

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2020, Vol. 41 ›› Issue (11): 2356.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20200319
Previous Articles Next Articles
SHAO Wei, LEE Jiyoung, LI Fangyuan, LING Daishun( )
)
Received:2020-06-02
Online:2020-11-10
Published:2020-11-06
Contact:
LING Daishun
E-mail:lingds@zju.edu.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
SHAO Wei, LEE Jiyoung, LI Fangyuan, LING Daishun. Organic Small Molecule Nanoparticles for Phototheranostics[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2356.
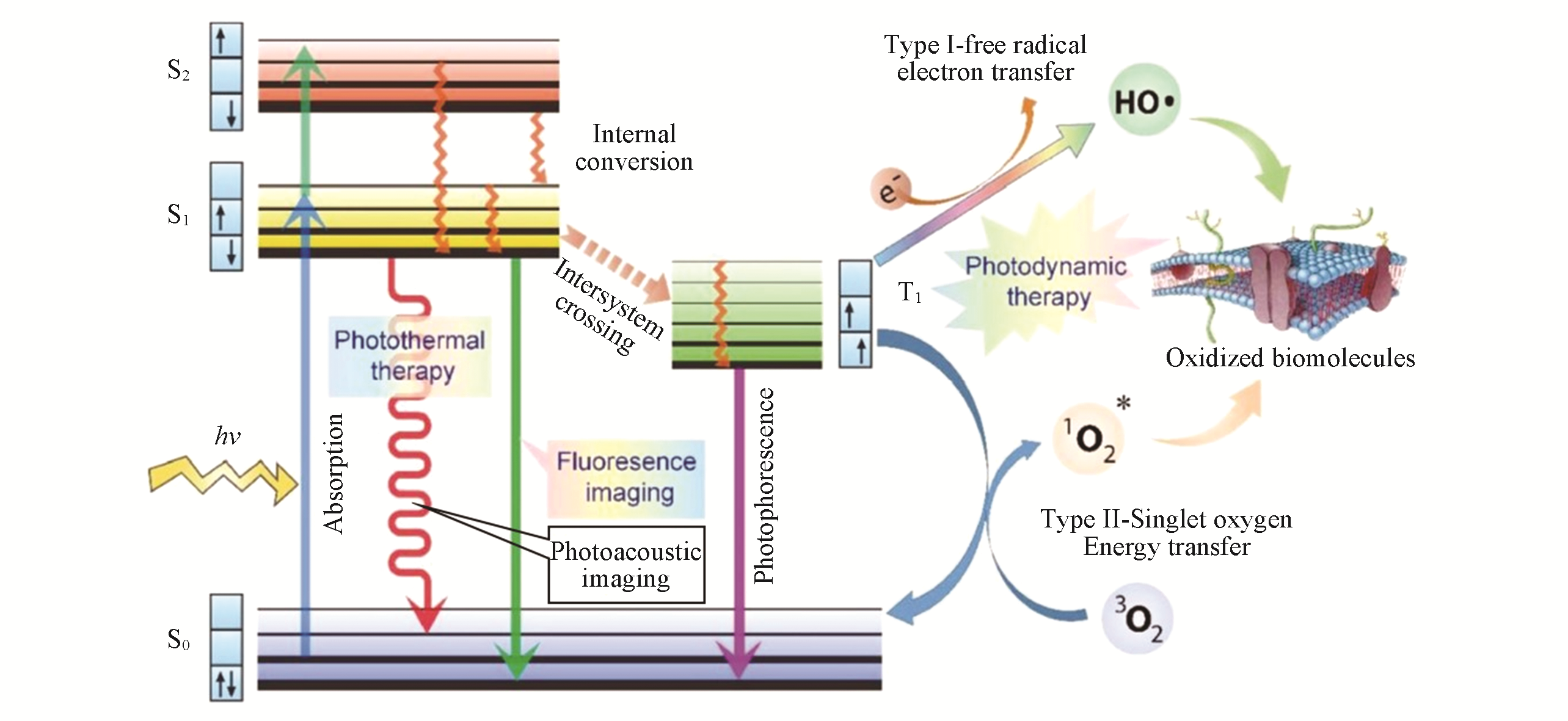
Fig.1 Jablonski diagram showing different photophysical and photochemical processes of photosensitizers under laser excitation employed in phototheranostics[23]Copyright 2017, Wiley?VCH.
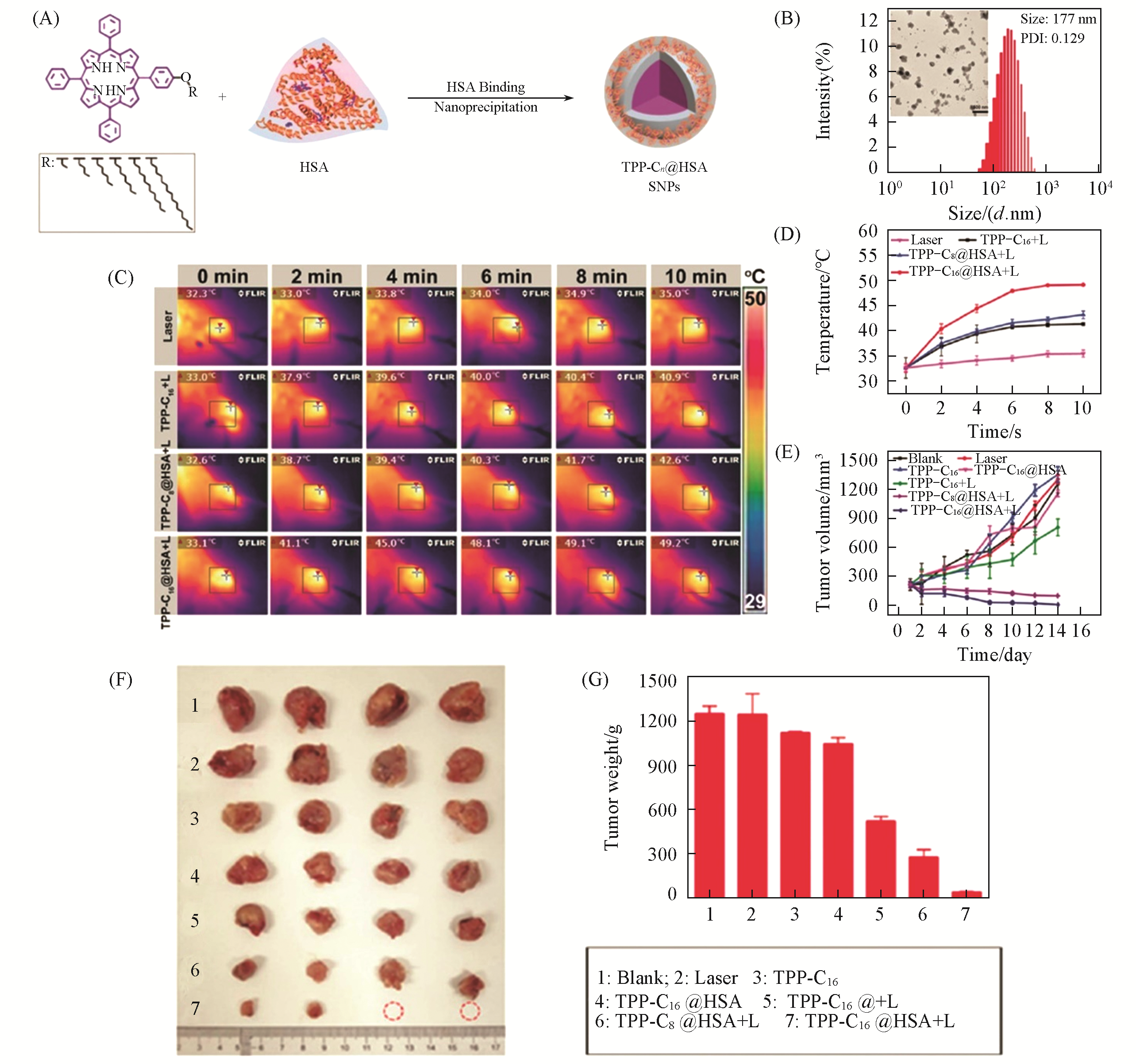
Fig.4 TPP?Cn@HSA SNPs for photothermal therapy[94](A) Self-assembly of the porphyrin derivatives and HSA into NPs (TPP-Cn@HSA SNPs); (B) size distribution and transmission electron microscopy(TEM) image of TPP-C16@HSA SNPs; (C) infrared thermal images of tumor-bearing mice treated with laser only, TPP-C16 NPs, TPP-C8@HSA SNPs, and TPP-C16@HSA SNPs plus irradiation, respectively; (D) temperature changes of tumor locations upon irradiation monitored by an infrared thermal camera in different groups; (E) relative tumor volumes; (F) tumor photographs; (G) tumor weight changes of mice treated with control, light illumination, TPP-C16, TPP-C16@HSA,TPP-C16+L, TPP-C8@HSA+L, and TPP-C16@HSA+L.Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry.
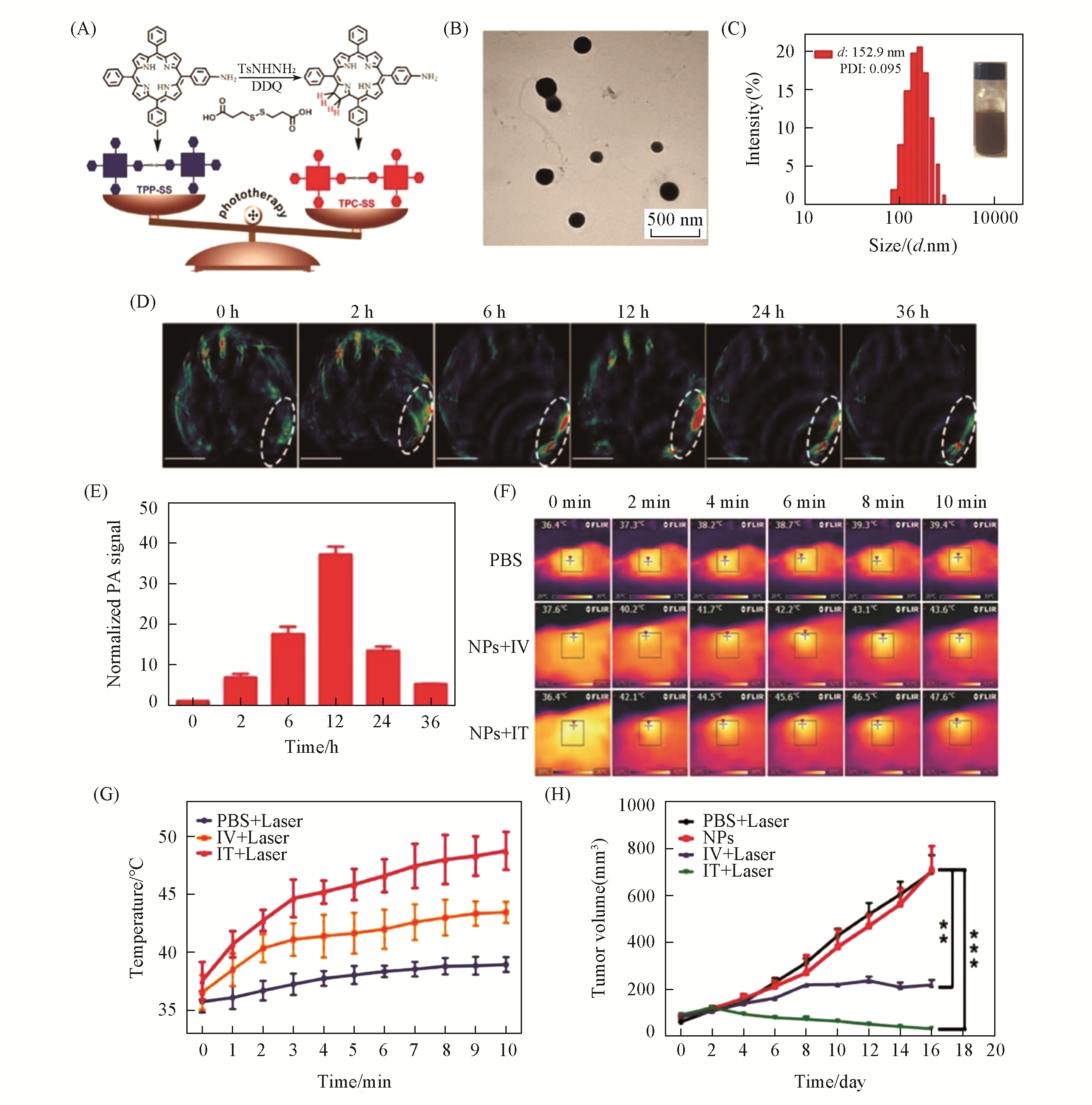
Fig.5 TPC?SS NPs for PAI?guided photothermal therapy[31](A) Schematic illustrations of the synthetic procedures of TPP-SS and TPC-SS; (B) TEM image of TPC-SS NPs; (C) DLS profile of TPC-SS NPs; (D) In vivo photoacoustic(PA) imaging of tumor tissue before and after i.v. injection of TPC-SS NPs upon 680 nm laser irradiation at different time points(0, 2, 6, 12, 24, and 36 h); (E) normalized PA signals in the tumor at different times; (F) infrared thermal images of U14 tumor-bearing mice injected with phosphate buffer saline(PBS) and TPC-SS NPs by intravenous and intratumor injection,respectively, exposed to 635 nm laser at a power density of 360 and 240 J/cm2 recorded at different time intervals, respectively; (G) temperature of tumors monitored by the infrared thermal camera in different groups upon laser irradiation; (H) relative tumor volume changes of mice treated with PBS+laser, only TPC-SS NPs, TPC-SS NPs by intravenous injection+laser and TPC-SS NPs by intratumor injection+Laser, statistical significance: **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001.Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
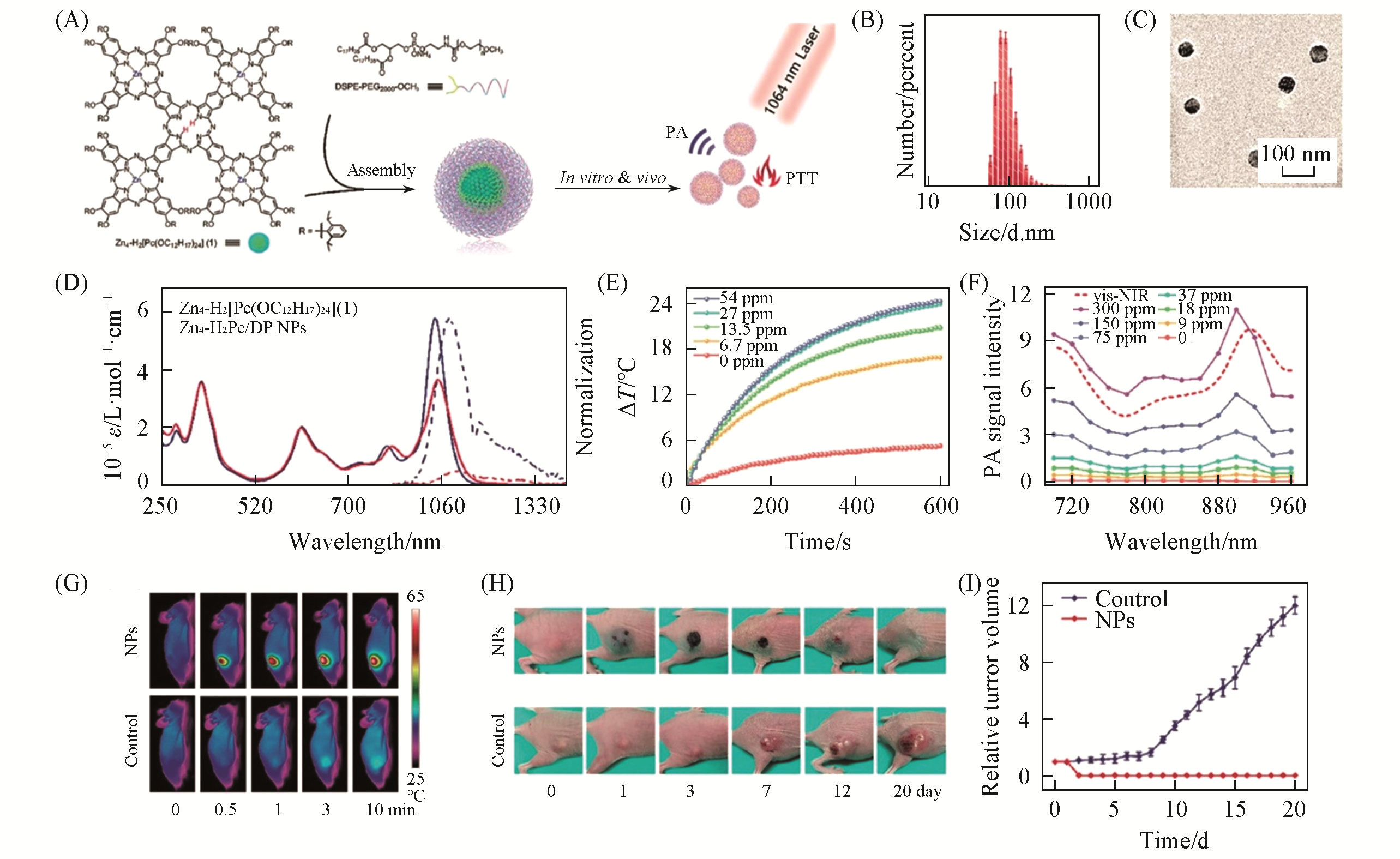
Fig.6 Zn4?H2Pc/DP NP for PAI?guided NIR?Ⅱ photothermal therapy[93](A) Illustration of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NP fabrication for photothermal therapy and photoacoustic imaging; (B) DLS profile of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NP; (C) TEM image of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NP; (D) UV-Vis-NIR absorption and fluorescence emission spectra of Zn4-H2· [Pc(OC12H17)24](1) in CH2Cl2 and Zn4-H2Pc/DP NPs in water, respectively; (E) temperature change curves of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NPs exposed to the 1064 nm laser at various concentrations(0.9 W/cm2, 10 min); (F) photoacoustic spectra of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NPs in the water at various concentrations(dashed line: vis-NIR absorption spectrum of Zn4-H2Pc/DP NPs); (G) IR thermal images of mice under irradiation at varied time intervals(0, 0.5, 1, 3 and 10 min); (H) digital photos of mice before and after treatment at varied time intervals(0, 1, 3, 7, 12 and 20 day); (I) tumor growth curves of mice in control and NPs after treatment (n=5).Copyright 2019, Royal Socity of Chemistry.
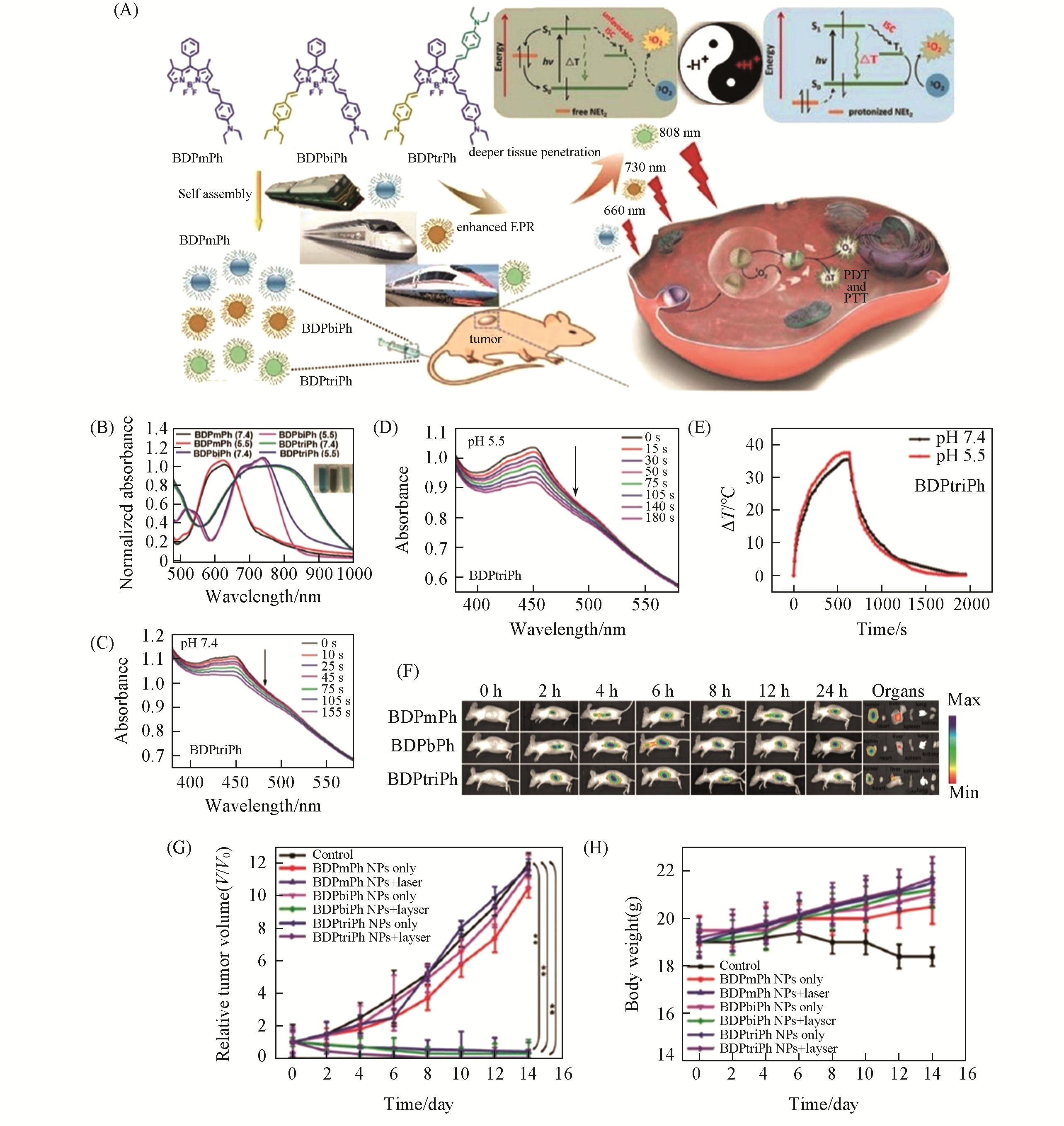
Fig.7 Penetration depth?tunable BODIPY?based nanoparticles for phototherapy[125](A) Schematic illustration of the preparation and application of BDPmPh, BDPbiPh, and BDPtriPh NPs and the mechanism of pH-triggered enhanced PTT/PDT; (B) normalized absorption spectra of BDPmPh, BDPbiPh, and BDPtriPh NPs in PBS at different pH(7.4 and 5.5); (C) degradation of 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran(DPBF) in the presence of BDPtriPh NPs in PBS at pH of 7.4; (D) degradation of DPBF in the presence of BDPtriPh NPs in PBS at pH of 5.5; (E) photothermal heating curves of BDPtriPh NPs in PBS at different pH(7.4 and 5.5); (F) In vivo fluorescence images of mice treated with BDPmPh, BDPbiPh, and BDPtriPh NPs for different times and biodistribution of the NPs in tumors and major organs;(G) tumor growth curves of the mice in different groups during the treatments;(H) body weight changes of the mice in different groups during the treatments.Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry.
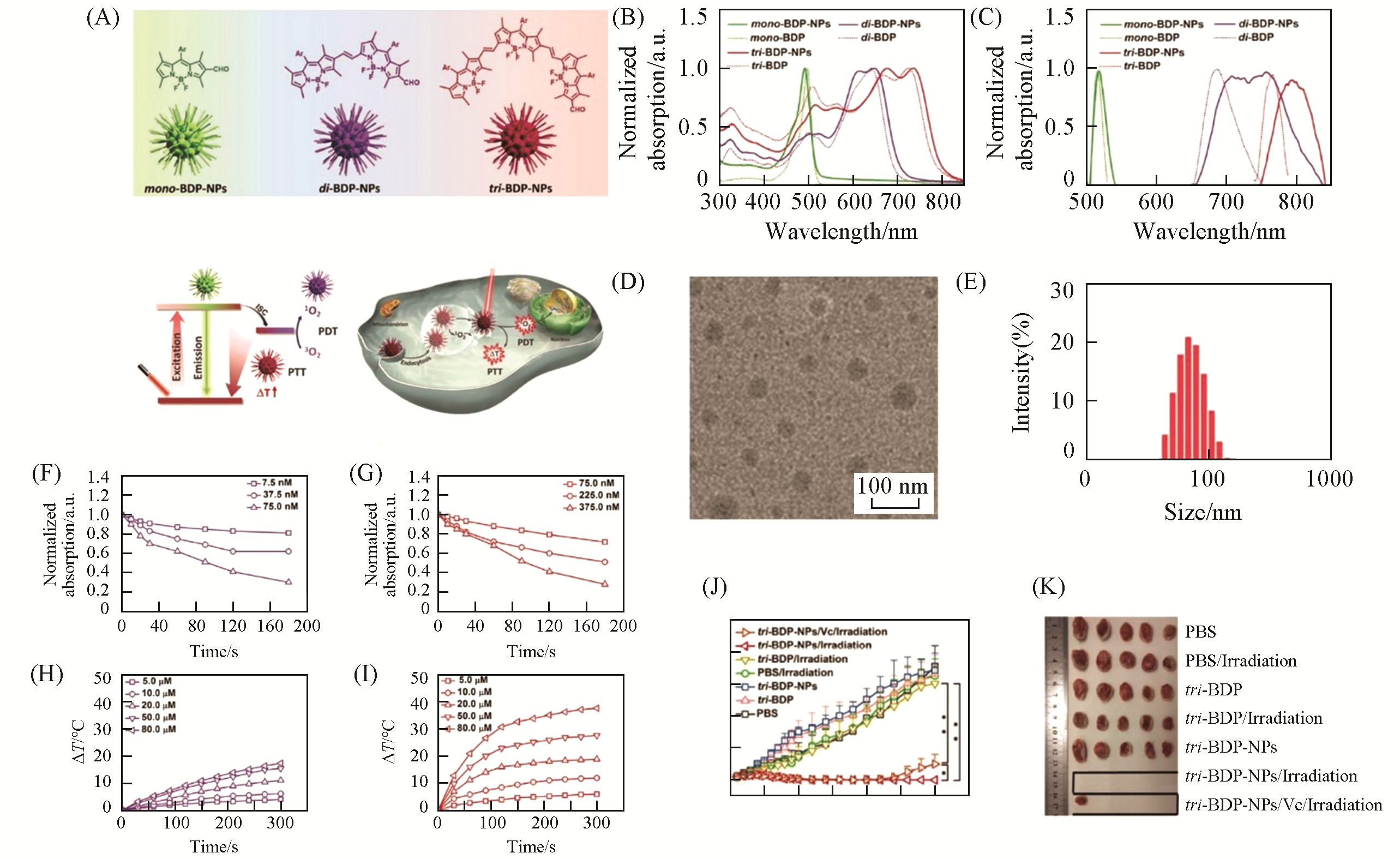
Fig.8 BODIPY?based nanoparticles with tunable phototherapeutic effect[123](A) The chemical structures and nanoparticles of CPs, photoconversion routes of the CPs, and synergistic PTT/PDT of tri-BDP-NPs against tumor cells under laser irradiation; normalized absorption spectra(B) and emission spectra(C) of mono-BDP-NPs, di-BDP-NPs, and tri-BDP-NPs as compared to free mono-BDP, di-BDP, and tri-BDP in DMSO; (D) TEM image of tri-BDP-NPs; (E) size distribution of tri-BDP-NPs determined by DLS; normalized absorbance of DPBF at 410 nm in the solutions of di-BDP-NPs(F) and tri-BDP-NPs(G) at different concentrations under 660 or 785 nm laser irradiation(0.5 W/cm2, 3 min); temperature elevations of di-BDP-NPs(H) and tri-BDP-NPs(I) under 660 or 785 nm laser irradiation(0.5 W/cm2, 5 min); (J) tumor growth curves of the mice in different groups; (K) photograph of tumors of the mice in different groups at the end of treatments.Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
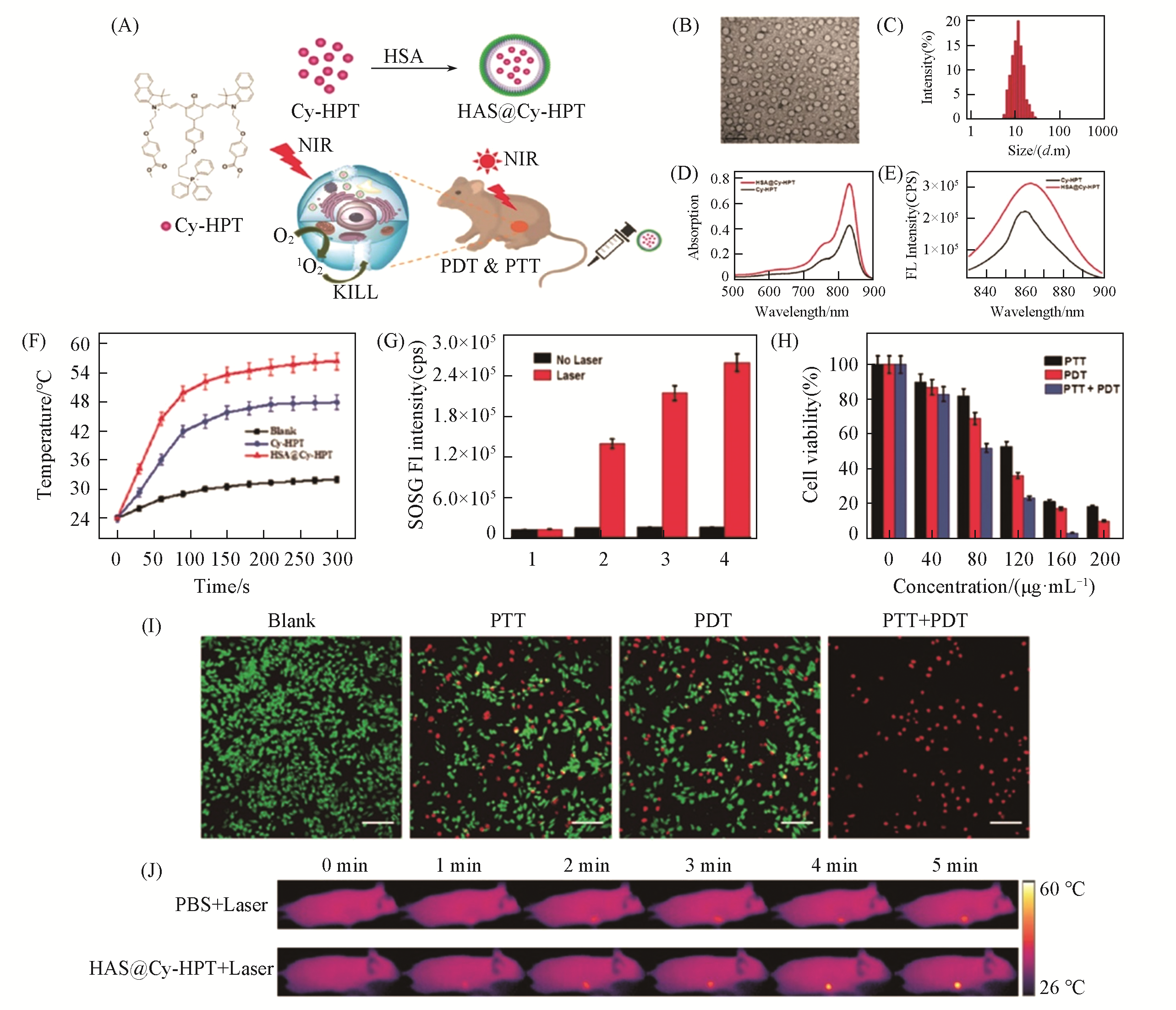
Fig.9 HSA@Cy?HPT for PTT and PDT[152](A) The chemical structure of Cy-HPT, preparation of HSA@Cy-HPT and NIR laser-induced PTT/PDT of HSA@Cy-HPT; (B) TEM image of HSA@Cy-HPT, scale bar: 20 nm; (C) size distribution of HSA@Cy-HPT determined by DLS;(D) absorption spectra of Cy-HPT and HSA@Cy-HPT;(E) fluorescence spectra of Cy-HPT and HSA@Cy-HPT;(F) photothermal heating curves of Cy-HPT, HSA@Cy-HPT and blank sample under laser irradiation;(G) fluorescence intensity of SOSG: 1. blank, 2. ICG,3. Cy-HPT and 4.HSA@Cy-HPT;(H) MTT assay results of PTT, PDT and synergistic PTT/PDT treatments with HSA@Cy-HPT in HepG2 cells; (I) fluorescence images of CalceinAM/PI co-stained HepG2 cells after PTT, PDT or synergistic PTT/PDT treatments with HSA@Cy-HPT; scale bar: 60 μm; (J) infrared thermographs of subcutaneous HepG2 tumor xenograft mice during a 5 min NIR laser irradiation.Copyright 2019, Royal Society of Chemistry.
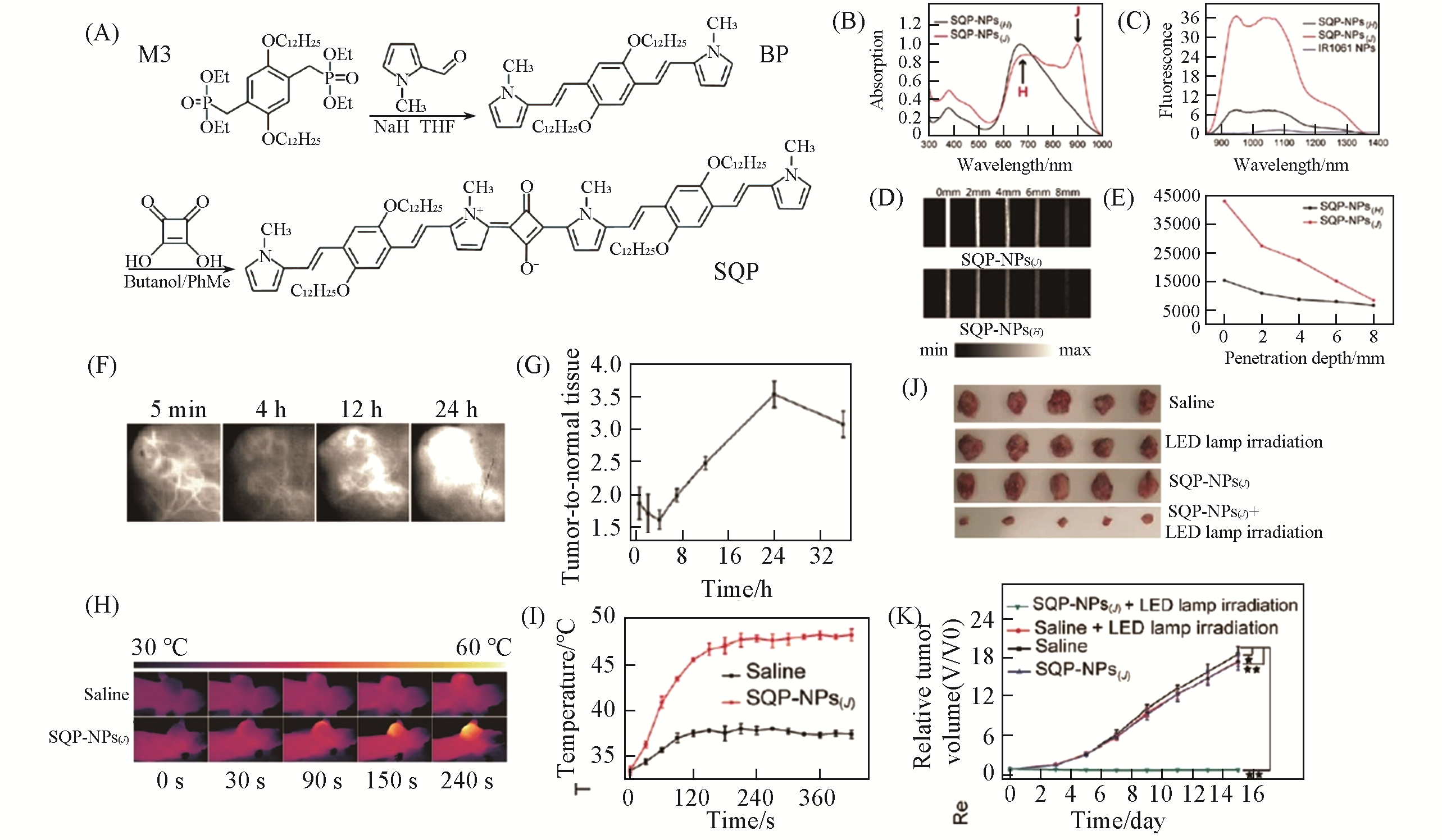
Fig.10 SQP?NPs(J) for NIR?II fluorescence imaging?guided PTT[165](A) Synthesis of SQP; (B) UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of the SQP-NPs(J) and SQP-NPs(H); (C) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence emission spectra of the SQP-NPs(J), SQP-NPs(H), and IR1061 NPs at the same concentration of 10μg/mL under 808 nm excitation; (D) NIR-II fluorescence images of the SQP-NPs(J) andSQP-NPs(H) at different depths; (E) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence intensity of the SQP-NPs(J) and SQP-NPs(H) at different depths; (F) NIR-Ⅱ fluorescence images of tumor sites at different times after administrating SQP-NPs(J); (G) tumor-to-normal tissue ratio of the tumor sites at different times after intravenous injection of SQP-NPs(J); (H) infrared thermographs of the tumor bearing mice after intravenous injection of saline and SQP-NPs(J) under laser irradiation(810 nm, 0.8 W·cm-2) at indicated time points; (I) temperature elevation curves of the tumors of the mice treated with saline and SQP-NPs(J) under laser irradiation; (J) photographs of the tumors of the mice in different groups after treatments; (K) tumor growth curves of the mice in different groups.Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry.
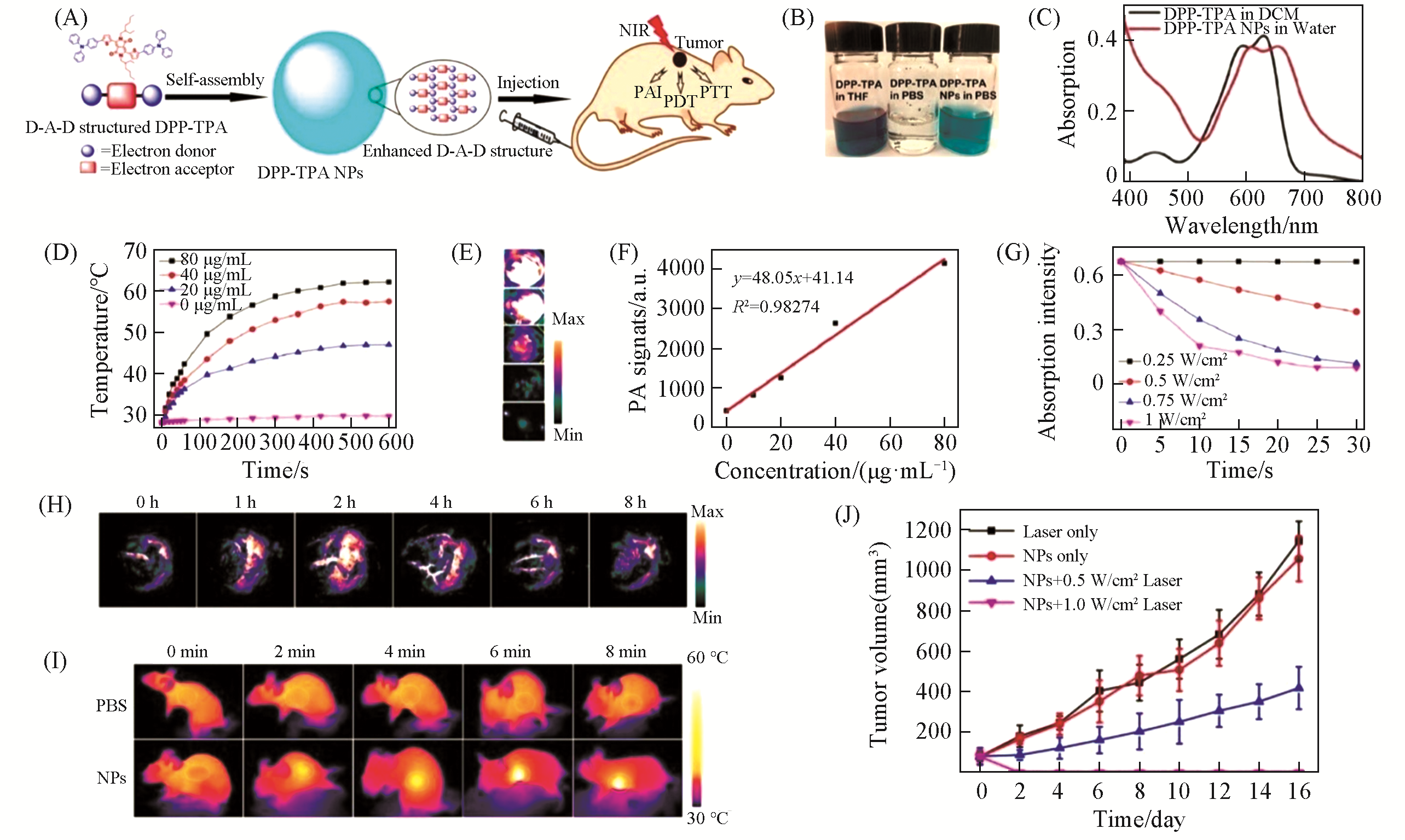
Fig.11 DPP?TPA NPs for PAI?guided synergistic PTT/PDT[58](A) Schematic demonstration of DPP-TPA NPs as phototheranostic agents for PAI-guided PTT/PDT; (B) photographs of DPP-TPA in THF and PBS, and DPP-TPA NPs in PBS; (C) UV-Vis absorption spectra of DPP-TPA in dichloromethane (DCM) and DPP-TPA NPs in PBS; (D) photothermal heating curves of DPP-TPA NPs with different concentrations(660 nm, 1.0 W/cm2); (E) PA images of DPP-TPA NPs with different concentrations; (F) linear relationship between the PA signal intensity and DPP-TPA NPs concentration; (G) absorption of DPP-TPA at 418 nm mixed with DPBF in DCM over time under 660 nm laser irradiation; (H) PA images of tumor sites at different time intervals after intravenous injection of DPP-TPA NPs into tumor-bearing mice; (I) infrared thermographs of tumor sites after injecting PBS and DPP-TPA NPs for 2 h under different laser irradiation times; (J) tumor volume changes of the mice in different groups.Copyright 2016, American Chemical Society.
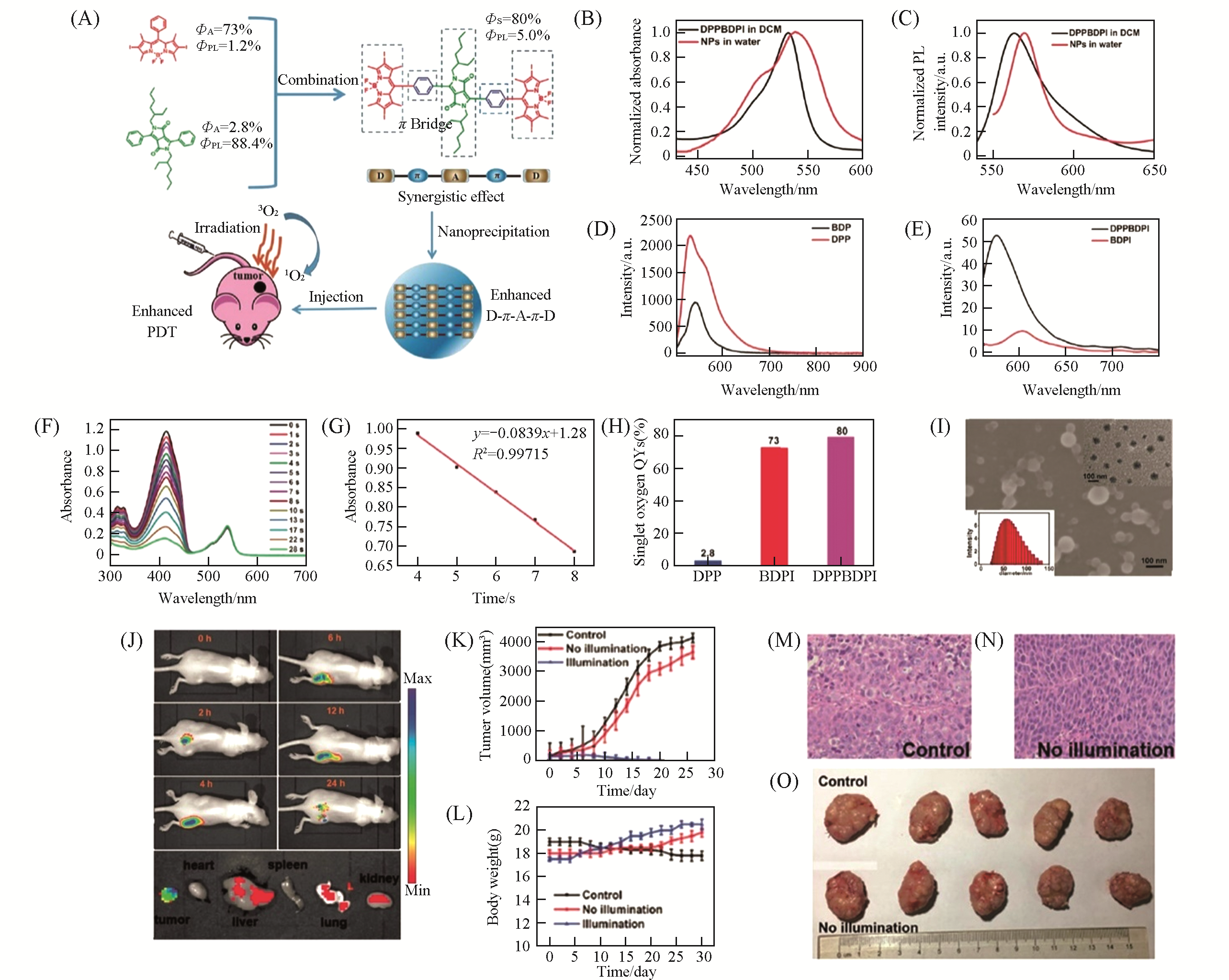
Fig.12 DPPBDPI NPs for enhanced PDT[67](A) Schematic illustration of the DPPBDPI NPs with enhanced 1O2 and fluorescence quantum yields as a theranostic agent for PDT. Normalized absorption(B) and emission spectra(C) of DPPBDPI in DCM and DPPBDPI NPs in water; (D) emission spectra of DPP and BDP in DCM, showing absolute PL quantum yields of 88.4% and 24.7%,respectively; (E) emission spectra of boron dipyrrome-thene(BDPI) and DPPBDPI, showing absolute photoluminescence(PL) quantum yields of 1.2% and 5.0%, respectively; (F) the degradation of DPBF in the presence of DPPBDPI in DCM and xenon lamp irradiation; (G) linear fit of the absorption and the irradiation time; (H) singlet oxygen quantum yields of DPP, BDPI and DPPBDPI; (I) scanning electron microscopy(SEM), transmission electron microscopy(TEM) and dynamic light scattering(DLS) of DPPBDPI NPs; (J) in vivo time-dependent fluorescence imaging and biodistribution of DPPBDPI NPs in the tumor, heart, liver, spleen, lung and kidney after injection for 24 h; (K) tumor volume change during treatment over a month; (L) the body weight change reported every two days; (M, N) H&E staining of the tumor histologic section for the control(M) and no illumination groups(N); (O) photographs of the tumors of the sacrificed mice after treatment.Copyright 2018, Royal Society of Chemistry.
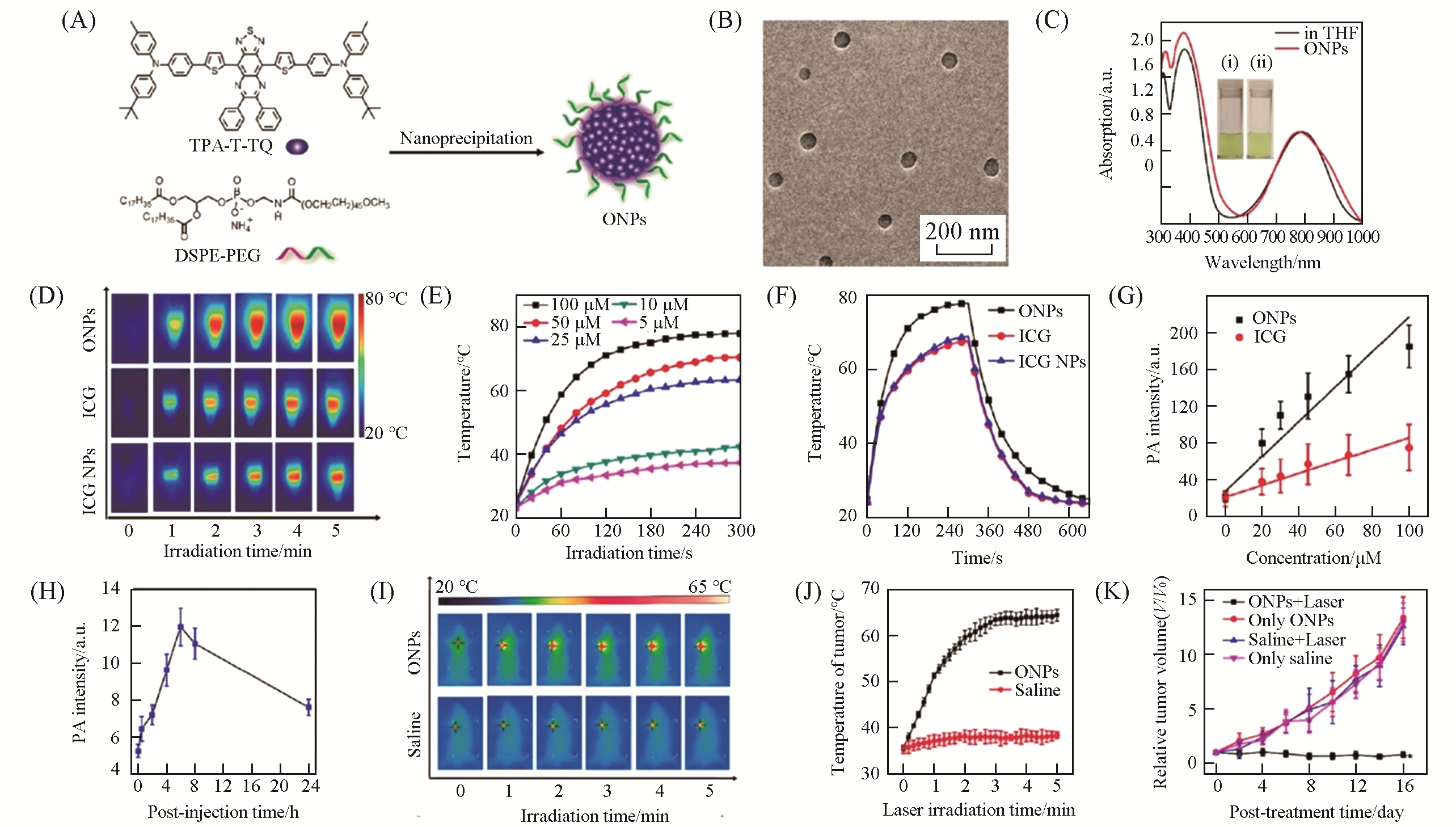
Fig.13 ONPs for PAI?guided PTT[63](A) Chemical structure of TPA-T-TQ and the nanoprecipitation method for the preparation of TPA-T-TQ ONPs; (B) TEM image of TPA-T-TQ ONPs; (C) UV-Vis-NIR absorption spectra of TPA-T-TQ in THF and TPA-T-TQ ONPs in water; (D) infrared thermographs of ICG, ICG NPs, and TPA-T-TQ ONPs under laser irradiation(808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2) for different times; (E) the photothermal heating curves of TPA-T-TQ ONPs with different concentrations(808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2); (F) comparison of the photothermal effects of ICG, ICG NPs, and TPA-T-TQ ONPs with the same concentration (100 μmol/L) under laser irradiation (808 nm 0.8 W/cm2); (G) PA intensities of ICG and TPA-T-TQ ONPs versus their concentrations; (H) PA intensity at the tumor site versus the time post-injection; (I) infrared thermographs of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice under laser irradiation(808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2) for different times; (J) the temperature of tumors of the mice treated with saline and TPA-T-TQ ONPs as a function of laser irradiation time(808 nm, 0.5 W/cm2); (K) tumor growth curves of the mice in different treatment groups.Copyright 2017, American Chemical Society.
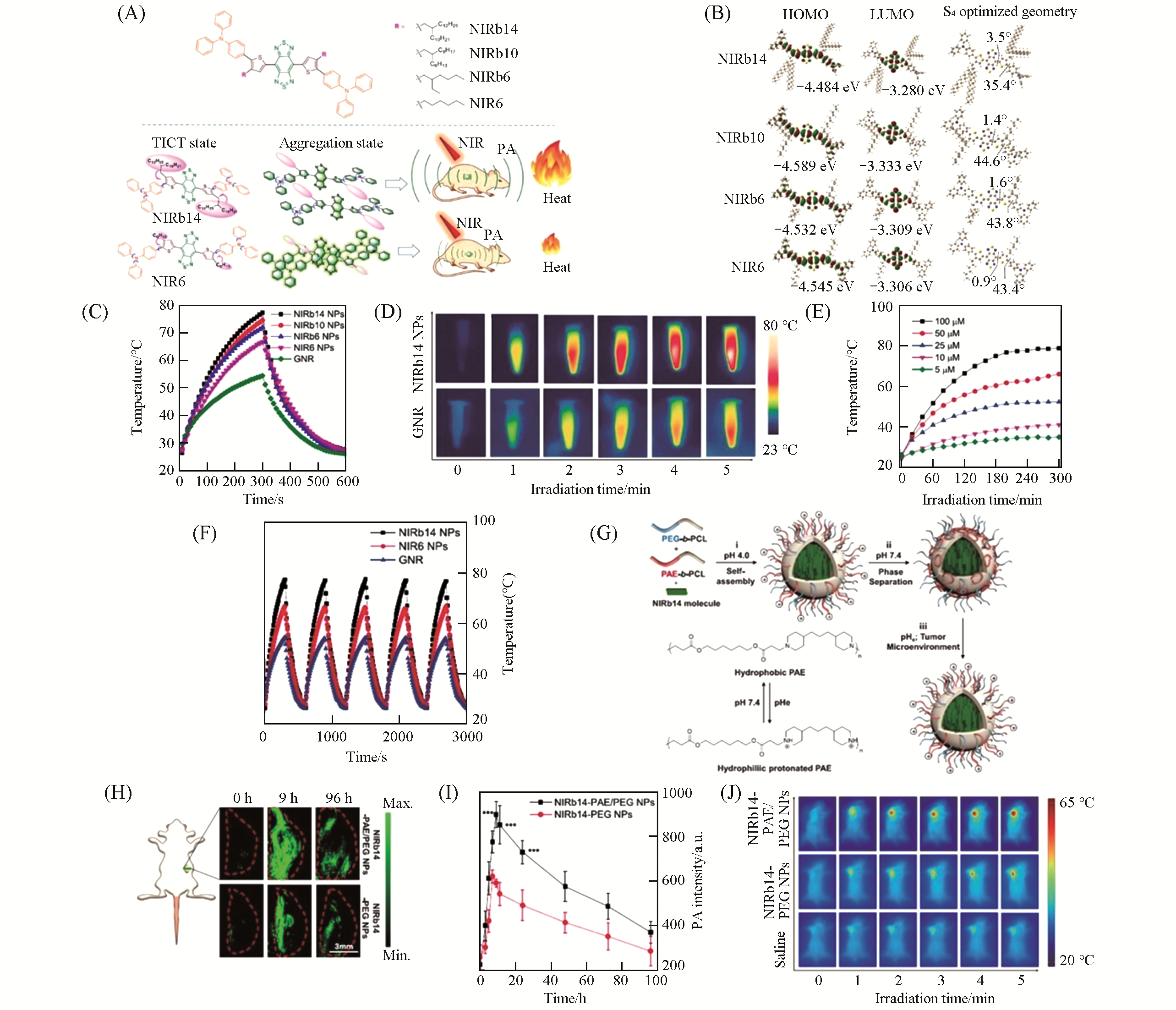
Fig.14 NIRb14 NPs for PAI?guided PTT[62](A) Chemical structures of NIRb14, NIRb10, NIRb6 and NIR6, and the schematic illustration of the TICT states of the molecules in solution and aggregation states;(B) highest occupied molecular orbital(HOMO), lowest unoccupied molecular orbital(LUMO) distributions and optimized S0 geometries of the molecules; (C) photothermal heating curves of NIRb14, NIRb10, NIRb6, NIR6 NPs, and GNRs with the same concentration(100 μmol/L, 808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2); (D) infrared thermographs of NIRb14 NPs(100 μmol/L) and GNRs under laser irradiation(808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2) for different times; (E) photothermal heating curves of NIRb14 NPs with different concentrations(808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2); (F) photothermal stability of NIRb14 NPs, NIR6 NPs, and GNRs during five heating/cooling cycles; (G) schematic illustration of the preparation of pH-responsive NIRb14-PAE/PEG NPs; (H) PA images of the tumor sites of mice before and after intravenous injection of NIRb14-PAE/PEG or NIRb14-PEG NPs; (I) PA intensity at the tumor site versus the time post-injection of NIRb14-PAE/PEG and NIRb14-PEG NPs, respectively; (J) infrared thermographs of 4T1 tumor-bearing mice under laser irradiation(808 nm, 0.8 W/cm2) for different times.Copyright 2019, American Chemical Society.
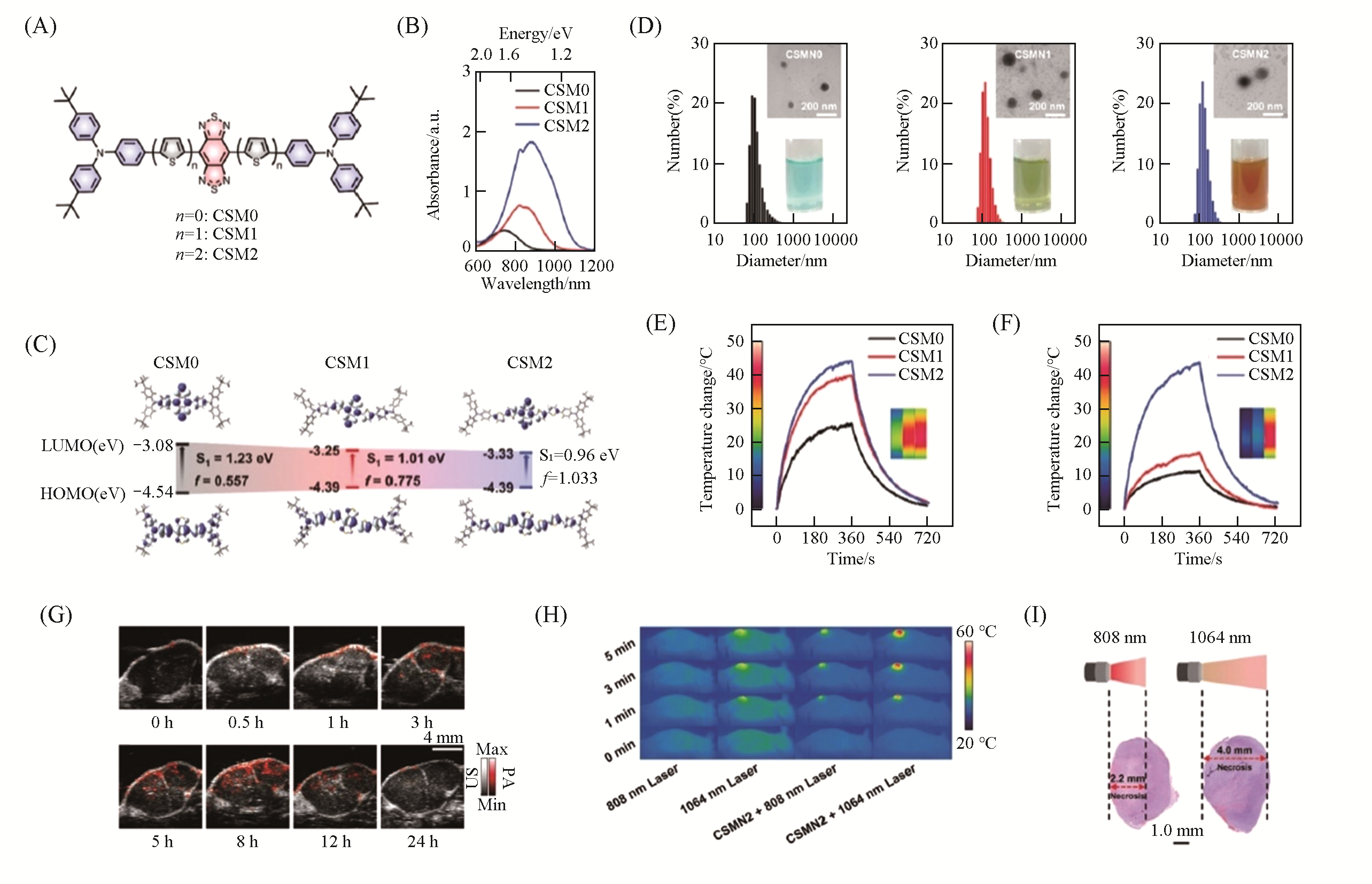
Fig.15 Molecularly engineered CSMN2 for PAI?guided NIR?II PTT[188](A) Chemical structures of CSM0—2; (B) Vis-NIR absorption spectra of CSM0—2 in chloroform; (C) frontier molecular orbital distributions, energy levels, and corresponding oscillator strengths for CSM0—2 calculated at the B3LYP/6-31G* level; (D) DLS profiles of CSMN0—2(insets are the TEM images and digital photographs of CSMN0—2 in water);photothermal heating curves of CSMN0—2(100 μmol/L) under 808(E) and 1064(F) nm laser irradiation with a power density of 1.0 W/cm2(inset shows the infrared thermographs of the samples after irradiating for 6 min, from left to right: CSMN0, CSMN1 and CSMN2, respectively); (G) PA images of the tumor site at different time intervals post-injection; (H) the infrared thermographs at the tumor sites in the groups of 808 nm laser, 1064 nm laser, CSMN2+808 nm laser and CSMN2+1064 nm laser during laser irradiation at different time intervals; (I) H&E staining of the whole tumors of the mice after the treatments of CSMN2+808 nm laser and CSMN2+1064 nm laser.Copyright 2020, Royal Society of Chemistry.
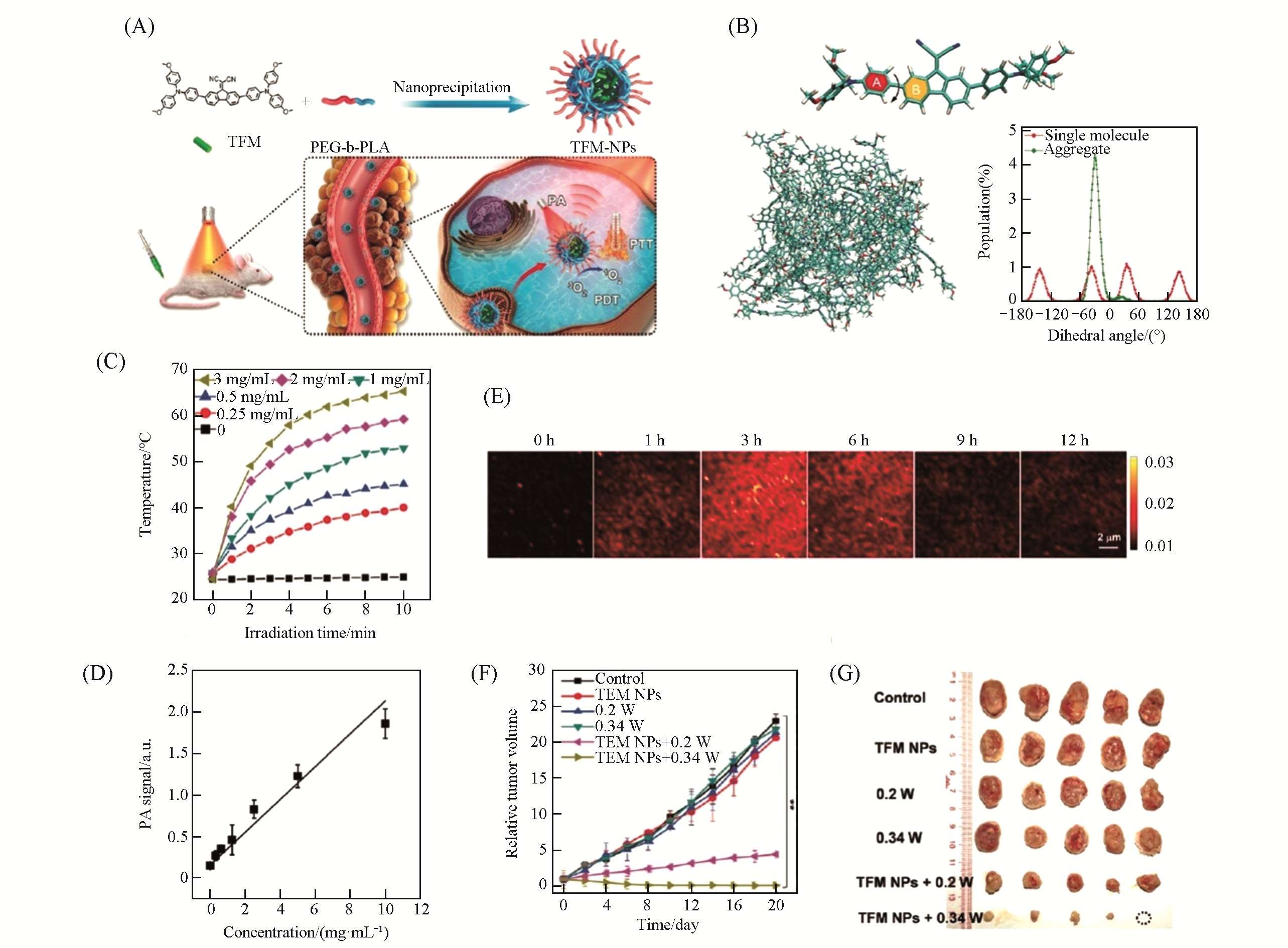
Fig.16 TFM NPs for PAI?guided PTT/PDT[72](A) Preparation of TFM NPs using nanoprecipitation method and the schematic illustration of the use of TFM NPs for PAI-guided PTT/PDT; (B) molecular dynamics(MD) simulations to study the molecular geometry of TFM in single molecular state and the packing style of TFM molecules in aggregation state; (C) photothermal heating curves of TFM NPs with different concentrations under laser irradiation(633 nm, 0.5 W/cm2); (D) PA intensities of TFM NPs at 680 nm at different concentrations; (E) PA images of EMT-6 tumor sites after intravenous injection of TFM NPs; (F) tumor growth curves of the mice in different groups; (G) tumor images collected from the mice in different groups after treatments.Copyright 2019, Wiley-VCH.
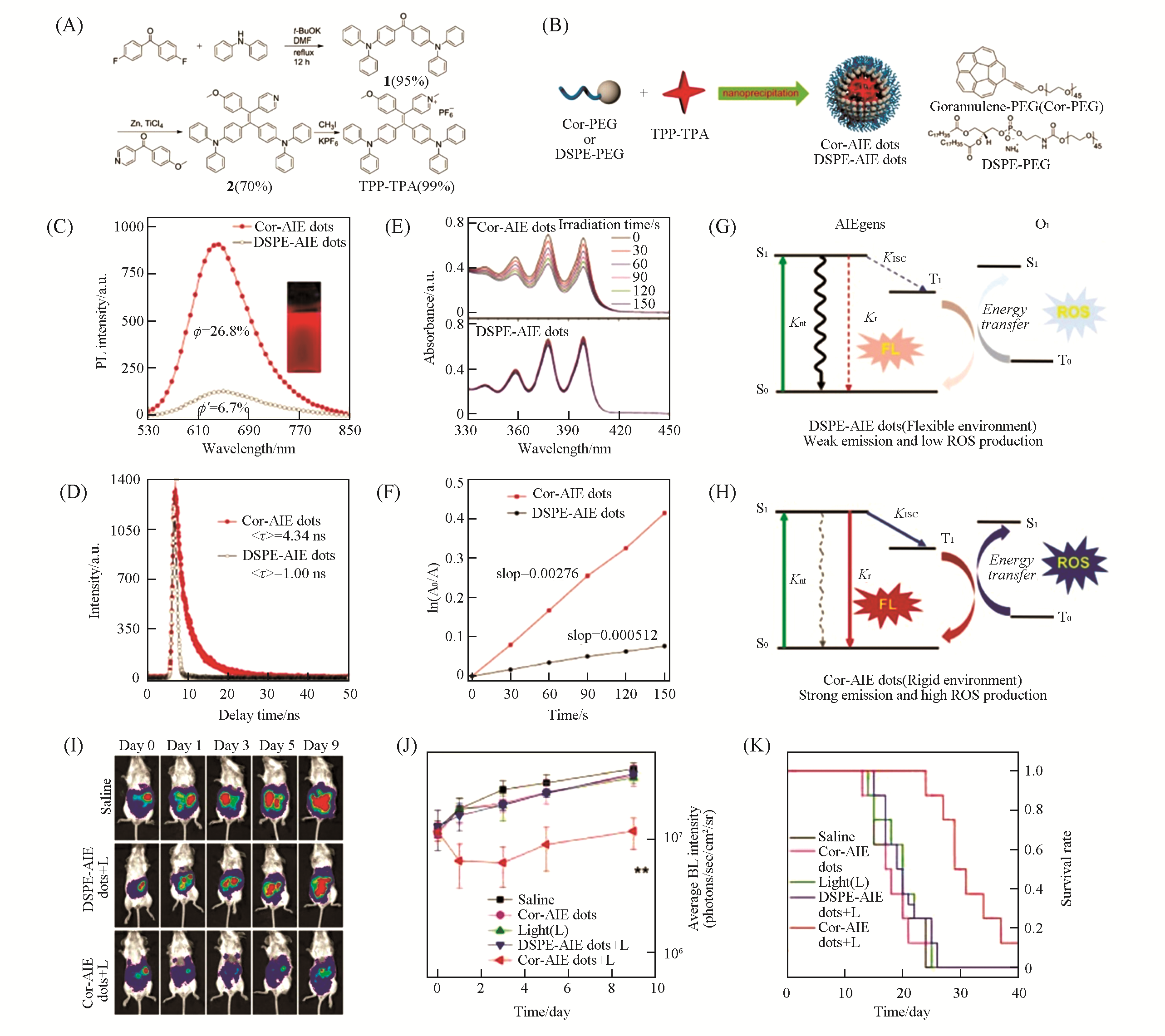
Fig.17 Cor?AIE dots for enhanced PDT[70](A) Synthesis of NIR-emissive TPP-TPA with indicated yield for each step; (B) schematic depiction of the preparation of Cor-AIE dots and DSPE-AIE dots using the nanoprecipitation method; PL(C) and fluorescence lifetime spectra(D) of Cor-AIE dots and DSPE-AIE dots; UV-Vis absorption spectra(E) and decomposition rate(F) of 9,10-anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)-dimalonic acid(ABDA) for Cor-AIE dots and DSPE-AIE dots under light irradiation; (G, H) Jablonski diagram showing the nonradiative, radiative, and ISC processes for DSPE-AIE dots and Cor-AIE dots; (I) time-dependent fluorescence images of peritoneal carcinomatosis-bearing mice in “Saline”, “DSPE-AIE dots+L” and “Cor-AIE dots+L” groups; (J) average fluorescence intensities of intraperito-neal tumors on days 0, 1, 3, 5 and 9 in different groups; (K) survival rate curves of the mice in different groups.Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
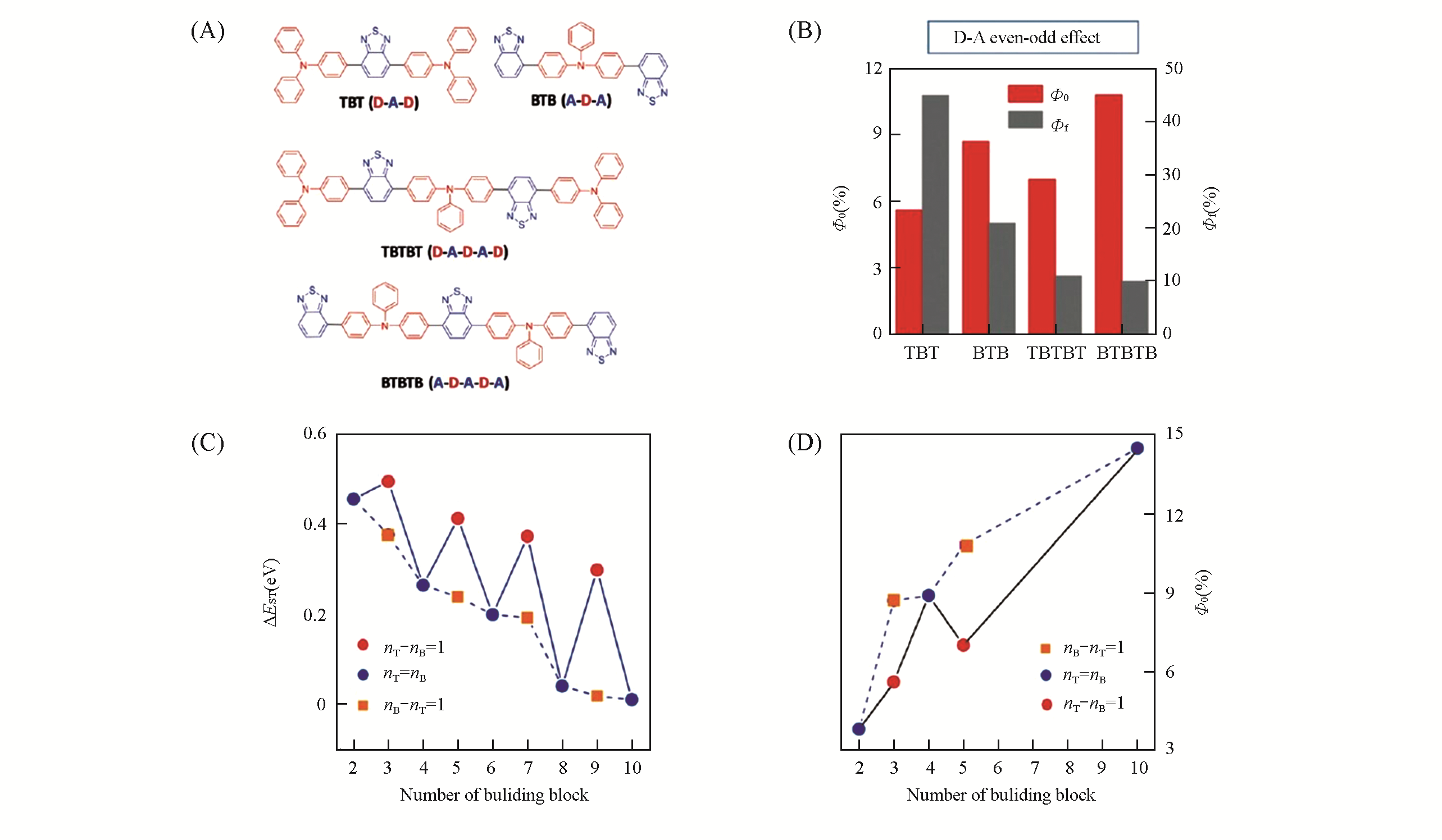
Fig.18 D?A even?odd effect on the photosensitization of the AIEgens[71]Chemical structures(A) and 1O2 and fluorescence quantum yields(B) of TBT, BTB, TBTBT and BTBTB;dependence of ΔEST(C) and 1O2 quantum yield(D) on the number of building blocks; nT =number of donor units(T); nB=number of acceptor units (B).Copyright 2018, Wiley-VCH.
| 1 | Ferrari M., Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2005, 5, 161—171 |
| 2 | Hong G., Diao S., Antaris A. L., Dai H., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10816—10906 |
| 3 | Huang X., Zhang W., Guan G., Song G., Zou R., Hu J., Acc. Chem. Res., 2017, 50, 2529—2538 |
| 4 | Kim H., Beack S., Han S., Shin M., Lee T., Park Y., Kim K. S., Yetisen A. K., Yun S. H., Kwon W., Hahn S. K., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1701460 |
| 5 | Li J., Rao J., Pu K., Biomaterials, 2018, 155, 217—235 |
| 6 | Lim E. K., Kim T., Paik S., Haam S., Huh Y. M., Lee K., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 327—394 |
| 7 | Liu Y., Bhattarai P., Dai Z., Chen X., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 2053—2108 |
| 8 | Ng K. K., Zheng G., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 11012—11042 |
| 9 | Qian J., Tang B. Z., Chem., 2017, 3, 56—91 |
| 10 | Yang B., Chen Y., Shi J., Chem., 2018, 4, 1284—1313 |
| 11 | Yang X., Yang M., Pang B., Vara M., Xia Y., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 10410—10488 |
| 12 | Zhu H., Cheng P., Chen P., Pu K., Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 746—765 |
| 13 | Cai Y., Wei Z., Song C., Tang C., Han W., Dong X., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2019, 48, 22—37 |
| 14 | He S., Song J., Qu J., Cheng Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 4258—4278 |
| 15 | Zhao J., Zhong D., Zhou S., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2018, 6, 349—365 |
| 16 | Wang L. V., Hu S., Science, 2012, 335, 1458—1462 |
| 17 | Weber J., Beard P. C., Bohndiek S. E., Nat. Methods, 2016, 13, 639—650 |
| 18 | Guo B., Chen J., Chen N., Middha E., Xu S., Pan Y., Wu M., Li K., Liu C., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1808355 |
| 19 | Jiang Y., Upputuri P. K., Xie C., Zeng Z., Sharma A., Zhen X., Li J., Huang J., Pramanik M., Pu K., Adv. Mater., 2019, 31, 1808166 |
| 20 | Lyu Y., Li J., Pu K., Small Methods, 2019, 3, 1900553 |
| 21 | Cheng L., Wang C., Feng L., Yang K., Liu Z., Chem. Rev., 2014, 114, 10869—10939 |
| 22 | Gai S., Yang G., Yang P., He F., Lin J., Jin D., Xing B., Nano Today, 2018, 19, 146—187 |
| 23 | Meng Z., Hou W., Zhou H., Zhou L., Chen H., Wu C., Macromol. Rapid Commun., 2018, 39, 1700614 |
| 24 | Guo M., Mao H., Li Y., Zhu A., He H., Yang H., Wang Y., Tian X., Ge C., Peng Q., Wang X., Yang X., Chen X., Liu G., Chen H., Biomaterials, 2014, 35, 4656—4666 |
| 25 | Li L., Liu Y., Hao P., Wang Z., Fu L., Ma Z., Zhou J., Biomaterials, 2015, 41, 132—140 |
| 26 | Jang B., Park J. Y., Tung C. H., Kim I. H., Choi Y., ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 1086—1094 |
| 27 | Lin J., Wang S., Huang P., Wang Z., Chen S., Niu G., Li W., He J., Cui D., Lu G., Chen X., Nie Z., ACS Nano, 2013, 7, 5320—5329 |
| 28 | Pan J., Yang Y., Fang W., Liu W., Le K., Xu D., Li X., ACS Appl. Nano Mater., 2018, 1, 2785—2795 |
| 29 | Guo L., Niu G., Zheng X., Ge J., Liu W., Jia Q., Zhang P., Zhang H., Wang P., Adv. Sci., 2017, 4, 1700085 |
| 30 | Wang Q., Dai Y., Xu J., Cai J., Niu X., Zhang L., Chen R., Shen Q., Huang W., Fan Q., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2019, 29, 1901480 |
| 31 | Zheng X., Wang L., Liu S., Zhang W., Liu F., Xie Z., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1706507 |
| 32 | Ngoune R., Peters A., von Elverfeldt D., Winkler K., Pütz G., J. Controlled Release, 2016, 238, 58—70 |
| 33 | Chen M., Tang S., Guo Z., Wang X., Mo S., Huang X., Liu G., Zheng N., Adv. Mater., 2014, 26, 8210—8216 |
| 34 | Liu Y., Wang Z., Liu Y., Zhu G., Jacobson O., Fu X., Bai R., Lin X., Lu N., Yang X., Fan W., Song J., Wang Z., Yu G., Zhang F., Kalish H., Niu G., Nie Z., Chen X., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 10539—10548 |
| 35 | Zhou J., Jiang Y., Hou S., Upputuri P. K., Wu D., Li J., Wang P., Zhen X., Pramanik M., Pu K., Duan, H. ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 2643—2651 |
| 36 | Guo Z., Zhu S., Yong Y., Zhang X., Dong X., Du J., Xie J., Wang Q., Gu Z., Zhao Y., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1704136 |
| 37 | Huang C. C., Chang P. Y., Liu C. L., Xu J. P., Wu S. P., Kuo W. C., Nanoscale, 2015, 7, 12689—12697 |
| 38 | Jiang X., Zhang S., Ren F., Chen L., Zeng J., Zhu M., Cheng Z., Gao M., Li Z., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 5633—5645 |
| 39 | Liu J., Zheng X., Yan L., Zhou L., Tian G., Yin W., Wang L., Liu Y., Hu Z., Gu Z., Chen C., Zhao Y., ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 696—707 |
| 40 | Zhang S., Sun C., Zeng J., Sun Q., Wang G., Wang Y., Wu Y., Dou S., Gao M., Li Z., Adv. Mater., 2016, 28, 8927—8936 |
| 41 | Lv G., Guo W., Zhang W., Zhang T., Li S., Chen S., Eltahan A. S., Wang D., Wang Y., Zhang J., Wang P. C., Chang J., Liang X. J., ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 9637—9645 |
| 42 | Dai C., Chen Y., Jing X., Xiang L., Yang D., Lin H., Liu Z., Han X., Wu R., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 12696—12712 |
| 43 | Ji X., Kong N., Wang J., Li W., Xiao Y., Gan S. T., Zhang Y., Li Y., Song X., Xiong Q., Shi S., Li Z., Tao W., Zhang H., Mei L., Shi J., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1803031 |
| 44 | Lin H., Gao S., Dai C., Chen Y., Shi J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 16235—16247 |
| 45 | Lin H., Wang Y., Gao S., Chen Y., Shi J., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1703284 |
| 46 | Tao W., Ji X., Zhu X., Li L., Wang J., Zhang Y., Saw P. E., Li W., Kong N., Islam M. A., Gan T., Zeng X., Zhang H., Mahmoudi M., Tearney G. J., Farokhzad O. C., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1802061 |
| 47 | Li S., Chen Y., Liu H., Wang Y., Liu L., Lv F., Li Y., Wang S., Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 6087—6094 |
| 48 | Robinson J. T., Welsher K., Tabakman S. M., Sherlock S. P., Wang H., Luong R., Dai H., Nano Res., 2010, 3, 779—793 |
| 49 | Sun W., Zhang X., Jia H. R., Zhu Y. X., Guo Y., Gao G., Li Y. H., Wu F. G., Small, 2019, 15, 1804575 |
| 50 | Jung H. S., Verwilst P., Sharma A., Shin J., Sessler J. L., Kim J. S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2018, 47, 2280—2297 |
| 51 | Luo S., Zhang E., Su Y., Cheng T., Shi C., Biomaterials, 2011, 32, 7127—7138 |
| 52 | Abrahamse H., Hamblin M. R., Biochem. J., 2016, 473, 347—364 |
| 53 | Ethirajan M., Chen Y., Joshi P., Pandey R. K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40, 340—362 |
| 54 | Goncalves M. S., Chem. Rev., 2009, 109, 190—212 |
| 55 | Kowada T., Maeda H., Kikuchi K., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 4953—4972 |
| 56 | Zhang Y., Lovell J. F., Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol., 2017, 9, e1420 |
| 57 | Cai X., Liu J., Liew W. H., Duan Y., Geng J., Thakor N., Yao K., Liao L. D., Liu B., Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1, 1556—1562 |
| 58 | Cai Y., Liang P., Tang Q., Yang X., Si W., Huang W., Zhang Q., Dong X., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 1054—1063 |
| 59 | Cai Y., Wei Z., Song C., Tang C., Huang X., Hu Q., Dong X., Han W., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 8967—8970 |
| 60 | Huang S., Upputuri P. K., Liu H., Pramanik M., Wang M., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2016, 4, 1696—1703 |
| 61 | Liang P., Wang Y., Wang P., Zou J., Xu H., Zhang Y., Si W., Dong X., Nanoscale, 2017, 9, 18890—18896 |
| 62 | Liu S., Zhou X., Zhang H., Ou H., Lam J. W. Y., Liu Y., Shi L., Ding D., Tang B. Z., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2019, 141, 5359—5368 |
| 63 | Qi J., Fang Y., Kwok R. T. K., Zhang X., Hu X., Lam J. W. Y., Ding D., Tang B. Z., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 7177—7188 |
| 64 | Wang Q., Xia B., Xu J., Niu X., Cai J., Shen Q., Wang W., Huang W., Fan Q., Mater. Chem. Front., 2019, 3, 650—655 |
| 65 | Zhang R., Xu Y., Zhang Y., Kim H. S., Sharma A., Gao J., Yang G., Kim J. S., Sun Y., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 8348—8353 |
| 66 | Zhao Z., Chen C., Wu W., Wang F., Du L., Zhang X., Xiong Y., He X., Cai Y., Kwok R. T. K., Lam J. W. Y., Gao X., Sun P., Phillips D. L., Ding D., Tang B. Z., Nat. Commun., 2019, 10, 768 |
| 67 | Zou J., Yin Z., Wang P., Chen D., Shao J., Zhang Q., Sun L., Huang W., Dong X., Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 2188—2194 |
| 68 | Alifu N., Zebibula A., Qi J., Zhang H., Sun C., Yu X., Xue D., Lam J. W. Y., Li G., Qian J., Tang B. Z., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 11282—11293 |
| 69 | Feng G., Liu B., Acc. Chem. Res., 2018, 51, 1404—1414 |
| 70 | Gu X., Zhang X., Ma H., Jia S., Zhang P., Zhao Y., Liu Q., Wang J., Zheng X., Lam J. W. Y., Ding D., Tang B. Z., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1801065 |
| 71 | Liu S., Zhang H., Li Y., Liu J., Du L., Chen M., Kwok R. T. K., Lam J. W. Y., Phillips D. L., Tang B. Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2018, 57, 15189—15193 |
| 72 | Wang D., Lee M. M. S., Xu W., Shan G., Zheng X., Kwok R. T. K., Lam J. W. Y., Hu X., Tang B. Z., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2019, 58, 5628—5632 |
| 73 | Zhang L., Li Y., Che W., Zhu D., Li G., Xie Z., Song N., Liu S., Tang B. Z., Liu X., Su Z., Bryce M. R., Adv. Sci., 2019, 6, 1802050 |
| 74 | Zhen S., Wang S., Li S., Luo W., Gao M., Ng L. G., Goh C. C., Qin A., Zhao Z., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28, 1706945 |
| 75 | Feng L., Zhu C., Yuan H., Liu L., Lv F., Wang S., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42, 6620—6633 |
| 76 | Kaeser A., Schenning A. P., Adv. Mater., 2010, 22, 2985—2997 |
| 77 | Li K., Liu B., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 6570—6597 |
| 78 | Wu C., Chiu D. T., Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52, 3086—3109 |
| 79 | Xu X., Liu R., Li L., Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 16733—16749 |
| 80 | Ehlerding E. B., Chen F., Cai W., Adv. Sci., 2016, 3, 1500223 |
| 81 | Guo R., Peng H., Tian Y., Shen S., Yang W., Small, 2016, 12, 4541—4552 |
| 82 | Jayaraman P., Gandhimathi C., Venugopal J. R., Becker D. L., Ramakrishna S., Srinivasan D. K., Adv. Drug Delivery Rev., 2015, 94, 77—95 |
| 83 | Mackowiak S. A., Schmidt A., Weiss V., Argyo C., von Schirnding C., Bein T., Brauchle C., Nano Lett., 2013, 13, 2576—2583 |
| 84 | Gao D., Guo X., Zhang X., Chen S., Wang Y., Chen T., Huang G., Gao Y., Tian Z., Yang Z., Mater. Today Bio., 2020, 5, 100035 |
| 85 | Chen D., Zhong Z., Ma Q., Shao J., Huang W., Dong X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2020, 12, 26914—26925 |
| 86 | Yang Z., Chen X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2019, 52, 1245—1254 |
| 87 | Cai Y., Si W., Huang W., Chen P., Shao J., Dong X., Small, 2018, 14, 1704247 |
| 88 | Gottfried J. M., Surf. Sci. Rep., 2015, 70, 259—379 |
| 89 | Du L., Qin H., Ma T., Zhang T., Xing D., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 8930—8943 |
| 90 | Jin H. G., Zhong W., Yin S., Zhang X., Zhao Y. H., Wang Y., Yuan L., Zhang X. B., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11, 3800—3808 |
| 91 | Li L., Yang Q., Shi L., Zheng N., Li Z., Li K., Qiao S., Jia T., Sun T., Wang Y., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019, 7, 2247—2251 |
| 92 | Li X., Peng X. H., Zheng B. D., Tang J., Zhao Y., Zheng B. Y., Ke M. R., Huang J. D., Chem. Sci., 2018, 9, 2098—2104 |
| 93 | Pan H., Li S., Kan J. L., Gong L., Lin C., Liu W., Qi D., Wang K., Yan X., Jiang J., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 8246—8252 |
| 94 | Zheng X., Wang L., Lei Z., Pei Q., Liu S., Xie Z., Mater. Chem. Front., 2019, 3, 1892—1899 |
| 95 | Zou Q., Abbas M., Zhao L., Li S., Shen G., Yan X., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 1921—1927 |
| 96 | Tian B., Wang C., Zhang S., Feng L., Liu Z., ACS Nano, 2011, 5, 7000—7009 |
| 97 | Younis M. R., Wang C., An R., Wang S., Younis M. A., Li Z. Q., Wang Y., Ihsan A., Ye D., Xia X. H., ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 2544—2557 |
| 98 | Cao Y., Dong H., Yang Z., Zhong X., Chen Y., Dai W., Zhang X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 159—166 |
| 99 | Han H. S., Choi K. Y., Lee H., Lee M., An J. Y., Shin S., Kwon S., Lee D. S., Park J. H., ACS Nano, 2016, 10, 10858—10868 |
| 100 | Jia Q., Ge J., Liu W., Liu S., Niu G., Guo L., Zhang H., Wang P., Nanoscale, 2016, 8, 13067—13077 |
| 101 | Kim Y. K., Na H. K., Kim S., Jang H., Chang S. J., Min D. H., Small, 2015, 11, 2527—2535 |
| 102 | Jiang Y., Li J., Zhen X., Xie C., Pu K., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1705980 |
| 103 | Guo B., Sheng Z., Kenry K., Hu D., Lin X., Xu S., Liu C., Zheng H., Liu B., Mater. Horiz., 2017, 4, 1151—1156 |
| 104 | Jiang Y., Upputuri P. K., Xie C., Lyu Y., Zhang L., Xiong Q., Pramanik M., Pu K., Nano Lett., 2017, 17, 4964—4969 |
| 105 | Wu J., You L., Lan L., Lee H. J., Chaudhry S. T., Li R., Cheng J. X., Mei J., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1703403 |
| 106 | Yin C., Wen G., Liu C., Yang B., Lin S., Huang J., Zhao P., Wong S. H. D., Zhang K., Chen X., Li G., Jiang X., Huang J., Pu K., Wang L., Bian L., ACS Nano, 2018, 12, 12201—12211 |
| 107 | Guo B., Sheng Z., Hu D., Liu C., Zheng H., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1802591 |
| 108 | Sun T., Han J., Liu S., Wang X., Wang Z. Y., Xie Z., ACS Nano, 2019, 13, 7345—7354 |
| 109 | Ding X., Liow C. H., Zhang M., Huang R., Li C., Shen H., Liu M., Zou Y., Gao N., Zhang Z., Li Y., Wang Q., Li S., Jiang J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 15684—15693 |
| 110 | Zhou M., Ku G., Pageon L., Li C., Nanoscale, 2014, 6, 15228—15235 |
| 111 | Wang C., Dai C., Hu Z., Li H., Yu L., Lin H., Bai J., Chen Y., Nanoscale Horiz., 2019, 4, 415—425 |
| 112 | Boens N., Leen V., Dehaen W., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2012, 41, 1130—1172 |
| 113 | Loudet A., Burgess K., Chem. Rev., 2007, 107, 4891—4932 |
| 114 | Li Y., Liu T., Liu H., Tian M. Z., Li Y., Acc. Chem. Res., 2014, 47, 1186—1198 |
| 115 | Banuelos J., Martin V., Gomez⁃Duran C. F., Arroyo Cordoba I. J., Pena⁃Cabrera E., Garcia⁃Moreno I., Costela A., Perez⁃Ojeda M. E., Arbeloa T., Lopez Arbeloa I., Chem. Eur. J., 2011, 17, 7261—7270 |
| 116 | Zhu H., Fan J., Du J., Peng X., Acc. Chem. Res., 2016, 49, 2115—2126 |
| 117 | Atilgan S., Ozdemir T., Akkaya E. U., Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 4065—4067 |
| 118 | Bozdemir O. A., Guliyev R., Buyukcakir O., Selcuk S., Kolemen S., Gulseren G., Nalbantoglu T., Boyaci H., Akkaya E. U., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2010, 132, 8029—8036 |
| 119 | Ekmekci Z., Yilmaz M. D., Akkaya E. U., Org. Lett., 2008, 10, 461—464 |
| 120 | Qi X., Jun E. J., Xu L., Kim S. J., Hong J. S., Yoon Y. J., Yoon J., J. Org. Chem., 2006, 71, 2881—2884 |
| 121 | Hu W., Ma H., Hou B., Zhao H., Ji Y., Jiang R., Hu X., Lu X., Zhang L., Tang Y., Fan Q., Huang W., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 12039—12047 |
| 122 | Huang L., Li Z., Zhao Y., Zhang Y., Wu S., Zhao J., Han G., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 14586—14591 |
| 123 | Ye S., Rao J., Qiu S., Zhao J., He H., Yan Z., Yang T., Deng Y., Ke H., Yang H., Zhao Y., Guo Z., Chen H., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1801216 |
| 124 | Zhang Y., Song N., Li Y., Yang Z., Chen L., Sun T., Xie Z., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019, 7, 4717—4724 |
| 125 | Zou J., Wang P., Wang Y., Liu G., Zhang Y., Zhang Q., Shao J., Si W., Huang W., Dong X., Chem. Sci., 2019, 10, 268—276 |
| 126 | Lu H., Mack J., Yang Y., Shen Z., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 4778—4823 |
| 127 | Awuah S. G., You Y., RSC Adv., 2012, 2, 11169—11183 |
| 128 | Zhang X. F., Yang X., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2013, 117, 5533—5539 |
| 129 | Zou J., Yin Z., Ding K., Tang Q., Li J., Si W., Shao J., Zhang Q., Huang W., Dong X., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 32475—32481 |
| 130 | Vegesna G. K., Sripathi S. R., Zhang J., Zhu S., He W., Luo F. T., Jahng W. J., Frost M., Liu H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5, 4107—4112 |
| 131 | Wu B., Xu L., Wang S., Wang Y., Zhang W., Polym. Chem., 2015, 6, 4279—4289 |
| 132 | Zhu S., Zhang J., Vegesna G., Luo F. T., Green S. A., Liu H., Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 438—441 |
| 133 | Liu L., Ruan Z., Li T., Yuan P., Yan L., Biomater. Sci., 2016, 4, 1638—1645 |
| 134 | Trofymchuk K., Valanciunaite J., Andreiuk B., Reisch A., Collot M., Klymchenko A. S., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019, 7, 5199—5210 |
| 135 | Tang Q., Xiao W., Huang C., Si W., Shao J., Huang W., Chen P., Zhang Q., Dong X., Chem. Mater., 2017, 29, 5216—5224 |
| 136 | Guo Z., Nam S., Park S., Yoon J., Chem. Sci., 2012, 3, 2760—2765 |
| 137 | Yapici I., Lee K. S., Berbasova T., Nosrati M., Jia X., Vasileiou C., Wang W., Santos E. M., Geiger J. H., Borhan B., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 1073—1080 |
| 138 | Mishra A., Behera R. K., Behera P. K., Mishra B. K., Behera G. B., Chem. Rev., 2000, 100, 1973—2012 |
| 139 | Lavis L. D., Raines R. T., ACS Chem. Biol., 2008, 3, 142—155 |
| 140 | Guieu V., Payrastre C., Madaule Y., Garcia⁃Alonso S., Lacroix P. G., Nakatani K., Chem. Mater., 2006, 18, 3674—3681 |
| 141 | Lacroix P. G., Malfant I., Payrastre C., Wolf J. G., Bonvoisin J., Nakatani K., Chem. Mater.,1998, 10, 1135—1140 |
| 142 | Bouit P. A., Rauh D., Neugebauer S., Delgado J. L., Di Piazza E., Rigaut S., Maury O., Andraud C., Dyakonov V., Martin N., Org. Lett., 2009, 11, 4806—4809 |
| 143 | Sun W., Guo S., Hu C., Fan J., Peng X., Chem. Rev., 2016, 116, 7768—7817 |
| 144 | Karton⁃Lifshin N., Segal E., Omer L., Portnoy M., Satchi⁃Fainaro R., Shabat D., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2011, 133, 10960—10965 |
| 145 | Liu Y., Zhou J., Wang L., Hu X., Liu X., Liu M., Cao Z., Shangguan D., Tan W., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138, 12368—12374 |
| 146 | Yin J., Kwon Y., Kim D., Lee D., Kim G., Hu Y., Ryu J. H., Yoon J., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136, 5351—5358 |
| 147 | Jian W. H., Yu T. W., Chen C. J., Huang W. C., Chiu H. C., Chiang W. H., Langmuir, 2015, 31, 6202—6210 |
| 148 | Pan J., Wang Y., Zhang C., Wang X., Wang H., Wang J., Yuan Y., Wang X., Zhang X., Yu C., Sun S. K., Yan X. P., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1704408 |
| 149 | Sheng Z., Hu D., Zheng M., Zhao P., Liu H., Gao D., Gong P., Gao G., Zhang P., Ma Y., Cai L., ACS Nano, 2014, 8, 12310—12322 |
| 150 | Yoon H. J., Lee H. S., Lim J. Y., Park J. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2017, 9, 5683—5691 |
| 151 | Strekowski L., Heterocyclic Polymethine Dyes: Synthesis, Properties and Applications, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2008, 1—10 |
| 152 | Huang Y., He N., Wang Y., Shen D., Kang Q., Zhao R., Chen L., J. Mater. Chem. B, 2019, 7, 1149—1159 |
| 153 | Chen X., Peng X., Cui A., Wang B., Wang L., Zhang R., J. Photochem. Photobiol., A, 2006, 181, 79—85 |
| 154 | Kovalska V. B., Volkova K. D., Losytskyy M. Y., Tolmachev O. I., Balanda A. O., Yarmoluk S. M., Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, 2006, 65, 271—277 |
| 155 | Volkova K. D., Kovalska V. B., Tatarets A. L., Patsenker L. D., Kryvorotenko D. V., Yarmoluk S. M., Dyes Pigm., 2007, 72, 285—292 |
| 156 | Escobedo J. O., Rusin O., Lim S., Strongin R. M., Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 2010, 14, 64—70 |
| 157 | Alagumalai A., FairoosM. K. M., Vellimalai P., Sil M. C., Nithyanandhan J., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 35353—35367 |
| 158 | Oswald B., Patsenker L., Duschl J., Szmacinski H., Wolfbeis O. S., Terpetschnig E., Bioconjugate Chem.,1999, 10, 925—931 |
| 159 | Karpenko I. A., Collot M., Richert L., Valencia C., Villa P., Mely Y., Hibert M., Bonnet D., Klymchenko A. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137, 405—412 |
| 160 | Sreejith S., Joseph J., Lin M., Menon N. V., Borah P., Ng H. J., Loong Y. X., Kang Y., Yu S. W., Zhao Y., ACS Nano, 2015, 9, 5695—5704 |
| 161 | Wu B., Lin Y., Li B., Zhan C., Zeng F., Wu S., Anal. Chem., 2018, 90, 9359—9365 |
| 162 | Umezawa K. C., D., Suzuki K., Anal. Sci., 2008, 24, 213—217 |
| 163 | Nakazumi H., Ohta T., Etoh H., Uno T., Colyer C. L., Hyodo Y., Yagi S., Synth. Met., 2005, 153, 33—36 |
| 164 | Gassensmith J. J., Baumes J. M., Smith B. D., Chem. Commun., 2009, 6329—6338 |
| 165 | Sun P., Wu Q., Sun X., Miao H., Deng W., Zhang W., Fan Q., Huang W., Chem. Commun., 2018, 54, 13395—13398 |
| 166 | Dou L., Liu Y., Hong Z., Li G., Yang Y., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 12633—12665 |
| 167 | Bin H., Yang Y., Zhang Z. G., Ye L., Ghasemi M., Chen S., Zhang Y., Zhang C., Sun C., Xue L., Yang C., Ade H., Li Y., J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2017, 139, 5085—5094 |
| 168 | Chen Z., Li J., Li M., Chen C., Xu S., Tang X., Chen L., Chen R., Huang W., Org. Lett., 2018, 20, 6376—6379 |
| 169 | Dutta P., Yang W., Lee W.H., Kang I. N., Lee S. H., J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22, 10840—10851 |
| 170 | Tang A., Zhan C., Yao J., Chem. Mater., 2015, 27, 4719—4730 |
| 171 | Tang A., Zhan C., Yao J., Zhou E., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1600013 |
| 172 | Yin Q. R., Miao J. S., Wu Z., Chang Z. F., Wang J. L., Wu H. B., Cao Y., J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3, 11575—11586 |
| 173 | Chavez Iii R., Cai M., Tlach B., Wheeler D. L., Kaudal R., Tsyrenova A., Tomlinson A. L., Shinar R., Shinar J., Jeffries⁃El M., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4, 3765—3773 |
| 174 | Thirion D., Rault⁃Berthelot J., Vignau L., Poriel C., Org. Lett., 2011, 13, 4418—4421 |
| 175 | Yang Y., Zhou Y., He Q., He C., Yang C., Bai F., Li Y., J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009, 113, 7745—7752 |
| 176 | Bulumulla C., Gunawardhana R., Kularatne R. N., Hill M. E., McCandless G. T., Biewer M. C., Stefan M. C., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 11818—11825 |
| 177 | Huang Y. F., Chang S. T., Wu K. Y., Wu S. L., Ciou G. T., Chen C. Y., Liu C. L., Wang C. L., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2018, 10, 8869—8876 |
| 178 | Kang W., Jung M., Cha W., Jang S., Yoon Y., Kim H., Son H. J., Lee D. K., Kim B., Cho J. H., ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 6, 6589—6597 |
| 179 | Lee J., Ko S.J., Lee H., Huang J., Zhu Z., Seifrid M., Vollbrecht J., Brus V. V., Karki A., Wang H., Cho K., Nguyen T. Q., Bazan G. C., ACS Energy Lett., 2019, 4, 1401—1409 |
| 180 | Lv L., Yu J., Sui X., Wu J., Dong X., Lu G., Liu X., Peng A., Huang H., J. Mater. Chem. C, 2019, 7, 5739—5747 |
| 181 | Qi J., Han J., Zhou X., Guo C., Yang D., Qiao W., Li Y., Ma D., Wang Z. Y., J. Phys. Chem. C, 2015, 119, 25243—25251 |
| 182 | Cheng K., Chen H., Jenkins C. H., Zhang G., Zhao W., Zhang Z., Han F., Fung J., Yang M., Jiang Y., Xing L., Cheng Z., ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 12276—12291 |
| 183 | Lan M., Zhang J., Zhu X., Wang P., Chen X., Lee C. S., Zhang W., Nano Res., 2015, 8, 2380—2389 |
| 184 | Kaur M., Choi D. H., Chem. Soc. Rev., 2015, 44, 58—77 |
| 185 | He H., Zheng X., Liu S., Zheng M., Xie Z., Wang Y., Yu M., Shuai X., Nanoscale, 2018, 10, 10991—10998 |
| 186 | Huang S., Liu W., Huang J., Wang X., Yang C., Bohra H., Liu Q., Wang M., ACS Appl. Bio. Mater., 2018, 1, 1109—1117 |
| 187 | Wu C., Huang X., Tang Y., Xiao W., Sun L., Shao J., Dong X., Chem. Commun., 2019, 55, 790—793 |
| 188 | Shao W., Wei Q., Wang S., Li F., Wu J., Ren J., Cao F., Liao H., Gao J., Zhou M., Ling D., Mater. Horiz., 2020, 7, 1379—1386 |
| 189 | Ding D., Li K., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Acc. Chem. Res., 2013, 46, 2441—2453 |
| 190 | Mei J., Leung N. L., Kwok R. T., Lam J. W., Tang B. Z., Chem. Rev., 2015, 115, 11718—11940 |
| 191 | Li K., Qin W., Ding D., Tomczak N., Geng J., Liu R., Liu J., Zhang X., Liu H., Liu B., Tang B. Z., Sci. Rep., 2013, 3, 1150 |
| 192 | Ding D., Goh C. C., Feng G., Zhao Z., Liu J., Liu R., Tomczak N., Geng J., Tang B. Z., Ng L. G., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2013, 25, 6083—6088 |
| 193 | Qi J., Li J., Liu R., Li Q., Zhang H., Lam J. W. Y., Kwok R. T. K., Liu D., Ding D., Tang B. Z., Chem., 2019, 5, 2657—2677 |
| 194 | Kenry Duan Y., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2018, 30, 1802394 |
| 195 | Fateminia S. M., Wang Z., Goh C. C., Manghnani P. N., Wu W., Mao D., Ng L. G., Zhao Z., Tang B. Z., Liu B., Adv. Mater., 2017, 29, 1604100 |
| 196 | Ji S., Ge J., Escudero D., Wang Z., Zhao J., Jacquemin D., J. Org. Chem., 2015, 80, 5958—5963 |
| 197 | Xu S., Yuan Y., Cai X., Zhang C. J., Hu F., Liang J., Zhang G., Zhang D., Liu B., Chem. Sci., 2015, 6, 5824—5830 |
| 198 | Wu W., Mao D., Xu S., Kenry, Hu F., Li X., Kong D., Liu B., Chem., 2018, 4, 1937—1951 |
| [1] | LIU Shuwei, JIN Hao, YIN Wanzhong, ZHANG Hao. Gemcitabine/polypyrrole Composite Nanoparticles for Chemo-photothermal Combination Ovarian Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(8): 20220345. |
| [2] | FAN Xiaohui, WANG Yang, YANG Yuanyuan, ZHANG Yuhong. Preparation and Properties of Gold Nanocages/Hyaluronic Acid Core-shell Nanocarriers with pH/Enzyme/ Photothermal Multiple Responses [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(4): 20210855. |
| [3] | WANG Xueli, SONG Xiangwei, XIE Yanning, DU Niyang, WANG Zhenxin. Preparation, Characterization of Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide and Its Killing Effect on Human Cervical Cancer Cells [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210595. |
| [4] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [5] | CHEN Hongda, ZHANG Hua, WANG Zhenxin. Development of Small Animals in vivo Fluorescence-photothermal Dual Mode Imaging System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [6] | LU Feng, GONG Yi, ZHAO Ting, ZHAO Ning, JU Wenwen, FAN Quli, HUANG Wei. Seedless Synthesis of Gold Nanorods with Narrow Absorption Using Binary Surfactant Mixture [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 700. |
| [7] | LIANG Yuxin, ZHAO Rong, LIANG Xinyue, FANG Xiaohong. Single-molecule Imaging and Analysis of Signal Transduction Proteins on Cell Membranes † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1127. |
| [8] | BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252. |
| [9] | WU Fengren,LIU Yongjia,LU Xuemin,ZHU Bangshang. Controllable Preparation of Polydopamine Modified Gold Nanoflowers and Its Application in Photothermal Therapy † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(3): 465. |
| [10] | WU Wenbo,LIU Bin. Two-photon Excitable Photosensitizers with Aggregation-induced Emission and Their Biomedical Applications † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(2): 191. |
| [11] | Yong ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN. Benzimidazole-Derived Fluorescence Enhancement Probe for Visual Detection of HClO † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2480. |
| [12] | ZHANG Shupeng, CHENG Youxing, REN Lei, WEN Kai, LÜ Xiaolin, YE Shefang, ZHOU Xi. Reparation and Photothermal Properties of Prussian Blue Nanoparticles with Different Morphologies† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(2): 359. |
| [13] | WANG Xueli,WANG Zhenxin. Preparation of a Targeted Tumor Nanocomposites for Combined Photodynamic-photothermal Therapy Based on Partially Reduced Graphene Oxide† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2018, 39(10): 2185. |
| [14] | JIANG Tingting, WANG Yuanfang, LIU Peilong, TIAN Yixia, LI Hao, HU Yongguo. Vancomycin Derivative Modified Silica-coated Silver Nanoplate for Surface-enhanced Raman Scattering Imaging and Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy of Vancomycin Resistant Bacterial Strains† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017, 38(5): 846. |
| [15] | ZHANG Tao, TANG Yongjia, XU Liang, LIU Keliang. Synthesis of a New Cyanoacrylate Monomer and Its Application in Fluorescence Imaging in vivo† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2016, 37(6): 1168. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||