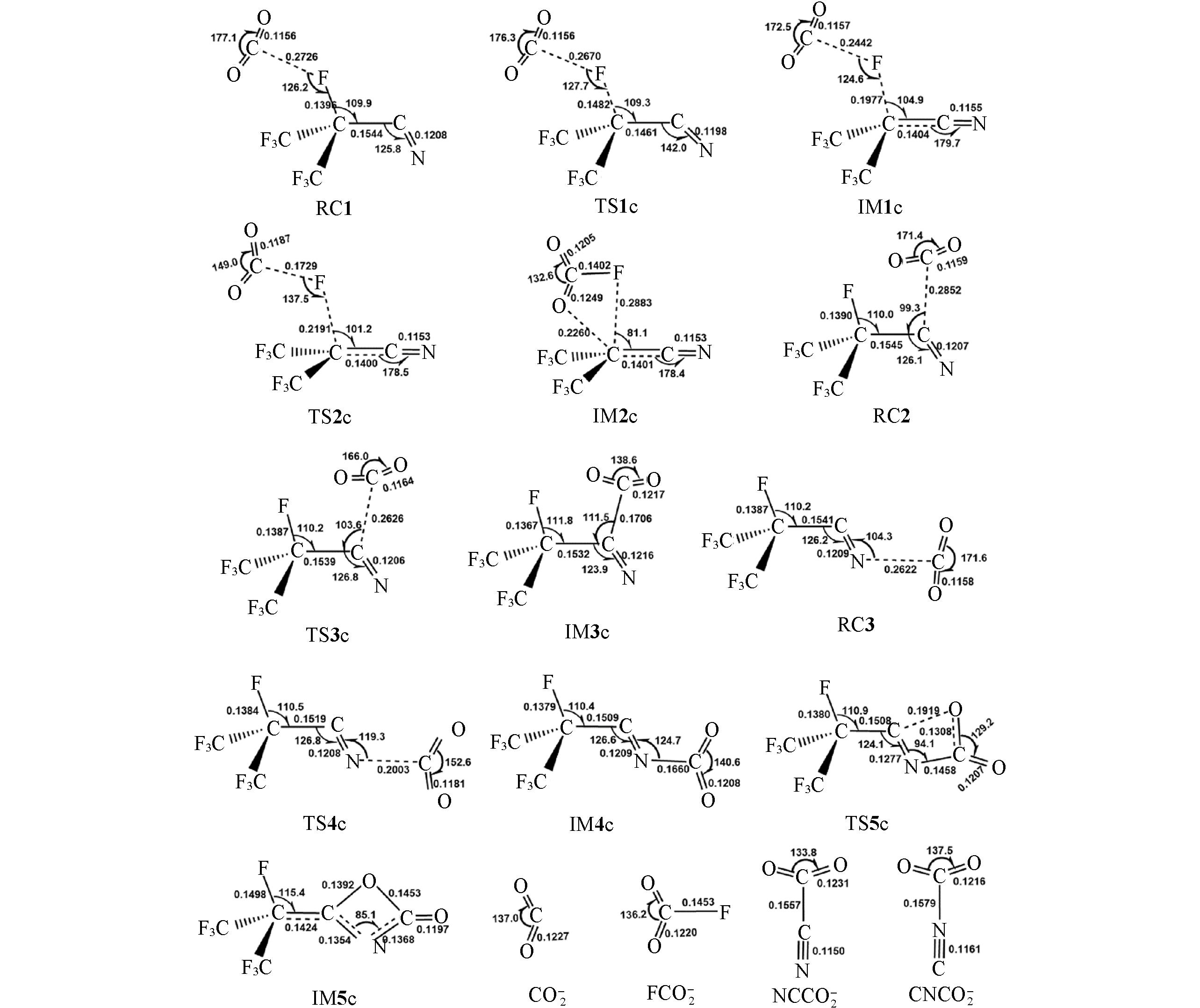
Fig.10 Geometries of the species involved in the C4-+CO2 reaction optimized at the M06?2X/AVTZ levelBond distances are in nm and angles are in degrees.
| Group | Mulliken charge/e | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4- | IM1c | IM3c | IM4c | |
| CN | -0.987 | -0.463 | -0.072 | -0.646 |
| F | -0.409 | -0.682 | -0.451 | -0.408 |
| CF3 | -0.179 | -0.289 | -0.182 | -0.108 |
| CO2 | 0 | -0.033 | -0.781 | -0.721 |
Table 3 Mulliken charges for various functional groups involved in C4- anion and intermediates calculated at the M06?2X/AVTZ level
| Group | Mulliken charge/e | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4- | IM1c | IM3c | IM4c | |
| CN | -0.987 | -0.463 | -0.072 | -0.646 |
| F | -0.409 | -0.682 | -0.451 | -0.408 |
| CF3 | -0.179 | -0.289 | -0.182 | -0.108 |
| CO2 | 0 | -0.033 | -0.781 | -0.721 |
| 1 | Rabie M., Fracnck C. M., Environ. Sci. Technol., 2018, 52(2), 369—380 |
| 2 | Wang B. S., Yu X. J., Hou H., Zhou W. J., Luo Y. B., Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 2020, 35(1), 21—33 |
| 王宝山, 余小娟, 侯华, 周文俊, 罗运柏. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(1), 21—33 | |
| 3 | Coetello M. G., Flynn R. M., Bulinski M., Fluorinated Nitriles As Dielectric Gases, US 20150083979, 2015⁃03⁃26 |
| 4 | Nechmi H. E., Beroual A., Girodet A., Vinson P., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2016, 23(5), 2587—2593 |
| 5 | Kieffel Y., Irwin T., Ponchon P., Owens J., IEEE Power Energy Mag., 2016, 14(2), 36—39 |
| 6 | Zhang X., Chen Q., Zhang J., Li Y., Song X., Ran Z., Tang J., IEEE Access, 2019, 7(2), 19100-19108 |
| 7 | Hu S., Zhou W., Yu J., Qiu R., Li H., IEEE Access, 2019, 7(1), 50159—50167 |
| 8 | Li Z., Ding W., Liu Y., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2019, 26(4), 1065—1072 |
| 9 | Wu Y., Wang C., Sun H., Murphy A. B., Rong M., Yang F., Chen Z., Niu C., Wang X., J. Phys. D., Appl. Phys., 2018, 51(15), 155206 |
| 10 | Yu X., Hou H., Wang B., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2018, 122(38), 7704—7715 |
| 11 | Gao K. L., Yan X. L., Liu Y., Wang B. S., Hu S. Z., Li Z. C., Trans. China Electrotech. Soc., 2020, 35(1), 3—20 |
| 高克利, 颜湘莲, 刘炎, 王宝山, 胡世卓, 李志闯. 电工技术学报, 2020, 35(1), 3—20 | |
| 12 | Suess L., Liu Y., Parthasarathy R., Dunning F. B., J. Chem. Phys., 2003, 119(24), 12890—12894 |
| 13 | Chen L., Zhang B., Li X., Yang T., J. Appl. Phys., 2020, 128(14), 143303 |
| 14 | Rankovic M., Chalabala J., Zawadzki M., Kocisek J., Slavicek P., Fedor J., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2019, 21(30), 16451 |
| 15 | Rankovic M., Kumar R., Nag P., Kocisek J., Fedor J., J. Chem. Phys., 2020, 152(24), 244304 |
| 16 | Zhao Y., Truhlar D. G., Theor. Chem. Acc., 2008, 120(1), 215—241 |
| 17 | Dunning T. H., J. Chem. Phys., 1989, 90(2), 1007—1023 |
| 18 | Scuseria G. E., Janssen C. L., Schaefer H. F., J. Chem. Phys., 1988, 89(12), 7382—7387 |
| 19 | Wood G. P. F., Radom L., Petersson G. A., Barnes E. C., Frisch M. J., Montgomery J. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 125(9), 094106 |
| 20 | Mackie I. D., Dilabio G. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2011, 135(13), 134318 |
| 21 | Knizia G., Adler T. B., Werner H. J., J. Chem. Phys., 2009, 130(5), 054104 |
| 22 | Anderson L. N., Oviedo M. B., Wong B. M., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2017, 13(4), 1656—1666 |
| 23 | Rienstar J. C., Tschumper G. S., Schaefer H. F, Nandi S., Ellison G. B., Chem. Rev., 2002, 102(1), 231—282 |
| 24 | Gauss J., Tajti A., Kallay M., Stanton J. F., Szalay P. G., J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 125(14), 144111 |
| 25 | Reiher M., Wolf A., J. Chem. Phys., 2004, 121(1), 2037—2047 |
| 26 | DeYonker N. J., Cundari T. R., Wilson A. K., J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 124(11), 114104 |
| 27 | Arbelo⁃Gonzalez W., Crespo⁃Otero R., Barbatti M., J. Chem. Theory Comput., 2016, 12(10), 5037—5049 |
| 28 | Bauernschmitt R., Ahlrichs R., Chem. Phys. Lett., 1996, 256(4), 454—464 |
| 29 | Klippebstein S. J., Yang Y., Ryzhov V., Dunbar R. C., J. Chem. Phys., 1996, 104(12), 4502—4516 |
| 30 | Troe J., Miller T. M., Viggiano A. A., J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 136(12), 121102 |
| 31 | Hou H., Yu X. J., Zhou W. J., Luo Y. B., Wang B. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(11), 2477—2484 |
| 侯华, 余小娟, 周文俊, 罗运柏, 王宝山. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(11), 2477—2484 | |
| 32 | Hou H., Wang B. S., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12), 3709—3715 |
| 侯华, 王宝山. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(12), 3709—3715 | |
| 33 | Yu X., Hou H., Wang B., J. Comput. Chem., 2017, 38(10), 721—729 |
| 34 | Zhang B., Uzelac N., Cao Y., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2018, 25(4), 1340—1350 |
| 35 | Bopp J. C., Roscioli J. R., Johnson M. A., Miller T. M., Viggiano A. A., Villano S. M., Wren S. W., Lineberger W. C., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111(7), 1214—1221 |
| 36 | Nechmi H. E., Beroual A., Girodet A., Vinson P., IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul., 2017, 24(2), 886—892 |
| 37 | Chachereau A., Hosl A., Franck C. M., J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys., 2018, 51(49), 495201 |
| [1] | 田润赛, 卢芊, 张洪滨, 张渤, 冯源源, 魏金香, 冯季军. 氮杂碳原位包覆Cu2O/Co3O4@C异质结构复合材料的设计构筑及高效储锂性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2592. |
| [2] | 赵淑芳, 黄骏. 分子筛材料的酸性和择形选择性的固体核磁共振研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(1): 165. |
| [3] | 杨飞,张晓平,李传宪,姚博,代抒彤,夏雪,孙广宇. 含芳香基团的梳状聚合物型降凝剂与沥青质协同改善合成蜡油的流变性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2019, 40(12): 2606. |
| [4] | 王文亮, 时宇杰, 王少华, 党泽攀, 李新平. 纤维素与废轮胎微波共热解规律及产物特性[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(5): 964. |
| [5] | 李为, 邬素华, 任欣欣. 辅助热稳定剂对钡锌复合体系性能的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2017, 38(11): 2089. |
| [6] | 张会兰, 易兵成, 王先流, 李碧云, 余哲泡, 娄向新, 张彦中. 用高度取向石墨烯/聚乳酸(Gr/PLLA)复合超细纤维构建神经导管[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(5): 972. |
| [7] | 屠国平, 何剑灵, 肖学章, 陈立新, 任钱江, 杜锡勇, 骆明儿. h-BN负载纳米NbH对LiBH4放氢性能的协同改性作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(10): 1757. |
| [8] | 沈成银, 李建权, 王宏志, 王玉杰, 王鸿梅, 黄超群, 李虎, 刘升, 储焰南. 多反应离子的质子转移反应质谱[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2012, 33(02): 263. |
| [9] | 姚同伟, 杜立波, 杨屹, 徐元超, 贾宏瑛, 刘扬. 阿魏酸丙三酯的分子内协同抗氧化作用研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2009, 30(7): 1431. |
| [10] | 聂小琴, 徐文国, 卢士香. 钒、铬团簇的电子亲合能、硬度与原子数的关系[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(8): 1629. |
| [11] | 徐文国, 白王军, 卢士香. SeHn/SeHn-(n=1~5)的结构、热化学及电子亲合能研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2008, 29(11): 2281. |
| [12] | 乔晓强, 张琳, 梁振, 张维冰, 张丽华, 张玉奎 . 蛋白质荧光标记中协同效应的高效液相色谱[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(9): 1657. |
| [13] | 曲雯雯, 谭宏伟, 刘若庄, 陈光巨 . 侧链间氢键的协同效应对环状多肽自组装的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2007, 28(2): 307. |
| [14] | 马亮亮,刘逸枫, 袁俊, 吴益华 . 疏水性咪唑类混合离子液体的物理化学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2006, 27(11): 2182. |
| [15] | 王长生, 齐学洁, 马英格, 杨忠志. 多肽中氢键强度的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2004, 25(6): 1111. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||