

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 39 ›› Issue (10): 2221.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20180465
收稿日期:2018-06-27
出版日期:2018-09-29
发布日期:2018-09-29
作者简介:联系人简介: 仇永清, 男, 博士, 教授, 博士生导师, 主要从事应用量子化学研究. E-mail:
基金资助:
LI Xiang, WANG Huiying, WANG Hongqiang, YE Jinting, QIU Yongqing*( )
)
Received:2018-06-27
Online:2018-09-29
Published:2018-09-29
Contact:
QIU Yongqing
E-mail:qiuyq466@nenu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用密度泛函理论(DFT) 方法对联吡啶RuⅡ/Ⅲ配合物的几何结构、 氧化还原性质、 UV-Vis光谱及二阶非线性光学(NLO) 性质进行计算. 研究结果表明, 醌基的引入能够有效增大第一超极化率(βtot) 值, 但醌基在氮苯基上位置的改变对βtot值影响不大. 分子轨道和自旋密度分布分析结果表明, 金属RuⅡ和副配体均能成为氧化中心, 并且氧化中心位置不同, 会导致配合物氧化态的电荷转移形式产生差别, 进而改变氧化态的βtot值. 氧化态配合物1b和2b的βtot值减小, 而配合物3b和4b的βtot值显著增大, 超瑞利散射方法计算的第一超极化率(βHRS) 值也符合此规律. 含时密度泛函理论(TD-DFT) 结果表明, 配合物本征态主要是金属到配体的电荷转移(MLCT/ML'CT), 而氧化态则是配体到金属的电荷转移(LMCT/L'MCT), 给、 受体发生明显改变. 因此, 通过改变副配体的种类及氧化还原反应, 可有效调节这类联吡啶RuⅡ/Ⅲ配合物的二阶NLO响应.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
李想, 王慧莹, 王洪强, 叶近婷, 仇永清. 联吡啶RuⅡ/Ⅲ配合物二阶非线性光学性质的理论研究. 高等学校化学学报, 2018, 39(10): 2221.
LI Xiang,WANG Huiying,WANG Hongqiang,YE Jinting,QIU Yongqing. Theoretical Studies on the Second-order Nonlinear Optical Properties of RuⅡ/Ⅲ Complexes of Bipyridyl†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2221.
| Complex | d(Ru—N1)/ nm | d(Ru—N2)/ nm | d(Ru—N3)/ nm | d(Ru—N4)/ nm | d(Ru—N5)/ nm | d(Ru—N6)/ nm | ∠N4—Ru—N5/ (°) | ∠N5—Ru—N6/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 0.21777 | 0.20924 | 0.20944 | 0.20901 | 0.21206 | 0.21142 | 85.12 | 77.60 |
| 1b | 0.21855 | 0.20870 | 0.20939 | 0.20973 | 0.21228 | 0.21253 | 83.38 | 77.22 |
| 2a | 0.21129 | 0.21158 | 0.21031 | 0.21012 | 0.21012 | 0.21030 | 89.22 | 77.93 |
| 2b | 0.21151 | 0.21146 | 0.21106 | 0.21035 | 0.21043 | 0.21105 | 88.55 | 77.86 |
| 3a | 0.21692 | 0.20917 | 0.20937 | 0.20922 | 0.21207 | 0.21142 | 84.97 | 77.55 |
| 3b | 0.21747 | 0.20863 | 0.20935 | 0.21007 | 0.21232 | 0.21272 | 83.12 | 77.22 |
| 4a | 0.21134 | 0.21133 | 0.21031 | 0.21013 | 0.21013 | 0.21031 | 89.28 | 77.95 |
| 4b | 0.21151 | 0.21150 | 0.21081 | 0.21070 | 0.21070 | 0.21082 | 86.75 | 77.93 |
Table 1 Selected bond distances and bond angles for complexes
| Complex | d(Ru—N1)/ nm | d(Ru—N2)/ nm | d(Ru—N3)/ nm | d(Ru—N4)/ nm | d(Ru—N5)/ nm | d(Ru—N6)/ nm | ∠N4—Ru—N5/ (°) | ∠N5—Ru—N6/ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 0.21777 | 0.20924 | 0.20944 | 0.20901 | 0.21206 | 0.21142 | 85.12 | 77.60 |
| 1b | 0.21855 | 0.20870 | 0.20939 | 0.20973 | 0.21228 | 0.21253 | 83.38 | 77.22 |
| 2a | 0.21129 | 0.21158 | 0.21031 | 0.21012 | 0.21012 | 0.21030 | 89.22 | 77.93 |
| 2b | 0.21151 | 0.21146 | 0.21106 | 0.21035 | 0.21043 | 0.21105 | 88.55 | 77.86 |
| 3a | 0.21692 | 0.20917 | 0.20937 | 0.20922 | 0.21207 | 0.21142 | 84.97 | 77.55 |
| 3b | 0.21747 | 0.20863 | 0.20935 | 0.21007 | 0.21232 | 0.21272 | 83.12 | 77.22 |
| 4a | 0.21134 | 0.21133 | 0.21031 | 0.21013 | 0.21013 | 0.21031 | 89.28 | 77.95 |
| 4b | 0.21151 | 0.21150 | 0.21081 | 0.21070 | 0.21070 | 0.21082 | 86.75 | 77.93 |
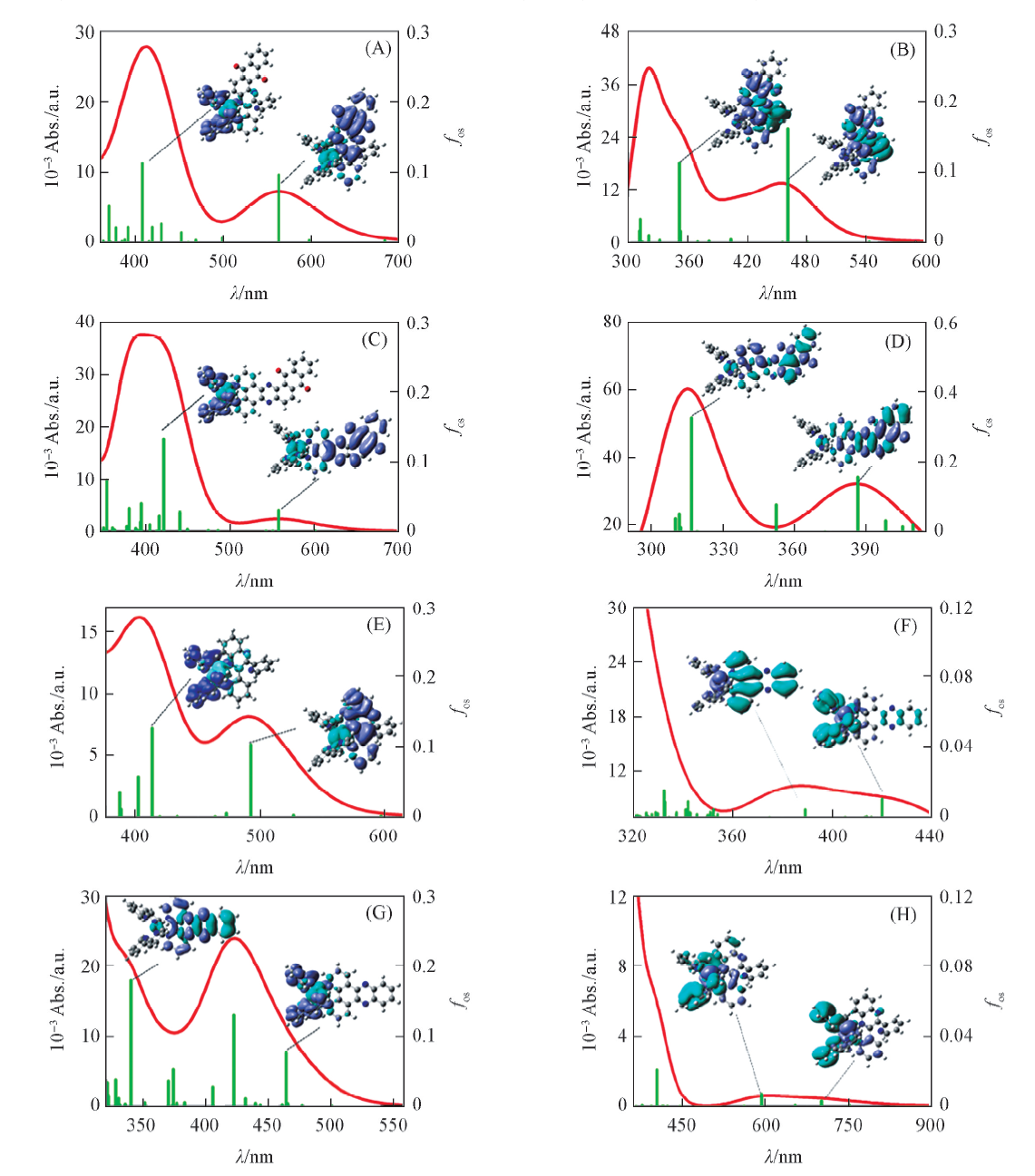
Fig.3 UV-Vis spectra of the complexes along with electron density difference maps(EDDM) corresponding to the most intense electronic transitions(A) 1a; (B) 1b; (C) 2a; (D) 2b; (E) 3a; (F) 3b; (G) 4a; (H) 4b. fos: Oscillator strengths.
| Complex | λ/nm | E/eV | fos | Major contributions* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 563(546)[ | 2.20 | 0.0965 | H-1→L(60%), H-2→L(31%) |
| 408(390) [ | 3.03 | 0.1130 | H-2→L+2(29%), H-1→L+2(24%), H-1→L+4(22%), H-2→L+4(14%) | |
| 2a | 558(440) [ | 2.22 | 0.0310 | H-1→L(98%) |
| 421(395) [ | 2.95 | 0.1327 | H-2→L+3(40%), H-1→L+4(35%), H-2→L+2(17%) | |
| 3a | 493(520) [ | 2.52 | 0.1037 | H-1→L(64%), H-2→L(23%) |
| 413(420) [ | 3.00 | 0.1266 | H-2→L+1(46%), H-1→L+2(27%), H-1→L+1(16%) | |
| 4a | 422(452) [ | 2.94 | 0.1298 | H-2→L+2(47%), H-1→L+3(36%), H-2→L+1(14%) |
| 340(350) [ | 3.64 | 0.1797 | H-4→L(69%), H-3→L+4(24%) | |
| 1b | 461 | 2.69 | 0.1625 | βH→ βL+1(27%), αH→αL(26%), βH-1→βL+1(20%), αH-1→αL(19%) |
| 351 | 3.53 | 0.1133 | αH-9→αL(29%), βH-10→βL+1(29%) | |
| 2b | 387 | 3.20 | 0.1578 | βH-2→ βL+1(41%), αH-2→αL(37%) |
| 317 | 3.92 | 0.3253 | βH-1→βL+5(22%), αH-1→αL+4(19%) | |
| 3b | 420 | 2.95 | 0.0104 | βH-11→βL(87%) |
| 389 | 3.19 | 0.0046 | βH-14→βL(62%) | |
| 4b | 701 | 1.77 | 0.0030 | βH-3→βL(81%), βH-6→βL(13%) |
| 592 | 2.09 | 0.0073 | βH-7→ βL(80%), βH-5→ βL(15%) |
Table 2 Calculated spectroscopic data of all studied complexes
| Complex | λ/nm | E/eV | fos | Major contributions* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | 563(546)[ | 2.20 | 0.0965 | H-1→L(60%), H-2→L(31%) |
| 408(390) [ | 3.03 | 0.1130 | H-2→L+2(29%), H-1→L+2(24%), H-1→L+4(22%), H-2→L+4(14%) | |
| 2a | 558(440) [ | 2.22 | 0.0310 | H-1→L(98%) |
| 421(395) [ | 2.95 | 0.1327 | H-2→L+3(40%), H-1→L+4(35%), H-2→L+2(17%) | |
| 3a | 493(520) [ | 2.52 | 0.1037 | H-1→L(64%), H-2→L(23%) |
| 413(420) [ | 3.00 | 0.1266 | H-2→L+1(46%), H-1→L+2(27%), H-1→L+1(16%) | |
| 4a | 422(452) [ | 2.94 | 0.1298 | H-2→L+2(47%), H-1→L+3(36%), H-2→L+1(14%) |
| 340(350) [ | 3.64 | 0.1797 | H-4→L(69%), H-3→L+4(24%) | |
| 1b | 461 | 2.69 | 0.1625 | βH→ βL+1(27%), αH→αL(26%), βH-1→βL+1(20%), αH-1→αL(19%) |
| 351 | 3.53 | 0.1133 | αH-9→αL(29%), βH-10→βL+1(29%) | |
| 2b | 387 | 3.20 | 0.1578 | βH-2→ βL+1(41%), αH-2→αL(37%) |
| 317 | 3.92 | 0.3253 | βH-1→βL+5(22%), αH-1→αL+4(19%) | |
| 3b | 420 | 2.95 | 0.0104 | βH-11→βL(87%) |
| 389 | 3.19 | 0.0046 | βH-14→βL(62%) | |
| 4b | 701 | 1.77 | 0.0030 | βH-3→βL(81%), βH-6→βL(13%) |
| 592 | 2.09 | 0.0073 | βH-7→ βL(80%), βH-5→ βL(15%) |
| Complex | Method | βx/a. u. | βy/a. u. | βz/a. u. | βtot/a. u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | CAM-B3LYP | 3348.38 | -189.06 | -1397.25 | 3633.14 |
| ωB97XD | 3351.94 | -492.59 | -1380.73 | 3658.49 | |
| 1b | CAM-B3LYP | -46.18 | 3304.03 | -1239.64 | 3529.22 |
| ωB97XD | 69.70 | 2995.24 | -1057.94 | 3177.36 | |
| 2a | CAM-B3LYP | 706.68 | -2659.16 | 168.53 | 2756.61 |
| ωB97XD | 629.65 | -2639.39 | 147.26 | 2717.44 | |
| 2b | CAM-B3LYP | 67.53 | 878.76 | -4.56 | 881.37 |
| ωB97XD | -18.38 | 673.47 | -206.74 | 704.72 | |
| 3a | CAM-B3LYP | -149.84 | -171.04 | -579.01 | 622.06 |
| ωB97XD | 7.59 | -239.25 | -551.49 | 601.20 | |
| 3b | CAM-B3LYP | -789.04 | 2143.38 | -774.23 | 2411.66 |
| ωB97XD | -721.11 | 1831.16 | -736.26 | 2101.25 | |
| 4a | CAM-B3LYP | -16.54 | 1372.57 | 8.84 | 1372.69 |
| ωB97XD | -15.32 | 1135.35 | 6.40 | 1135.47 | |
| 4b | CAM-B3LYP | -96.98 | 3738.85 | 149.25 | 3743.09 |
| ωB97XD | -20.99 | 3655.68 | 253.09 | 3664.49 |
Table 3 Individual components of first hyperpolarizabilities and total effective values
| Complex | Method | βx/a. u. | βy/a. u. | βz/a. u. | βtot/a. u. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | CAM-B3LYP | 3348.38 | -189.06 | -1397.25 | 3633.14 |
| ωB97XD | 3351.94 | -492.59 | -1380.73 | 3658.49 | |
| 1b | CAM-B3LYP | -46.18 | 3304.03 | -1239.64 | 3529.22 |
| ωB97XD | 69.70 | 2995.24 | -1057.94 | 3177.36 | |
| 2a | CAM-B3LYP | 706.68 | -2659.16 | 168.53 | 2756.61 |
| ωB97XD | 629.65 | -2639.39 | 147.26 | 2717.44 | |
| 2b | CAM-B3LYP | 67.53 | 878.76 | -4.56 | 881.37 |
| ωB97XD | -18.38 | 673.47 | -206.74 | 704.72 | |
| 3a | CAM-B3LYP | -149.84 | -171.04 | -579.01 | 622.06 |
| ωB97XD | 7.59 | -239.25 | -551.49 | 601.20 | |
| 3b | CAM-B3LYP | -789.04 | 2143.38 | -774.23 | 2411.66 |
| ωB97XD | -721.11 | 1831.16 | -736.26 | 2101.25 | |
| 4a | CAM-B3LYP | -16.54 | 1372.57 | 8.84 | 1372.69 |
| ωB97XD | -15.32 | 1135.35 | 6.40 | 1135.47 | |
| 4b | CAM-B3LYP | -96.98 | 3738.85 | 149.25 | 3743.09 |
| ωB97XD | -20.99 | 3655.68 | 253.09 | 3664.49 |
| λ/nm | Complex | βHRS | DR | ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1340 | 1a | 1971 | 4.052 | 3431.36 | 3648.75 | 1.06 |
| 2a | 2294 | 2.653 | 3156.94 | 5658.11 | 1.79 | |
| 3a | 945 | 1.672 | 586.81 | 2926.60 | 4.99 | |
| 4a | 996 | 1.575 | 415.97 | 3164.49 | 7.61 | |
| 1b | 1369 | 5.988 | 2687.59 | 1681.42 | 0.63 | |
| 2b | 263 | 1.632 | 144.69 | 824.15 | 5.70 | |
| 3b | 984 | 6.967 | 1995.84 | 929.46 | 0.47 | |
| 4b | 1118 | 6.595 | 2242.47 | 1176.88 | 0.52 | |
| 1460 | 1a | 1720 | 3.931 | 2958.42 | 3262.73 | 1.06 |
| 2a | 2080 | 2.595 | 2811.85 | 5192.71 | 1.85 | |
| 3a | 854 | 1.646 | 491.94 | 2664.96 | 5.42 | |
| 4a | 923 | 1.604 | 452.36 | 2909.57 | 6.43 | |
| 1b | 1225 | 6.003 | 2405.38 | 1498.92 | 0.62 | |
| 2b | 248 | 1.712 | 169.81 | 761.05 | 4.48 | |
| 3b | 868 | 6.948 | 1759.72 | 824.75 | 0.47 | |
| 4b | 1057 | 6.621 | 2122.31 | 1104.83 | 0.52 | |
| 1907 | 1a | 1323 | 3.677 | 2211.28 | 2640.79 | 1.19 |
| 2a | 1701 | 2.48 | 2211.21 | 4355.04 | 1.97 | |
| 3a | 704 | 1.618 | 366.37 | 2210.52 | 6.03 | |
| 4a | 792 | 1.679 | 501.08 | 2448.21 | 4.89 | |
| 1b | 1002 | 5.934 | 1962.49 | 1246.42 | 0.64 | |
| 2b | 223 | 1.963 | 216.13 | 643.79 | 2.98 | |
| 3b | 704 | 6.696 | 1417.76 | 721.08 | 0.51 | |
| 4b | 943 | 6.666 | 1896.26 | 973.62 | 0.51 |
Table 4 βHRS, βJ values, as well as the ρ and DR of all complexes calculated at the CAM-B3LYP/6-31G*/SDD level in acetonitrile, using wavelengths of 1340, 1460, and 1907 nm
| λ/nm | Complex | βHRS | DR | ρ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1340 | 1a | 1971 | 4.052 | 3431.36 | 3648.75 | 1.06 |
| 2a | 2294 | 2.653 | 3156.94 | 5658.11 | 1.79 | |
| 3a | 945 | 1.672 | 586.81 | 2926.60 | 4.99 | |
| 4a | 996 | 1.575 | 415.97 | 3164.49 | 7.61 | |
| 1b | 1369 | 5.988 | 2687.59 | 1681.42 | 0.63 | |
| 2b | 263 | 1.632 | 144.69 | 824.15 | 5.70 | |
| 3b | 984 | 6.967 | 1995.84 | 929.46 | 0.47 | |
| 4b | 1118 | 6.595 | 2242.47 | 1176.88 | 0.52 | |
| 1460 | 1a | 1720 | 3.931 | 2958.42 | 3262.73 | 1.06 |
| 2a | 2080 | 2.595 | 2811.85 | 5192.71 | 1.85 | |
| 3a | 854 | 1.646 | 491.94 | 2664.96 | 5.42 | |
| 4a | 923 | 1.604 | 452.36 | 2909.57 | 6.43 | |
| 1b | 1225 | 6.003 | 2405.38 | 1498.92 | 0.62 | |
| 2b | 248 | 1.712 | 169.81 | 761.05 | 4.48 | |
| 3b | 868 | 6.948 | 1759.72 | 824.75 | 0.47 | |
| 4b | 1057 | 6.621 | 2122.31 | 1104.83 | 0.52 | |
| 1907 | 1a | 1323 | 3.677 | 2211.28 | 2640.79 | 1.19 |
| 2a | 1701 | 2.48 | 2211.21 | 4355.04 | 1.97 | |
| 3a | 704 | 1.618 | 366.37 | 2210.52 | 6.03 | |
| 4a | 792 | 1.679 | 501.08 | 2448.21 | 4.89 | |
| 1b | 1002 | 5.934 | 1962.49 | 1246.42 | 0.64 | |
| 2b | 223 | 1.963 | 216.13 | 643.79 | 2.98 | |
| 3b | 704 | 6.696 | 1417.76 | 721.08 | 0.51 | |
| 4b | 943 | 6.666 | 1896.26 | 973.62 | 0.51 |
| [1] | Cui Y., Liu Q.D., Bai D. R., Jia W. L., Tao Y., Wang S., Inorg. Chem., 2005, 44, 601—609 |
| [2] | Lan Y.Z., Cheng W. D., Wu D. S., Li X. D., Zhang H., Gong Y. [J]., Chem. Phys. Lett., 2003, 372, 645—649 |
| [3] | Kim H.M., Cho B. R., J. Mater. Chem., 2009, 19, 7402—7409 |
| [4] | Asselberghs I., Clays K., Persoons A., Ward M.D., McCleverty J., J. Mater. Chem., 2004, 14, 2831—2839 |
| [5] | Coe B.J., Pilkington R. A., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2014, 118, 2253—2268 |
| [6] | Bonnet S., Comments Inorg.Chem., 2015, 35, 179—213 |
| [7] | Liu Z., Sadler P. J., Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 1174—1185 |
| [8] | Howerton B.S., Heidary D. K., Glazer E. C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134, 8324—8327 |
| [9] | Balzani V., Credi A., Venturi M., ChemSusChem, 2008, 1, 26—58 |
| [10] | King A.W., Wang L., Rack J. J., Acc. Chem. Res., 2015, 48, 1115—1122 |
| [11] | Sato O., Acc. Chem. Res., 2003, 36, 692—700 |
| [12] | Klein M., Pankiewicz R., Zalas M., Stampor W., Sci. Rep., 2016, 6, 30077 |
| [13] | Kaufhold S., Petermann L., Staehle R., Rau S., Coord. Chem. Rev., 2015, 304/305, 73—87 |
| [14] | Bessette A., Cibian M., Ferreira J.G., DiMarco B. N., Belanger F., Desilets D., Meyer G. J., Hanan G. S., Dalton Trans., 2016, 45, 10563—10576 |
| [15] | Prier C.K., Rankic D. A., MacMillan D. W. C., Chem. Rev., 2013, 113, 5322—5363 |
| [16] | Eckenhoff W.T., Eisenberg R., Dalton Trans., 2012, 41, 13004—13021 |
| [17] | Wang J., Zhang M.Y., Zou H. Y., Yu H. L., Wang W. Y., Song H. J., Li X. Q., QiuY. Q., Chem. J. Chinese Universites, 2013, 34(12), 2791—2797 |
| (王娇, 张梦颖, 邹海艳, 于海玲, 王文勇, 宋红娟, 李晓倩, 仇永清. 高等学校化学学报, 2013, 34(12), 2791—2797) | |
| [18] | Zhao M., Yu H.X., Li X. H., Huang X., J. Mol. Sci., 2017, 02, 159—163 |
| (赵岷, 于蕙瑄, 李新华, 黄醒. 分子科学学报, 2017, 02, 159—163) | |
| [19] | Whittemore T.J., White T. A., Turro C., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140, 229—234 |
| [20] | Becke A.D., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648—5652 |
| [21] | Grimme S., J. Chem. Phys., 2006, 124, 034108 |
| [22] | Schwabe T., Grimme S., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2006, 8, 4398—4401 |
| [23] | Andrae D., Häußermann U., Dolg M., Stoll H., Preuß H., Theor. Chim. Acta, 1990, 77, 123—141 |
| [24] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Scalmani G., Barone V., Mennucci B., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Caricato M., Li X., Hratchian H. P., Izmaylov A. F., Bloino J., Zheng G., Sonnenberg J. L., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J.,Ishida M.,Nakajima T.,Honda Y.,Kitao O.,Nakai H.,Vreven T.,Montgomery J. A. Jr., Peralta J. E.,Ogliaro F., Bearpark M., Heyd J. J., Brothers E., Kudin K. N., Staroverov V. N.,Keith T., Kobayashi R.,Normand J., Raghavachari K.,Rendell A., Burant J. C., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Cossi M., Rega N., Millam J. M., Klene M., Knox J. E., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R.,Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J.W.,Martin R. L.,Morokuma K.,Zakrzewski V.G., Voth G. A., Salvador P.,Dannenberg J. J., Dapprich S.,Daniels A. D.,Farkas O., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V.,Cioslowski J.,Fox D. J., Gaussian 09, Revision D. 01, Gaussian Inc., Wallingford CT, 2013 |
| [25] | Sim F., Chin S., Dupuis M., Rice J.E., J. Phys. Chem., 1993, 97, 1158—1163 |
| [26] | Plaquet A., Guillaume M., Champagne B., Castet F., Ducasse L., Pozzo J.L., Rodriguez V., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2008, 10, 6223—6232 |
| [27] | Guillaume M., Champagne B.T., Markova N., Enchev V., Castet F. D. R., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2007, 111, 9914—9923 |
| [28] | Ye J.T., Wang L., Wang H. Q., Pan X. M., Xie H. M., Qiu Y. Q., Org. Electron., 2017, 47, 152—161 |
| [29] | Fihey A., Perrier A.L., Maurel F. O., J. Photochem. Photobiol. A, 2012, 247, 30—41 |
| [30] | Pielak K., Bondu F., Sanguinet L., Rodriguez V., Champagne B.T., Castet F. D. R., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2017, 121, 1851—1860 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [3] | 郑雪莲, 杨翠翠, 田维全. 全椅式边含薁缺陷石墨烯纳米片的二阶非线性光学性质[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210806. |
| [4] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| [5] | 程媛媛, 郗碧莹. ·OH自由基引发CH3SSC |
| [6] | 王园月, 安梭梭, 郑旭明, 赵彦英. 5-巯基-1, 3, 4-噻二唑-2-硫酮微溶剂团簇的光谱和理论计算研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220354. |
| [7] | 周成思, 赵远进, 韩美晨, 杨霞, 刘晨光, 贺爱华. 硅烷类外给电子体对丙烯-丁烯序贯聚合的调控作用[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(10): 20220290. |
| [8] | 黄罗仪, 翁约约, 黄旭慧, 王朝杰. 车前草中黄酮类成分结构和性质的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2752. |
| [9] | 马丽娟, 高升启, 荣祎斐, 贾建峰, 武海顺. Sc, Ti, V修饰B/N掺杂单缺陷石墨烯的储氢研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2842. |
| [10] | 钟声广, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 电中性团簇MCu2Ox(M=Cu2+, Ce4+, Zr4+)上甲烷和二氧化碳直接合成乙酸的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(9): 2878. |
| [11] | 卓增庆, 潘锋. 基于软X射线光谱的锂电池材料的电子结构与演变的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(8): 2332. |
| [12] | 柳扬, 李清波, 孙杰, 赵显. Ga对在AlN衬底上直接生长石墨烯的远程催化[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2271. |
| [13] | 郑若昕, 张颖, 徐昕. 低标度XYG3双杂化密度泛函的开发与测评[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2210. |
| [14] | 王建, 张红星. 四配位铂磷光发射体结构与光物理性质关系的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2245. |
| [15] | 胡伟, 刘小峰, 李震宇, 杨金龙. 金刚石纳米线氮空位色心的表面与尺寸效应[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2021, 42(7): 2178. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||