

高等学校化学学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 1743.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20150218
收稿日期:2015-03-23
出版日期:2015-09-10
发布日期:2015-08-21
作者简介:联系人简介: 夏文生, 男, 博士, 教授, 主要从事催化和理论化学研究. E-mail:基金资助:
CHEN Rongfang, XIA Wensheng*( ), WAN Huilin*(
), WAN Huilin*( )
)
Received:2015-03-23
Online:2015-09-10
Published:2015-08-21
Contact:
XIA Wensheng,WAN Huilin
E-mail:wsxia@xmu.edu.cn;hlwan@xmu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
采用密度泛函理论(DFT)计算了CH4在电中性(CeO2)m(m=1~3)团簇上的活化情况, 并对其机理进行了探讨. 计算结果表明, 甲烷C—H键在团簇上的活化为亲核加成模式, 电子由团簇流向甲烷C—H反键轨道, 使甲烷C—H键削弱而得以活化, 反应的过渡态为四中心结构. 团簇的桥氧位活化甲烷C—H键的活性大于端氧位, 而三重桥氧位的活性高于二重桥氧位. 团簇中作用位点Ce和O原子的电荷布居与其活化甲烷C—H的能力密切相关. 溶剂的存在不仅降低了甲烷C—H活化自由能垒, 而且使与甲烷作用的团簇各位点的活性差异缩小.
中图分类号:
TrendMD:
陈蓉芳, 夏文生, 万惠霖. 中性团簇(CeO2)m(m=1~3)活化甲烷C—H的密度泛函理论计算. 高等学校化学学报, 2015, 36(9): 1743.
CHEN Rongfang, XIA Wensheng, WAN Huilin. Density Functional Theory Studies on the C—H Bond Activation of Methane by(CeO2)m(m=1—3)†. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2015, 36(9): 1743.
| Reaction | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Predicted by others | Experiment | |
| CH4→CH3+H | 432.2 | 432.2[ | 438.1[ |
| CeO2→CeO+O | 597.9 | 598.3[ | 646.0±19.2[ |
Table 1 Comparison of the predicted bond energies at the level of B3LYP/SDD+TZVP
| Reaction | Eb/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Predicted by others | Experiment | |
| CH4→CH3+H | 432.2 | 432.2[ | 438.1[ |
| CeO2→CeO+O | 597.9 | 598.3[ | 646.0±19.2[ |
| Species | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | Species | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP | B3PW91 | CCSD(T) | B3LYP | B3PW91 | CCSD(T) | ||
| CeO2+CH4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TS | 133.1 | 128.4 | 124.7 |
| CeO2…CH4 | -5.9 | -3.3 | -23.0 | Product | 43.5 | 50.2 | 21.8 |
Table 2 Relative energies of various compounds in the reaction of CeO2 + CH4 predicted at the level of B3LYP/SDD+TZVP, B3PW91/SDD+TZVP and CCSD(T)//B3LYP/ SDD+TZVP
| Species | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | Species | ΔE/(kJ·mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B3LYP | B3PW91 | CCSD(T) | B3LYP | B3PW91 | CCSD(T) | ||
| CeO2+CH4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | TS | 133.1 | 128.4 | 124.7 |
| CeO2…CH4 | -5.9 | -3.3 | -23.0 | Product | 43.5 | 50.2 | 21.8 |
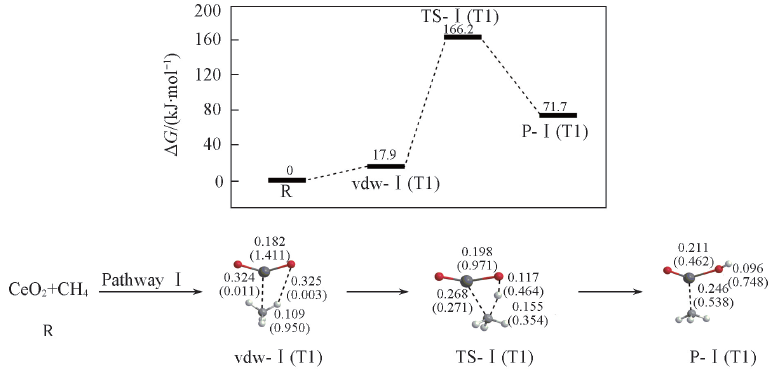
Fig.2 Potential energy surface(at 298 K) and optimized geometries of the product(P), van der Waals(vdw) complex, and transition state(TS) of CH4 activations on the CeO2 cluster at the B3LYP/SDD+TZVP levelThe Wiberg bond orders are included in parentheses. Bond lengths are in nm.
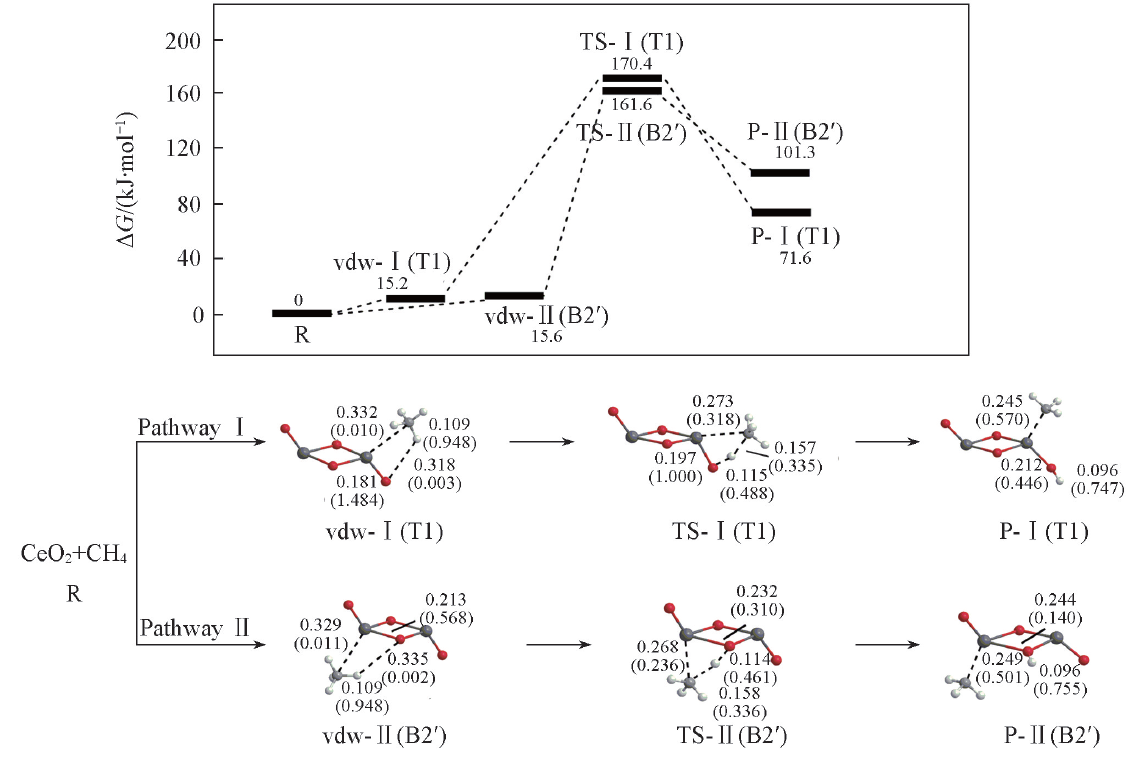
Fig.3 Potential energy surfaces(at 298 K) and optimized geometries of the products(P), van der Waals(vdw) complexes, and transition states(TS) of CH4 activations on the Ce2O4 cluster at the B3LYP/SDD+TZVP levelThe Wiberg bond orders are included in parentheses. Bond lengths are in nm.
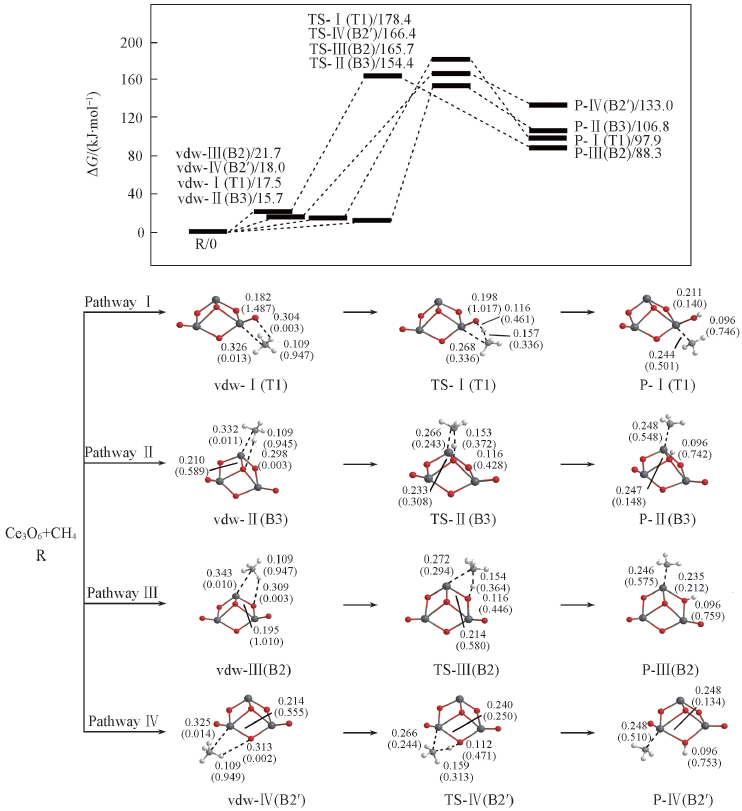
Fig.4 Potential energy surfaces(at 298 K) and optimized geometries of the products(P), van der Waals(vdw) complexes, and transition states(TS) of CH4 activations on the Ce3O6 cluster at the B3LYP/SDD+TZVP levelThe Wiberg bond orders are included in parentheses. Bond lengths are in nm.
| Cluster | C—H activation pathway | q/e(at active sites in clusters w/o CH4) | q/e | νimg/cm-1 (TS) | ΔGvdw/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔG*/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔGr/ (kJ· mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce(free clusters) | O(free clusters) | Ce (TS) | O (TS) | Cluster (TS) | CH4 (TS) | ||||||
| CeO2(A) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.266 | -1.133 | 2.372 | -1.087 | 0.190 | -0.190 | 1295i | 17.9 | 166.2 | 71.7 |
| Ce2O4(B) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.485 | -1.113 | 2.533 | -1.064 | 0.168 | -0.168 | 1214i | 15.2 | 170.4 | 71.6 |
| Ⅱ(B2') | 2.485 | -1.372 | 2.534 | -1.301 | 0.182 | -0.182 | 1292i | 15.6 | 161.6 | 101.3 | |
| Ce3O6(C) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.549 | -1.092 | 2.560 | -1.048 | 0.149 | -0.149 | 1295i | 17.5 | 178.4 | 97.9 |
| Ⅱ(B3) | 2.494 | -1.434 | 2.526 | -1.354 | 0.159 | -0.159 | 1176i | 15.7 | 154.4 | 106.8 | |
| Ⅲ(B2) | 2.494 | -1.303 | 2.525 | -1.262 | 0.145 | -0.145 | 764i | 21.7 | 165.7 | 88.3 | |
| Ⅳ(B2') | 2.549 | -1.367 | 2.587 | -1.313 | 0.177 | -0.177 | 1258i | 18.0 | 166.4 | 133.0 | |
Table 3 Predicted reaction energetics(at 298 K) for methane on the(CeO2)m(m=1—3) clusters, imaging frequency(νimg) of transition states TS, and NBO charge population analysis on the clusters and CH4 species in TS and the Ce and O atoms interacted with/without CH4, at the level of B3LYP/SDD+TZVP*
| Cluster | C—H activation pathway | q/e(at active sites in clusters w/o CH4) | q/e | νimg/cm-1 (TS) | ΔGvdw/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔG*/ (kJ· mol-1) | ΔGr/ (kJ· mol-1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ce(free clusters) | O(free clusters) | Ce (TS) | O (TS) | Cluster (TS) | CH4 (TS) | ||||||
| CeO2(A) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.266 | -1.133 | 2.372 | -1.087 | 0.190 | -0.190 | 1295i | 17.9 | 166.2 | 71.7 |
| Ce2O4(B) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.485 | -1.113 | 2.533 | -1.064 | 0.168 | -0.168 | 1214i | 15.2 | 170.4 | 71.6 |
| Ⅱ(B2') | 2.485 | -1.372 | 2.534 | -1.301 | 0.182 | -0.182 | 1292i | 15.6 | 161.6 | 101.3 | |
| Ce3O6(C) | Ⅰ(T1) | 2.549 | -1.092 | 2.560 | -1.048 | 0.149 | -0.149 | 1295i | 17.5 | 178.4 | 97.9 |
| Ⅱ(B3) | 2.494 | -1.434 | 2.526 | -1.354 | 0.159 | -0.159 | 1176i | 15.7 | 154.4 | 106.8 | |
| Ⅲ(B2) | 2.494 | -1.303 | 2.525 | -1.262 | 0.145 | -0.145 | 764i | 21.7 | 165.7 | 88.3 | |
| Ⅳ(B2') | 2.549 | -1.367 | 2.587 | -1.313 | 0.177 | -0.177 | 1258i | 18.0 | 166.4 | 133.0 | |
| Species | Ggas/a.u. | Gsolv/a.u. | Δ | ΔGgas/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGsolv/(kJ·mol-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | -40.509685 | -40.562719 | -139.2 | |||||||
| CeO2(A) | -625.769905 | -625.766078 | 10.0 | |||||||
| CeO2(A)+CH4 | -666.279590 | -666.328797 | -129.2 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.272785 | -666.332007 | -155.5 | 17.9 | -8.4 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.216277 | -666.277172 | -159.9 | 166.2 | 135.5 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.252288 | -666.306037 | -141.1 | 71.7 | 59.8 | |||||
| Ce2O4(B) | -1251.615246 | -1251.626692 | -30.1 | |||||||
| Ce2O4(B)+CH4 | -1292.124931 | -1292.189411 | -169.3 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.119134 | -1292.187597 | -179.7 | 15.2 | 4.8 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.118978 | -1292.187314 | -179.4 | 15.6 | 5.5 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.060019 | -1292.132049 | -189.1 | 170.4 | 150.6 | |||||
| TS-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.063375 | -1292.134880 | -187.7 | 161.6 | 143.2 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.097646 | -1292.153706 | -147.2 | 71.6 | 93.7 | |||||
| P-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.086332 | -1292.148290 | -162.7 | 101.3 | 107.9 | |||||
| Ce3O6(C) | -1877.475699 | -1877.492891 | -45.1 | |||||||
| Ce3O6(C)+CH4 | -1917.985384 | -1918.055610 | -184.3 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.978710 | -1918.055626 | -201.9 | 17.5 | -0.1 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.979392 | -1918.053792 | -195.3 | 15.7 | 4.7 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.977104 | -1918.056477 | -208.4 | 21.7 | -2.4 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.978539 | -1918.055939 | -203.2 | 18.0 | -0.9 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.917443 | -1917.999296 | -214.9 | 178.4 | 147.8 | |||||
| TS-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.926594 | -1918.000597 | -194.3 | 154.4 | 144.4 | |||||
| TS-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.922263 | -1917.998085 | -199.1 | 165.7 | 150.9 | |||||
| TS-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.922012 | -1918.001456 | -208.6 | 166.4 | 142.1 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.948078 | -1918.026277 | -205.3 | 97.9 | 76.9 | |||||
| P-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.944706 | -1918.016064 | -187.4 | 106.8 | 103.7 | |||||
| P-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.951740 | -1918.016930 | -171.2 | 88.3 | 101.4 | |||||
| P-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.934711 | -1918.012010 | -202.9 | 133.0 | 114.4 | |||||
Table 4 Free energies(G), solvation free energies(ΔGsolv) and relative free energies(ΔG for van der Waals complex formation, for the C—H activation barrier, for the reaction, relative to CH4+cluster) in the gas phase and in the solvent(water) at the level of B3LYP/SDD+TZVP
| Species | Ggas/a.u. | Gsolv/a.u. | Δ | ΔGgas/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔGsolv/(kJ·mol-1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH4 | -40.509685 | -40.562719 | -139.2 | |||||||
| CeO2(A) | -625.769905 | -625.766078 | 10.0 | |||||||
| CeO2(A)+CH4 | -666.279590 | -666.328797 | -129.2 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.272785 | -666.332007 | -155.5 | 17.9 | -8.4 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.216277 | -666.277172 | -159.9 | 166.2 | 135.5 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -666.252288 | -666.306037 | -141.1 | 71.7 | 59.8 | |||||
| Ce2O4(B) | -1251.615246 | -1251.626692 | -30.1 | |||||||
| Ce2O4(B)+CH4 | -1292.124931 | -1292.189411 | -169.3 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.119134 | -1292.187597 | -179.7 | 15.2 | 4.8 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.118978 | -1292.187314 | -179.4 | 15.6 | 5.5 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.060019 | -1292.132049 | -189.1 | 170.4 | 150.6 | |||||
| TS-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.063375 | -1292.134880 | -187.7 | 161.6 | 143.2 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -1292.097646 | -1292.153706 | -147.2 | 71.6 | 93.7 | |||||
| P-Ⅱ(B2') | -1292.086332 | -1292.148290 | -162.7 | 101.3 | 107.9 | |||||
| Ce3O6(C) | -1877.475699 | -1877.492891 | -45.1 | |||||||
| Ce3O6(C)+CH4 | -1917.985384 | -1918.055610 | -184.3 | 0 | 0 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.978710 | -1918.055626 | -201.9 | 17.5 | -0.1 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.979392 | -1918.053792 | -195.3 | 15.7 | 4.7 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.977104 | -1918.056477 | -208.4 | 21.7 | -2.4 | |||||
| vdw-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.978539 | -1918.055939 | -203.2 | 18.0 | -0.9 | |||||
| TS-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.917443 | -1917.999296 | -214.9 | 178.4 | 147.8 | |||||
| TS-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.926594 | -1918.000597 | -194.3 | 154.4 | 144.4 | |||||
| TS-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.922263 | -1917.998085 | -199.1 | 165.7 | 150.9 | |||||
| TS-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.922012 | -1918.001456 | -208.6 | 166.4 | 142.1 | |||||
| P-Ⅰ(T1) | -1917.948078 | -1918.026277 | -205.3 | 97.9 | 76.9 | |||||
| P-Ⅱ(B3) | -1917.944706 | -1918.016064 | -187.4 | 106.8 | 103.7 | |||||
| P-Ⅲ(B2) | -1917.951740 | -1918.016930 | -171.2 | 88.3 | 101.4 | |||||
| P-Ⅳ(B2') | -1917.934711 | -1918.012010 | -202.9 | 133.0 | 114.4 | |||||
| [1] | Rodriguez J. A., Ma S., Liu P., Hrbek J., Evans J., Perez M., Science, 2007, 318, 1757—1760 |
| [2] | Kaspar J., Fornasiero P., Graziani M., Catal. Today, 1999, 50, 285—298 |
| [3] | Zhang H. L., Ren L. H., Lu A. H., Li W. C., Chin. J. Catal., 2012, 33, 1125—1132 |
| (张慧丽, 任丽会, 陆安慧, 李文翠. 催化学报, 2012, 33, 1125—1132) | |
| [4] | Zhang B., Li D., Wang X. Y., Catal. Today, 2010, 158, 348—353 |
| [5] | Cargnello M., Jaen J. J. D., Garrido J. C. H., Bakhmutsky K., Montini T., Gamez J. J. C., Gorte R. J., Fornasiero P., Science, 2012, 337, 713—717 |
| [6] | Gennard S., Cora F., Catlow C. R. A., J. Phys. Chem. B, 1999, 103, 10158—10170 |
| [7] | Skorodumova N. V., Simak S. I., Lundqvist B. I., Abrikosov I. A., Johansson B., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2002, 89(16), 166601-1—166601-4 |
| [8] | Skorodumova N. V., Baudin M., Hermansson K., Phys. Rev. B, 2004, 69(7), 075401-1—075401-8 |
| [9] | Chen H. L., Peng W. T., Ho J. J., Hsieh H. M., Chem. Phys., 2008, 348, 161—168 |
| [10] | Chen H. T., Choi Y., Liu M., Lin M. C., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111, 11117—11122 |
| [11] | Chen H. L., Liu S. H., Ho J. J., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2006, 110, 14816—14823 |
| [12] | Wu X. N., Zhao Y. X., Xue W., Wang Z. C., He S. G., Ding X. L., Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12, 3984—3997 |
| [13] | Frisch M.J., Trucks G. W., Schlegel H. B., Scuseria G. E., Robb M. A., Cheeseman J. R., Montgomery J. A., Vreven T., Kudin K. N., Burant J. C., Millam J. M., Iyengar S. S., Tomasi J., Barone V., Mennucci B., Cossi M., Scalmani G., Rega N., Petersson G. A., Nakatsuji H., Hada M., Ehara M., Toyota K., Fukuda R., Hasegawa J., Ishida M., Nakajima T., Honda Y., Kitao O., Nakai H., Klene M., Li X., Knox J. E., Hratchian H. P., Cross J. B., Bakken V., Adamo C., Jaramillo J., Gomperts R., Stratmann R. E., Yazyev O., Austin A. J., Cammi R., Pomelli C., Ochterski J. W., Ayala P. Y., Morokuma K., Voth G. A., Salvador P., Dannenberg J. J., Zakrzewski V. G., Dapprich S., Daniels A. D., Strain M. C., Farkas O., Malick D. K., Rabuck A. D., Raghavachari K., Foresman J. B., Ortiz J. V., Cui Q., Baboul A. G., Clifford S., Cioslowski J., Stefanov B. B., Liu G., Liashenko A., Piskorz P., Komaromi I., Martin R. L., Fox D. J., Keith T., Al-Laham M. A., Peng C. Y., Nanayakkara A., Challacombe M., Gill P. M. W., Johnson B., Chen W., Wong M. W., Gonzalez C., Pople J. A., Gaussian 03, Revision B. 04, Wallingford CT, Gaussian Inc., 2004 |
| [14] | Lee C. T., Yang W. T., Parr R. G., Phys. Rev. B, 1988, 37(2), 785—789 |
| [15] | Becke A. D., J. Chem. Phys., 1993, 98, 5648—5652 |
| [16] | Golden D. M., Denson S. W., Chem. Rev., 1969, 69, 125—137 |
| [17] | Kordis J., Gingerich K. A., J. Chem. Phys., 1977, 66, 483—491 |
| [18] | Harris N., Shaik S., Schroder D., Schwarz H., Helv. Chim. Acta, 1999, 82, 1784—1797 |
| [19] | Hwang D. Y., Mebel A. M., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2002, 106, 12072—12083 |
| [20] | Wang Y. G., Yang X. F., Hu L. H., Li Y. D., Li J., Chin. J. Catal., 2014, 35, 462—467 |
| (王阳刚, 杨水峰, 胡林华, 李亚栋, 李隽. 催化学报, 2014, 35, 462—467) | |
| [21] | Meng L., Lin J. J., Pu Z. Y., Luo L. F., Jia A. P., Huang W. X., Luo M. F., Lu J. Q., Appl. Catal. B: Environ., 2012, 119, 117—122 |
| [22] | Zuo Y., Huang X. S., Li L. P., Li G. S., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2013, 1(2), 374—380 |
| [23] | Ding X. L., Wu X. N., Zhao Y. X., He S. G., Acc. Chem. Res., 2012, 45, 382—390 |
| [24] | Fu G., Chen Z. N., Xu X., Wan H. L., J. Phys. Chem. A, 2008, 112(4), 717—721 |
| [1] | 何鸿锐, 夏文生, 张庆红, 万惠霖. 羟基氧化铟团簇与二氧化碳和甲烷作用的密度泛函理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(8): 20220196. |
| [2] | 周雷雷, 程海洋, 赵凤玉. Pd基多相催化剂上CO2加氢反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220279. |
| [3] | 周紫璇, 杨海艳, 孙予罕, 高鹏. 二氧化碳加氢制甲醇多相催化剂研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220235. |
| [4] | 杨丹, 刘旭, 戴翼虎, 祝艳, 杨艳辉. 金团簇电催化二氧化碳还原反应的研究进展[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(7): 20220198. |
| [5] | 任娜娜, 薛洁, 王治钒, 姚晓霞, 王繁. 热力学数据对1, 3-丁二烯燃烧特性的影响[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220151. |
| [6] | 宋颖颖, 黄琳, 李庆森, 陈立妙. CuO/BiVO4光催化剂的制备及光催化CO2还原性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20220126. |
| [7] | 常云飞, 廖明义, 温佳明. NaBH4/MCl x 体系对液体端羧基氟橡胶的还原及还原机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(6): 20210835. |
| [8] | 黄汉浩, 卢湫阳, 孙明子, 黄勃龙. 石墨炔原子催化剂的崭新道路:基于自验证机器学习方法的筛选策略[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(5): 20220042. |
| [9] | 王明智, 郑燕萍, 翁维正. CeO2负载的PdO与Ce1‒x Pd x O2‒δ 物种的甲烷催化燃烧性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(4): 20210816. |
| [10] | 张诗昱, 何润合, 李永兵, 魏士俊, 张兴祥. 辐照交联制备低分子量聚丙烯腈纤维锂硫电池正极材料及其储硫机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210632. |
| [11] | 闭格宁, 肖小华, 李攻科. 微波辅助萃取多物理场耦合模型的构建及验证[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(3): 20210739. |
| [12] | 孙翠红, 吕立强, 刘迎, 王妍, 杨静, 张绍文. 硝酸异丙酯与Cl原子、 OH和NO3自由基反应的机理及动力学[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(2): 20210591. |
| [13] | 常斯惠, 陈涛, 赵黎明, 邱勇隽. 离子液体增塑生物基聚丁内酰胺的热分解机理[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220353. |
| [14] | 温志国, 谯在银, 田冲, Borzov Maxim, 聂万丽. FLPs催化烯胺还原活性研究及反应机理探讨[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220555. |
| [15] | 刘洋, 李旺昌, 张竹霞, 王芳, 杨文静, 郭臻, 崔鹏. Sc3C2@C80与[12]CPP纳米环之间非共价相互作用的理论研究[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2022, 43(11): 20220457. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||