

Chem. J. Chinese Universities ›› 2019, Vol. 40 ›› Issue (12): 2480.doi: 10.7503/cjcu20190366
• Analytical Chemistry • Previous Articles Next Articles
Yong ZHANG( ),Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN
),Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN
Received:2019-07-01
Online:2019-12-04
Published:2019-12-04
Contact:
Yong ZHANG
E-mail:zy0340907@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
TrendMD:
Yong ZHANG,Cheng SHEN,Zhirong XING,Guiqi CHEN,Zi LU,Zhibing HOU,Xuemei CHEN. Benzimidazole-Derived Fluorescence Enhancement Probe for Visual Detection of HClO †[J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019, 40(12): 2480.
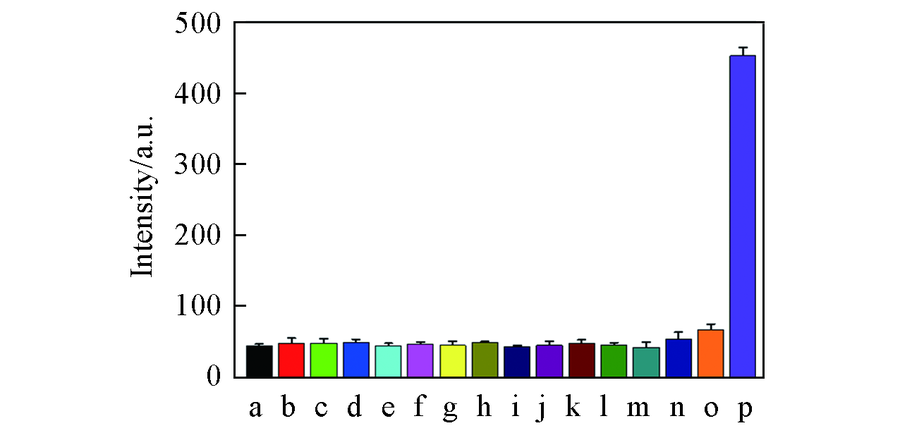
Fig.1 Fluorescent response of ZY12(10 μmol/L, a) to different analytes(30 μmol/L, b—p) Analyte: b. F-; c. Cl-; d. Br-; e. I-; f. Ac-; g. C$O_{3}^{2-}$; h.$N_{3}^{-}$; i. N$O_{2}^{-}$; j. N$O_{3}^{-}$; k. S2-; l. S$O_{3}^{2-}$; m. SCN-; n. t-BuOOH; o. H2O2; p. ClO-.
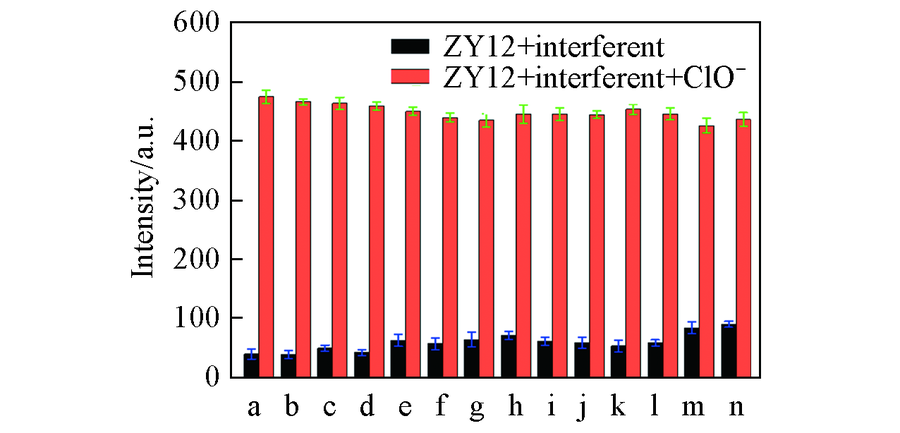
Fig.2 Effect of ClO- on ZY12(10 μmol/L) in the presence of different interferents(100 μmol/L) Interferent: a. F-; b. Cl-; c. Br-; d. I-; e. Ac-; f. C$O_{3}^{2-}$; g.$NO_{3}^{-}$; h. N$O_{2}^{-}$; i. N$O_{3}^{-}$; j. SCN-; k. S2-; l. S$O_{3}^{2-}$; m. t-BuOOH; n. H2O2.
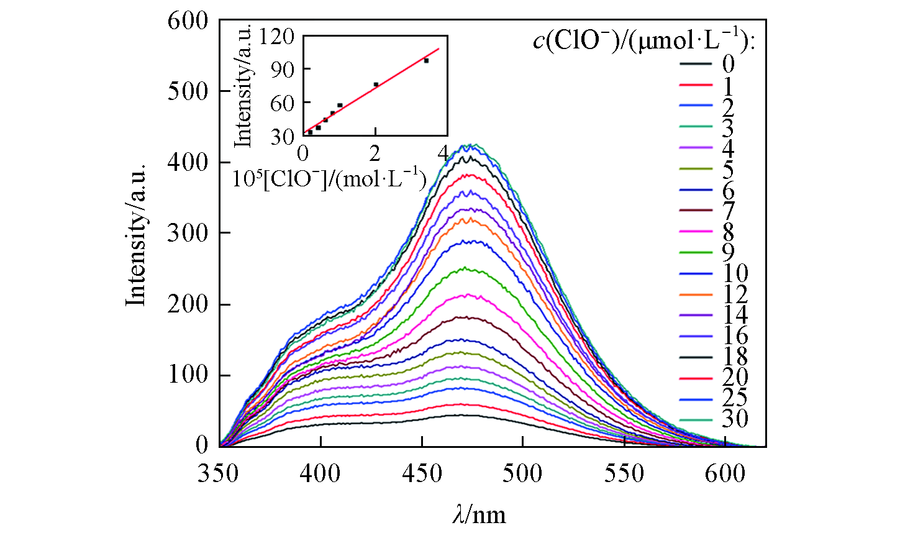
Fig.3 Fluorescence intensity changes of ZY12(10 μmol/L) upon gradual addition of ClO-(0—30 μmol/L) The inset shows the linear relationship between the fluorescence intensity of ZY12 and concentrations of ClO-.
| Fluorescent probe | λex/λem(nm) | Solvent | Detection limit/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | 370/495 | PBS/DMSO(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.31 | [ |
| 1b | 398/455 | PBS/CH3CN(volume ratio 8:2) | 0.36 | [ |
| L1 | 405/505 | PBS | 0.67 | [ |
| BDP-OX | 488/538, 589 | PBS/DMSO(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.85 | [ |
| HA | 340/460, 570 | PBS/DMF(volume ratio 99:1) | 0.70 | [ |
| ZY12 | 322/472 | EtOH/H2O(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.28 | This work |
| Fluorescent probe | λex/λem(nm) | Solvent | Detection limit/(μmol·L-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HQ | 370/495 | PBS/DMSO(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.31 | [ |
| 1b | 398/455 | PBS/CH3CN(volume ratio 8:2) | 0.36 | [ |
| L1 | 405/505 | PBS | 0.67 | [ |
| BDP-OX | 488/538, 589 | PBS/DMSO(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.85 | [ |
| HA | 340/460, 570 | PBS/DMF(volume ratio 99:1) | 0.70 | [ |
| ZY12 | 322/472 | EtOH/H2O(volume ratio 1:9) | 0.28 | This work |
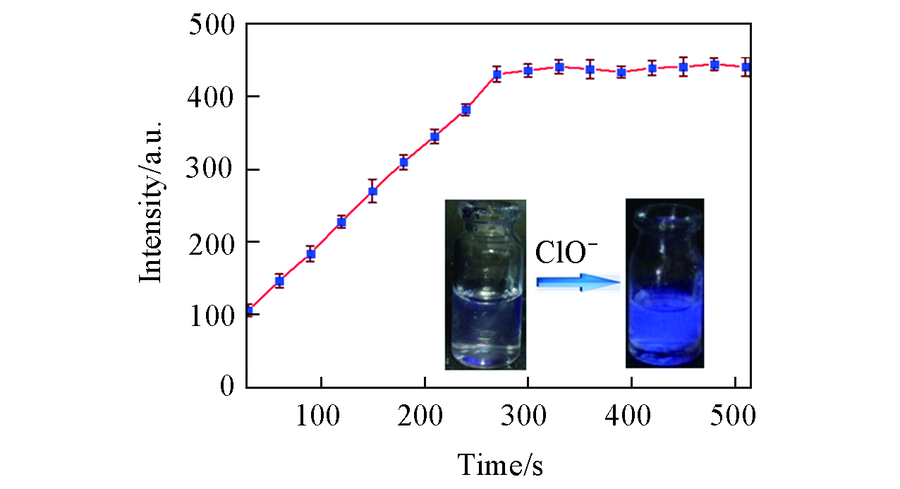
Fig.4 Time-dependent fluorescence intensity changes of ZY12(10 μmol/L) in the presence of ClO-(30 μmol/L) The inset shows the fluorescence color of ZY12 before(left) and after(right) addition of ClO- under UV light(365 nm).
| Water sample | ClO- added/(μmol·L-1) | ClO- found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 10.0 | 9.60 | 96.0 | 3.8 |
| 20.0 | 19.30 | 96.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 30.81 | 102.7 | ||
| Mineral water | 10.0 | 9.71 | 97.1 | 3.0 |
| 20.0 | 19.52 | 97.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 30.73 | 102.3 | ||
| Changjiang river water | 10.0 | 10.32 | 103.2 | 4.7 |
| 20.0 | 19.10 | 95.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 31.29 | 104.3 |
| Water sample | ClO- added/(μmol·L-1) | ClO- found/(μmol·L-1) | Recovery(%) | RSD(%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tap water | 10.0 | 9.60 | 96.0 | 3.8 |
| 20.0 | 19.30 | 96.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 30.81 | 102.7 | ||
| Mineral water | 10.0 | 9.71 | 97.1 | 3.0 |
| 20.0 | 19.52 | 97.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 30.73 | 102.3 | ||
| Changjiang river water | 10.0 | 10.32 | 103.2 | 4.7 |
| 20.0 | 19.10 | 95.5 | ||
| 30.0 | 31.29 | 104.3 |
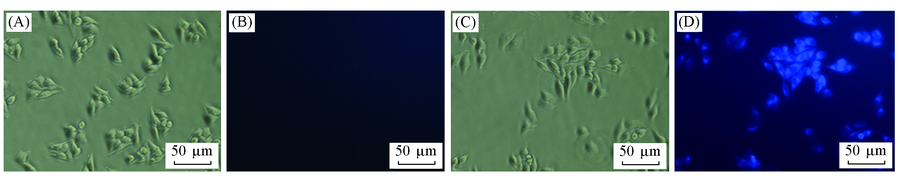
Fig.7 Bright-field(A, C) and fluorescence(B, D) images of HeLa cells treated with probe ZY12(10 μmol/L)(A, B) and treated with probe ZY12(10 μmol/L) and NaClO (50 μmol/L) for 30 min(C, D)
| [1] |
Zhang Y. R., Liu Y., Feng X., Zhao B. X ., Sens. Actuat. B: Chem., 2017,240, 18— 36
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.08.066 URL |
| [2] |
Zhang R., Song B., Yuan J. L ., Trends Anal. Chem., 2018,99, 1— 33
doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2017.11.015 URL |
| [3] |
Sun M. T., Yu H., Zhu H. J., Ma F., Zhang S., Huang D. J., Wang S. H ., Anal. Chem., 2014,86, 671— 677
doi: 10.1021/ac403603r URL pmid: 24308562 |
| [4] |
Yue Y. K., Huo F. J., Yin C. X., Escobedo J. O., Strongin R. M ., Analyst, 2016,141, 1859— 1873
doi: 10.1039/c6an00158k URL pmid: 26883493 |
| [5] |
Baldus S., Heeschen C., Meinertz T., Zeiher A. M., Eiserich J. P., Münzel T., Simoons M. L., Hamm C. W ., Circulation, 2003,108, 1440— 1445
doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000090690.67322.51 URL pmid: 12952835 |
| [6] |
Yang Y. C., Lu H. H., Wang W. T., Liau I ., Anal. Chem., 2011,83, 8267— 8272
doi: 10.1021/ac202077x URL pmid: 21950322 |
| [7] | Li H. D., Fan J. L., Peng X.J ., Prog. Chem., 2017,29(1), 17— 35 |
| ( 李海东, 樊江莉, 彭孝军 . 化学进展, 2017,29(1), 17— 35) | |
| [8] | Bai L., Huo S. H., Chen J., Lu X. Q ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2019,40(1), 41— 46 |
| ( 白蕾, 霍淑慧, 陈晶, 卢小泉 . 高等学校化学学报, 2019,40(1), 41— 46) | |
| [9] |
Wang Y. B., Zhao B. X ., Chinese J. Org. Chem., 2016,36(7), 1539— 1554
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 URL |
|
( 王延宝, 赵宝祥 . 有机化学, 2016,36(7), 1539— 1554)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201511038 URL |
|
| [10] | Yang J. J., Yu Y. W., Wang B. X., Jiang Y. L ., Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2017,38(7), 1198— 1202 |
| ( 杨敬敬, 俞岳文, 王炳祥, 江玉亮 . 高等学校化学学报, 2017,38(7), 1198— 1202) | |
| [11] |
Hu J. J., Wong N. K., Gu Q. S., Bai X. Y., Ye S., Yang D ., Org. Lett., 2014,16, 3544— 3547
doi: 10.1021/ol501496n URL pmid: 24950390 |
| [12] |
Yuan L., Lin W. Y., Song J. Z., Yang Y. T ., Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 12691— 12693
doi: 10.1039/c1cc15762k URL pmid: 22037995 |
| [13] |
Cheng X. H., Jia H. Z., Long T., Feng J., Qin J. G., Li Z ., Chem. Commun., 2011,47, 11978— 11980
doi: 10.1039/c1cc15214a URL pmid: 21959955 |
| [14] |
Liu J. W., Yin Z ., Talanta, 2019,196, 352— 356
doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.086 URL pmid: 30683375 |
| [15] |
Wu Y. C., You J. Y., Guan L. T., Shi J., Cao L., Wang Z. Y ., Chinese J. Org. Chem., 2015,35(12), 2465— 2486
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201507022 URL |
|
( 吴彦城, 尤嘉宜, 关丽涛, 石杰, 曹梁, 汪朝阳 . 有机化学, 2015,35(12), 2465— 2486)
doi: 10.6023/cjoc201507022 URL |
|
| [16] |
Wang G., Qi H. P., Yang X. F ., Luminescence, 2013,28(2), 97— 101
doi: 10.1002/bio.2344 URL pmid: 22298443 |
| [17] |
Shortreed M., Kopelman R., Kuhn M., Hoyland B ., Anal. Chem., 1996,68, 1414— 1418
doi: 10.1021/ac950944k URL pmid: 8651501 |
| [18] |
Wang X. M., Wang X. H., Feng Y., Zhu M. Z., Yin H., Guo Q. X., Meng X. M ., Dalton Trans., 2015,44, 6613— 6619
doi: 10.1039/c5dt00012b URL pmid: 25757874 |
| [19] |
Long L. L., Wu Y. J., Wang L., Gong A. H., Hu F. L., Zhang C ., Chem. Commun., 2015,51, 10435— 10438
doi: 10.1039/c5cc03972j URL pmid: 26028189 |
| [20] |
Zhang B. B., Yang X. P., Zhang R., Liu Y., Ren X. L., Xian M., Ye Y., Zhao Y. F ., Anal. Chem., 2017,89, 10384— 10390
doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02361 URL pmid: 28868883 |
| [21] |
Kang J., Huo F. J., Yue Y. K., Wen Y., Chao J. B., Zhang Y. B., Yin C. X ., Dyes Pigm., 2017,136, 852— 858
doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2016.09.048 URL |
| [22] |
Guo T., Cui L., Shen J. N., Wang R., Zhu W. P., Xu Y. F., Qian X. H ., Chem. Commun., 2013,49, 1862— 1864
doi: 10.1039/c3cc38471c URL |
| [23] |
Zhao Y., Li H. Y., Xue Y. Y., Ren Y. H ., Sens. Actuat. B: Chem., 2017,241, 335— 341
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2016.10.092 URL |
| [24] |
Goswami S., Paul S., Manna A ., Dalton. Trans., 2013,42, 10097— 10101
doi: 10.1039/c3dt51238j URL pmid: 23732748 |
| [25] |
Goswami S., Maity S., Maity A. C., Das A. K ., Sens. Actuat. B: Chem., 2014,204, 741— 745
doi: 10.1016/j.snb.2014.08.024 URL |
| [1] | ZHAO Yongmei, MU Yeshu, HONG Chen, LUO Wen, TIAN Zhiyong. Bis-naphthalimide Derivatives for Picronitric Acid Detection in Aqueous Solution [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(3): 20210765. |
| [2] | TANG Qian, DAN Feijun, GUO Tao, LAN Haichuang. Synthesis and Application of Quinolinone-coumarin-based Colorimetric Fluorescent Probe for Recognition of Hg2+ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(2): 20210660. |
| [3] | WANG Di, ZHONG Keli, TANG Lijun, HOU Shuhua, LYU Chunxin. Synthesis of Schiff-based Covalent Organic Framework and Its Recognition of I ‒ [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220115. |
| [4] | LIU Miao, LIU Ruibo, LIU Badi, QIAN Ying. Synthesis, Two-photon Fluorescence Imaging and Photodynamic Therapy of Lysosome-targeted Indole-BODIPY Photosensitizer [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2022, 43(10): 20220326. |
| [5] | LI Anran, ZHAO Bing, KAN Wei, SONG Tianshu, KONG Xiangdong, BU Fanqiang, SUN Li, YIN Guangming, WANG Liyan. ON-OFF-ON Double Colorimetric and Fluorescent Probes Based on Phenanthro[9,10-d]imidazole Derivatives and Their Living Cells Imaging [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2403. |
| [6] | HUANG Shan, YAO Jiandong, NING Gan, XIAO Qi, LIU Yi. Efficient Determination of Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Based on Graphene Quantum Dots Fluorescent Probes [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(8): 2412. |
| [7] | CHEN Hongda, ZHANG Hua, WANG Zhenxin. Development of Small Animals in vivo Fluorescence-photothermal Dual Mode Imaging System [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(3): 725. |
| [8] | YANG Xinjie, LAI Yanqiong, LI Qiuyang, ZHANG Yanli, WANG Hongbin, PANG Pengfei, YANG Wenrong. An Enzyme-free and Label-free Fluorescent Probe for Detection of Microcystin-LR Based on Circular DNA-Silver Nanoclusters [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(12): 3600. |
| [9] | CHEN Weiju, CHEN Shiya, XUE Caoye, LIU Bo, ZHENG Jing. Fluorescent Probe for Hypoxia-triggered Imaging and Cancer Therapy [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2021, 42(11): 3433. |
| [10] | HUANG Jialing,LIU Fengjiao,WANG Tingting,LIU Cuie,ZHENG Fengying,WANG Zhenhong,LI Shunxing. Nitrogen and Sulfur co-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Accurate Detection of pH in Gastric Juice† [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(7): 1513. |
| [11] | BAI Cuiting, YUE Renye, LUO Liegao, MA Nan. Quantitative Analysis of MicroRNA Content by Fluorescence Imaging in Cancer Cells Using Dual-color Fluorescence Nanosensor † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1252. |
| [12] | LIANG Yuxin, ZHAO Rong, LIANG Xinyue, FANG Xiaohong. Single-molecule Imaging and Analysis of Signal Transduction Proteins on Cell Membranes † [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(6): 1127. |
| [13] | SHAO Wei, LEE Jiyoung, LI Fangyuan, LING Daishun. Organic Small Molecule Nanoparticles for Phototheranostics [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2356. |
| [14] | WU Qian, CHENG Dan, LÜ Yun, YUAN Lin, ZHANG Xiaobing. Monitoring of Peroxynitrite Variation During Liver Injury Adopting a Far Red to Near-infrared Fluorescent Probe with Large Stokes Shift [J]. Chem. J. Chinese Universities, 2020, 41(11): 2426. |
| [15] |
WANG Jinjin,QI Shaolong,DU Jianshi,YANG Qingbiao,SONG Yan,LI Yaoxian.
Synthesis of Benzothiazole Fluorescent Probe for Detection of N2H4·H2O and HS |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||